mucogingival defects
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
27 Terms
Examples of MGD
Gingival/soft tissue recession
Lack of keratinized gingiva (<1mm)
Decreased vestibular depth
Periodontal probe extends to or past MGJ
Aberrant frenum/muscle position/attachment (pull) Gingival excess
Abnormal colo
normal mucoginival condition has an abscess of what
disease state
if the patient has lack of keratinized tissue is it always a mucogingival defect?
NO, Commonly observed in absence of underlying disease state
if the patient has Aberrant frenum and decreased vestibular depth is it always a mucogingival defect?
no
what is the periodontal biotype influenced by ?
genetics and environment
periodontal biotype include what
gingival biotype, bone morphology, and tooth dimension
thin scalloped
Slender, triangular-shaped crown
Thin, delicate, friable (tears/bleeds easily) soft tissue with thin alveolar bone
Narrow zone of keratinized tissue
Accentuated scalloped gingival margin contour
what biotype has Greater tendency for onset, progression of mucogingival deformity
thin scalloped
thick scalloped
Slender, triangular-shaped crown
Thick, fibrotic gingiva
Narrow-to-moderate zone of keratinized tissue
Accentuated scalloped gingival margin contour
which biotype is Prone to development of mucogingival deformity
thick scalloped
thick flat
Wide, square-shaped crown
Thick, dense, and fibrotic tissue
Wide band of keratinized tissue
Flat gingival margin contou
what biotype is More resilient and less susceptible to inflammation and trauma than thin- and thick- scalloped biotypes
thick flat
how many different biotypes can one person have in their mouth?
any amount. Varies among different teeth
thick flat

thick scalloped
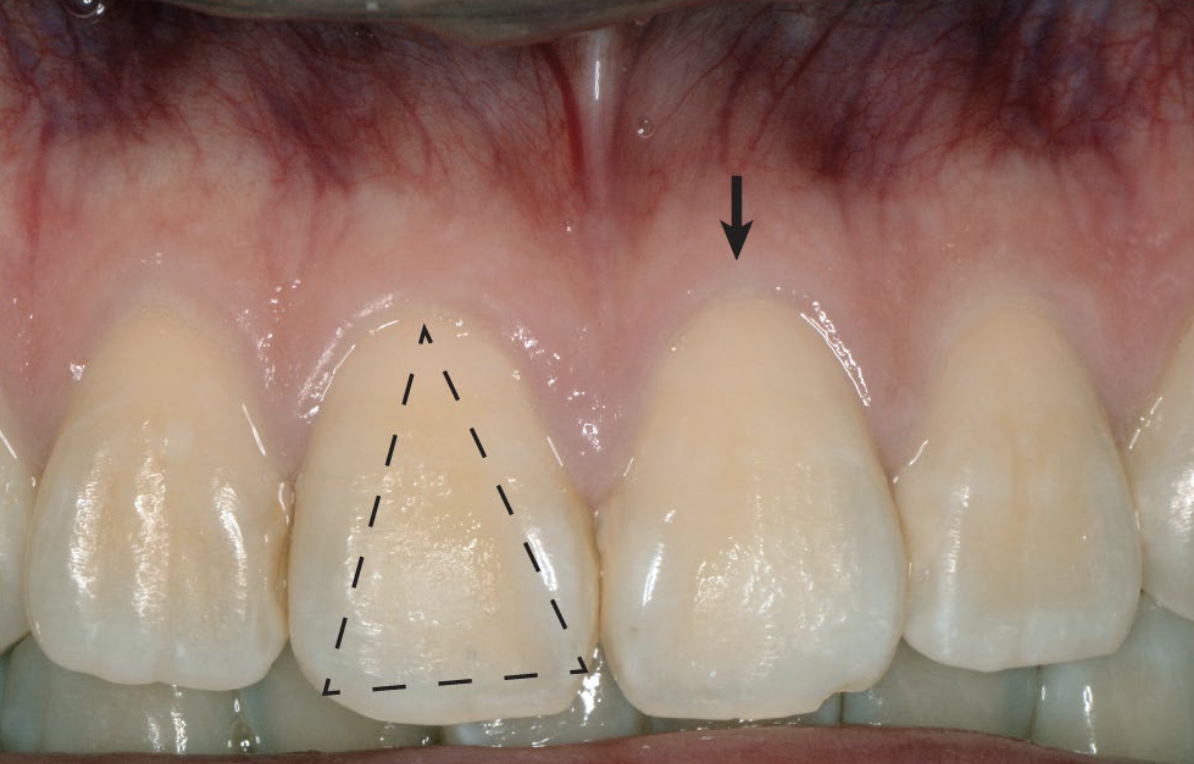
thin scalloped
what tissue type is a risk factor for recession
thin tissue biotype
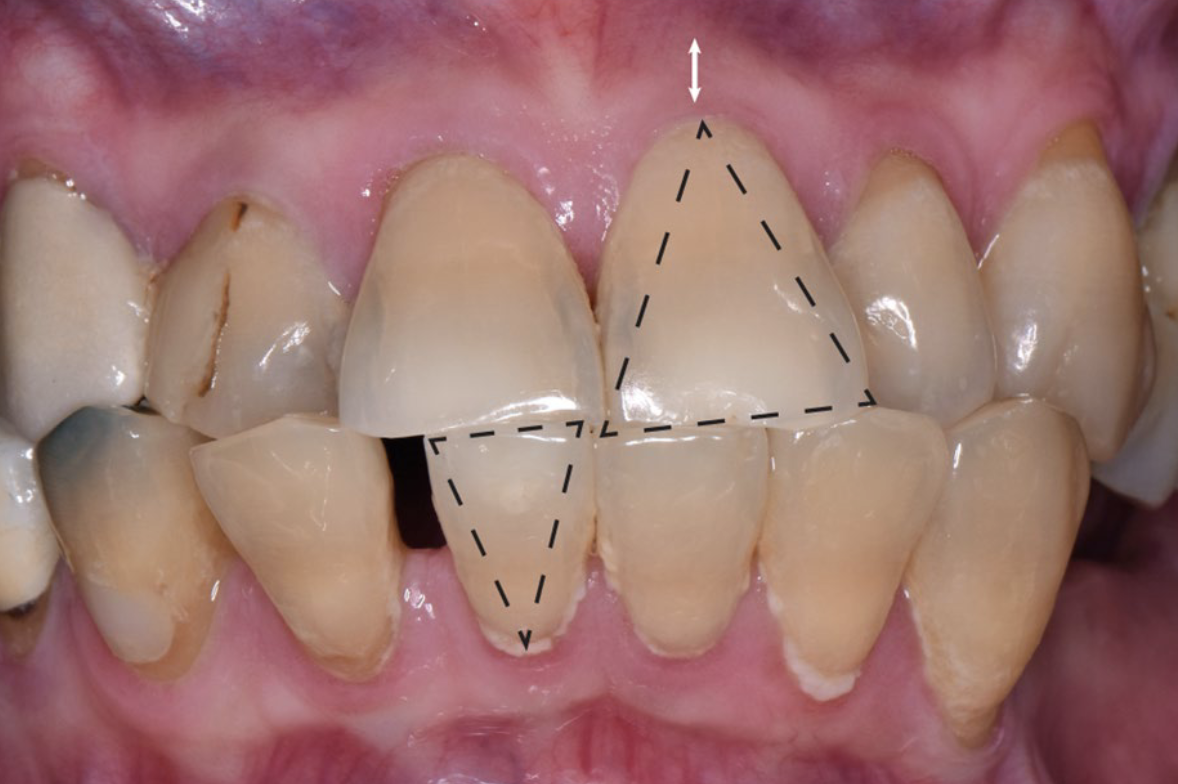
Miller classification
Based on level of gingival margin with respect to mucogingival junction and underlying alveolar bone
issue with the miller
Does not clearly define amount of interproximal soft/hard tissue loss needed to differentiate Class III from Class IV
miller class 1
Marginal tissue that does not extend to mucogingival junction
miller class 2
Marginal tissue recession that extends to or beyond MGJ with no periodontal loss in interdental area
miller class 3
Marginal tissue recession that extends to or beyond MGJ with interdental bone or soft-tissue loss and/or malpositioning of teeth
miller class 4
Marginal tissue recession that extends beyond MGJ with severe loss of interdental bone to level corresponding to most apical extent of marginal tissue recession
cairo
Uses objective identifiable criterion (clinical attachment level) to classify extent and severity of soft tissue recession
cairo type 1 (RT1)
Gingival recession with no loss of interproximal attachment
cairo type 2 (RT2)
Gingival recession with loss of interproximal attachment
Amount of interproximal attachment loss less than or equal to buccal attachment loss
cairo type 3 (RT3)
Gingival recession with loss of interproximal attachment
Amount of interproximal attachment loss greater than buccal loss