MEDRADSC 3K03 Lecture 7 - Image Reconstruction and CT Numbers
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
15 Terms
DFOV is also called a
Zoom or target
What does DFOV determine?
How much raw data is used to reconstruct an image → diameter of reconstructed image
DFOV/SFOV cannot be larger than DFOV/SFOV
DFOV, SFOV
Small DFOV
Takes small portion of data and fills with matrix
Large DFOV
Condenses large amts of tissue into matrix, more data per pixel so decreases spatial resol
Image center
When reconstructing image, in addition to identifying DFOV diameter, must specify which part of SFOV we want
How can we specify which part of the SFOV we want?
Cartesian coordinates
Mathematical X & Y coordinates
RAS coordinates
Right/left, ant/post, sup/inf
Still cartesian but based on body locations
When is a narrow WW used?
Show tissues of similar densities, small difference in CT number
Values spread out over available greyscale
Small differences are going to be assigned separate shades of gray
Why do we want a narrow window to visualize the brain?
CSF, white and gray matter all have CT numbers close together
When do we use a wide WW?
To visualize tissues that vary greatly; can also decrease visualization of noise
Downside of a wide WW
Dec image contrast, difficult to see differences between gray and white matter
What are the different WW, WL needed for when visualizing a CT scan of the thorax?
Mediastinum
Air filled lungs
Ribs and calcifications
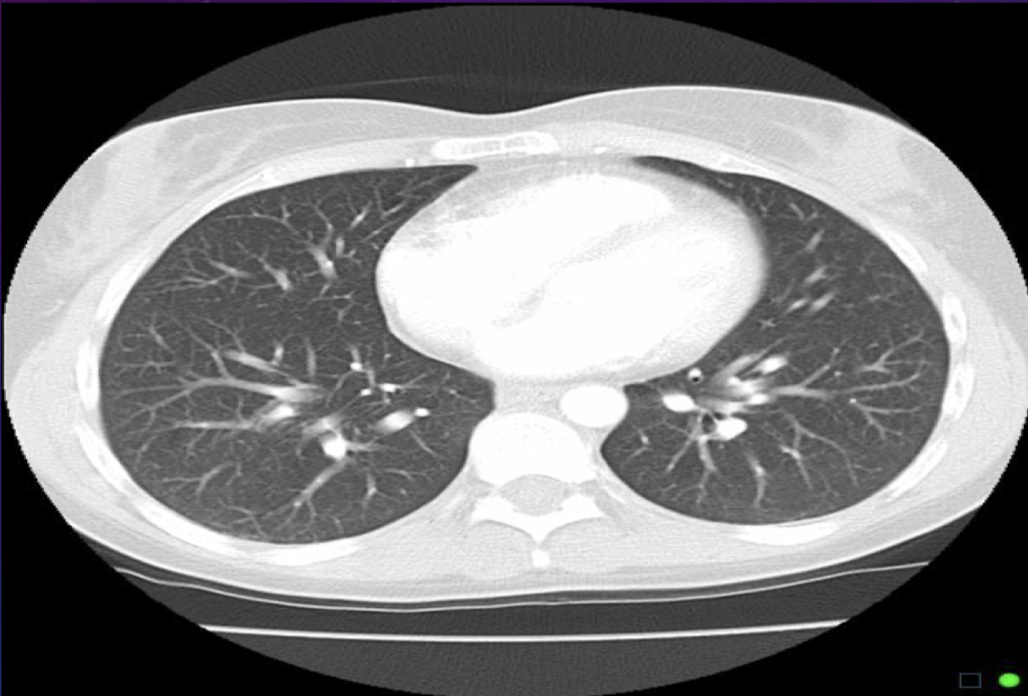
For a lung window for a thorax scan, why do we want a wide WW?
To show more gray for smaller structures
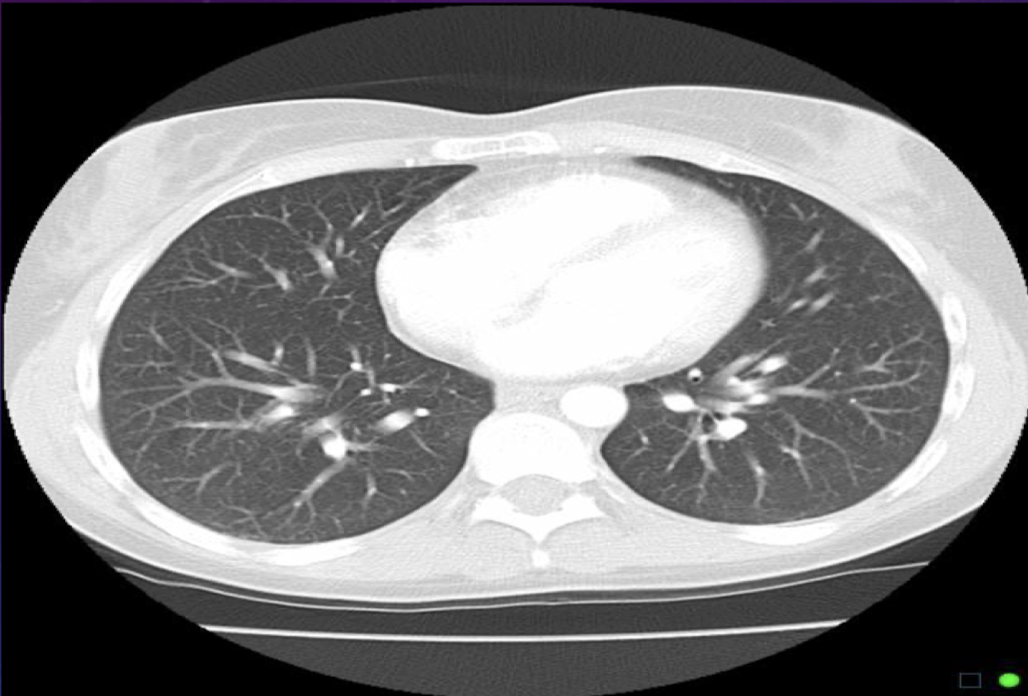
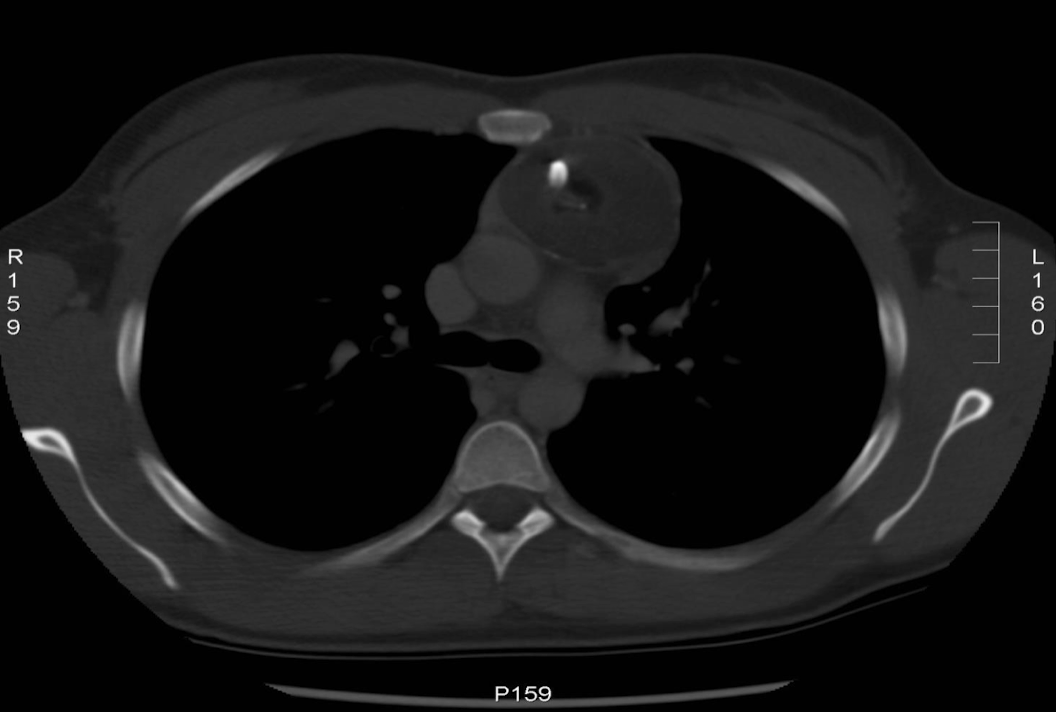
When do we need a bone window for a thorax scan?
Requested if pt has suffered any trauma or if looking for calcifications
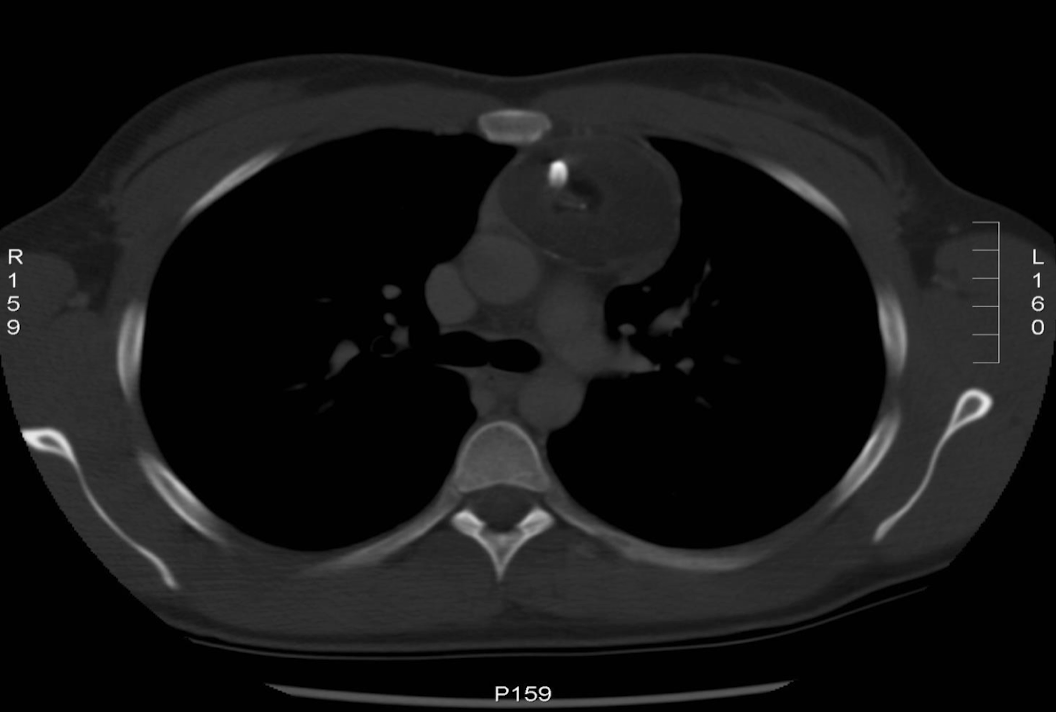
What can we see in a mediastinal window for a thorax scan that we can’t see in a lung scan?
Pulmonary artery