Cell Structure and Function
1/56
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
57 Terms
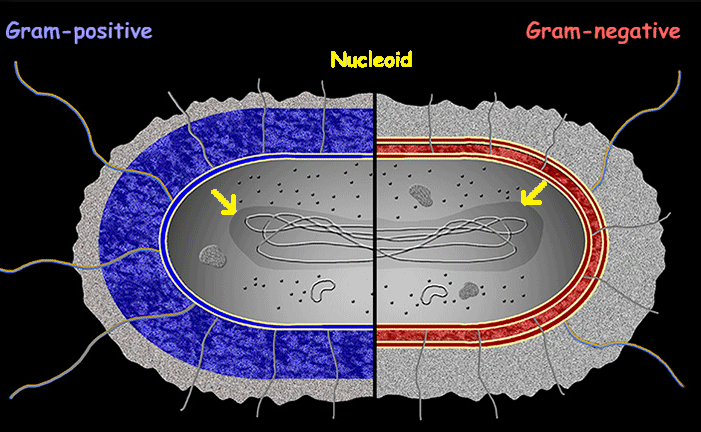
Nucleoid
The region within a prokaryotic cell where the genetic material is located, typically not enclosed by a membrane.


Genosphore
A type of spore in certain fungi that carries genetic material, often involved in reproduction and genetic diversity.


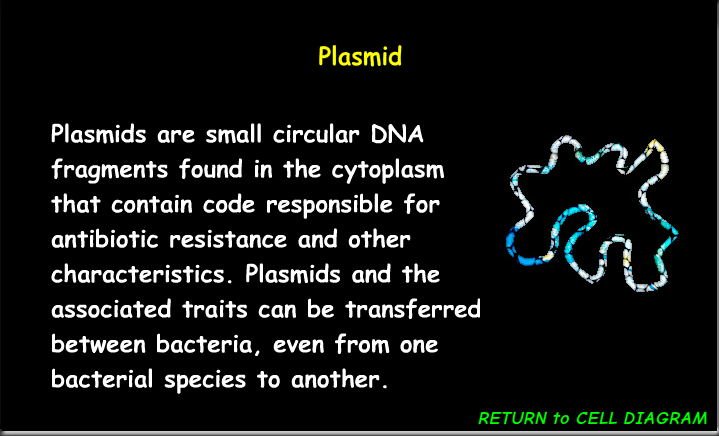
Plasmid
A small, circular piece of DNA found in prokaryotic cells that can replicate independently of the chromosomal DNA, often carrying genes that confer advantageous traits.
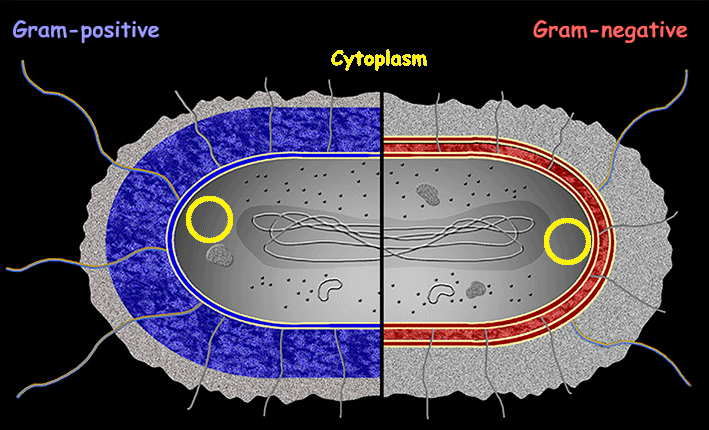
Cytoplasm
The gel-like substance inside a cell that surrounds the organelles and is the site of many metabolic processes.


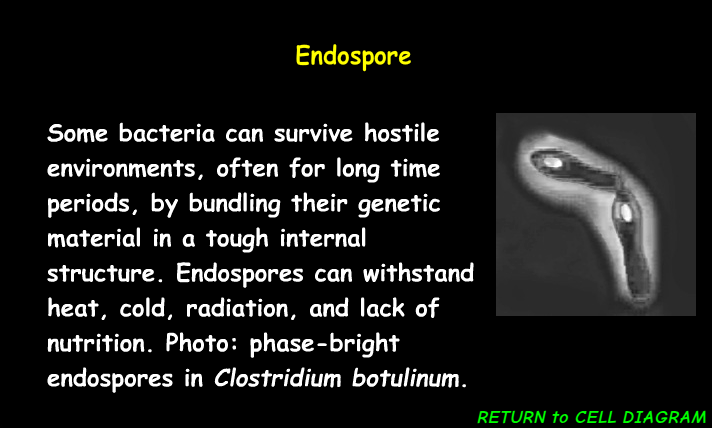
Endospore
dormant structures formed within the cytoplasm of certain bacteria, enabling survival under harsh conditions.
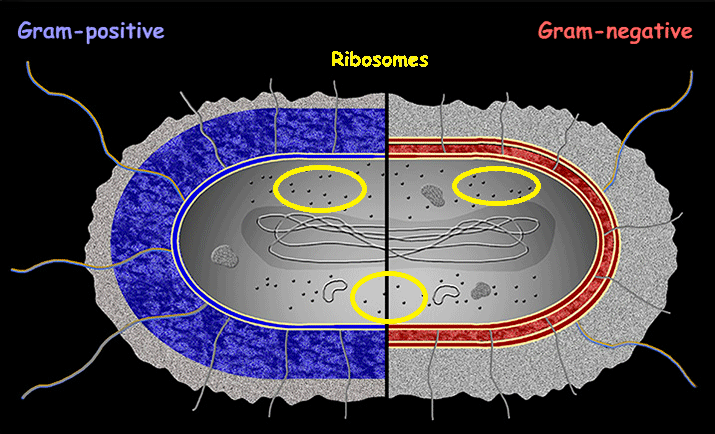
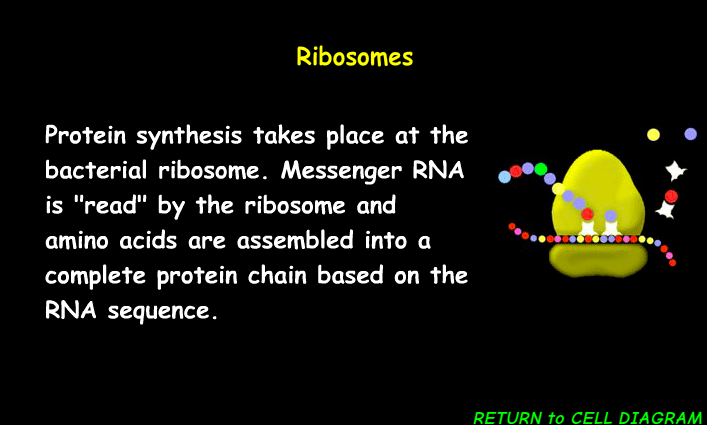
Ribosomes
The main function of ribosomes is to synthesize proteins by reading genetic information from messenger RNA (mRNA) and linking amino acids together
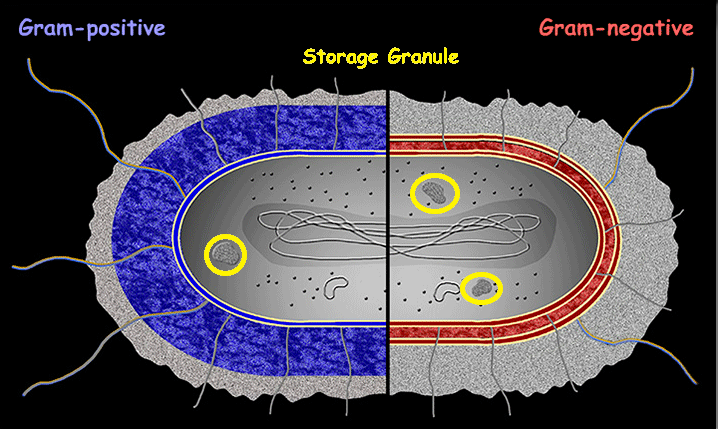
Storage Granules
stores essential nutrients and other materials for a cell

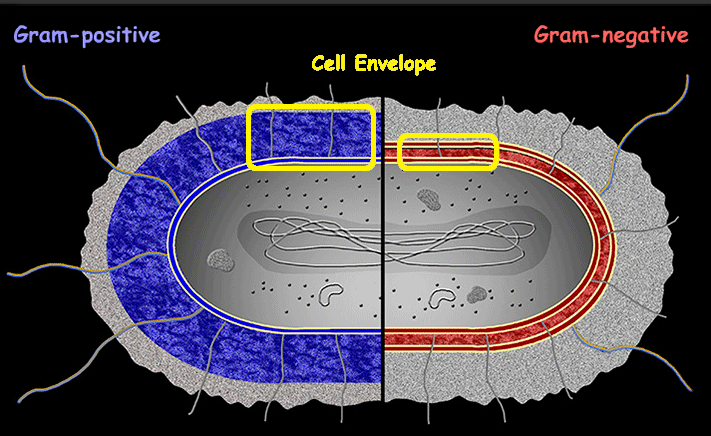
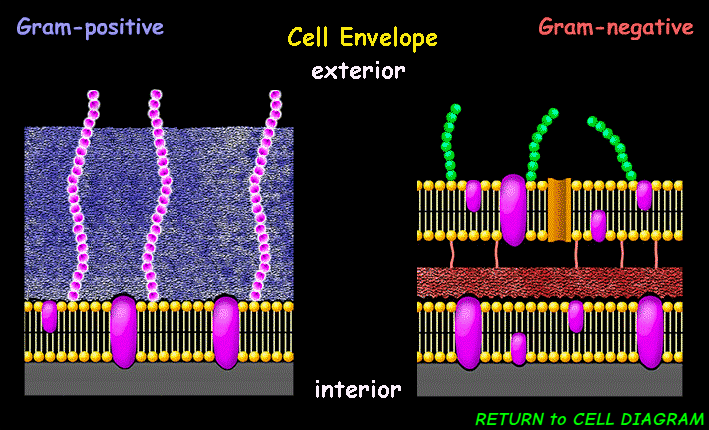
Cell Envelope (CE)
protects the cell from its environment, regulates the passage of substances, maintains structural integrity, and plays a role in bacterial adhesion and infection.
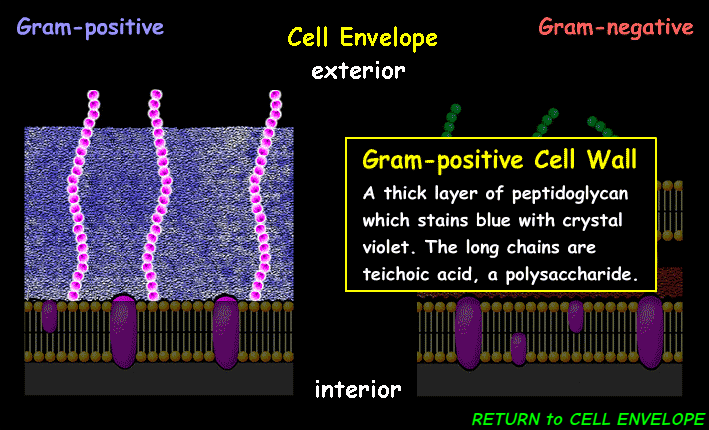
(CE) Gram-Positive Cell Wall
protects the cell, maintains its shape, and facilitates interaction with the environment
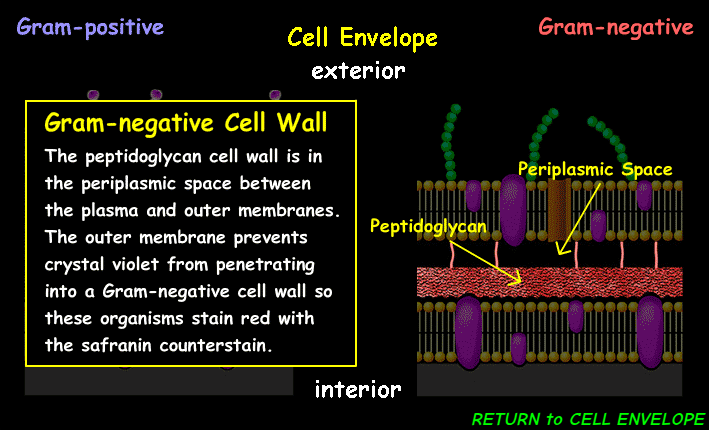
(CE) Gram-Negative Cell Wall
Acts as a barrier against drugs and chemicals, maintaining cell shape and integrity, and playing a role in immune response
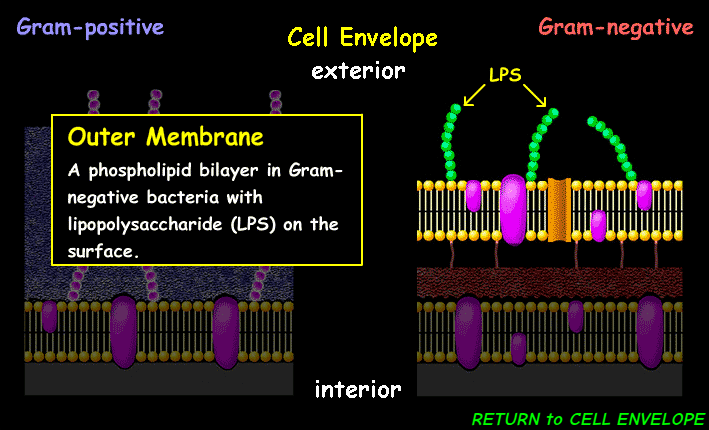
(CE) Outer Membrane
Acts as a selective barrier in Gram-negative bacteria, protecting against toxic substances like antibiotics and external insults
(CE) Cytoplasmic Membrane
a protective, selectively permeable barrier that surrounds the cell's interior and controls the transport of substances. It regulates what enters and exits the cell

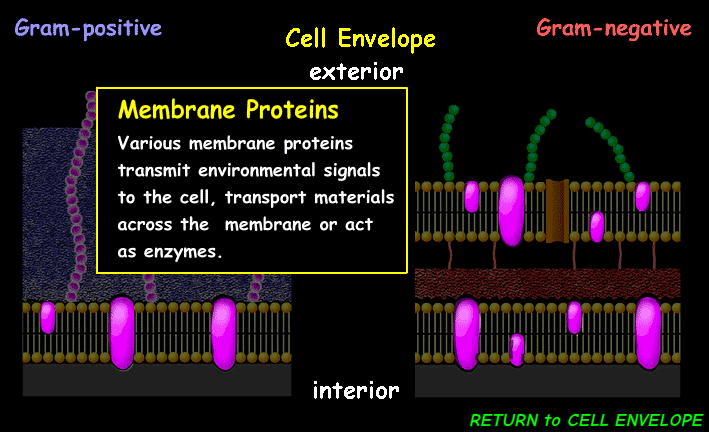
(CE) Membrane Proteins
transports molecules across the cell membrane, act as receptors for signals, facilitates enzymatic activity, and helps with cell to cell recognition and adhesion
(CE) Porin
Their primary function is the passive transport of hydrophilic molecules, such as water, ions, and nutrients, across these membranes. They also help regulate cellular permeability, allowing waste to exit and preventing the entry of toxins and detergents


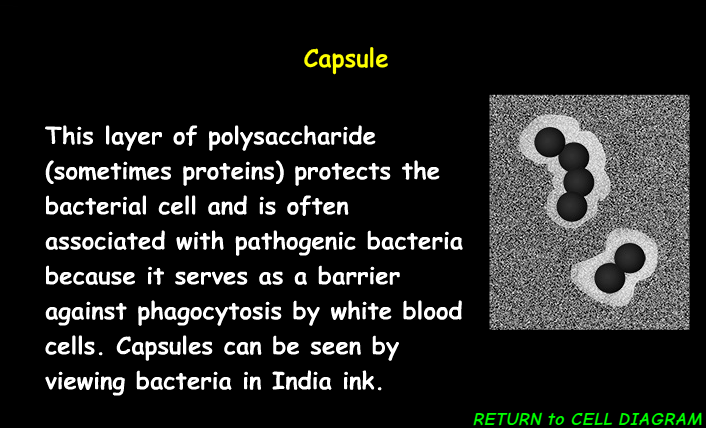
Capsule
The capsule in a prokaryotic cell provides protection, aids in adhesion, and helps it survive in its environment
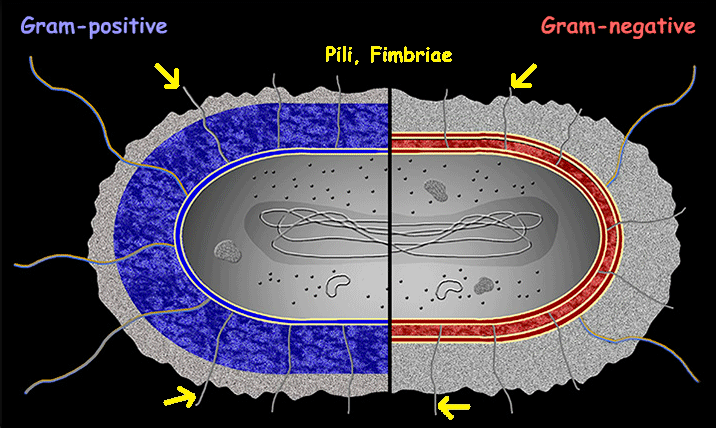
Pili, Fimbriae
Pili and fimbriae are hair-like appendages on bacterial cells that primarily function in adhesion to surfaces, host tissues, and other cells


Flagella
The primary function of flagella in prokaryotic cells is motility, enabling them to move by swimming

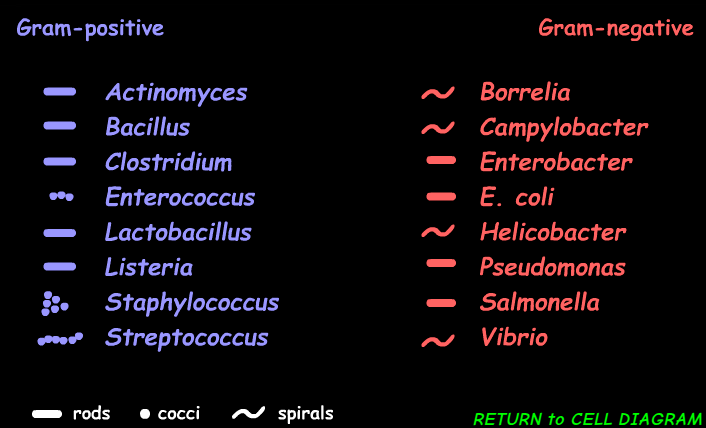
Gram Positive & Negative Bacteria Examples
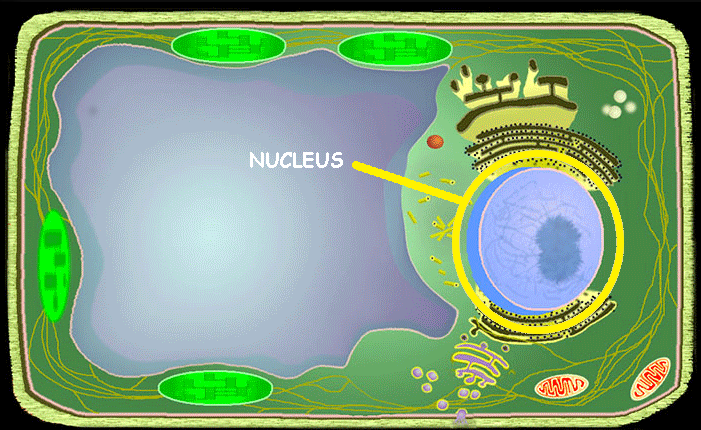
Nucleus
A part of the cell containing hereditary information and is responsible for growth and reproduction; the "command center" of the cell.

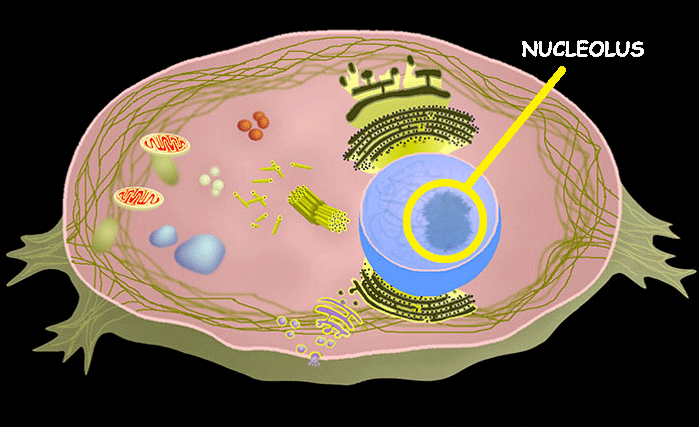
Nucleolus
Makes ribosomes

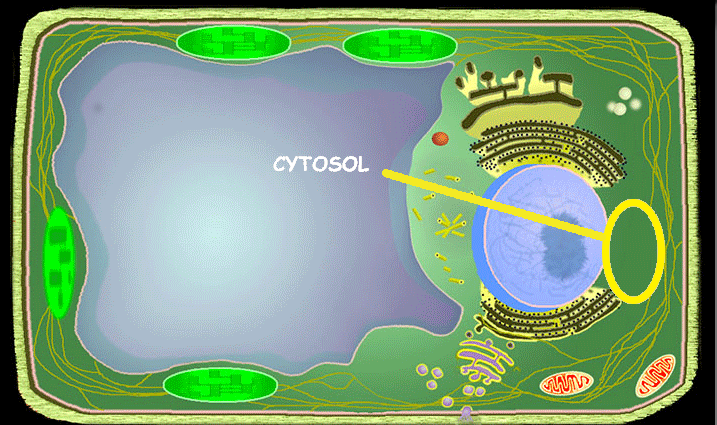
Cytosol/Cytoplasm
Cytosol is the fluid portion of the cytoplasm, while cytoplasm includes both the cytosol and all other components within the cell membrane, such as organelles like the nucleus, mitochondria, and ribosomes

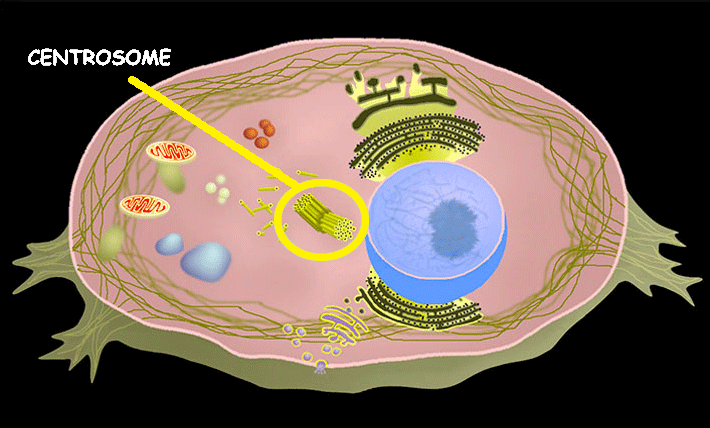
Centrosome
Centrosomes function as the primary microtubule-organizing centers in animal cells, playing a critical role in cell division by assembling the mitotic spindle. They also organize microtubules to maintain cell shape, polarity, and intracellular transport, and form the base of cilia and flagella.

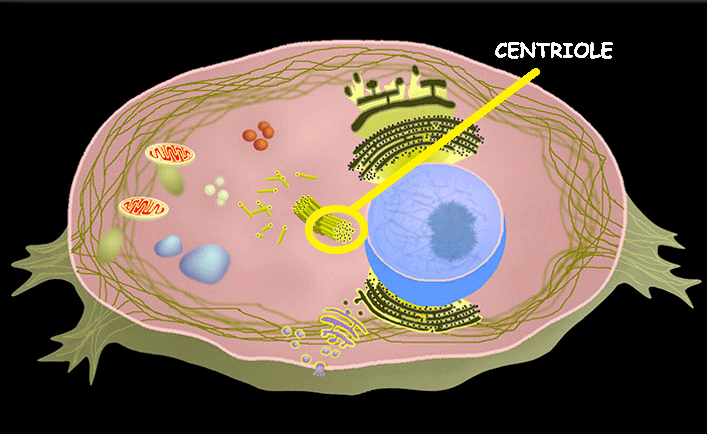
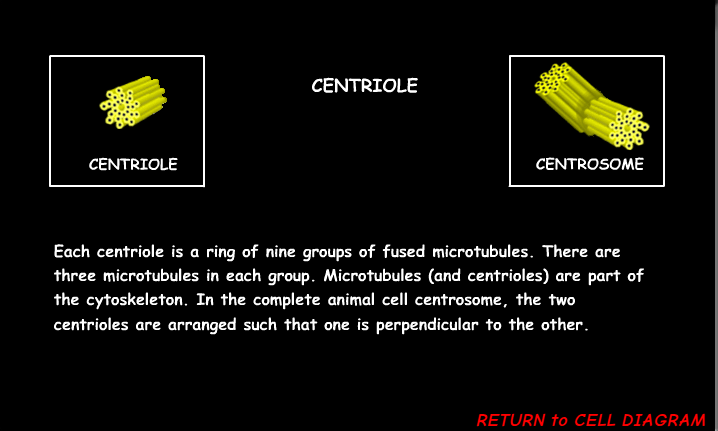
Centriole (Animals Only)
Helps with cell division
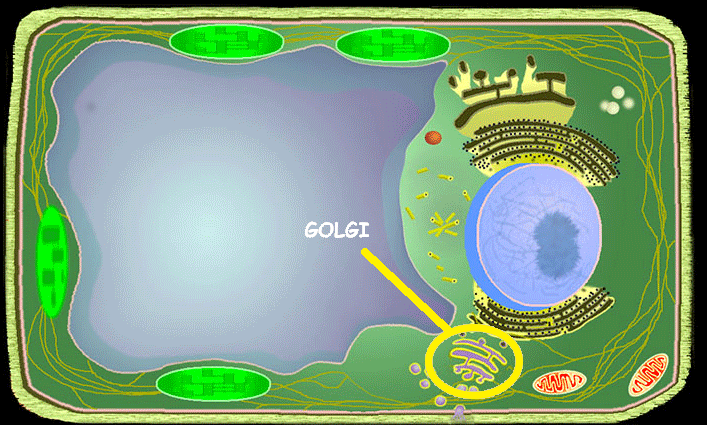
Golgi Apparatus
A cell structure that helps make and package materials to be transported out of the cell or for storage inside the cell.


Lysosomes
Cell organelle filled with enzymes needed to break down certain materials in the cell, such as large food particles or old parts of the cell.


Peroxisomes
Peroxisomes protect the cell from its own production of toxic hydrogen peroxide

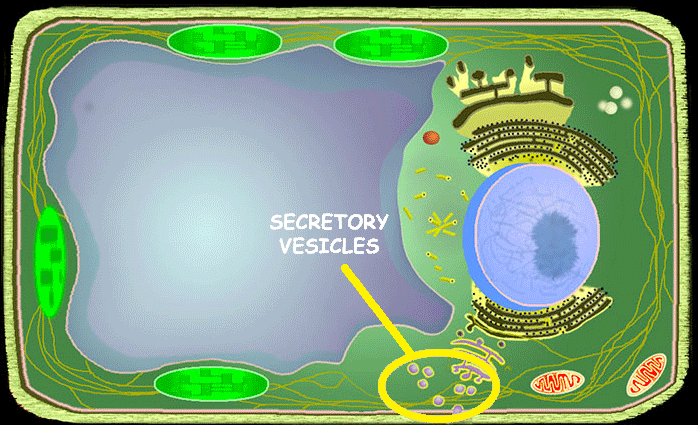
Secretory Vesicles
Secretory vesicles function to transport and release substances from the cell

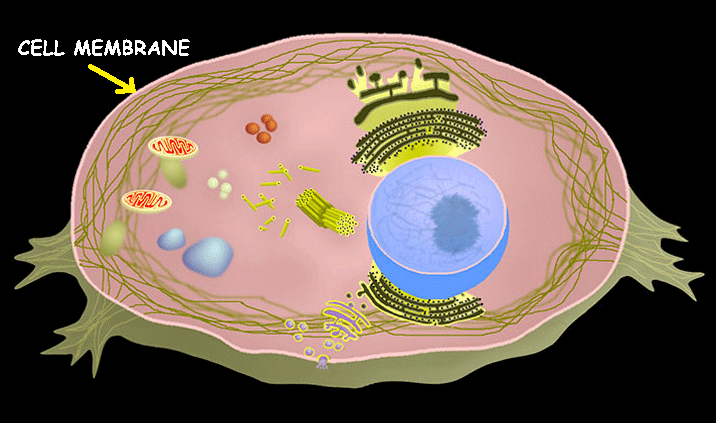
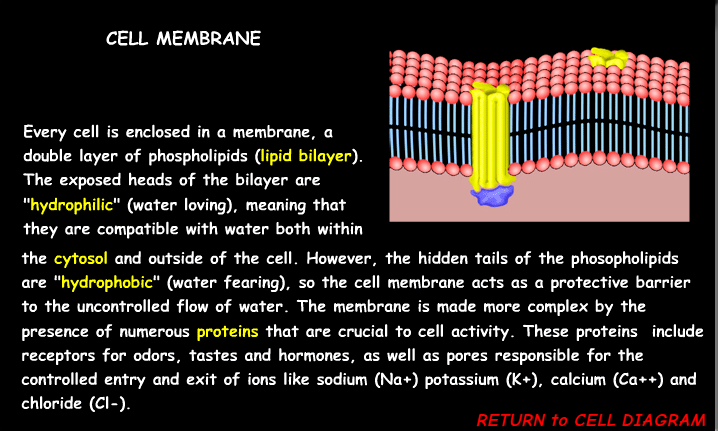
Cell Membrane
The cell membrane's primary function is to act as a protective barrier that separates the cell's interior from its external environment, while also regulating the passage of substances in and out of the cell
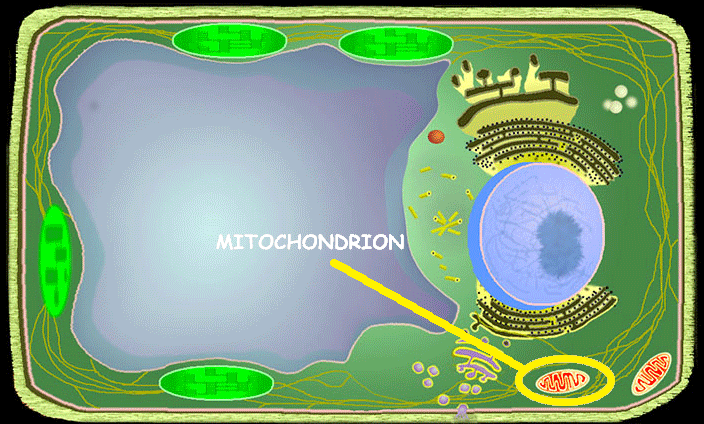
Mitochondrion
An organelle containing enzymes responsible for producing energy. (Metabolism/respiration)

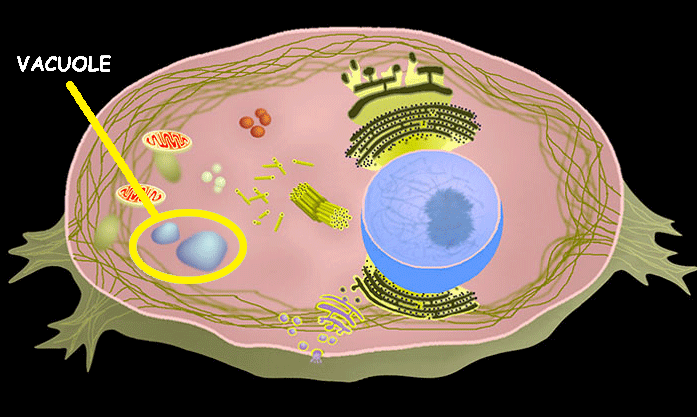
Vacuole
Saclike storage structure in the cell. can store water, nutrients, and even toxic substances.

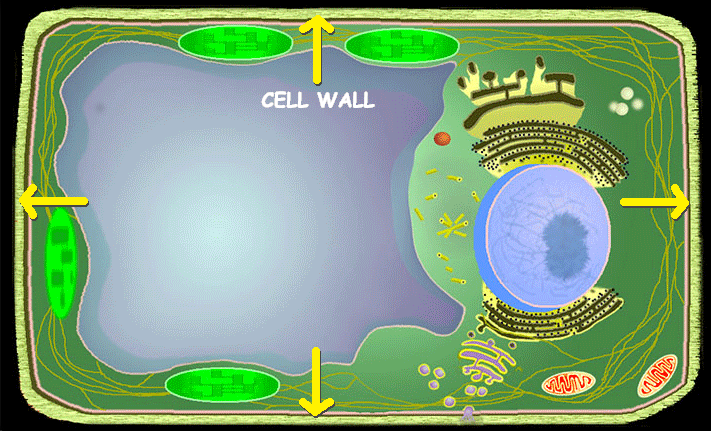
Cell Wall (Plants Only)
The cell wall's primary function is to provide support, shape, and protection to the cells of plants, fungi, bacteria, and algae

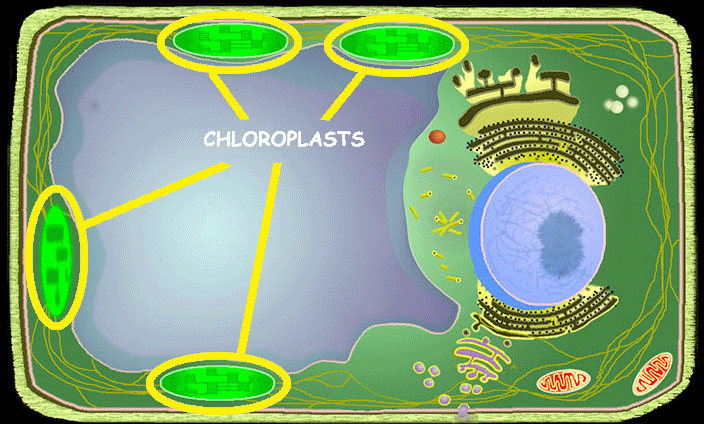
Chloroplasts (Plants Only)
Chloroplasts are vital plant cell organelles that carry out photosynthesis, converting light energy, water, and carbon dioxide into glucose (sugar) and oxygen

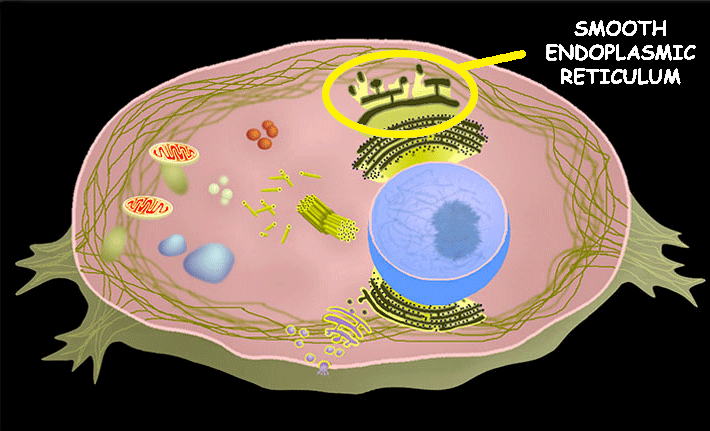
Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum
No ribosomes, but makes lipids (fats)

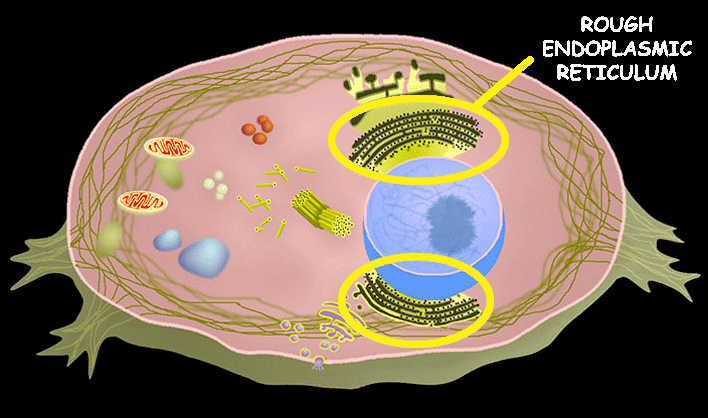
Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum
The main function of the rough endoplasmic reticulum (RER) is the synthesis, folding, modification, and transport of proteins

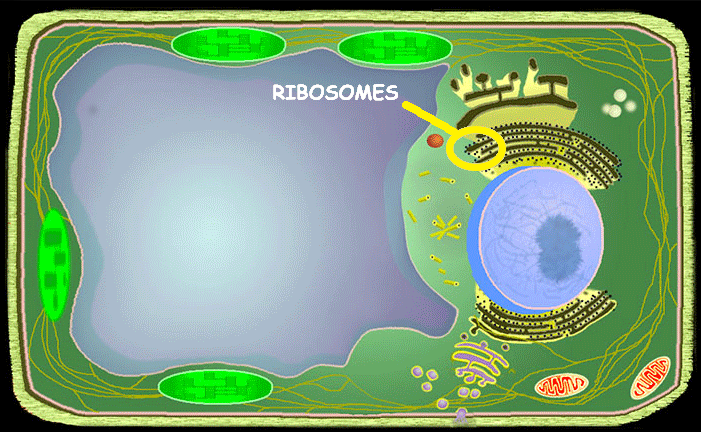
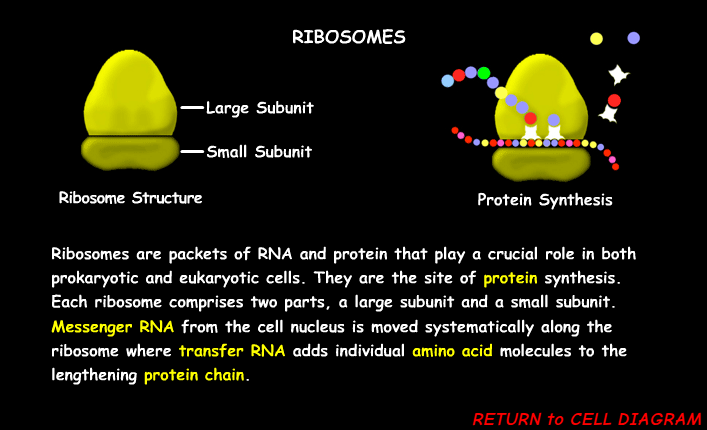
Ribosomes
A small particle in the cell that can make proteins. “Protein Synthesis”
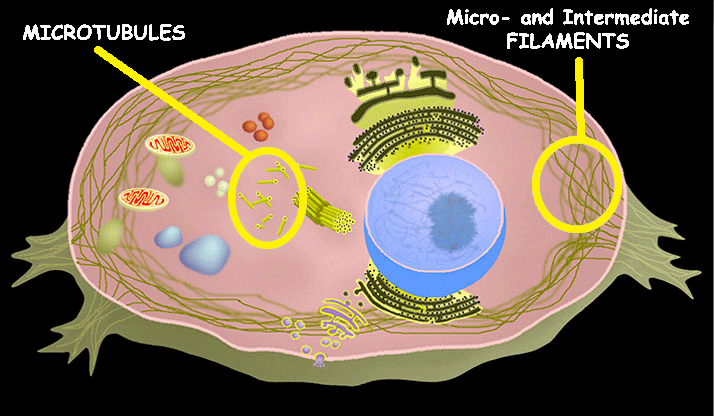
Cytoskeleton
The cytoskeleton is a network of protein filaments that provides structural support, helps cells maintain their shape, and enables cell movement

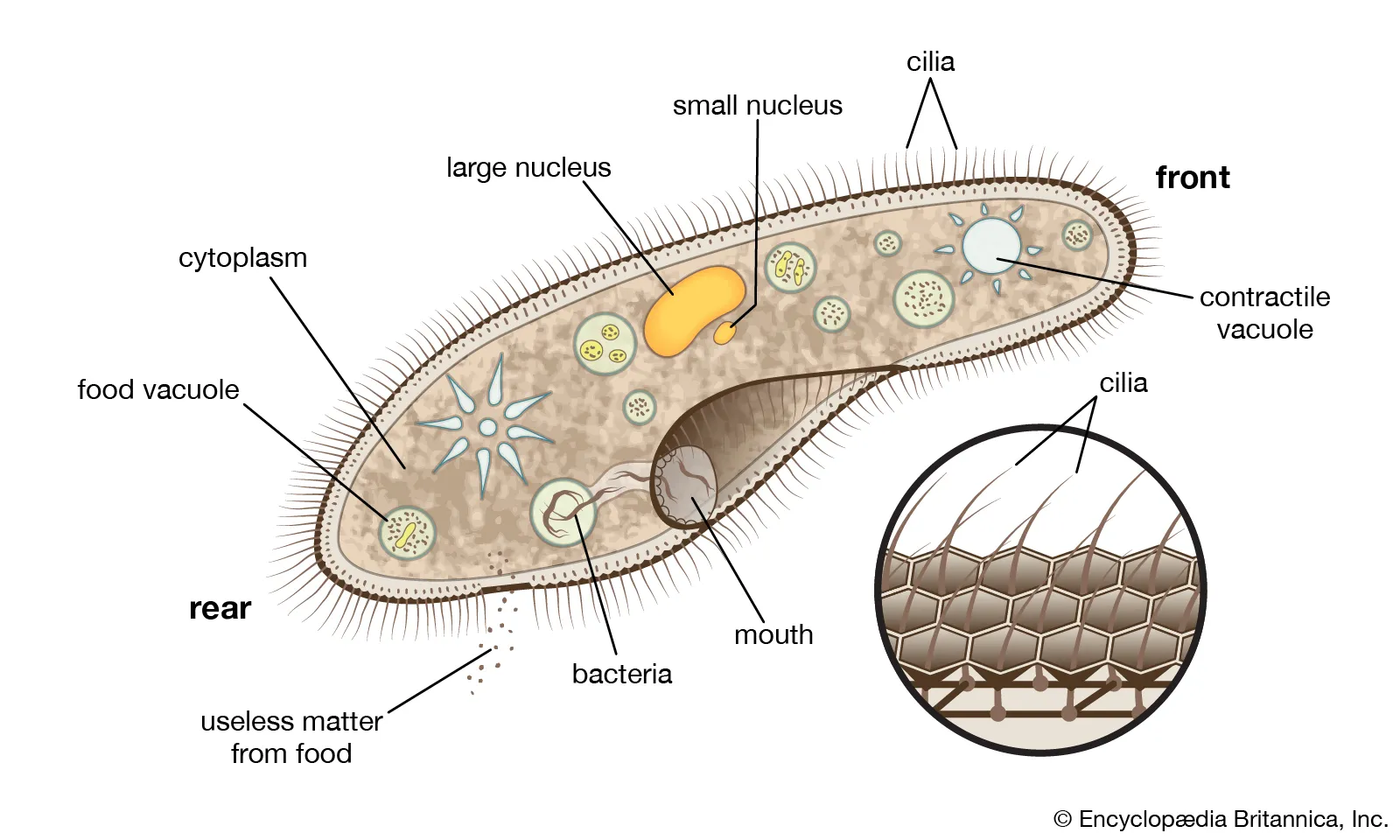
Cilia
Short Hairs used to move the cells
Passive Transport
The movement of molecules across the cell membrane without energy (ATP)
All move from a higher concentration, to a lower one.
Osmosis
The movement of water
Hypotonic
When H20 enters the cell, and it gets bigger
Hypertonic
When H20 leaves the cell, and it shrinks
Isotonic
When H20 enters and leaves the cells equally
Diffusion
Diffusion is any molecule (solute) moving from a high to low concentration.
Simple, and Facilitated diffusion both move the solute from high to low, but the latter needs help from specialized proteins.
ATP
Adensosine Triphosphate
Active Transport
Moves molecules against the concentration gradient using ATP
List the 3 main types of Active Transport
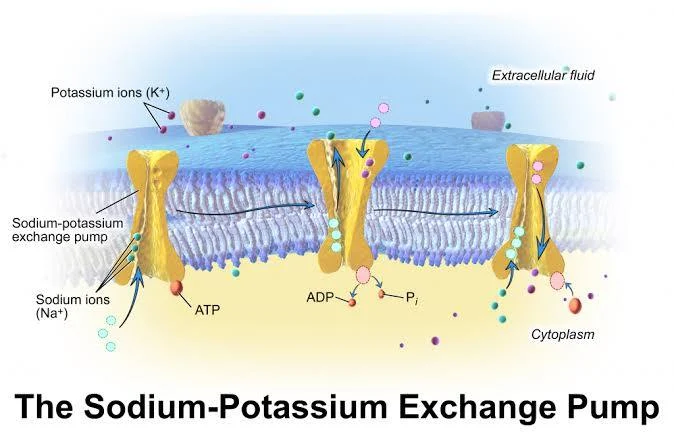
Membrane Pumps
Endocytosis (Phagocytosis; “Solids”, and Pinocytosis; “Liquids”)
Exocytosis
Membrane Pumps
Carrier Proteins that move substances form areas of low concentration to areas of high concentration
Ex: Sodium-Potassium Pump
Endocytosis (ENDO = Enter)
A process by which cells ingest fluid, macromolecules or other large particles
Phagocytosis involves the cell engulfing large, solid particles like bacteria, while pinocytosis is the process of a cell ingesting smaller particles and liquids, such as nutrients and ions
What is the first photosynthetic bacteria?
Cyanobacteria
Exocytosis (EXO = Exit)
A process by which a substance leaves a cell through a vesicle
Ex: Removing waste