Environmental Science Exam 2
1/81
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Salas Class
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
82 Terms
Asian Carp Example
Asian carp are invasive fish that were brought to the U.S. in the 1960s to clean fish farms, but they escaped into rivers, spread quickly, and now threaten to disrupt ecosystems like the Great Lakes.
Species Interactions
Mutualism , Predation/Parasitism / Herbivory , Competition
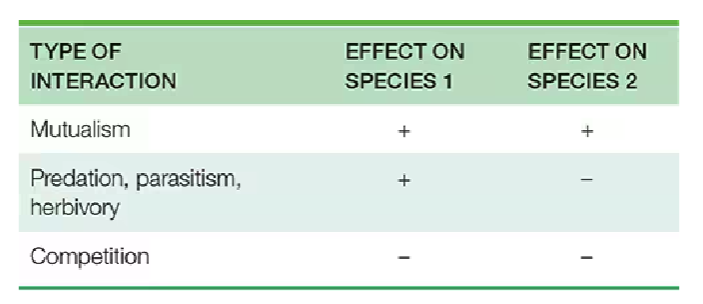
Competition
organisms that seek the same resources have a relationships
Intra vs inter species
Intra - takes place between members of the same species
Inter - takes between members of different species
Competitive exclusion
if one species is a stronger competition , it may excluded other species from than resources
Species coexistence
if no single competitor excludes others, species live side by side.
Resource partitioning
over many generations natural selection may favor , where individuals use shared resources in different ways.
Character Displacement
where competing species diverge and develop different characteristics
Predation
is the process by which individuals of one species (predators) capture , kill and consume individuals of another (prey).
Parasitism
is a relationship where one organism depends on the other for nourishment.
Herbivory
animals feed on the tissues of plants
Mutualism
is a relationship where two or more species benefit each other
Ecological Communities
community
trophic levels
Community
is an assemblage of populations of organisms living in the same area at the same time
Trophic level
Species in a community
are given a rank within
the feeding hierarchy
producers, primary , secondary , tertiary , detritivores , decomposers
Producers
use photosynthesis or chemosynthesis to make their own sugars.
Primary Consumers
consume producers
Secondary Consumers
prey on primary consumers
Tertiary Consumers
prey on secondary consumers
Detritivores
scavenger waste and dead bodies
Decomposers
break down non-living matter into smaller molecules that cycle back into soil
Food chain vs Food web
food chain - The flow of energy and feeding relationships from lower to
higher trophic levels is depicted
Food webs - incorporate all of the interlinking food chains
within an entire community, showing the map of energy
flow.
Keystone species
A species that has an impact far greater than its
abundance .
‘‘ Ecosystem Engineers’’
Keystone species - examples
beavers , otters and wolves
Keystone species - Trophic cascade
If top predators are
lost, primary
consumers will
overconsume
producers and alter
the entire ecosystem
Ecological Disturbance
is any event that has rapid and drastic effects on the community and ecosystem
Resistance
A community that resists change and remains stable
Resilience
A community that is changed by a disturbance but returns
to its original state
Succession
Severe disturbances may eliminate all or most of the species in a community, initiating a series of changes
Pioneer Species
Succession begins with the colonization
such as grasses and forbs, spread
over long distances easily and are adapted for growing
quickly
Climax Community
pioneers are overtaken by longer-living
such as hardwood trees
Primary Succession
occurs when a disturbance removes all plants or soil life
lichens secrete acids that break down rock , beginning the process of soil formation
Secondary Succession
begins with a disturbance that alters the community
but leaves the soil life intact.
– Farming, fires, storms, and landslides are examples.
Introduced species
are non-native arrivals in a community brought by people
Invasive Species
Most fail to establish populations, but the ones that thrive
Eradication vs Control vs Prevention
Eradication - the total elimination of a population, is very difficult and expensive
Ecological restoration
devise ways to restore altered areas to their condition before industrialized
civilization.
Ecological restoration may have two aims:
– Restore the functionality of an ecosystem.
– Return a community to its “pre-settlement” condition
Earth’s Biomes
Despite communities being in very different locations, they often have similar structure and function.
Biome
biomes are classified primarily by dominant plant type and vegetation structures , which is turn is the results of climate
Climate determines biomes
Temperature -
Precipitation -
Climate diagrams / Climatographs -depict
seasonal changes in temperature and precipitation and
help to tell the story of a biome.
Temperature deciduous forest
are found at midlatitudes and have relatively even precipitation throughout
the year.
Temperate grassland
Temperature differences between winter and summer are more extreme and
rainfall diminishes
Temperature rainforest
are rich in rainfall, but still found in midlatitudes
tropical rainforest
have dark, damp interiors, lush vegetation, and highly diverse
communities.
tropical dry forest
have wet and dry seasons that each occupy about half of the year.
savanna
tropical grasslands interspersed with acacias or other
trees.
desert
driest biome, receiving less than 25 cm of rain per year
tundra
also very dry but are consistently cold all year
boreal forest
taiga, are also cold, but receive more precipitation
than tundras
chaparral
is found in only
a few small patches
throughout the world
Chesapeake Bay watershed example
The Chesapeake Bay watershed is the land area where rivers and streams drain into the Chesapeake Bay.
Because of too many nutrients (pollution) and the loss of oysters (a keystone species), the bay became polluted, leading to low oxygen (hypoxia). Efforts are now being made to restore it.
👉 In short: Too much pollution + fewer oysters = unhealthy bay.
Environmental Systems
systems - is a network of relationships among parts that influence each other through the exchange of energy, matter, or information
Positive and Negative feedback loop
Positive Feedback
occur when increased output in a system leads to increased input, which
further stimulates output.
Negative Feedback
results when the system moving in one direction acts as an input that cause
the system to move in the opposite direction
Describe the process of eutrophication
Nutrient input 🌱
Extra nutrients (nitrogen and phosphorus) enter water from fertilizers, manure, or sewage.
Algal bloom 🌊
The nutrients act like “food” → algae and phytoplankton grow rapidly on the water’s surface.
Light blocked ☀
Thick algae prevent sunlight from reaching underwater plants (like grasses). These plants die off.
Decomposition 🦠
When algae die, decomposer bacteria break them down. This process uses up oxygen in the water.
Oxygen depletion (hypoxia) 💨
Oxygen levels drop so low that fish, crabs, and other aquatic life can’t survive.
Dead zones ⚠
The area becomes nearly lifeless, with very few species able to live there.
impacts of run- off
runoff - precipitation that flows over land and into
waterways, might define the Chesapeake Bay watershed as a system
significance of high concentration of nutrients (N&P)
High N & P → algal blooms → oxygen loss → harm to aquatic ecosystems.
Resulting hypoxia
Hypoxia = low oxygen in water caused by too many nutrients and algal decay, which leads to the death of aquatic organisms.
describe how energy and matter flow through an ecosystem
Energy Flow ⚡
Starts with the sun → plants (producers) capture sunlight through photosynthesis.
Moves through food chains → plants → herbivores → carnivores → decomposers.
Lost as heat at each step (cannot be recycled).
👉 Energy flows one way only, from the sun to producers to consumers, then out as heat.
Matter Flow 🌍
Matter is recycled in cycles (carbon, nitrogen, water, phosphorus).
Example: Plants take in carbon dioxide → animals eat plants → decomposers return carbon to soil/air.
Unlike energy, matter circulates continuously within the ecosystem.
💡 Easy way to remember:
Energy = one-way street (sun → food chain → heat).
Matter = recycling loop (used again and again).
Production
The rate at which energy is converted to biomass
primary production
The conversion of solar energy into chemical bonds in sugars
gross
The total energy captured by producers.
net production
The energy left after plants use some for their own respiration.
why do difference ecosystems have different levels of productivity
Ecosystem productivity depends on sunlight, temperature, water, and nutrients. That’s why tropical rainforests and coral reefs are highly productive, while deserts and tundras are low.
What does it mean that nitrogen and phosphorus are limiting nutrients
Nitrogen and phosphorus are called limiting nutrients because they are usually scarce, and their availability sets the limit for plant and algae growth in an ecosystem.
relating to dead zones
Too much N & P → algae boom → oxygen gone → dead zone forms.
biogeochemical cycling
Biogeochemical cycles are the natural pathways by which elements and compounds (matter) move through living organisms (bio), the earth (geo), and the atmosphere (chemical).
biogeochemical cycling - sources
When a reservoir releases more materials than it accepts
biogeochemical cycling - sinks
When a reservoir accepts more materials than it releases
the water cycle
summarizes how water flows as a solid, liquid, and gas, through our environment
Evaporation
Converts water from a liquid to gaseous form , taking it to the atmosphere.
Increased by warmth , wind, and a high degree of exposure.
Transpiration
is the release of water vapor by plants through their leaves.
transpiration and evaporation both leave any substances dissolved in water behind
precipitations
when it condenses into rain or snow.
▪ May be taken up into plants or used by animals, but
most of it flows as runoff into surface waters
the carbon cycle
describes the routes that carbon takes through the environment
the carbon cycle - explain how carbon cycle through the environment
Carbon moves between the air, living things, water, and Earth through processes like photosynthesis, respiration, decomposition, combustion, and geological activity.
the carbon cycle - why is this cycle significant for climate change
The carbon cycle matters for climate change because humans are adding too much carbon to the air, upsetting the natural balance, and making the planet warmer.
nitrogen cycle
Under the right conditions, nitrogen can become
biologically active and enter the biosphere and
lithosphere
nitrogen cycle - explain how nitrogen cycle through the environment
Nitrogen goes from the air → soil → plants → animals → back to the soil → and finally back to the air.
nitrogen cycle - the significance of nitrogen fixation
Nitrogen fixation is important because plants and animals can’t use nitrogen gas from the air.
nitrogen cycle - significance nitrogen fixing bacteria
Nitrogen-fixing bacteria change nitrogen gas into a form plants can use to gro
haber - bosch process
enabled people to artificially fix nitrogen, greatly enhancing agriculture.
haber - bosch process - implications of this process on population
In simple terms: these cycles directly affect population growth, decline, survival, or extinction, because they control how much food, oxygen, and livable habitat are available.