Ganong Chapter 37: Renal Function and Micturition
1/207
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
208 Terms
What makes up the nephron?
Renal tubule + glomerulus
Is the diameter of the afferent or efferent arteriole larger?
Afferent arteriole
What are the layers that separate blood from glomerular filtrate?
Capillary endothelium
Specialized epithelium of the capsule
Structure of the Glomerular Capillary Endothelium
Fenestrated
Pores 70-90 nm in diameter
Completely surrounded by glomerular basement membrane and podocytes
Podocytes have pseudopodia that interdigitate to form filtration slits along the capillary wall
Glomerular Basement Membrane
Basal lamina
Does not contain visible gaps or pores
Functionally permits the free passage of neutral substances up to 4 nm in diameter and almost totally excludes those with diameters greater than 8 nm
Mesangial Cells
Located between the basal lamina and endothelium
Contractile and play a role in regulation of glomerular filtration
Secrete the extracellular matrix, take up immune complexes, and are involved in the progression of glomerular disease
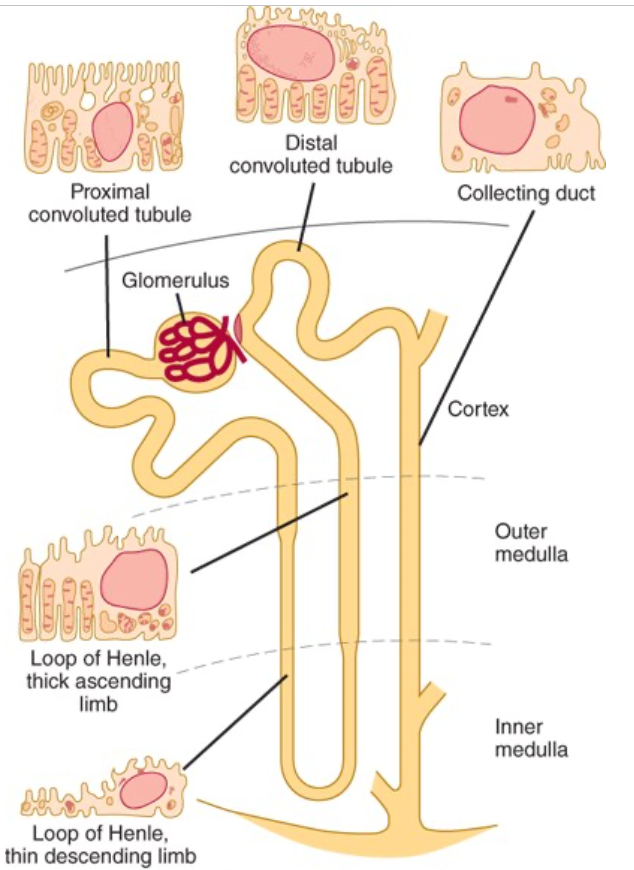
Structure of the Proximal Convoluted Tubule
Wall made up of a single layer of cells that interdigitate with one another and are united by apical tight junctions
Between the cells are extensions of the extracellular space called the lateral intercellular spaces
Luminal edges of the cells have a striated brush border
Structure of the Loop of Henle
Descending portion of the loop and proximal portion of the ascending limb made up of thin, permeable cells
The thick portion of the ascending limb is made up of thick cells containing many mitochondria
Cortical nephrons have short loops of Henle
Juxtamedullary nephrons have long loops extended down into the medullary pyramids
What makes up the juxtaglomerular apparatus?
Macula densa
Neighboring lacis cells
Renin-secreting granular cells in the afferent arteriole
Structure of the Distal Convoluted Tubule
Starts at the macula densa
Epithelium is lower than that of the proximal tubule
No distinct brush border
Structure of the Collecting Ducts
Pass through the renal cortex and medulla to empty into the pelvis of the kidney at the apexes of the medullary pyramids
Epithelium is made up of principal cells (P cells) and intercalated cells (I cells)
Principal Cells (P cells)
Relatively tall
Have few organelles
Involved in Na+ reabsorption and vasopressin-stimulated water reabsorption
Intercalated Cells (I cells)
Present in smaller numbers
Also found in the distal tubules
Have more microvilli, cytoplasmic vessels, and mitochondria
Concerned with acid secretion and HCO3- transport
Renal Medullary Interstitial Cells (RMICs)
Specialized fibroblast-like cells
Major site of COX-2 and prostaglandin synthase (PGES) expression
What is the major prostanoid synthesized in the kidney?
PGE2
Function of PGE2
Important paracrine regulator of salt and water homeostasis
Where is PGE2 secreted from?
Renal medullary interstitial cells (RMICs)
Macula densa
Cells in the collecting ducts
Where are PGI2 and other prostaglandins secreted from?
The arterioles and glomeruli
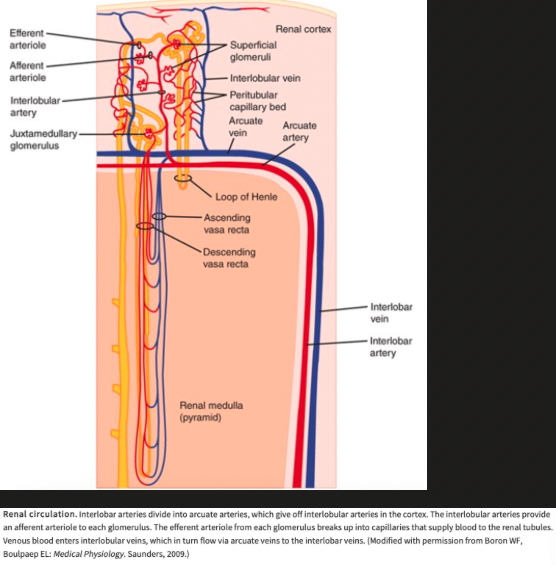
What are afferent arterioles branches of?
Interlobular arteries
What do efferent arterioles become?
Peritubular capillaries before draining into interlobular veins
What are the only capillaries in the body that drain into arterioles?
Glomerular capillaries
Where do efferent arterioles from the juxtamedullary glomeruli drain into?
Efferent arterioles from the juxtamedullary glomeruli drain into a peritubular network and into vessels that form hairpin loops (vasa recta)
Descending vasa recta have a nonfenestrated endothelium that contains a facilitated transporter for urea
Ascending vasa recta have a fenestrated endothelium
How much blood is in the renal capillaries at any given time?
30-40 mL
Renal Circulation
Where do the renal lymphatics drain?
Via the thoracic duct
Renal Capsule
Limits swelling if the kidney becomes edematous and renal interstitial pressure rises which decreases GFR and enhances and prolongs anuria in AKI
What do renal nerves contain?
Many postganglionic sympathetic efferent fibers and a few afferent fibers
Cholinergic Innervation of the Kidney
Via the vagus nerve
Sympathetic Preganglionic Innervation of the Kidney
Comes primarily from the lower thoracic and upper lumbar segments of the spinal cord
Where are cell bodies of the post ganglionic neurons of the kidney located?
In the sympathetic ganglion chain, in the superior mesenteric ganglion, and along the renal artery
Where are sympathetic fibers distributed in the kidney?
Afferent and efferent arterioles
Proximal and distal tubules
Juxtaglomerular apparatus
What is the innervation of the thick ascending loop of Henle?
Dense nonadrenergic innervation
Where do renal nociceptive afferents enter the spinal cord?
In the thoracic and upper lumbar dorsal roots
Renorenal Reflex
An increase in ureteral pressure in one kidney leads to a decrease in efferent nerve activity to the contralateral kidney which permits and increase in its excretion of Na+ and water
How much blood per minute do the kidneys receive in a resting adult?
1.2-1.3 L of blood per minute or just under 25% of the cardiac output
Determining Renal Blood Flow with the Fick Principle
By measuring the amount of a given substance taken up per unit of time and dividing this value by the arteriovenous difference for the substance across the kidney
Renal Plasma Flow (RPF)
Equals the amount of a substance excreted per unit of time divided by the renal arteriovenous difference as long as the amount in the red cells is unaltered during passage through the kidney
Any excreted substance can be used if its concentration in arterial and renal venous plasma can be measured and if it is not metabolized, stored, or produced by the kidney and does not itself affect blood flow
Measuring RPF using PAH
RPF can be measured by infusing p-aminohippuric acid (PAH) and determining its urine and plasma concentrations
PAH is filtered by the glomeruli and secreted by the tubular cells so its extraction ratio is high
When PAH is infused at low doses, 90% of the PAH in arterial blood is removed in a single circulation through the kidney
Can calculate RPF by dividing the amount of PAH in the urine by the plasma PAH level, ignoring the level in renal venous blood
Peripheral venous plasma PAH concentration is essential identical to that in the arterial plasma reaching the kidney
Value obtained called the effective renal plasma flow (ERPF) to indicate that the level in renal venous plasma was not measured

Extraction Ratio
Arterial concentration minus renal venous concentration divided by arterial concentration
Effective renal plasma flow (ERPF)/extraction ratio = actual RPF
Calculating Renal Blood Flow Using the Hematocrit
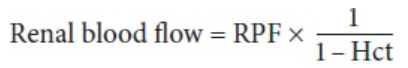
What is the glomerular capillary pressure when mean systemic arterial pressure is 100 mmHg?
Around 45 mmHg
What is the pressure drop across the glomerulus?
The pressure drop across the glomerulus is only 1-3 mmHg but a further drop occurs in the efferent arteriole so that the pressure in the peritubular capillaries is about 8 mmHg
What is the pressure in the renal vein?
About 4 mmHg
What % of systemic arterial pressure is glomerular capillary pressure?
About 40% of systemic arterial pressure
Action of Norepinephrine on Renal Blood Flow
Constricts renal vessels
Greatest effect of injected norepinephrine on interlobular arteries and afferent arterioles
Action of Dopamine on Renal Blood Flow
Causes renal vasodilation and natriuresis
Effect of Angiotensin II on Renal Blood Flow
Exerts a constrictor effect on both the afferent and efferent arterioles
Effect of Prostaglandins on Renal Blood Flow
Increase blood flow in the renal cortex and decrease blood flow in the renal medulla
Effect of Acetylcholine on Renal Blood Flow
Renal vasodilation
What effect does a high protein diet have on renal blood flow?
High protein diet raises glomerular capillary pressure and increases renal blood flow
What does stimulation of the renal nerves result in?
Increases renal secretion by direct action of released norepinpehrine on B1-adrenergic receptors on the juxtaglomerular cells and it increases Na+ reabsorption, probably by a direct action of norepinephrine on renal tubular cells
What is order of responses seen as renal nerves are stimulated to increasing extents?
First response is an increase in the sensitivity of the granular cells in the juxtaglomerular apparatus
Followed by renin secretion
Then increased Na+ reabsorption
Last, renal vasoconstriction with decreased glomerular filtration and renal blood flow
What occurs following strong stimulation of the sympathetic noradrenergic nerves to the kidneys?
Causes a marked decrease in renal blood flow which is mediated by a1-adrenergic receptors and to a lesser extent by postsynaptic a2-adrenergic receptors
What is the response of renal blood flow when systemic blood pressure falls?
The vasoconstrictor response produced by decreased discharge in the baroreceptor nerves includes renal vasoconstriction
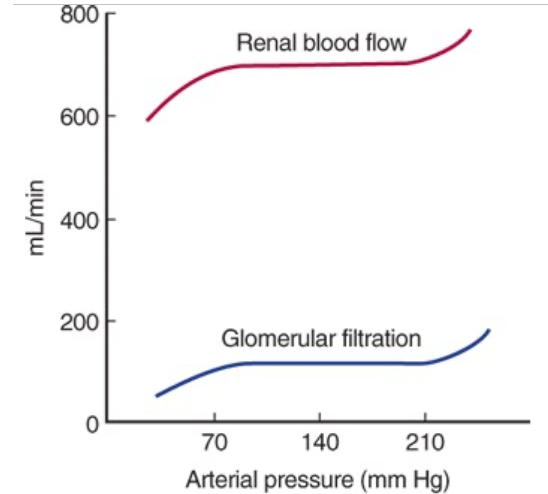
Autoregulation of Renal Blood Flow
When the kidney is perfused at moderate pressures (90-220 mmHg in the dog), the renal vascular resistance varies with the pressure so renal blood flow is relatively constant
Prevented by administration of drugs that paralyze vascular smooth muscle
At low perfusion pressures, angiotensin II appears to play a role by constricting the efferent arterioles, maintaining the GFR
Renal Cortical Blood Flow
Renal cortical blood flow is relatively great and little oxygen is extracted from the blood
What is the rate of renal cortical blood flow?
5 ml/g of kidney tissue/min
What is the PO2 of the renal cortex?
About 50 mmHg
Renal Medullary Blood Flow
Maintenance of the osmotic gradient in the medulla requires a relatively low blood flow
Metabolic work is being done, particularly to reabsorb Na+ in the thick ascending limb of Henle, so relatively large amounts of O2 are extracted from the blood in the medulla
What is the rate of blood flow in the renal medulla?
About 2.5 ml/g/min in the outer medulla
About 0.6 ml/g/min in the inner medulla
What is PO2 in the renal medulla?
About 15 mmHg, making the medulla vulnerable to hypoxia if flow is reduced further
Glomerular Filtration Rate (GFR)
The amount of plasma ultrafiltrate formed each minute
What is equine GFR?
~2-2.1 mL/kg/min
How is GFR measured?
Can be measured in experimental animals and humans by measuring the plasma level of a substance and the amount of that substance that is excreted
Substance to be used must be freely filtered through the glomeruli and neither secreted or reabsorbed by the tubules
Also must be nontoxic and not metabolized by the body
Inulin is used in humans and most animals
Renal Plasma Clearance
Volume of plasma from which a substance is completely removed by the kidney in a given amount of time (usually minutes)
GFR Equation
GFR = concentration of X in urine (Ux) x urine flow per unit of time (V)/arterial plasma level of X (Px) = clearance of X (CX)
Clearance of Creatinine (CCr)
Can also be used to determine GFR, but some creatinine is secreted by the tubules so clearance of creatinine will be slightly higher than inulin
More common is the use of PCr values as an index of renal function
What % of renal filtrate is normally reabsorbed?
99% or more
Factors that Govern Filtration Across the Glomerular Capillaries
Size of the capillary bed
Permeability of the capillaries
Hydrostatic and osmotic pressure gradients across the capillary wall
GFR Equation for Each Nephron
Kf = glomerular ultrafiltration coefficient
Product of the glomerular capillary wall hydraulic conductivity (i.e. its permeability) and the effective filtration surface area
PGC - mean hydrostatic pressure in the glomerular capillaries
PT - mean hydrostatic pressure in the tubule (Bowman's space)
piGC - oncotic pressure of the plasma in the glomerular capillaries
piT - oncotic pressure of the filtrate in the tubule (Bowman's space)
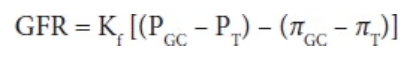
How many times more permeable are glomerular capillaries than skeletal muscle capillaries?
About 50 times more
What types of substances are freely filtered through the glomerulus?
Neutral substances with effective molecular diameters of less than 4 nm
What type of substances are not filtered through the glomerulus at all?
Neutral substances with diameters of more than 8 nm
What is the rate of filtration in the glomerulus for substances between 4 and 8 nm in diameter?
Filtration is inversely proportional to diameter
How does filtration of anionic substances 4 nm in diameter relate to neutral substances of the same size?
Filtration of anionic substances 4 nm in diameter is less than half that of neutral substances of the same size
What is the filtration of cationic substances compared to neutral substances?
Filtration of cationic substances is greater than that of neutral substances
Where does most of the protein in the urine come from?
Most of the protein in the urine is not filtered but comes from shed tubular cells
What can alter the glomerular ultrafiltration coefficient (Kf)?
Kf can be altered by the mesangial cells, with contraction of these cells producing a decrease in Kf that is largely due to a reduction in the area available for filtration
Agents that Cause Contraction of Mesangial Cells
Endothelins
Angiotensin II
Vasopressin
Norepinephrine
Platelet-activating factor
Platelet-derived growth factor
Thromboxane A2
PGF2
Leukotrienes C4 and D4
Histamine
Agents that Cause Mesangial Cell Relaxation
ANP
Dopamine
PGE2
cAMP
Why is pressure in the glomerular capillaries higher than in other capillary beds?
The afferent arterioles are short, straight branches of the interlobular arteries and the efferent arterioles have a relatively high resistance
What opposes renal capillary hydrostatic pressure?
Capillary hydrostatic pressure is opposed by the hydrostatic pressure in Bowman’s capsule and the oncotic pressure gradient across the glomerular capillaries
The oncotic pressure of Bowman’s capsule is normally negligible so the oncotic pressure gradient is essentially equal to the oncotic pressure of the plasma proteins
Net Filtration Pressure (PUF) of the Glomerular Capillaries
Net filtration pressure is 15 mmH at the afferent end of the glomerular capillaries, but it falls to zero (filtration equilibrium is reached) proximal to the efferent end of the glomerular capillaries
This is because fluid leaves the plasma and the oncotic pressure rises as blood passes through the glomerular capillaries
A decrease in the rate of rise of the delta curve produced by an increase in RPF would increase filtration because it would increase the distance along the capillary in which filtration was taking palce
What limits exchange across glomerular capillaries?
Exchange across the glomerular capillaries is flow-limited rather than diffusion-limited
Factors that Affect the GFR
Changes in renal blood flow
Changes in glomerular capillary hydrostatic pressure
Changes in systemic blood pressure
Afferent or efferent arteriolar constriction
Changes in hydrostatic pressure in Bowman’s capsule
Ureteral obstruction
Edema of kidney inside tight renal capsule
Change in concentration of plasma proteins: dehydration, hypoproteinemia, etc (minor factors)
Changes in Kf
Changes in glomerular capillary permeability
Changes in effective filtration surface area
Filtration Fraction
Ratio of GFR to RPF
Normally 0.16-0.20
GFR varies less than RPF
When there is a fall in systemic blood pressure, the GFR falls less than the RPF because of efferent arteriolar constriction and the filtration fraction rises
Tubular Function
The amount of any substance (X) that is filtered is the product of the GFR and the plasma level of the substance (CInPx)
The tubular cells may add more of the substance to the filtrate (tubular secretion), may remove some or all of the substance from the filtrate (tubular reabsorption), or may do both
The amount of the substance excreted per unit of (UxV) time equals the amount filtered plus the net amount transferred by the tubules
Amount filtered by the tubules represented by Tx
Clearance of the substance equals the GFR if there is no net tubular secretion or reabsorption, exceeds the GFR if there is net tubular secretion, and is less than the GFR if there is net tubular reabsorption
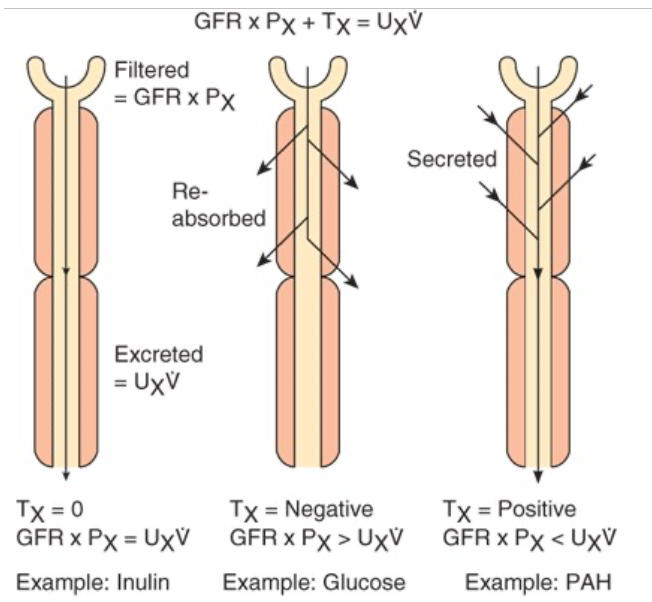
Mechanisms of Tubular Reabsorption and Secretion
Small proteins and some peptide hormones are reabsorbed in the proximal tubules by endocytosis
Other substances are secreted or reabsorbed in the tubules by passive diffusion between cells and through cells by facilitated diffusion down chemical or electrical gradients or active transport against the gradients
The tubular epithelium is a leaky epithelium
Tight junctions between cells permit passage of some water and electrolytes - paracellular pathway
Transport Maximum (Tm)
Maximal rate that renal active transport systems can transport a particular solute
The amount of a particular solute transported is proportional to the amount present up to the Tm for the solute, but at higher concentrations, the transport mechanism is saturated and there is no appreciable increment in the amount transported
What % of sodium is reabsorbed in the proximal tubule?
60%
What % of sodium is reabsorbed in the thick ascending limb?
30%
What % of sodium is reabsorbed in the distal convoluted tubule?
7%
What % of sodium is reabsorbed in the collecting duct?
3%
Function of the Na/glucose CT in the Proximal Tubule
Na+ uptake, glucose uptake
Function of the Na+/Pi CT in the Proximal Tubule
Na+ uptake, Pi uptake
Function of the Na+/Amino Acid CT in the Proximal Tubule
Na+ uptake, amino acid uptake
Function of the Na/Lactate CT in the Proximal Tubule
Na+ uptake, lactate uptake
Function of the Na/H Exchanger in the Proximal Tubule
Na+ uptake, H+ extrusion
Function of the Cl/Base Exchanger in the Proximal Tubule
Cl- uptake, HCO3- reabsorption
Function of the Na-K-2Cl CT in the Thick Ascending Limb
Na+ uptake, Cl- uptake, K+ uptake