1. biological molecules
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/101
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
102 Terms
1
New cards
4 common elements in biological molecules
carbon, hydrogen, nitrogen and oxygen
2
New cards
what are monomers usually based on
carbon
3
New cards
in hydrogen bonding what part of the water molecule has a negative charge
oxygen
4
New cards
what does a condensation reaction produce
water
5
New cards
what reaction must occur in order to form a monomer from a polymer
condensation
6
New cards
What are monosaccharides known as
simple sugars
7
New cards
general formula of monosaccharides
(CH20)n
8
New cards
glucose formula
C6H12O6
9
New cards
Two types of glucose
alpha and beta
10
New cards
what do alpha glucose molecules combine to form
starch and glycogen
11
New cards
what do beta glucose molecules combine to form
celloluse
12
New cards
3 reducing sugars
glucose, galactose and fructose
13
New cards
2, 5 carbon hexoses
fructose and galactose
14
New cards
6 carbon pentose
deoxyribose
15
New cards
what do 2 monosaccharides combine to form
disaccharide
16
New cards
what bond links the 2 subunits between sugars
glycosidic bonds
17
New cards
glucose + glucose forms
maltose
18
New cards
glucose + galactose forms
lactose
19
New cards
glucose + fructose forms
sucrose
20
New cards
long chains of monosaccharides form
polysaccharides
21
New cards
is starch insoluble or soluble?
insoluble
22
New cards
what is starch a mixture of?
amylose and amylopectin
23
New cards
why is the digestion of amylopectin quicker than amylose
have more intramolecular hydrogen bonds, more branches which can be broken
24
New cards
where is cellulose found
only plants
25
New cards
test for reducing sugars and non reducing sugars
benedicts test
26
New cards
What does Benedict's solution reduce
copper II ions to copper I ions
27
New cards
3 ways cellulose gives strength
long unbranched chains, which run parallel to one another and form hydrogen bonds between them
28
New cards
what do the cellulose molecules group to form
microfibrils
29
New cards
how many carbon atoms does a fructose molecule have
6
30
New cards
what are cellulose molecules made by
condensation reactions
31
New cards
What are triglycerides formed by
condensation reactions
32
New cards
What is a tryglyceride composed of?
1 glycerol and 3 fatty acids
33
New cards
what are lipids used as
insulation and as an energy store
34
New cards
what do lipids contain
carbon, hydrogen, oxygen
35
New cards
what are lipids soluble in
organic solvents ie alcohol and acetone
36
New cards
2 main groups of lipids
triglycerides and phospholipids
37
New cards
what low ratio do triglycerides have
low mass to energy ratio
38
New cards
what do triglycerides produce when oxidised
water
39
New cards
What makes triglycerides insoluble in water?
hydrophobic tails
40
New cards
what makes a fatty acid unsaturated
double bond between two carbon atoms
41
New cards
a long chain of of carbon atoms in a fatty acid means that it is
hydrophobic
42
New cards
phospholipid is made up of
2 fatty acids and a glycerol
43
New cards
phosphate group is (to do with water)
hydrophilic
44
New cards
test for lipids
Emulsion test - ethanol and water shaken
45
New cards
what are the C=O bonds
ester bonds
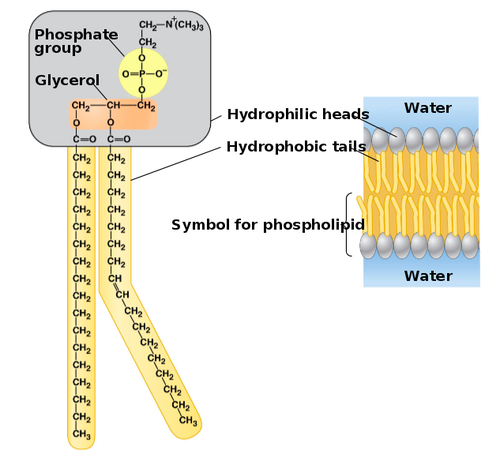
46
New cards
what is the cell wall made of
murin
47
New cards
what does hydrolysis of a lipid produce
fatty acids
48
New cards
what do proteins function as
enzymes, hormones and oxygen transporters
49
New cards
what do proteins form to make
skin, hair, feathers and nails
50
New cards
How many naturally occurring amino acids are there?
20
51
New cards
2 amino acids form to make
a dipeptide
52
New cards
what bond does the formation of a dipeptide produce
peptide bond
53
New cards
what shape do individual amino acids show
tetrahedral
54
New cards
what is the name of the simplest amino acid
glycine
55
New cards
what is the r-Group for the simplest amino acid
hydrogen atom
56
New cards
the 2 sulfur containing amino acids
cysteine and methionine
57
New cards
what bonds hold amino acids together
peptide bonds
58
New cards
What is the primary structure of a protein?
the number, type and sequence of amino acids
59
New cards
what does the primary structure determine
the proteins function in the end
60
New cards
the three parts of the generalised structure of amino acids
amino group(basic), r- group, carboxyl group (acidic)
61
New cards
how is the secondary structure of a protein formed
weak negatively charged nitrogen and oxygen atoms interact with the weak positively charged hydrogen atoms, forming hydrogen bonds
62
New cards
whats released in a condensation reaction
water
63
New cards
what should you look for when identifying a peptide bond
where nitrogen is bonded to a carbon which as a double bond with oxygen
64
New cards
two structure of secondary proteins
alpha helix and beta pleated sheets
65
New cards
why are beta pleated sheets formed
the protein folds so that two parts of the polypeptide chain are parallel to each other, enabling hydrogen bonds to form between them
66
New cards
why does the alpha helix form
the amino acid chain coils into a right- handed helix and hydrogen bonds form between between the oxygen and hydrogen atoms that have been brought together
67
New cards
how is the tertiary structure formed
after secondary structures have formed, the molecule bends and folds into a 3-D globular shape
68
New cards
all globular proteins display what type of structure
tertiary
69
New cards
give an example of a globular protein and where its found
myoglobin, found in muscle cells
70
New cards
what are the hydrogen bonds between in tertiary structures
the r groups
71
New cards
what are the hydrogen bonds between in secondary structures
amino and carboxyl groups
72
New cards
What is tertiary structure?
3d folding of polypeptide chain due to hydrogen and disulphide bonds
73
New cards
way's starch has adapted for its function in plant cells
insoluble - doesn't affect water potential
74
New cards
what is quaternary structure
two or more polypeptide chains
75
New cards
what reaction forms proteins
condensation
76
New cards
2 examples of quaternary proteins
haemoglobin and collagen
77
New cards
what does every amino acid possess
an amino end and a carboxyl acid end
78
New cards
what stabilises the secondary structure of proteins
hydrogen bonds
79
New cards
what do the pockets formed by tertiary structure hold
substrates
80
New cards
what's the name of the pockets formed by tertiary structure
active sites
81
New cards
what is cellular metabolism
the sum of all the reactions carried out out by cells
82
New cards
2 types of metabolic reactions
catabolic and anabolic
83
New cards
catabolic reaction
substance breakdown and release energy
84
New cards
anabolic reaction
chemical reactions take in energy to synthesise complex molecules from simple molecules
85
New cards
what are catabolic reactions in terms of energy
exergonic - give out energy
86
New cards
what are anabolic reaction in terms of energy
endergonic - take in energy
87
New cards
induced fit model
when the substrate enters the active site it induces a change in the shape of the enzyme - enables an enzyme - substrate complex
88
New cards
name of a protein that contains a non amino part
conjugate protein
89
New cards
name of the non amino group on the protein
prosthetic group
90
New cards
intracellular enzymes
produced and function inside the cell
91
New cards
extracellular enzymes
secreted by cells and catalyse reactions outside cells
92
New cards
example of catabolic reactions
cellular respiration and hydrolysis
93
New cards
examples of anabolic reactions
protein synthesis and photosynthesis
94
New cards
what type of proteins are enzymes
globular
95
New cards
why does a lower temperature slow the rate of reactions
less successful collisions between substrate and active site, collide with less energy
96
New cards
equation for pH
-log10(H)
97
New cards
what do competitive inhibitors bind to
the active site of the enzyme
98
New cards
what do non competitive inhibitors bind to
the enzyme at a position other than the active site
99
New cards
What are competitive inhibitors?
Molecules that bind to the active site of an enzyme and inhibit the ability of the substrate to bind.
100
New cards
What are non-competitive inhibitors?
bind to another part of an enzyme, causing the enzyme to change shape and making the active site less effective