15: instrumental
1/24
Earn XP
Description and Tags
115 blair
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
25 Terms
what is a satiety signal
it suppresses hunger when we are full and energy needs are met
what are 4 major satiety signals and where do they come from
insulin: from pancreas to convert glucose to energy
leptin: from fat cells when they are large (body has a lot of fat)
PYY3-36 & GLP-1 (glucagon-like protein 1): from intestines to signal gut is full
what are the gut-derived hormones
leptin, GLP-1, Ghrelin
what is ghrelin
hormone produced by stomach when empty (hunger signal)
what are brain signals that promote hunger
orexigenic signals (hunger = orexia)
what are brain signals that suppress hunger
anorexigenic signals (anorexia = satiety)
what role does ventromedial hypothalamus (VMH) have on appetite
it is anorexigenic: suppresses hunger
when it is lesioned rats have enhanced appetite and maintain homeostasis at higher weight
what role does lateral hypothalamus (LH) have on appetite
it is orexigenic: promote hunger
LH lesions cause rats to have suppressed appetite & maintain homeostasis at lower weight
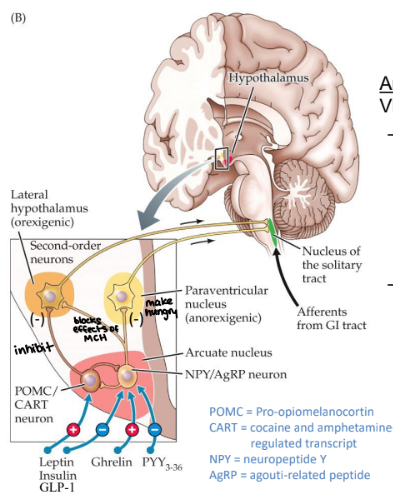
what does the arcuate nucleus do
projects to LH and VMH, contains: appetite supressing POMC/CART neurons & appetite-enhancing AgRP/NPY neurons
what hormones affect POMC/CART neurons and what does it do when activated
excited by leptin, insulin, & GLP-1
when activated, releases a-melanocyte-stimulating hormone (a-MSH) to inhibit LH
what hormones affect AgRP/NPY neurons and what does it do when activated
excited by ghrelin, inhibited by insulin, leptin, GLP-1, & PYY
releases NPY to inhibit appetite-suppressing neurons in paraventricular nucleus (PVN)
releases AgRP to block effects of a-MSH in LH
what happens when mice can’t produce leptin
it becomes obese because fat cells can not communicate to turn off hunger
can leptin help obese people lose weight
no, they don’t suffer from leptin deficiency, they suffer from leptin insensitivity so they typically have higher than normal levels of leptin (likely since they have more fat)
what are GLP-1 agonists
ozempic, wegovy, saxenda
revolution in weight loss
what is anorexia nervosa and can it be treated
pathological loss of appetite (anorexia) that originates in nervous system (nervosa)
not treatable with appetite stimulating drugs (psychological!)
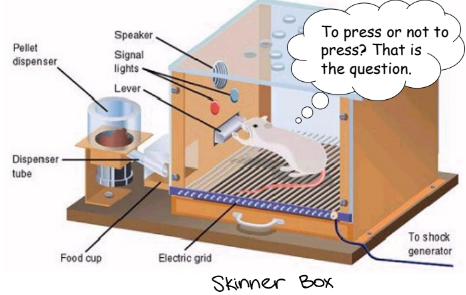
what is operant (instrumental) conditioning
learning to choose or act rather than expect (pavlovian)
subject learns to perform non-innate operant response to obtain reinforcing outcome
a discriminative stimulus can signal when the outcome is available to be earned
what are the types of operant reinforcement
positive: reward reinforcer
negative: aversive stimulus is stopped
punishment: delivery of aversive stimulus
extinction: withholding expected delivery of reward
what is the mesolimbocortical pathway & why is it important
originates from dopamine neuron cell bodies in VTA which sends axons to cortex, hippocampus, nucleus accumbens
important for motivation & reward
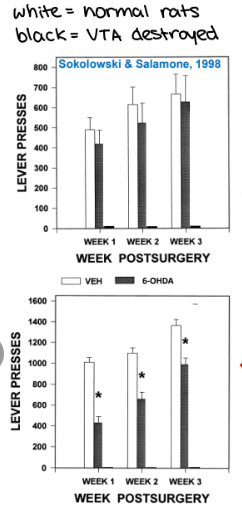
what happened when rats mesolimbocortical pathway was lesioned
after being trained to press lever for cocaine, they stopped pressing lever even though they would get cocaine, so VTA is necessary for rewarding feeling
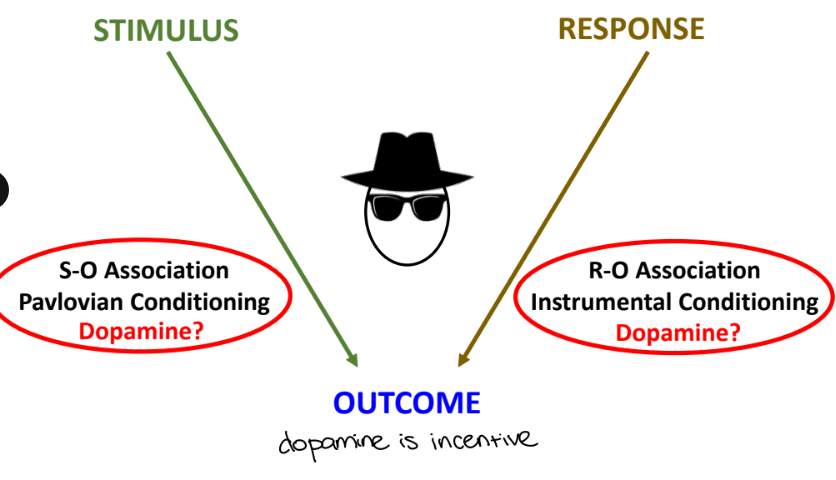
what is the hedonic/reward theory of midbrain dopamine function
dopamine acts as a positive reinforcer for instrumental behaviors
dopamine = liking
what happened when rats mesolimbocortical pathway was lesioned and there was a condition of easy work & hard work
lesion did not significantly reduce response rates for easy work, but did for hard work
what is incentive salience theory of midbrain dopamine function
dopamine release triggers a feeling of wanting, which drives motivation/incentive to work for an outcome
dopamine = wanting
what is the motivation to exert effort
when it is expected to have a good return on investment, so VTA dopamine neurons may be activated by an incentive
when a monkey was taught that a CS (visual stimulus) would deliver a US (juice) what happened to dopamine (DA) neurons in VTA
baseline: DA responds to only US
late training: DA responds to CS but not US
extinction: DA responds to CS and inhibited when the expected US stops
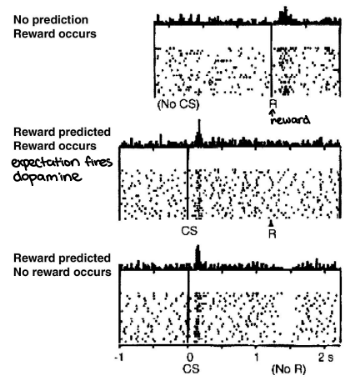
what is the prediction error theory of midbrain dopamine function
dopamine release occurs when the outcome is better than expected
dopamine = surprise
δ prediction error = Rearned − Rexpected