[20] ERDN - Part 2
1/148
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
149 Terms
What is the contraindicated route for pain management in burn patients?
IM due to damage to muscles
True or false? Codeine is considered a strong opioid and is the drug of choice for burn pain
False; codeine is just a weak opioid. Morphine is the DOC.
Morphine:
Route
WOF
Antidote
IV
Respiratory depression
Naloxone
Naloxone can be administered via ________ route in emergencies
Intranasal
The diet of choice for burn patients in the first 48 hours
TPN
The patient should be on NPO because burn patients due to the decreased flow to the GIT, which can lead to paralytic ileus
Nutrition for burn patients: increased or decreased?
Calories
Carbohydrates
Protein
Increased calories and carbohydrates due to hypermetabolism
Increased protein for tissue repair
Vitamins given for:
Skin integrity
Metabolism
Infection prevention
Vitamin A
Vitamin B
Vitamin C
The stress ulcer common in burn patients
Curling’s ulcer due to thinner GI lining
Why are PPIs and H2 blockers given to burn patients?
To prevent Curling’s ulcer
Thermoregulation problem during:
Emergent phase
Acute and recovery phase
Hypothermia due to skin loss
Low grade fever due to inflammation
Hypothermia prevention:
Remove ____ clothing
Cover with ____ blanket
____ room temperature
____ ____ at bedside
____ fluids
Wet
Warm
Increased
Heat lamp
Warmed
What is the 1st line of defense of the body?
Skin
Isolation precautions for burn patients?
Reverse isolation
Most effective way to prevent infections?
Handwashing
Vaccine given to burn patients
Tetanus vaccine
Solution used for wound irrigation in burn patients
NSS because it’s isotonic and sterile
The most common gram-positive bacteria causing burn wound infections
Staphylococcus aureus
The most common gram-negative bacteria causing burn wound infections
Pseudomonas aeruginosa
Debridement of burn wounds is done using a ________ dressing technique, and the first action before performing it is administering ________
Wet-to-dry; analgesics
Surgical intervention for full thickness burns
Skin grafting
What are the 4 types of skin grafting?
Isograft
Allograft
Xenograft
Autograft
Identify the type of skin grafting being described:
From identical twins
From other humans
From animals
From self
Isograft
Allograft
Xenograft
Autograft
Common donor site for autografts?
Anterolateral thigh
Most common type of shock
Hypovolemic shock
Most fatal type of shock
Septic
Deds ka na within 24 hours
Involved: blood
A. Hypovolemic shock
B. Cardiogenic shock
C. Distributive shock
D. Neurogenic shock
A. Hypovolemic shock
Involved: heart
A. Hypovolemic shock
B. Cardiogenic shock
C. Distributive shock
D. Neurogenic shock
B. Cardiogenic shock
Involved: blood vessels
A. Hypovolemic shock
B. Cardiogenic shock
C. Distributive shock
D. Neurogenic shock
C. Distributive shock
D. Neurogenic shock
What are the 2 types of distributive shock?
Septic shock
Anaphylactic shock
Provide the cause of the following:
Hypovolemic shock
Cardiogenic shock
Distributive shock
Neurogenic shock
Decreased blood volume
Decreased cardiac output
Massive vasodilation
SCI
What causes massive vasodilation in:
Septic shock
Anaphylactic shock
Cytokine release
Histamine release
Vital signs: ↓ BP, ↑ HR, ↑ RR
A. Hypovolemic shock
B. Cardiogenic shock
C. Distributive shock
D. Neurogenic shock
A. Hypovolemic shock
B. Cardiogenic shock
C. Distributive shock
What type of shock causes bradycardia due to loss of SNS response?
Neurogenic shock
What are the 3 stages of shock?
Compensatory
Progressive
Irreversible
Which of the following best describes the compensatory stage of shock?
A. Severe hypotension, MODS, lactic acidosis
B. SNS activation, vasoconstriction, normal BP
C. Anuria, metabolic acidosis, irreversible damage
B. SNS activation, vasoconstriction, normal BP
Which of the following best describes the progressive stage of shock?
A. Severe hypotension, MODS, lactic acidosis
B. SNS activation, vasoconstriction, normal BP
C. Anuria, metabolic acidosis, irreversible damage
A. Severe hypotension, MODS, lactic acidosis
Which of the following best describes the irreversible stage of shock?
A. Severe hypotension, MODS, lactic acidosis
B. SNS activation, vasoconstriction, normal BP
C. Anuria, metabolic acidosis, irreversible damage
C. Anuria, metabolic acidosis, irreversible damage
What is the first sign of shock?
Restlessness
Which physiologic responses occur during the compensatory stage? SATA
A. Activation of SNS
B. Release of aldosterone & ADH
C. Vasoconstriction → cool skin
D. Blood flow shunted to heart & brain
E. Severe hypotension
A. Activation of SNS
B. Release of aldosterone & ADH
C. Vasoconstriction → cool skin
D. Blood flow shunted to heart & brain
Which physiologic responses occur during the irreversible stage? SATA
A. Asystole
B. Comatose state
C. Apnea
D. Oliguria
E. Anuria
A. Asystole
B. Comatose state
C. Apnea
E. Anuria
BP starts to drop
A. Compensatory
B. Progressive
C. Irreversible
B. Progressive
Characterized by decompensation and severe hypoperfusion
A. Compensatory
B. Progressive
C. Irreversible
B. Progressive
Respiratory alkalosis
A. Compensatory
B. Progressive
C. Irreversible
A. Compensatory
Metabolic acidosis
A. Compensatory
B. Progressive
C. Irreversible
B. Progressive
C. Irreversible
Oliguria
A. Compensatory
B. Progressive
C. Irreversible
A. Compensatory
B. Progressive
Which interventions provide respiratory support in shock? SATA
A. Intubation
B. 100% oxygen via NRB mask
C. Incentive spirometry
D. Mechanical ventilation
A. Intubation
B. 100% oxygen via NRB mask
D. Mechanical ventilation
IV access for shock should be established with ________ large-bore catheters, ideally ≤ ______ gauge
2; 18
Type of fluid used for fluid replacement in shock
Crystalloids
The first-choice crystalloid for fluid replacement in shock
PLR
The second-choice crystalloid for fluid replacement in shock
PNSS
The position used in shock management to improve venous return
Modified Trendelenburg
The drug given to correct severe metabolic acidosis in shock
Sodium bicarbonate (NaHCO₃)
How to treat underlying cause of hypovolemic shock?
Control bleeding → PIE (pressure, ice, elevate)
How to treat underlying cause of cardiogenic shock?
Give inotropes → dobutamine and dopamine
How to treat underlying cause of anaphylactic shock?
IM epinephrine
How to treat underlying cause of septic shock?
Antibiotics
How to treat underlying cause of neurogenic shock?
Immobilize
First-line vasopressor for shock
Norepinephrine
The target MAP in shock management using vasopressors is > ___ mmHg
65
What are the common causes of airway obstruction? (Hint: AIA)
AIA
Allergic reaction
Infection
Angioedema
What type of medications cause angioedema leading to airway obstruction?
ACE inhibitors
REMEMBER: ACE stands for angioedema, cough, elevated potassium
Disease process of airway obstruction:
Obstruction → absent ventilation → ____ & ____
Hypoxemia; hypercapnia
Disease process of airway obstruction:
Hypoxemia → ____
Hypercapnia → ____
Hypoxia
Acidosis
Disease process of airway obstruction:
Hypoxia and acidosis → ____ arrest → death
Cardiopulmonary
BONUS: disease process of airway obstruction
Obstruction → absent ventilation → impaired gas exchange → hypoxemia and hypercapnia → hypoxia + acidosis → cardiopulmonary arrest → death
Able to cough
A. Partial airway obstruction
B. Complete airway obstruction
A. Partial airway obstruction
Unable to cough, breathe, or speak
A. Partial airway obstruction
B. Complete airway obstruction
B. Complete airway obstruction
Wheezing
A. Partial airway obstruction
B. Complete airway obstruction
A. Partial airway obstruction
Universal sign: clutching of neck
A. Partial airway obstruction
B. Complete airway obstruction
B. Complete airway obstruction
Cyanosis
A. Partial airway obstruction
B. Complete airway obstruction
B. Complete airway obstruction
Stridor
A. Partial airway obstruction
B. Complete airway obstruction
B. Complete airway obstruction
Intervention: encourage to cough forcefully
A. Partial airway obstruction
B. Complete airway obstruction
A. Partial airway obstruction
Intervention: Heimlich maneuver
A. Partial airway obstruction
B. Complete airway obstruction
B. Complete airway obstruction
Airway obstruction interventions for conscious:
Adults/children
Infant (<1 yo):
____
____
Pregnant/obese
Heimlich
Back blows
Chest thrust
Chest thrust
Airway obstruction: The correct management for an unconscious choking victim
Continue CPR
Airway obstruction: The method used to remove a visible foreign object from the mouth
Finger sweep method
Airway obstruction: The finger sweep method is contraindicated if the object is ___
Invisible
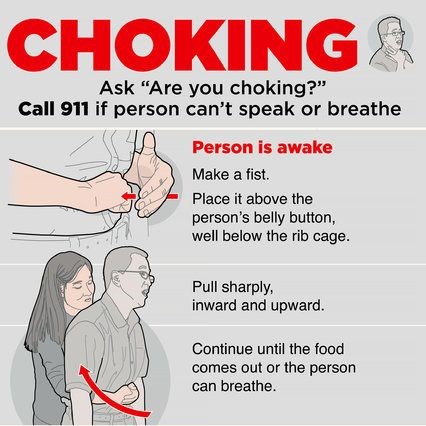
Airway obstruction: The Heimlich maneuver involves a quick ____ thrust performed above the ____ and below the ____ ____
Abdominal; umbilicus; xiphoid process
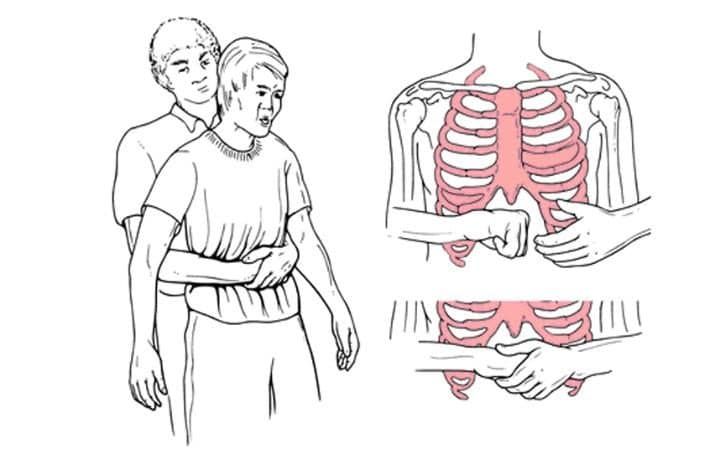
BONUS: Heimlich maneuver
Heat-induced illness: What age group is the most at risk? Why?
Older adults d/t decreased sweating mechanism → decreased heat loss
Heat-induced illness: What are the causes of heat exhaustion/stroke? (Hint: HIP)
HIP
Hot environment
Inadequate fluid intake
Physical activity
Early effects of heat exposure causing fluid & electrolyte imbalance
A. Heat illness
B. Heat exhaustion
C. Heat stroke
A. Heat illness
Result of prolonged heat exposure (hours–days) → dehydration and ↓ perfusion
A. Heat illness
B. Heat exhaustion
C. Heat stroke
B. Heat exhaustion
Untreated heat exhaustion
A. Heat illness
B. Heat exhaustion
C. Heat stroke
C. Heat stroke
Failure of thermoregulation due to hypothalamic dysfunction
A. Heat illness
B. Heat exhaustion
C. Heat stroke
C. Heat stroke
Core temp > 40°C → protein denaturation, cytokine release, multiorgan failure
A. Heat illness
B. Heat exhaustion
C. Heat stroke
C. Heat stroke
Heat-induced illness: The structure in the brain responsible for temperature regulation that fails in heat stroke
Hypothalamus
Heat-induced illness: The absence of sweating due to hypothalamic failure
Anhidrosis
Heat-induced illness: The process in which high temperature damages proteins within cells
Protein denaturation
Heat-induced illness: Hyperthermia leads to protein denaturation, resulting in ________ and systemic inflammation
Encephalopathy
Heat-induced illness: The life-threatening end result of shock and systemic inflammation in heat stroke
Multiorgan failure
Heat-induced illness: A 25-year-old athlete collapses during a marathon. His core temp is 41.5°C, and he has hot, dry skin and confusion. Which event most likely triggered his neurologic symptoms?
A. Vasoconstriction from dehydration
B. Metabolic alkalosis
C. Excessive sweating
D. Protein denaturation and cerebral inflammation
D. Protein denaturation and cerebral inflammation
REMEMBER: Heat stroke causes protein denaturation → encephalopathy → CNS s/sx
Heat-induced illness: A patient with heat stroke is found hypotensive, with poor urine output and metabolic acidosis. What physiologic process led to this condition?
A. Cytokine-mediated vasodilation and tissue hypoperfusion
B. Vasoconstriction and decreased cardiac output
C. Hypothermia-induced shivering
D. Hypoglycemia
A. Cytokine-mediated vasodilation and tissue hypoperfusion
≥ 40°C
A. Heat stroke
B. Heat exhaustion
A. Heat stroke
< 40°C
A. Heat stroke
B. Heat exhaustion
B. Heat exhaustion
Anhidrosis → dry, hot
A. Heat stroke
B. Heat exhaustion
A. Heat stroke
Diaphoresis → moist; F&E loss
A. Heat stroke
B. Heat exhaustion
B. Heat exhaustion
Severe CNS s/sx: confusion, severe, coma
A. Heat stroke
B. Heat exhaustion
A. Heat stroke
Mild CNS s/sx: restlessness. anxiety, headache
A. Heat stroke
B. Heat exhaustion
B. Heat exhaustion
HypoTachyTachy
A. Heat stroke
B. Heat exhaustion
A. Heat stroke