Chemistry - SL Stoich Formulas & Equations
0.0(0)Studied by 5 people
Card Sorting
1/28
Earn XP
Description and Tags
definitons + formulas and some bonding stuff
Last updated 6:08 AM on 4/22/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
29 Terms
1
New cards
covalent molecular
* doesn’t conduct electricity
* soft
* low melting/boiling points
* soft
* low melting/boiling points
2
New cards
covalent network
* doesn’t conduct electricity
* hard substance
* no free moving charged particles
* high melting point/boiling point (many covalent bonds need to bebroken)
* hard substance
* no free moving charged particles
* high melting point/boiling point (many covalent bonds need to bebroken)
3
New cards
metallic bonding
* conducts electricity well
* malleable
* usually high melting/boiling points
* conducts heat well
* malleable
* usually high melting/boiling points
* conducts heat well
4
New cards
ionic bonding
* metal and non-metal bonding
* transfer of electrons
* high melting/boiling point
* can conduct electricity **only in molten state**
* transfer of electrons
* high melting/boiling point
* can conduct electricity **only in molten state**
5
New cards
covalent bonding
* non-Metals ONLY
* SHARING of electrons
* SHARING of electrons
6
New cards
Reactions in which elements burn in air or oxygen
* element + oxide (g) → elemental oxide (s)
* eg. Lithium (s) + Oxide (s) → Lithium Oxid (s)
* eg. Lithium (s) + Oxide (s) → Lithium Oxid (s)
7
New cards
Combustion
1. Hydrocarbon + Oxygen -→ Carbon Dioxide + Water
2. eg. ethene + oxygen → carbon dioxide (g) + water (l/g
\
8
New cards
==**Reactive**== Metal + Water
* Metal + Water → Metal Hydroxide (aq)+ Hydrogen
* Potassium + Water → Potassium Hydroxide (aq) + Hydrogen (g)
* 2K (g)+ 2H2O (l) → 2KOH(aq) + H2 (g)
* Potassium + Water → Potassium Hydroxide (aq) + Hydrogen (g)
* 2K (g)+ 2H2O (l) → 2KOH(aq) + H2 (g)
9
New cards
Metal + Acid (metal hydroxide or oxide)
* metal + acid → Salt + Water
* zinc + hydrochloric acid → Zinc chloride (aq) + Water (l)
* Zn + 2HCI → ZnCl2 (aq) + H2O (l)
\
* zinc + hydrochloric acid → Zinc chloride (aq) + Water (l)
* Zn + 2HCI → ZnCl2 (aq) + H2O (l)
\
10
New cards
Acid + Base (carbonate/hydrocarbonate)
* Carbonate + Acid → salt + carbon dioxide + water
* calcium carbonate (s) + nitric acid (aq) → calcium chloride (aq) + Carbon dioxide (g) + water (l)
* CaCO3 (s) + HNO3 (aq) → CaCl2 (aq) + CO2 (g) + H2O (l)
\
* calcium carbonate (s) + nitric acid (aq) → calcium chloride (aq) + Carbon dioxide (g) + water (l)
* CaCO3 (s) + HNO3 (aq) → CaCl2 (aq) + CO2 (g) + H2O (l)
\
11
New cards
Generally Soluble IONS (no exceptions)
* Na (+)
* NO3 (-)
* NH4 (+)
* K (+)
* CH3COO (-)
* NO3 (-)
* NH4 (+)
* K (+)
* CH3COO (-)
12
New cards
Generally Soluble - Cl (-), Br (-), I (-)
Exceptions: Ag (+) , Pb (+)
13
New cards
General soluble SO4 (2-), Cr2O7 (2-)
Exceptions:
* Pb (2+)
* Ba (2+)
* Ag (+)
* Ca (2+)
* Pb (2+)
* Ba (2+)
* Ag (+)
* Ca (2+)
14
New cards
Generally @@insoluble -@@ CO3 (2-), PO4 (3-), S (2-)
Exceptions:
* NA (+)
* K (+)
* NH4 (+)
* NA (+)
* K (+)
* NH4 (+)
15
New cards
Generally Insoluble - OH (-)
Exceptions:
* Na (+)
* K (+)
* NH4 (+)
* ^^Ba (2+)^^
* ^^Ca (2+)^^
* Barium & Calcium are soluble with hydroxide ONLY
\
* Na (+)
* K (+)
* NH4 (+)
* ^^Ba (2+)^^
* ^^Ca (2+)^^
* Barium & Calcium are soluble with hydroxide ONLY
\
16
New cards
NA
* Avagadros Constant
* 6.02 x 10^23
* 6.02 x 10^23
17
New cards
Significant figures:
How many dp’s are used in the final anser of addition & subtraction
How many dp’s are used in the final anser of addition & subtraction
no more dp’s than the term with the l**east number of dp’s**
18
New cards
Rounding should always be…
last step
19
New cards
Significant Figures:
How many dp’s does multiplication/division - final answer
How many dp’s does multiplication/division - final answer
same as the factor with the least number of figures
20
New cards
Definition of a mole
A __**mole**__ of substance is the __**amount of substance**__ that contains as many ^^specified particles^^ (ie. atoms, ions, molecules, electrons and so on) as there are atoms of carbon-12 in __**exactly**__ __12g__ __**carnon-12**__
21
New cards
1 mole =
* 6.02 x 10^23
* Avagadros Constant
* Avagadros Constant
22
New cards
number of moles
* number of particles/avagadro’s number
* n for moles is lowercase bc divided
* n for moles is lowercase bc divided
23
New cards
number of particles
number of moles **x** avagadro’s number
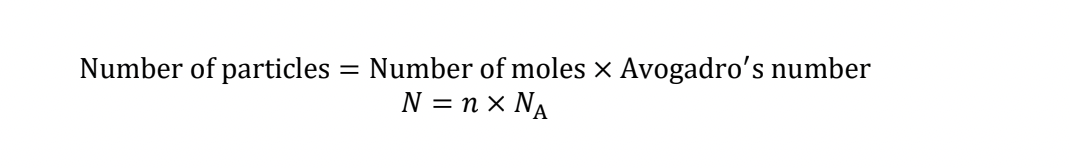
24
New cards
n
no. of moles
25
New cards
N
no. of particles
26
New cards
m(g)
mass
27
New cards
M
Molar mass
28
New cards
Mass =
* number of moles x molar mass
* m(g) = n(mol) x M (gmol^-1)
* m(g) = n(mol) x M (gmol^-1)
29
New cards
Combined equation
* can find number of particles if given only. mass & vice versa