World War 2
4.0(1)
4.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/47
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
48 Terms
1
New cards
Adolf HItler
The dictator of Germany during world war 2

2
New cards
Benito Mussolini
The Dictator of Italy during world war 2

3
New cards
Winston Churchill
The Prime minister of Great Britain during world war 2

4
New cards
Joseph Stalin
The Dictator of the soviet union during world war 2

5
New cards
Non-Aggression Pact
Agreement between Germany and the USSR not to fight each other. They also agreed to divide Poland

6
New cards
Battle of Britain
The German air force launched an all-out air battle to destroy the British Royal Air Force

7
New cards
Great Depression
The economic crisis beginning with the stock market crash in 1929 and continuing through the 1930s

8
New cards
Pearl Harbor
Surprise attack by the Japanese on December 7, 1941 that resulted in the United States' entry into world war 2

9
New cards
Japanese Internment
In 1942 the U.S. Government removed more than 100,000 people of Japanese birth and ancestry from their homes on the pacific coast to relocation centers

10
New cards
Nazi
A German member of Adolf Hitler's political party

11
New cards
Holocaust
The Nazi campaign to exterminate the Jews during world war 2

12
New cards
Fascism
A political system headed by a dictator that calls for extreme nationalism and racism and no tolerance of opposition

13
New cards
Isolationism
A national policy of avoiding involvement in world affairs

14
New cards
Emperor Hirohito
The Emperor of Japan during WWII. His people viewed him as a god

15
New cards
Harry Truman
The 33rd President of the US. Led the U.S. to victory in WWII making the decision to use atomic weapons for the first time.

16
New cards
Allied Powers
Countries that worked together during WW2: Great Britain, US, France and Russia

17
New cards
Axis Powers
Alliance of Germany, Italy, and Japan during World War II.

18
New cards
Tojo Hideki
Military leader of Japan leading up to, and during World War II

19
New cards
WWII in Europe began with
Hitler's invasion of Poland in 1939
20
New cards
Cause of WWII
Treaty of Versailles leaving Germany angry and weak

21
New cards
Treaty of Versailles
Treaty that ended WWI. It blamed Germany for WWI and handed down harsh punishment.

22
New cards
Atomic Bomb
American scientists developed a bomb based on atomic energy, which was used against the Japanese cities of Hiroshima and Nagasaki.

23
New cards
Concentration Camps
Prison camps used under the rule of Hitler in Nazi Germany. Jewish people, were generally starved or worked to death, or killed immediately.

24
New cards
Battle of Stalingrad
Decisive battle in German invasion of Russia, the Germans were surrounded and systemically destroyed

25
New cards
Hiroshima
City in Japan, the first to be destroyed by an atomic bomb, in 1945

26
New cards
D-Day
Allied invasion of France on June 6, 1944

27
New cards
United Nations
An international organization formed after WWII to promote international peace.

28
New cards
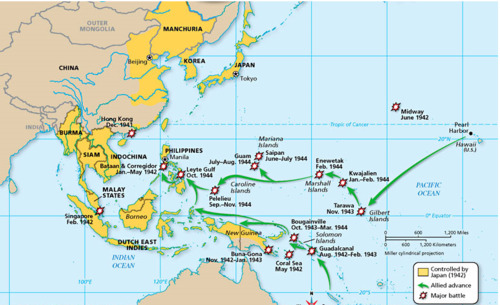
Island Hopping
A military strategy used during World War II that involved selectively attacking specific enemy-held islands and bypassing others
29
New cards
Charles de Gaulle
leader of the French government

30
New cards
FDR
the President of the US during WWII. He was the only president in U.S. history to be elected to four terms

31
New cards
D-Day
Allied invasion of France on June 6, 1944

32
New cards
Battle of the Bulge
A 1944-1945 battle in which Allied forces turned back the last major German offensive of World War II.

33
New cards
Battle of Midway
1942 World War II battle between the United States and Japan, a turning point in the war in the Pacific

34
New cards
Anti-Semitism
Hatred of Jews

35
New cards
Lend-Lease Act
The laws passed by the U.S. allowing us to give aid to Great Britain during WWII

36
New cards
Albert Einstein
escaped Germany and informed FDR about the Germans working on an Atomic Bomb, his scientific theories helped the Allies make the Atomic Bomb instead.

37
New cards
Manhattan Project
A secret U.S. project for the construction of the atomic bomb.

38
New cards
Battle of Moscow
The first Russian victory in World War II
39
New cards
Battle of Leningrad
city under attack for over 900 days; 3 million Soviets were blockaded in by Germany and over a million of them died.
40
New cards
Georgi Zhukov
Soviet general; led troops in keeping Moscow from falling to the Germans
41
New cards
Battle of the Atlantic
Germany's naval attempt to cut off British supply ships by using submarines called u-boats.
42
New cards
Neville Chamberlain
Great British prime minister who advocated peace and a policy of appeasement
43
New cards
Appeasement
A policy of giving things to an aggressor in the hopes of avoiding war.
44
New cards
Invasion of Manchuria
Japan took over in 1931. Invaded for resources
45
New cards
Rape of Nanking
In late 1937, Japan conquered the Chinese city of Nanking. Chinese civilians were brutalized and thousands were killed. The event shocked Western powers and contributed to sanctions against Japan.
46
New cards
Blitzkrieg
"Lighting war", typed of fast-moving warfare used by German forces against Poland in 1939
47
New cards
Dunkirk
port in France from which 300,000 Allied troops were evacuated when their retreat by land was cut off by the German advance in 1940
48
New cards
Rape of East Prussia
The destruction of the Easternmost province of Germany when the Russians arrived after years of war. Thousands of civilians were killed, raped or tortured.