part 1 - Comprehensive Overview of Labor and Delivery Pain Management in Obstetrics
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
42 Terms
normal contractions are
- coordinated
- involuntary
- intermittent
contraction cycle
- increment
- acme
- decrement
- interval
increment
increasing strength
acme
peak; greatest strength
decrement
decreasing strength
interval
elapsed time from beginning of one contraction until the beginning of the next contraction; minutes
cycle & pattern
- frequency
- duration
- intensity
frequency
beginning of 1 uterine contraction to beginning of the next
duration
beginning of a uterine contraction to the end of that same contraction
intensity
strength of contraction (mild, moderate, strong) & its assessed by palpation
uterine body
- upper 2/3 of uterus contracts actively to push fetus down
- lower 1/3 remains less active to promote downward passage of fetus
cervical changes
effacement & dilation
effacement
thinning & shortening of the cervix
dilation
opening of the cervix
components of birth process
- powers
- passage
- passenger
- psyche
powers
- uterine contractions
- maternal pushing efforts
passage
- consists of maternal bony pelvis & soft tissues
- pelvic brim divides bony pelvis into: false pelvis & true pelvis
true pelvis
- inlet (upper pelvic opening)
- midpelvis (pelvic cavity)
- outlet (lower pelvic opening)
passenger
- the fetus
- anatomic & positional variables influence labor
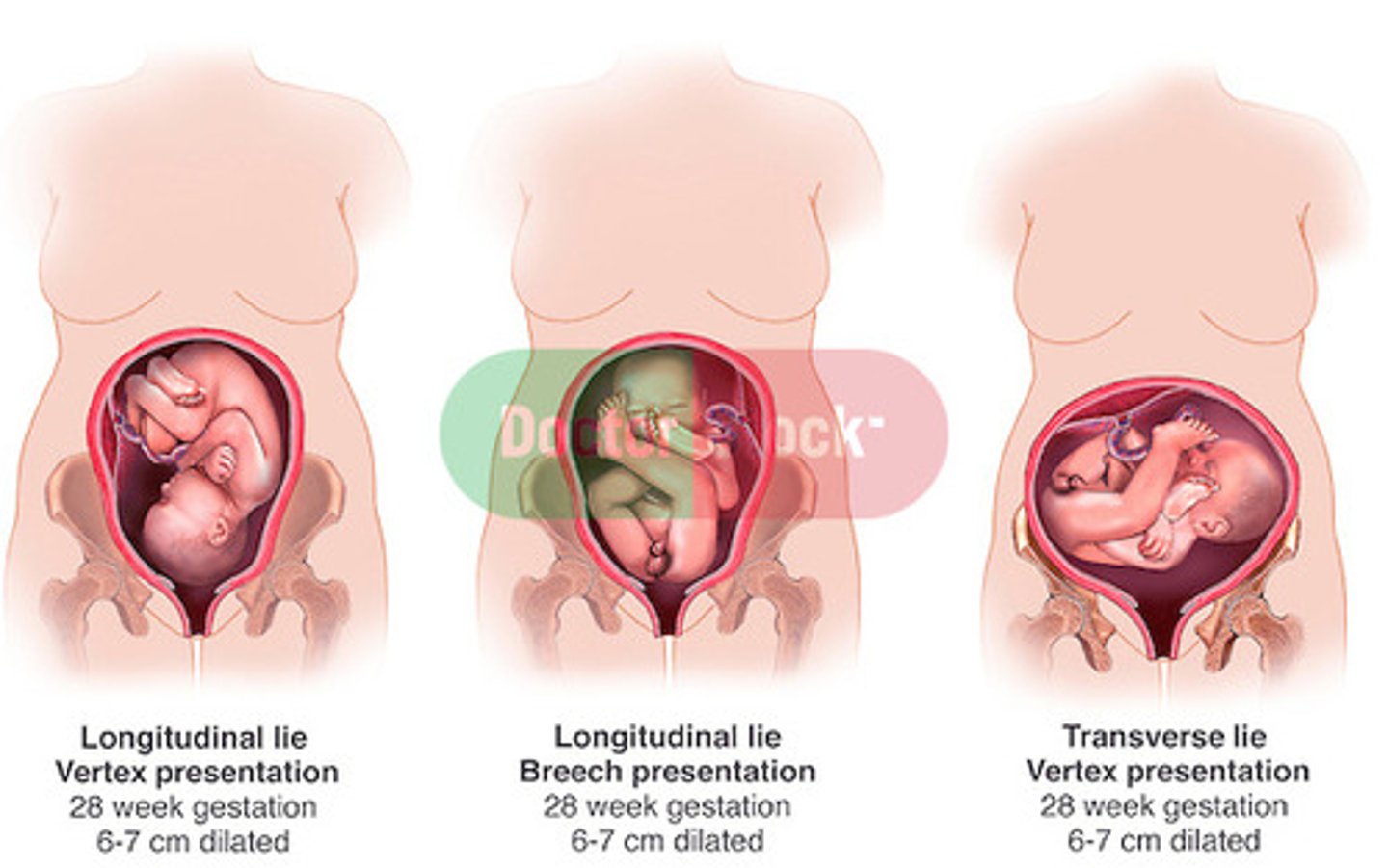
fetal lie
orientation of the long axis of the fetus to the long axis of the woman
- longitudinal
- transverse
- oblique
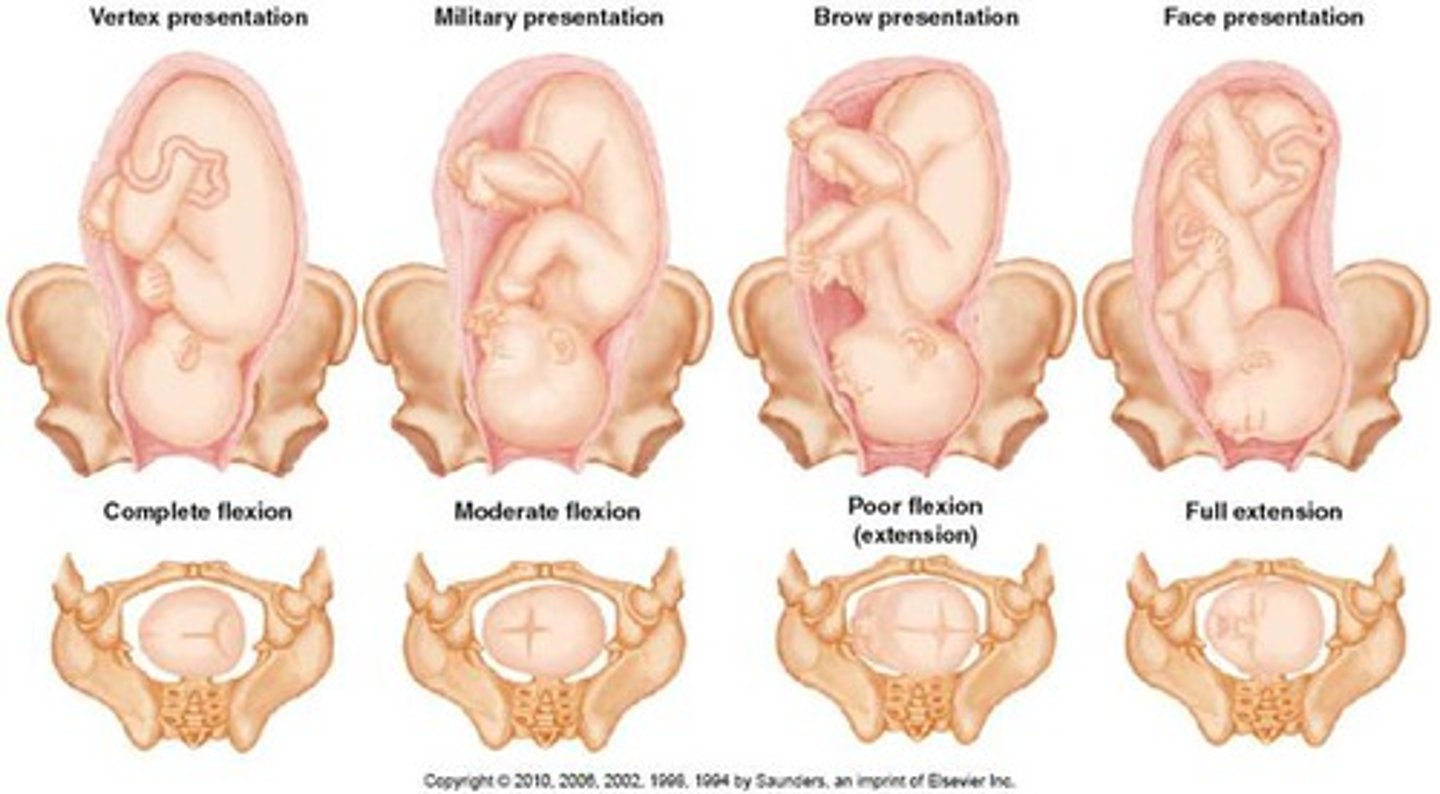
attitude
relation of fetal body parts to one another
- flexion
- extension
presentation
- cephalic
- breech
- shoulder
fetal part that enters the pelvis is termed the "presenting part"
fetal head
- bones
- sutures
- fontanels
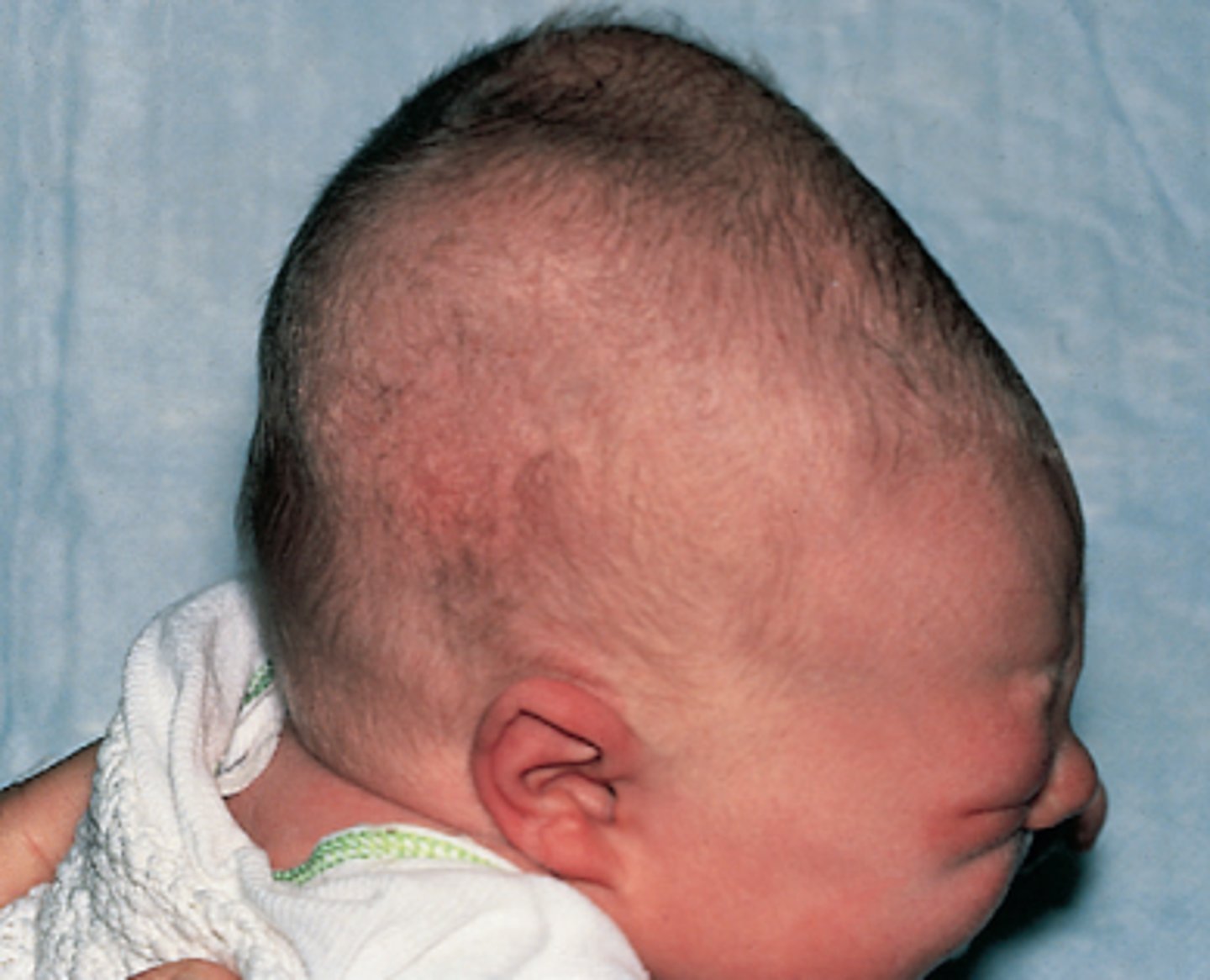
molding of the head
occurs with normal vaginal deliveries causing misshapen or elongated scalp
as uterus contracts
blood flow is diminished
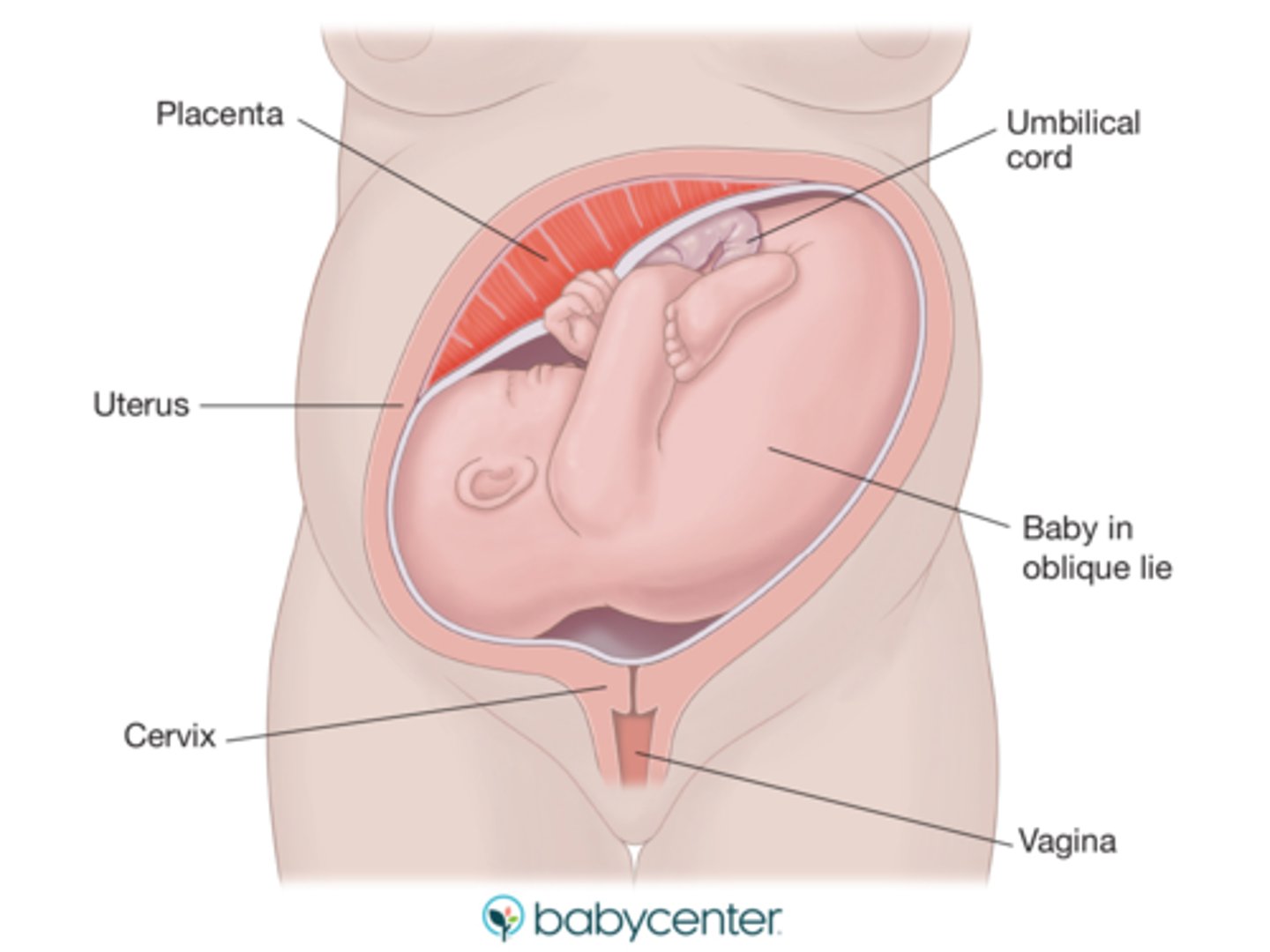
oblique lie
lying at an angle to the mother and converts to transverse or horizontal during labor
cephalic presentation
fetal head enters pelvis
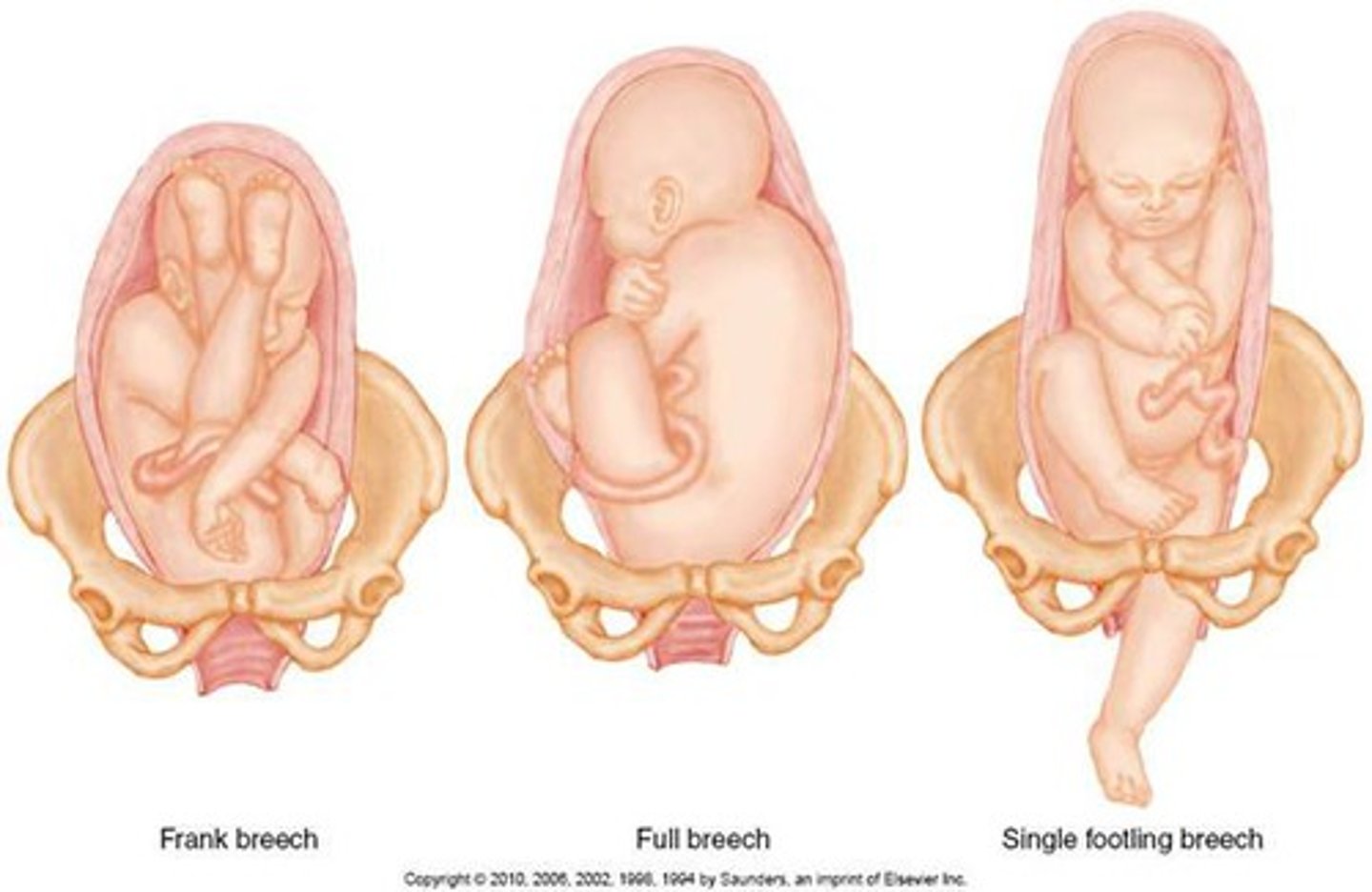
breech presentation
fetal buttocks or legs enter pelvis 1st
shoulder presentation
baby is in transverse or horizontal position at delivery, must be turned
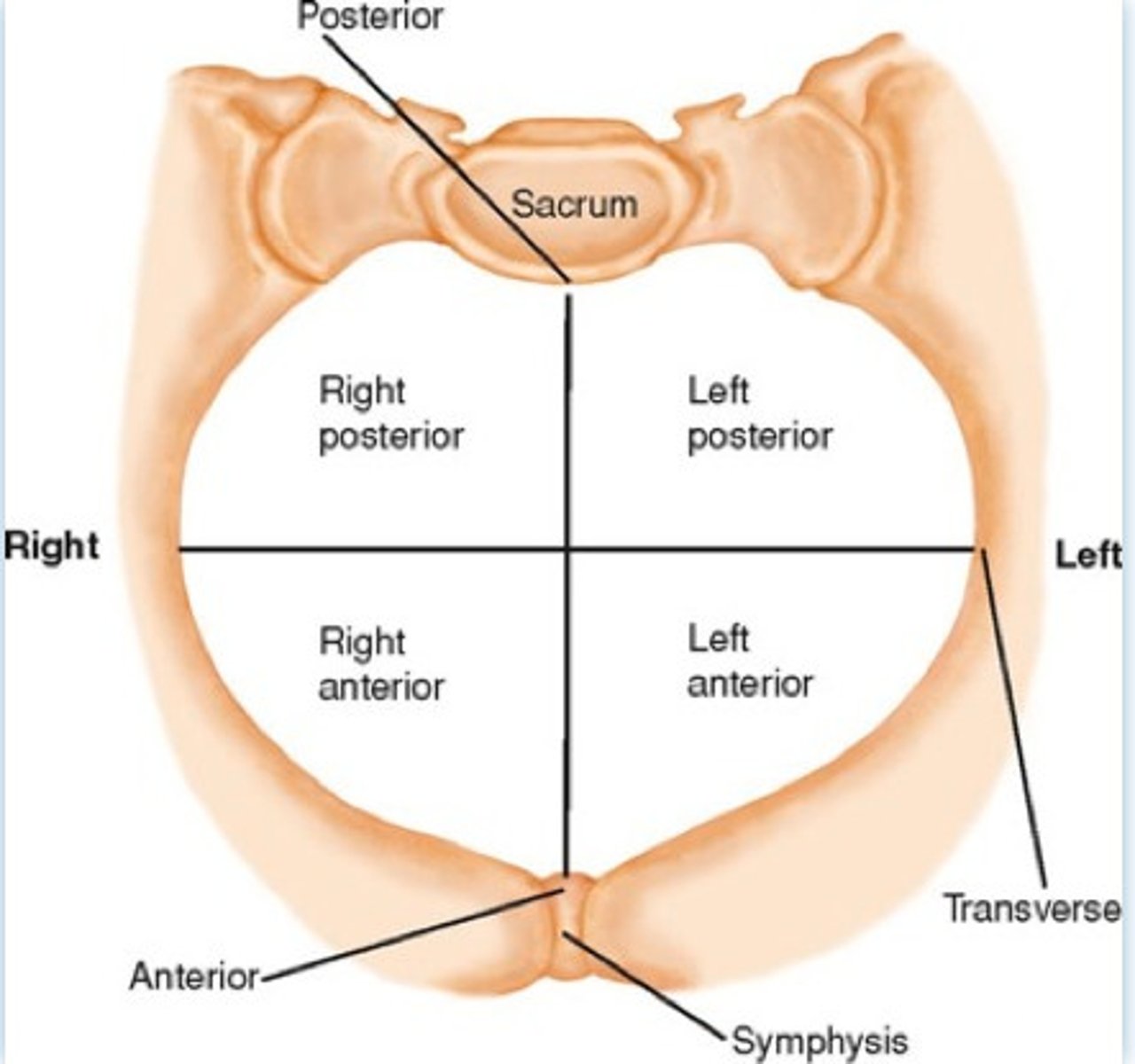
position
- describes location of a fixed reference pt on presenting part in relation to 4 quadrants of maternal pelvis
position abbreviations
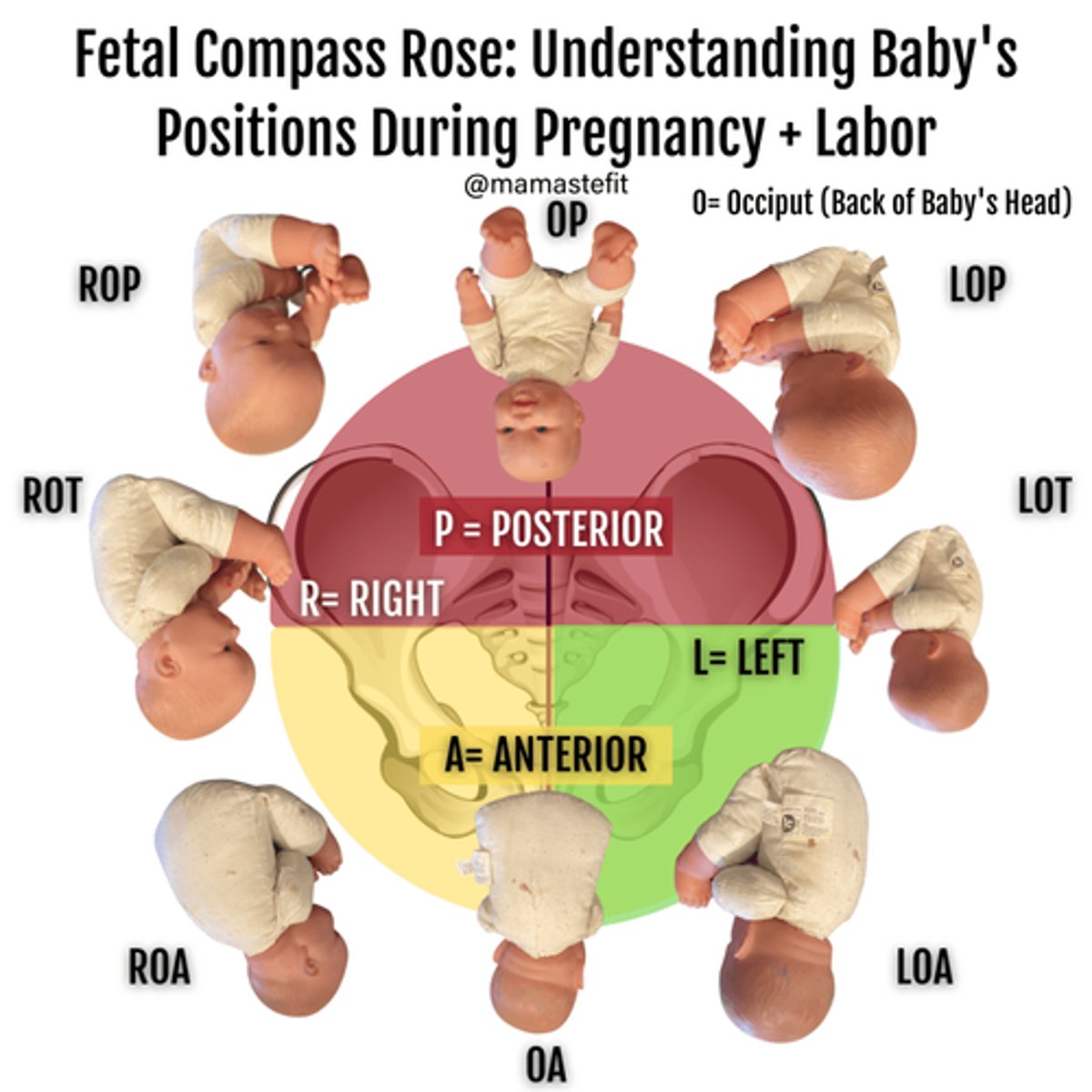
indicates relationship between the fetal presenting part & maternal pelvis
(i.e. ROA, LOA)
- 1st letter: Right (R) or Left (L)
- 2nd letter: Occiput (O), Mentum (M), Sacrum (S)
- 3rd letter: Anterior (A), Posterior (P), Transverse (T)
fetal compass rose
psyche
- anxiety
- culture & expectations
- birth as an experience
- support
psyche: anxiety
- catecholamines are released in response to anxiety & fear
- inhibits uterine contractions & blood flow to the placenta
psyche: culture
assess personal values & expectations
psyche: birth as an experience
physical & emotional experience that forever changes a woman & her family
psyche: support
continuous support has a positive effect on labor
true labor: contractions
- usually have a consistent pattern of increasing frequency, intensity, & duration
- contractions tend to increase with walking
- contractions typically begin in lower back & gradually sweep around to lower abdomen
true labor: discomfort
- may persist as back pain in some women
- discomfort often resembles menstrual cramps during early labor
true labor: cervix
- includes progressive effacement & dilation (most important characteristic)
false labor: contractions
- inconsistent in frequency, duration, & intensity
- contractions do not change or may decrease w/ activity
false labor: discomfort
- felt in the abdomen & groin
- discomfort may be more annoying than truly painful