Skeletal System
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
Bone Classification: By Shape
Long - Longer than wide (support mobility, energy storage blood cell)
Short - Cube shaped, stability, limit move, distribute
Flat - provide protection, broad surface, hematopoesis
Irregular - form = function
Sesamoid - pattela, protects tendons, ligaments, from wear and tear
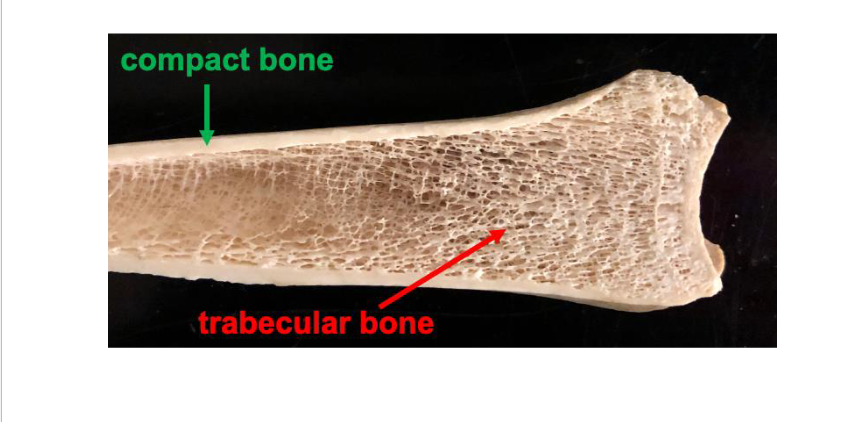
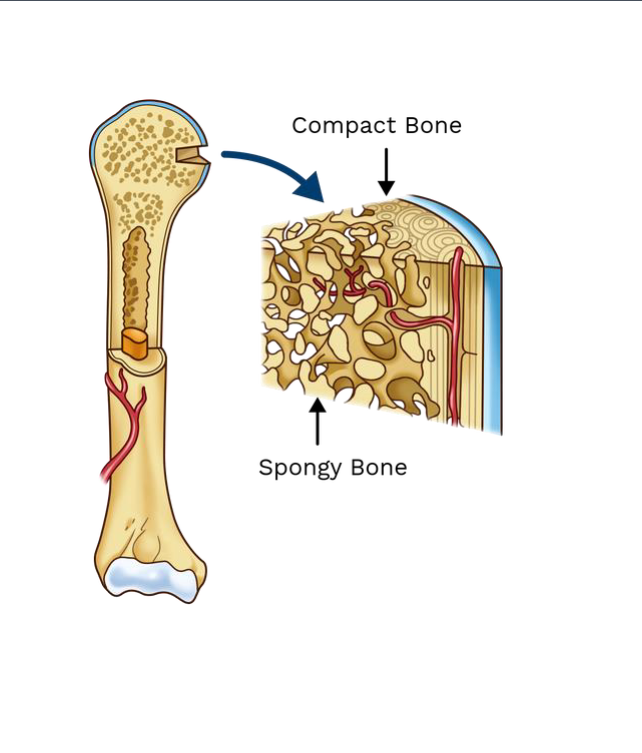
Bone Tissue
Cortical Bone: Compact Bone
Trabecular bone: Spongy Bone
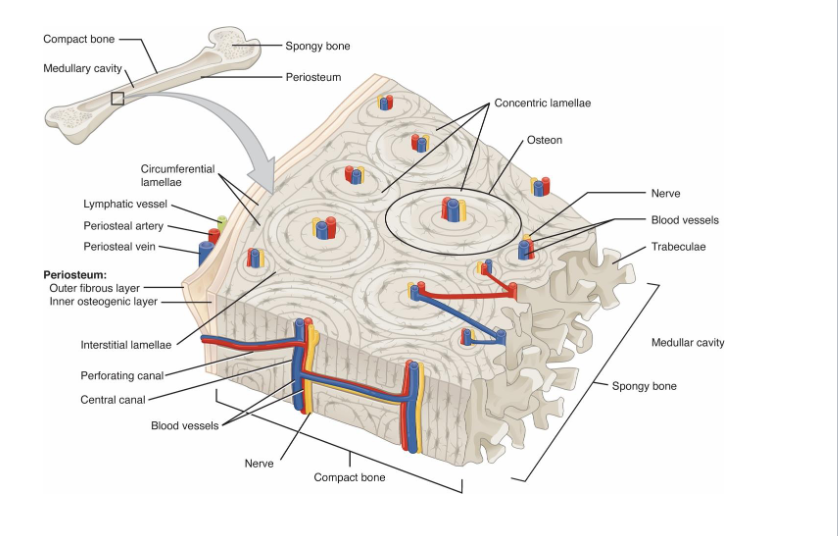
Microscopic Structure of Compact Bone
Osteons: Central Canal, Concentric Lamellae, Lacunae, Canaliculi
Perforating Canals
Compact: Rigid outter shell
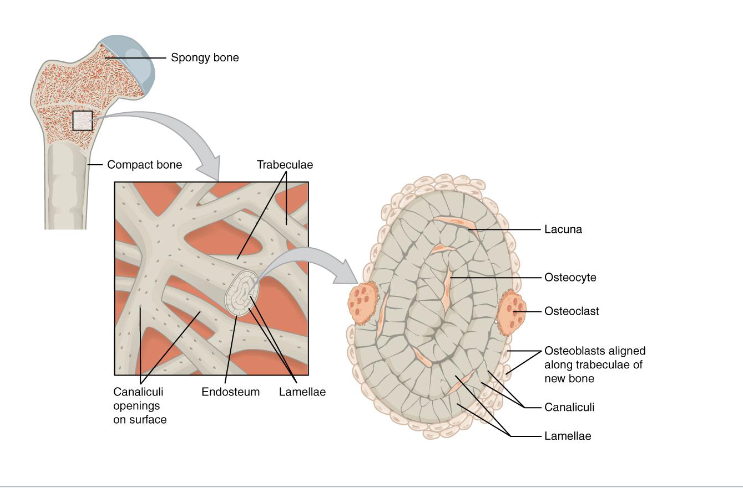
Microscopic Structure of Spongy Bone
Trabeculae and red marrow spaces
Orientation along stress line
Spongy: Distritube forces equally reduces weight, support marrow
Bone is a Type of Connective Tissue
Cells
Gels
Fibers
Bone Cells
Osteoprogenitor cells: Stem cell can become osteoblast
Osteoblast: Build
Osteocytes
Osteoclasts: use enzymes and acids to breakdown bone
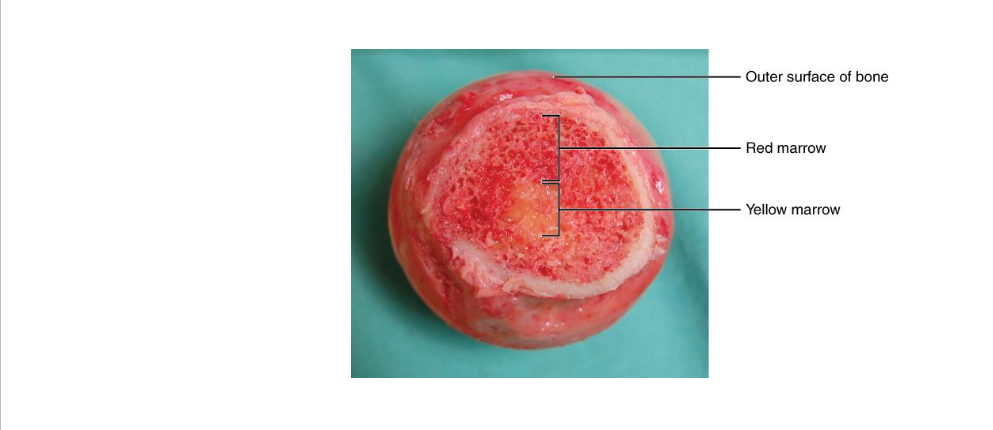
Red Bone Marrow
Function and regulation
Locations in Adults v Infrants
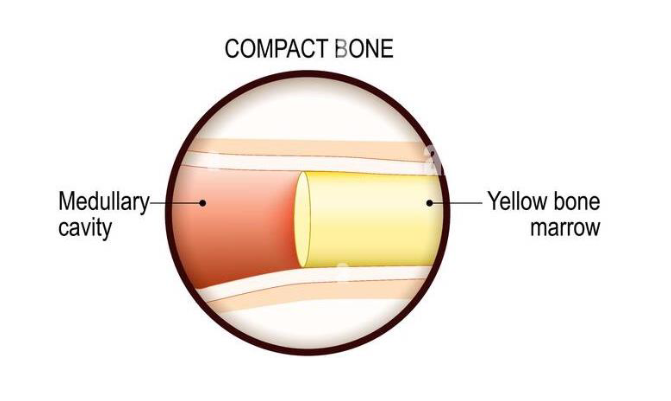
Yellow bone Marrow
Function and Composition
Locations in Adults v Infants
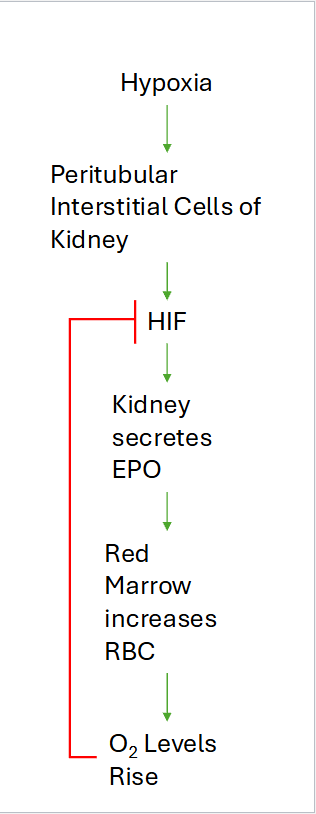
Yellow to Red Conversion
A patient undergoing chemotherapy develops sever anemia and fatigue. Blood tests show a drastic drop in all blood cell types. Which type of bone marrow is most likely affected, and why would chemotherapy case this condition?
Red bones marrow
Red marrow rapid growth
A mountain climber moves from sea level to 12,000 ft elevation for several months. Predcit what happens to the proportion of red and yellow marrow and explain why?
Yellow marrow convert to Red marrow
Red marrow goes up. Yellow Marrow goes down
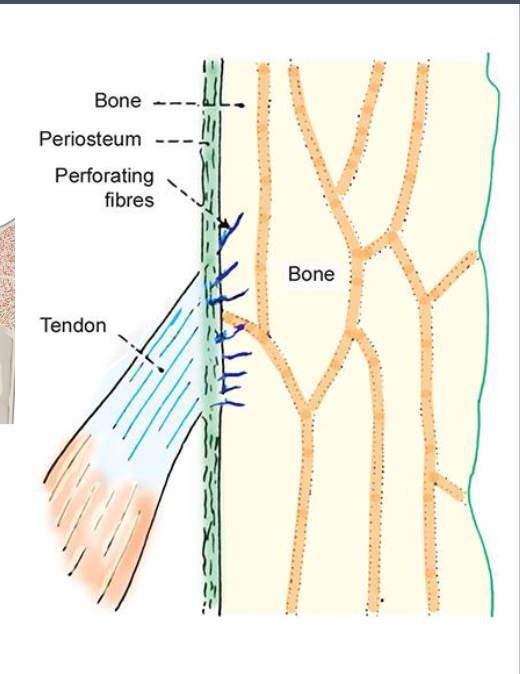
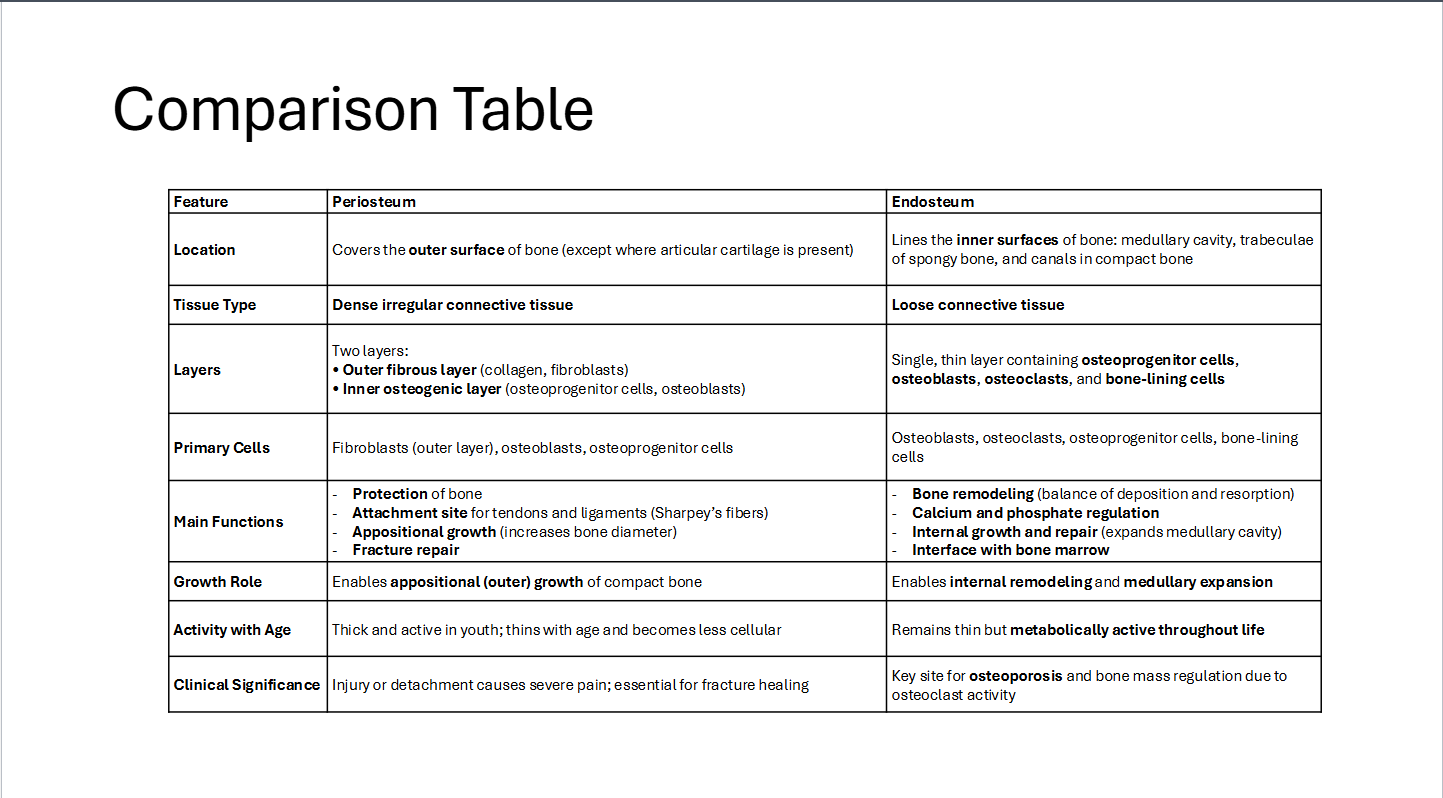
Periosteum and Endosteum
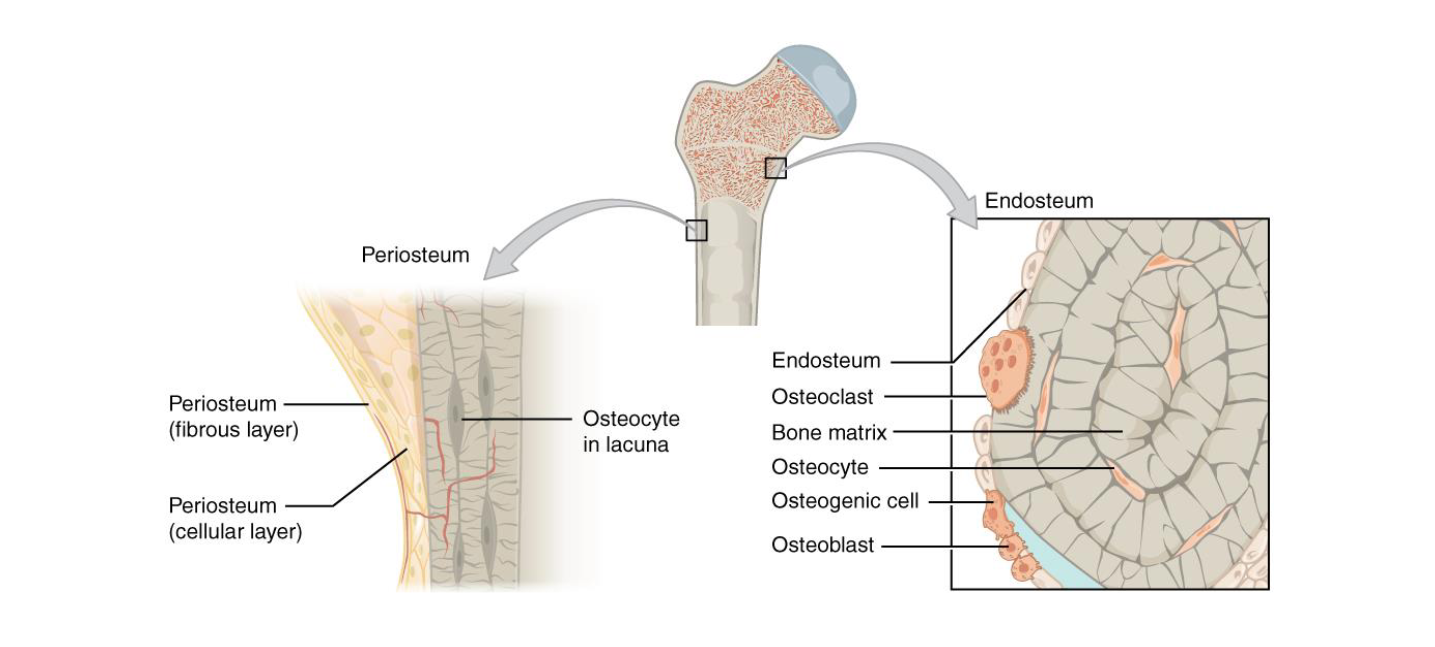
Periosteum
Organization and composition
4 Functions
Appositional growth
Repair
Attachment Site
Protection
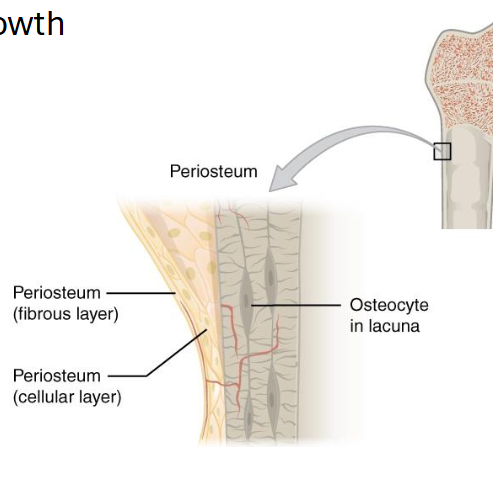
Do you think periosteum is thicker in adults or children?
Children because they still growth
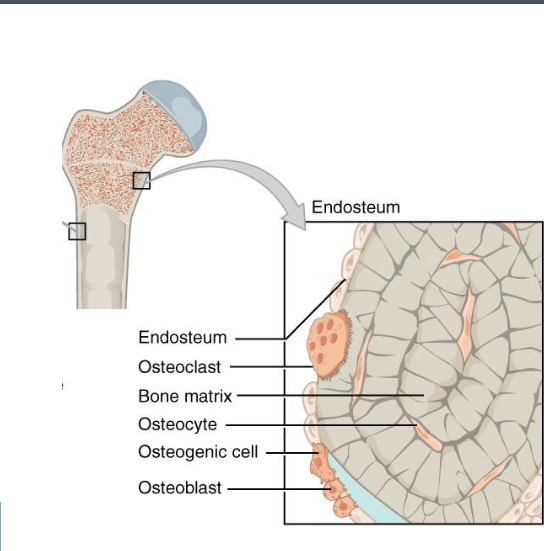
Endosteum
Organization and composition
Function
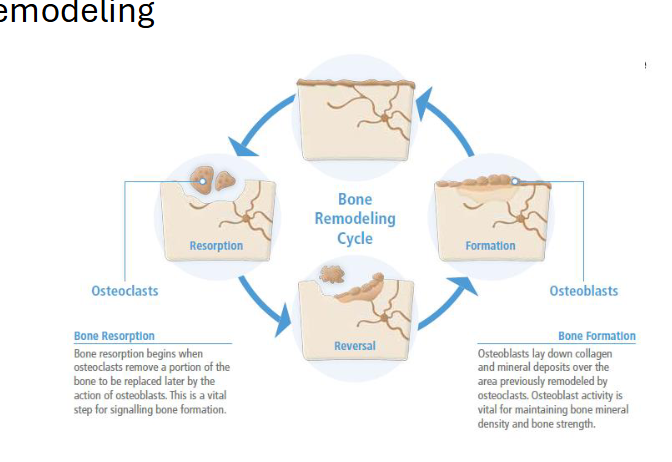
Bone remodeling
Comparison Table
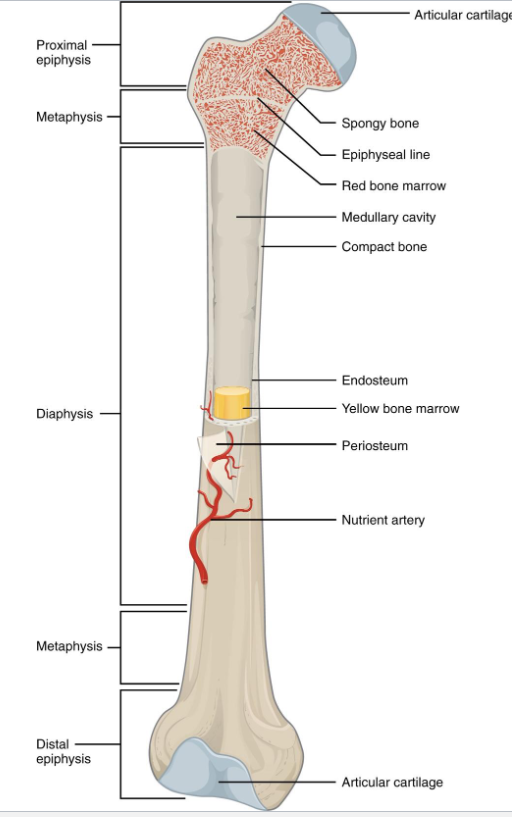
Gross Anatomy of a Long Bone
Diaphysis, Epiphysis, Metaphysis
Medullary cavity, Articular Cartilage
Periosteum, Endosteum
Name two functions of the periosteum
Protection, repair
Which bone cell type is responsible for bone resorption?
Osteoclasts
The periosteum is thick and highly osteogenic in which age group?
Child
What type of bone marrow predominates in infants, and why?
Red because they need to growth
What type of bone marrow predominates in adults, and why?
Yellow to storage energy
The functional signigicance of the medullary cavity is to:
A: Strengthen compact bone
B: Reduce bone mass and store marrow
C: Anchor muscles
D: Provide attachment for ligaments
B: Reduce bone mass and store marrow
Remember when you were younger and you bumped your ankle with your scooter. Why does this cause suck immediate pain even though bone tissue itself isn’t hight innervated?
Periosteum is highly innvervated
In a growing child, why might the periosteum the thicker and more active than in an older adult, even before considering remodeling?
Children are still growth so their bones be thicker