Neuro-Cytology & Histology
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/147
Last updated 4:41 PM on 1/31/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
148 Terms
1
New cards
What are the cellular elements of the nervous system?
1. neurons
2. glia
2
New cards
Role of neurons
* building blocks of NS
* responsible for processing information by **electrical conduction and chemical transmission**
* responsible for processing information by **electrical conduction and chemical transmission**
3
New cards
How many neurons are estimated to be in the adult brain?
100 billion neurons
4
New cards
Describe the axons of the neurons
long
\
ie: motor neuron from cerebral cortex to sacral spinal cord can be **1m**
\
ie: motor neuron from cerebral cortex to sacral spinal cord can be **1m**
5
New cards
Role of glia
* glue
* **neuronal support**
* **neuronal support**
6
New cards
Are there more glia or neurons in the system?
outnumber neurons 1:10
7
New cards
How do neurons connect to each other?
Synapses
8
New cards
Parts of a basic neuron
1. dendrites
2. soma
3. axons
9
New cards
Describe how messages are communicated in neurons
1. dendrites **receive** signals
2. perikaryon **receives** signals
3. axons **transmits** signals
10
New cards
Synapse
the electrochemical communication site
11
New cards
In a synapse, what initiates the release of neurotransmitter?
electrical impulse
12
New cards
What organelles are found in the perikaryon?
* (1 or more) nucleolus
* ER
* ribosome
* golgi apparatus
* mitochondria
* lysosomes and vacuoles
* microtubules
* ER
* ribosome
* golgi apparatus
* mitochondria
* lysosomes and vacuoles
* microtubules
13
New cards
What is the function of the Nucleolus
* contains cell DNA
* involved with transcription of ribosomal RNA
* responsible for mitosis and cell growth
* synthesizes proteins, hormones, neurotransmitters
* involved with transcription of ribosomal RNA
* responsible for mitosis and cell growth
* synthesizes proteins, hormones, neurotransmitters
14
New cards
Functions of the endoplasmic reticuli?
Smooth ER:
* continuous with outer nuclear membrane
Rough ER:
* involved in water-soluble protein synthesis
* Nissl substance
* continuous with outer nuclear membrane
Rough ER:
* involved in water-soluble protein synthesis
* Nissl substance
15
New cards
Function of Ribosomal clumps
responsible for steroid metabolism, drug detoxification, carbohydrate metabolism
16
New cards
What color do the Nissl bodies stain?
^^Blue, due to RNA’s basophilic nature^^
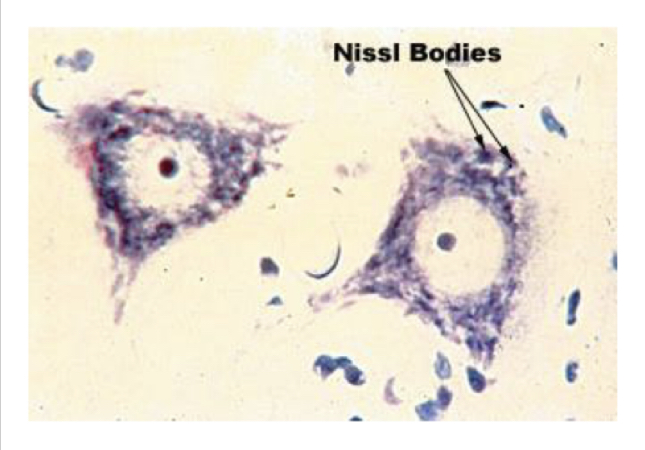
17
New cards
Where can you find Nissl bodies abundantly?
gonadal cells and liver
18
New cards
Function of Golgi apparatus
* process and package synthesized proteins
* neurotransmitters bud off from GA and are shipped to axon terminal
* neurotransmitters bud off from GA and are shipped to axon terminal
19
New cards
Function of mitochondria
provide energy for protein synthesis
20
New cards
Functions of lysosomes and vacuoles
hold whatever has been packaged
21
New cards
Function of microtubules
* anterograde transport
* retrograde transport
* retrograde transport
22
New cards
Anterograde transport
* transport the molecules produced in the **soma to the synapses**
* neurotransmitters via this transport
* neurotransmitters via this transport
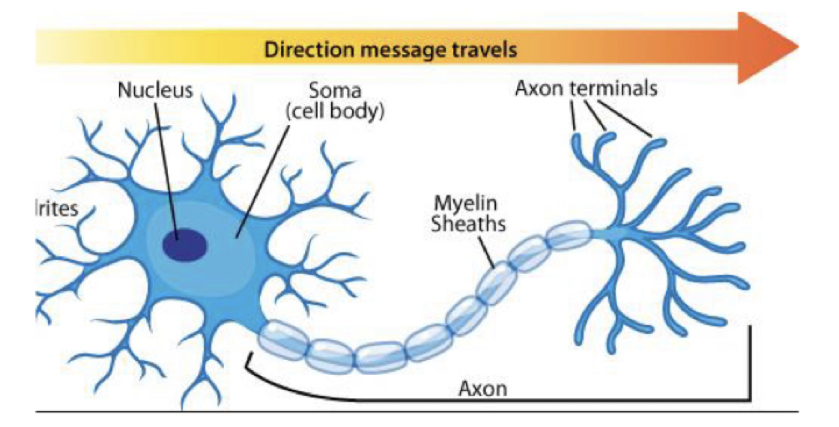
23
New cards
Retrograde transport
* transport the molecules from the **synapse to the soma**
* trophins, viral infections through this pathway
* trophins, viral infections through this pathway
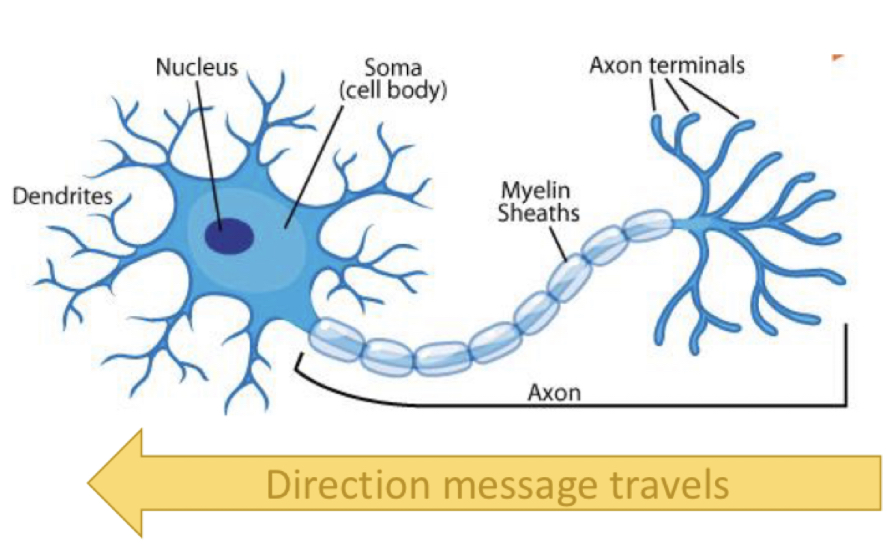
24
New cards
Example of infection that travels via retrograde transport
herpes virus
\
enters the soma after being transported from the dendrites, dormant on ganglionic neuron until activated
\
enters the soma after being transported from the dendrites, dormant on ganglionic neuron until activated
25
New cards
Capsid
icosahedral protein cage
26
New cards
Envelope
lipid bilayer
27
New cards
What does chickenpox reactivate into? Where does the dormant state hang out?
1. Shingles
2. Dorsal root ganglion
28
New cards
What is occurs during neurogensis?
1. nucleus disappears
2. reduction in active protein synthesis
29
New cards
Adult __ replenishes some cerebral cortical neurons
mitosis
30
New cards
What disorder is observed when neurogenesis does not occur?
dementia
31
New cards
What happens when neurons do not regenerate?
they are lost
32
New cards
Describe the neuronal membrane
Fluid phospholipid bilayer
* hydrophobic core
* hydrophilic inner and outer surfaces
* proteins can move within the plane of the membrane
* hydrophobic core
* hydrophilic inner and outer surfaces
* proteins can move within the plane of the membrane
33
New cards
What does protein synthesis in neuronal cells create?
* cytoplasmic protein
* membrane bound protein
* secretory protein
* membrane bound protein
* secretory protein
34
New cards
Transcription
35
New cards
Translation
36
New cards
Steps of Protein synthesis
1. ribosomes enter the cytoplasm
2. transcription
3. translation
37
New cards
Prion
protein infectious particle
38
New cards
What can happen when there is an error in protein synthesis?
* misfolding of the proteins
* introduces infection prions that cause neurodegenerative disease
* introduces infection prions that cause neurodegenerative disease
39
New cards
Creutzfeld-Jakob Disease
* AKA **spongiform encephalopathy**
* causes holes in the brain
* occurs in only humans
* causes holes in the brain
* occurs in only humans
40
New cards
What stain is used to visualize nerve tissue?
Silver nitrate stain
41
New cards
What type of stain is used to visualize neurons?
golgi stain

42
New cards
Function of sensory neurons
receive direct connections from sensory receptor cells (non-neuronal cells)
43
New cards
Function of motor neurons
end on muscles, glands for movements
44
New cards
Functions of interneurons
connect to a small area of the CNS
45
New cards
Functions of projection neurons
relay information to different areas through long axons
46
New cards
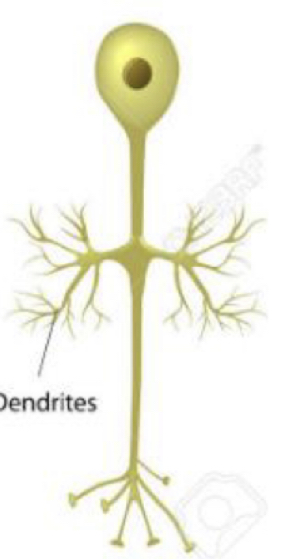
What type of neuron is this?
Unipolar
47
New cards

What type of neuron is this?
pseudo-unipolar neuron
48
New cards
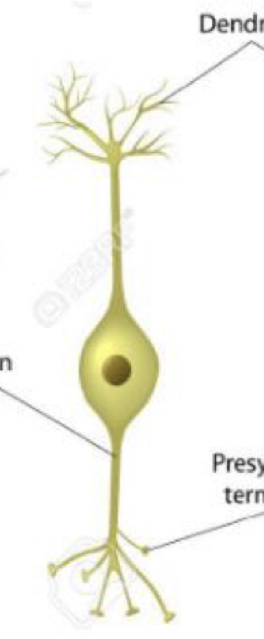
What type of neuron is this?
Bipolar neuron
49
New cards
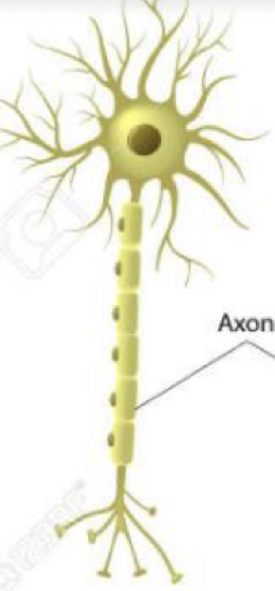
What type of neuron is this?
Multipolar
50
New cards
Axon hillock
* initial segment of the axon at the soma
* most electrically excitable part of the cell
* decision to propagate an action potential happens here
* all input (excitatory/inhibitory) is summed at the hillock
* most electrically excitable part of the cell
* decision to propagate an action potential happens here
* all input (excitatory/inhibitory) is summed at the hillock
51
New cards
Are RNA and Nissl bodies present on axons?
some RNA, but NO nissl
52
New cards
What increase the speed of signals on axons?
myelin
53
New cards
Axoplasm
cell cytoplasm found in an axon
54
New cards
Axonal transport
transport of mitochondria, lipids, synaptic vesicles through the cytoplasm of the axon
55
New cards
Anterograde axoplasmic transport
transport along the axon towards the presynaptic terminal
56
New cards
Retrograde axoplasmic transport
transport neurotrophic back to the soma
57
New cards
Examples of retrograde axoplasmic transport
1. damaged organelles and recycled plasma membrane
2. trophins
58
New cards
SLOW anterograde axoplasmic transport
1-10mm per day
59
New cards
FAST anterograde axoplasmic transport
50-400mm per day
60
New cards
what do we use to transport vesicles from the axon to the soma
dynein
61
New cards
What is an ocular example of interrupted axonal transport?
Swollen optic nerve, disc edema
\
disc margins blur, cup becomes smaller, disc appears elevated
\
disc margins blur, cup becomes smaller, disc appears elevated
62
New cards
Parts of a synapse
1. axon terminal of sending cell
2. synaptic cleft
3. dendrite of the receiving cell
63
New cards
Axosomatic synapse
axon to cell body
\
NOT common in the CNS
\
NOT common in the CNS
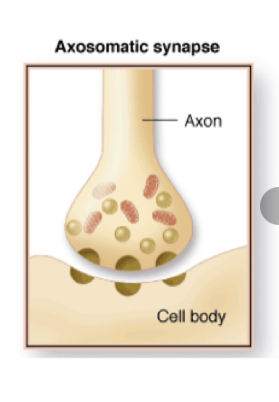
64
New cards
Axodendritic synapse
axon to dendrite
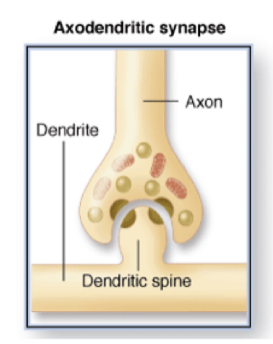
65
New cards
Axoaxonic synapse
axon to axon
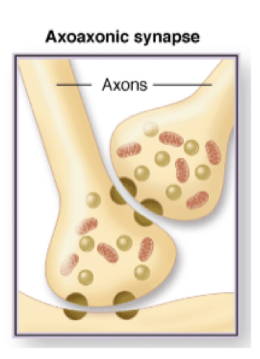
66
New cards
What is special about axodendritic synapses
dendritic tree generates action potential, important for temporo-spatial summation of a signal
67
New cards
What is special about a axoaxonic synapse
cause powerful effects
68
New cards
Temporo-spatial summation
convergence of signal in time and space
69
New cards
Simple and facilitated diffusion
maintain Na+ and K+ gradients
70
New cards
leak channels
channels open during resting potential
71
New cards
resting potential range
\-30mV to -90mV
72
New cards
What ion has a higher concentration inside the cell at equilibrium?
K+
73
New cards
What ion concentration is at a higher concentration outside the cell at equilibrium?
Na+ and Cl-
74
New cards
At rest, what is the extracellular charge? What is the intracellular charge?
1. positive
2. negative
75
New cards
equilibrium potential
stable concentration gradient across the membrane
76
New cards
is the resting membrane polarized? why?
yes, because of the ionic concentration gradient
77
New cards
Depolarized
more positive membrane potential, more Na+ inside
78
New cards
Hyperpolarized
more negative membrane potential, more K+ outside
79
New cards
What are the different ion-specific channels in the neuronal membrane
1. leak
2. mechanical distortion channels
3. protein ligand gated channels
4. voltage gated channels
5. phosphorylation gated channels
80
New cards
Mechanical distortion channels
found in skin, stretches membrane of the sensory ending
81
New cards
protein ligand gated channels
* chemical messenger, neurotransmitter is the ligand
* activates G-protein
* releases a second messenger that augments ligand binding
* activates G-protein
* releases a second messenger that augments ligand binding
82
New cards
Voltage gated channels
open when membrane potential reaches its action potential of about -50 to -55mv
83
New cards
Phosphorylation gated channels
intracellular enzyme mediated
84
New cards
If more K+ channels are open
* K+ can cross membrane easier
* closer to the K+ equilibrium potential
* closer to the K+ equilibrium potential
85
New cards
If more Na+ channels open
* Na+ can cross membrane easier
* closer to the Na+ equilibrium potential
* closer to the Na+ equilibrium potential
86
New cards
What is important about *Na-K pump using ATP?*
controls osmolarity
\
without it, water would rush in and **lyse the cell**
\
without it, water would rush in and **lyse the cell**
87
New cards
Resting potential for glia is closer to what ion?
K+
88
New cards
Resting potential of neurons is what?
more positive that K+
89
New cards
What happens if there is a malfunction in the **second messenger ligand system**?
* depression
* migraine
* diabetes
* osteoporosis
* migraine
* diabetes
* osteoporosis
90
New cards
absolute refractory period
occurs after depolarization, when summation does not occur
91
New cards
depolarization produces an __ __ spike
action potential
92
New cards
Saltatory conduction
myelinated nerves allow for current to jump from a **node of ranvier** to another, allowing for faster conduction velocity
93
New cards
What ion channels are found densely on Nodes of Ranvier?
Na+ channels
94
New cards
dendritic spines
extensions of dendrites that sometimes act as preferred sites for some types of synapses
95
New cards
macroglia
astrocytes and oligodendrocytes
96
New cards
What embryonic tissue are macroglia derived from?
neuro-ectoderm
97
New cards
What are the different types of astrocytes and where are they found?
1. fibrous - white matter
2. protoplasmic - gray matter
3. mueller cells - retina
98
New cards
What are the functions of astrocytes?
* structural support to developing neurons
* metabolic support/homeostasis
* recycle excess glutamate
* blood brain barrier
* tripartite synapse
* metabolic support/homeostasis
* recycle excess glutamate
* blood brain barrier
* tripartite synapse
99
New cards
How do astrocytes help with the blood-brain barrier
* astrocytes feet form a barrier
* separates neutrophil and blood
* separates neutrophil and blood
100
New cards
How do astrocytes form tripartite synapse
join additional neurons to modulate a signal