IPS1: Inorganic Chemistry Part 1 - Fundamentals - (A2) Atoms and It's Electronic Structure
1/21
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Proverbs 16:3
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
Atom
the smallest unit that retains the properties of an element
fundamental unit of matter
Dalton's theory
all matter is composed of atoms and these cannot be made or destroyed
Atomic structure
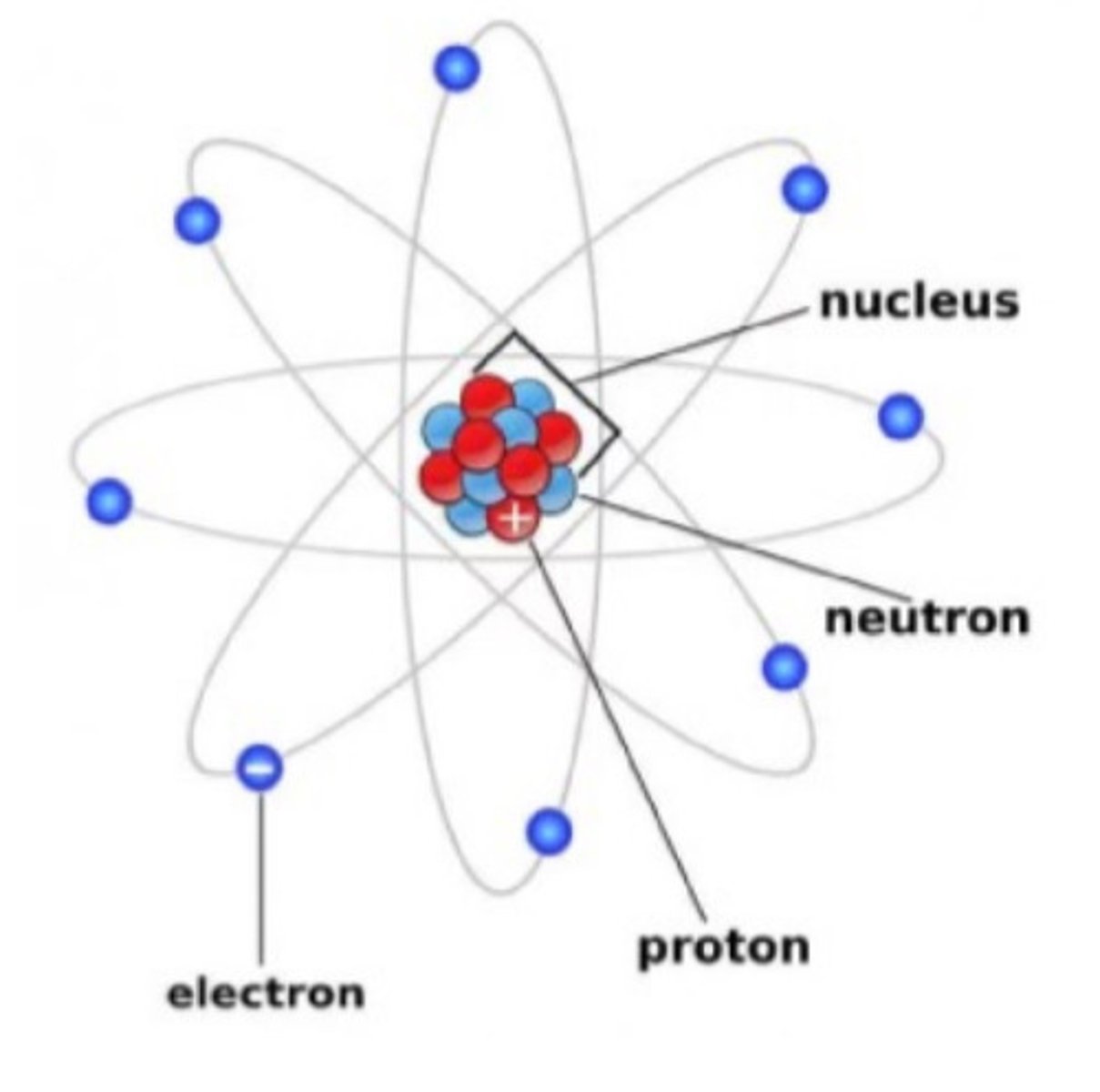
Fundamental particles of matter
Electron
Proton
Neutron
Electron
(e-)
mass: 0.00054858 amu
charge: 1-
Proton
p or p+
mass: 1.0073 amu
charge: 1+
Nuetron
n or n°
mass: 1.0087 amu
charge: none
Atomic number (Z)
the number of protons in the nucleus of an atom that determines its identity
Mass number (A)
sum of the number of proton and the number of neutrons in its nucleus
Mass number
proton + neutron
atomic number + neutron
Isotopes
atoms of the same element with different masses
atoms containing the same number of protons but different numbers of neutrons
Isotope example
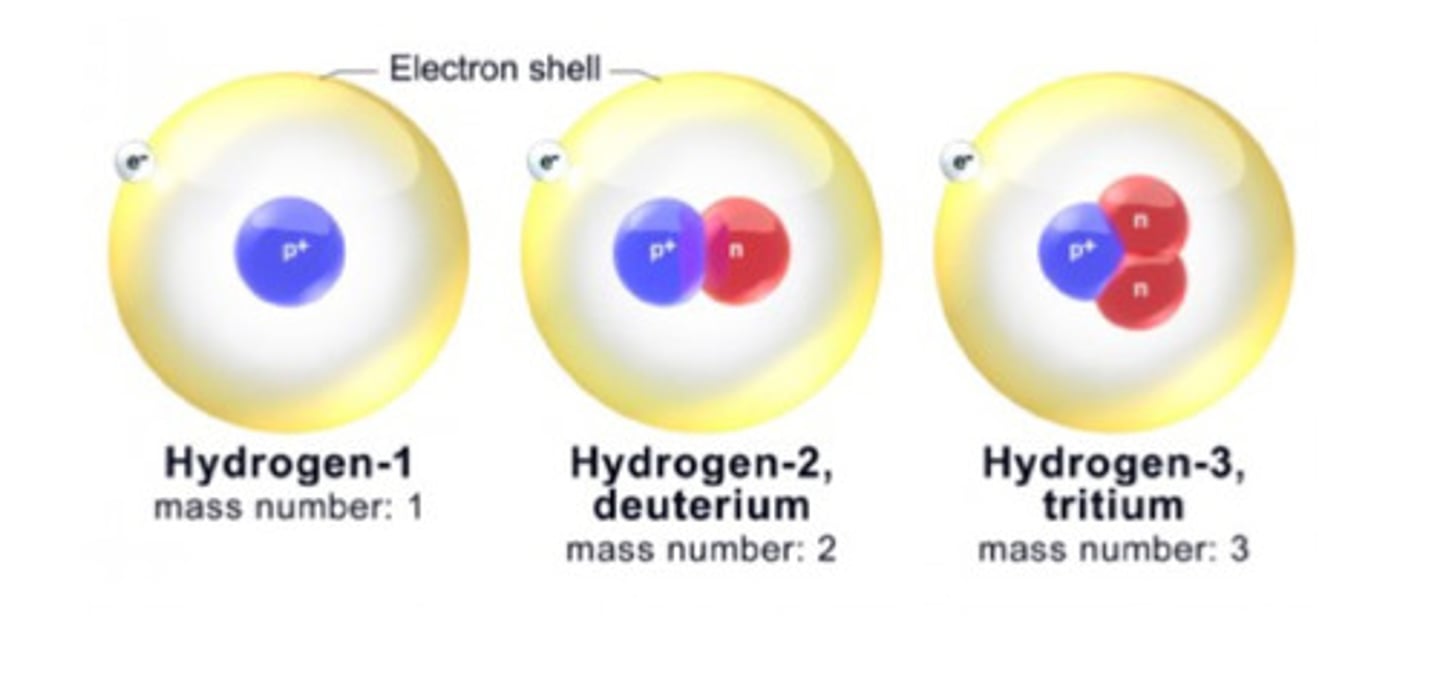
Nuclide symbol
represent the composition of the nucleus
Nuclide symbol

Carbon-12
98.9% of carbon exist as what isotope
Carbon-13
1.1% of carbon exist as what isotope
Carbon-14
< 0.0001%
Isobars
same mass numbers
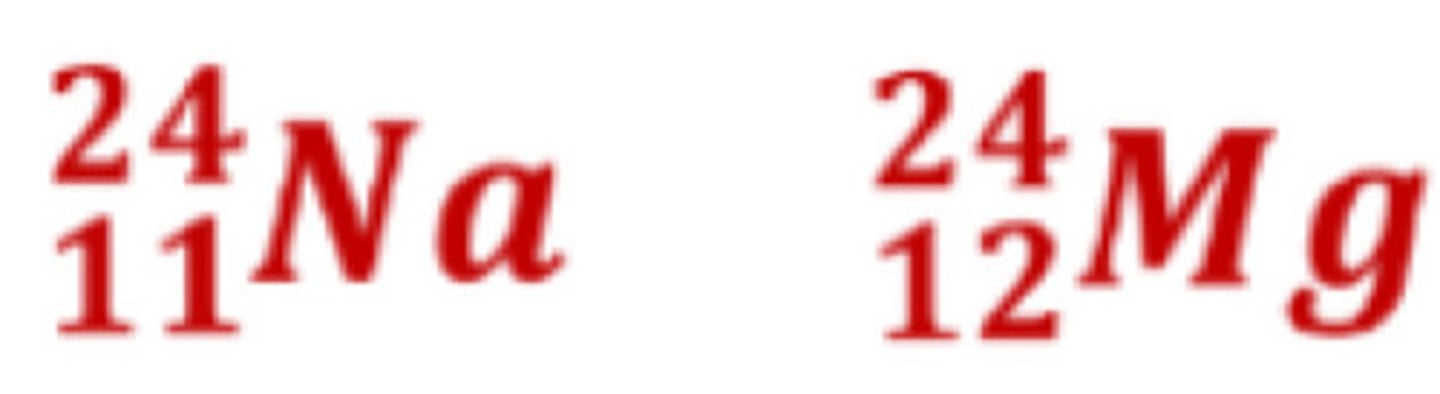
Isotones
same number of neutrons

Atomic weight
weighted average of masses (mass number) of all isotopes of an element
fractional numbers not integers
Pure subtances
copper wire and water are
Endothermic process
Melting is what process?