Influenza Virus Structure, Pathogenesis, and Vaccination Strategies
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
17 Terms
Influenza
- Disease of the lower respiratory tract (Larynx, trachea, bronchial tubes, and alveoli)
i. alveolar macrophages destory microorganisms in the lungs
ii. respiratory mucus protects mucosal surfaces
- Signs and symptoms
i. Pharyngitis, congestion, cough, and myalgia
ii. sudden fever distinguishes flu from a common cold
- causative organism: influenza virus
Virion
complete, fully developed viral particle composted of a nucleic acid, protein coat, and sometimes an envelope
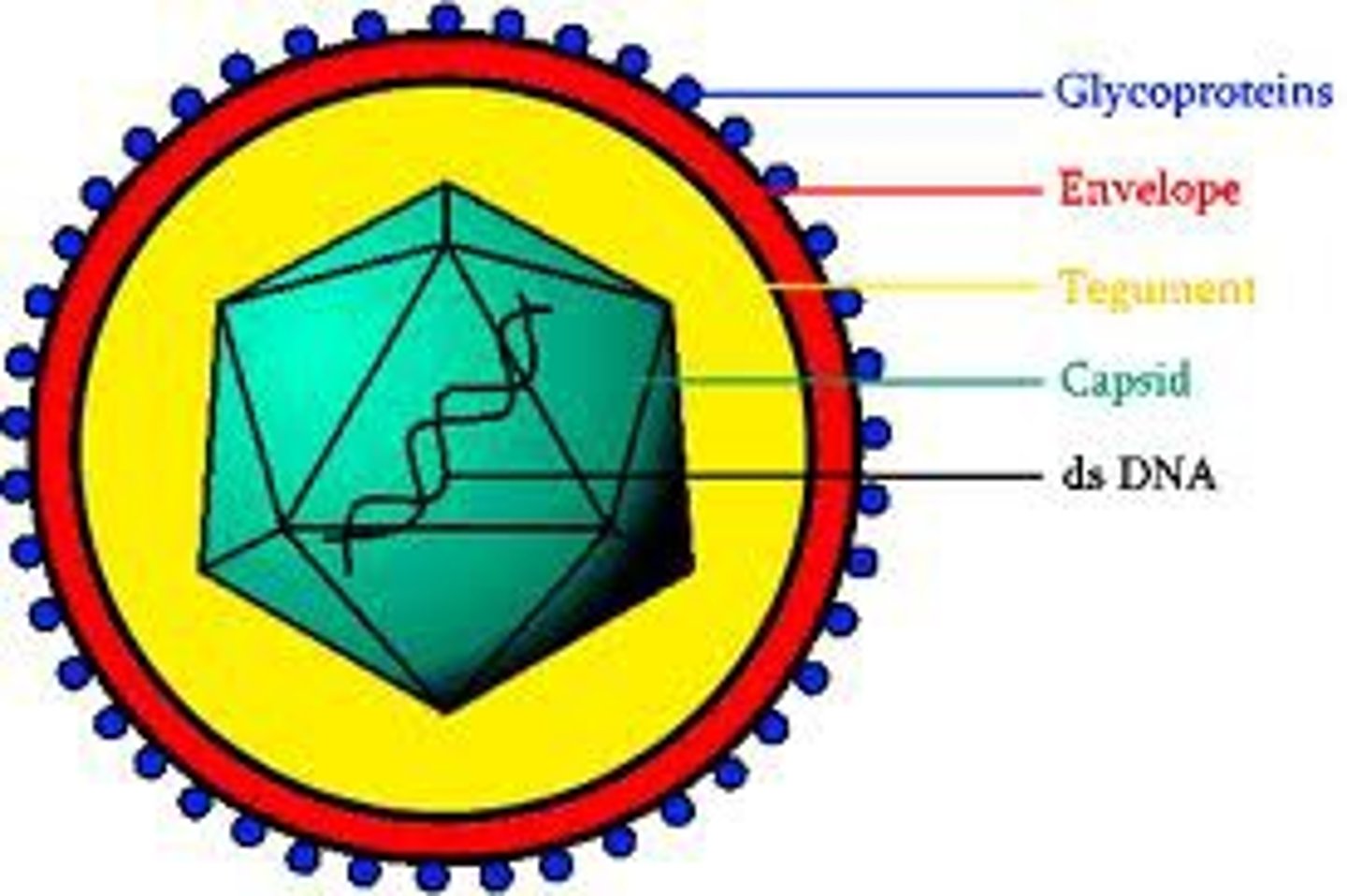
Nucleic Acid
DNA or RNA (Never Both)!
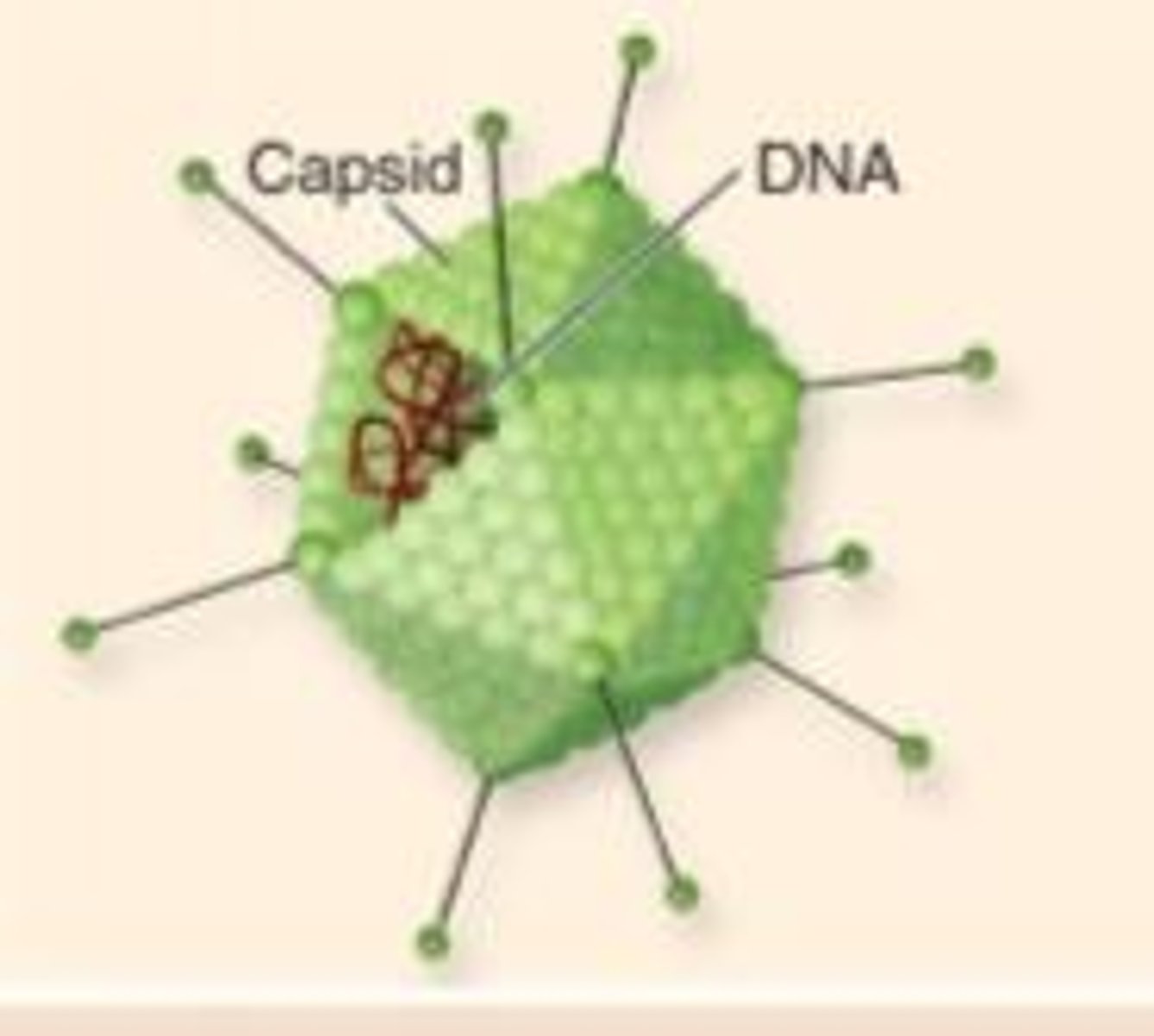
Capsid
protective protein coat
- made of subunits called capsomeres
- arrangement of capsomeres - characteristic of a particular type
Envelope
coating seen outside the capsid in some viruses
- made up of combinations of lipids, proteins, and carbohydrates
Nonenveloped (naked) viruses vs Enveloped Virus
viruses whose capsid is not covered by an envelope vs viruses within an envelope
Spikes
protein structures that extend outward from the capsid in some viruses that are used for attachment
Influenza Virus Key Details
- Belong to the family ORTHOMYXOVIRIDAE
- Strains are named by:
i. type (A,B, or C)
ii. Location and date of original identification
iii. Type of Antigens (H and N)
- A/Singapore/1/80 (H1N2)
-Influenza Virus A and B can cause the flu
i. Virus A is the most important/problematic
Genome
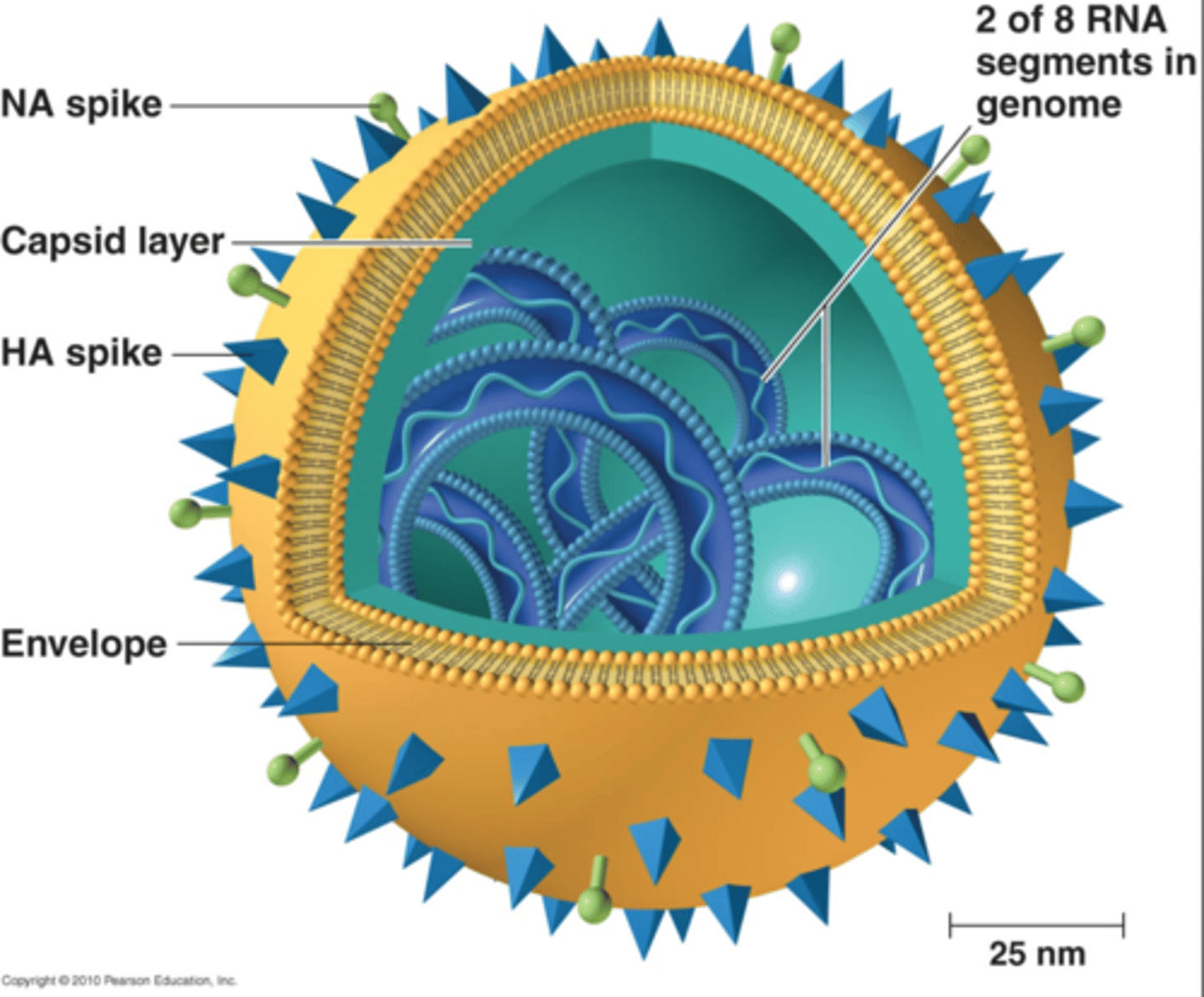
- looks like a sphere
- contains EIGHT RNA segments
- containing the genome is the CAPSID layer
- Outside of the capsid is the ENVELOPE = a phospholipid bilayer
- SPIKES are distributed throughout: (Hemagglutinin spikes (HA) or Neuraminidase spikes (NA)
i. HA spikes are more common
Hemagglutinin (HA) spikes
Recognize and attach to host cells
- involved in haemagglutination (clumping of RBCs)
- stimulate formation of antibodies
Neuraminidase (NA) spikes
Helps the virus separate from the infected cell after reproduction
- also stimulate formation of antibodies, but to lesser extent than H
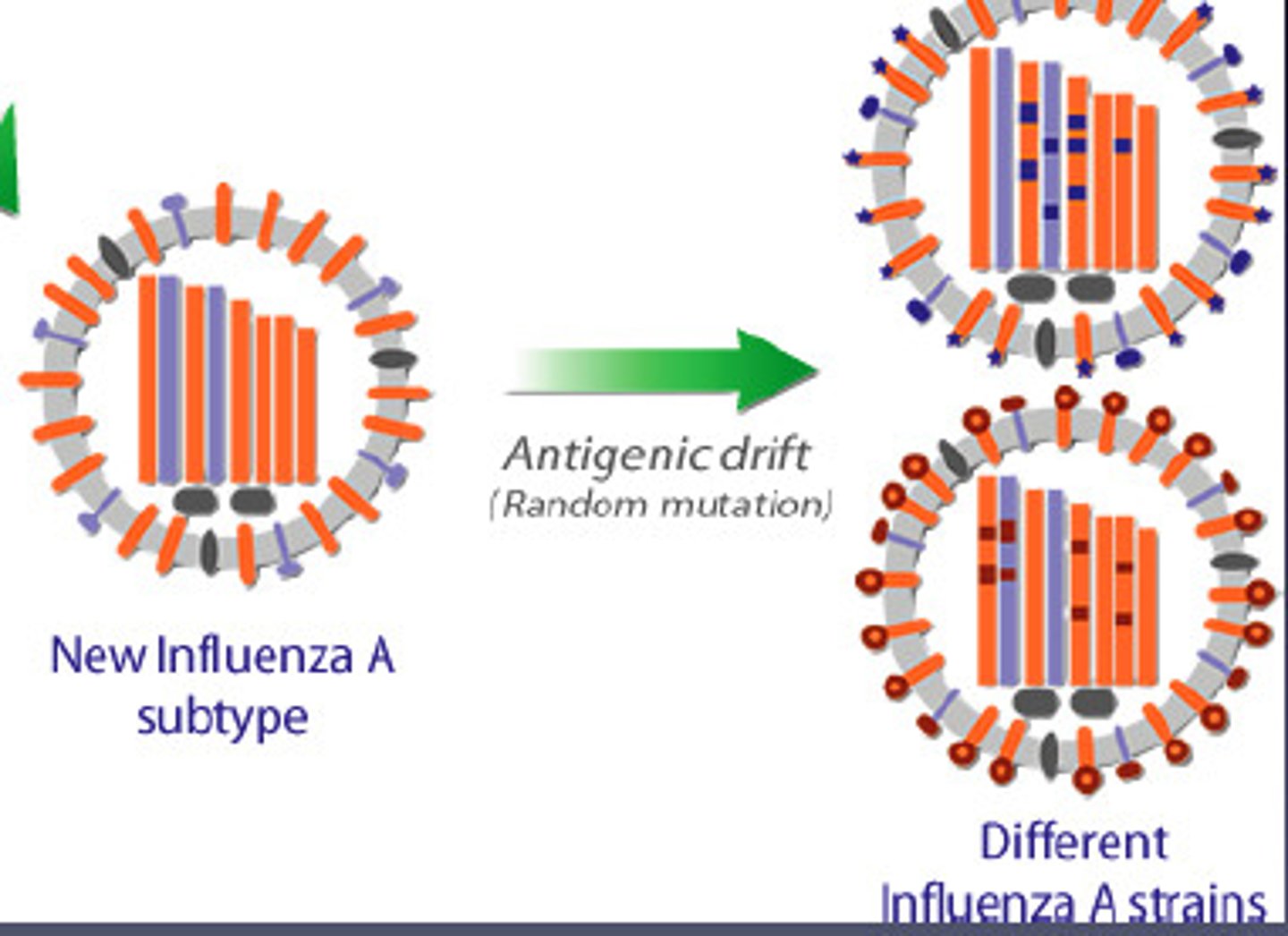
Antigenic Drift
- Minor antigenic changes in HA and NA (Due to mutations)
- Allow the virus to elude some host immunity
- Lead to epidemics
Antigenic Shifts
- Changes great enough to evade most immunity
- Major genetic recombination, called reassortment
- Involve the reassortment of the eight RNA segments
- Leads to pandemics
Example:
- Avian, swine, and mammalian strains
- swine serve as "mixing vessels" for new strains
- TRIPLE REASSORTMENT
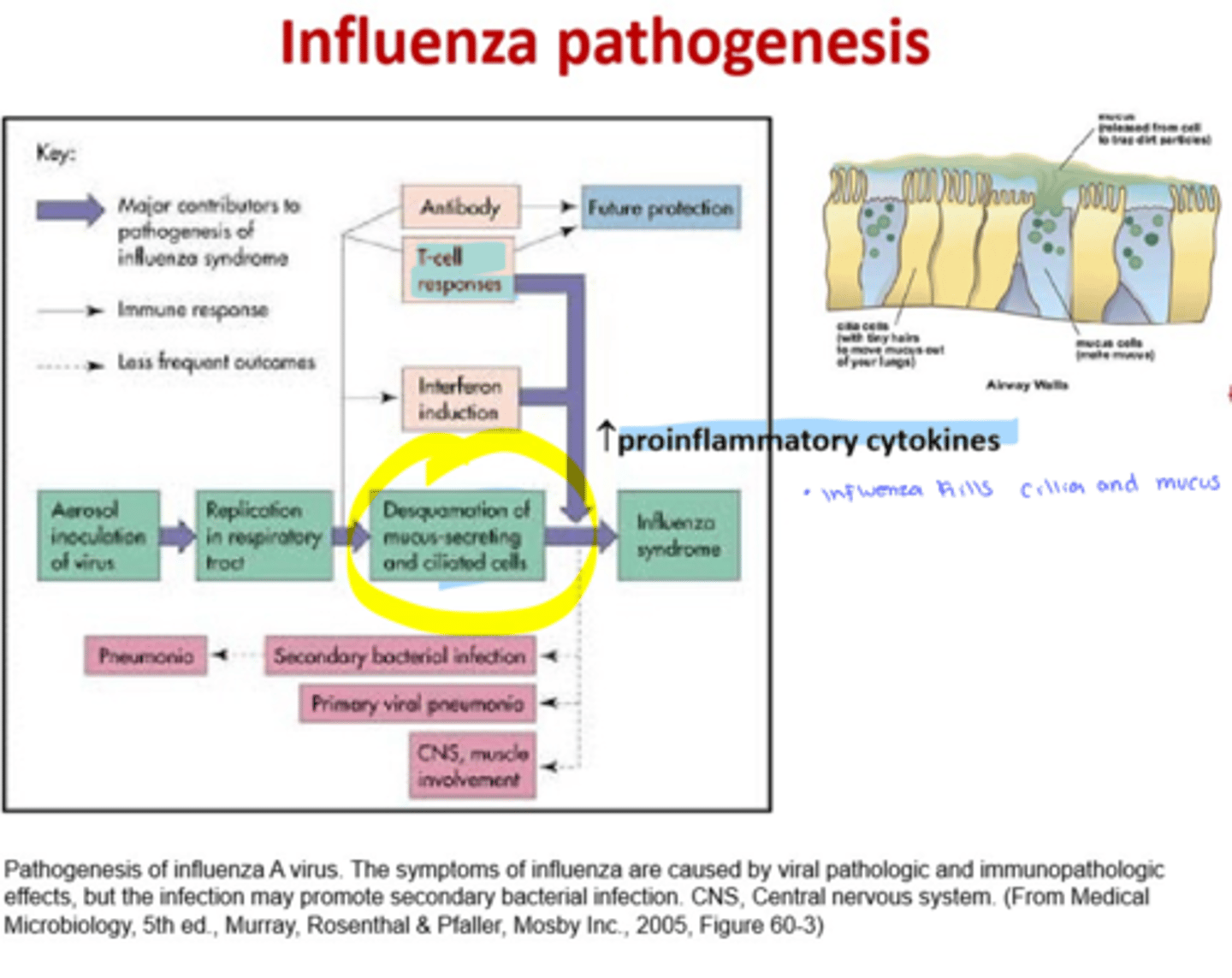
Influenza Pathogenesis
- Enters via respiratory route
- Virus causes damage to the epithelial cells of lung
- Flu patients are susceptible to secondary bacterial infections
- 1% mortality, usually the very young and very old
Influenza Epidemology
- Infection provides some immunological protection from similar strains
- Concern that changes in type A influenza viruses may cause
Influenza Diagnosis/ Treatment
- signs and symptoms during a community-wide outbreak are often diagnostic
- TREATMENT involves supportive care to relieve symptoms
Examples: Oseltamivir (Tamiflu - Oral), Zanamivir (Relenza - mist) can be administered EARLY IN INFECTION
- both inhibit neuraminidase (prevent escape of the virus from the infected cell)
- Prevented by immunization with a multivalent vaccine
Influenza Vaccines
- Multivalent vaccine for the most important strains
- Composition of the vaccine determined ANNUALLY by the identification of circulating viruses
i. labor-intensive to produce
- Does not provide long-term immunity
- Bad some years due to:
i. bad strain
ii. less exposure
iii. problems with vaccine - mutated while being developed - only 30-40% effective
SEE LAST SLIDE MMWR INFORMATION