Anatomy 8/21/2023
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
28 Terms
How many pairs of spinal nerves are there?
31 pairs:
8 cervical
12 thoracic
5 lumbar
5 sacral
1 coccygeal
What do typical spinal nerves arise from?
Dorsal and ventral roots connected to the spinal cord
How long is the typical spinal cord?
1-3 mm in length
What happens as the typical spinal nerve exits the intervertebral foramen?
It bifurcates (splits) into ventral and dorsal rami.
What is the significance of L1-L5?
They have to travel more inferiorly to exit since the spinal cord stops growing before the spinal column.
What do ventral root cells bodies arise from?
Grey matter in spinal cord
What kind of fibers do the ventral root contain?
only motor fibers
What does the ventral root do with nerve fibers?
It carries the motor fibers in nature to skeletal muscle and to non-striated muscle and glands
What do dorsal root cell bodies arise from?
Unipolar neurons in spinal ganglia located on dorsal root
What kind of fibers do dorsal roots contain?
only sensory fibers
What does the dorsal root do with nerve fibers?
It carries sensory fibers in nature from the periphery (skin receptors, muscle receptors, joint receptor) to the central nervous system
What kind of fibers comprise of spinal cord?
Both sensory and motor fibers
What kind of fibers comprise of ventral and dorsal rami?
Both sensory and motor fibers
What is the purpose of the dorsal root ganglion?
It is where the dorsal neuron is located
What is the purpose of the dorsal ramus?
It provides motor supply to deep back and sensory supply to back.
If there is pressure on a ventral root...
There could be motor complications
If there is pressure on a dorsal root...
There could be sensory complications
Spinal Membranes & Nerve Roots
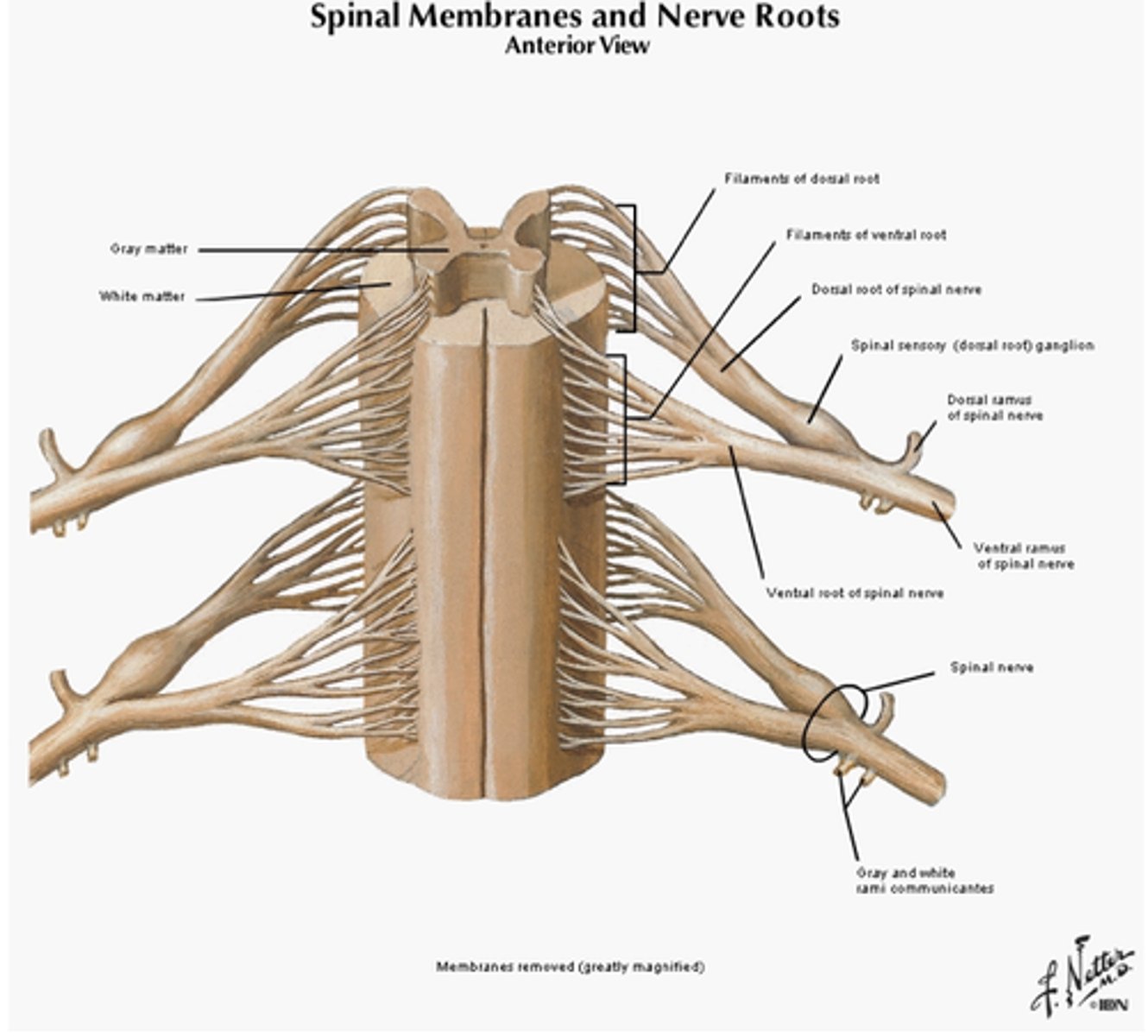
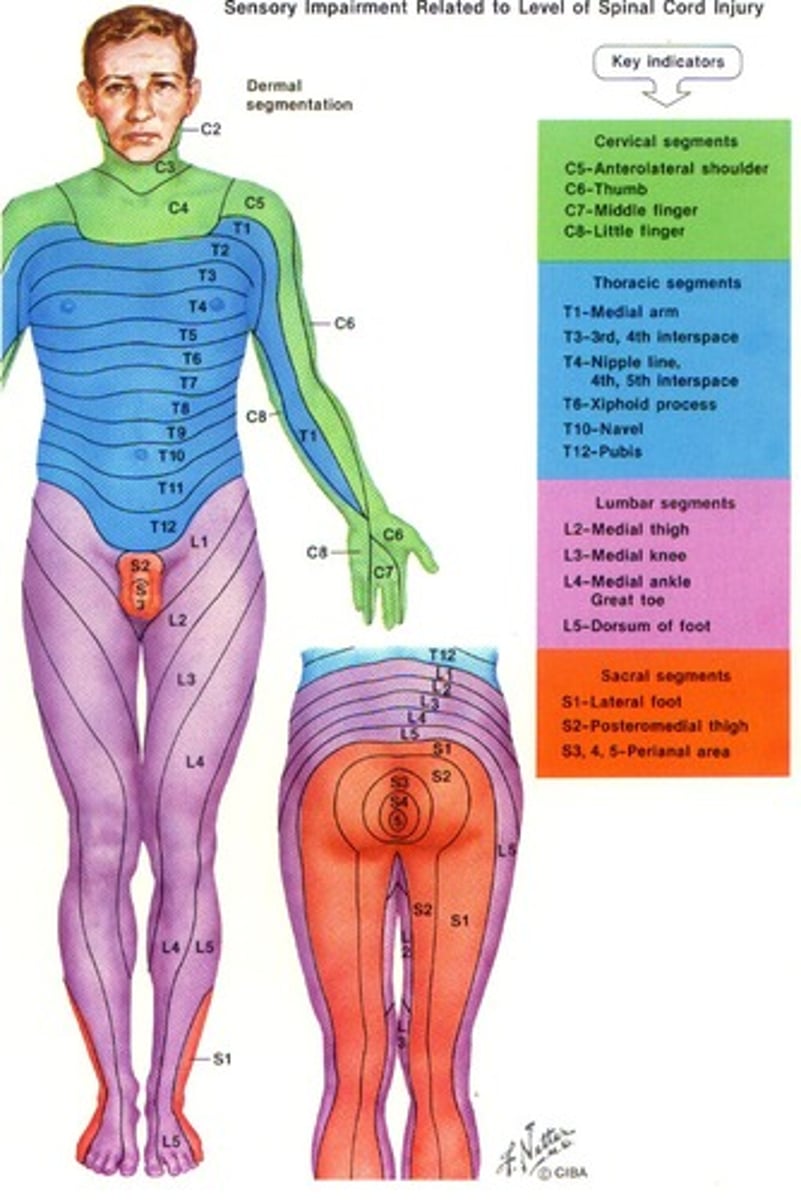
What is a dermotome?
The area of skin supplied with afferent nerve fibers by a single dorsal nerve root and its corresponding spinal nerve
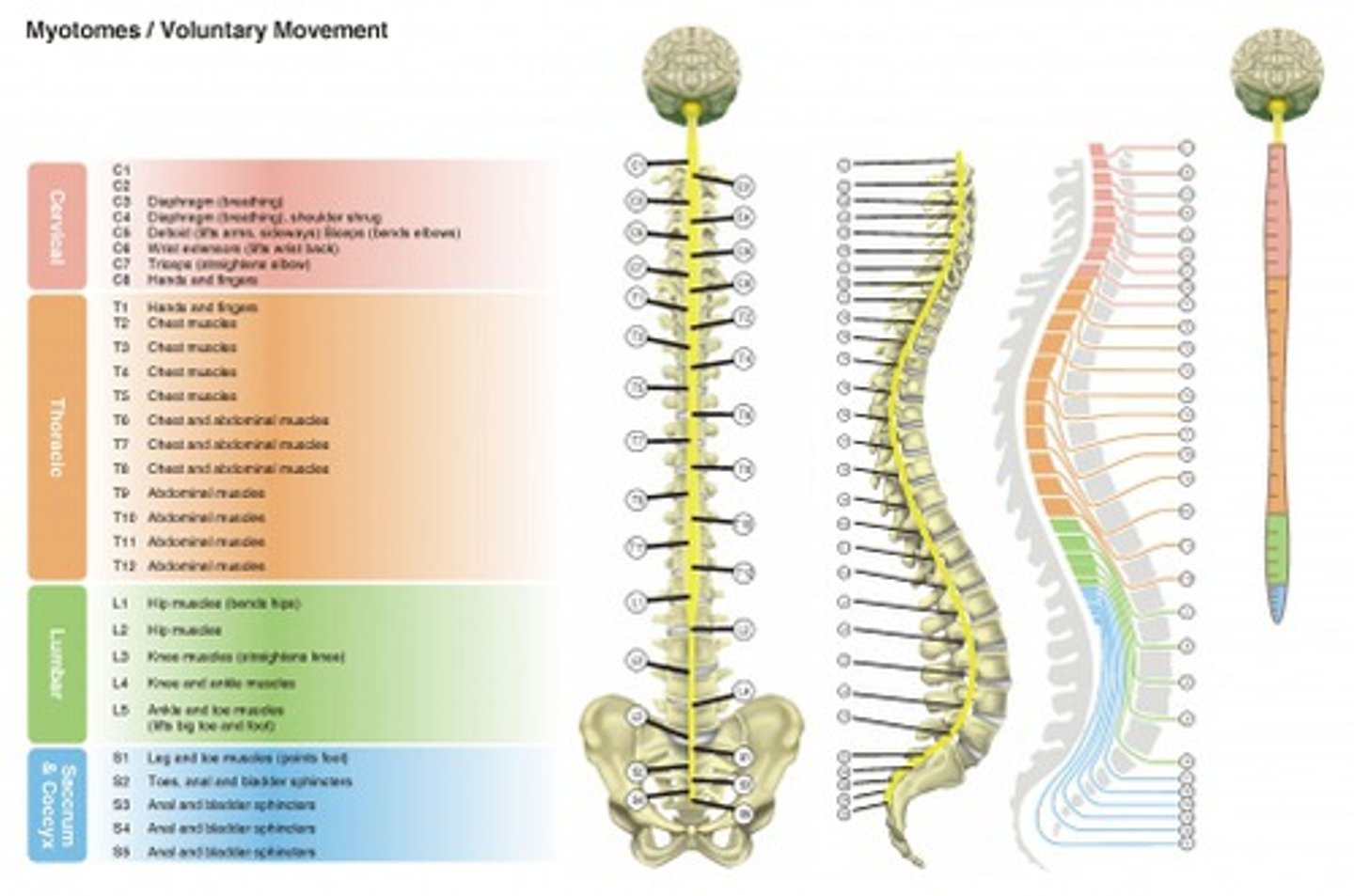
What is a myotome?
A group of muscles innervated by a single ventral root and corresponding spinal nerve. Typically displayed in chart form from listing all of the muscles innervated by a particular spinal nerve.
Sclerotome
An area of bone innervated by a single dorsal nerve root and corresponding spinal nerve
Denervation of...
list muscles innervated by that nerve
Sensory loss to...
describe area supplied by that nerve
What is the neurologic deficit if the musculocutaneous nerve is lesioned?
Denervation of: coracobrachialis m., biceps brachii m., and brachialis m.,
Sensory loss: lateral aspect of forearm
Unable to bend elbow holding anything weighted in hand correlates to...
Severe weakness of elbow flexion
Difficulty turning door knobs and opening jars correlates to...
Moderate weakness of forearm supination
Difficulty lifting arm over head with any weight in arm correlates to...
Slight weakness of shoulder flexion with adduction
No sensation in outer boarder of forearm correlates to...
Pt c/o (complains of) loss of sensation outside surface of forearm