Replication of DNA (mRBA strand)
1/16
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
17 Terms
What must happen to DNA before cell division can occur?
DNA replication
What determines the production of a protein?
DNA
What are the six requirements needed for DNA replication to occur?
ATP - provides energy for DNA replication to occur
DNA polymerase - adds nucleotides to the free 3’ end of the growing strand (a primer must be present for this to work)
DNA template strand - provides the correct sequence for the DNA polymerase to complement
Ligase - joins DNA fragments together
Primers - binds to the 3’ end of the template strand in order for DNA polymerases to work
Four types of free DNA nucleotides - added to the 3’ end of the growing strand (a primer must be present for this to work)
Primers
A single-stranded sequence of nucleotides that provide a starting point for DNA replication
What two enzymes are required for DNA replication?
DNA polymerases and ligase
How is DNA replicated on the leading strand?
Continuously in one fragment
How is DNA replicated on the lagging strand?
In short fragments that are then joined together by ligase
What are the two growing DNA strands called that are made during DNA replication?
The leading strand and the lagging strand
What are the four stages of DNA replication on the leading strand?
DNA is unwound and unzips as the hydrogen bonds break between the bases. This forms two template strands
A primer binds to the 3’ end of the template strand
DNA polymerase goes along the template strand, adding new complementary nucleotides to the template strand (in the 5’ to 3’ direction of the new growing strand)
The DNA strands twist to form a double helix
What are the five stages of DNA replication on the lagging strand?
DNA is unwound and unzips as the hydrogen bonds break between bases. This forms two template strands. This process occurs at several locations on the DNA molecule
Many primers bind at various points along the template strand
DNA polymerase goes along the template strand, adding new complementary nucleotides to the template strand (in the 5’ to 3’ direction of the new growing strand). This produces several fragments
The fragments are joined together by the enzyme ligase
The DNA strands twist to form a double helix
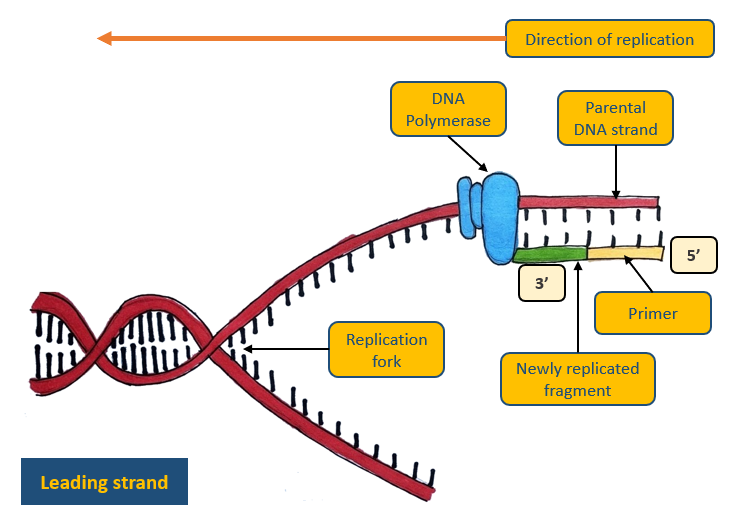
Diagram: leading strand
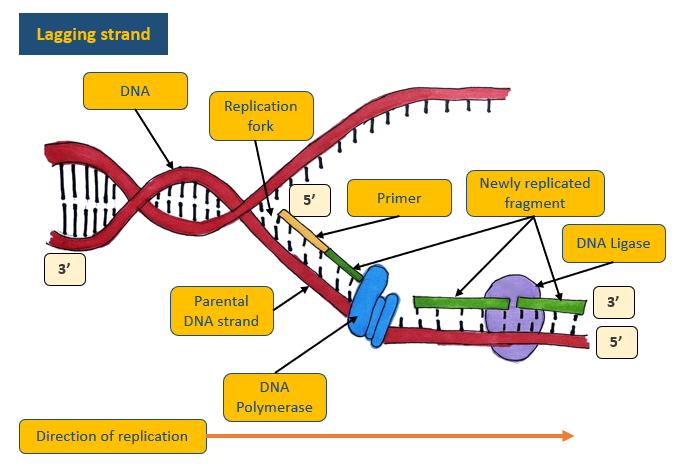
Diagram: lagging strand
In what direction does DNA polymerase add nucleotides to a growing strand?
From the 3’ end to the 5’ end
Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR)
A technique used to create many copies of DNA, occurring in vitro (outside the body of an organism)
What are the four requirements needed for PCR to work?
DNA nucleotides
DNA polymerase
DNA template strand
Primers - that are complementary to the specific target sequences at the two ends of the regions of DNA being amplified
What are the five steps in PCR?
The DNA mixture is heated to 92-98°C to separate the DNA strands (breaking the weak hydrogen bonds between bases)
The temperature of the mixture is reduced to 50-64°C so that primers can bind to target sequences in the DNA. The primers are specific to two target sequences at the two ends of the region to be amplified
The mixture is then heated to 72°C so heat tolerant DNA polymerase can replicate the region of DNA
The first cycle produces two identical molecules of DNA
The second cycle produces four identical molecules of DNA and this is repeated to create a large DNA bank
What are three practical applications of PCR?
Blood can be gathered from families to settle paternity suits
Blood, semen, or tissue can be gathered from crime scenes to identify any person(s) involved
Embryonic cells can be gathered from a prenatal diagnosis to diagnose genetic diseases