immunology exam 1
1/152
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
153 Terms
families under order cyclophylidea
taenia solium (pork tapeworm)
taenia saginata (beef tapeworm)
Echinococcus
Hymenolepis nana
families under order pseudophyllidea
Diphyllobothrium latum
human sparaganosis
domain for cestodes and trematodes
eukarya: membrane bound organelles
kingdom animalla
lack of cell wall
multicellular
locomotion
heterotrophs: can’t produce own food
usually has sexual reproduction
phylum platyhelminthes
(flatworms)
self fertilization
parenchyma in body cavity
ladder like nervous system
flame cells (excretion and osmoregulation)
phylum platyheminthes classes
Turbellaria (mostly free living)
trematoda
monogenea
fish ectoparasites
cestoda (tapeworm)
subclass digenea
digenetic trematodes
flukes
lifecycle
at least 2 hosts
DH + snail IH
maybe more IH
economic losses
medical importance
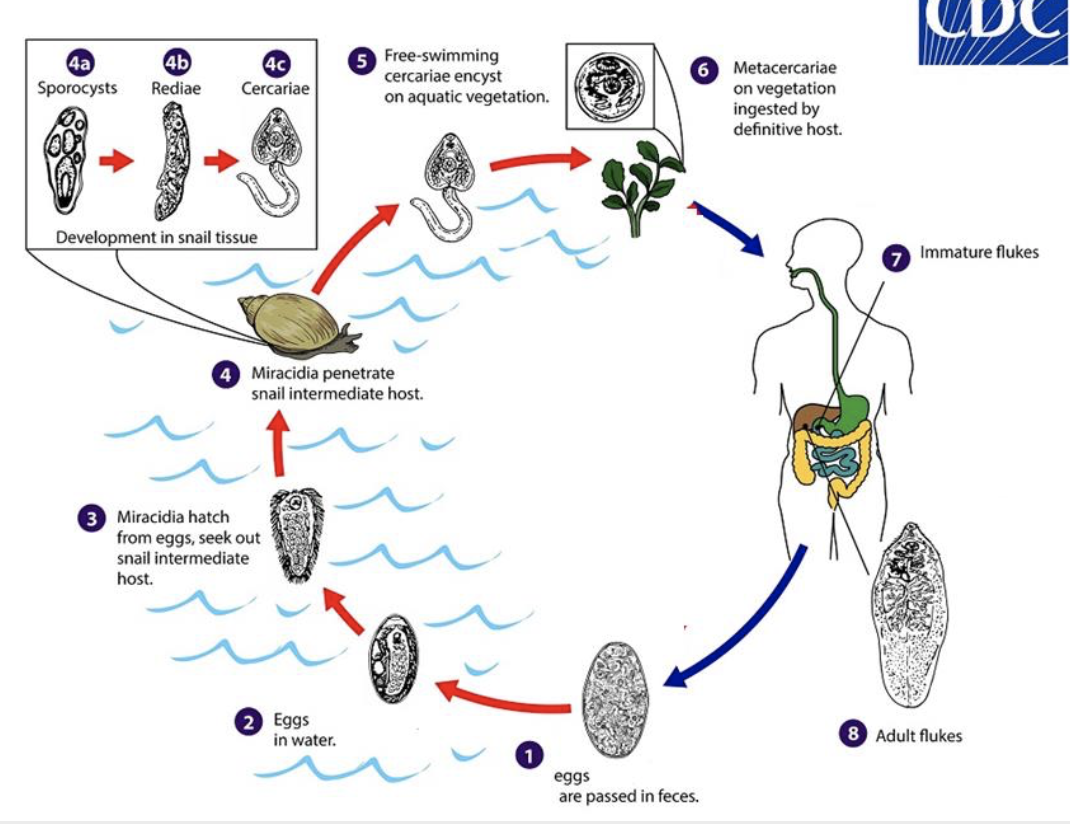
generalized life cycle of trematodes
eggs passed in feces
eggs in water
miracidia hatch from eggs, sneak out snail IH
miracidia penetrate snail IH
sporocyst
rediae
cercariae
free swimming cercariae encyst on aquatic vegetation
metacercariae on vegetation ingested by DH
immature flukes
adult flukes
trematodes metamorphosis
cercariae → adult worm in DH
cercariae → metacercariae → adult worm in DH
egg (released by DH) → miracidium → sporocyst
trematodes asexual reproduction
sporocyst → secondary sporocyst
sporocyst → rediae → secondary rediae
polyembryony formation of >1 embryo from a single fertilized ovum or in a single seed
polyembryony
formation of >1 embryo from a single fertilized ovum or in a single seed
trematodes sexual reproudction
adult worm in DH → egg
trematodes morphology
lack circulatory, skeletal, and respiratory systems
parenchyma
ventral sucker
digestive tract
nervous system
tegument
parenchyma
fills space between body wall and guy
attachment points
passage of materials
trematode digestive tract
mouth surrounded by oral sucker
pharynx
esophagus
cecum
cecum
bifurcates
unbranched/ branched
blind
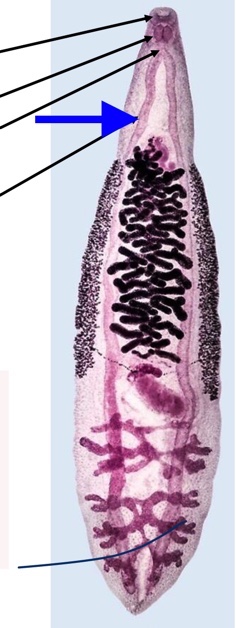
mouth surrounded by oral sucker
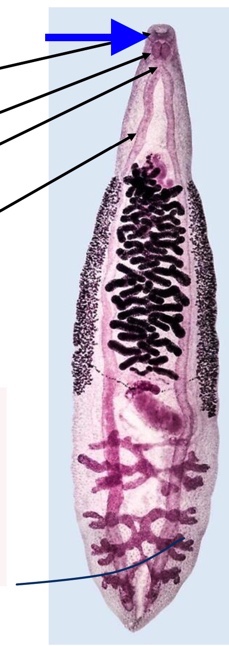
pharynx
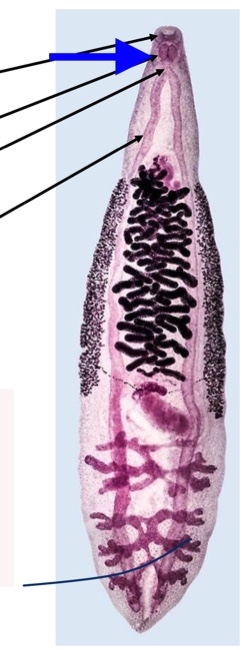
espohagus
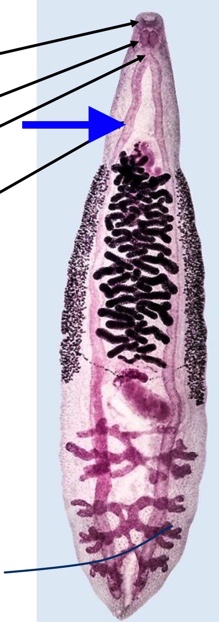
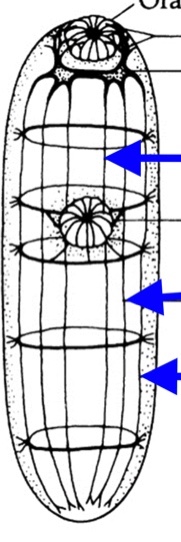
Trematode Nervous system
cerebral (brain ganglion)
nerve chords
sensory endings
chemoreceptors
tangoreceptors
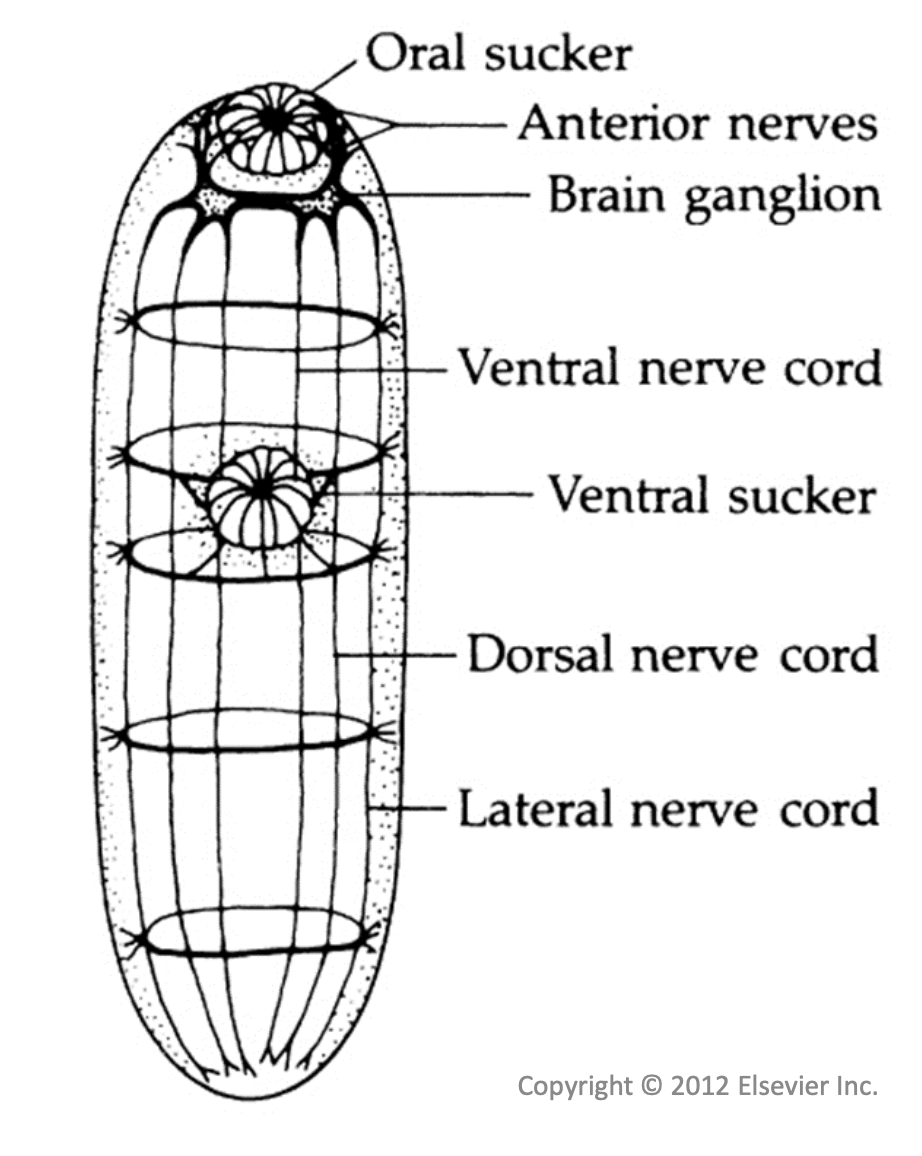
Brain ganglion
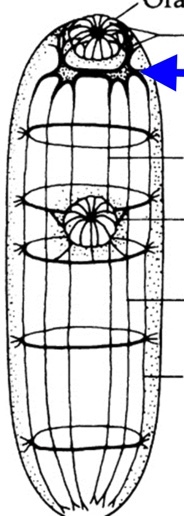
anterior nerves
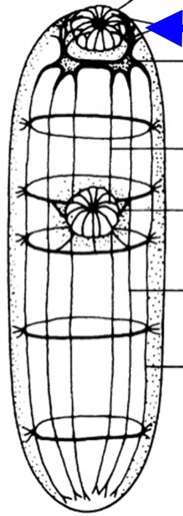
nerve cords
center to outer: ventral dorsal lateral
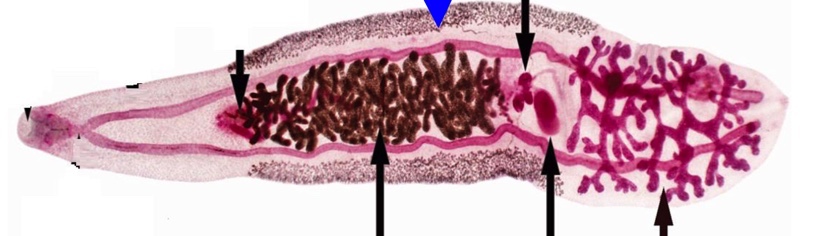
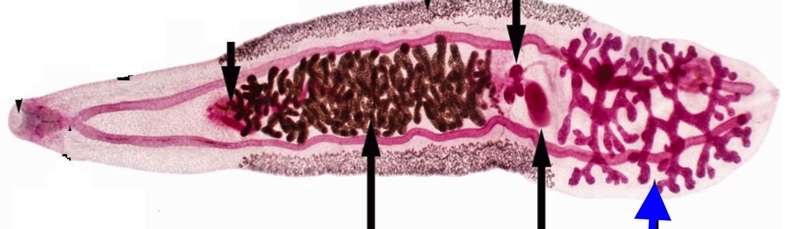
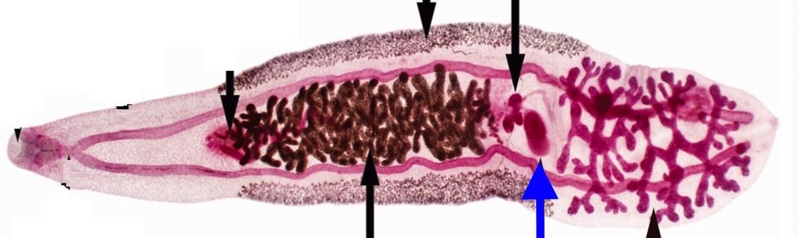
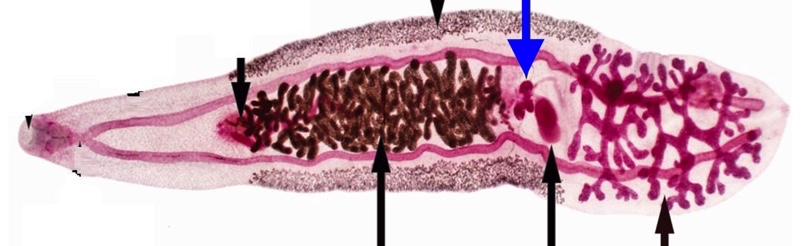
trematode reproduction
monecious: except schistosomes
both ovaries and testes
can self fertilize
mainly cross fertilize
vitellaria
testes
seminal receptable
ovaries
uterus
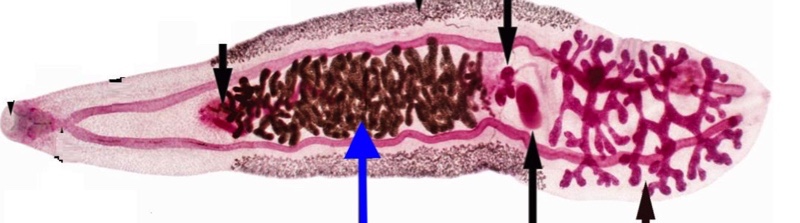
Tegument
synctium
function
hydrolytic enzymes: defesnes
muscles: movement
materials: in and out
synctium
mutlinucleated tissue with no cell boundaries
inside DH
intestinal flukes: only in intestine
liver flukes
lung flukes: only in lungs
blood flukes
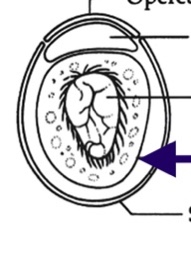
Trematode Egg morphology
operculum (not in all species)
viscous cushion
developing miracidium
vitelline membrane
operculum (not in all species)
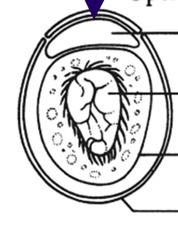
viscous cushion
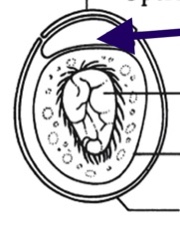
developing miracidium
vitelline membrane
shell
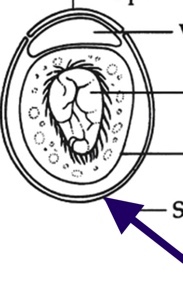
miracidium morphology
100 um
sensory papilla
cephalic ganglion “brain”
cilated epidermal plate
apical gland
lateral gland
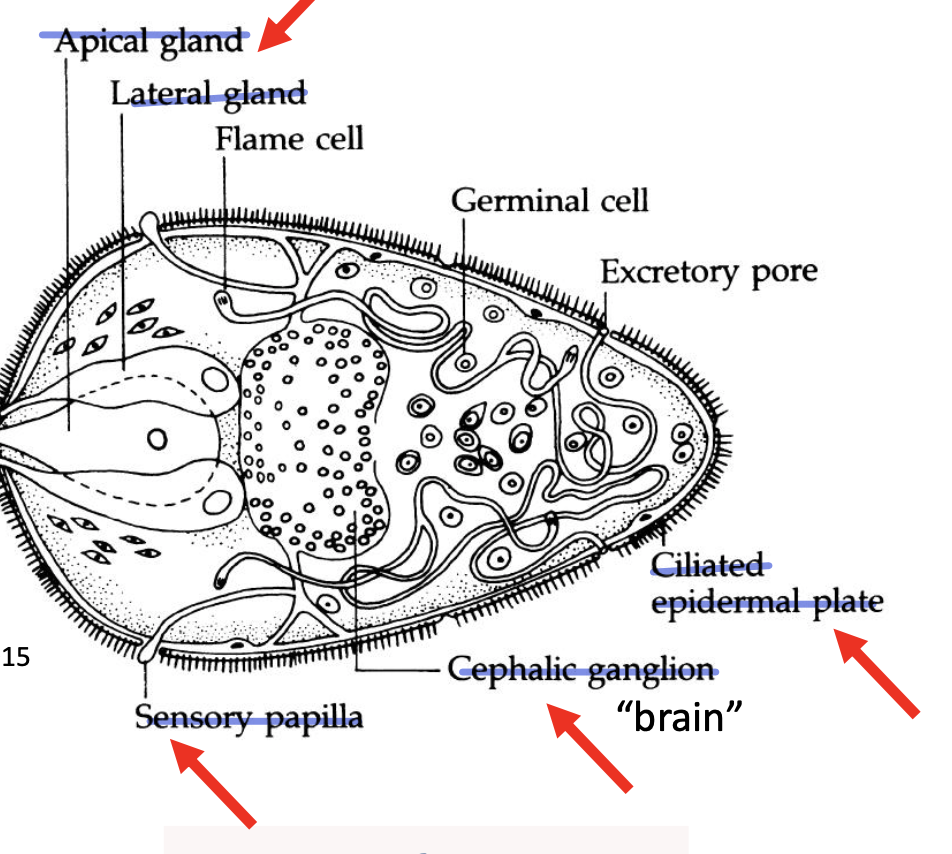
sensory papilla in miracidium
photoreceptors
georeceptors
chemoreceptors
Miracidium behavior
find and infect snail within 24 hours
miracidium host finding (environmental cues)
or - to light, gravity, temp
snail hosts → similar responses
parasite goes to same location as hosts
miracidium host finding (host cues)
→ miraxone: snail chemicals (amino acids, fatty acids, NH3)
→ attract miracidia
miracidia attraction measured by
rate of change of direction (RCD)
far from snail: fast swimming and lower RCD
moves to other spaces
close to snail
increase RCD and slow swimming
stays close to host
swimming speed
miracidia infection of snail
respond to components of snail mucus
wrong cues → leave
correct cues → penetrate snail
inside snail → metamorphis
sporocyst and redia
loses cilia
new tegument
microvilli
absorption
no mouth/ digestive system
geminal sac embryos
daughter either secondary sporocyst of rediae
become cercariae
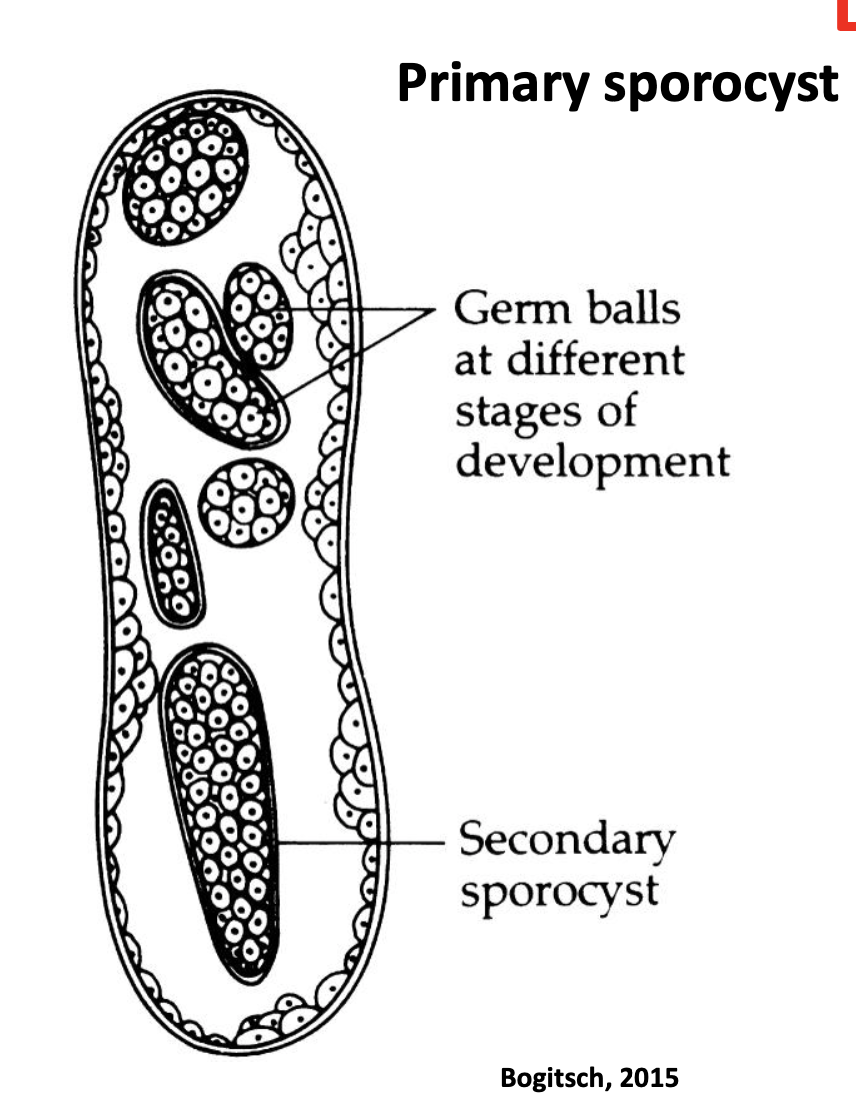
primary sporocyst
germ balls at different stages of development
secondary sporocyst inside
redia
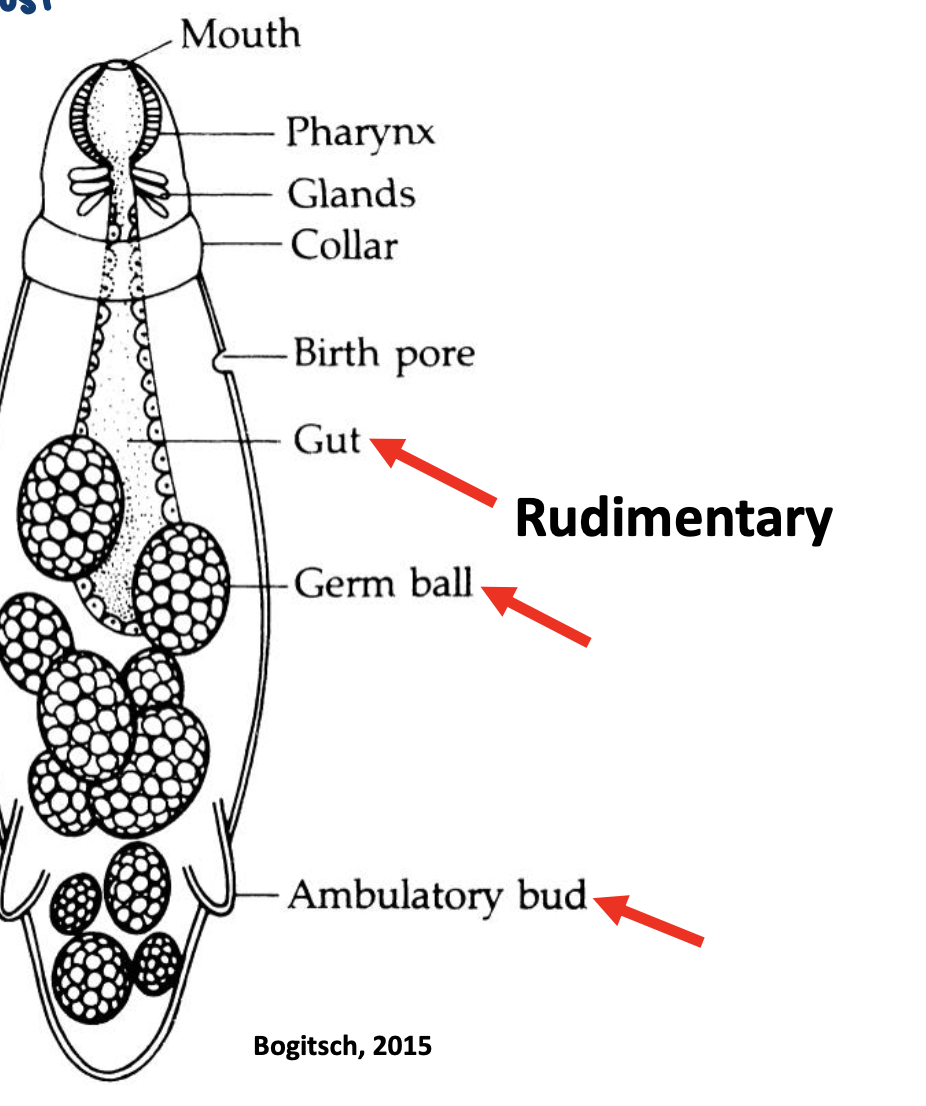
rudimentary area
gut
germ ball
ambulatory bud
also has
mouth
pharynx
glands
collar
birth pore
effects of sporocysts and rediae on snail host
parasitic castration
bigger snail → more space and tissue
ex: redia move to reproductive structures
feed on and destroy tissue
ex: hormone manipulation
schistomomin
small peptide hormone → normal reproduction
larvae stimulate overproduction
inhibits snail reproduction
cercaria morphology
head and tail
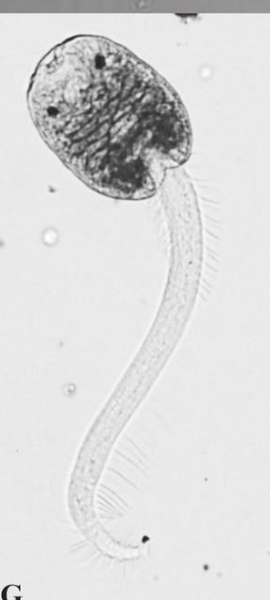
cercaria behavior
a. exit snail
escapes glands (enzymes)
external environment
short lived (1-3 days)
swim/crawl → encyst / infect host
cercarie development pathways
encyst on vegetation → metacercaria
penetrate 2nd IH → metacercaria
penetrate DH → adult worm
cercaria: species which encyst on plants
in water → find plant
post acetabular glands produce mucus
attach to plant
shed tail
cystogenous glands
produce metacercaria
species that infect 2nd IH and DH
in water → find suitable host
spatial location
light, gravity, temp, host cues
same location as host
temporal location
circadian release
same time as host
infection of host
mucous glands → attachment
sheds tail
penetration glands
enzymes → digest tissue
cercariae that infect 2nd IH inside host
cystogenous glands → metacercariae
cercaria infects DH inside host
migration in host → adult worm
cercarial success (not all make it)
schistosomes
many species → east host is specific
bird schistosomes
cercaria seek bird in water, however bird signals are similar to humans (movement, shadow, warmth, skin chemicals)
cercariae penetrate human → wrong host → cercariae dies
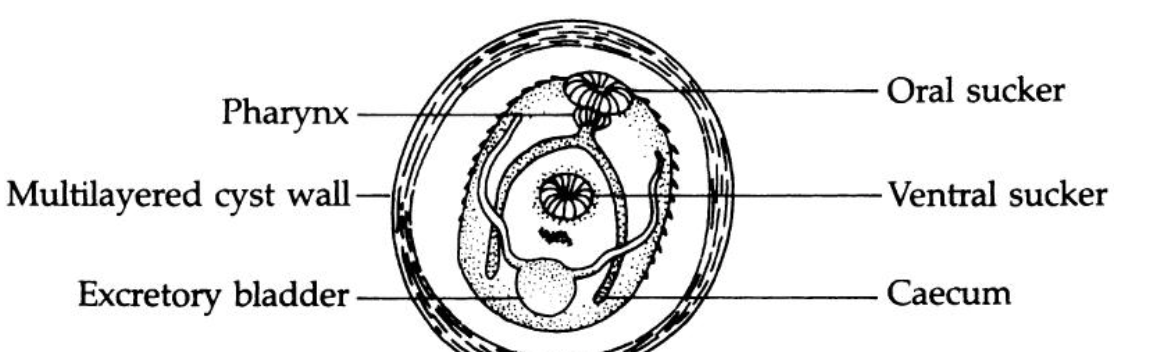
metacercaria
transmission stage
multilayered cyst wall
species that encyst on vegetation: thick and complex
species that encyst on 2nd IH: thin and simple
inside DH
responds to complex stimuli
excysts
develops into adult worm
trematode generalized life cycle
eggs are passed in feces
eggs in water
miracidia hatch from eggs and seek out snail intermediate host
miracidia penetrate snail intermediate host
sporocyst → rediae → cercariae
free swimming cercariae encyst on aquatic vegetation
metacercariae on vegetation ingested by definitive host
immature fluke
adult fluke
how foodborne diseases are passed through food ingestion
pathogen / parasites
biotoxins
chemicals
foodborn trematode infections
larval stage in food
zoonotic infections
domestic or wild animals
human replaces DH in lifecycle
distribution of foodborn trematodes
east asia
south america
prevalence of foodborn trematodes
2 millions DALYs/yr
>7000 deaths/year
Clonorchis sinesis and opisthorchis viverinni lifecycle differences from the general life cycle
snail eats egg
miracidia develop inside the intermediate host
2nd IH is a freshwater fish
DH (piscivores)
reservior hosts
non-human DH
source of infection
adults live in bile duct
clonorchis sinesis
oriental liver fluke
opisthorchis viverrini
cat liver fluke
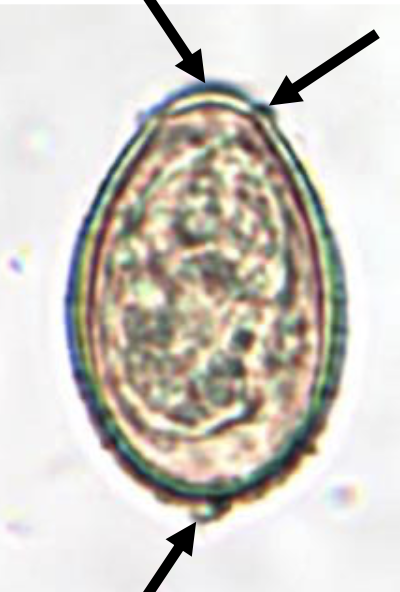
clonorchis sinesis egg morphology
30 × 15 um
operculum
shoulders
abopercular knob
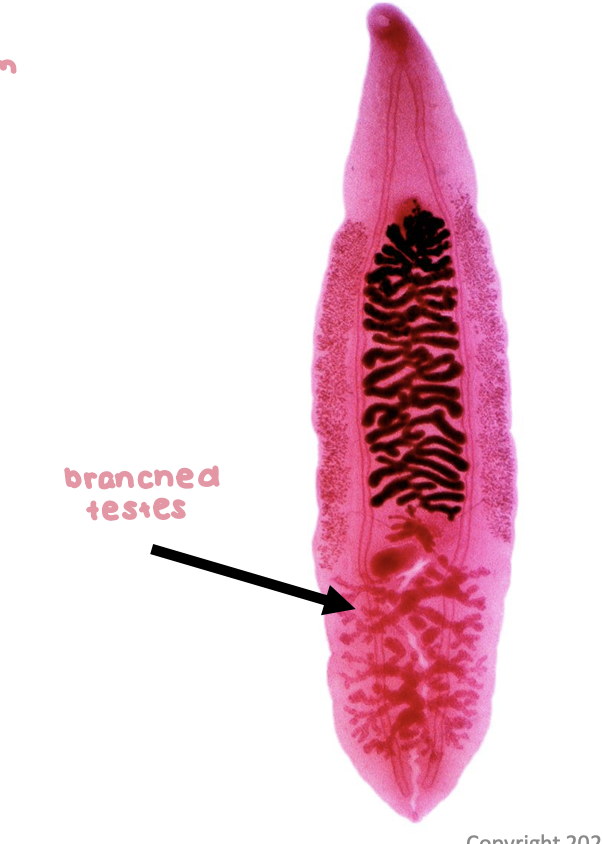
clonorchis sinesis adult morphology
2 x .5 cm
branched testes
clonorchis sinesis pathology
adults in bile duct destroy lining
damage depends on intensity of infection
< 100 worms → asymptomatic
100 - 1000 → nausea, diarrhea, pain
> 1000 → fever, pain jaundice
thickening and blockage of duct
hepatomegaly
liver enlargement
cholangitis: inflammation of duct
opisthorchis viverrini difference in morphology
has lobed testes compaired to clonorchis sinesis which has branched testes
Clonorchis sinesis and opisthorchis viverinni diagnosis
detect fibrosis by ultrasound
detect eggs in feces
cholangiocarcinoma (CCA)
cancer in the bile ducts
mainly due to opisthorchis viverrini
reasons for cholangiocarcinoma due to o. viverrini
mechanical injury: oral and ventral suckers damage duct epithelium
lesions and ulcers
eggs trapped in ulcer → inflammation
toxic metabolic secretions
mitogenic → stimulate host cell proliferation and cancer
may induce transcriptional changes in host cells
immunopathology
NO released by immune cells because parasite antigens
excess NO may be mutagenic and inhibit DNA repair
Fasciola hepatica
sheep liver fluke
in cattle and sheep
liver rot
humans
2-17 million cases worldwide
rare in US
Fasciola hepatica life cycle
same as the general life cycle
DH/ reservoirs: cattle, sheep, humans
inside DH
metacercaria excysts in SI and juvenile penetrates intestinal wall
migrates through abdominal cavity
penetrates Glison’s capsule
juveniles develop in liver → liver rot
migrate to bile duct → adults
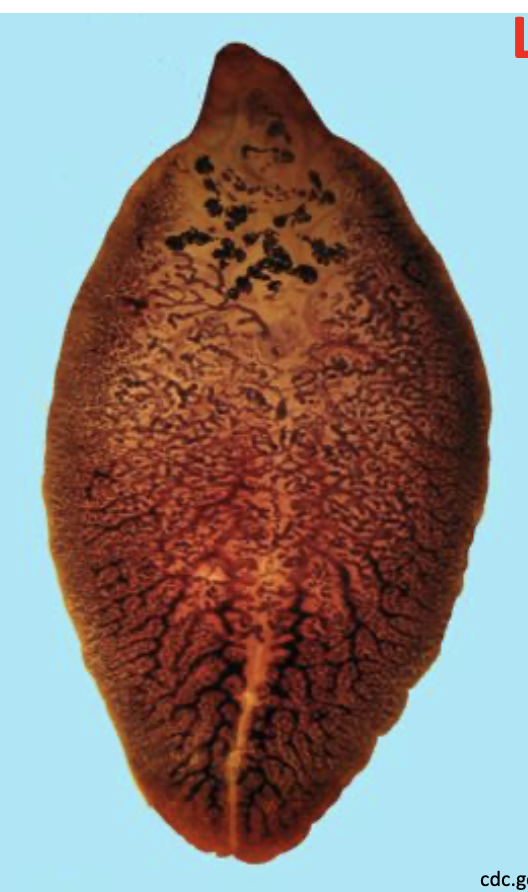
Fasciola hepatica adult morphology
3 × 1 cm
highly branched cecae
highly branched testes
“shoulders”
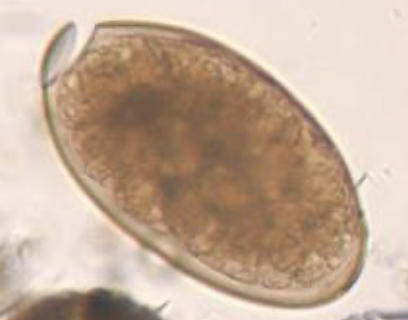
Fasciola hepatica eggs morphology
140-75 um
operculum
diagnosis
eggs in feces (sheep, cattle, humans)
pathology of Fasciola hepatica (migrating juveniles)
ulcers in eptopic (wrong) sites
brain, eyes, skin
pathology of Fasciola hepatica ( juveniles in liver )
acute fascioliasis (around 8 weeks)
necrosis: tissue death
hepatomegaly: capsule may rupture
pathology of Fasciola hepatica ( adults in bile duct )
chronic fascioliasis (> 12 weeks)
blockage of bile duct
proline secretion: collagen and fibrous tissue in duct walls
back pressure → liver atrophy → cirrhosis
paragonimus westermani (oriental lung fluke)
2nd IH is crustaceans
DH: humans
eggs found through sputum or feces
inside DH
first step same as fasciola hepatica - metacercaria excysts in SI and juvenile penetrates intestinal wall
penetrates through diaphragm
develop in lungs
paragonimus westermani adult morphology
1 x .07 cm
red/brown
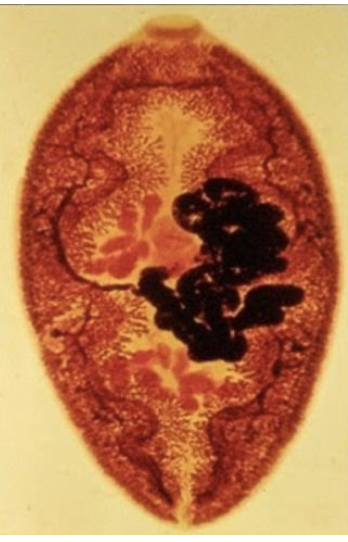
paragonimus westermani egg morphology
100 × 50 um
operculum
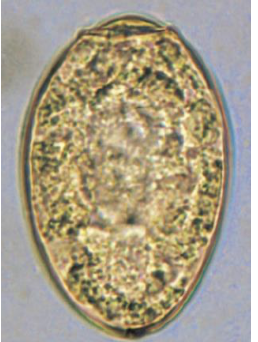
paragonimus westermani diagnosis
eggs in sputum (anything coughed up)
paragonimus westermani pathology (migrating juveniles)
ulcers in ectopic sites
brain eyes skin
paragonimus westermani pathology (acute)
cough, pain
paragonimus westermani pathology (chronic)
may mimic bronchitis or tuberculosis
blood tinged sputum
praziquantel (PZQ)
1970s
wide range of platyhelminths
clonorchis, opisthorchis, paragonimus
very safe
exact mode of action unclear
exposure to PZQ
rapid, sustained muscular contraction
paralysis → worm can’t attach
tegumental disruption
exposure of antigens on worms surface
PZQ effects can be linked to
disruption of voltage gated Ca 2+ channels in tegument
rapid influx of Ca2+
disruption of functions
treatment for fasciola hepatica
PZA does not work
triclabendazole (TCBZ)
damage to: tegument (ion pumps), mitochondria, microtubules
control strategies for food born trematoda
kill adult worms: medicine, PZQ
reduce environmental contamination
sanitation
don’t use night soil (human feces)
snail control
control reservoir hosts
Snail control
physical removal: expensive
molluscicides: copper sulfate or sodium pentachlorophenate
ecotoxicity
difficulties
recolonization
self fertilizing
control for C. sinensis and o. viverrini
no nigh soil in fish farming ponds
proper prep of fish
control for fasciola hepatica
boil vegetables that grow in water
paragonimus westermani
properly prep 2nd IH
avoid drunken crab
avoid medicinal crab juices
schistosomiasis (snail fever)
blood flukes
200 million infections worldwide
3rd only malaria and hookworm
mainly in Africa, south america, asia
schistosome life cycle difference from trematodes
no metacercaria or redia
cercariae infects DH
cercariae penetrates through skin
in DH
cercariae lose tails during penetration and become schistosomulae
circulation
migrate to portal blood in liver and mature into adults
paired adult worms (male and female)
migrate to
S.mansoni and S. japonicum in mesenteric venules of bowel/rectum (laying eggs that circulate to the liver and shed in stools)
s. haematobiumL in venous plexus of bladder
difference between schistosomes and other trematodes
dioecious
live in blood vessels
non-operculated eggs
no redia (larval stage in snail)
no metacercaria
not food borne