biology 1500 exam 1 (chapter 1-4)
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/139
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
140 Terms
1
New cards
Is water polar or non-polar? Why?
polar; it has an unequal sharing of electrons which creates an unequal charge
2
New cards
What is a polar covalent bond?
A covalent bond in which electrons are not shared equally
3
New cards
What is a hydrogen bond?
A weak bond between a hydrogen atom with a partial positive charge and another atom with a partial negative charge
4
New cards
What is electronegativity?
ability of an atom to attract electrons
5
New cards
What would be the effect on the properties of water if oxygen and hydrogen had the same electronegativity?
Water wouldn't be cohesive and wouldn't be able to bond with other water molecules. Other things wouldn't dissolve in water. Water would be a nonpolar molecule.
6
New cards
What are the four emergent properties of water?
cohesive behavior, ability to moderate temperature, expansion upon freezing, versatility as a solvent
7
New cards
What is cohesion?
Ability of water molecules to attract each other via hydrogen bonds
8
New cards
what is adhesion?
Ability of matter to stick to other substances
9
New cards
What is the result of cohesion?
high surface tension
10
New cards
T/F: cohesion doesn't contribute to the transport of nutrients and water in plants
False
11
New cards
How does water moderate air temperature
by absorbing heat from air that is warmer and releasing the stored heat to air that is cooler
12
New cards
Why is water an effective heat bank?
It can absorb/release a large amount of heat with only a slight change in its own temperature.
13
New cards
Kinetic energy
energy of motion
14
New cards
thermal energy
kinetic energy associated with the random movement of atoms or molecules; reflects the total amount of kinetic energy
15
New cards
Temperature
A measure of the average kinetic energy in matter
16
New cards
Does temperature depend on volume?
No. Thermal energy depends on volume
17
New cards
T/F: whenever two objects of different temperatures are brought together, thermal energy passes from cooler to warmer until the same temp.
False. Moves from warmer to colder
18
New cards
Heat
the transfer of thermal energy
19
New cards
Calorie
Amount of heat required to raise the temperature of 1 g of water by 1°C. Conversely, a calorie is also the amount of heat that 1 g of water releases when it cools by 1°C
20
New cards
kilocalorie
Amount of heat needed to raise the temperature of 1 kg of water by 1°C
21
New cards
specific heat
Measure of how well a substance resists changing its temperature when it absorbs or releases heat.
22
New cards
Why does water have a high specific heat?
Much of the added energy is required to break hydrogen bonds.
23
New cards
When water evaporates, what is broken?
Hydrogen bonds
24
New cards
heat of vaporization
the quantity of heat a liquid must absorb for 1 g of it to be converted from the liquid to the gaseous state
25
New cards
T or F: Heat is absorbed when hydrogen bonds break and heat is released when hydrogen bonds form
T
26
New cards
What causes ice to float?
hydrogen bonds make water less dense by making it more ordered
27
New cards
Why is floating ice important?
* otherwise, lakes would freeze solid
* no life would exist in some areas
* no life would exist in some areas
28
New cards
Solvent
A liquid substance capable of dissolving other substances
29
New cards
Solute
Substance being dissolved
30
New cards
aqueous solution
a solution in which water is the solvent
31
New cards
Why is water a versatile solvent?
due to its polarity, which allows it to form hydrogen bonds easily
32
New cards
hydration shell
When each ion is completed surrounded by a sphere of water molecules
33
New cards
T or F: a compound needs to be ionic to dissolve in wate
F
34
New cards
Hydrophilic
\n water loving
35
New cards
Hydrophobic
Water fearing
36
New cards
hydrogen ion
When a hydrogen atom goes to another molecule and leaves its electron behind
37
New cards
hydroxide ion
A negatively charged ion made of oxygen and hydrogen.
38
New cards
Hydronium ion
hydrogen ion combines with a water molecule to form a hydronium ion, H3O(+)
39
New cards
Buffer
a substance that minimizes changes in pH in a solution
40
New cards
Stanely Miller experiment
* Abiotic synthesis of organic compounds happened near volcanoes
* created a fake system to represent the ocean, atmosphere, and rain water
* created a fake system to represent the ocean, atmosphere, and rain water
41
New cards
Stanley Miller experiment results
* A variety of organic molecules was found that were common in organisms and complex molecules like amino acids/hydrocarbons were also found
* molecules found were formaldehyde, hydrogen cyanide, amino acids and hydrocarbons
* molecules found were formaldehyde, hydrogen cyanide, amino acids and hydrocarbons
42
New cards
conclusion of stanley miller's experiment
Organic life may have been synthesize abiotically on early earth
43
New cards
How many valence electrons does carbon have?
4, meaning that it can form 4 bonds
44
New cards
What type of bond does carbon have with other elements?
Covalent bonds
45
New cards
Carbon chains form skeletons of organic molecules. How can the skeletons differ
vary in length and shape
46
New cards
What are the carbon skeletons?
Branched, rings, straight
47
New cards
Hydrocarbons
organic molecules consisting of only carbon and hydrogen
48
New cards
What are the major components of petroleum?
hydrocarbons
49
New cards
T or F: hydrocarbons are hydrophillic
F. They are hydroPHOBIC
50
New cards
do hydrocarbons release a lot of energy?
Yes. (Gasoline is made of hydrocarbons)
51
New cards
Isomer
compounds with the same chemical formula but different structures
52
New cards
isomer vs. isotope
* Isotope: the same element but it has a different amount of neutrons which change the atomic mass
* isomer: compounds that have the same elements present but have a different overall structure which changes the function of the molecule
* isomer: compounds that have the same elements present but have a different overall structure which changes the function of the molecule
53
New cards
What are the three types of isomers?
structural, cis-trans, enantiomers
54
New cards
structural isomer
differ in the covalent arrangements of their atoms. a molecule can be a straight chain and the same molecule could be branches
55
New cards
cis-trans isomers
have the same covalent bonds but differ in spatial arrangements around a double bond
56
New cards
Enantiometers
* Isomers that are mirror images of each other
* like your left hand and right hand
* like your left hand and right hand
57
New cards
What do the distinctive properties of an organic molecule depend on?
Arrangement of carbon skeletons AND the various chemical groups attached to the skeleton
58
New cards
Functional group
Components of carbon skeletons that are most commonly involved in chemical reactions
59
New cards
What are the seven functional groups?
* hydroxyl
* carbonyl
* carbonyl
* amino
* sulfhydral
* phosphate
* methyl
* carbonyl
* carbonyl
* amino
* sulfhydral
* phosphate
* methyl
60
New cards
Characteristics of hydroxyl group
* OH
* forms hydrogen bonds with water
* Compound name: Alcohol (Ethanol)
* Hydrophilic
* polar
* forms hydrogen bonds with water
* Compound name: Alcohol (Ethanol)
* Hydrophilic
* polar
61
New cards
Characteristics of Carbonyl group
* C=O
* sugars with ketone groups (ketoses) or aldehydes (aldoses)
* compound: ketones or aldehyde
* Hydrophilic
* polar
* sugars with ketone groups (ketoses) or aldehydes (aldoses)
* compound: ketones or aldehyde
* Hydrophilic
* polar
62
New cards
Characteristics of carboxyl group
* COOH
* acts like an acid
* Carboxylic acid or organic acid
* Hydrophilic
* polar
* acts like an acid
* Carboxylic acid or organic acid
* Hydrophilic
* polar
63
New cards
Characteristics of Amino group
* NH2
* Acts as a base
* Compound:Amine
* Hydrophilic
* (Half of it is an acid, the other side is a base)
* polar
* Acts as a base
* Compound:Amine
* Hydrophilic
* (Half of it is an acid, the other side is a base)
* polar
64
New cards
Characteristics of Sulfhydryl group
* SH
* can form a "cross-link" that stabilize protein structures
* compound: Thiol
* HYDROPHOBIC
* polar
* can form a "cross-link" that stabilize protein structures
* compound: Thiol
* HYDROPHOBIC
* polar
65
New cards
Characteristics of Phosphate group
* OPO3 (2-)
* contributes a negative charge
* when attached, gives the molecule the ability to react with water which releases energy
* Hydrophillic
* compound: organic phosphate \\n -polar
* contributes a negative charge
* when attached, gives the molecule the ability to react with water which releases energy
* Hydrophillic
* compound: organic phosphate \\n -polar
66
New cards
Characteristics of Methyl group
* -CH3
* affect the expression of genes
* affects the shape and function of sex hormones
* compound name: methylated compound
* nonpolar
* affect the expression of genes
* affects the shape and function of sex hormones
* compound name: methylated compound
* nonpolar
67
New cards
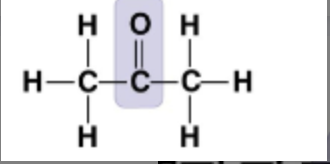
What molecule is this?
* Ketone/Acetone
* Carbonyl group
* Carbonyl group
68
New cards
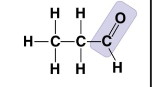
What molecule is this?
* Propanal (An Aldehyde)
* Carbonyl group
* Carbonyl group
69
New cards
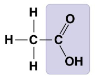
What molecule is this?
* Acetic Acid
* Carboxyl group
* Carboxyl group
70
New cards
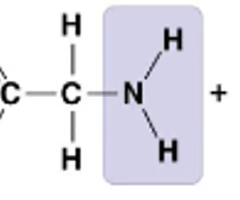
What molecule is this?
* Glycine
* Amino Acid
* Amino Acid
71
New cards
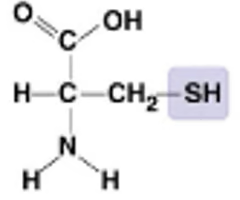
What molecule is this?
* Cysteine (Sulfhydral group)
72
New cards
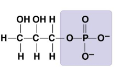
What molecule is this?
* Glycerol Phosphate
* Phosphate group
* Phosphate group
73
New cards
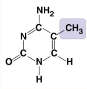
What molecule is this?
* 5-Methylcystosine
* Methyl group
* Methyl group
74
New cards
Estradiol and testosterone are similar in structure but differ in....??
The chemical groups that attach to the rings of the carbon skeleton
75
New cards
T or F: EVEN if two molecules have the same molecular make up, if they are shaped different, they have the same function.
F. They have different functions. A different shape means a different function.
76
New cards
What characteristics distinguish the living from the nonliving?
* Made up of cells (one or more)
* Needs energy
* Reproduction
* Growth and Development
* Contains DNA, proteins, carbohydrates and lipids
* Able to maintain homeostasis
* Responds to the environment
* Evolutionary adaptation
* Order or Organization
* Needs energy
* Reproduction
* Growth and Development
* Contains DNA, proteins, carbohydrates and lipids
* Able to maintain homeostasis
* Responds to the environment
* Evolutionary adaptation
* Order or Organization
77
New cards
List the levels of life's organizational hierarchy from smallest to largest, starting with atoms and ending with the biosphere.
Atoms (molecules), organelles, cells, tissue, organs, organ system, organism, population, community, ecosystem, biosphere
78
New cards
What are the roles of natural selection and mutations in evolution?
* individuals with inherited or advantageous traits are better suited for the environment and will survive and reproduce.
* Over time, a big portion of those individuals will have advantageous traits.
* Over time, a big portion of those individuals will have advantageous traits.
79
New cards
What are the goals of taxonomy?
The goals of taxonomy are to name species and classify them based on evolutionary relationships.
80
New cards
List and describe the four main groups of eukaryote.
* Plantae-of plants produce their own sugars and food molecules by photosynthesis.
* Fungi- absorb nutrients in dissolved form from surroundings
* Animalia-Animals obtain food by eating and digesting organisms.
* Protists- Protists are organisms that aren't any of the above (Plants, Fungi and Animalia.) \n \n
* Fungi- absorb nutrients in dissolved form from surroundings
* Animalia-Animals obtain food by eating and digesting organisms.
* Protists- Protists are organisms that aren't any of the above (Plants, Fungi and Animalia.) \n \n
81
New cards
What are the components of the scientific inquiry?
Making observations, forming hypotheses, experimentation, analysis of data and inductive reasoning.
82
New cards
What is the difference between a hypothesis and a theory?
* Hypothesis- Explanation based on observations, prior knowledge or assumptions, that can lead to a testable prediction.
* Theory- explanation that create new hypotheses but is supported by a large body of evidence. (assumed to be correct until further technology and knowledge proves it to be wrong).
* Theory- explanation that create new hypotheses but is supported by a large body of evidence. (assumed to be correct until further technology and knowledge proves it to be wrong).
83
New cards
Describe each of the five characteristics of life.
* Cells. (Basic unit of life)
* Obtain and use energy. (A living thing must be able to use energy to do work).
* Reproduction. (A living thing must be able to reproduce and create more of its species).
* Responds to the Environment. (A living thing must responds to the environment that it is in to survive and adapt)
* Adapts and evolves. (Animals are able to respond and change when the environment is changing to ensure better survival )
* Obtain and use energy. (A living thing must be able to use energy to do work).
* Reproduction. (A living thing must be able to reproduce and create more of its species).
* Responds to the Environment. (A living thing must responds to the environment that it is in to survive and adapt)
* Adapts and evolves. (Animals are able to respond and change when the environment is changing to ensure better survival )
84
New cards
Matter
Anything that has mass and takes up space
85
New cards
Element
A pure substance made of only one kind of atom
86
New cards
Compound
A substance made up of atoms of two or more different elements joined by chemical bonds
87
New cards
What four elements make up 96% of living matter?
carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen
88
New cards
What is the difference between essential elements and trace elements?
* Essential elements are elements that required for an organism to survive and live a healthy life
* Trace elements are only needed in small amounts
* Trace elements are only needed in small amounts
89
New cards
Neutron
A subatomic particle that has no charge and that is found in the nucleus of an atom
90
New cards
Proton
A subatomic particle that has a positive charge and that is found in the nucleus of an atom
91
New cards
Electron
A subatomic particle that has a negative charge
92
New cards
atomic number
the number of protons in the nucleus of an atom
93
New cards
atomic mass
mass of protons and neutrons in the element
94
New cards
Isotope
An atom with the same number of protons and a different number of neutrons from other atoms of the same element.
95
New cards
electron shell
An energy level representing the distance of an electron from the nucleus of an atom.
96
New cards
Energy
The ability to do work or cause change
97
New cards
What are radioactive isotopes? Give one medical application that uses them.
* Isotopes that are unstable because they constantly lose subatomic particles (decay) which gives off energy.
* We use radioactive isotopes when it comes to diagnostic tests (CT scans).
* We use radioactive isotopes when it comes to diagnostic tests (CT scans).
98
New cards
What subatomic particle is directly involved in chemical reactions between atoms?
Electrons
99
New cards
What is potential energy?
energy that is stored or position
100
New cards
What are valence electrons?
electrons in the outermost shell