Business Informatics I
1/173
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
174 Terms
Why is information an important ressource for organisations?
-Globalisation (management of a global market)
-Increasing importance of the information economy (knowledge and information-based market economies)
-Change in the organisational structures (decentralisation, less hierarchy, location independence, etc.)
-Emergence of the networked enterprise (Relationships with customers, suppliers and employees supported by electronic means of communication)
How can Information Technology (IT) be defined?
IT is the hardware and software a business uses to achieve its objectives.
How can Information Systems (IS) be defined?
ISs are the interrelated components that manage information to: Support decision-making and control, help with analysis, visualisation, and product creation.
Which six strategic business objectives do organisations try to achieve by investing in information systems?
-Operational Excellence: Achieve operational efficiency and thus increase profits.
-New products, services and business models: Information Systems enable firms to create new products, services and business models.
-Customer and supplier intimacy: Customers who are served well, become repeat customers who purchase more. Similarly, the more a business engages with suppliers, the more it can contribute to reduce costs.
-Improved decision making: Without accurate information, managers must use forecasts, best guesses, and luck, resulting in misallocation of resources, inventory, employees.
-Competitive Advantage: Achieving the previous business goals allows them to reach a competitive advantage, which means offering better products at lower prices.
-Survival: Businesses may need to invest in information systems out of necessity. It is simply the cost of doing business (e.g. Citibank's introduction of ATMs Federal and state regulations and reporting requirements).
What is data?
A stream of raw facts.
What is information?
Data shaped into meaningful, useful form.
What is feedback?
Feedback is the output returned to appropriate members of an organisation to help evaluate or correct input stage.
What is the difference between computers and information systems?
Computers and software are technical foundation and tools, similar to the material and tools used to build a house.
What are the three basic activities in an information system that provide information for organisations?
Input, Processing, and Output
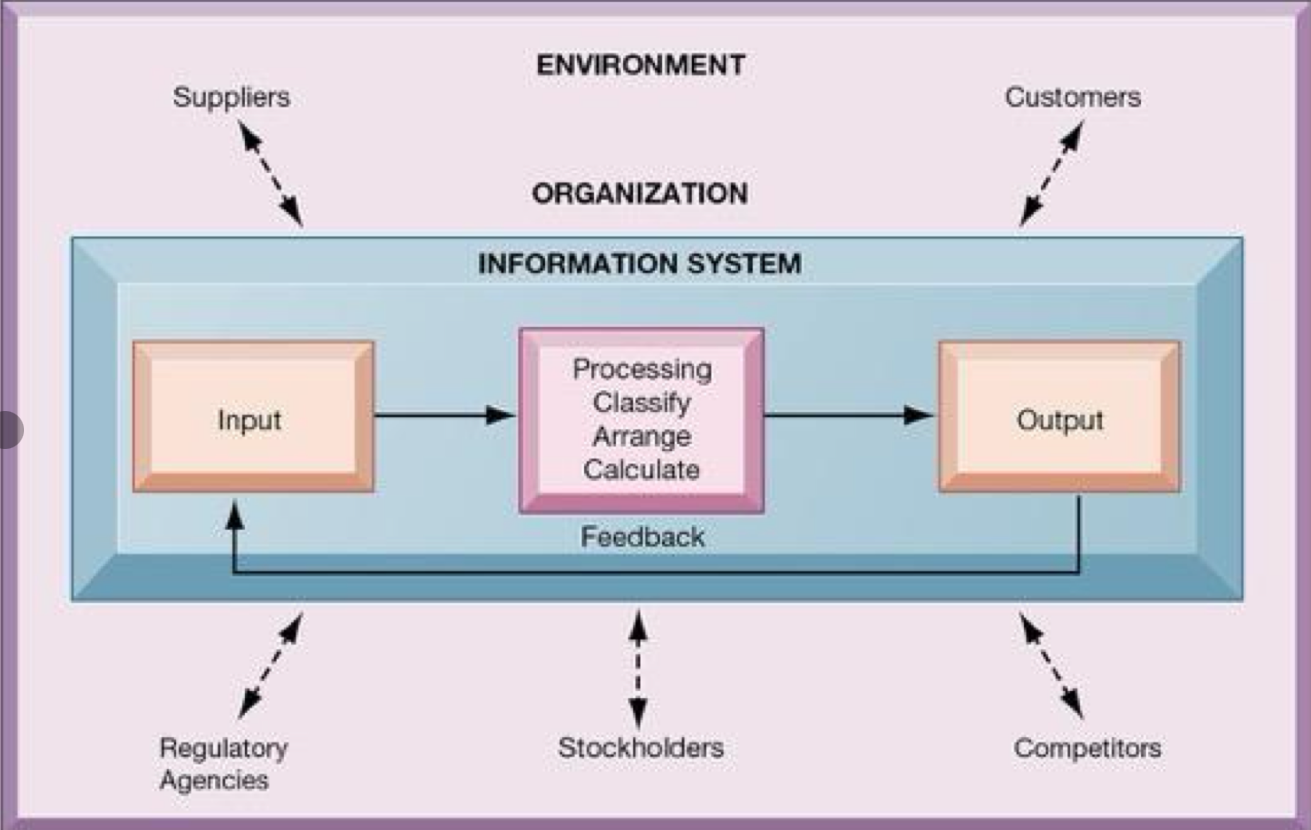
What are the three dimensions of information systems?
-Organisations
-Management
-Technology
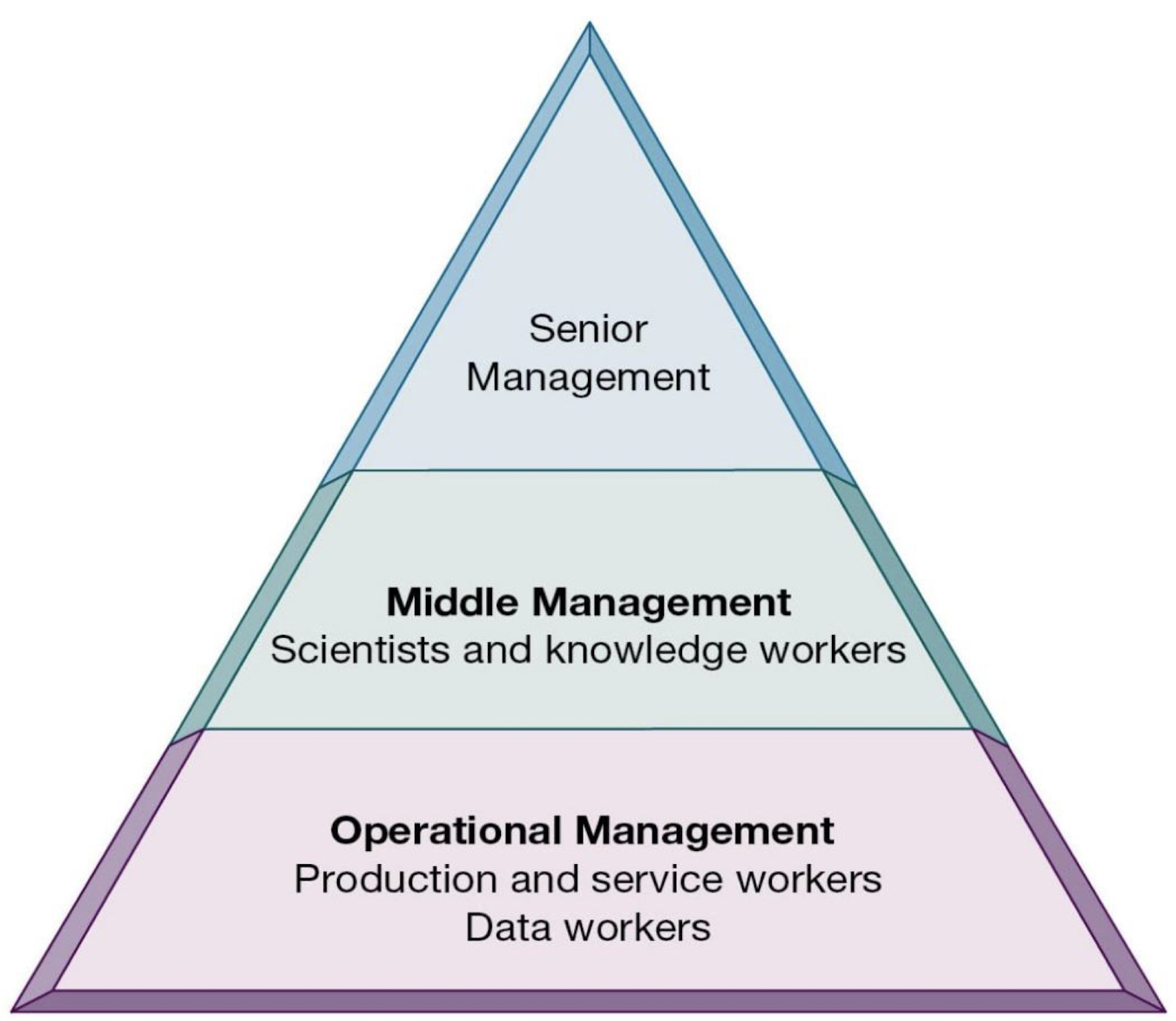
What does the hierarchy in a business organisation typically look like?
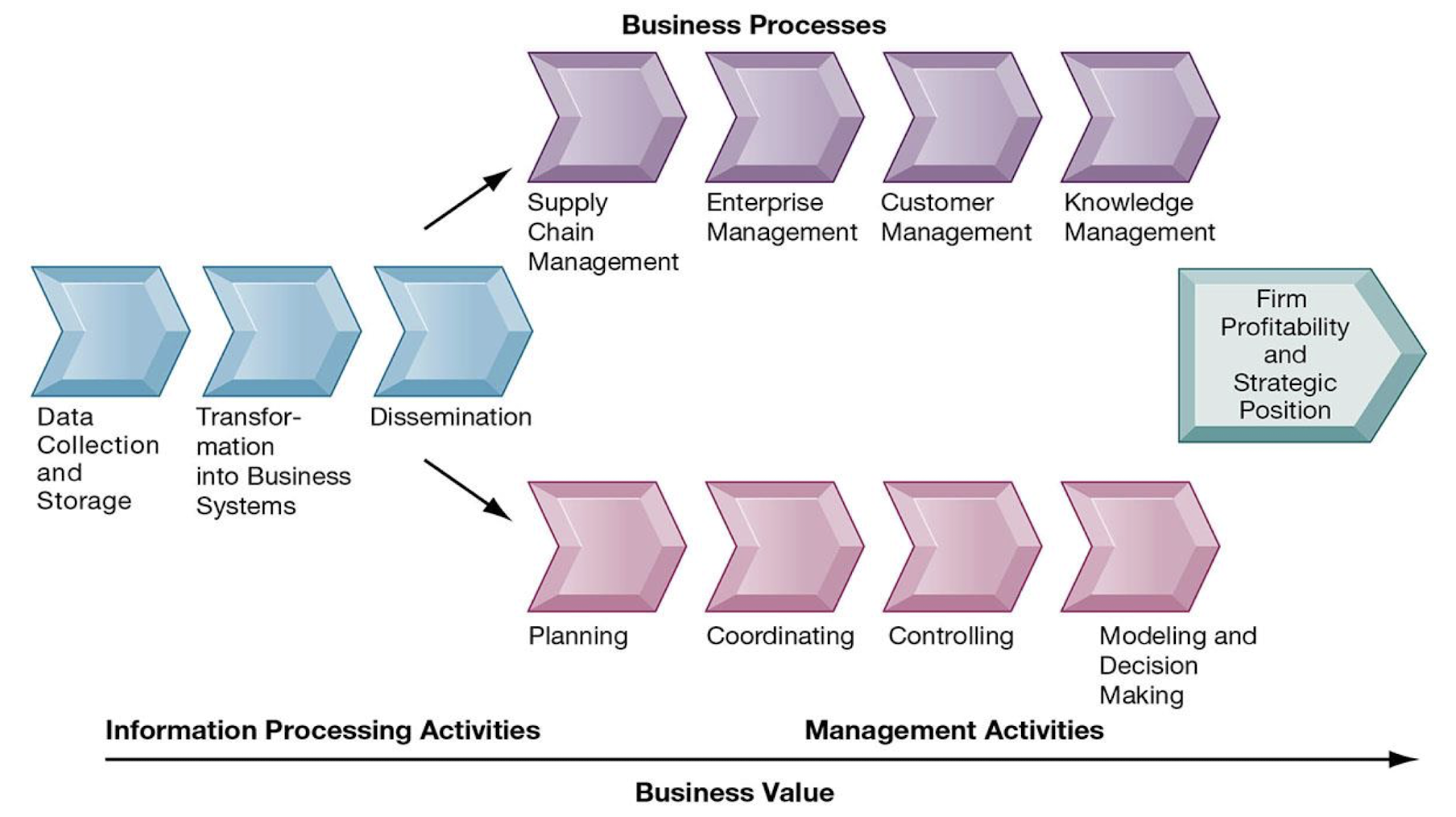
What is the business information value chain?
What is Business Informatics?

What is an organisation from a technical perspective?
An organisation is a stable, formal social structure that processes resources from the environment to produce outputs.
What are the key properties of an organisation from a technical perspective?
• More stable than an informal group: longevity and routineness
• Formal legal entity: internal rules and procedures that must follow the laws
• Social structure: collection of social elements
What are the 3 elements of an organisation from a technical perspective?
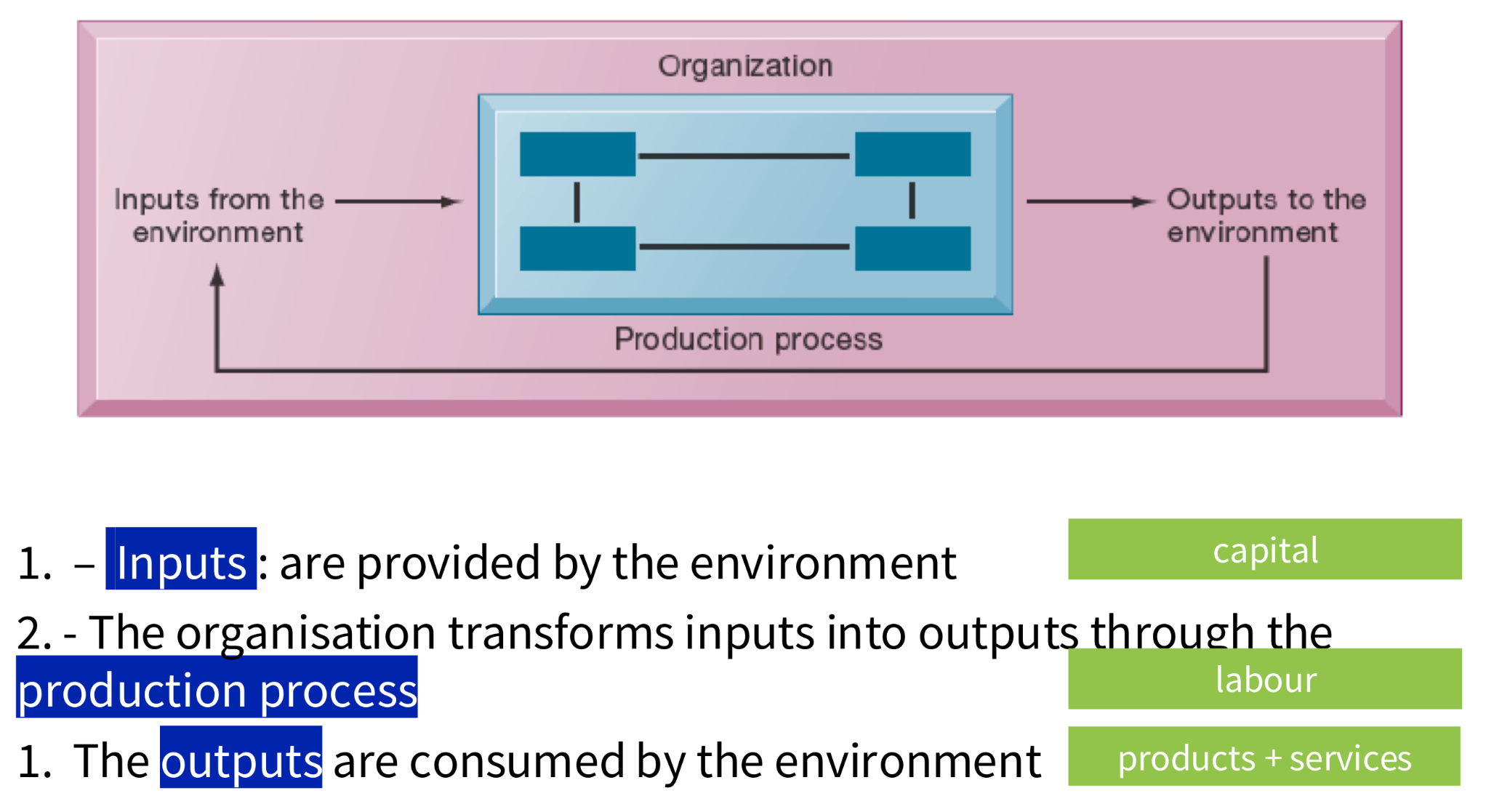
What is an organisation from a behavioural perspective?
An organisation is a collection of rights, privileges, obligations, responsibilities delicately balanced over a period of time through conflict and conflict resolution.
What are the 2 key properties of an organisation from a behavioural perspective?
• This definition emphasises group relationships, values, and structures.
• People working in organisations have arrangements and feelings which are not discussed in any formal rulebook
What is the behavioural view of an organisation?
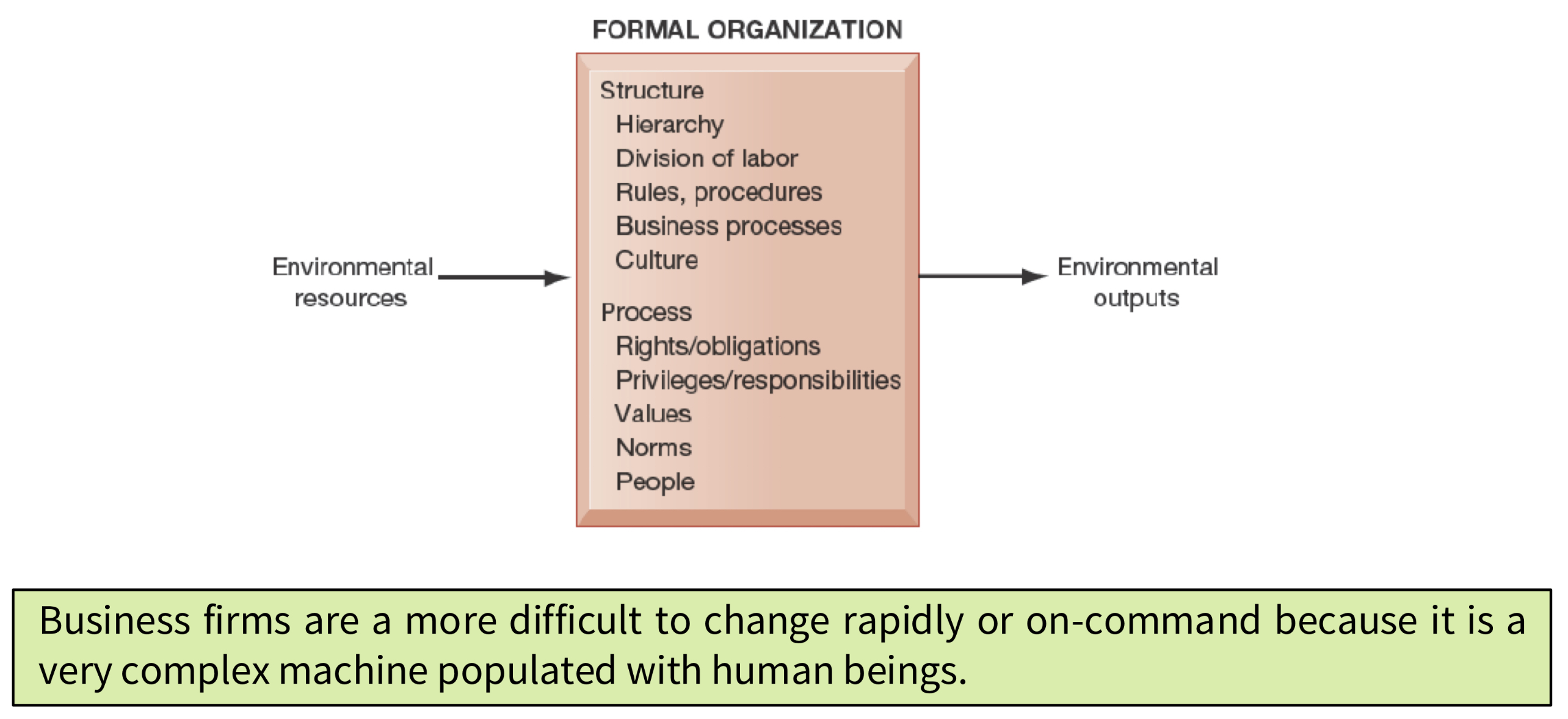
What is the difference between the technical and behavioural perspective of organisations?
The technical definition embeds organisations in a competitive market.
The behavioural definition focuses on individual firms and its inner working.
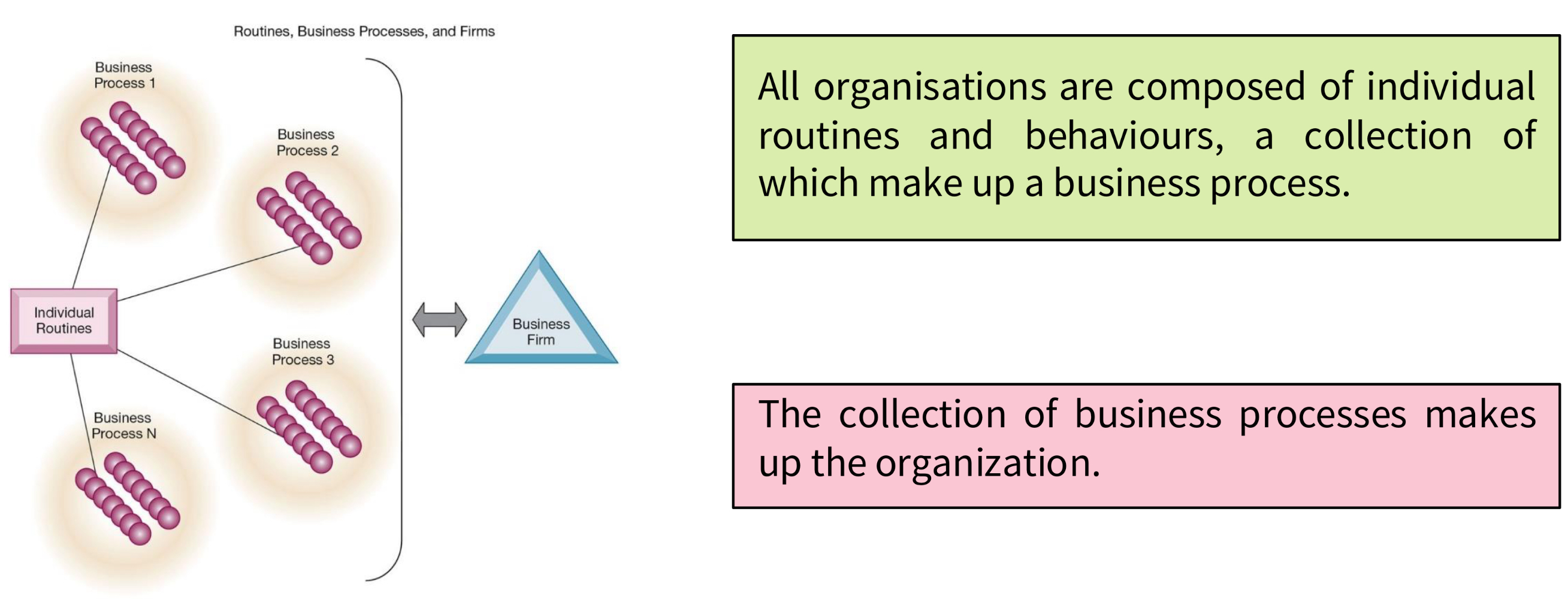
What are routines, business processes, and firms?
What is organisational culture?
Organisational culture are the “rules” taken for granted, rarely announced or discussed, which define how and where to produce, and who produces.
What are disruptive technologies?
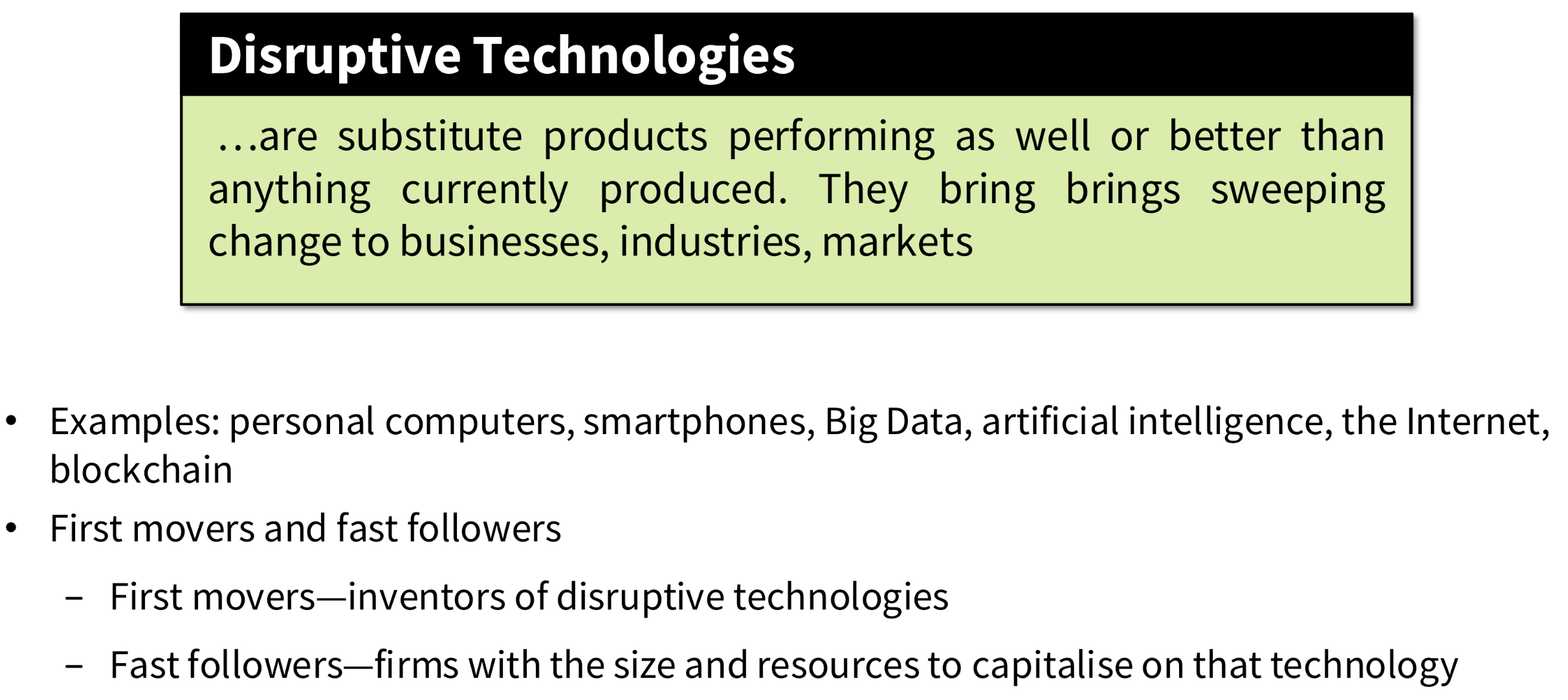
What organisational types exist?
-Entreprenureal structure: Young, small firm in a fast-changing environment. It has a simple structure and is managed by an entrepreneur serving as its single chief executive officer (e.g. small start-up business).
-Machine bureaucracy: Large bureaucracy exists in a slowly changing environment, producing standard products. It is dominated by a centralised management team and centralised decision-making (e.g. mid-size manufacturing firm).
-Divisionalised bureaucracy: Combination of multiple machine bureaucracies, each producing a different product or service, all topped by one central headquarters (e.g. large manufacturing firms).
-Professional bureaucracy: Knowledge-based organisation where goods and services depend on the expertise and knowledge of professionals. Dominated by department heads with weak centralised authority (e.g. Hospital, Universities).
How can information systems reduce the amount of levels in an organisation?
Information systems can reduce the number of levels in an organisation by providing managers with information to supervise larger numbers of workers and by giving lower-level employees more decision-making authority.
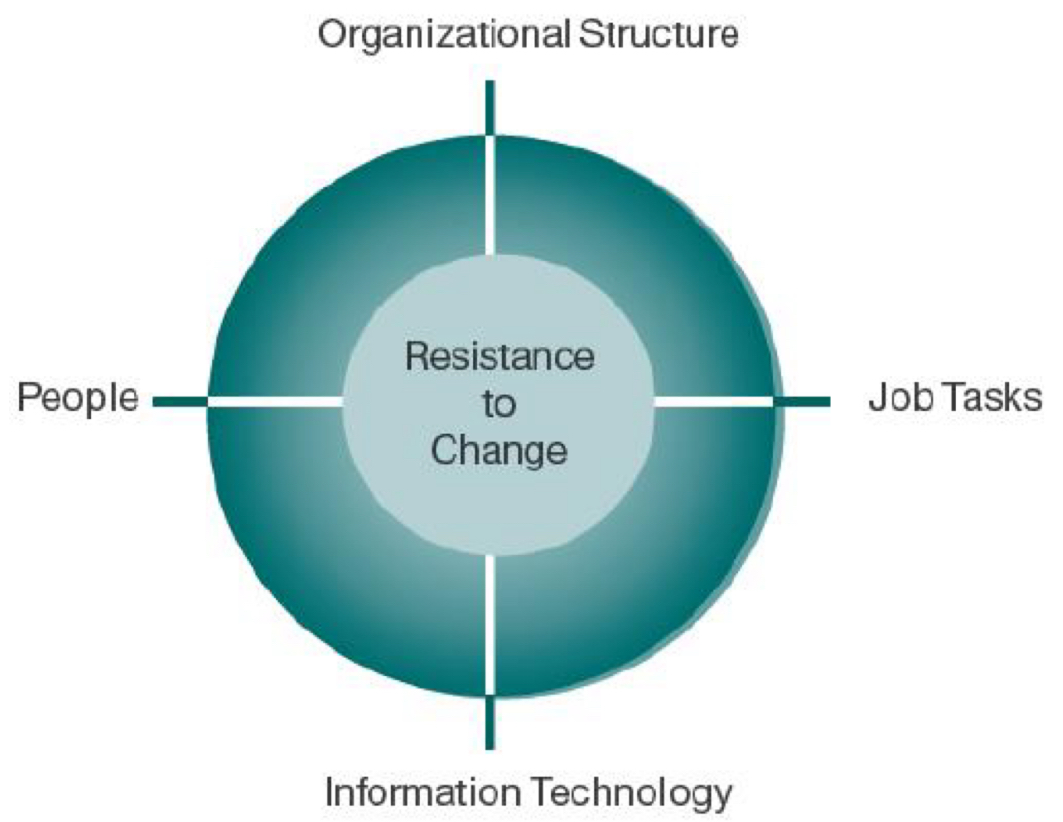
Which four factors affect information systems innovations adaption?
- Structure of organisation
- Tasks affected by innovation
- Nature of the innovation
- Culture of organisation
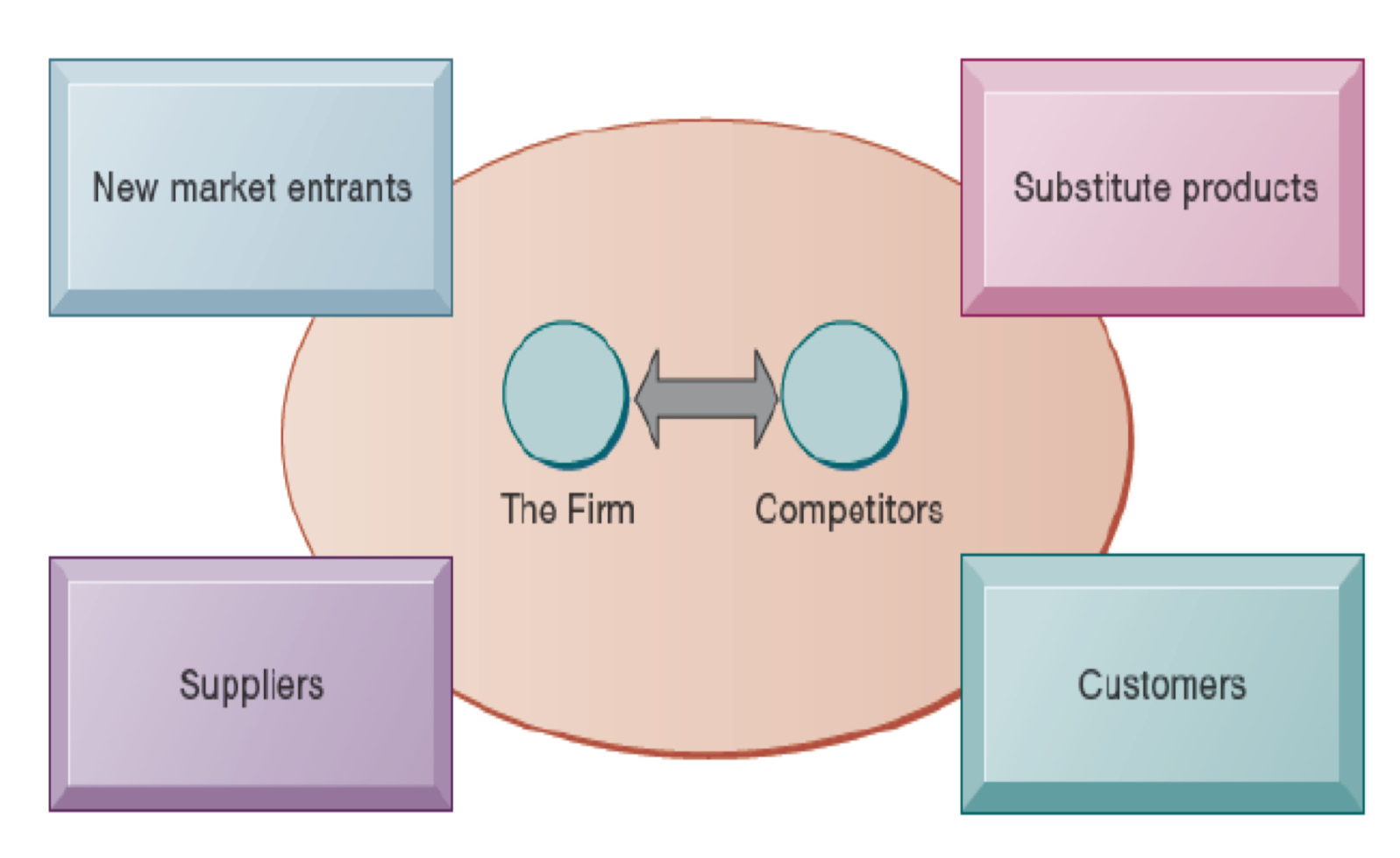
What is Porter‘s competitive forces model?
What are switching costs?
Costs in the form of lost time or resource expenditure that a customer or a company suffer from when changing from one supplier or information system to a competitor or a competing system.
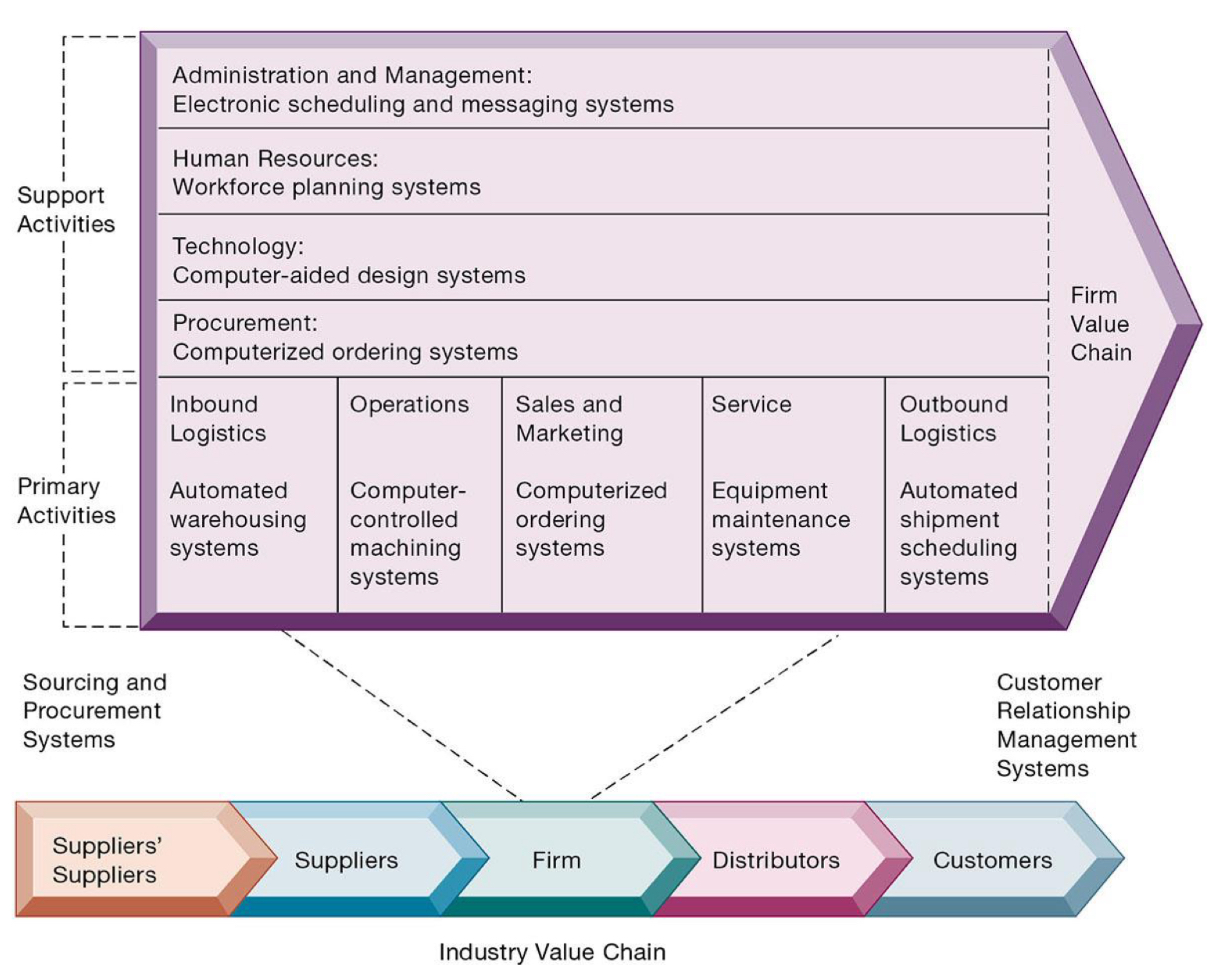
What is the value chain model?
The value chain model is a business model that includes a series of activities, each one adding value to products or services.
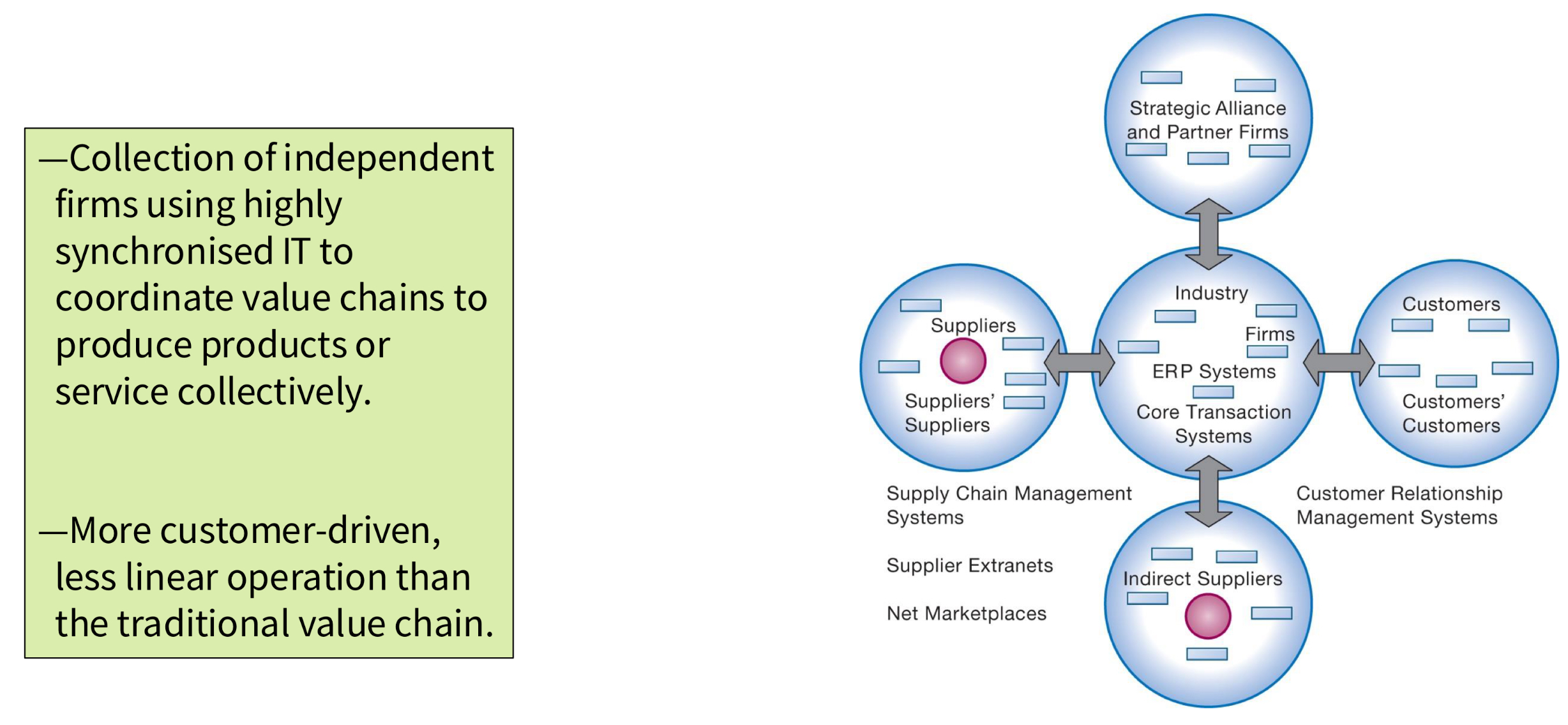
What is the value web?
What are models for the value of a network?
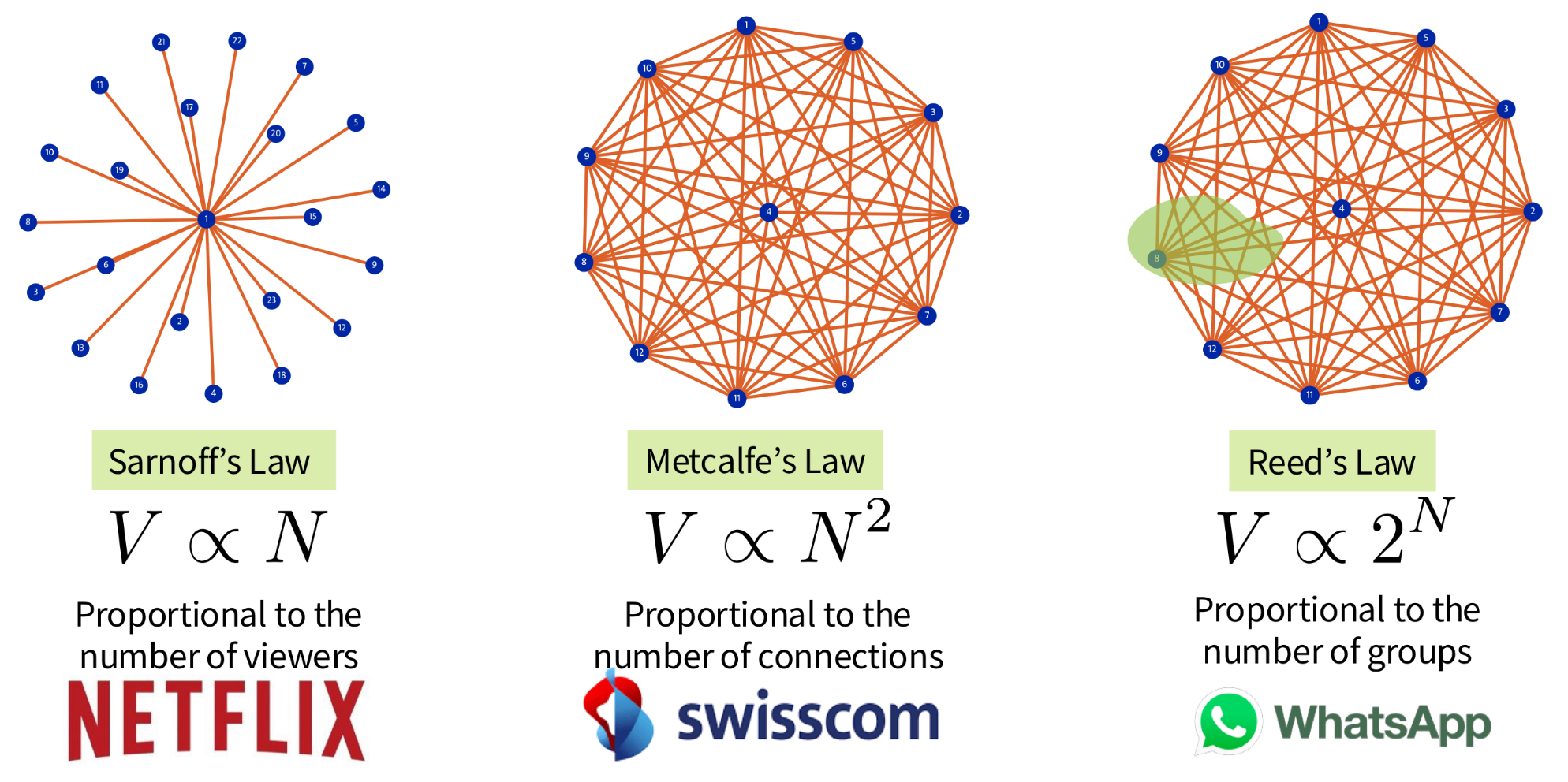
What are Strategic Information Systems (SIS)?
Strategic Information Systems are present at every level of the organisation. They influence goals, operations, products, services or relationships with the corporate environment to give the company a competitive advantage.
What types of decisions exist?
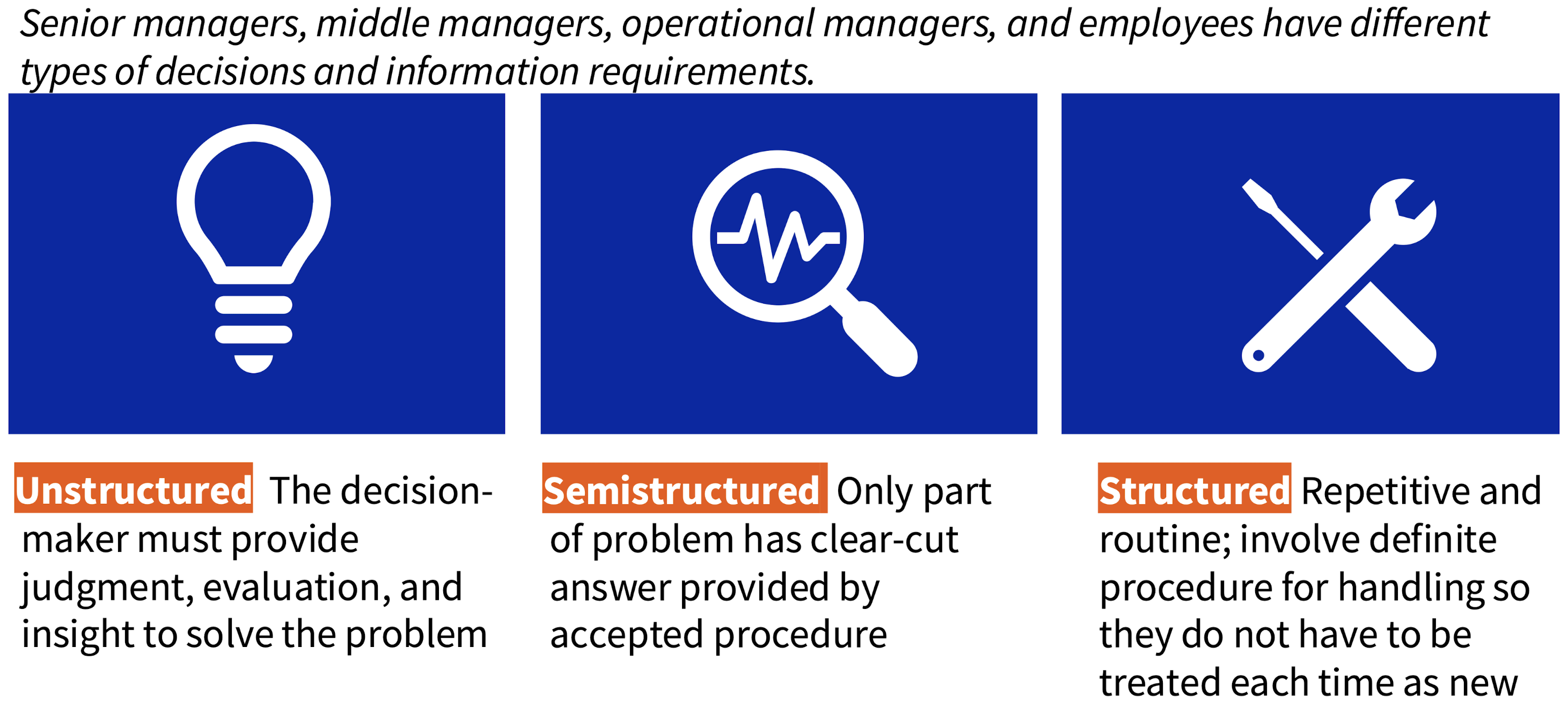
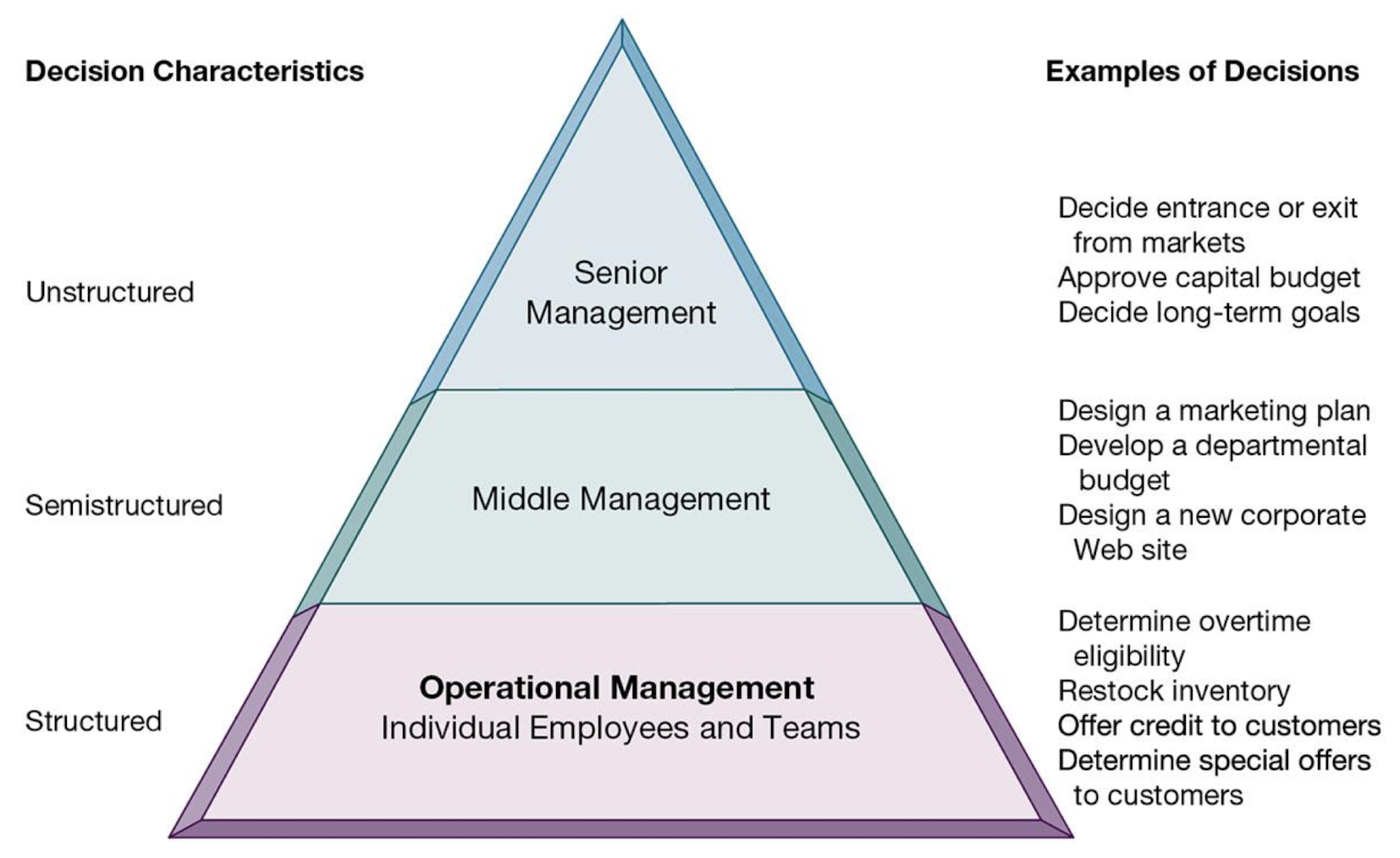
What kind of decisions do senior managers, middle managers and operational managers usually make?
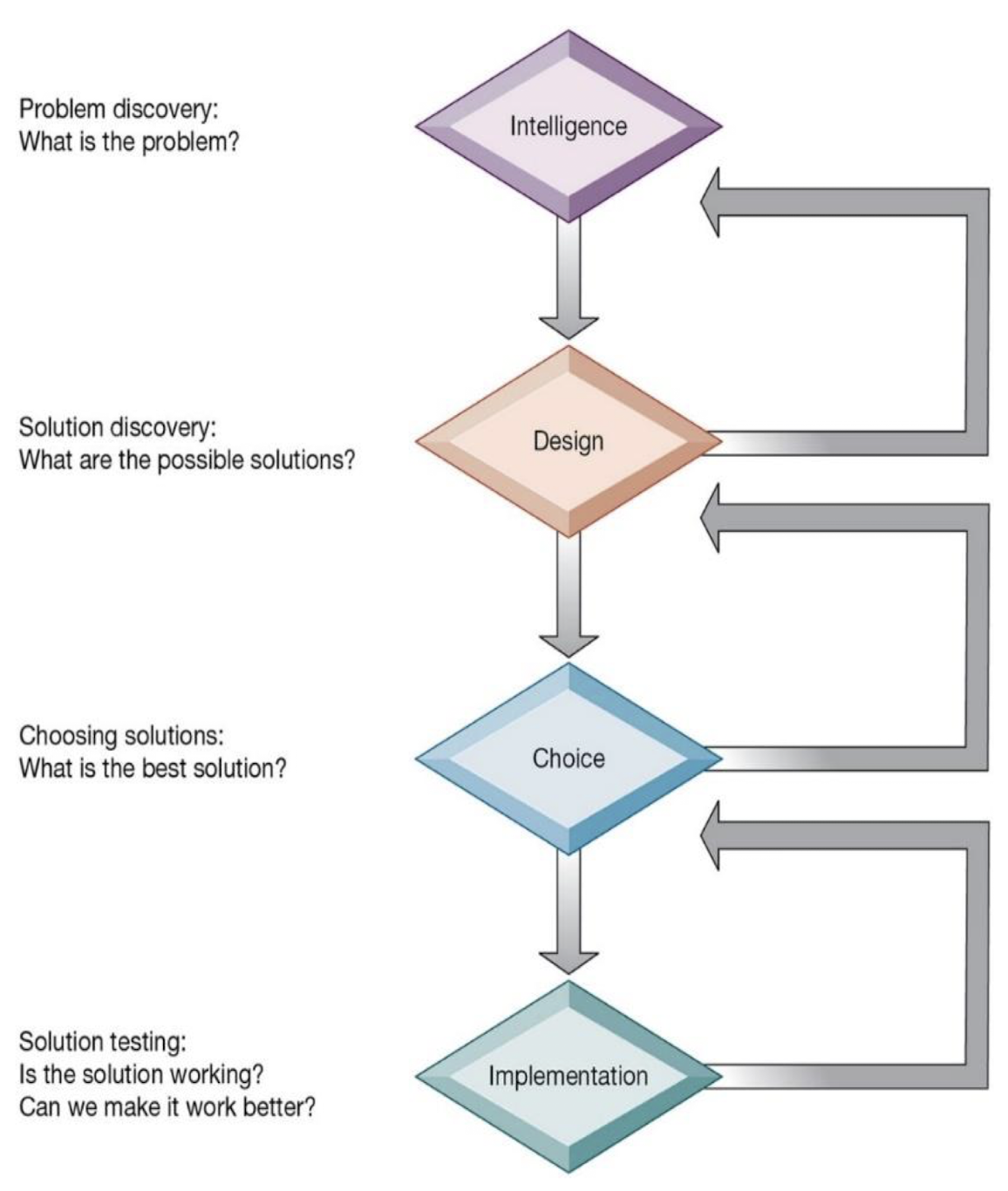
What are the stages in the decision-making process?
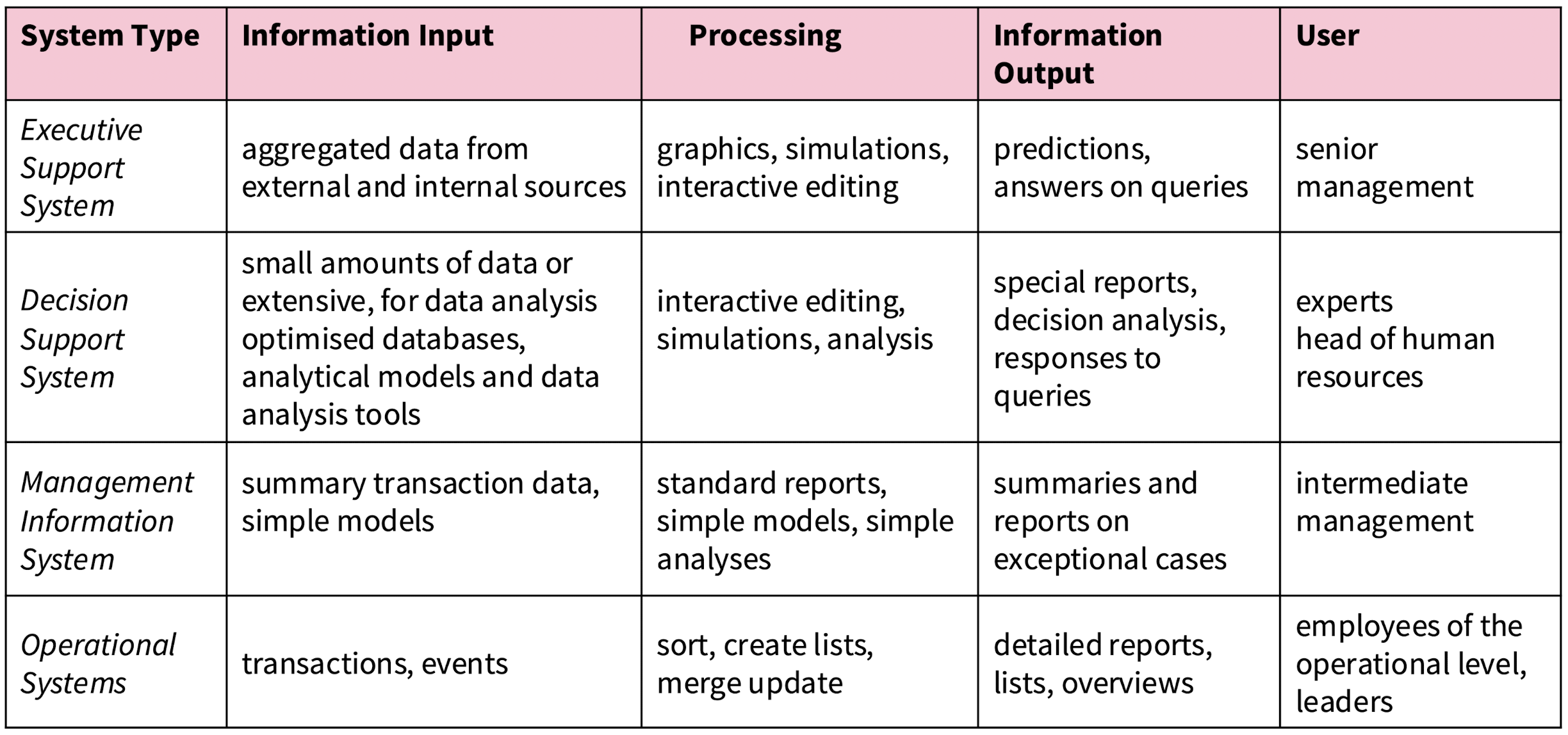
What are the four main types of application systems?
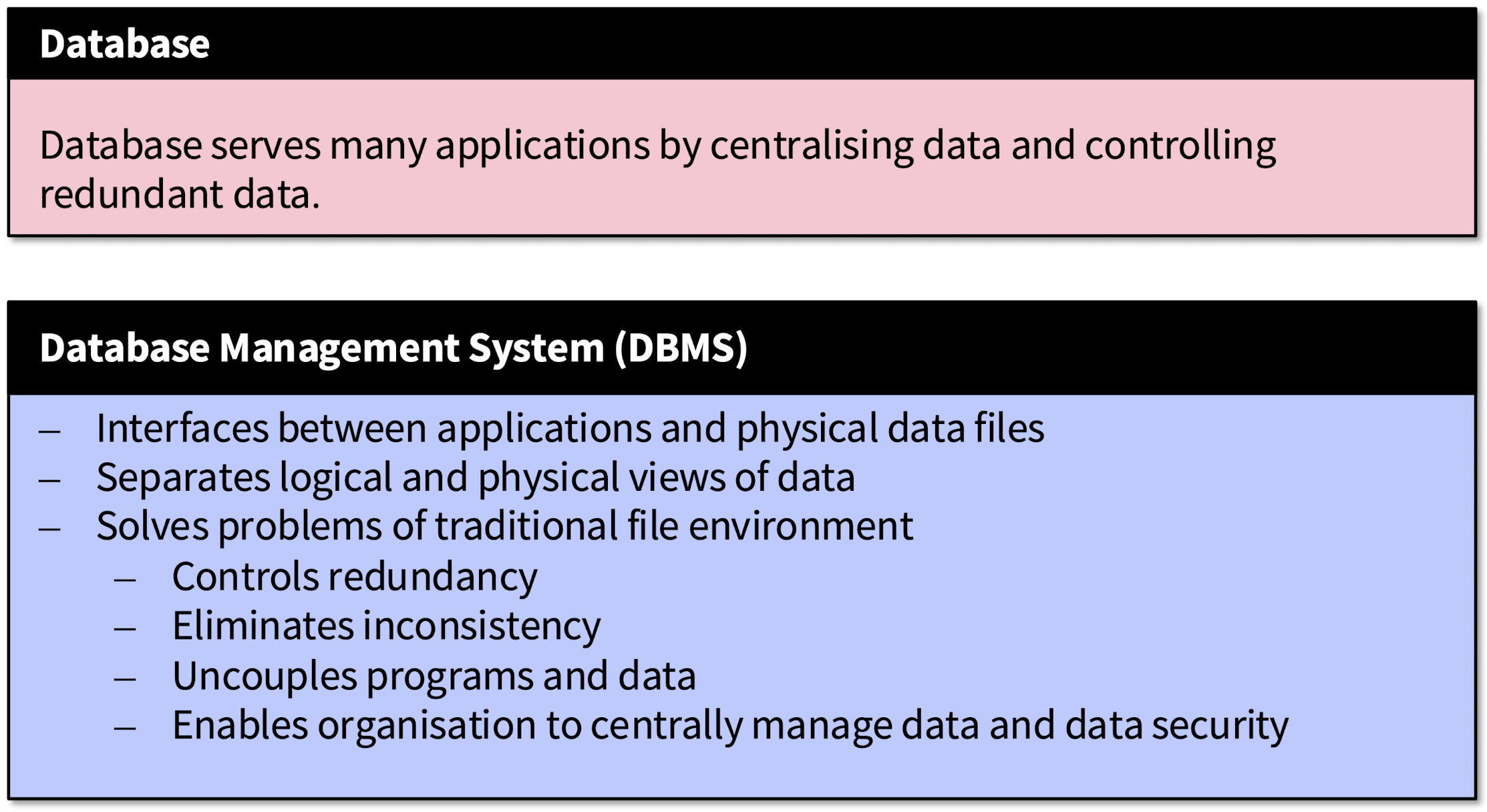
What are databases and Database Management Systems (DBMS)?
What are relational DBMS?

What is normalization in databases?

What is a business process?
A business process is a flow of material, information, and knowledge. They are composed of logically related tasks that define how specific business operations are performed. They may be tied to a functional area of an organisation or be cross-functional.
What is a business?
A business is a collection of business processes.
What are examples of functional business processes?
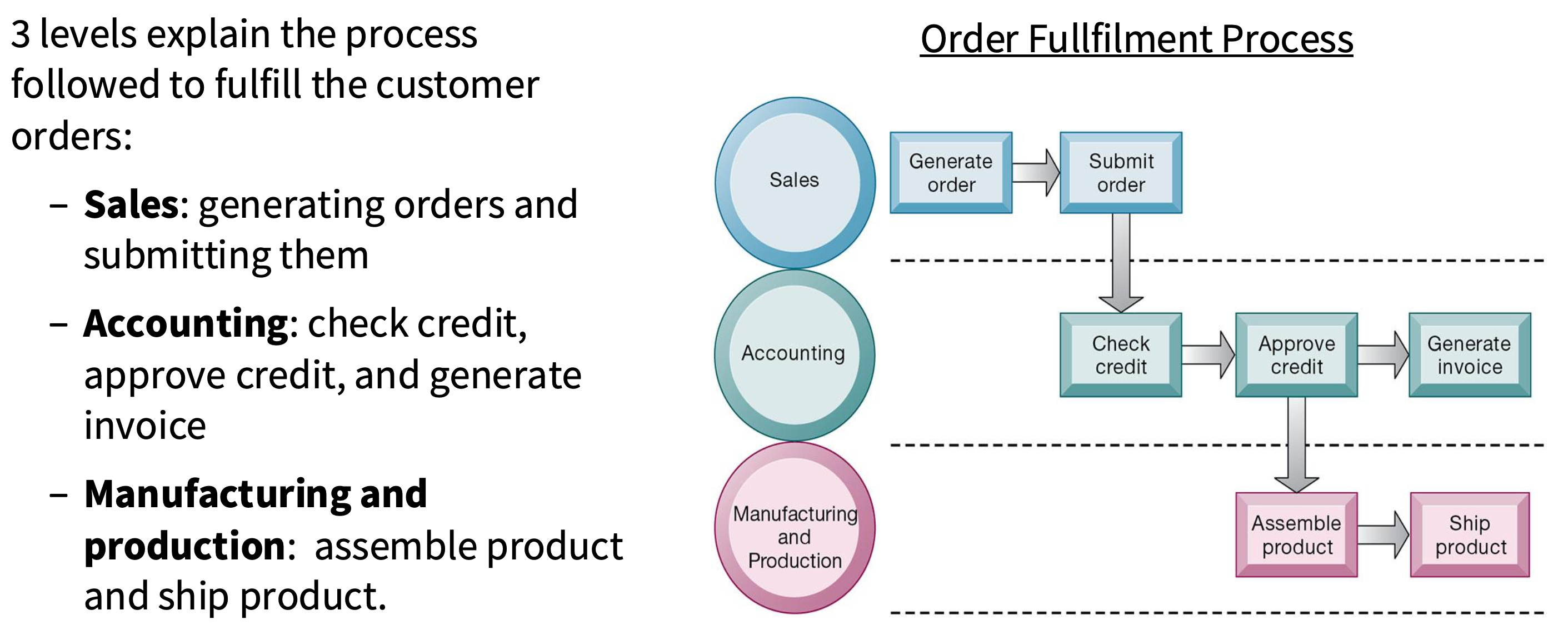
What is the order fulfillment process?
How do information systems improve business processes?
1. Increasing efficiency of existing processes
―Automating steps that were manual
2. Enabling entirely new processes
―Changing the flow of information
―Replacing sequential steps with parallel steps
―Eliminating delays in decision making
―Supporting new business models
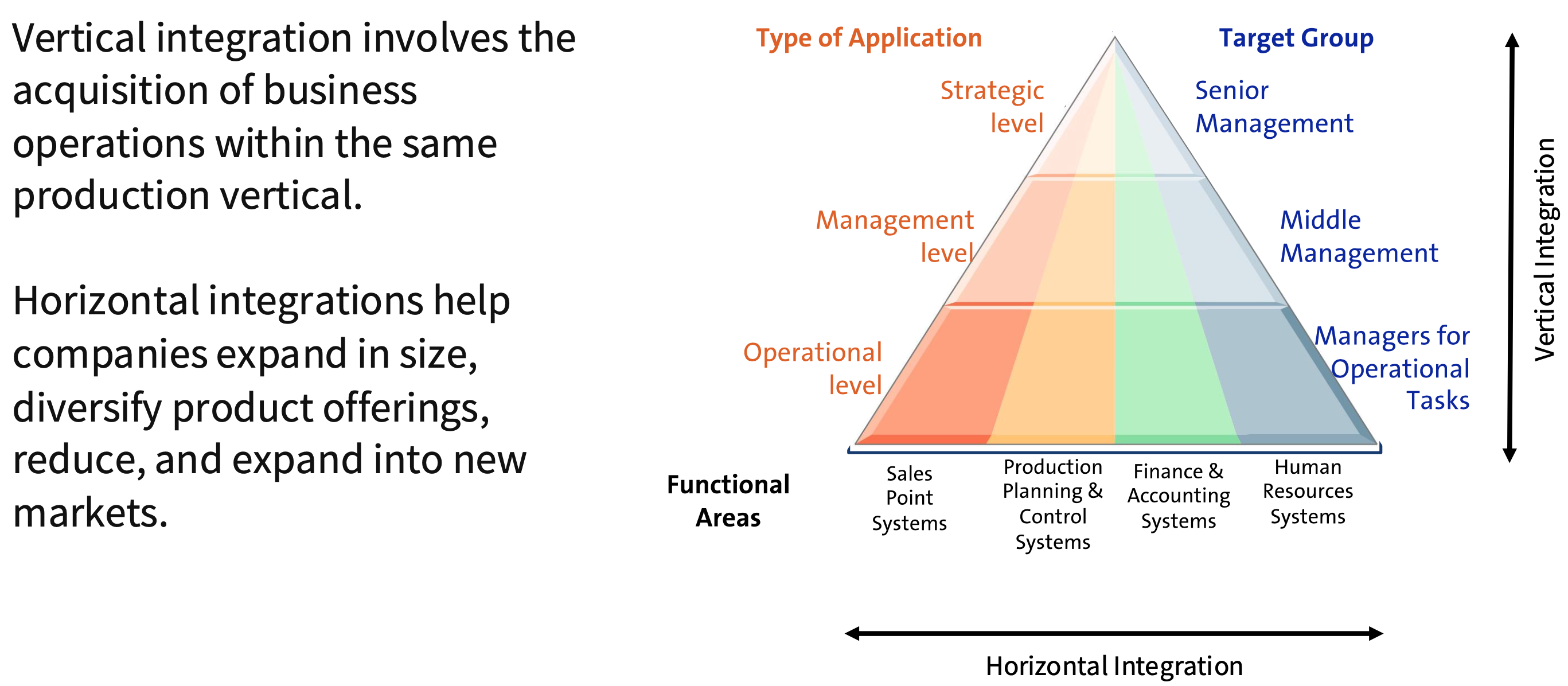
In the model of data integration, what is physical integration and logical integration?
―Physical Integration: a central database to which all applications are connected,
―Logical Integration: brings the data structures of distributed subsystems into harmony
In the model of functional integration, what is task-oriented functional integration and data-centric functional integration?
―Task-oriented functional integration: bundles the execution of similar tasks or functions by a task carrier
―Data-centric functional integration: when the data to be used is the same the tasks are assigned to the same task carrier
What are other models of integration?
―Method Integration: the coordination and use of the same methods in different functions
―Program Integration: aims at the coordination of individual modules within the framework of an integrated system.
What are the directions of integration?
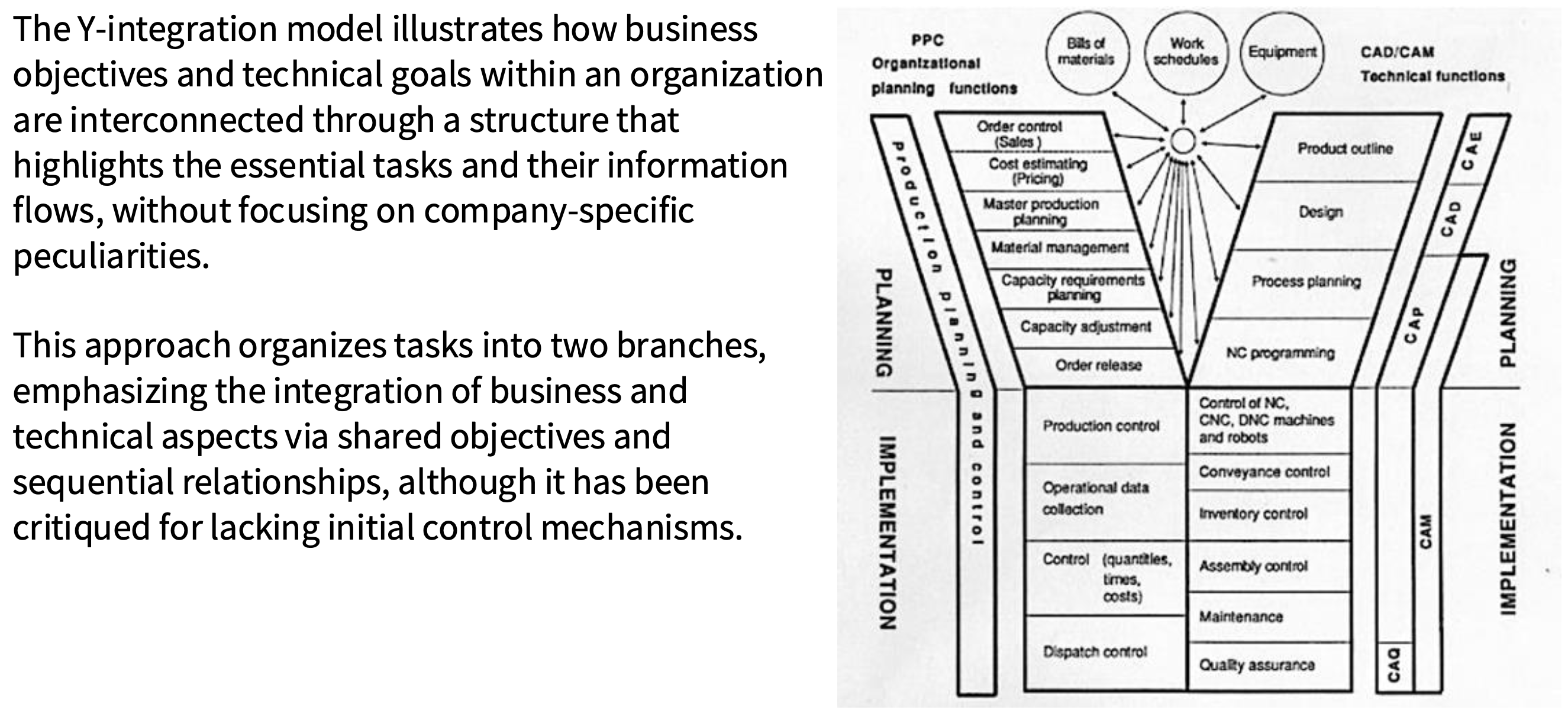
What is Scheer’s Y-Integration Model?
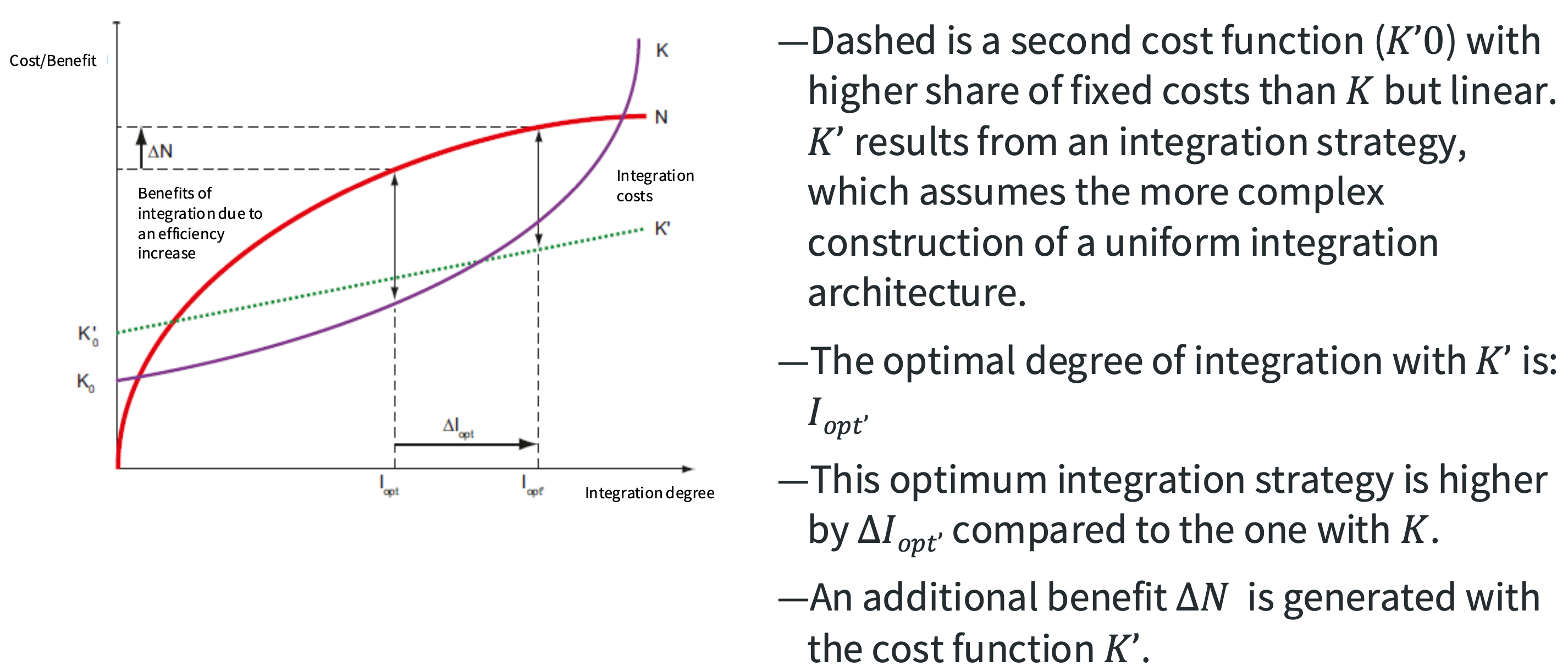
What is a rational explanation of integration decisions?
What are the four major enterprise-wide application systems?
―Internal Focus:
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems
―Inter-company Focus:
Supply chain management systems (SCM)
Customer relationship management systems (CRM)
Knowledge management systems (KMS)
What are enterprise applications?
Enterprise applications automate processes that span multiple business functions and organisational levels and may extend outside the organisation
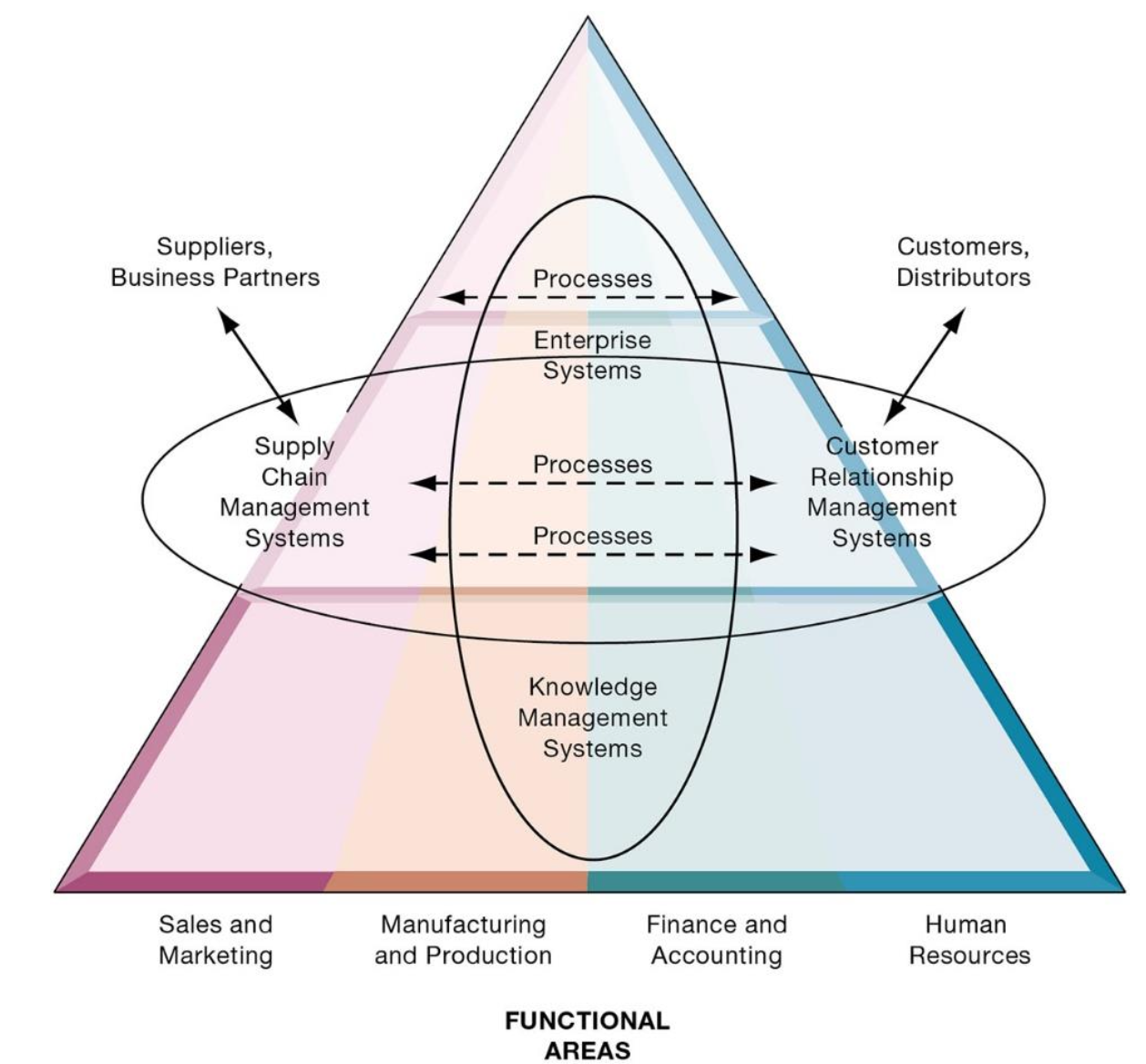
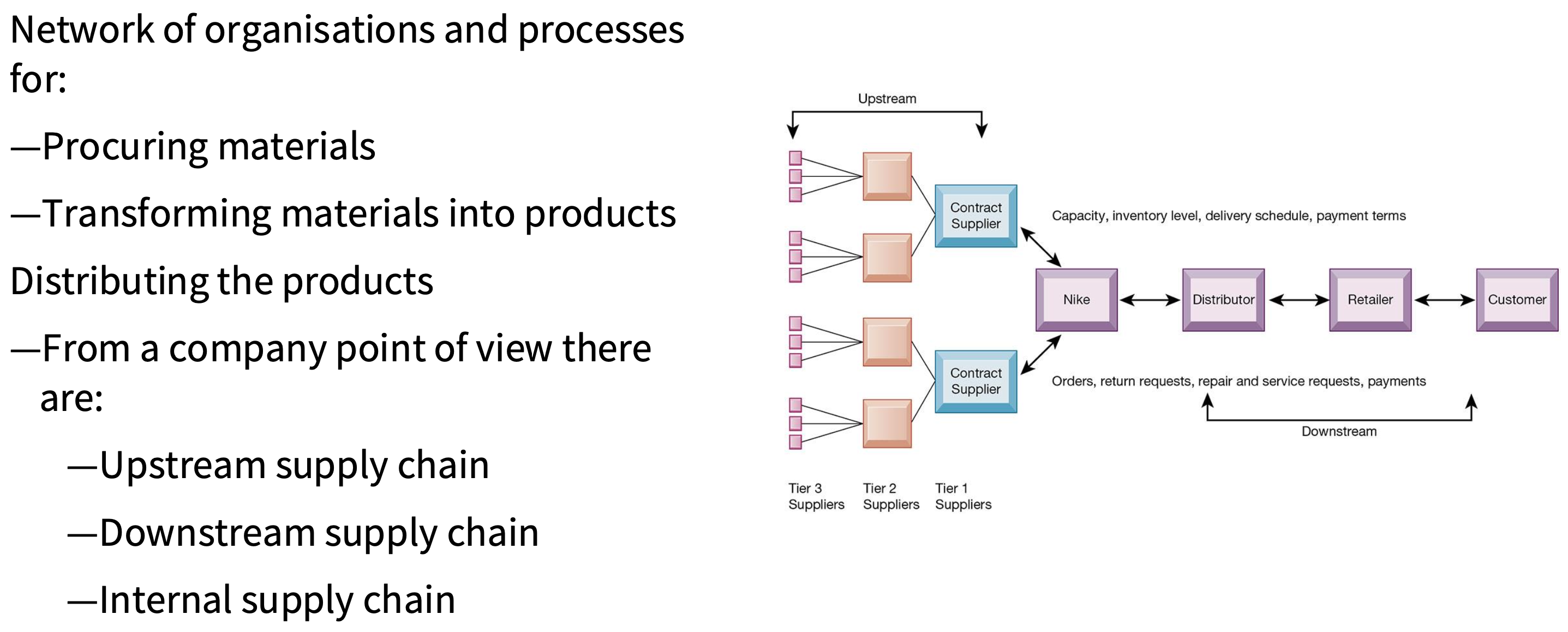
What are Supply Chain Management (SCM) Systems?
Inter-organisational systems: They are not limited by organisational boundaries.
Typically, they:
―automate the flow of information across organisational boundaries.
―manage relationships with suppliers, purchasing firms, distributors, and logistics companies.
―manage shared information about orders, production, inventory levels, etc..
Objective: to move correct amount of product from source to point of consumption as quickly as possible and at lowest cost
What are Knowledge Management Systems (KMS)?
Intra-organisational systems
Typically, they:
―manage processes for capturing and applying knowledge and expertise
―collect relevant knowledge and make it available wherever needed in the enterprise to improve business processes and management decisions
―link firm to external sources of knowledge
What are Customer Relationship Management (CRM) Systems?
Linked to the environment: They are not limited by organisational boundaries.
Typically, they:
―help manage relationship with customers
―co-ordinate business processes that deal with customers in sales, marketing, and customer service
Objectives: optimise revenue, improve customer satisfaction, increase customer retention, identify and retain most profitable customers, increase sales, etc.
What are intranets and extranets?
Technology platforms that increase integration and expedite the flow of information
―Intranets
Internal networks based on Internet standards.
Often are private access area in company’s website.
―Extranets
Company websites accessible only to authorised vendors and suppliers.
Facilitate collaboration.
What is E-business, E-commerce, and E-government?

What is Electronic Data Interchange (EDI)?
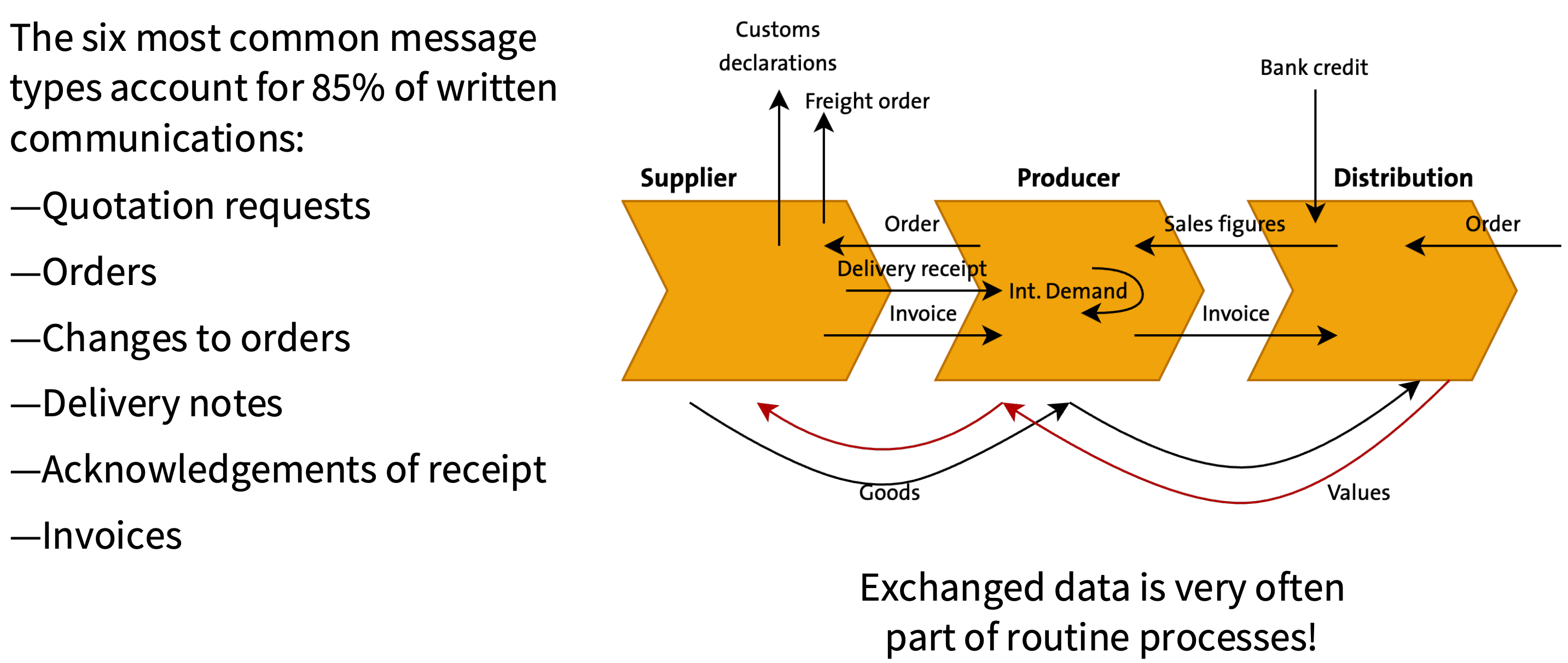
Electronic Data Interchange (EDI) is the computer-to-computer exchange of business documents in a standard electronic format between business partners.
Electronic Data Interchange does not correspond to a specific system but stands for a variety of standards and procedures for electronic data exchange.
What are the most common message types exchanged between businesses?
What are Enterprise Ressource Planning (ERP) Systems?
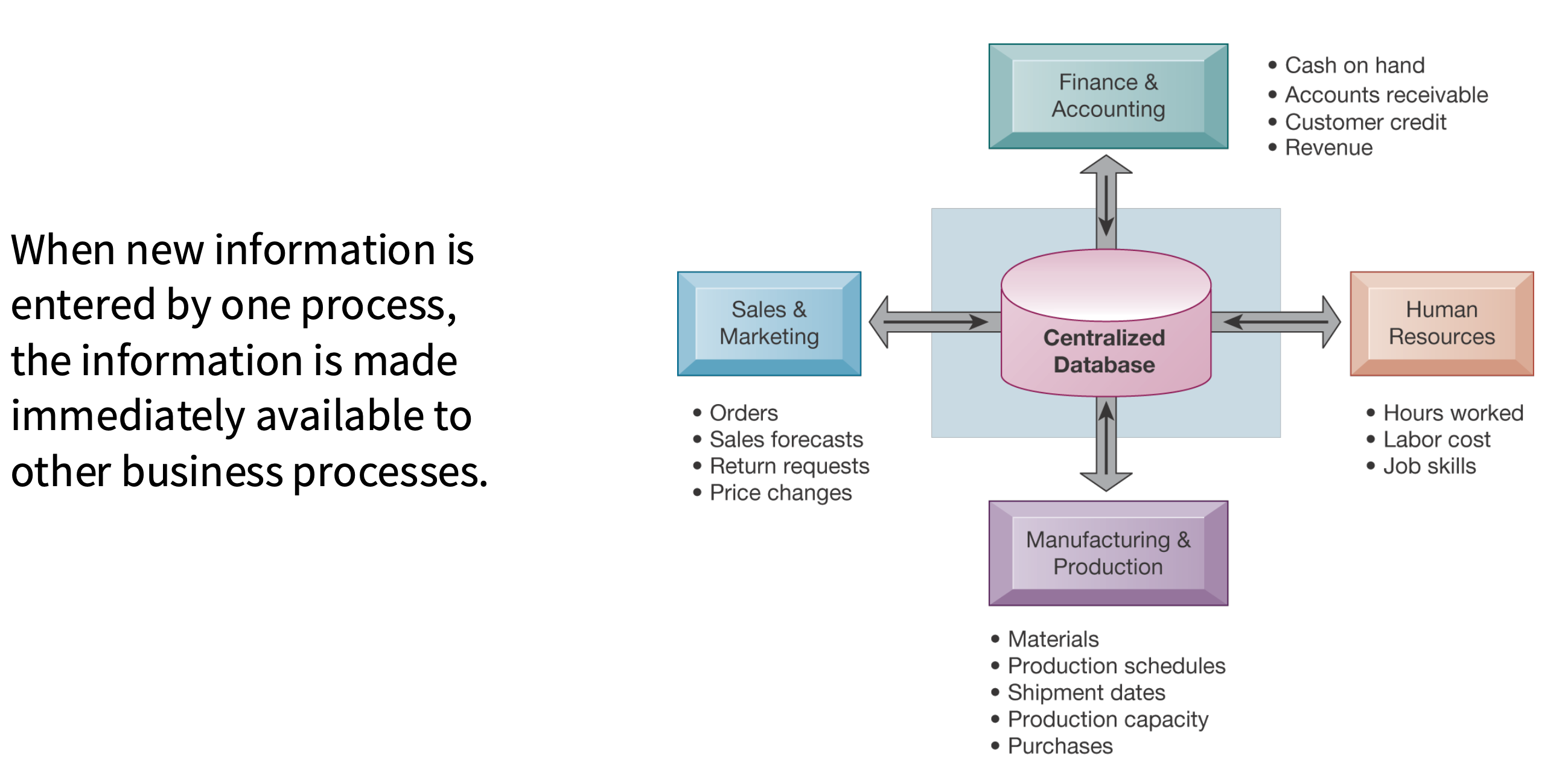
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems are integrated enterprise-wide application systems that serve to coordinate important internal processes of a company.
What does an ERP System look like?
What does a supply chain look like?
How is the supply chain managed?
Inefficiencies add into a company’s operating costs
―Can waste up to 25 percent of operating expenses
Just-in-time strategy vs. stockpiles
―Just-in-time:
Components arrive as they are needed
Finished goods shipped after leaving assembly line
―Safety stock
buffer for lack of flexibility in supply chain
What is the Bullwhip Effect?
Information about product demand gets distorted as it passes from one entity to next across supply chain. Upstream, demand may be amplified as downstream companies build safety stock
What are Supply Chain Planning Systems?
Supply chain planning systems allow to:
―Model existing supply chain
―Enable demand planning
―Optimise sourcing, manufacturing plans
―Establish inventory levels
―Identify transportation modes
What are Supply Chain Execution Systems?
Supply chain execution systems manage flow of products through distribution centers and warehouses.
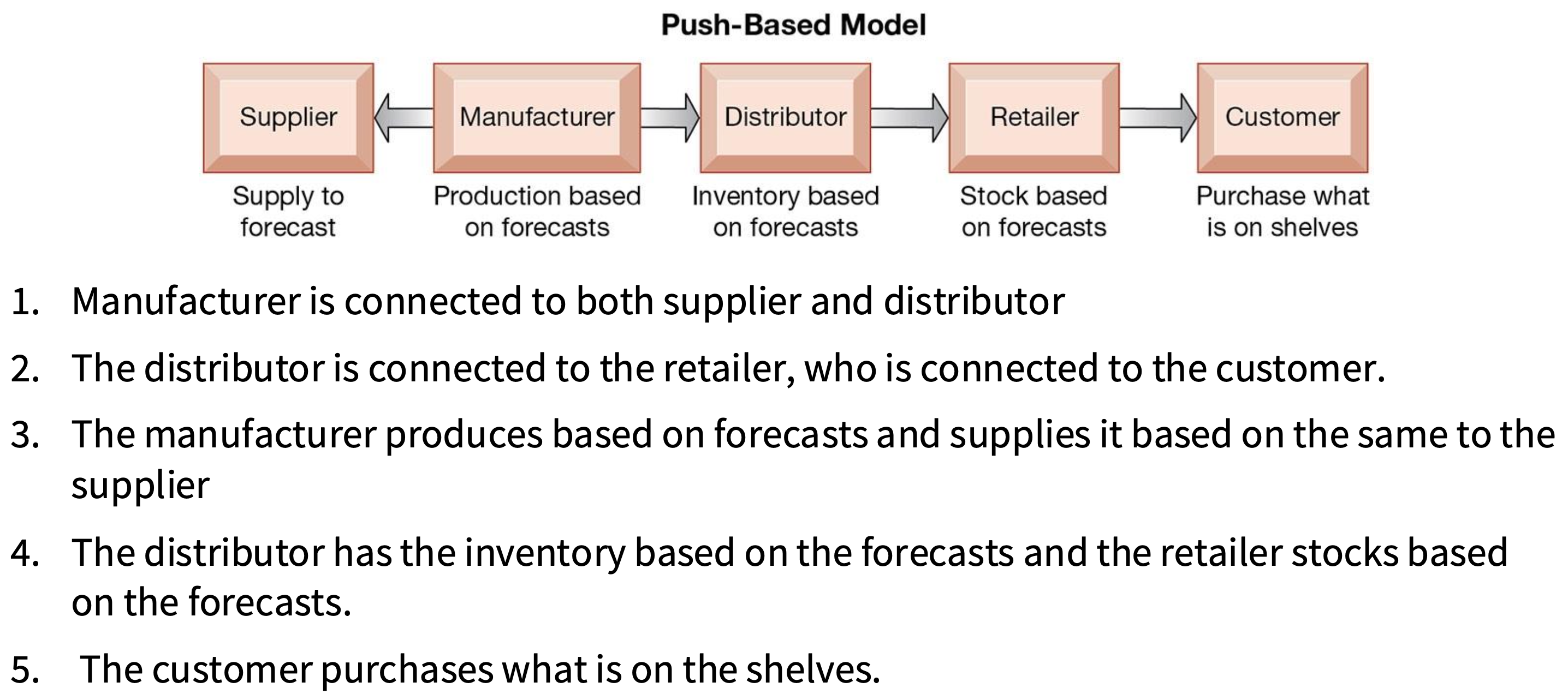
What is the push-based supply chain model?
What is the pull-based supply chain model?
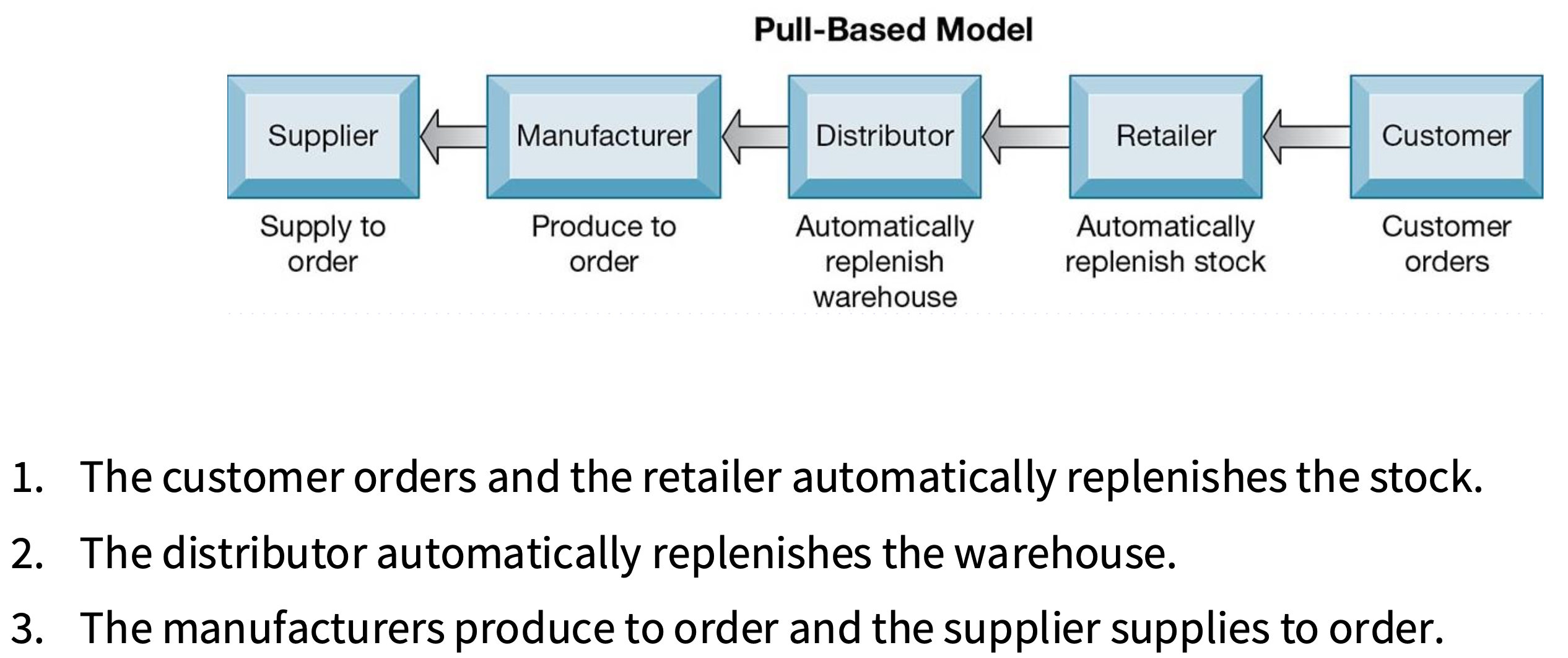
What is the emerging internet-driven supply chain model?
What tools are typically included in CRM packages?
CRM packages typically include tools for:
―Sales force automation (SFA):
―Sales prospect and contact information
―Sales quote generation capabilities
―Customer service:
―Assigning and managing customer service requests
―Web-based self-service capabilities
―Marketing:
―Capturing prospect and customer data, scheduling and tracking direct-marketing mailings or e-mail
―Cross-selling
What tools are included in more comprehensive CRM packages?
More comprehensive packages have modules for:
―Partner relationship management (PRM)
―Integrating lead generation, pricing, promotions, order configurations, and availability
―Tools to assess partners’ performances
―Employee relationship management (ERM)
―Setting objectives, employee performance management, performance-based compensation, employee training
What are operational and analytical CRM’s?

What is the Churn Rate?
―Number of customers who stop using or purchasing products or services from a company
―Indicator of growth or decline of firm’s customer base
What are E-Businesses?
E-Businesses are those that use information and communication technology to optimise coordination of internal and inter-company service creation processes.

What is E-Commerce?
E-Commerce refers in particular to electronic support of commercial activities that are directly related to the purchase or sale of products or services.

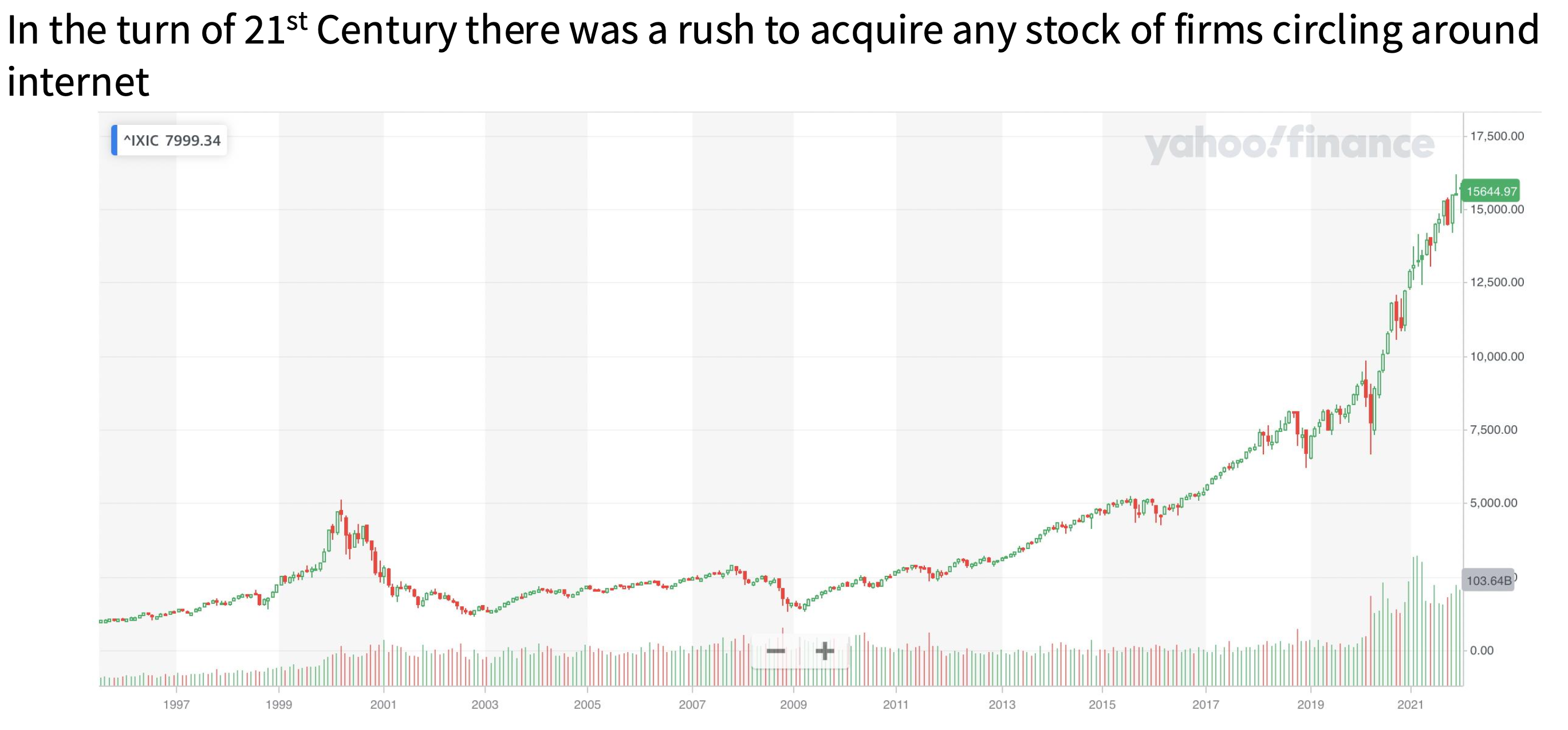
What is the Dot-Com bubble?
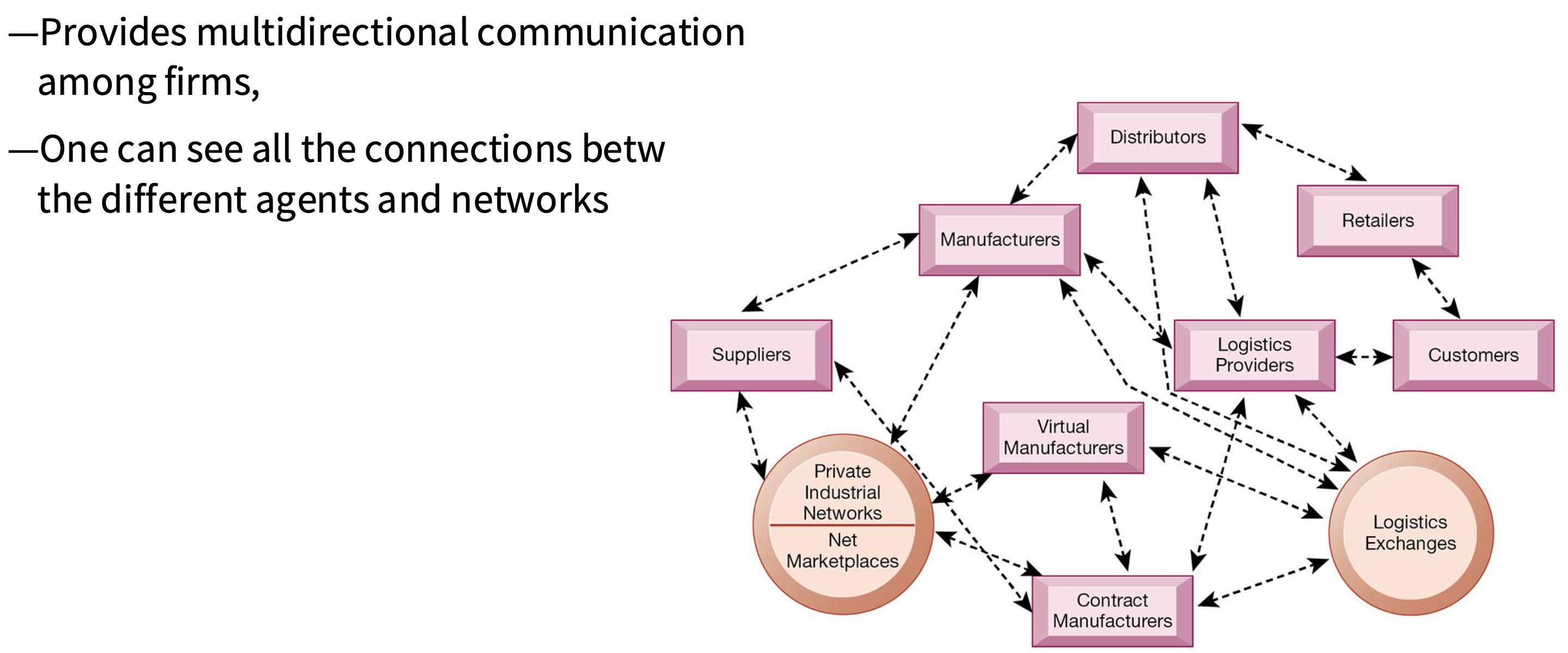
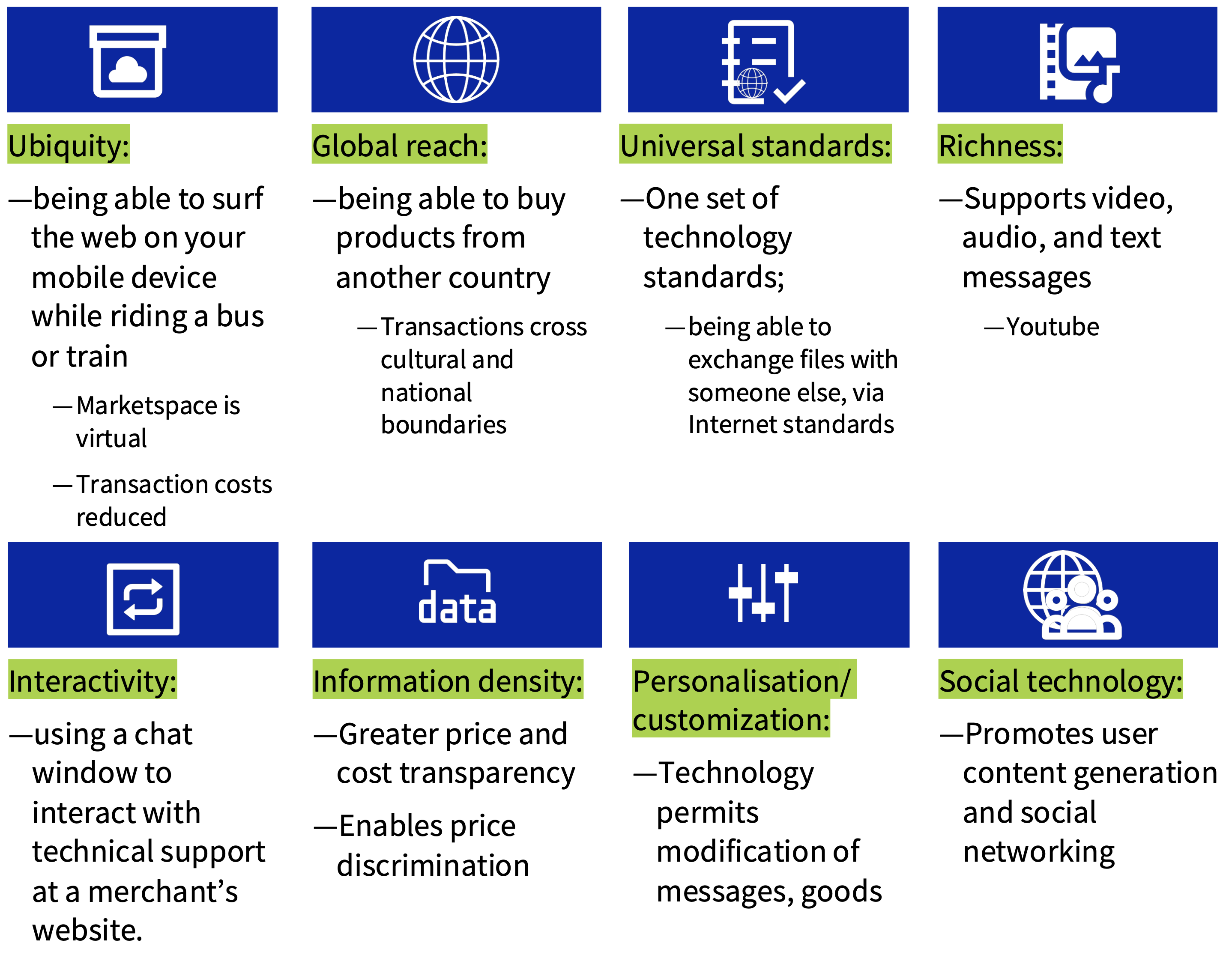
Why is E-Commerce so important?
What are digital goods?
―Goods that can be delivered over a digital network
―Cost of producing first unit is almost entire cost of product
―Costs of delivery over the Internet very low
―Marketing costs remain the same; pricing highly variable
―Industries with digital goods are undergoing revolutionary changes (publishers, record labels, etc.)
What are the three major types of E-Commerce?
Business-to-consumer (B2C)
Example: Amazon.com
Business-to-business (B2B)
Example: Elemica
Consumer-to-consumer (C2C)
Example: eBay
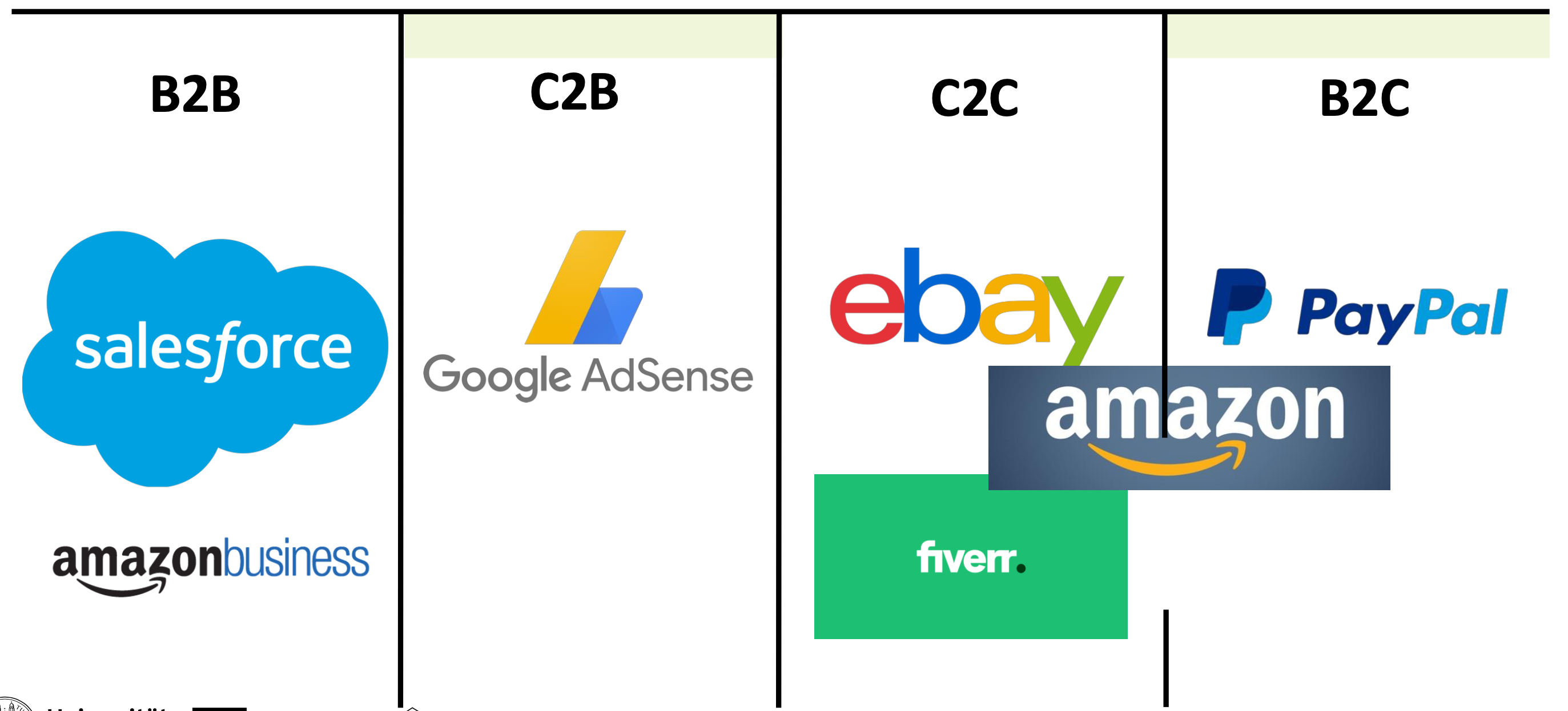
What E-Commerce business models exist?

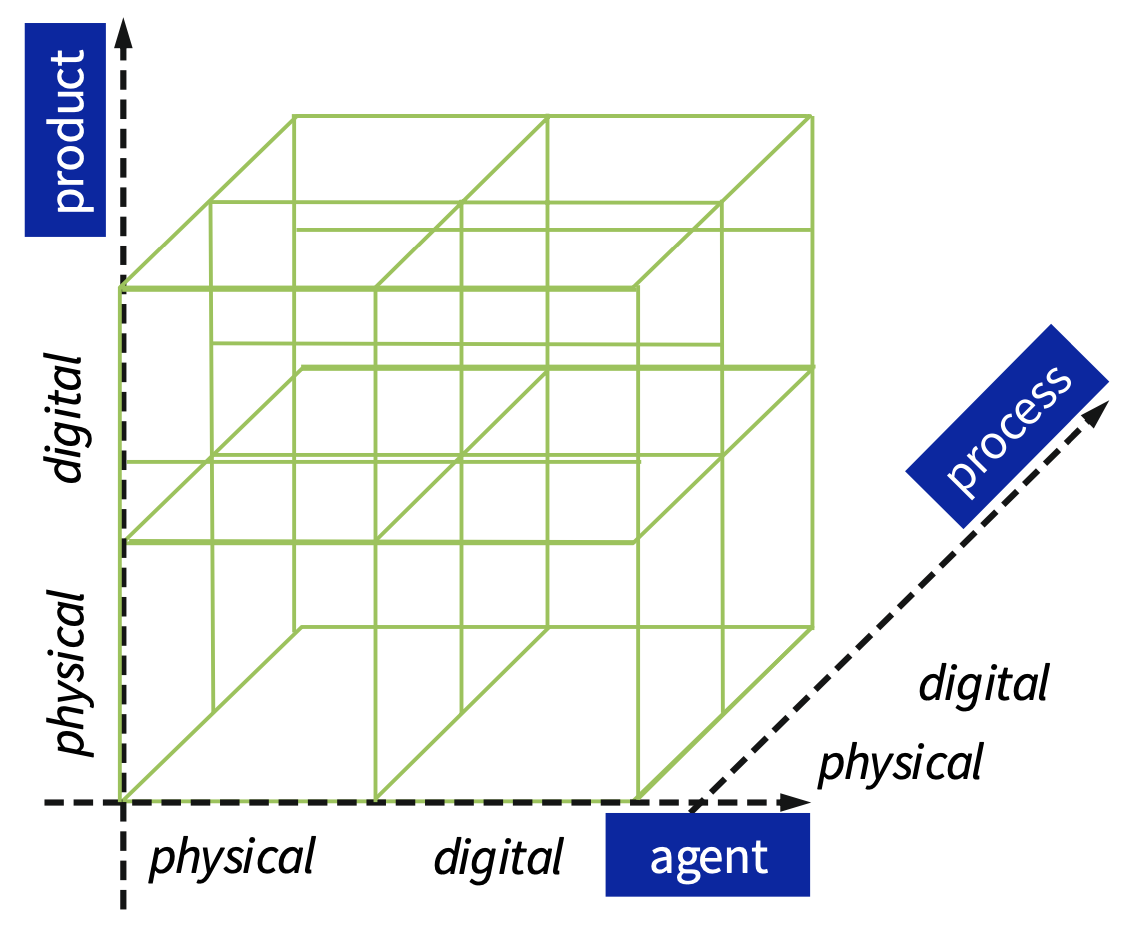
What are the dimensions of E-Commerce?
If the product, agent, and process are all physical:
Classic trade (physical exchange of goods and services between economic entities)
If the product, agent, and process are all digital:
Core E-Commerce (digitally represented representatives (realised with agent technology, for example) trade digital goods using digital business transactions
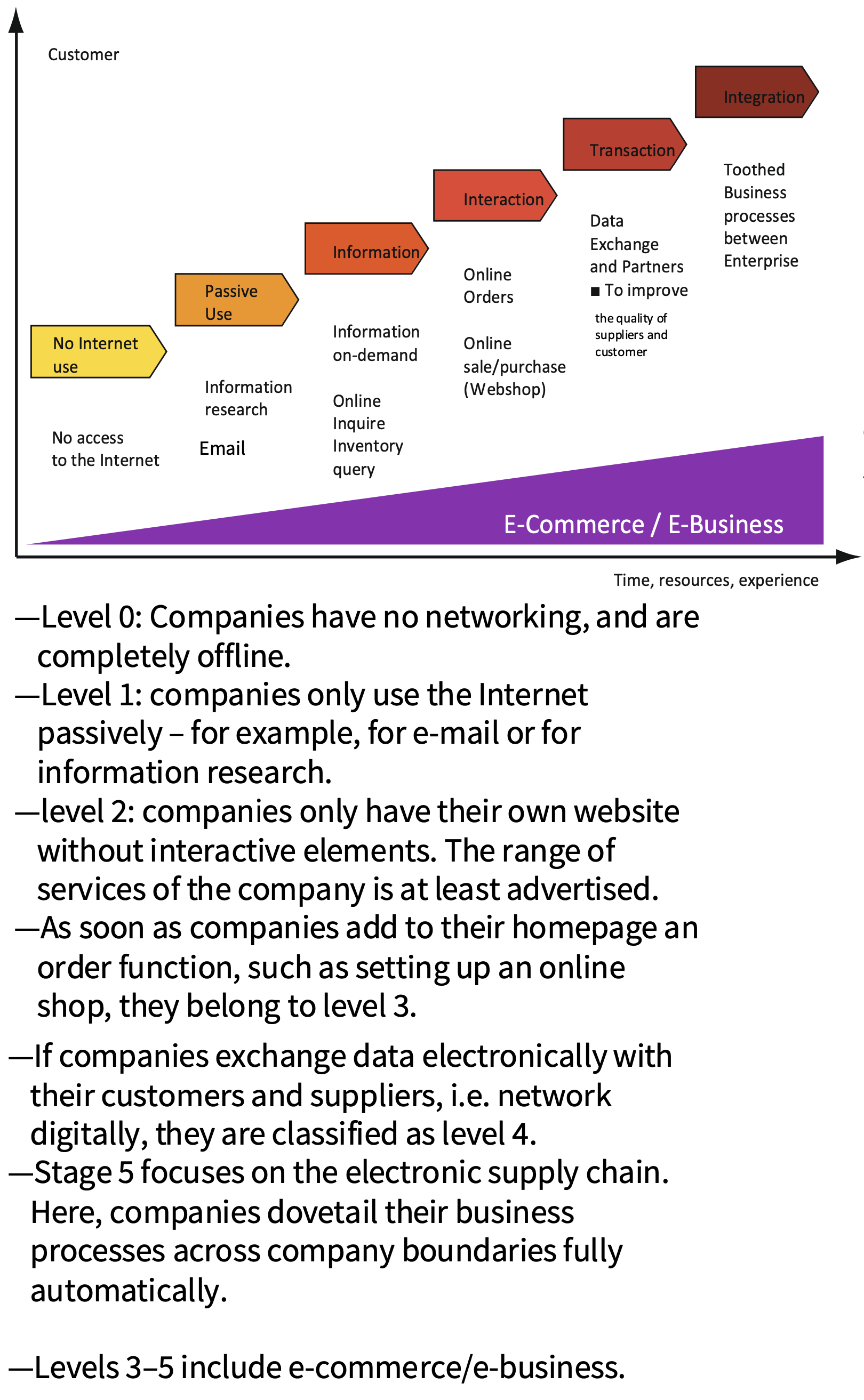
What are the phases of E-Commerce in a firm?
What is Electronic Data Interchange (EDI)?
EDI is Computer-to-computer exchange of standard transactions such as invoices and purchase orders.
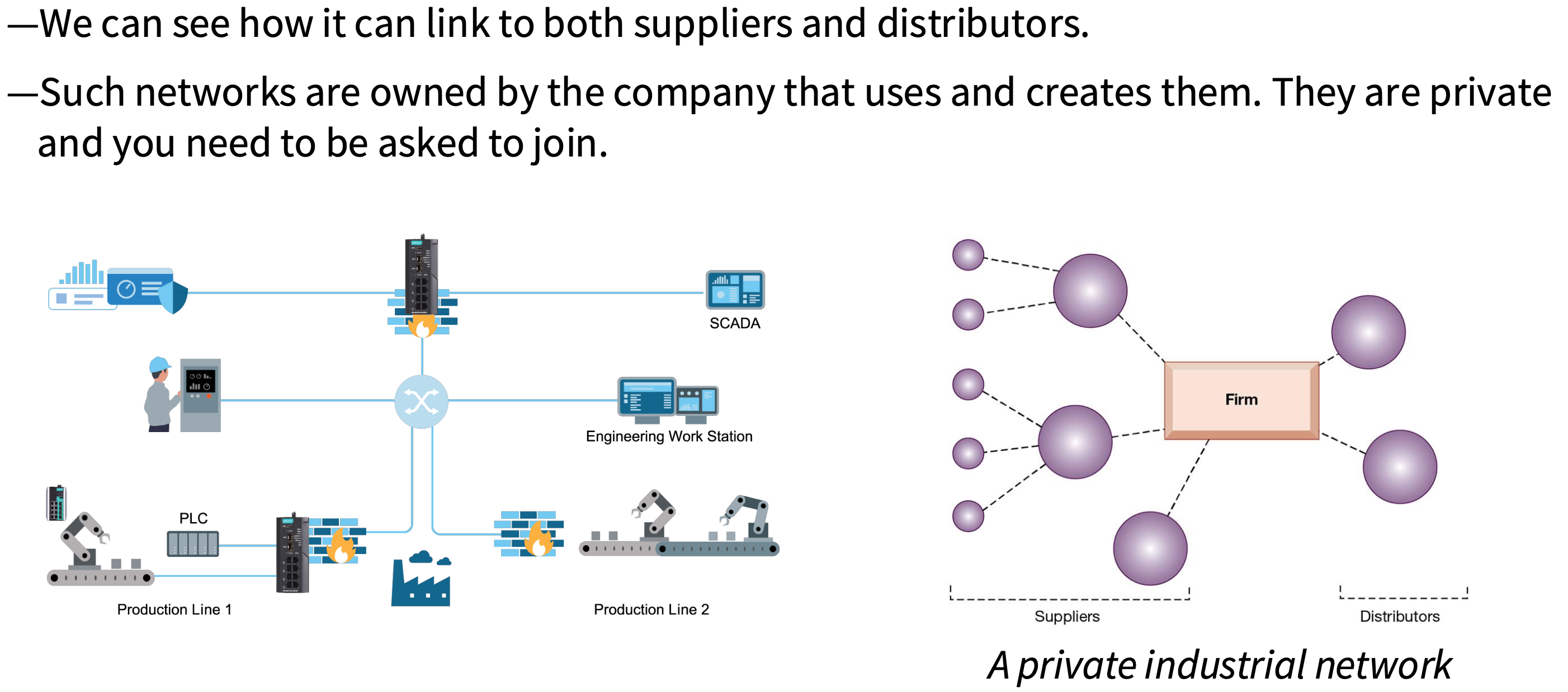
What is a private industrial network?
What is a net marketplace?

What is an intermediary?
Intermediary is an economic entity that mediates between other economic entities in the broadest sense due to information imperfections.
What is the transaction cost in traditional markets and electronic markets?
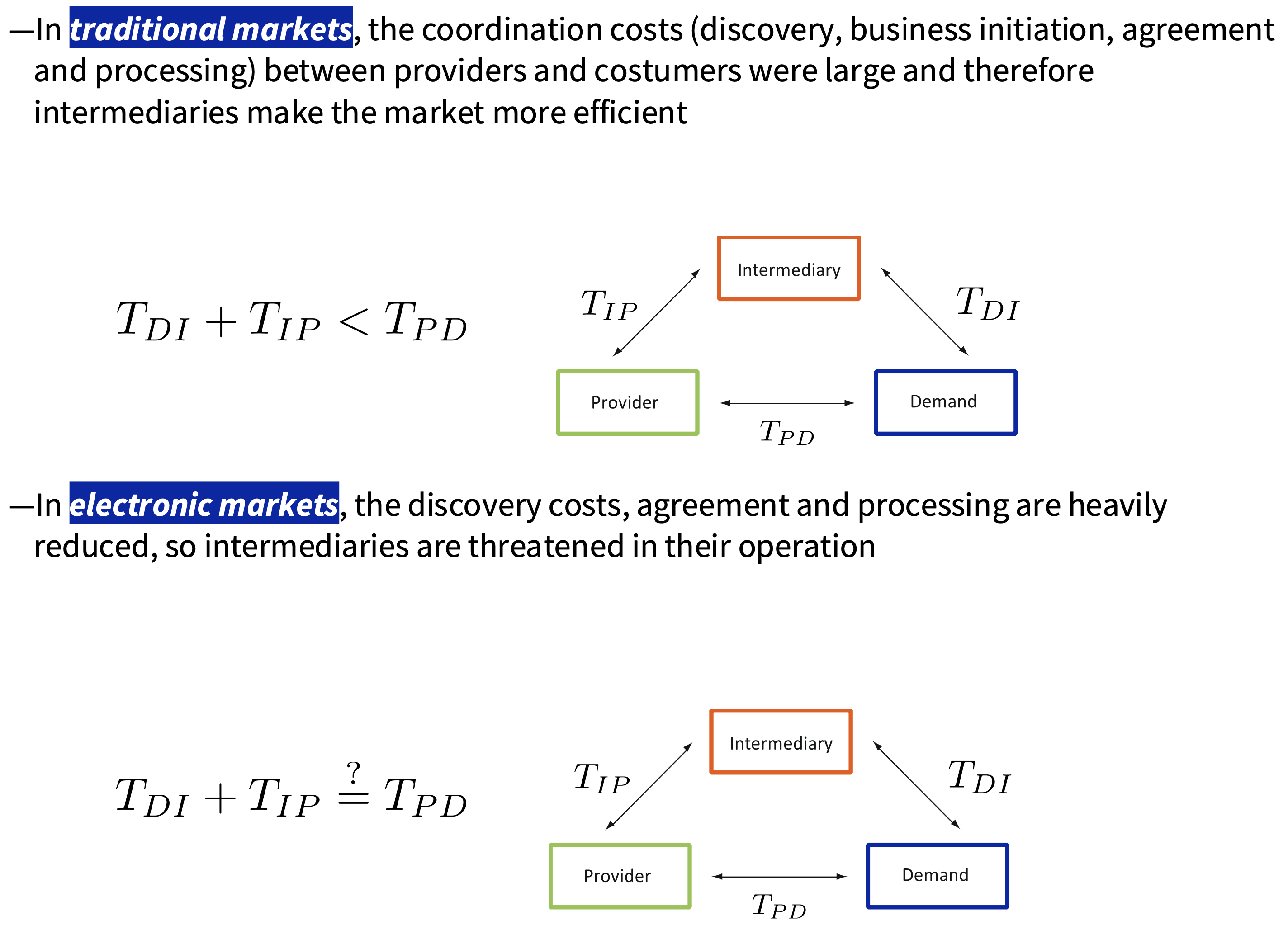
What are the possible cases depending on the transaction costs?
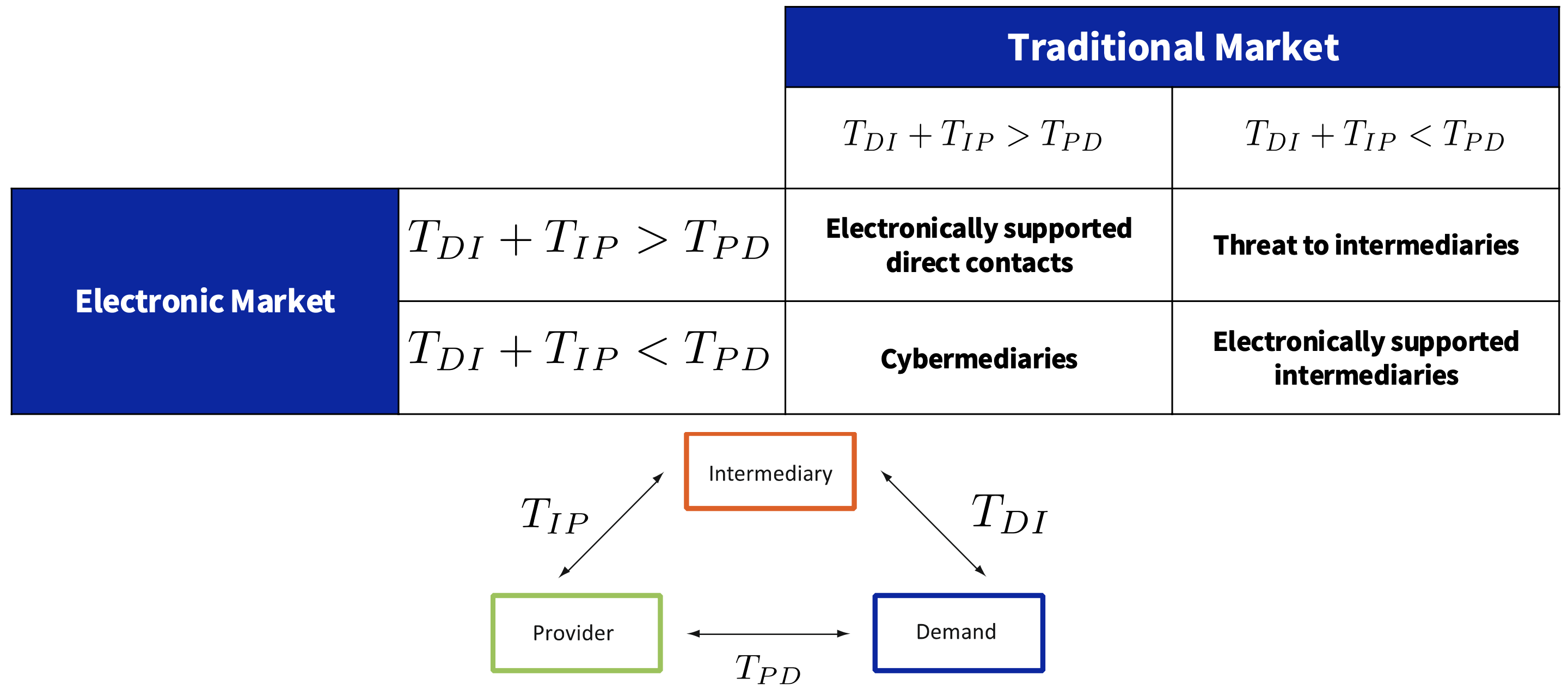
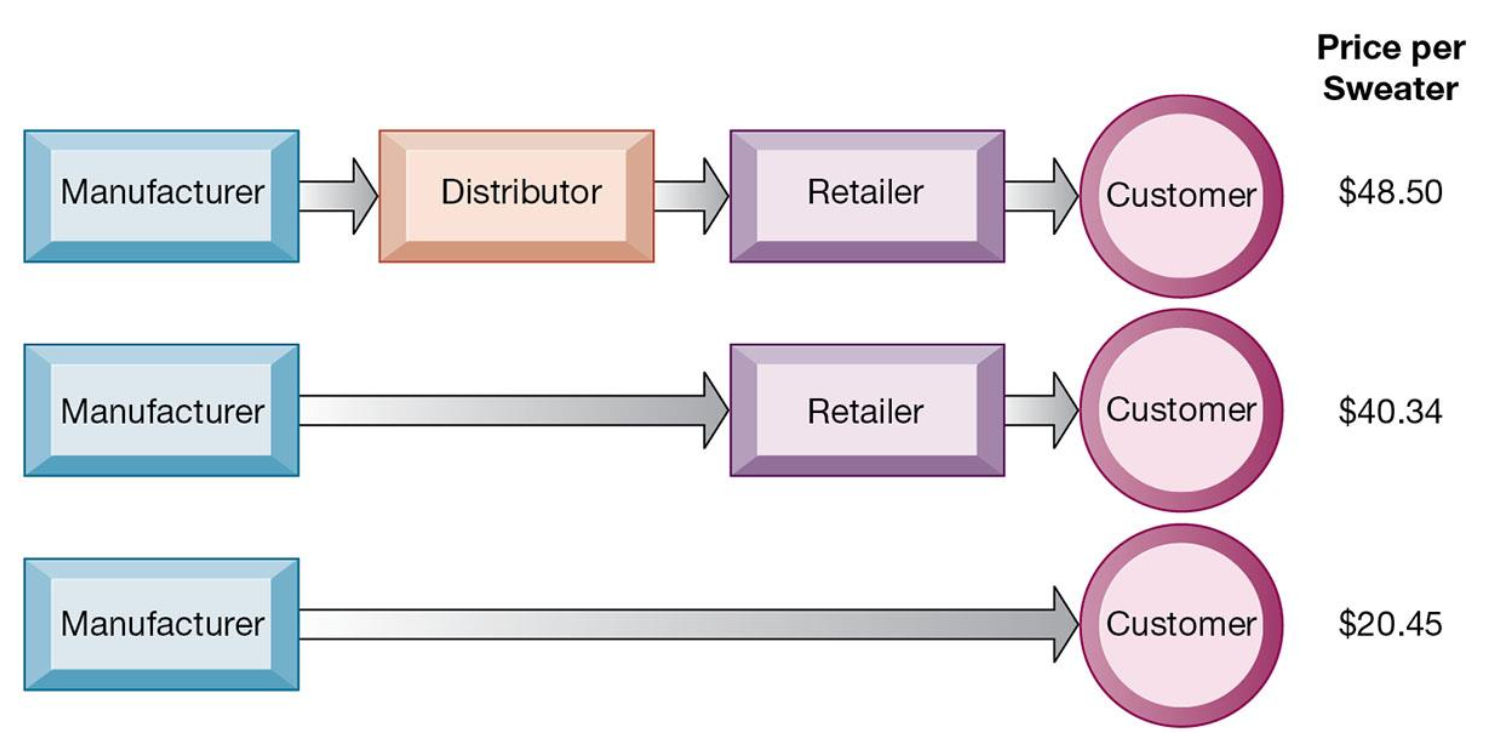
What is disintermediation?
Disintermediation is the elimination of organisational units (e.g., trading levels) or business process steps that are responsible for certain mediation actions in the value chain.
What is reintermediation?
Reintermediation is the shift of the role of intermediary within the value chain to another, new carrier.
What are business models?
Business models describe how a company generates, provides, and distributes products or services, thus demonstrating the company’s contribution to customers and value chains
What is the distribution model and the capital model?
The distribution model depicts which goods are offered or sold via which distribution channels to the customer.
The capital model depicts the financial dimensions of the company. It contains statements about the type and form of financing the company’s activities. The capital model is divided in two:
― The revenue model: describes how a company generates revenue, makes profits and achieves a higher return on investment (ROI).
― The financing model: contains statements about the type and form of financing of the company’s activities.
What revenue models are most commonly used in E-commerce?
― Advertising model: Attract large number of visitors and expose them to advertising (e.g. YouTube).
― Revenue model: Generate revenue by selling goods to customers (e.g. Amazon).
― Subscribers model: Generate revenue through a subscription fee, which allows users to access some or all of the content (e.g. Netflix).
― Free/freemium model: Basic services are free, and more advanced features are locked behind a paywall (e.g. Duolingo).
― Transaction fees model: Companies receive a fee for enabling or executing a transaction (e.g. PayPal):
― Affiliate model: Websites (affiliates) direct visitors to merchant websites and receive a brokerage fee or commission in return (e.g. YouTubers with sponsorships).
What is long tail marketing?
Marketing at all scales and demographics.
What are the different marketing and advertising formats in E-commerce?
―Search
―Display ads
―Video and rich media
What is an example of website visitor tracking?

What is website personalization?
The website is personalized based on the portfolio and recent market trends.

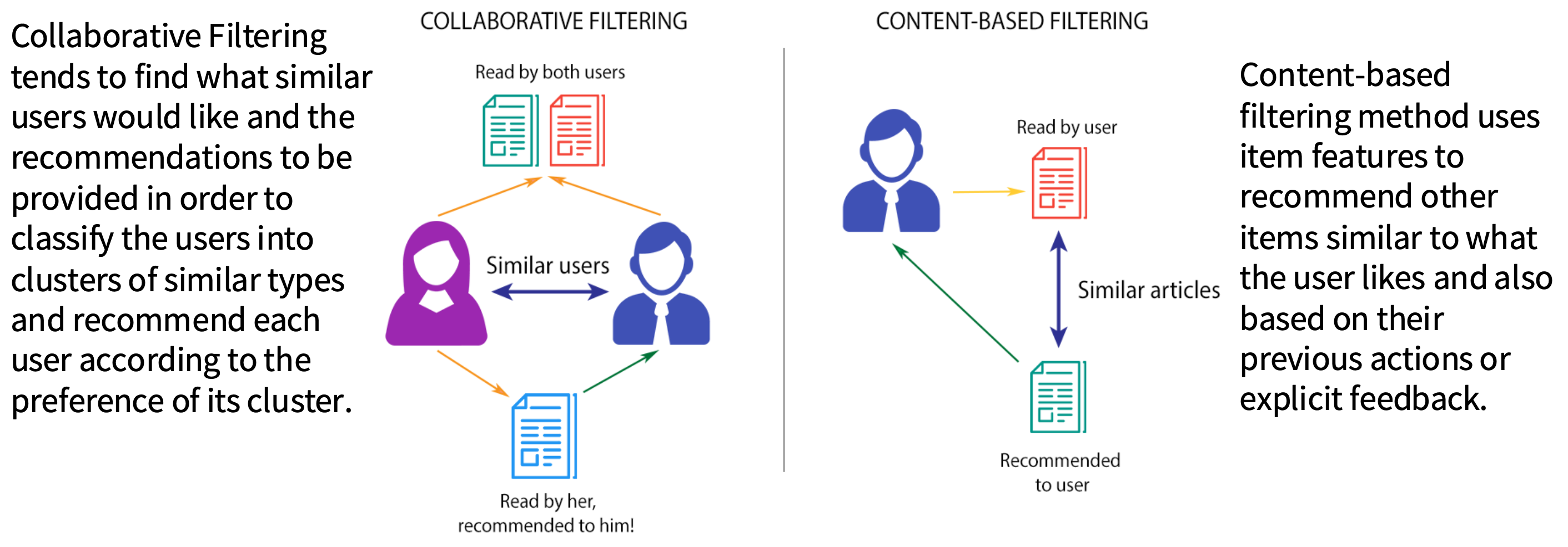
What is collaborative filtering and content-based filtering in recommender systems?
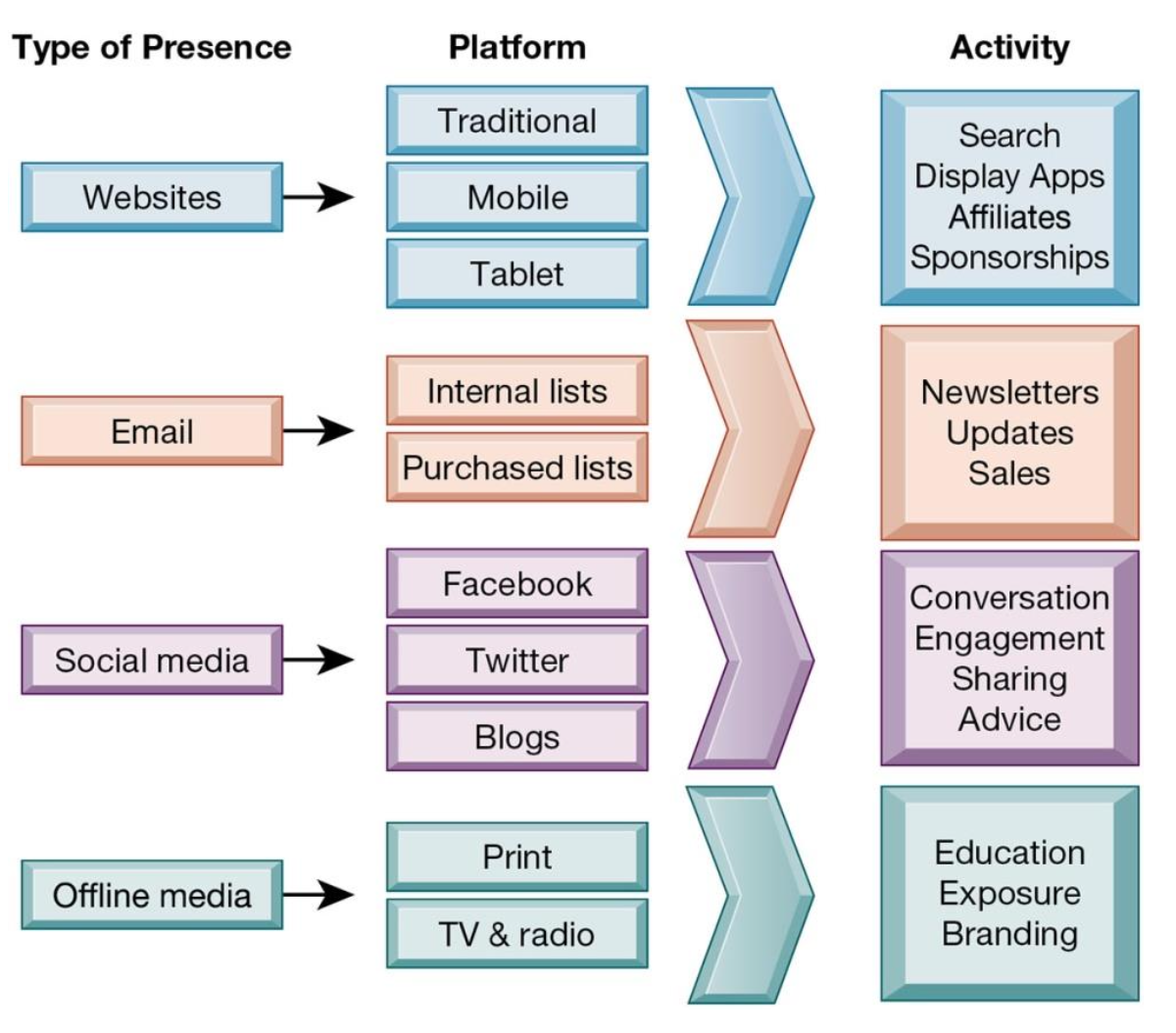
What Issues Must Be Addressed When Building an E-commerce Presence?

What types of presence of an E-commerce are there and what are they used for?