Infections and osteoporosis
1/83
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
84 Terms
Paronychia
A soft tissue infection of the proximal or lateral nail folds that is the MOST common nail infection
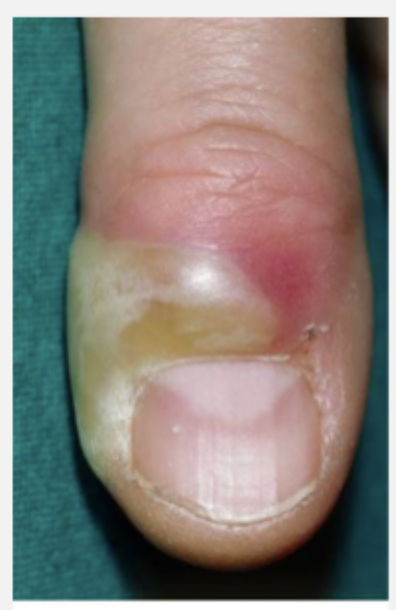
minor trauma (nail biting, picking at hangnail, manicure), staph aureus
Acute causes of paronychia
Repetitive exposure to water or irritants (dishwashers, gardeners, housekeepers), Candida albicans
Chronic causes of paronychia
Warm soaks, oral abx (Clindamycin, augmentin), avoid trauma, I&D with partial/total nail bed removal (since there’s fluctuance)
7 y/o patients presents with pain on the hand. Mother notes that the child has been biting his nails. On physical exam the nail bed is red and swollen TTP, there is fluctuance around the nail and the nail plate is discolored. What is your treatment plan?
Avoid the triggers, topical antifungal (miconazole)
18 y/o male presents to the clinic for hand pain that has been going on the last few weeks. He says that he works as a gardener during the day. On physical exam you note the affected nail fold is swollen and lifted off the plate, as well as nail plate hypertrophy with ridges, and nail fold retraction. What is your non-operative treatment plan?
Nail plate removal
18 y/o male presents to the clinic for hand pain that has been going on the last few weeks. He says that he works as a gardener during the day. On physical exam you note the affected nail fold is swollen and lifted off the plate, as well as nail plate hypertrophy with ridges, and nail fold retraction. Non-operative management is non-successful, what is your treatment plan?
Felon finger
A subcutaneous abscess of the the fingertip pulp that may spread from paronychia OR trauma (splinters, needlesticks)
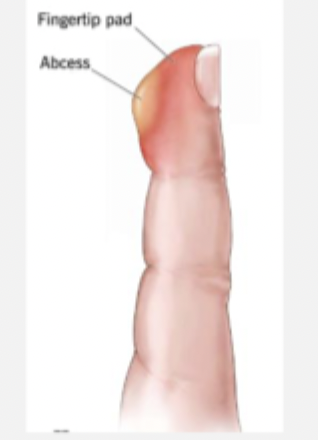
Staph Aureus (m/c), gram neg orgs (immunosuppressed)
What organisms cause felon finger
I&D, abx, maybe hospital admission
45 y/o woodworker presents to the ER for hand pain. He notes that this started a little while after getting a splinter in his finger and describes his pain as throbbing 10/10. On physical exam you note erythema and edema over the distal phalanx proximal to the DIP with localized purulence at finger tip. What is your treatment plan?
oral abx for early, close observation and follow up
45 y/o woodworker presents to the ER for hand pain. He notes that this started a little while after getting a splinter in his finger and describes his pain as throbbing 10/10. On physical exam you note erythema and edema over the distal phalanx proximal to the DIP. What is your treatment plan?
osteomyelitis of distal phalanx, septic joint arthritis of DIP joint, fexor tenosynovitis
Complications of a untreated felon finger
Hx of trauma, r/o fracture/foreign body
When do you need imaging for felon finger
Pyogenic flexor tenosynovitis
A infection along the flexor tendon sheath that can be caused by penetrating trauma over the volar side OR a spread from felon, septic joint, or deep infection
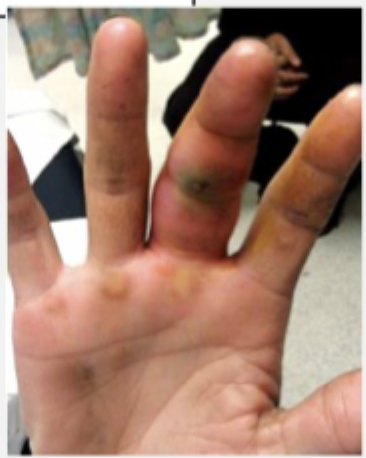
pain with passive extension, held in flexion for comfort, fusiform swelling of finger (sausage digit), tenderness to palpation along the flexor tendon sheath
4 Kanavel’s Signs of Pyogenic flexor tenosynovitis
Admit, splint, elevate, IV abx and observation
34 y/o male presents to ED for finger pain on the 3rd digit. He states that 24-48 hrs ago he was bit by his cat on his hand. On physical exam you note pain is exacerbated by passive extension, fusiform swelling of the finger, and TTP along the flexor tendon. What is your non-op treatment (rare, probably never going to do this…)?
I&D of finger, CALL ORTHO
34 y/o male presents to ED for finger pain on the 3rd digit. He states that 24-48 hrs ago he was bit by his cat on his hand. On physical exam you note pain is exacerbated by passive extension, fusiform swelling of the finger, and TTP along the flexor tendon. 24 hours after trying to go non-op, you see no improvement. What is your operative treatment plan?
Impaired PNM function (hyperglycemia, immunosuppression), Poor wound healing (microvascular complication), ischemia (vascular insufficiency), Charcot neuro osteoarthropathy (peripheral neuropathy)
Why are DM patients prone to infection?
Charcot neuro osteoarthropathy
A progressive, destructive condition affecting the bones, joints, and soft tissues of the foot and ankle
Stage 1 (fragmentation, acute)
Which stage of Charcot neuro osteoarthropathy am I describing - swelling, erythema, warmth, bone resorption
Stage 2 (Coalescence)
Which stage of Charcot neuro osteoarthropathy am I describing - Decreased inflammation, bone healing begins
Stage 3 (reconstruction/chronic)
Which stage of Charcot neuro osteoarthropathy am I describing - foot deformity stabilizes, but there’s permanent structural changes
Foot deformity and ulcer formation (rock-bottom deformity → increased ulcer risk), Loss of protective sensation (patients fail to notice injuries), PVD (reduced blood flow impairs healing), Bacterial entry (chronic ulcers serve as a portal of entry)
How does Charcot foot lead to infection?
Diabetic foot infections
What is the most common medical complication of DM that is ALSO the most common cause of nontraumatic LE amputation?
MSSA, MRSA, polymicrobial, gram neg bacilli
Most common pathogens of diabetic wounds
Plantar wound ulceration, redness, warmth, induration, swelling, often no pain, MALODOR (girl let me tell you)
What clinical findings are you going to see for diabetic wound infections?
CBC, ESR, CRP, HbA1C, Blood cultures (SIRS signs), Transcutaneous oxygen pressures (GOLD STANDARD for evaluating wound healing potential), ABIs, xrays (fragmentation of Charcot, lytic lesions), MRI (osteomyelitis r/o)
What work up do you want for a diabetic foot?
Offloading with total contact casting (TCC) → Charcot restraint orthotic walker (CROW) → custom show (often used for 4 months); get blood sugar under control
Treatment plan for diabetic wound infections
Oral Abx (1-2 weeks of augmentin, keflex (cephalexin), levaquin (levofloxacin)), wound care, pressure off-loading
Treatment for Infected Charcot’s foot - Mild MSSA
Oral Abx (1-2 weeks of Clindamycin, doxycycline, TMP-SMX), wound care, pressure off-loading
Treatment for Infected Charcot’s foot - Mild MRSA
IV Abx (unasyn, Ceftriaxone, clindamycin, pip-taz), wound care, maybe surgery
Treatment for Infected Charcot’s foot - Moderate/severe MSSA
IV Abx (daptomycin, linezolid, VANC), wound care, maybe surgery
Treatment for Infected Charcot’s foot - Moderate/severe MSRA
amputation
Treatment for Infected Charcot’s foot - severe non healing infections
proper foot care, glycemic control, tobacco cessation, prescription custom diabetic insoles, podiatry
Prevention of Charcot’s foot infections
Post-op wound infections
The most common complication following orthopaedic trauma and joint replacement surgery - defined as in infection of the surgical site within 30 days or 90 days if an implant was used
Increases cost of surgery 3x, decreases patient satisfaction, increases morbidity/mortality, prolonged hospital stay
Cons of Post-op wound infections
Chronic medication conditions, open fractures, longer procedure time, 1L+ blood loss, multiple assistants, dirty wounds, previous infections
Causes of Post-op wound infections - usually staph aureus (50% MRSA)
CBC, ESR, CRP (most predictive), X-rays, MRI (only if there’s a concern for deep infections)
Patient presents to the ER for pain over his surgical site. PSHx is positive for a hip replacement 2 weeks ago. He also reports that is is draining. On physical exam you note erythema, drainage, tenderness on palpation, and his hardware is exposed. What diagnostics do you want?
Call ortho, oral abx, wound care
Patient presents to the ER for pain over his surgical site. PSHx is positive for a hip replacement 2 weeks ago. He also reports that is is draining. On physical exam you note erythema, drainage, and tenderness on palpation. What is your treatment plan - let’s say its non-op?
Call ortho, surgical debridement, oral abx (IF hardware is infected use IV abx), wound care
Patient presents to the ER for pain over his surgical site. PSHx is positive for a hip replacement 2 weeks ago. He also reports that is is draining. On physical exam you note erythema, drainage, tenderness on palpation, and his hardware is exposed. What is your treatment plan?
prophylactic abx at time of incision, clean environment, fast, efficient surgeon with a good assistant, medical optimization of ill patients
How do you prevent post-op wound infections?
Necrotizing fasciitis
A life threatening bacterial deep soft tissue infection that rapidly spreads along the fascial planes that can develop quickly and have high morbidity/mortality if not found promptly
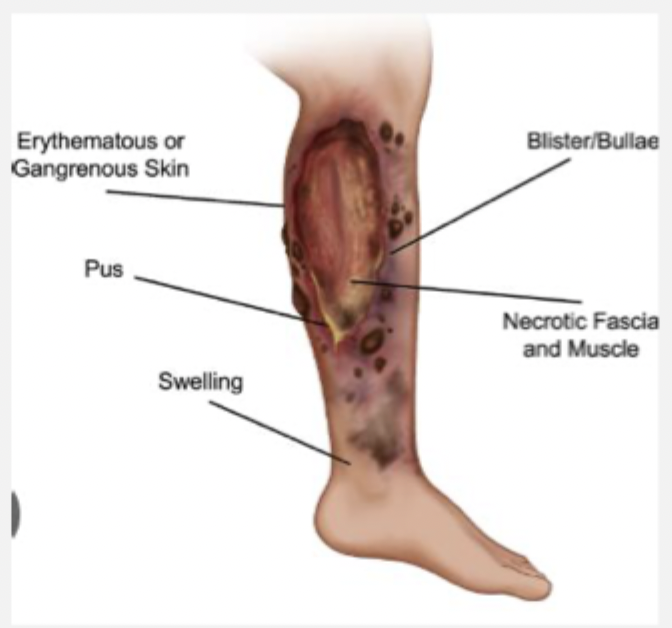
recent surgery, DM, trauma, IV drug use
Risk factors for Necrotizing fasciitis
Strept pyogenes (group A strep - m/c), staph A, clostridium perfringens (Gas gangrene), vibrio vulnificus (salt water exposure)
Common bacterial causes of Necrotizing fasciitis
CBC (wbcs), CMP (BUN, creat), Coags (DIC r/o), Xray, CT (most helpful), LRINEC score
35 y/o patient presents to the ED for leg pain. He states that he was out surfing yesterday and caught his leg on his board. Vitals are as follows, 90/63, 134 bpm, 103.5 temp. On physical exam you note blackish blisters on the skin that when pressed feel like rice krispies - when you do this your patient screams. What diagnostics do you want?
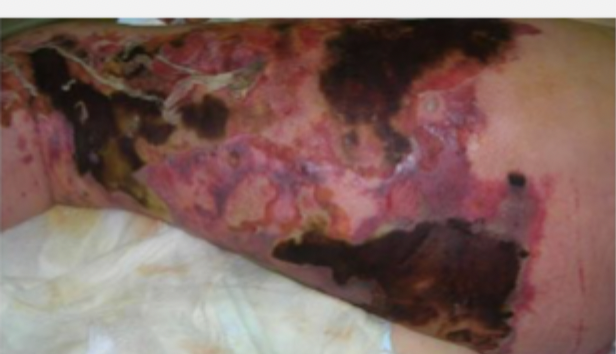
Emergency radial debridement + IV broad spectrum (pen, clinda, metro, AMG), extremity amputation
35 y/o patient presents to the ED for leg pain. He states that he was out surfing yesterday and caught his leg on his board. Vitals are as follows, 90/63, 134 bpm, 103.5 temp. On physical exam you note blackish blisters on the skin that when pressed feel like rice krispies - when you do this your patient screams. Labs reveal leukocytosis and AKI. CT shows thickening of the fascia as well as bubbles along the fascial planes. What is your game plan?
hematogenous spread, contiguous spread from local infection, direct inoculation from penetrating trauma (iatrogenic)
How do bones get infected
Staph A (most common), salmonella (sickle cell), pseudomonas (DM or IV drug users)
Pathogens for osteomyelitis
recent trauma or surgery, open, immunocomp, hx of IV drug use, tobacco use, PVD, DM, chronic non-healing wound
Risk factors for osteomyelitis
Acute (under 2 weeks, rapid), Chronic (more than 6 weeks, necrotic bone), vertebral (IV drug use)
Classifications of osteomyelitis
CBC (WBC), ESR, CRP (most sensitive), Blood cultures, X-rays, MRI (most sensitive), Bone biopsy and culture (GOLD STANDARD)
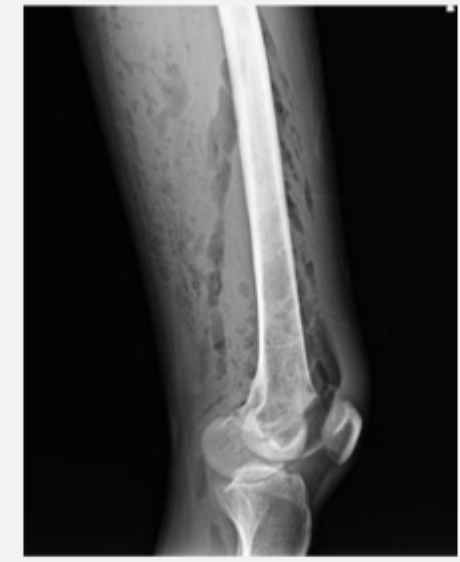
45 y/o male presents to the ED with hand pain. On physical exam you note tenderness over the thumb that is red and swollen with a small open wound. Vitals are stable with an exception of a fever. What diagnostics you want?
Surgical debridement + IV abx (Vanc or pip-taz) through a PICC line 6 weeks (tailor to culture results); may require amputation
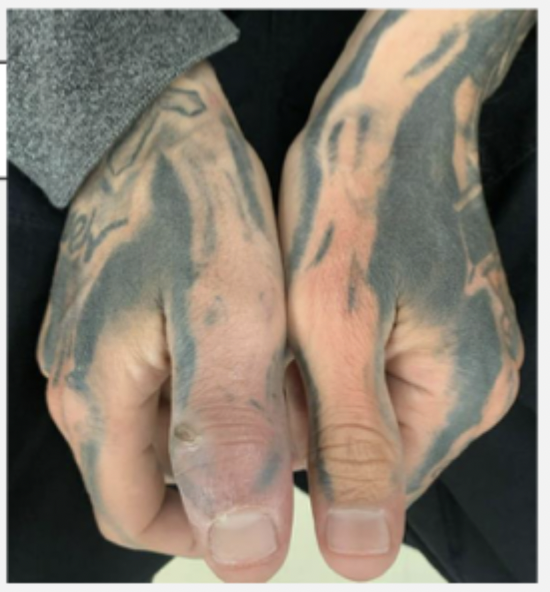
45 y/o male presents to the ED with hand pain. On physical exam you note tenderness over the thumb that is red and swollen with a small open wound. Vitals are stable with an exception of a fever. Xrays show bone lucency, sclerosis, erosive changes, and periosteal reactions. MRI shows edema in T2 imaging. What is your treatment plan?
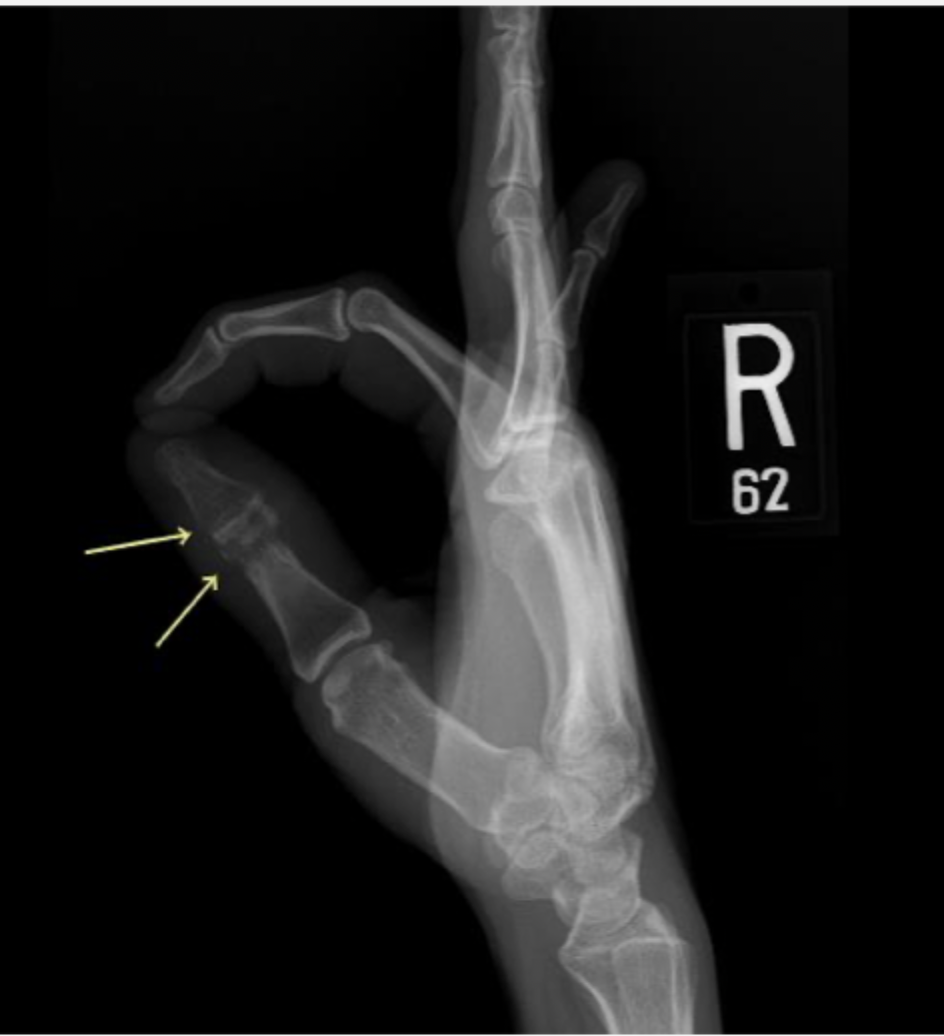
Suppressive Abx (Call ID)
45 y/o male presents to the ED with hand pain. On physical exam you note tenderness over the thumb that is red and swollen with a small open wound. Vitals are stable with an exception of a fever. Xrays show bone lucency, sclerosis, erosive changes, and periosteal reactions. MRI shows edema in T2 imaging. Homeboy does NOT want surgery, utterly refuses it. What is your treatment plan?
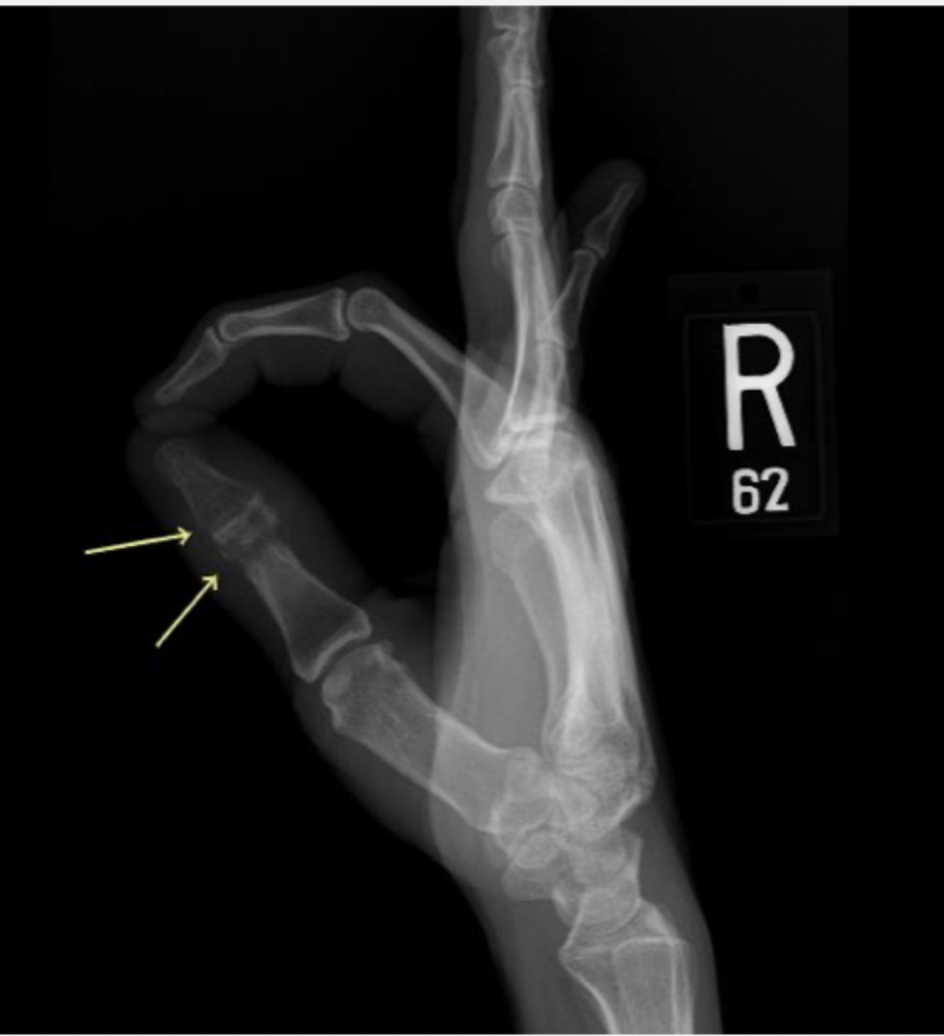
septic joint infection
Inflammation of a joint space due to infection - most commonly the knee (m/c), hip, shoulder, SI (IV drug use)
Staph A (most common), Neisseria gonorrhoeae (sexually active young adults), pseudo (IV drug use)
Common pathogens of septic joint infections
Hematogenous spread (other site, IV drug use), direct inoculation, contiguous spread
How does the bacteria get into the joint in a septic joint infection
CBC, ESR, CRP, Joint aspiration (gold standard - get a cell count (50 K), gram stain culture, crystals, culture), Xray, MRI (osteomyelitis r/o)
Patient presents to the ER for knee pain. The knee is swollen, bright red, warm and tender to the touch. The patient was brought in in a wheelchair as it is SO painful to walk and the patient cannot tolerate passive range of motion. What diagnostics you want?
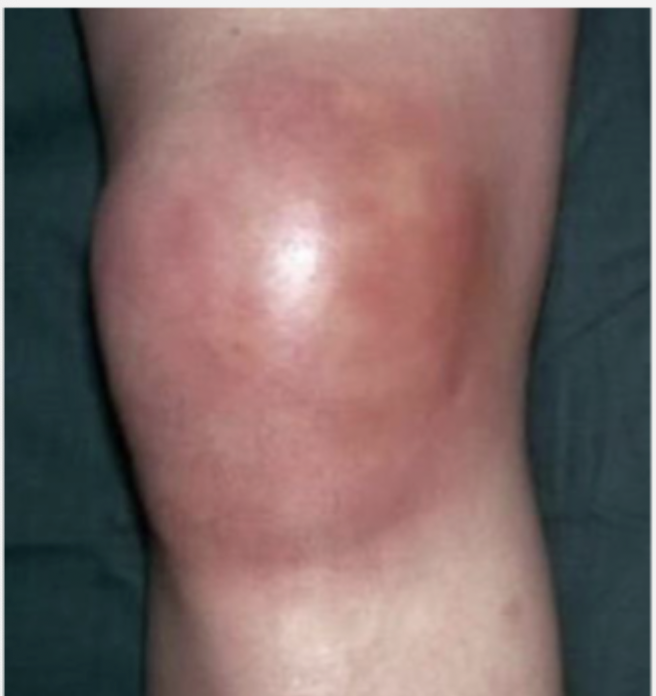
Surgery, irrigation and debridement of the infection joint with intraoperative cultures, broad spectrum abx until cultures get back (AFTER op)
Patient presents to the ER for knee pain. The knee is swollen, bright red, warm and tender to the touch. The patient was brought in in a wheelchair as it is SO painful to walk and the patient cannot tolerate passive range of motion. There’s 50K cells in the joint fluid and leukocytosis. What is your treatment plan?
profound, extensive cartilage damage (septic arthritis), joint destruction, osteomyelitis, sepsis
Septic joint can have complications in 8 hours what are they?
Osteoporosis
A disease of progressive bone loss associated with an increased risk of fractures - most common metabolic bone disease
Age, menopause, metabolic abnormalities (thyroid), female (4x)
etiology of osteoporosis
person hx of prior fx, age, estrogen deficiency, female, white, low BMI, family hx
Risk factors of primary osteoporosis
wrist (50-60 yrs), vertebral (60-70), hip (70-80)
Common osteoporotic fractures
glucocorticoids, long term thyroid replacement therapy, anticonvulsive therapies, smoking, EtOH, sedentary lifestyle
Risk factors of secondary osteoporosis
HISTORY, CBC, CMP (calcium), Vitamin D level, thyroid stimulating hormone, sex hormone levels, PTH
What is used to diagnose osteoporosis?
Bone mineral density (BMD)
An indirect indicator of bone quality and strength (quantity of Ca2+ per unit of bone)
xrays, CTs, nuclear med (decreased radiodensities), DEXA (most effective, most accurate, least radiation - do before a bone breaks)
BMD is measured by
lumbar spine (L1-L4), Hip (femoral neck, trochanter region, total hip, Ward’s triangle), wrist (1/3 distal end of the radius)
Where does a DEXA scan measure
T score
Which DEXA score compares a patient’s bone density with that of a young adult - are they healthy, low, or nah
Z score
Which DEXA score compares a patient’s bone density with that of other patients matched for age, race, and sex - for the peds
less than -2.5 (-1- -2.5 is osteopenic; if there’s fragility fractures than its severe)
A DEXA T score of what is considered osteoporosis (greater than -1 is normal)
Women over 65, men over 70, post menopausal women and men 50-69 with low BMI, past hx of fracture, meds that increase bone loss, disease/conditions that increase bone loss; broken bones after age 50, monitor treatment effectiveness
Recommendations for BMD test
1-2 after starting/changing medications, 1-2 years in a patient not being treated
When should a BMD be repeated
Fracture risk assessment tool (FRAX)
What tool can be used to predict fracture risk of patients
Vitamin D (800-1000 IU), calcium (1000-2000 mg/day)
Non-pharm treatment for osteoporosis
Postmenopausal women and men over 50 with T score less than -2.5 OR osteopenic with a 3% 10 yr risk of hip fractures
Whose getting drugs for osteoporosis for primary fracture prevention
fracture of spine or hip, fracture of proximal humerus, pelvis, distal radius if osteopenic
Whose getting drugs for osteoporosis for secondary fracture prevention
Bisphosphonates (take with full glass of water 1st thing in the morning, sit up for 30-60 min, for 3-5 years)
1st line pharm therapy for osteoporosis that decreases osteoclast reabsorption and increase their apoptosis
vertebral; ibandronate
All bisphosphonates have been shown to reduce _______________ in the 1st year, all except __________ reduce non-vertebral or hip fracture risk
Esophageal disorders, gastric disorders (gastric bypass), inability to maintain upright 30 min after taking the medication, CKD (GFR between 35-39), allergy, hx of atypical femur fracture or jaw necrosis secondary to bisphosphonates
C/I to oral bisphosphonates
Atypical femoral fracture (subtrochanteric and femoral shaft region), osteonecrosis of the jaw
Complications of bisphosphonates
beaking (localized cortical thickening), arises from minimal or no trauma, prodromal pain before the fracture, hx of bisphosphonate use
How do you tell its a atypical femoral fracture
Teriparatide (1x daily injection, T score under -3.5, multiple fractures, increases osteosarcoma risk)
A synthetic form of PTH that is used for treat osteoporosis by stimulating the formation of new bone (decreases vertebral and nonvertebral)
Denosumab (SC injection q 6 months by health care professional, rare cases of AFF and ONJ, watch kidneys due to hypocalcemia)
A mab that inhibits RANKL to decrease bone reabsorption - good for peeps who cannot tolerate orals but have high fracture risk
diet with adequate calcium and vitamin D, physical activity, avoid protein malnutrition, participate in regular weight bearing activity, avoid all smoking - even 2nd hand, avoid heavy and regular drinking
Ways to prevent osteoporosis