Molecular Cell Biology: Cell Types, Microscopy, and Stem Cells
1/50
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
51 Terms
What are the fundamental units of life?
Cells
What invention led to the discovery of cells?
The microscope
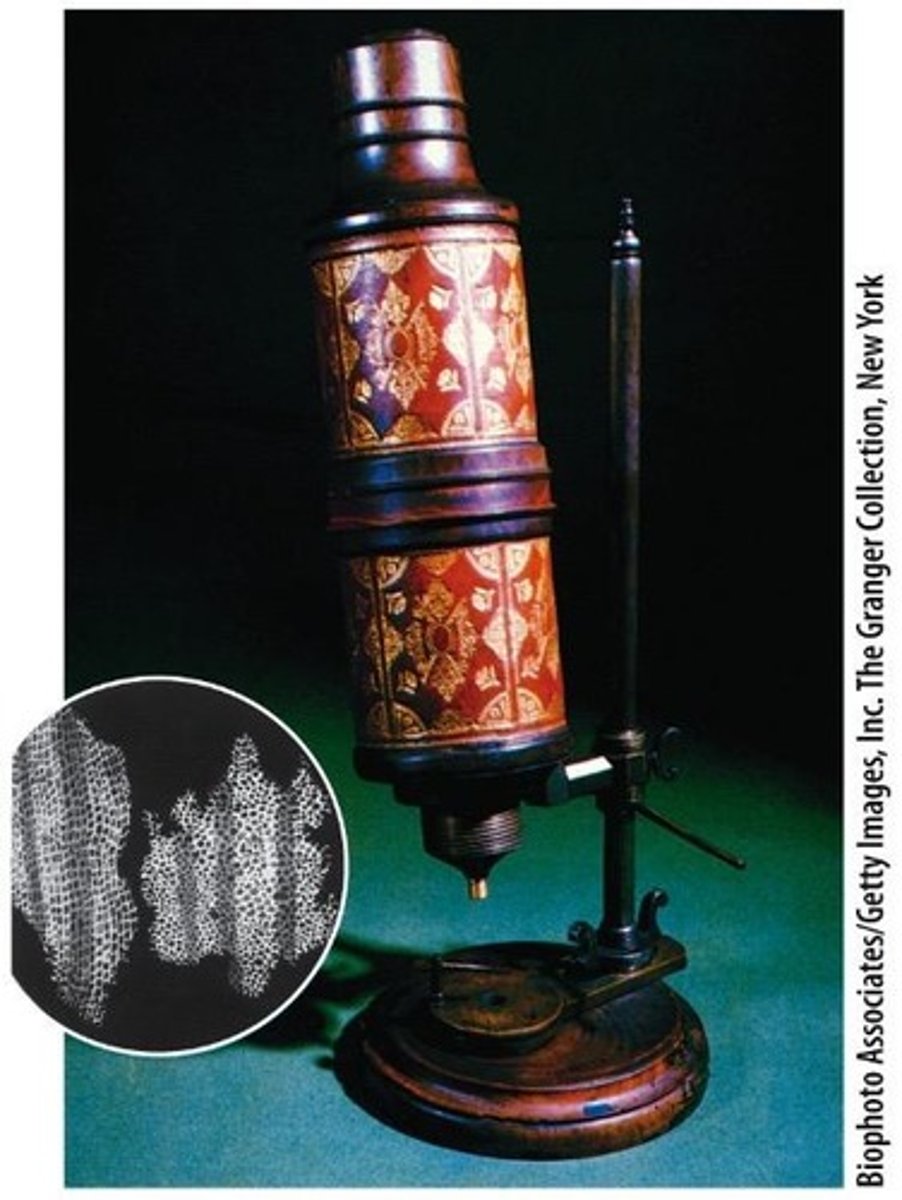

Who invented the single lens microscope?
Leewenhoek
What type of microscopy allows quick views of tissue and cellular morphology?
Traditional Bright Field microscopy
What is a limitation of traditional Bright Field microscopy?
Limited resolution; small organelles like mitochondria may not be visible
What is the purpose of staining in microscopy?
To make transparent objects visible, though it can be toxic
What is Phase Contrast Microscopy used for?
To view highly transparent objects without staining and to see living cells
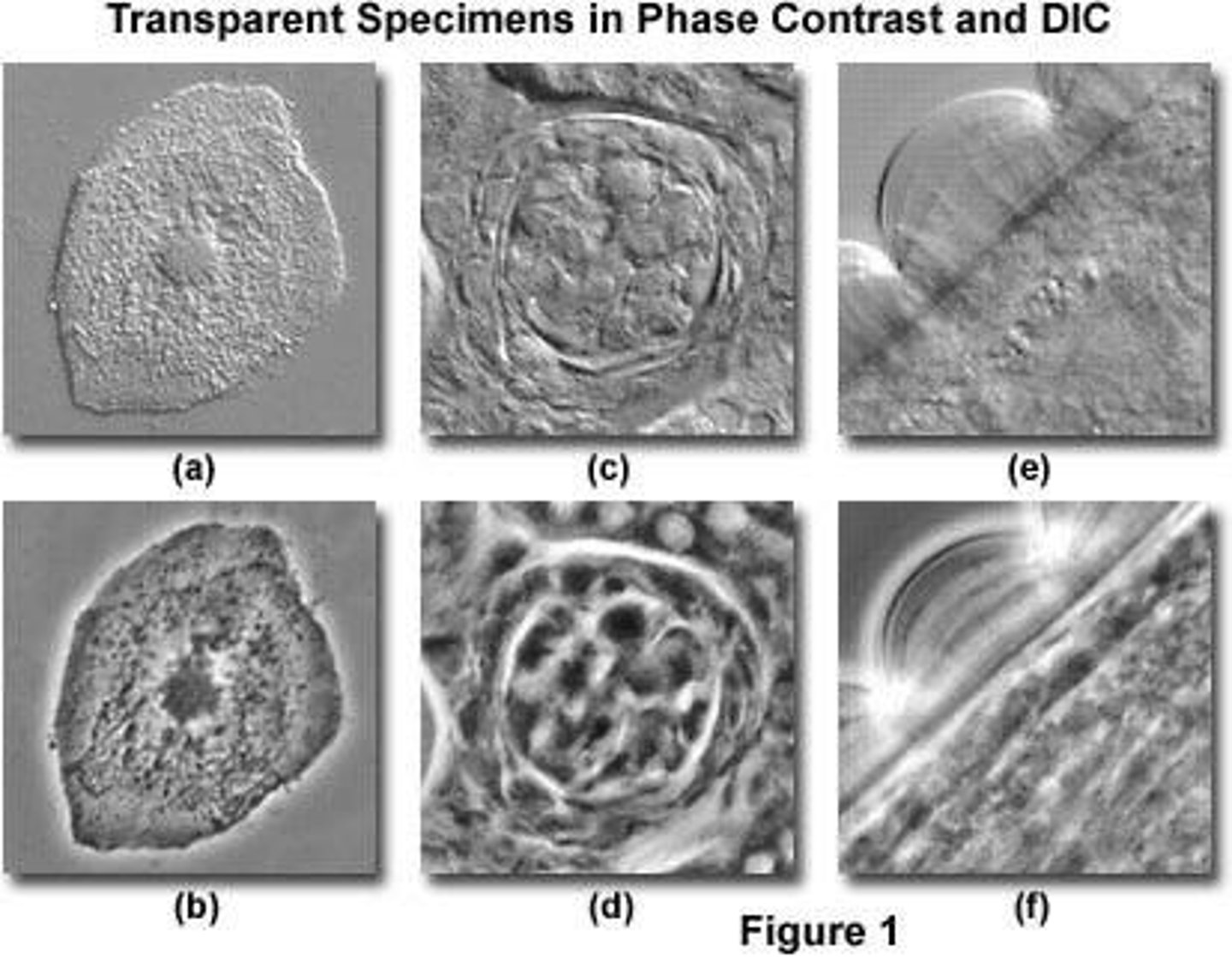
What is a key advantage of Differential Interference Contrast (DIC) microscopy?
Increases resolution and avoids the glowing ring artifact of Phase Contrast
What does Fluorescence Microscopy utilize to generate images?
Fluorescence from cell or subcellular structures
What distinguishes Electron Microscopy from light microscopy?
It uses an electron beam instead of light, allowing for much greater resolution
What are the three main tenets of Cell Theory?
1. All organisms are composed of one or more cells. 2. The cell is the structural unit of life. 3. Cells arise only by division from pre-existing cells.
What type of organism is described as having its own ribosomes and performing oxidative phosphorylation?
Mitochondria
What is the typical size range of viruses?
5-300 nm
What surrounds the genetic material of a virus?
A protein capsid
What type of genetic material can viruses have?
DNA or RNA
What is the role of the Golgi Apparatus in a cell?
To package proteins
What process can a cell perform that involves converting glucose to energy?
Glycolysis or the citric acid cycle
What is a unique ability of some bacteria related to nitrogen?
They can convert nitrogen in the soil to amino acids
What is the main function of the extracellular matrix (ECM) in cells?
To provide structural and biochemical support to surrounding cells
What type of microscopy is best suited for viewing living organisms in a polluted lake?
Phase-contrast microscopy
What determines viral specificity for a certain host?
The virus' surface proteins.
What is a bacteriophage?
A virus that infects bacteria, lacking organelles and cannot replicate without hijacking a host cell.
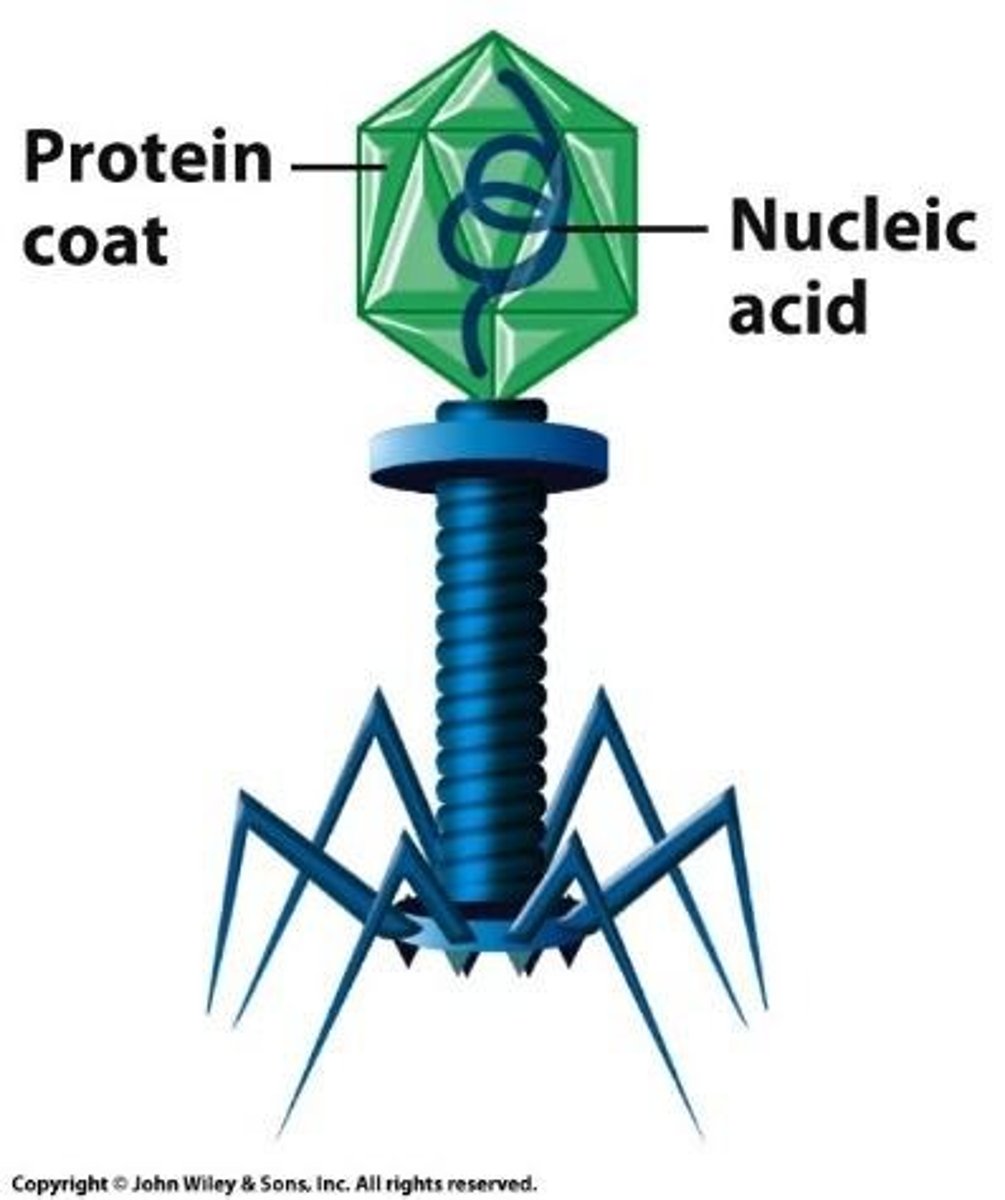
What are the two domains of prokaryotes?
Domain Archae and Domain Bacteria.
What do prokaryotes lack?
Membrane-bound organelles and a nucleus.
What is the typical size of prokaryotic cells?
0.1-5 microns in diameter.
What is the typical size of eukaryotic cells?
10-100 microns in diameter.
What type of energy transformation occurs in eukaryotes?
Chemical energy is transformed into ATP via glycolysis and the Citric Acid Cycle (CAC) inside mitochondria.
What organelles are involved in energy transformation in eukaryotes?
Chloroplasts and mitochondria.
What is the endomembrane system?
A system of membranes that includes the endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, lysosomes, and vesicles.
What is the function of lysosomes?
To degrade phagocytized or endocytosed materials and other cellular matter.
What is differential centrifugation?
A multistep process to isolate subcellular compartments by centrifuging at increasing forces.
What is the purpose of primary culture cells?
To obtain cells directly from an organism, which have limited capacity to proliferate.
What are HeLa cells?
Cultured tumor cells isolated from a cancer patient, Henrietta Lacks, in 1951.
What are adult stem cells?
Cells that self-renew and are multipotent, capable of differentiating into a limited number of mature cell types.
What are embryonic stem cells?
Pluripotent cells isolated from blastocysts capable of differentiating into every cell type.
What is the difference between allogenic and autologous stem cell transplants?
Allogenic transplants are non-self and received from a donor, while autologous transplants are self-derived.
What are induced pluripotent stem cells (iPS cells)?
Reprogrammed somatic cells made pluripotent, avoiding ethical issues and being autologous.
What is transdifferentiation?
The direct conversion of one type of differentiated cell into another without passing through a stem cell state.
What is the typical size of mitochondria?
Approximately 1 micron in length.
What is the role of the cytoskeleton in eukaryotic cells?
To support the nuclear envelope, carry out mitosis, and facilitate vesicle transport.
What is the function of peroxisomes?
Detoxification and fatty acid metabolism.
What is the purpose of the Golgi apparatus?
To target and package proteins made by the rough endoplasmic reticulum for their final destination.
What is the significance of the extracellular matrix (ECM)?
It provides extracellular protection and support for cells.
What is the function of flagella and cilia in eukaryotic cells?
To provide locomotion.
What is the typical measurement unit for organelles smaller than mitochondria?
Nanometers (nm).
What is the process of glycolysis?
The breakdown of glucose to produce ATP, occurring in both prokaryotes and eukaryotes.
What is the role of ribosomes in cells?
To synthesize proteins using mRNA as a template.
What are the characteristics of cyanobacteria?
They are photosynthetic bacteria that generate ATP via oxidative phosphorylation and are ancestors to chloroplasts.
What is the significance of the nuclear envelope?
It contains the DNA genome within the nucleus of eukaryotic cells.
What is the function of the centrosome?
To organize microtubules and facilitate cell division.
What is the role of glycogen granules in cells?
To store glucose for energy.