Bio 14 Week 2 Nervous System Pt. 2
1/61
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
62 Terms
Neurons and Glia
Two Broad Categories of Nerve Cells
Neurons
electrically excitable nerve cells that can receive and transmit signals
Glia
nerve cells that provide mechanical and metabolic support to neurons
Astrocytes/ependymal cells/oligodendrocytes/microglia
CNS neuroglial cell types in vertebrates
satellite cells/schwann cells
PNS neuroglial cell types in vertebrates
Astrocytes
CNS glia that are
involved in formation of the blood brain barrier
deliver nutrients
maintain extracellular K+ homeostasis
Ependymal cells
CNS glia that line the spinal cord and brain ventricles; produce cerebrospinal fluid (CSF).
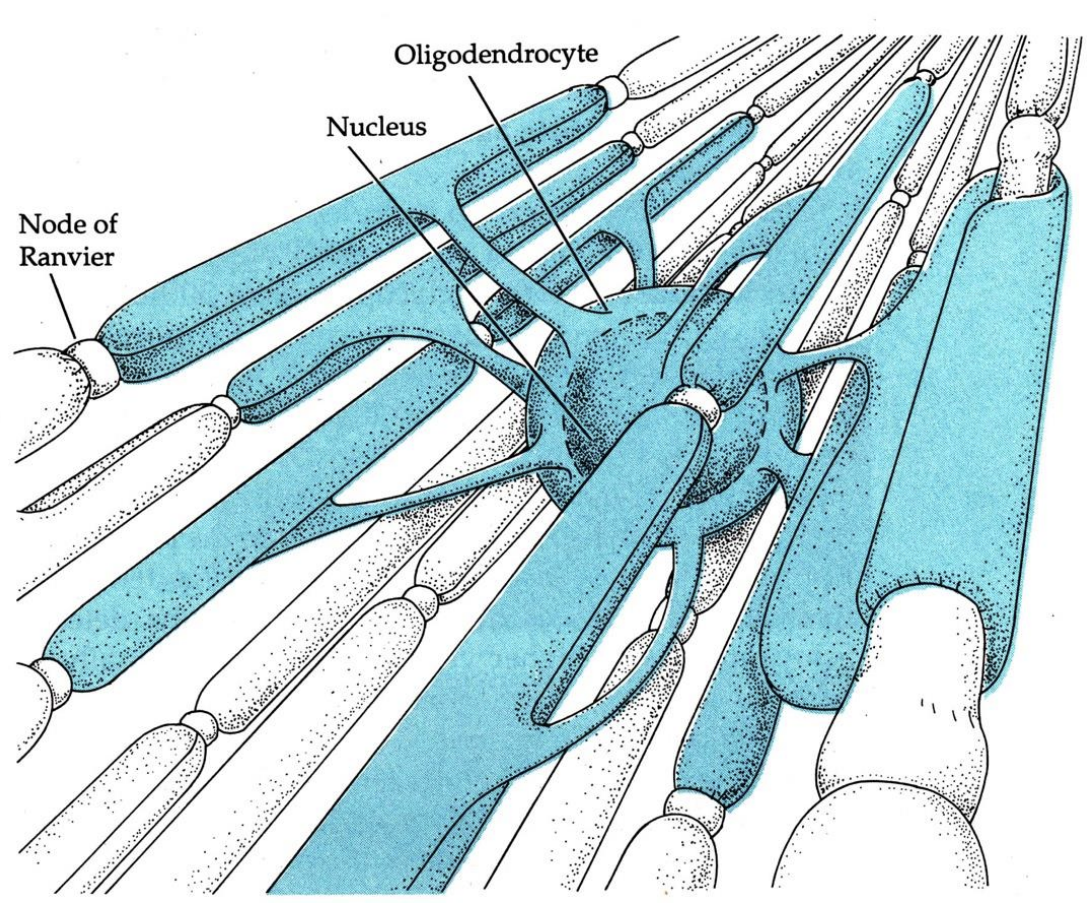
oligodendrocytes
CNS glia that forms myelin in the CNS
microglia
CNS glia that are the immune cells of the brain; responsible for inflammatory responses and removing debris and pathogens.
satellite cells
PNS glia that surrounds neuron cell bodies in the ganglia of the peripheral nervous system (PNS).
Schwann cells
PNS glia that forms myelin in the peripheral nervous system (PNS) and assist with neuron regeneration after injury.

Dendrites
Often more than one per cell.
Have a tapering diameter, getting smaller the further they are from the cell body.
Receive information on the cell body and on the ends of small "spines."
Do not have a myelin sheath.
Axon Initial Segment (AIS)
Located near the cell body.
Expresses a specialized combination of proteins and ion channels.
Segregates the axon from the dendrite and soma.
Typically shapes and generates information before it is conducted down the axon.
Axons
Usually only one per cell.
Have a constant diameter, unlike dendrites.
Sometimes have a myelin sheath.
Conduct/send information.
Axon Terminal
The site of neurotransmitter release to generate signals in other cells, such as muscle cells.
K+
Ions with greater concentration inside the cell
Na+, Cl-, Ca2+
Ions with greater concentration outside the cell
negative (-70 mV)
the cell interior is _____ relative to the outside of the cell
Graded potentials, action potentials
General types of membrane potential changes in neurons
Graded potentials
membrane potential changes in neurons that are due to something external: sensory stimulus or neurotransmitters
action potentials
membrane potential changes in neurons that are intrinisic: generated by the cell
passive/dendrites/cell body
Graded potentials are ______ responses that occur primarily in the _______ and _______ of neurons. The size of the change depends on the strength of the stimulus.
self-propagating
Generally, graded potentials are not _________. They are confined to the area where the stimulus was applied, and the size of the change in potential depends on the strength of the stimulus. A stronger stimulus will create a larger graded potential.
Na+ , K+ , Ca2+
Action potentials are generated by activity of voltage-gated ion channels selective for ______
Action Potential Threshold
The membrane potential at which an action potential will occur. In neurons, this is often around -50 mV.
Threshold Depolarization
The unstable membrane potential where Na⁺ ions flowing into the cell exceed the flow of K⁺ ions out of the cell, triggering the action potential. It is referred to as a "point of no return," initiating the feedforward cycle of the action potential.
Feedforward Cycle
The action potential process that is initiated once the threshold is reached, leading to an explosive depolarization followed by repolarization of the cell membrane. This cycle is self-propagating and continues down the axon without further external stimuli.
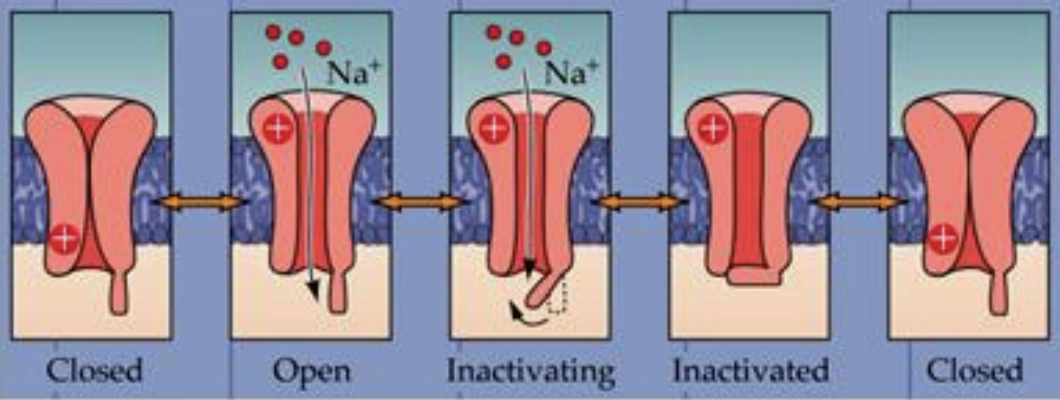
Na⁺ Channels
Open Briefly (~1 millisecond): The ______ open in response to membrane depolarization, allowing Na⁺ to flow into the cell.
Inactivate Rapidly: After opening, the _______ close quickly even if depolarization is still happening.
Closed Until Resting Potential: The _______ remain closed until the resting membrane potential is restored.
K⁺ Channels
Open in Response to Depolarization: These channels open slower than Na⁺ channels after depolarization.
K⁺ Flow Out of the Cell: K⁺ moves out of the cell through the open channels, helping to repolarize the membrane.
Close When Membrane is Repolarized: The _______ close when the membrane potential returns to its resting values.
Hyperpolarization
The slower opening of K⁺ channels is indeed a key factor in __________
Depolarizing phase
Increasing number of Na+ channels opening
(K+ channels are also stimulated by the depolarization, but are slower to open)
Repolarizing phase
Increasing numbers of Na+ channels inactivating
More K+ channels are now open than Na+ channels are open
passive spread/action potential
The _______ of membrane potential changes extends only short distances. So the membrane potential change would diminish rather quickly over a relatively short distance if the _______ was not generated
integral membrane
Voltage-gated channels are _______ ______ proteins
4 homologous domains/6 membrane spanning regions
Voltage-gated channels usually have ________ with _________ in each domain
symmetry
Voltage-gated channels typically have 4-fold ____
Na+ channels/Ca2+ channels
Types of voltage-gated channels that have 4 very highly homologous domains in 1 channel protein
K+ channels
Types of voltage-gated channels made up of 4 distinct, yet homologous, subunits
Pore loops (ion selectivity)
These ________ determine which ions the channel is selective for. For example, the Na+ channel has a specific _______ that allows only Na+ to pass through while excluding other ions.
pore loop
each domain of a voltage-gated ion channel typically has its own ________
S4 transmembrane region
each domain in a voltage-gated ion channel contains an _______ for voltage sensing/activation
third/positively/hydrophilic
Every ______ amino acid in the S4 region is a _______ charged amino acid (arginine or lysine) → S4 region is _______
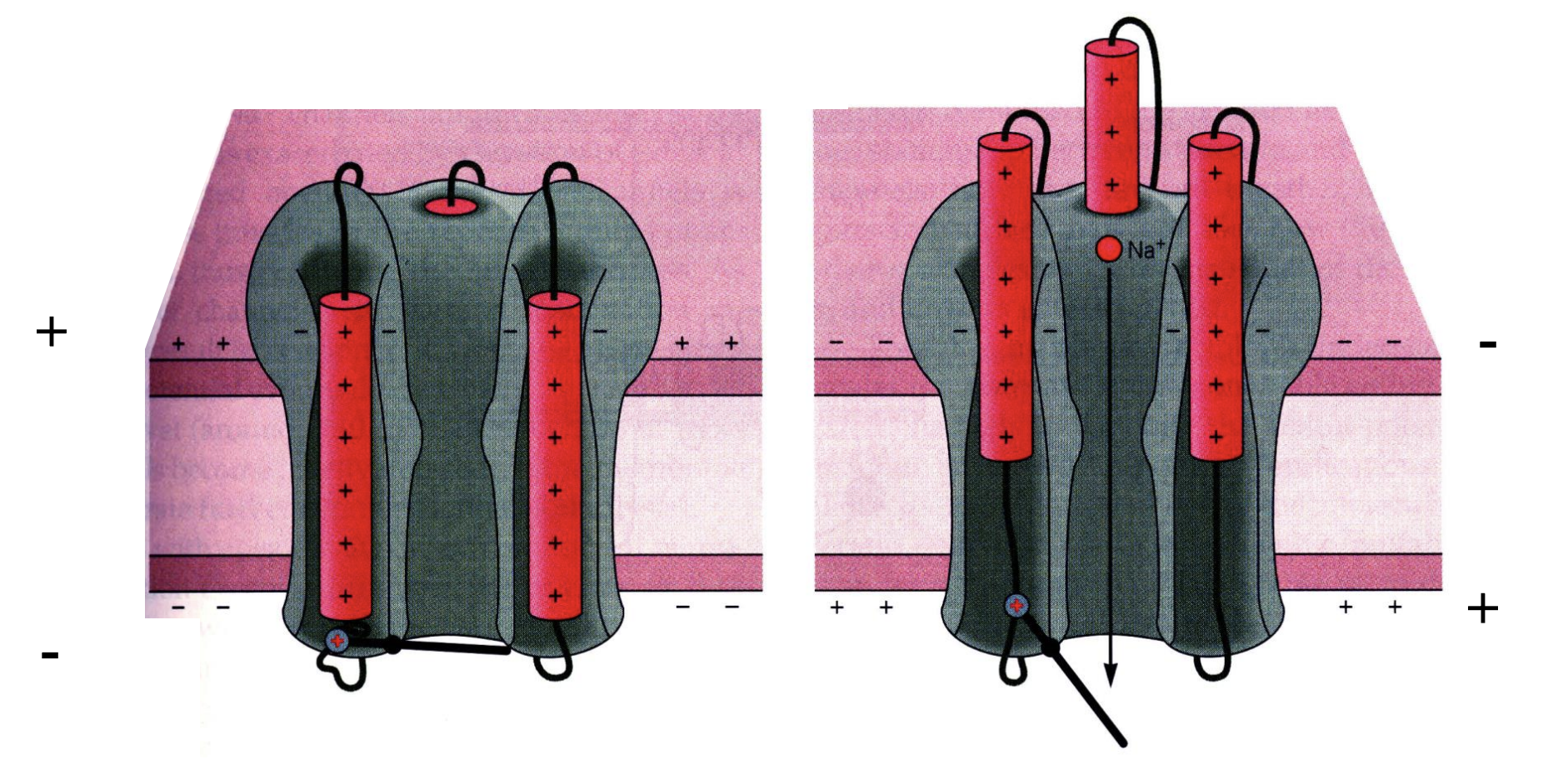
outward helical twist of S4
For S4, membrane depolarization causes the _____
channel opening (more + charges in cell)
the outward helical twist of S4 leads to _____
Inactivation Loop (Na⁺ Channel)
Closes the channel by "plugging" the pore of the channel once it has been activated (opened).
It closes very quickly even if the membrane remains depolarized to ensure that the ion channel is only open for a short period
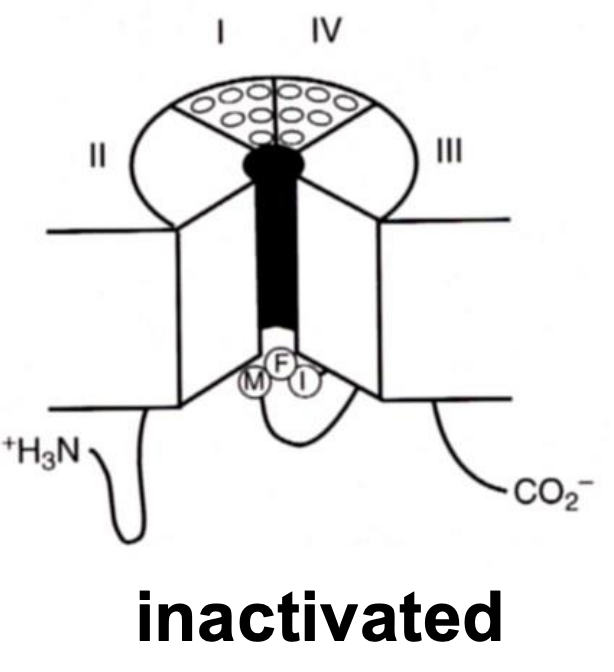
Ball and Chain Mechanism (K⁺ Channel)
inactivation mechanism where a segment of amino acids moves into the pore and blocks it after the channel opens
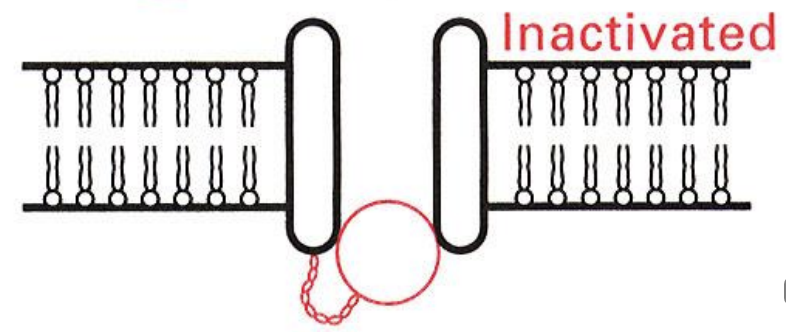
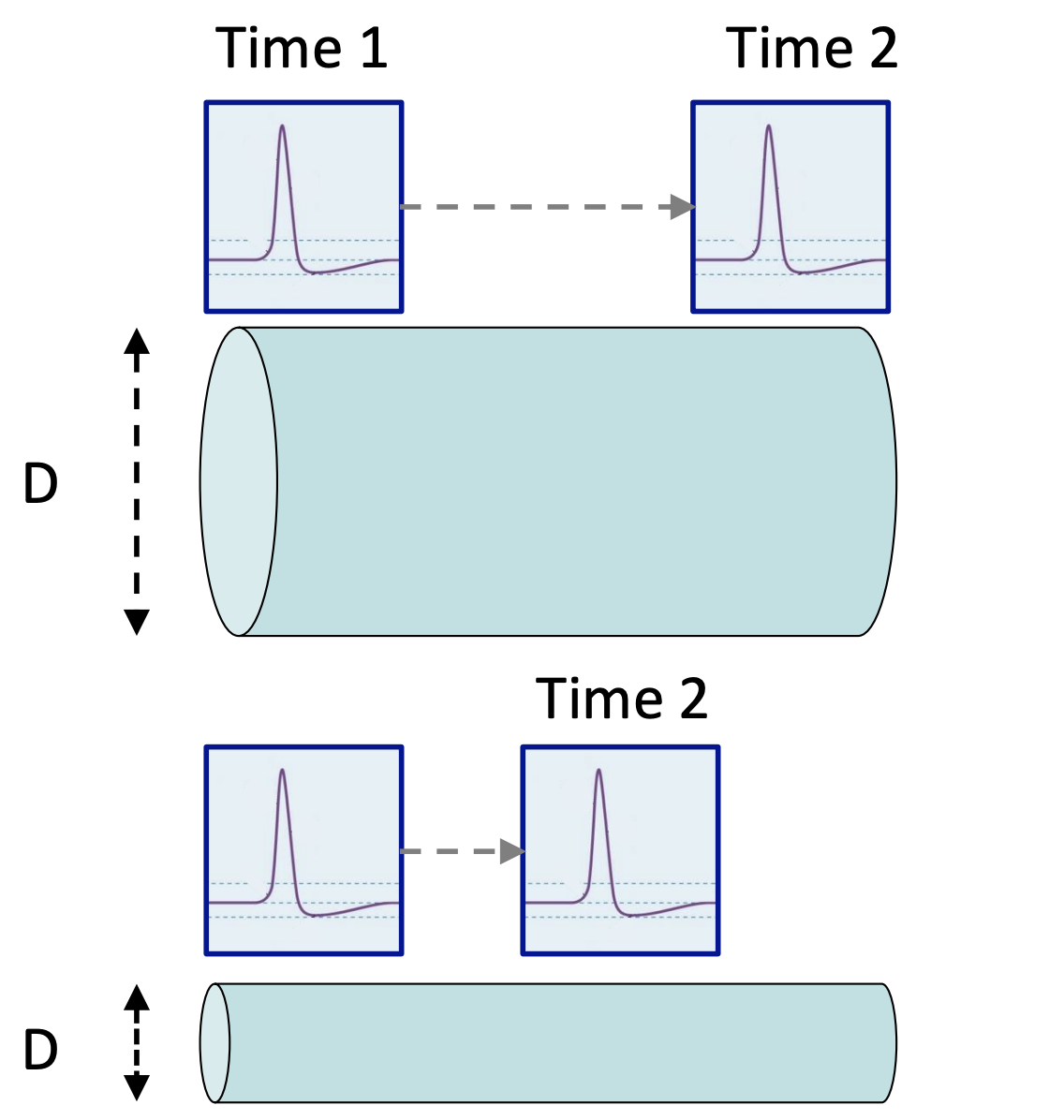
axon diameter/myelination
The conduction velocity (speed) of action potentials vary as a function of _____ and _____
decreased internal resistance
Axons with larger diameters have higher conduction velocities due to __________ to flow of charge
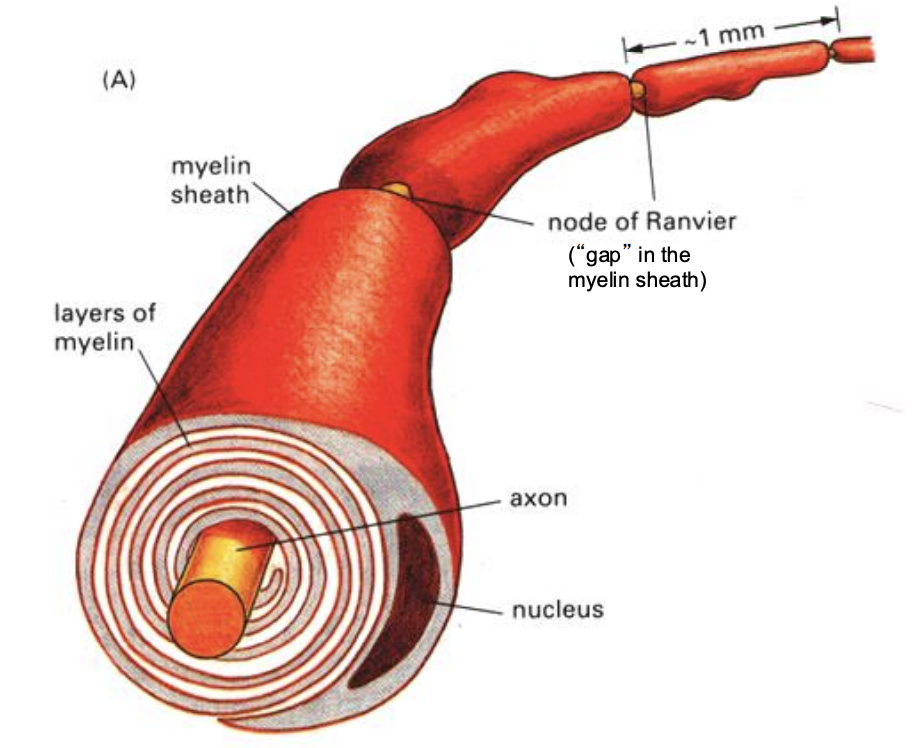
Myelin
a lipid-rich layer coating the axons of some neurons
Vertebrates
Myelin is only found in _______
Myelin formation
• Myelin is formed by glial cells that wrap themselves around the axon multiple time
• As each additional layer is formed, the cytoplasm continues to be squeezed out and the glial membranes get more closely packed together
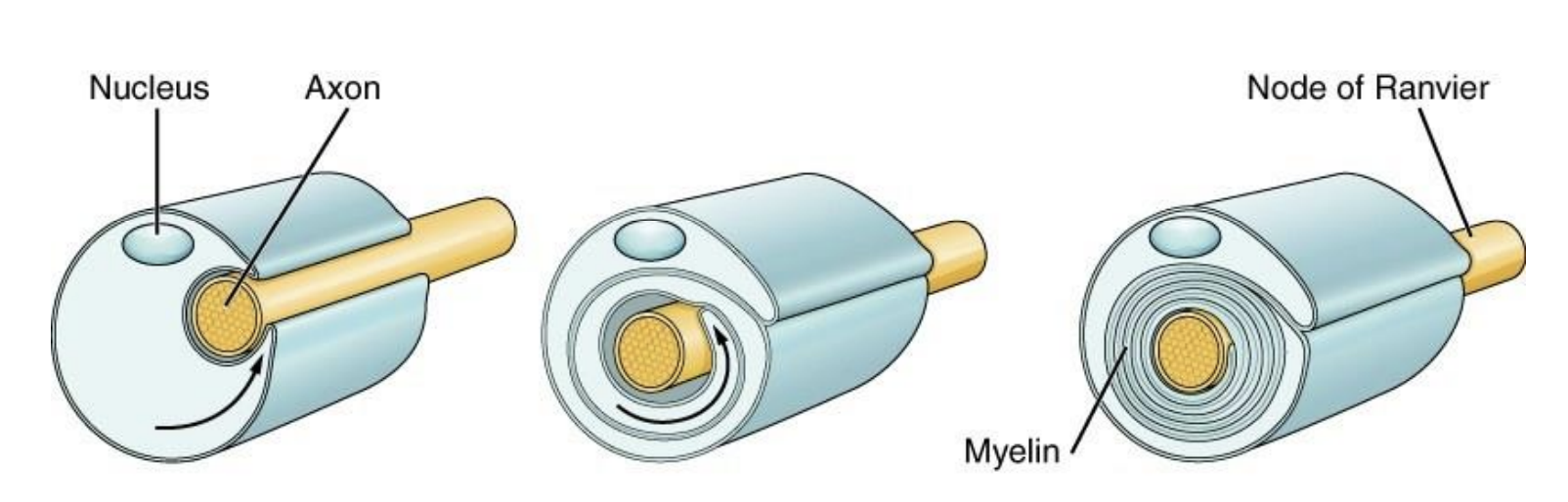
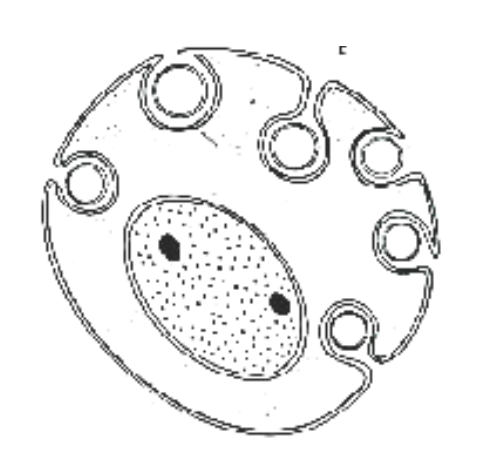
ONE
Individual Schwann cells form myelin sheath around ___ axon
30%
In about ___ of the peripheral axons, Schwann cells help form a myelin sheath around a single axon
loose wraps/multiple axons
Majority of Schwann cells form _______ around _______ THIS IS NOT MYELIN!
individual/multiple
In the CNS, ______ oligodendrocytes form myelin sheaths around ______ axons
Capacitance
the ability to store charge
decreases/capacitance
Myelin _____ the _______ of the axon membrane
separation of charges/attraction of ions
Greater ________ myelin, decreased _______ across membrane and decreased ability to store charge
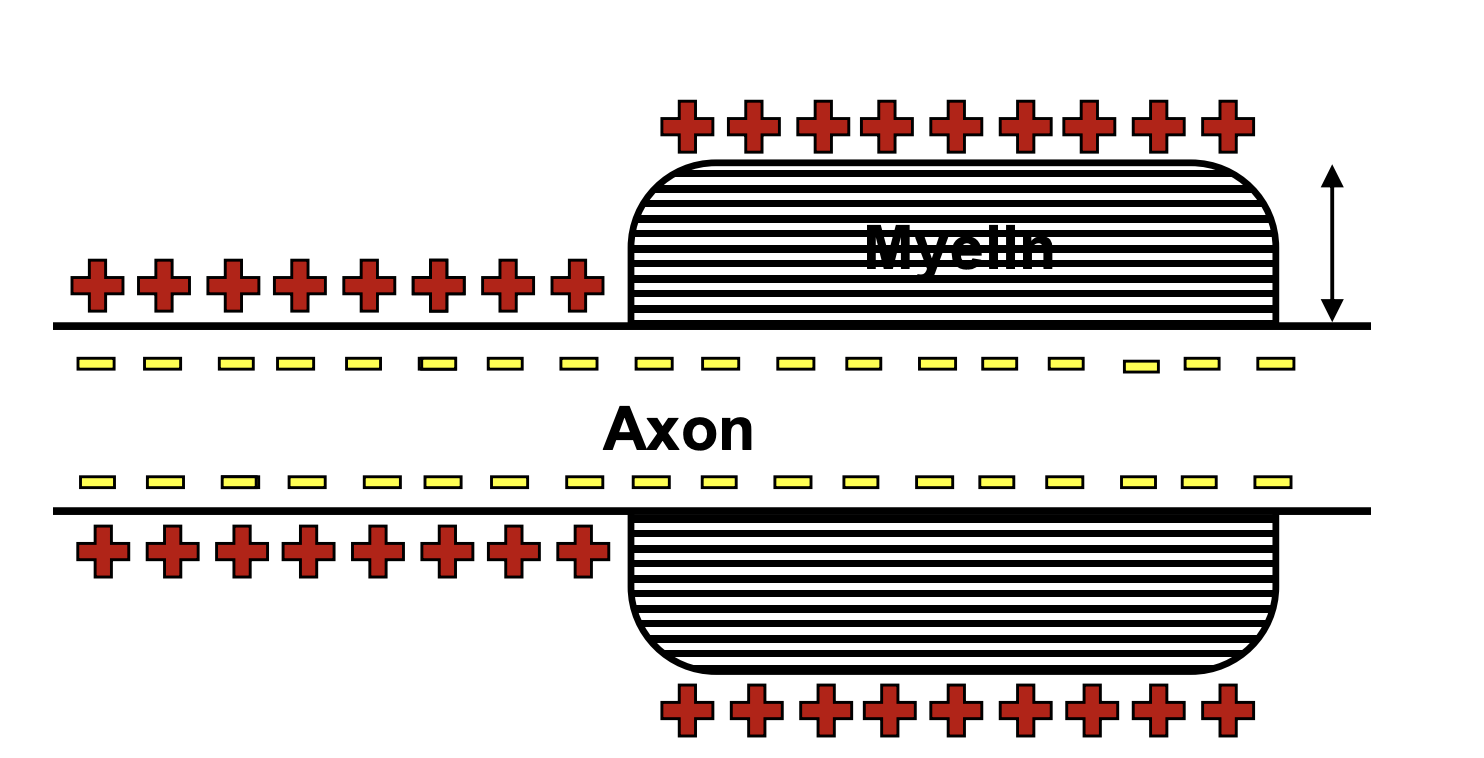
few/myelin sheath
there are very ___ Na and K channels under the ______
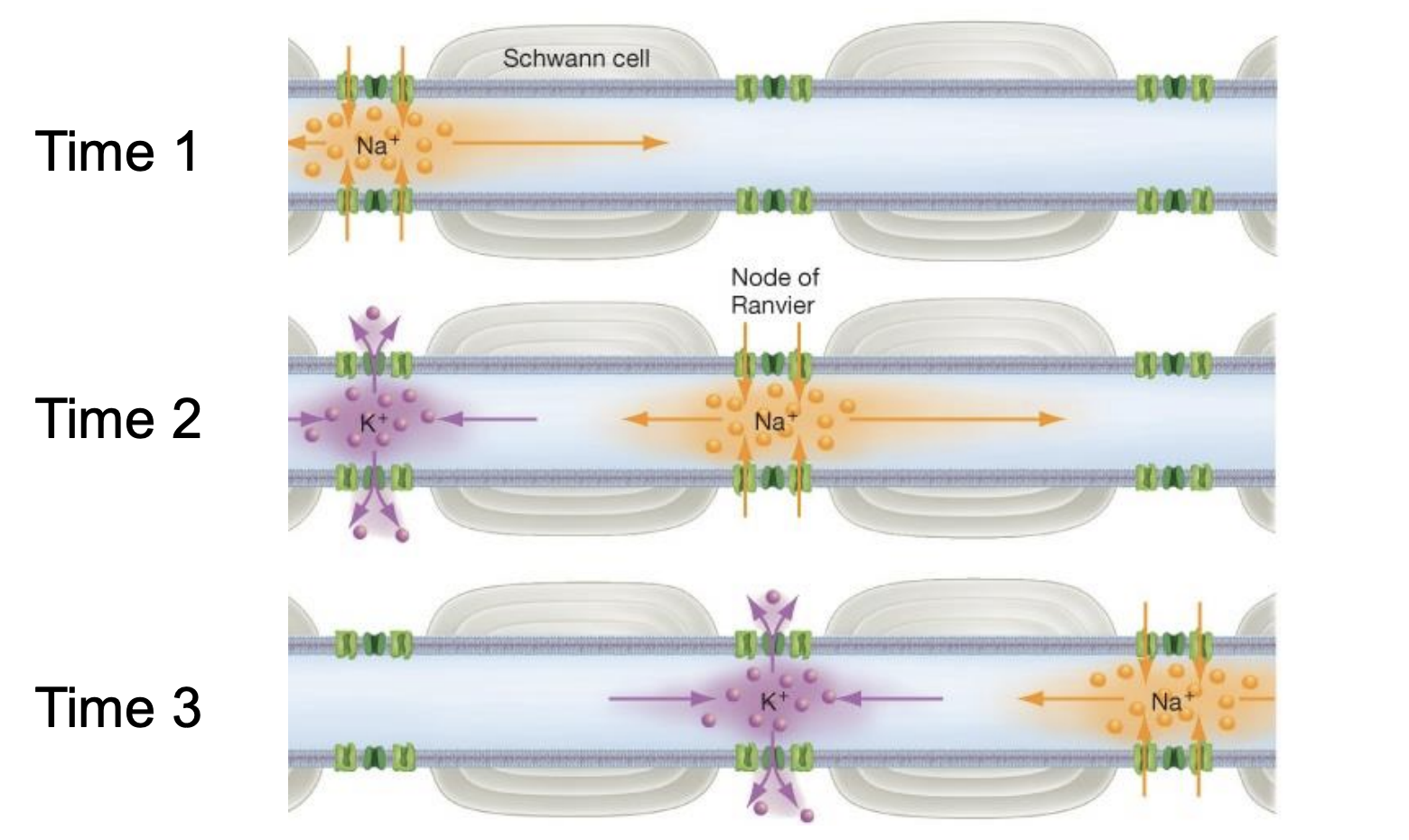
saltatory conduction
process in myelinated axons where action potentials jump from one Node of Ranvier to the next along the axon, instead of traveling the entire length of the axon
Node of Ranvier
periodic gaps in the myelin sheath that insulates nerve axons
energy/signal transmission
Saltatory conduction allows the action potential to move much faster by "jumping" between nodes. This reduces the _____ required and speeds up ______.