Autopsy Final Exam
1/258
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
259 Terms
Ages 1-4
80% male
Inexperienced swimmer
Seizure disorder
Environmental (slippery ground, very cold water)
Ethanol
Discuss the risk factors which contribute to an increased incidence of drowning (6)
cutis anserina
spasm of erector pili muscles that can be a sign of immersion in drowning deaths
cutis anserina (spasm of erector pili muscles)
washerwoman hands
white or hemorrhagic edema fluid present in the nostrils, mouth, airways
large, bulky hyperinflated lungs, completely occupying the pleural cavities
brick-red, large edema fluid, white hemorrhagic foam in trachea, subpleural hemorrhages (paltauf’s spots)
water in stomach
conjunctival hemorrhage (drowning = asphyxia)
dilation of right ventricle
nonspecific brain swelling
hemorrhage of mastoid bones or petrous portion of temporal bone
condition of body: floating head down, butt up; animal activity could be present
dry drowning = lungs do not exhibit heavy, boggy, edematous appearance seen in drowning cases - laryngeal spasms ??
List the expected gross findings associated with drowning.
survival of 24 hours or more post immersion
define what constitutes a near drowning
pneumonia
pulmonary edema
diffuse alveolar damage/acute respiratory distress (hyaline membranes)
sepsis
DIC (disseminated intravascular coagulation)
brain death due to hypoxic encephalopathy (transtentorial herniation)
discuss the most common causes of death in near drownings
natural: cardiac, respiratory, metabolic, neurologic, unlikely at MEO unless sudden or unknown medical condition
accidental: drowning, asphyxia, MVA, firearms, fire/burn deaths/ electrocution
differentiate injuries from accidental and natural deaths in children as discussed in lecture
TEN4FACES
Torso
Ears
Neck
Bruising anywhere on a child 4 months or younger
Frenulum
Auricular area
Cheek
Eyelids
Scleral hemorrhage
Contusions, abrasions
Radiographic: fractures along growth plate of long bones, periosteum shearing, spiral/transverse fractures, head trauma, rib fractures
Head injuries: subdural, arachnoid hemorrhages
Abdominal: liver lacerations
Neglect: appears skeletal, subcu fat has tacky, sticky feeling, empty bowel, sunken eyes and soft globes
Parent claims child a “poor eater”
describe injuries seen in battered child syndrome
Battered child syndrome = repeated and deliberate physical abuse
Impulse homicides = acute injury/minimal evidence of chronic abuse; symmetric, well-demarcated, patterns; typically a child “annoys” adult and child is punished
Scalding burns, cigarette burns
Accidental will be more irregular, on anterior portion of body, splash marks
Gentle = asphyxia, smothering
external/internal findings absent
Can’t diagnose from autopsy alone - scene and toxicology report very important
SIDS vs. smothering
Usually not considered homicide unless multiple children have died
differentiate between the different types of homicides in children
soot in airways, ischemia or hemorrhagic necrosis in globus pallidus and perivascular foci of demyelination in deep white matter
autopsy findings from CM poisoning?
renal failure, shock, ARDs, pneumonia, pulmonary embolism
autopsy findings from delayed death after CM poisoning
Charred body
Pugilistic attitude = flexion of upper extremities
Complete absence of fingers, toes, portions of extremities
Heat fractures and no ST hemorrhage
Heat epidural = blood boiling out of venous sinuses; chocolate or brown in color, spongy or crumbly; frontal/temporal/parietal areas of brain
Black carbonaceous matter in upper and lower airway indicates if decedent was alive prior to the fire
autopsy findings from death due to burn injury (6)
Cherry red lividity = accumulation of oxyhemoglobin in tissues due to under utilization - not specific!
Death not immediate = hemorrhagic pancreatitis, erosions/focal hemorrhages of GI mucosa, pneumonia, acute tubular necrosis in kidneys, myocardial fiber necrosis
paradoxical undressing (terminal hallucinations)
autopsy findings for death from hypothermia
Impairment of the driver
Human factors: speed, recklessness, falling asleep
Environmental factors: slick pavement, icy roads, construction, fog
Analyze the causes of common motor vehicle accident injuries according to lecture
Driver = rectangular or linear abrasion/contusion angling downwards from left neck or shoulder toward anterior midline of chest
Passenger = angle downwards from right neck or shoulder area
Lap belt may produce horizontal linear contusion or abrasion of the abdomen
Contrast the injuries that occur to passengers with and without using seatbelts, according to lecture.
No restraints = can be thrown from the vehicle
Full ejection = numerous injuries result when victim lands on firm surface
Could be crushed or trapped beneath vehicle = traumatic asphyxia
Partial ejection = body may be crushed or amputated
Argue the utility of vehicular restraint devices according to lecture
epidural hematoma
laceration of the middle meningeal artery
breaking of temporal bone
bleeding between dura and skull
subarachnoid hematoma
rupture of AVM or aneurysm, head injury
bleeding within the subarachnoid space
subdural hematoma
typically from trauma
tearing of the bridging veins, between brain and dura
coup
brain injury at the site of impact
countercoup
brain injury opposite the site of impact
larger
common in MVA
number
location
distribution
presence of satellite injuries
characteristics: length, shape, orientation, appearance of margins, marginal or adjacent abrasion, depth and structures injured, direction of wound track
clothing defects
List the important factors to document for stab wound injuries (6)
circular defect with marginal abrasion
inverted margins
soot and stippling
entrance wounds
irregular defect whose edges can be re-approximated
stellate, beveled, slit, crescent
everted margins
no marginal abrasion, but can be shored (collar of abrasion)
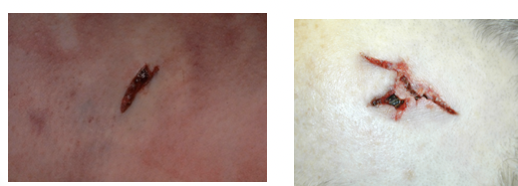
exit wound
entry wound
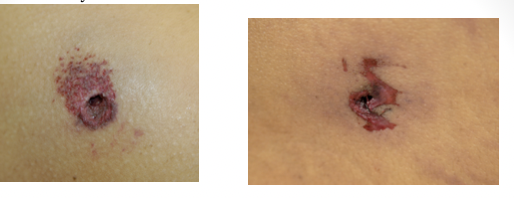
exit wound
congestive and heavy lungs
little food in GI tract
distended and full bladder
sedation
foam cone
drug users: track marks, skin popping
cocaine = MI with no other risk factors
list potential autopsy findings in overdoses cases as discussed in lecture.
scratch
abrasion caused by sharp object passed across the skin
heaping of surface layers in front of the object leaves clean area at the start and tags at the end
e.g. fingernails, thorn, pin
graze
abrasion that occurs when there is movement between the skin and some rough surface (e.g. road rage)
impact abrasion
abrasion with more force and less duration
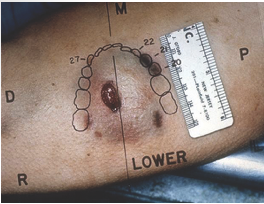
pressure abrasion
abrasion caused by crushing of superficial layers of skin; associated with bruise of surrounding area; force less, duration more
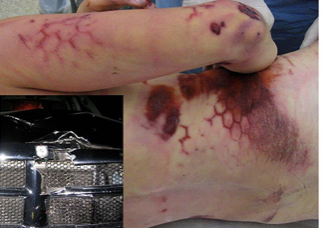
patterned abrasion
post mortem insect bites can mimic
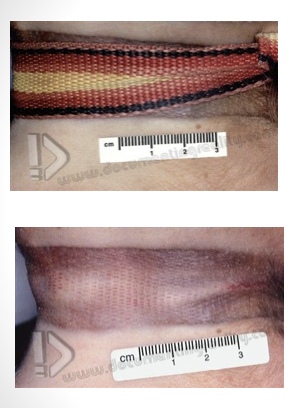
contusion
bruises due to rupture of vessels, usually capillaries; no loss of continuity of skin
pulmonary contusion
caused by extreme chest trauma; excess fluid interferes with gas exchange leading to hypoxia (e.g. explosions, traffic accidents, falls, sport injuries, falls)
basilar skull fracture
battle’s sign behind ear and raccoon/panda eyes indicate?
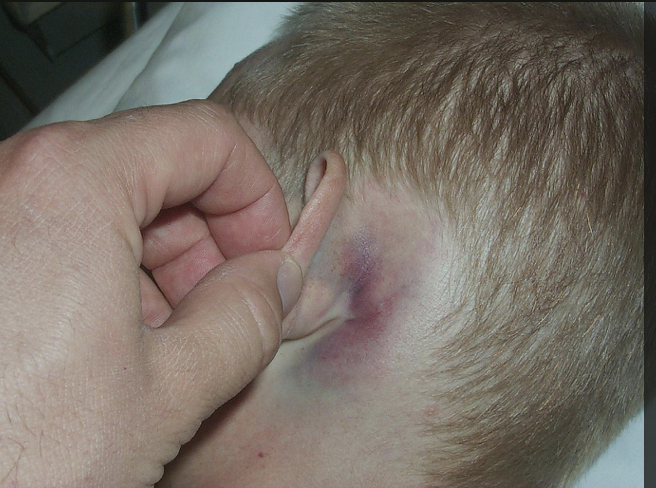
laceration
irregular edges, hair bulbs crushed, less hemorrhage, wound bridging, varying depth
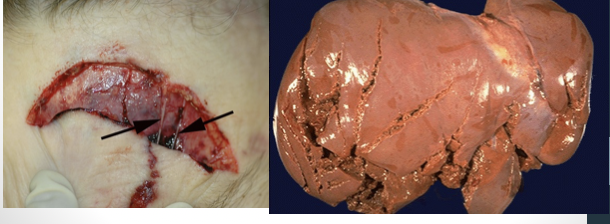
split laceration
occurs by crushing of the skin between two hard objects
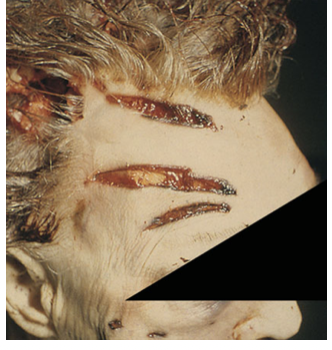
stretch laceration
common in high velocity intraoral GSW
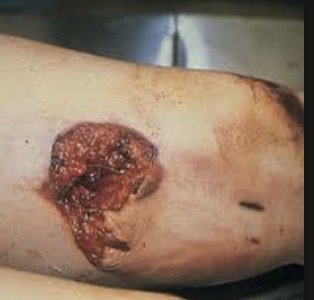
avulsion
degloving accidents

tearing laceration
ripping of skin and tissue from impact by or against object
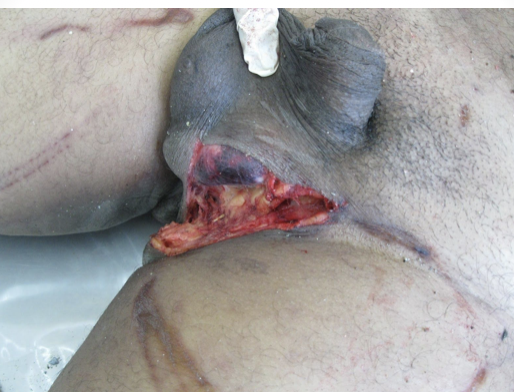
compound
fracture in which bone protrudes through skin
incised wound
clean, cut edges, well-defined, free from contusions
spindle-shaped
lots of hemorrhage from clean cut vessels
deeper at the beginning and more shallow at the end (“tailing”)
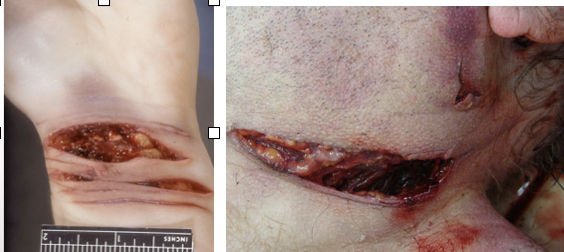
defensive wound
grasping surfaces of hands - flap wound created
ulnar border of forearm
dorsum or plantar surface of hand
lower limbs - sexual assault
stab wound
depth > length
width of wound < width of weapon - stretching of skin
clean cut edges
punctures around concealed parts of the body (axilla, vagina, rectum, nostrils)
abrasion
contusion
laceration
fracture
4 types of blunt force trauma
removing the tension caused by the elastic fibers in the skin is necessary to evaluate the true shape
isolating the area by cutting it from the surrounding skin and subcutis or with transparent tape
describe the procedure necessary to evaluate the true shape of a stab wound
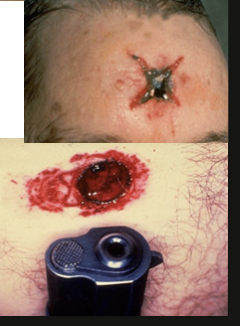
contact gunshot wound
circular and smaller
stellate over scalp
burning /blackening of immediate wound edges
soot within tissues
muzzle mark
inverted wound margins
back spatter = blood sucked up into the barrel of the weapon
close range gunshot wound
almost always circular
inverted edges
collar of abrasion
burning effects
tattooing/stippling
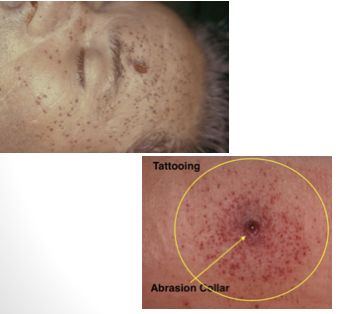
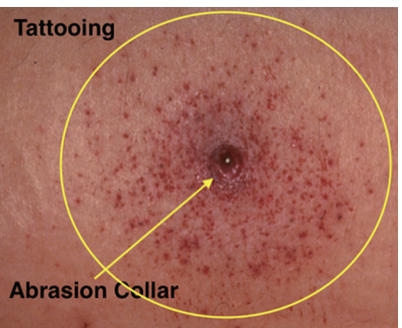
medium/distant range gunshot wound
from less than 0.5 meters to several kilometers away
abrasion collar around entry wound
wound is inverted
ring of dirt or grease ring
bullet striking sideways – may produce rectangular lacerated wound
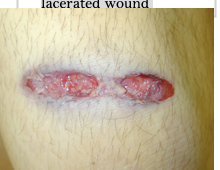
tangential gunshot wound
tears with skin tag formation
short range shotgun wound
6 inches – 6 feet
soot soiling vanishes after 1 foot
tattooing
single wound
rat hole injury
separate wad injury as an abrasion or bruise
distant range shotgun wound
>6 feet
no soot
number of separate pellet holes increase progressively around main wound
wad often takes lower trajectory
6-10 meters, central hole may shrink to nothing
suffocation
strangulation
chemical asphyxia
three types of asphyxial deaths
smothering
suffocation due to mechanical obstruction of the nose and mouth
choking
suffocation due to obstruction of airway; no petechiae
mechanical suffocation
pressure on chest and abdomen making it impossible to breath; most accidents
face and neck are deep purple from congestion; petechiae of conjunctiva and sclera, confluent scleral hemorrhage
strangulation
occlusion of BV in neck secondary to external pressure
mechanism of death = cerebral hypoxia secondary to obstruction of vessels bringing oxygenated blood to the brain
NOT due to compression of the trachea
cyanosis, petechial hemorrhages of conjunctiva, sclera and periorbital skin
hanging
type of strangulation
usually pale face, protruding tongue and dried out mucus drips from nose with no petechiae depending on the degree
tardieu spots on heart and pooling of blood in the LE and forearms
furrow in neck
may see sclera or conjunctival hemorrhage/strap muscle hemorrhage/hyoid bone or thyroid cartilage fracture but not always
ligature strangulation
pressure on neck applied by object tightened by force other than body weight
most commonly associated with rape
death due to occlusion of carotid arteries with cerebral hypoxia
blood gets to head but can’t drain = congested face, numerous petechiae of sclera and conjunctiva, periorbital and face skin too
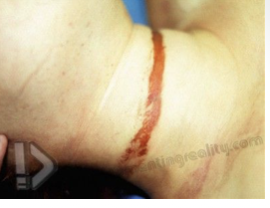
manual strangulation
strangulation from hand, forearm or another limb; occludes vessels on neck
congestion of face, petechial hemorrhages, fingernail marks, hemorrhage in the strap muscles, hyoid fracture, abrasions/contusions on neck
can’t say antemortem if no significant hemorrhage around hyoid/thyroid
chemical asphyxia
gases that prevent utilization of oxygen at the cellular level
carbon monoxide most common
helium, hydrogen cyanide, hydrogen sulfide
cyanide poisoning
bitter almond scent
tox - 200 mg lethal
internal organs = bright pink
damage, blood-stainined stomach lining
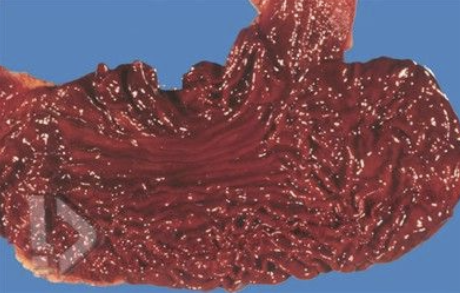
hydrogen sulfide
green discoloration of brain
exposure by proximity to waste water treatment facilities, landfills and farms with manure storage
supine, naked, spread, legs
bite marks and bruising - breasts, inner thighs
double swab method for bites! (wet then dry swab)
trauma to vagina/anus
contusions in posterior 5-7 o’clock
semen deposits - UV light (don’t need sperm to prove)
common COD - strangulation, BFT, stabbing
swabs of mouth, rectum, and vagina
fingernails
describe potential autopsy findings in a sexual assault/rape case as presented in lecture.
objectivity - based on facts and not personal opinions or other influences
internalize the importance of upholding professional ethical standards when arriving at a manner of death, as discussed in class
contact
what distance?
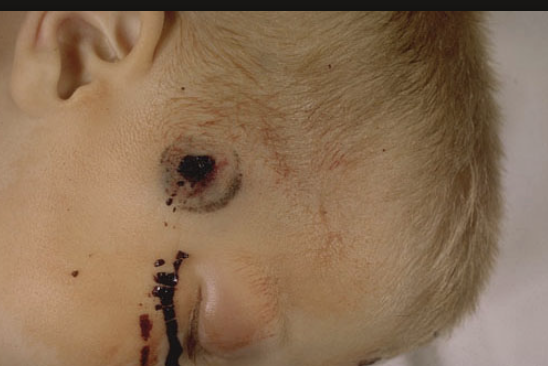
contact
what distance?
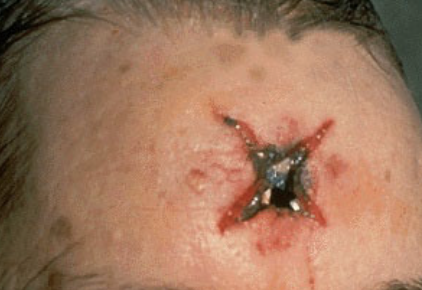
contact
what distance?
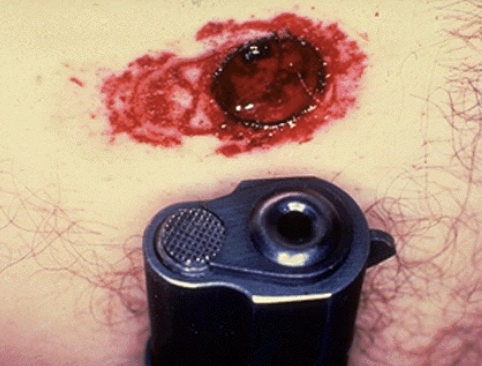
close range
what distance?
close range
what distance?
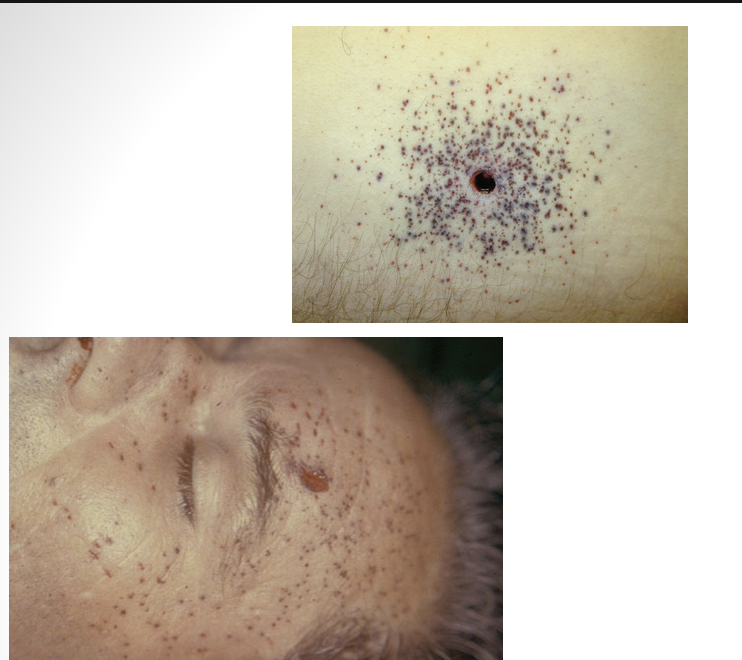
medium range
what distance?

medium range
what distance?
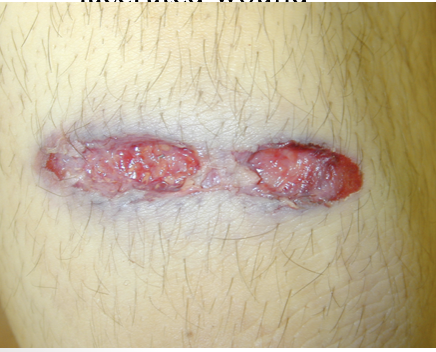
tangential
what distance?
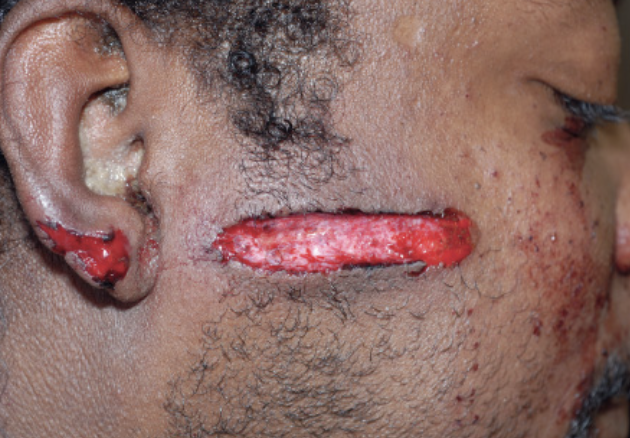
contact
what distance?
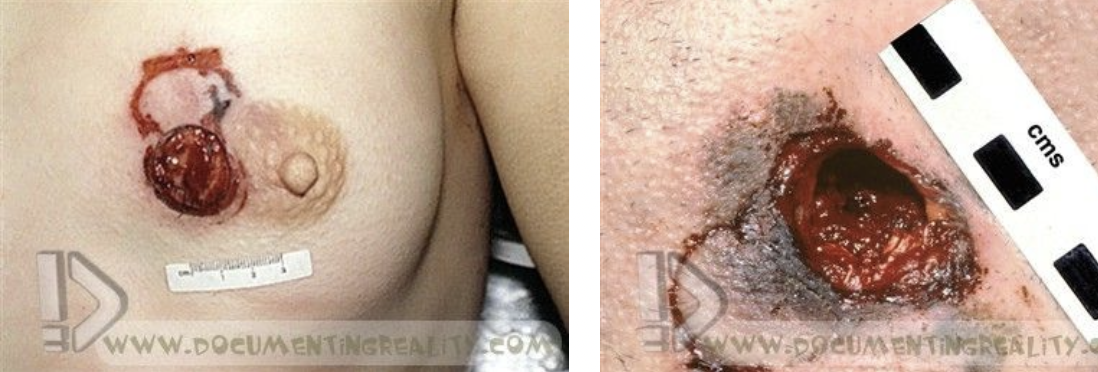
near contact
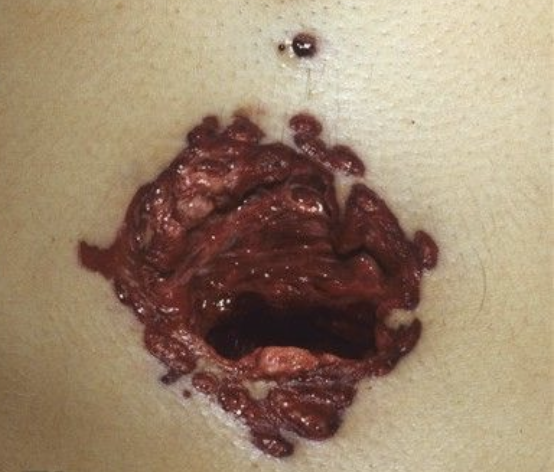
short range
what distance?
return organs to body and suture
family makes arrangements with the funeral home
funeral home contacts the hospital or ME to schedule pick up
state laws vary on who can pick up and transport (funeral home directors vs. private contractors)
ALWAYS maintain chain of custody
security must be involved
verify ID on the remains and personal belongings with the transport
release authorization form
usually handled by appropriately trained staff
documentation:
document deceased with the local county recorder
death registration form
burial permit form
OUTLINE THE PROCEDURE FOR RELEASING A BODY AFTER AN AUTOPSY IS COMPLETE
Final anatomic diagnosis = concise summary of anatomic diagnosis
Gross + histological examination
Most serious to least serious to include cause and mechanism of death
Clinical summary = brief synopsis of all hx gathered
Pertinent clinical issues and pathologic findings relating to the FAD
Grossing findings = external and internal findings; include photographs and radiographs; NO DX OR INTERPRETATION
Microscopic findings
Additional findings = tox, micro, molecular or chromosomal studies
Clinicopathological summary = “final note” that sums up the entire case and states the COD
DESCRIBE THE COMPONENTS OF AN AUTOPSY REPORT (6)
Staff can provide QA for the hospital by thoroughly reviewing medical history
Autopsy can provide QC by providing definitive dx and comparing clinical to autopsy findings - any notable variations must be documented
Unexpected pathologies are not uncommon, but could mean life vs. death!
DESCRIBE THE ROLE AUTOPSIES CAN PLAY IN HOSPITAL QUALITY MANAGEMENT
Training (initial and continuing)
Turnaround time - respect among health care professionals
PADs in 2 days, FADs in 60 days
Improving rates - fully staffed and well-trained team
Regional autopsy centers - create centralized area for data collection as well as training
IDENTIFY WAYS TO MAINTAIN QUALITY IMPROVEMENT IN AUTOPSY PRACTICE (4)
National Association of Medical Examiners (NAME) = primary accredidation body for ME and coroners
American Board of Medicolegal Death Investigators (ABMDI) = individual certificates of death investigators and medicolegal investigations
ANSI National Accreditation Board (ANAB) = international standard; crime labs, law enforcement agencies, ME offices
IDENTIFY ACCREDITING BODIES FOR AUTOPSY PRACTICE (3)
Autopsied generally not covered by medicare, medicaid, or most insurances
Private, non-forensic can cost a family 5000
Forensic autopsies - government service (taxes) and not charged to families
Drug overdose costs taxpayers ~2600
Shooting victims ~6000
Medicare payments are bundled into overall service payments for hospital autopsies
Hospitals receive full payment, whether or not an autopsy is performed
~$1200-$1300
Not seen as cost effective or necessary
ARGUE THE DIFFICULTIES THAT EXIST WHEN IT COMES TO AUTOPSY BILLING
determine:
gestational age
time of death
underlying abnormalities
COD
evaluate:
pregnancy
obstetric care
assess diagnostic and therapeutic procedures, treatment courses
generate data
research
medical teaching
legal evidence gathering
provide genetic info for future pregnancies:
cytogenetic analysis
SNP microarray/LOH
discuss the purposes of performing a perinatal or infant autopsy (8)
body weight
body length (crown to heel and crown to rump)
head circumference (occipital-frontal)
chest circumference (nipple line)
nipple separation
arm span (3rd digits)
xiphoid → pubis
xiphoid → umbilicus
abdominal circumference (umbilicus)
umbilical cord stump (LxD, # of vessels)
penis length
hand length, bilateral
foot length, bilateral (most reliable)
list the body measurements taken during the external examination of perinatal autopsy (13)?
interpupillary distance
inner canthal
outer canthal
interalar distance (width of nose)
philtrum (nose to upper lip)
upper lip thickness
lower lip thickness
mouth commissure
palpebral fissure, bilateral
pupils, bilateral
external ear helix (2), bilateral
fontanelles in 2D (easier after skin reflection if possible)
list the face/head measurements taken during the external examination of perinatal autopsy (12)
May or may not have access
Causes of pregnancy loss in the second trimester are different from early pregnancy losses
Obstetric care/treatment and labor/delivery
How could the mother’s health affect the child?
Diabetes
Environmental factors - smoking, drinking
Family history and genetics that could impact the child
defend the significance of reviewing the mother’s medical chart prior to performing an infant autopsy.
Requires consent if:
Gestational age is greater than 20 weeks
Body weight is greater than 500 grams
Less than 20 weeks usually surg path
Talking to family for consent and disposition of body before performing the autopsy
Consent ONLY following death
Mother and father have equal rights - need agreement
Ability to accept/decline, choose limitations:
“Minimize disfigurement”
External only
Certain organs only
Research only
No extremities or head
May or may not want to know the sex
No photos
All tissue returned with body
examine the unique importance of verifying consent with perinatal specimens
Assessment of anomalies/malformations vs. medical disease
Letulle method almost always - important to preserve anatomic relationships
defend the significance of an extensive external examination.
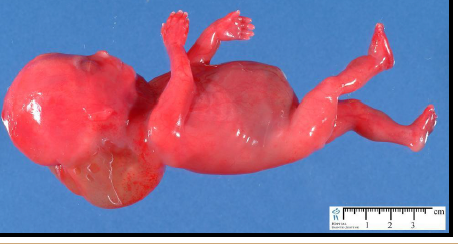
maceration
degenerative changes in fetal tissue when retained in utero
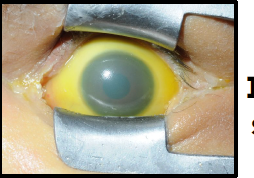
icteric sclera
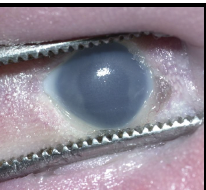
iris coloboma
missing iris portion of eye
moebius sequence
paralysis of facial nerves, unable to form facial expressions
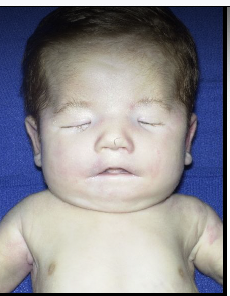
cloverleaf deformity
enlarged anterior fontanelle, other cranial sutures fused, hydrocephalus, macrocephaly
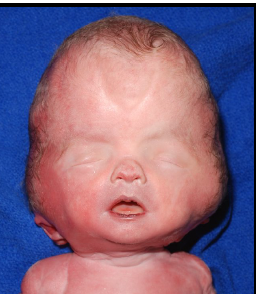
nuchal cord
umbilical cord around neck
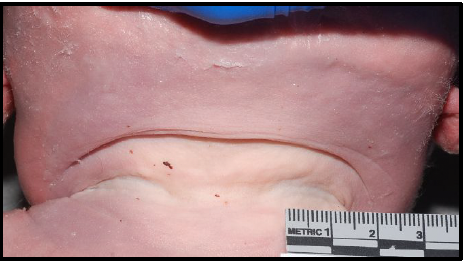
cystic hygroma
lymphatic obstruction leading to fluid accumulation
cleft palate
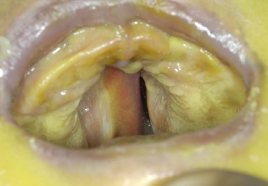
high arch
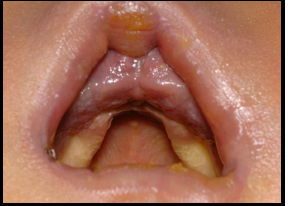
macrognathia
abnormally large jaws
clinodactyly
abnormal curvature of 5th digit associated with down syndrome
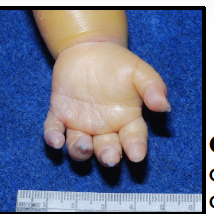
amniotic band syndrome
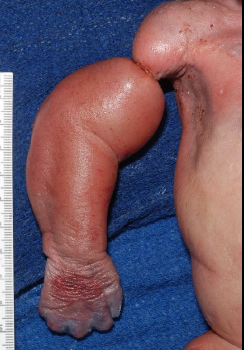
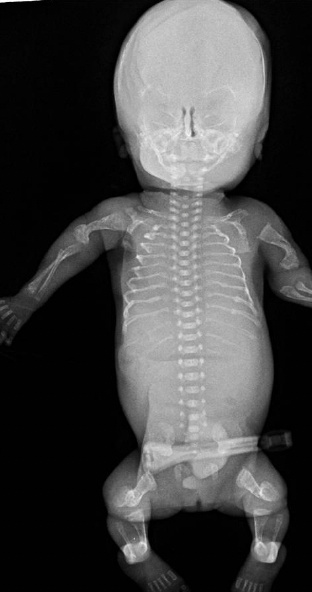
osteogenesis imperfecta
abnormally formed bones due to insufficiency or absent type I collagen production; most severe form is lethal
short, bent limbs
multiple fractures
short, beaded ribs
reduction or absence of cranial vault ossification
blue sclera