AP Human Geography: Unit 4 Political Geography
1/59
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
60 Terms
Political geography
A subdivision of human geography focused on the nature and implications of the evolving spatial organization of political governance and formal political practice on the Earth's surface. It is concerned with why political spaces emerge in the places that they do and with how the character of those spaces affects social, political, economic, and environmental understandings and practices.
State
A politically organized territory that is administered by sovereign government and is recognized by a significant portion of the international community. A state has a defined territory, a permanent population, a government, and is recognized by other states.
Territoriality
In political geography, a country's or more local community's sense of propertyand attachment toward its territory, as expressed by its determination to keep it inviolable and strongly defended
Sovereignty
Ability of a state to govern its territory free from control of its internal affairs by other states.

Nation
a large aggregate of people united by common descent, history, culture, or language, inhabiting an area
Nation-state
a sovereign state whose citizens or subjects are relatively homogeneous in factors such as language or common descent.
Democracy
government based on the principle that the people are the ultimate soverign and have the final say over what happens within the state.

Multinational state
States with more than one nation within its borders
Multistate nation
Nation that stretches across borders and across states
Colonialism
rule by an autonomous power over a subordinate and alien people and place.
Centripetal
forces that tend to unify a country- such as widespread commitment to a national culture, shared idealogical objectives, and a common faith

Centrifugal
forces that tend to divide a country- such as internal religious, inguistic, ethnic, or ideologiacal differences.

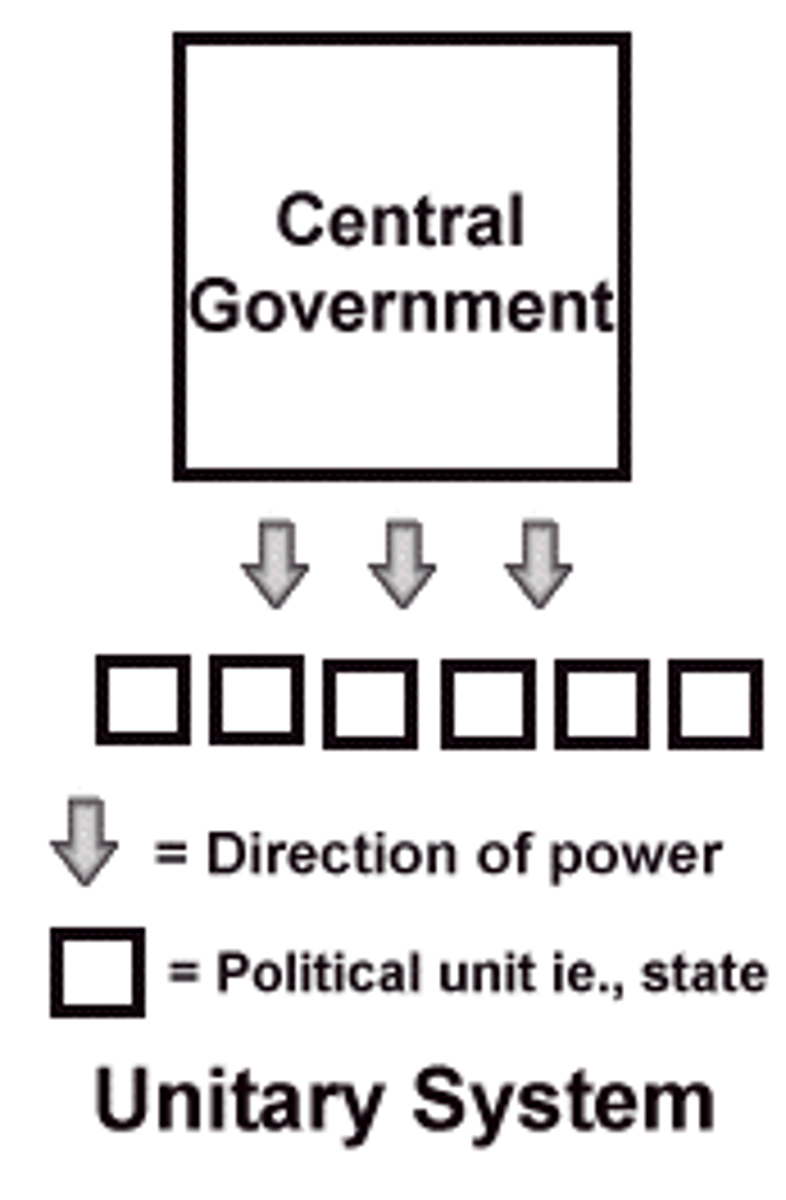
Unitary State
centralized government and administration that exercises power equally over all parts of the state
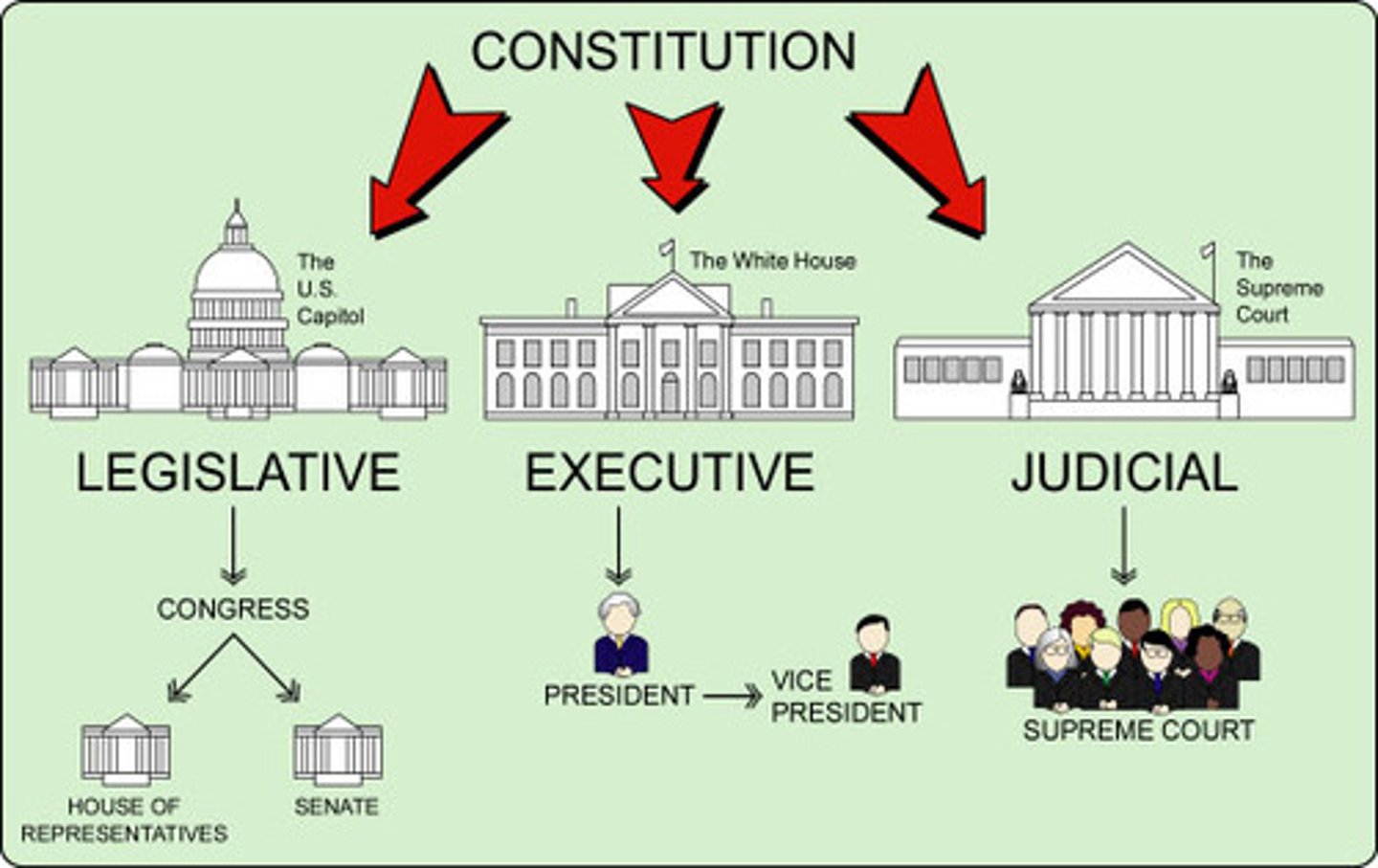
Federal State
shares power between the federal government and the local governments
Devolution
the transfer of powers and responsibilities from the federal government to the states
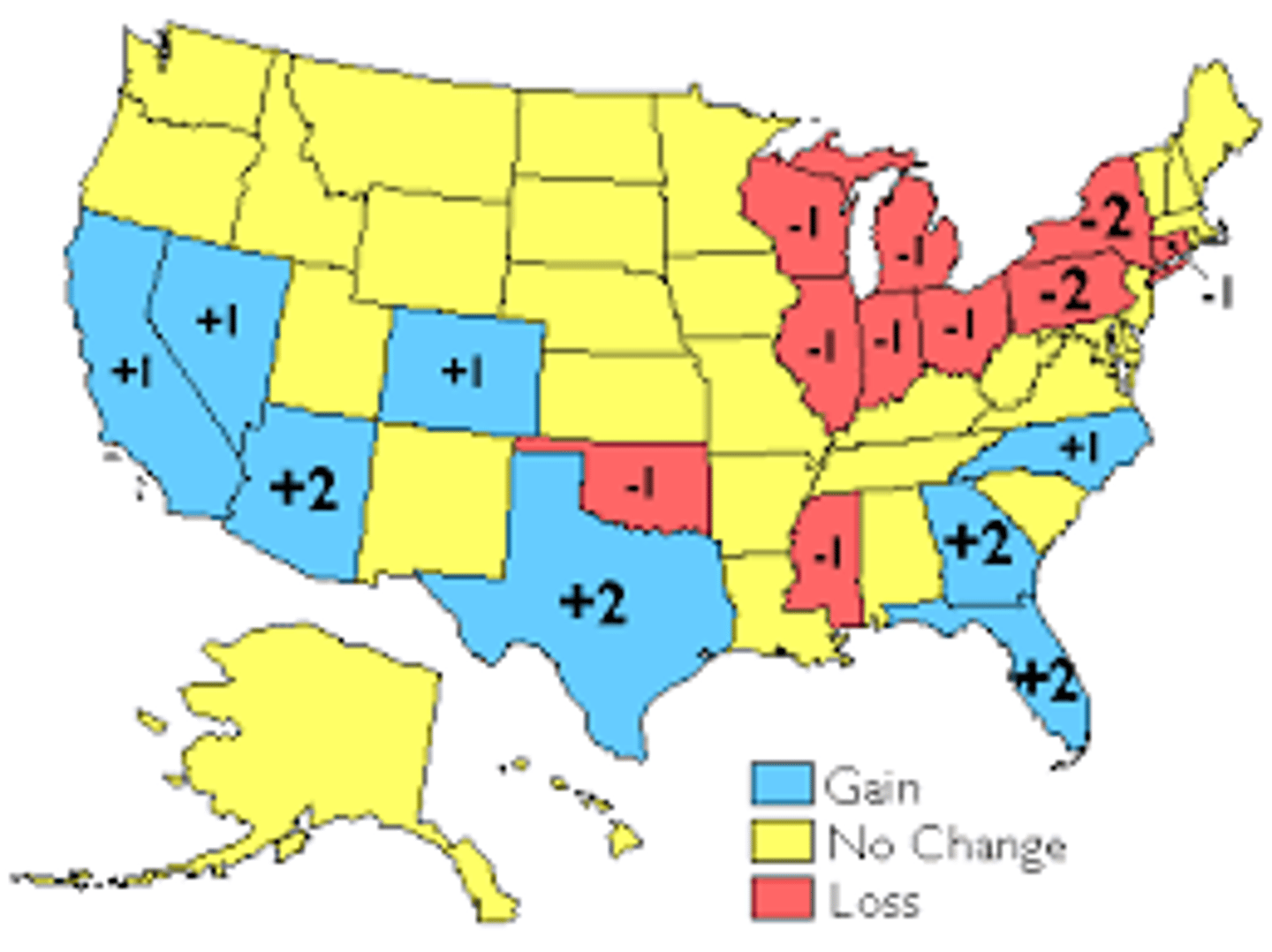
Reapportionment
process by which representative districts are switched according to population shifts, so that each district encompasses approximately the same number of people
Balance of power
A condition of roughly equal strength between opposing countries or alliances of countries.
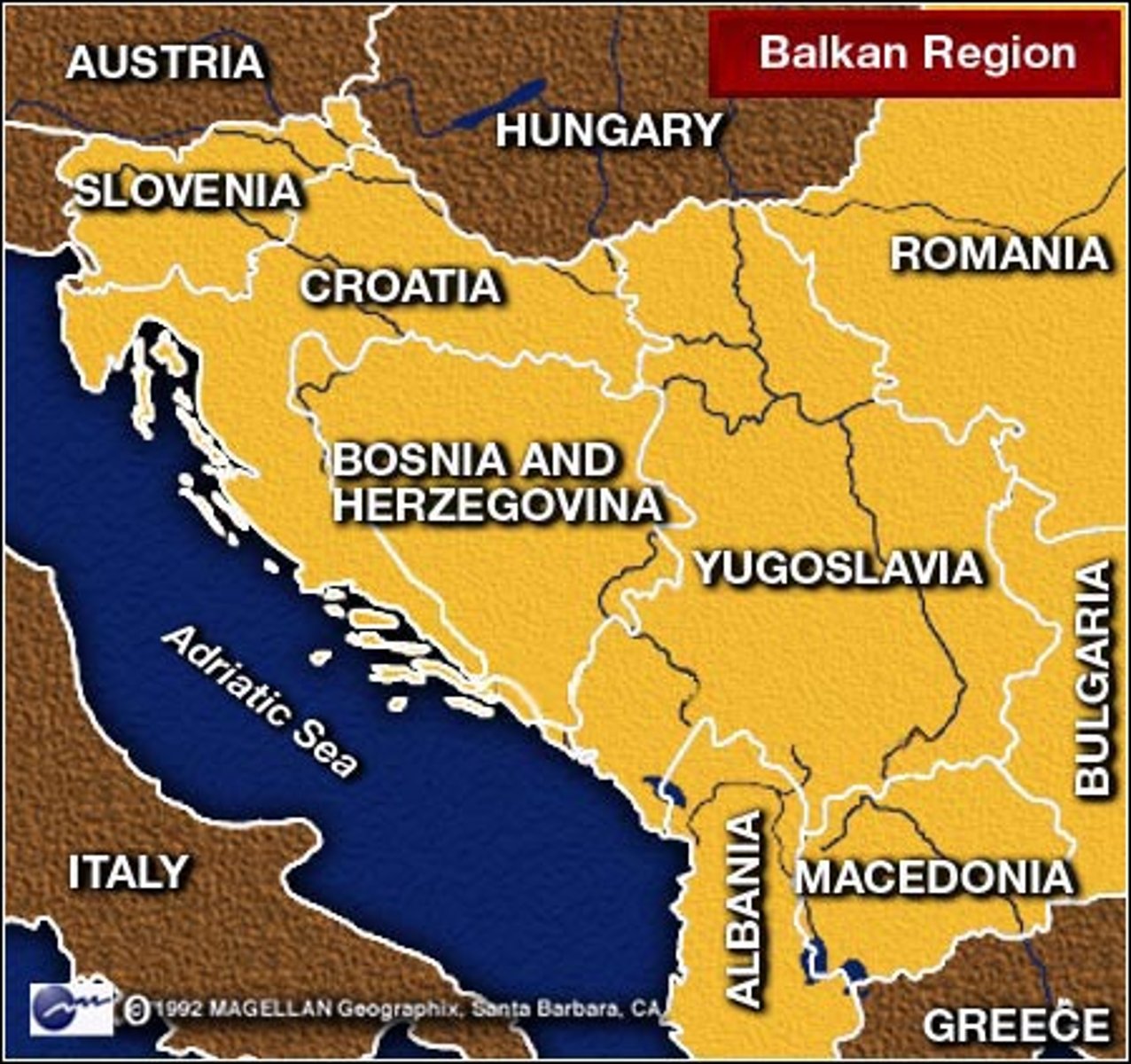
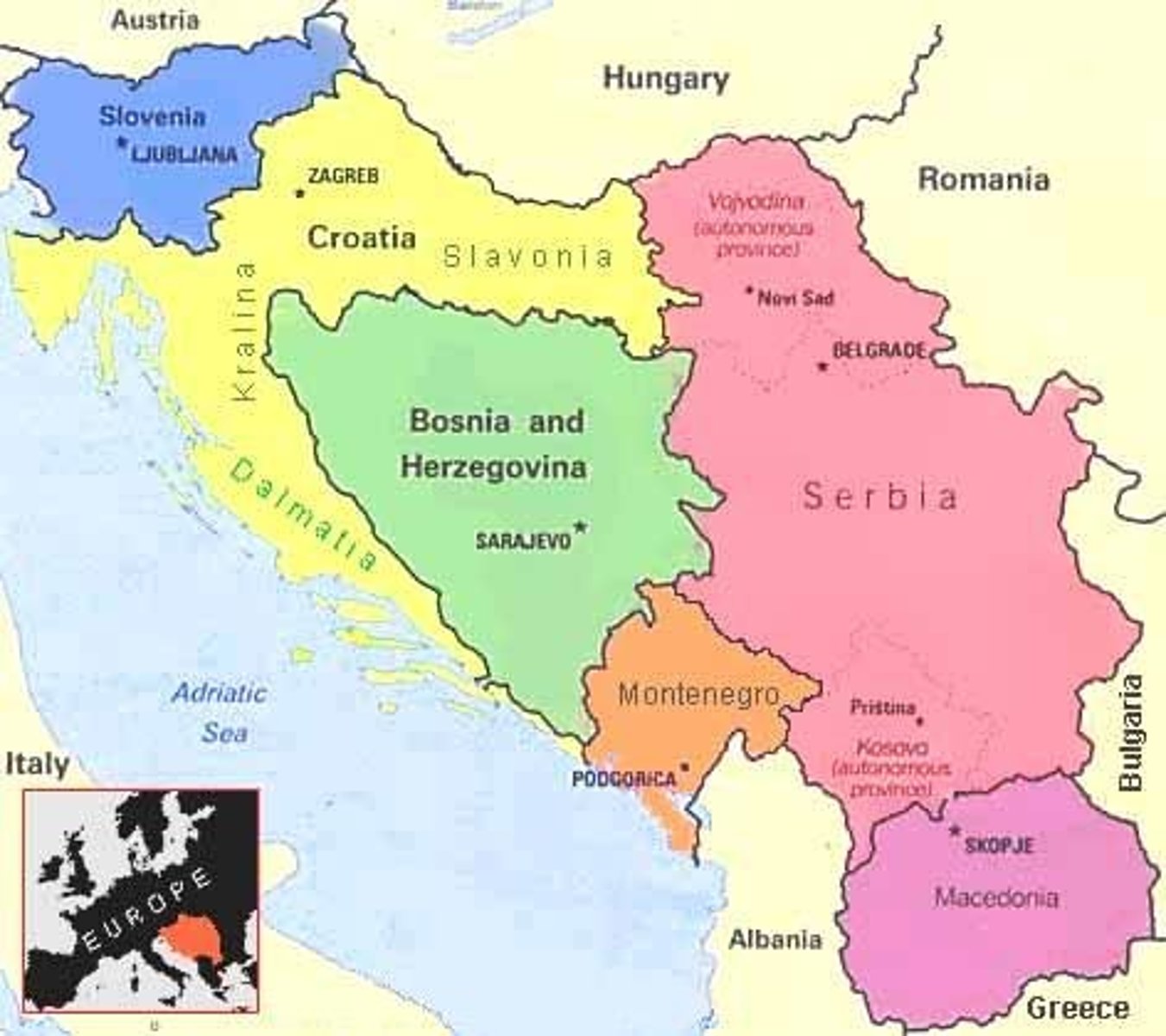
Balkanization
Process by which a state breaks down through conflicts among its ethnicities (usually referencing Yugoslavia)
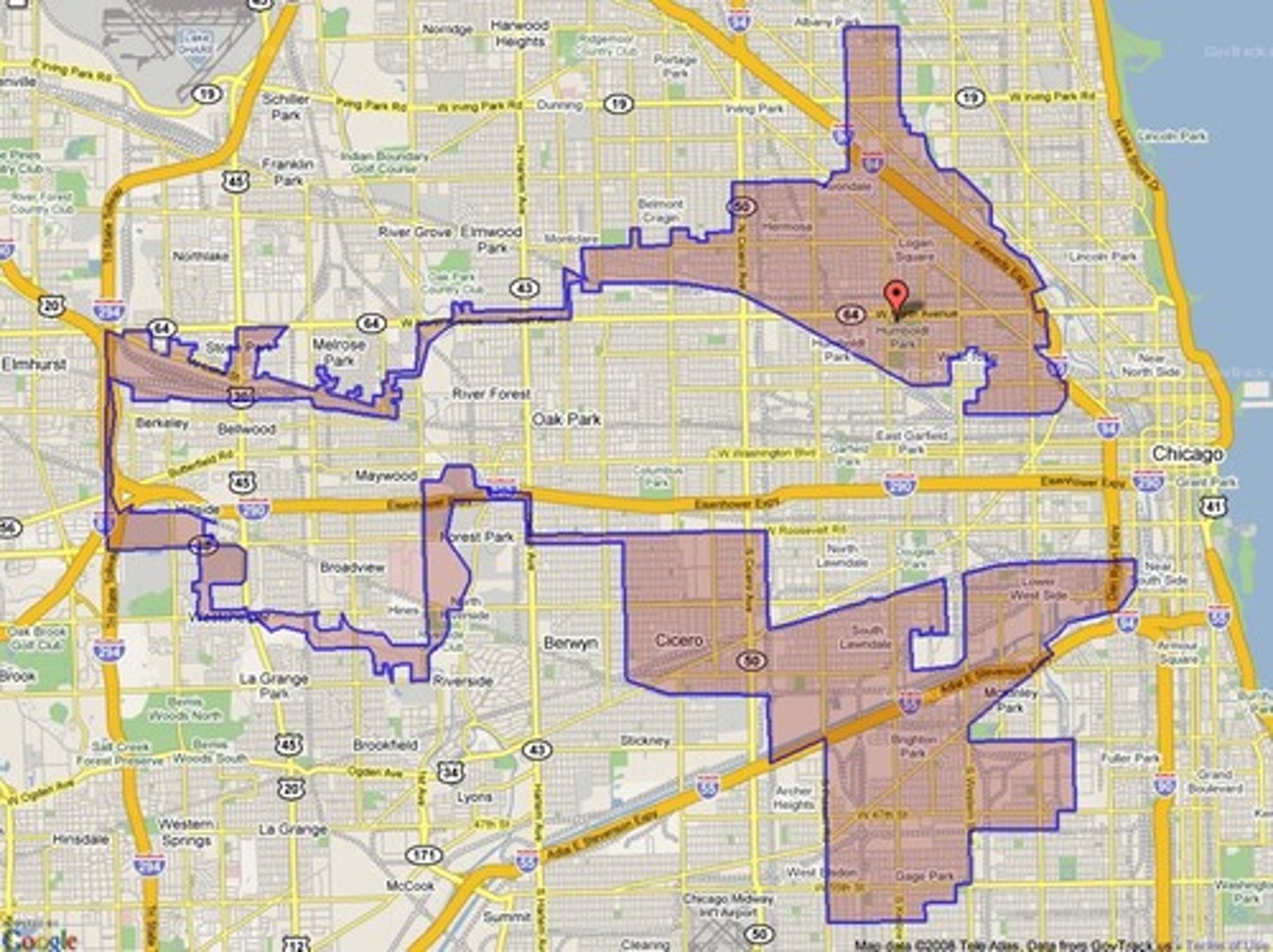
Gerrymandering
Process of redrawing legislative boundaries for the purpose of benefiting the party in power.
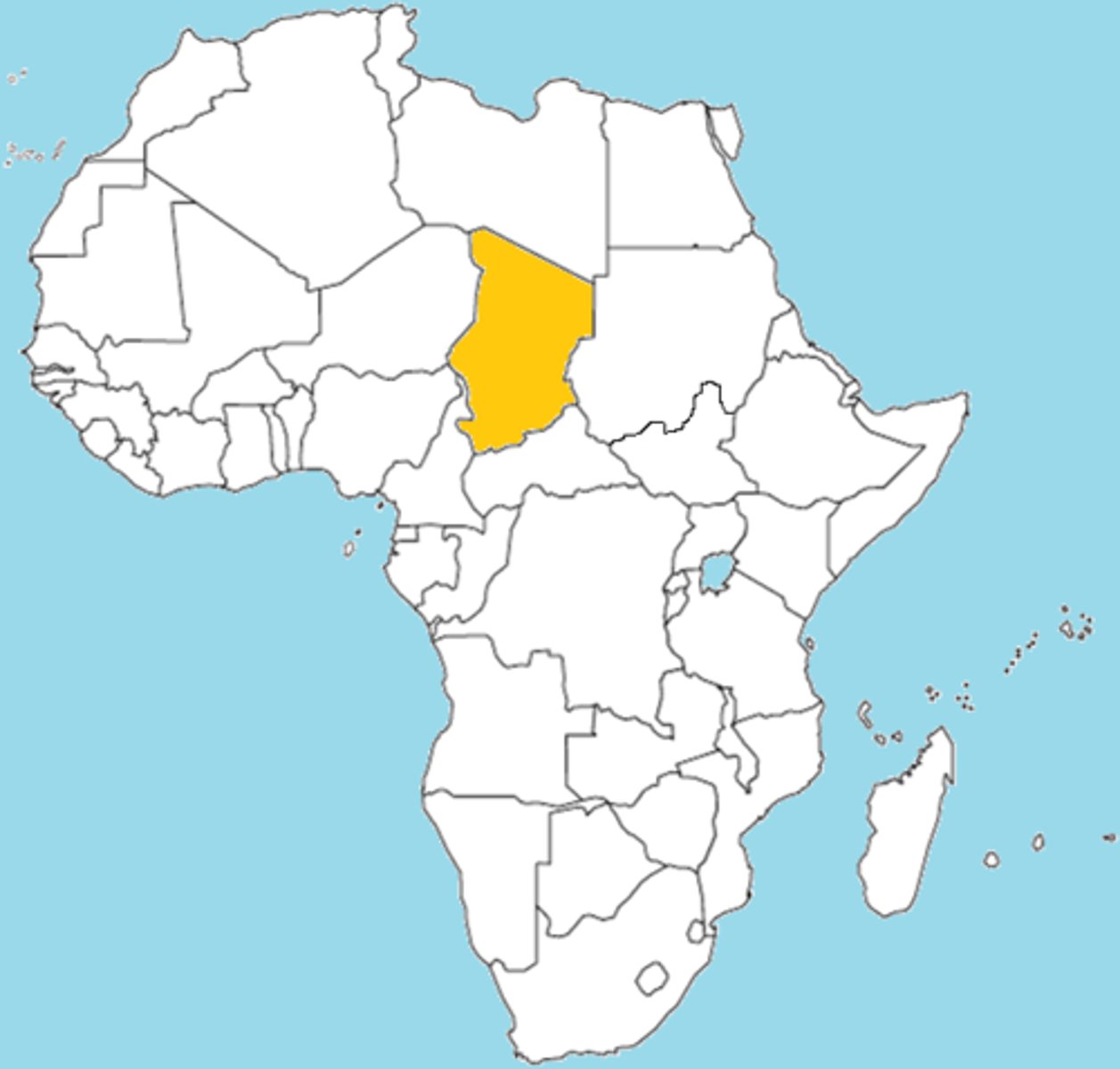
Landlocked State
A state that does not have a direct outlet to the sea.
Chokepoint examples
Straight of Hormuz, Panama Canal
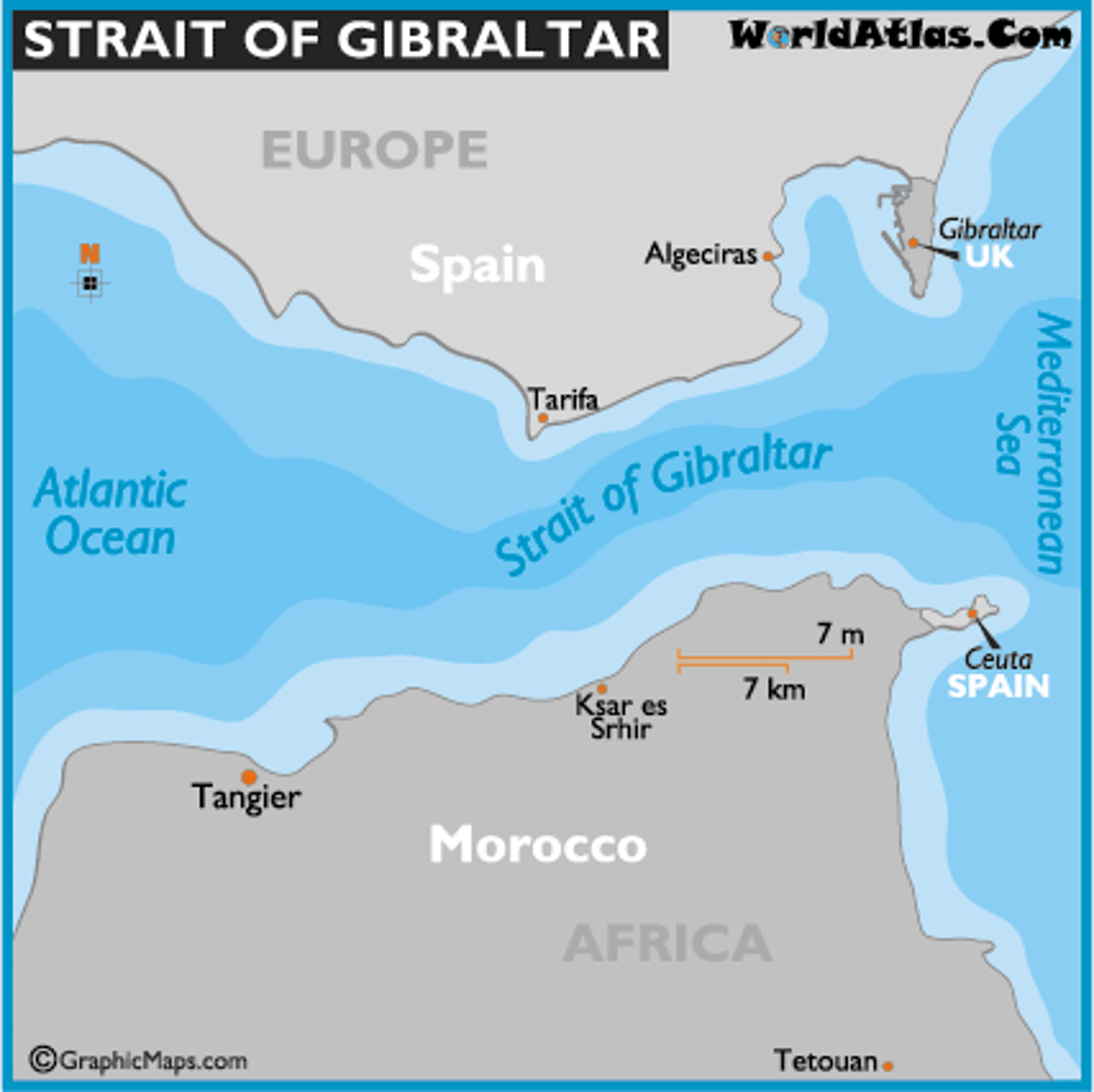
Irrendentism
the policy of a state wising to incorporate within itself territory inhabited by people who have ethnic or linguistic links with the country but that lies within a neighboring state
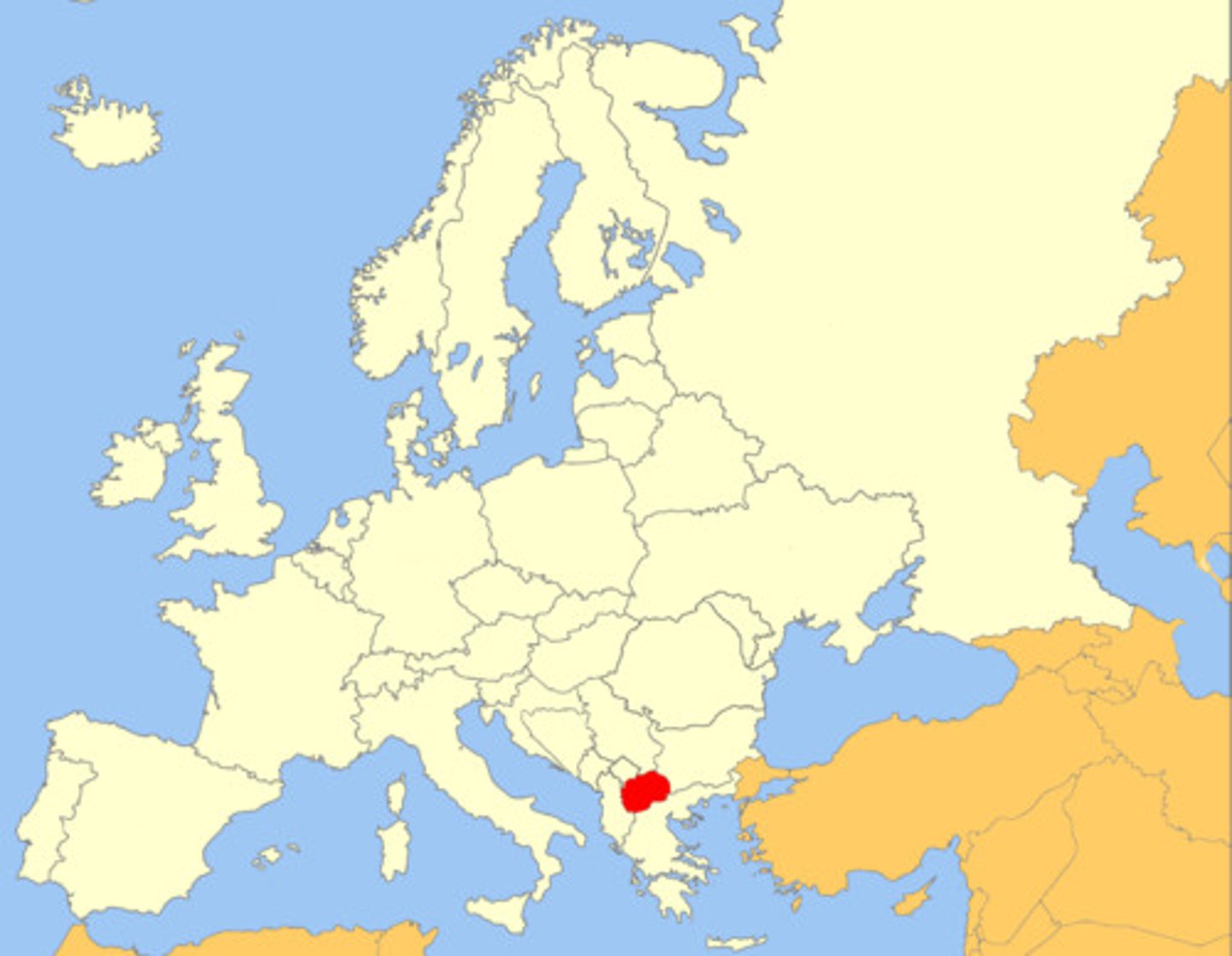
Shatterbelt
an area of instability between regions with opposing political and cultural values
consequent boundary
boundaries that are based on traits like religion and language
geometric boundary
Political boundaries that are defined and delimited by straight lines.
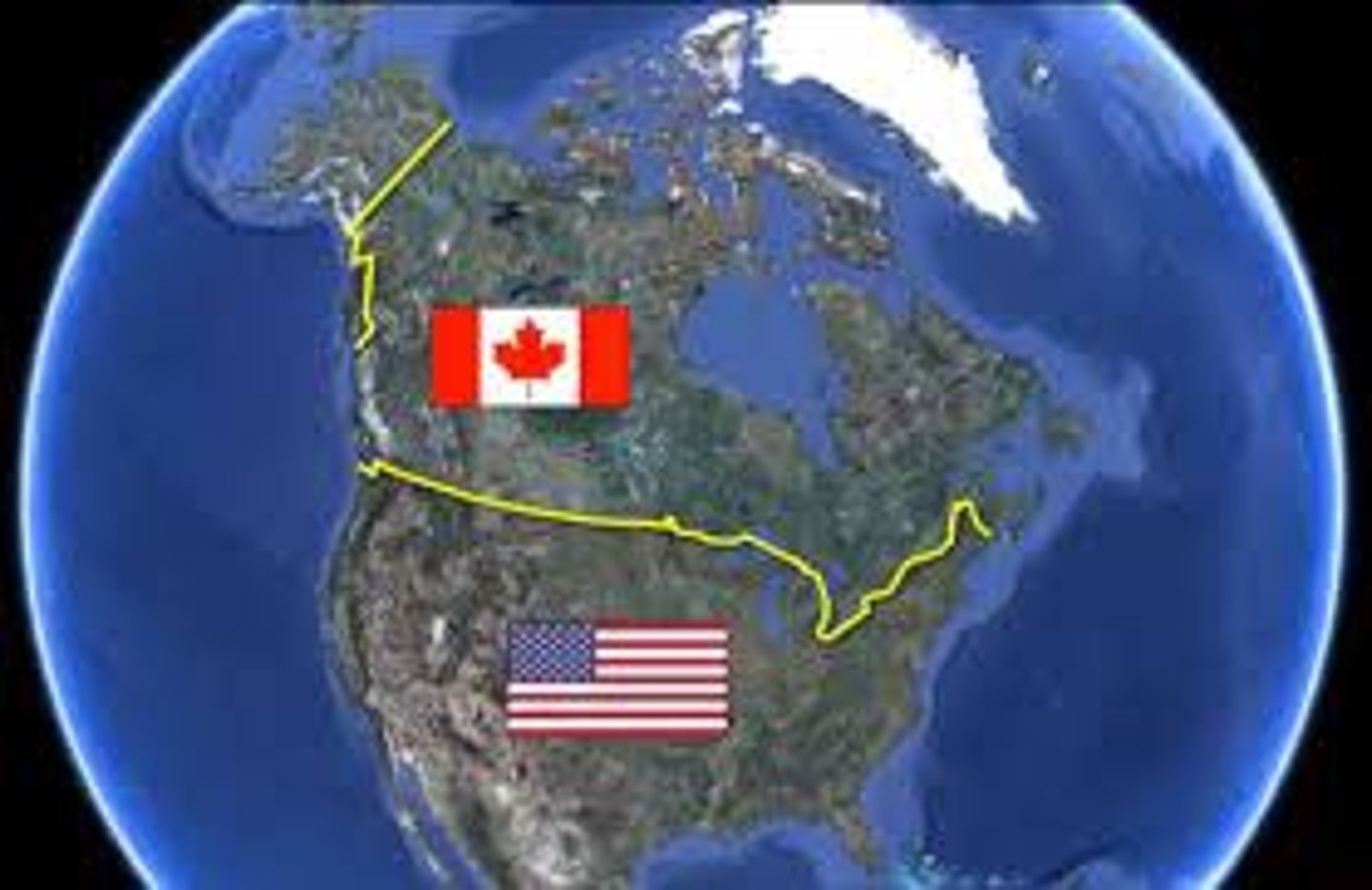
physical boundary
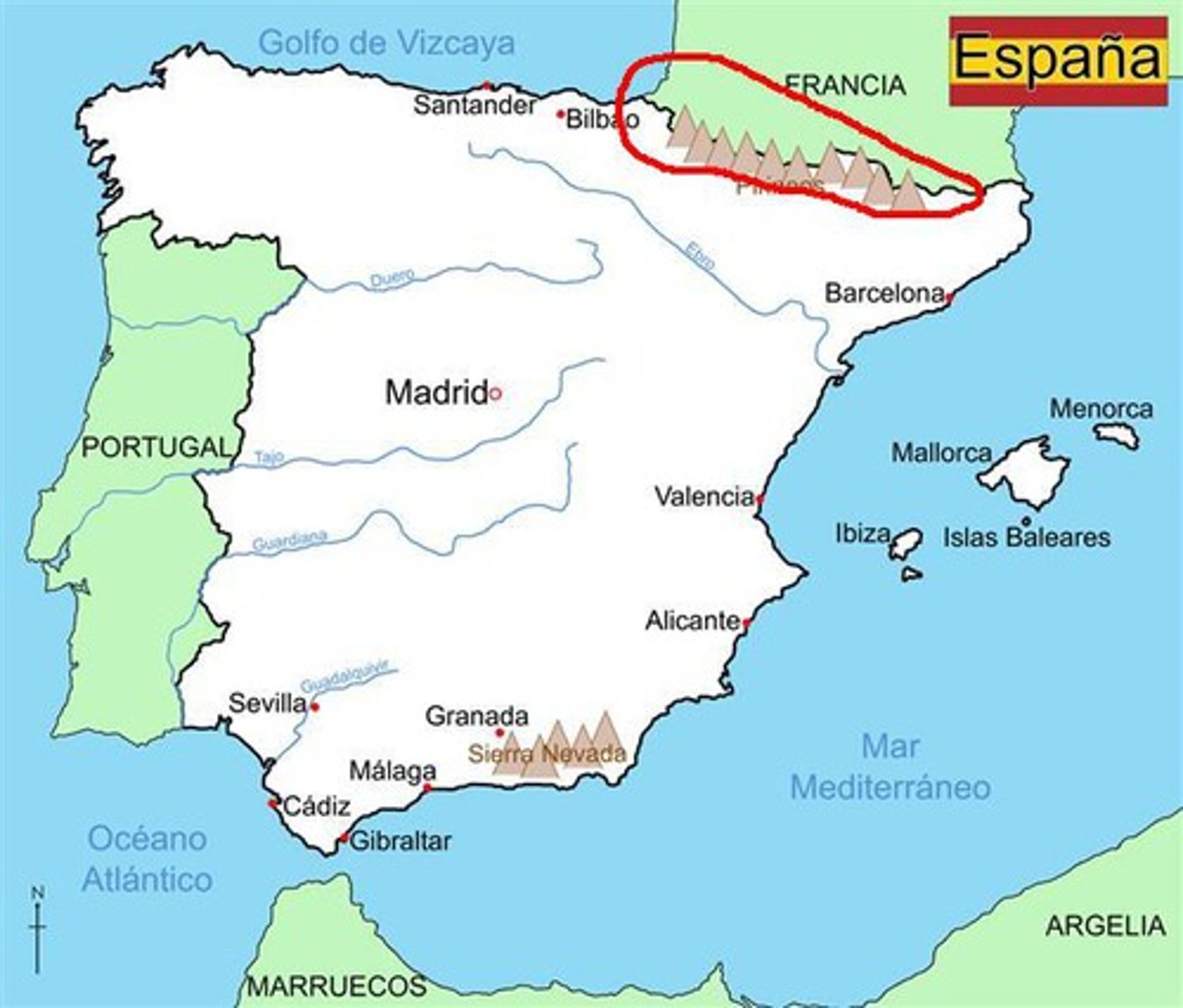
Political boundaries that correspond with prominent natural features such as mountain ranges or rivers.
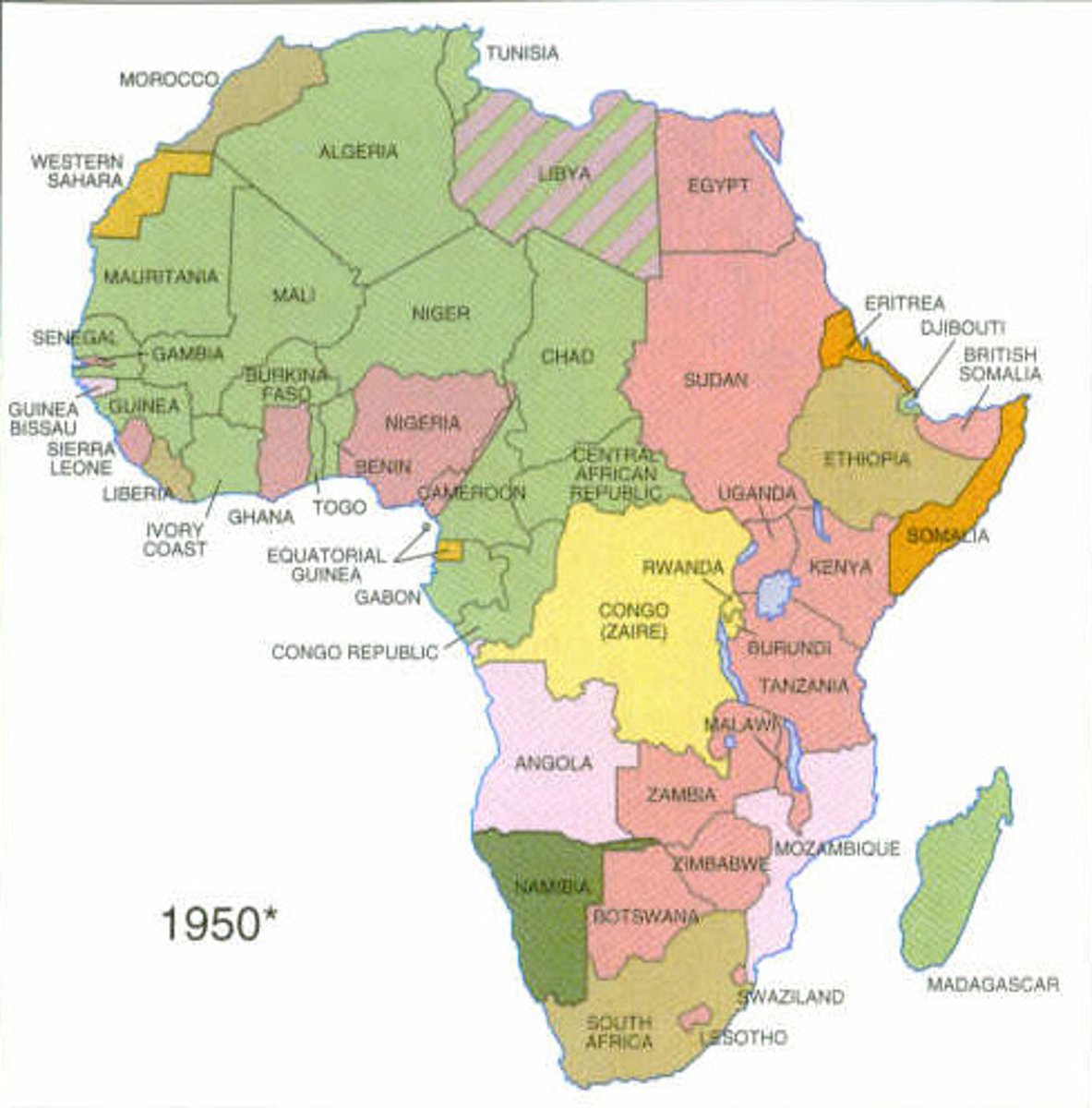
superimposed boundary
a boundary line placed over and ignoring an existing cultural pattern (ex: former colonizers in Sub-Saharan Africa drew borders around many ethnicities without any regard for these differences)
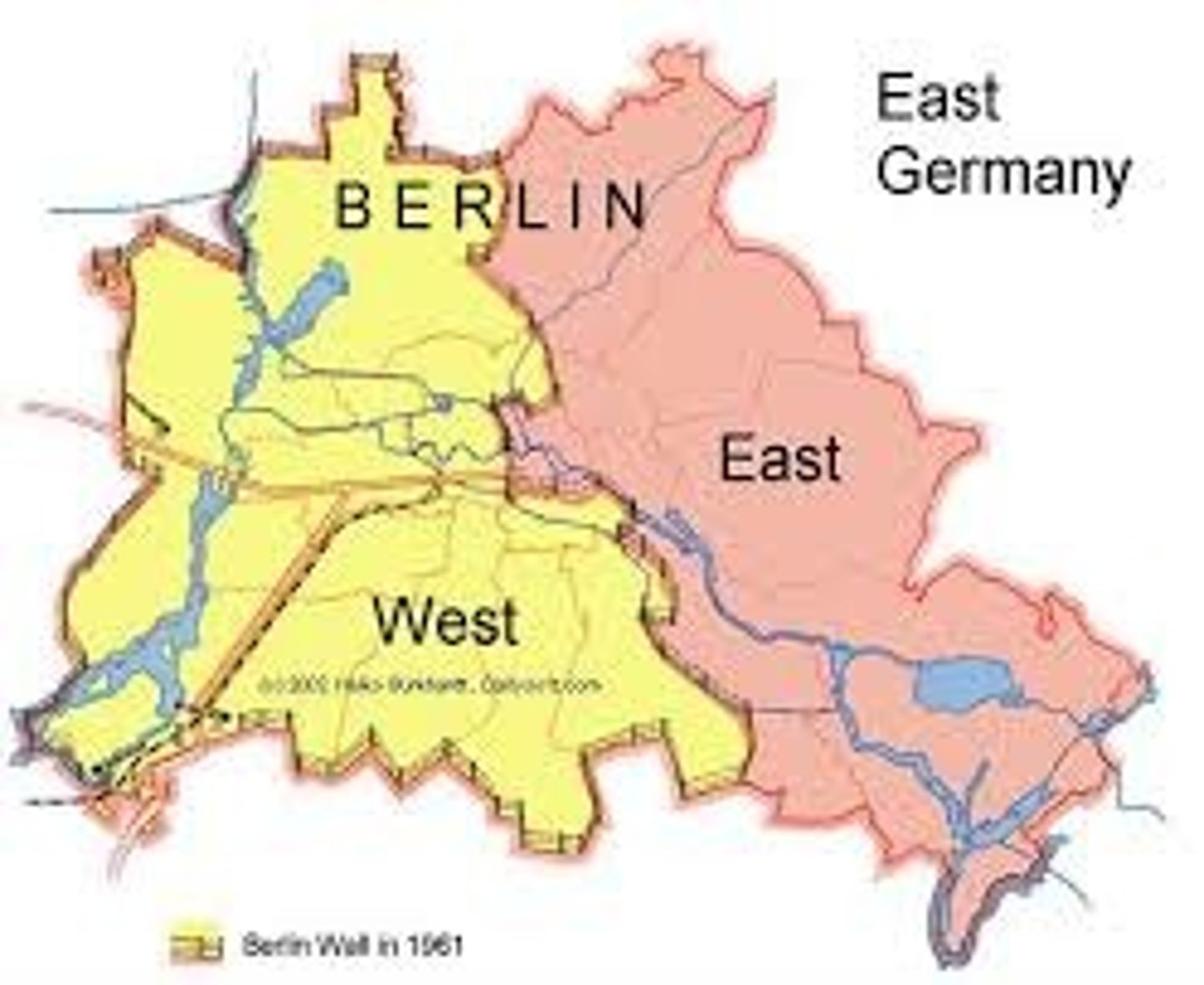
relic boundary
a former boundary line that is still discernible and marked by some cultural landscape features
antecedent boundary
A boundary line established before an area is populated

subsequent boundary
a boundary line that is established after the area in question has been settled and that considers the cultural or political characteristics of the bounded area
United Nations
An international organization formed after WWII to promote international peace, security, and cooperation.

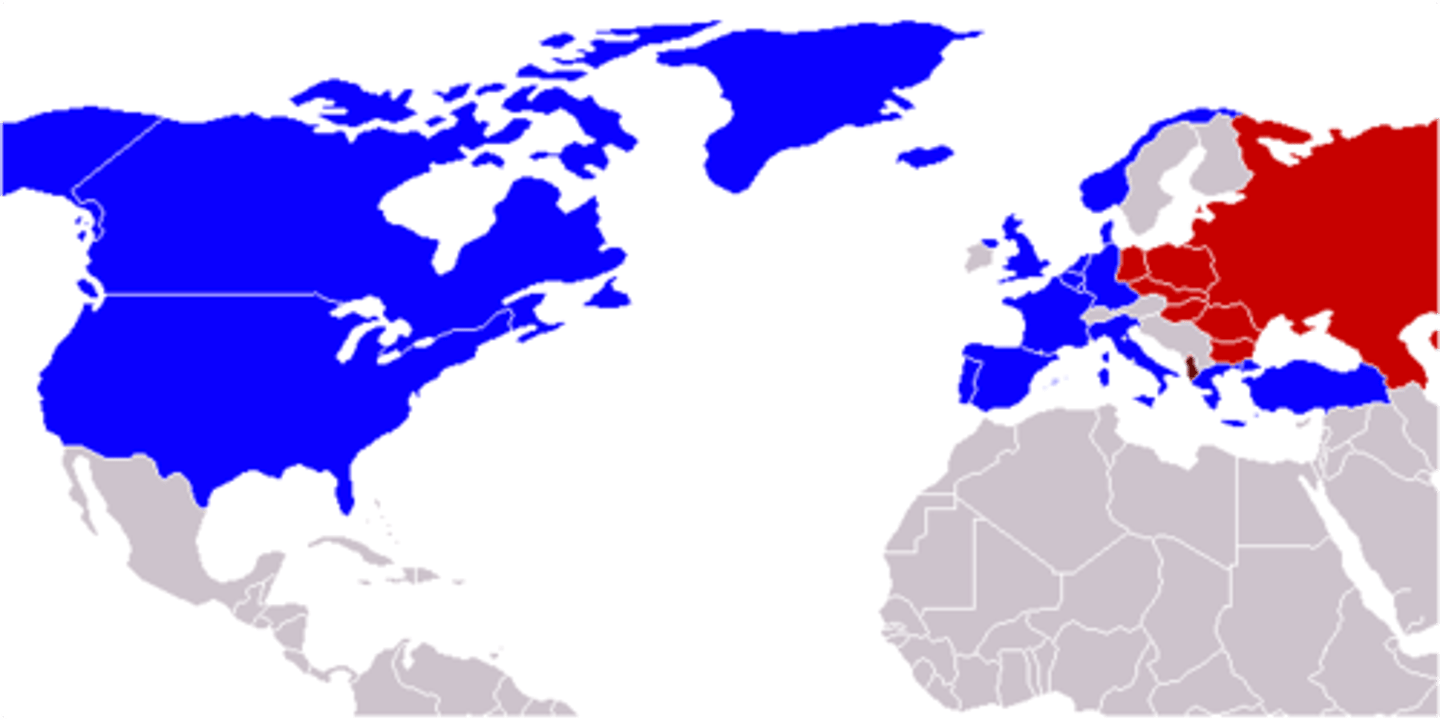
NATO (North Atlantic Treaty Organization)
A 1949 defense alliance initiated by the US, Canada, and 10 Western European nations
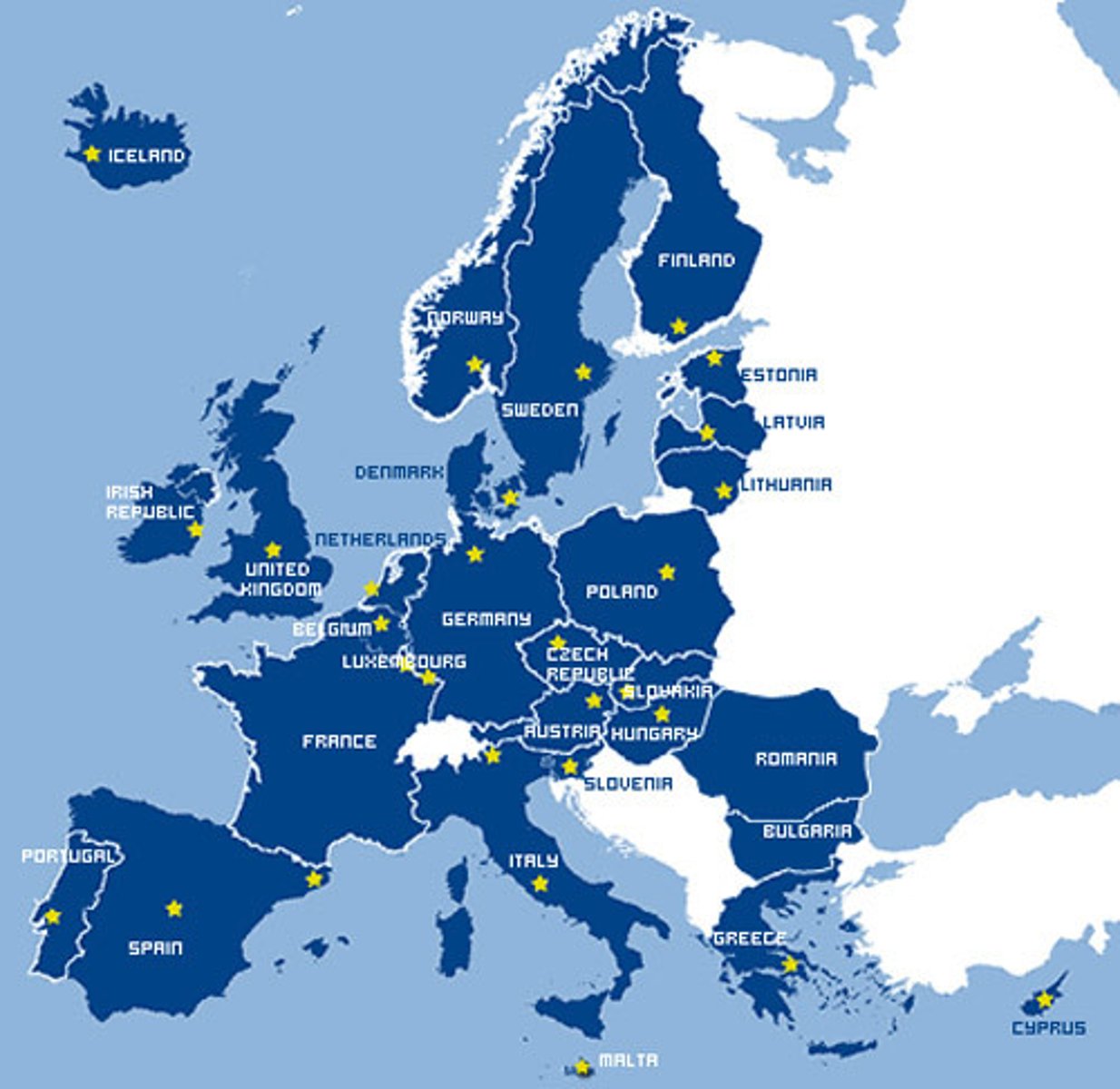
European Union (EU)
an economic association established in 1957 by a number of Western European countries to promote free trade and open borders among its members
NAFTA (North American Free Trade Agreement)
Allows open trade between the US, Mexico, and Canada.

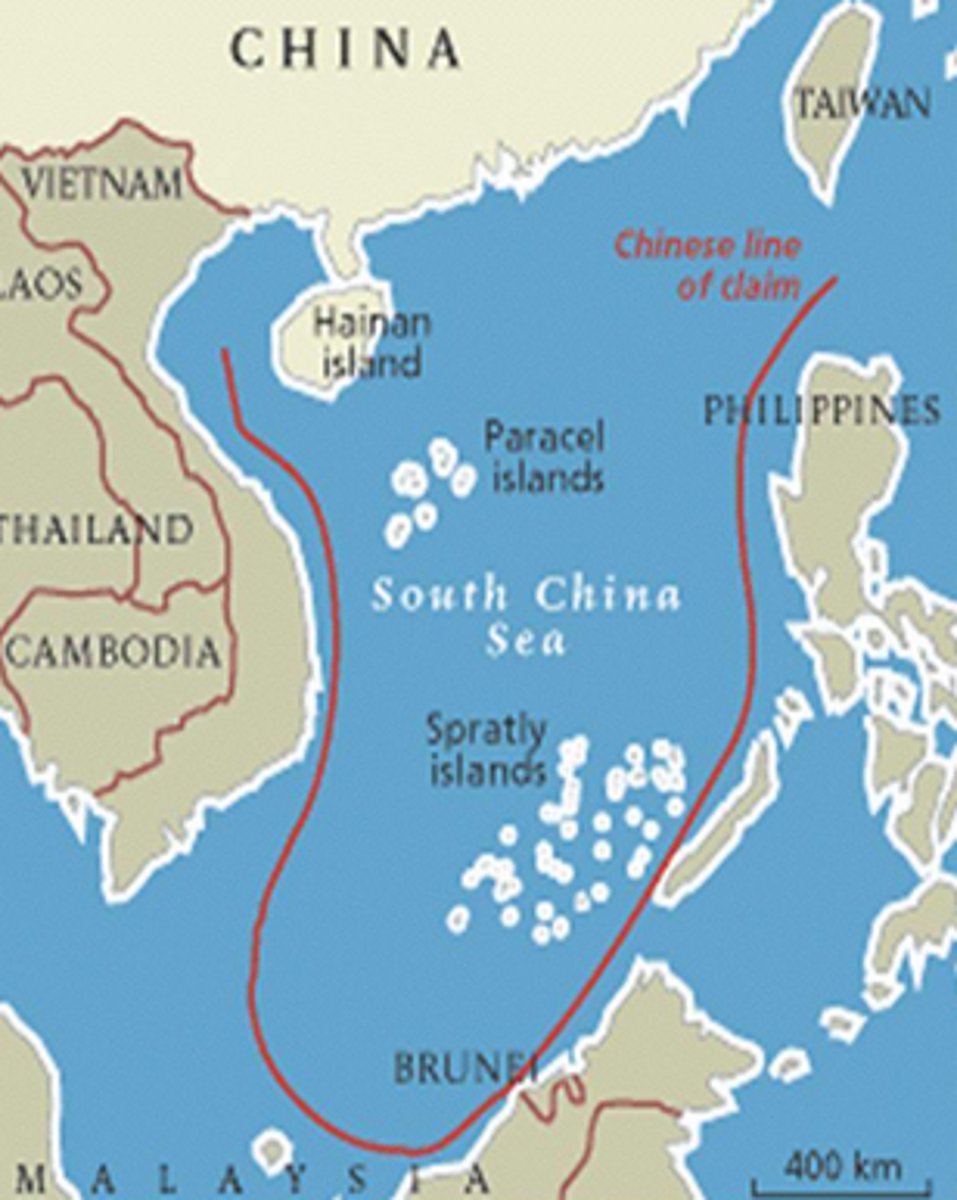
South China Sea disputes
China, Vietnam, the Philippines, Taiwan, Malaysia and Brunei all have competing claims sovereignty over ocean areas and the Paracels and the Spratly Islands
ISIS
Islamic State of Iraq and Syria, terrorist group

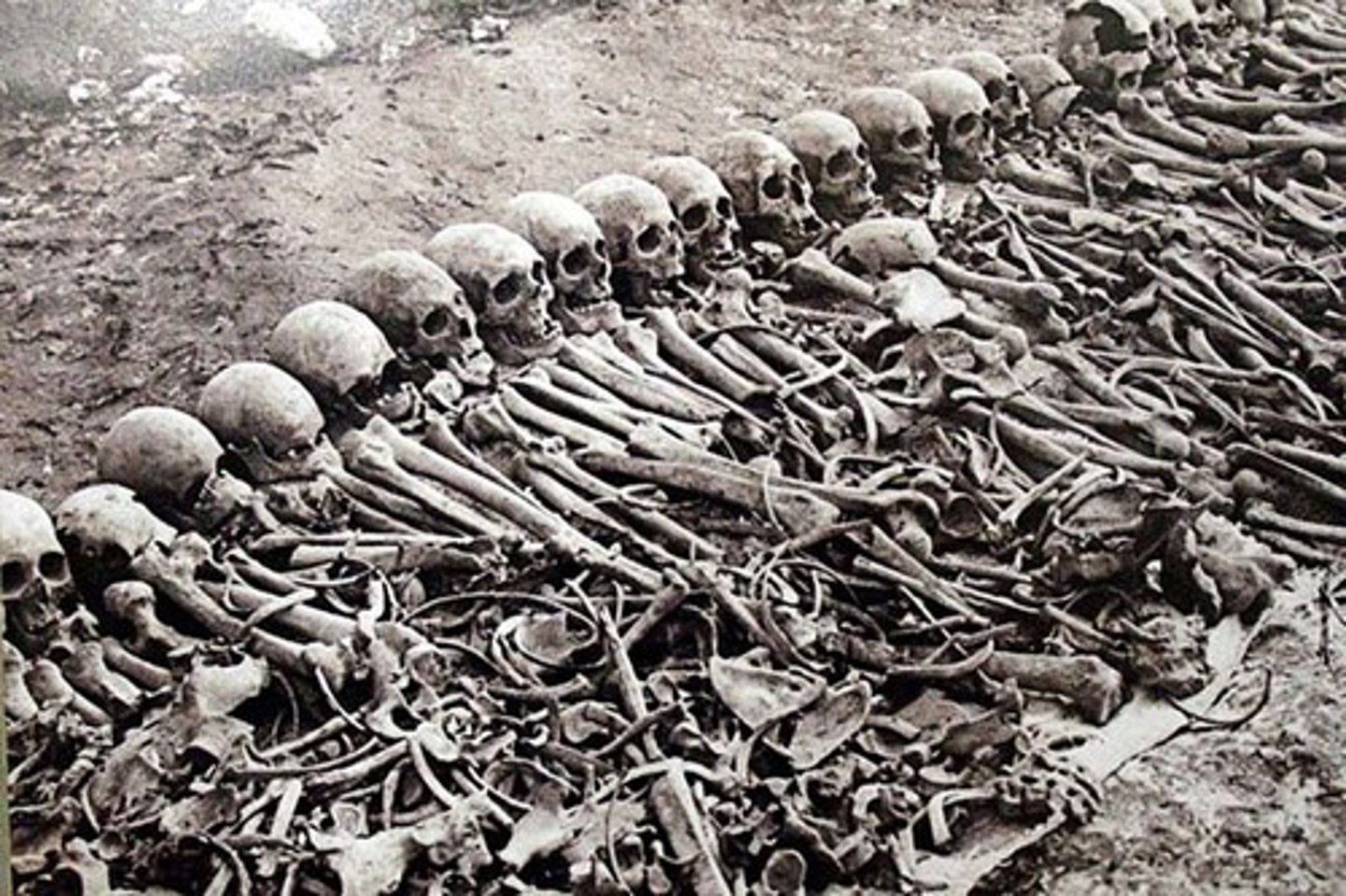
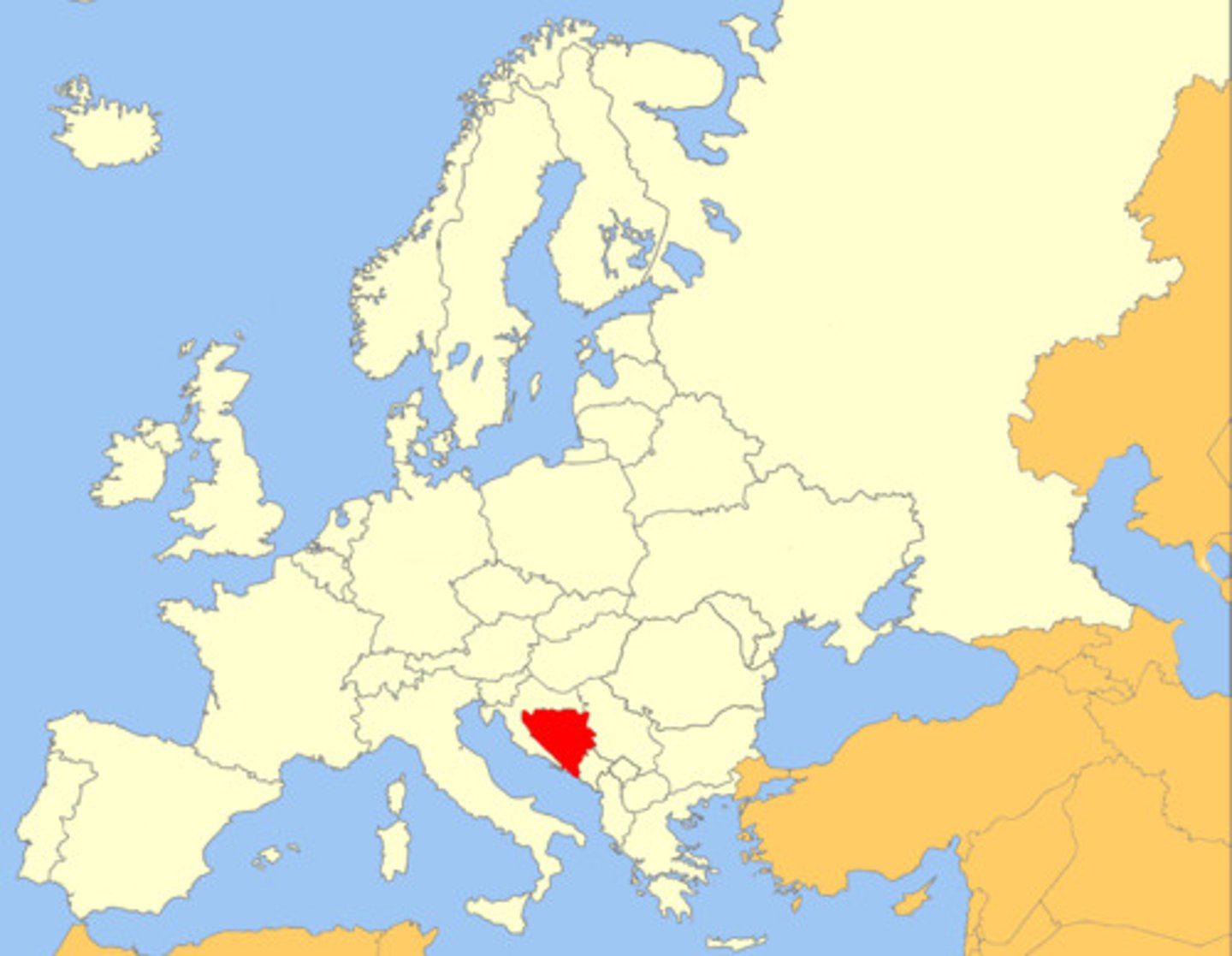
Bosnian Genocide
Between April 1992 and November 1995, Serbia set out to "ethnically cleanse" Bosnian territory by systematically killing Muslims and Croats.
Holocaust
A methodical plan orchestrated by Hitler to ensure German supremacy. It called for the elimination of Jews, non-conformists, homosexuals, non-Aryans, and mentally and physically disabled.

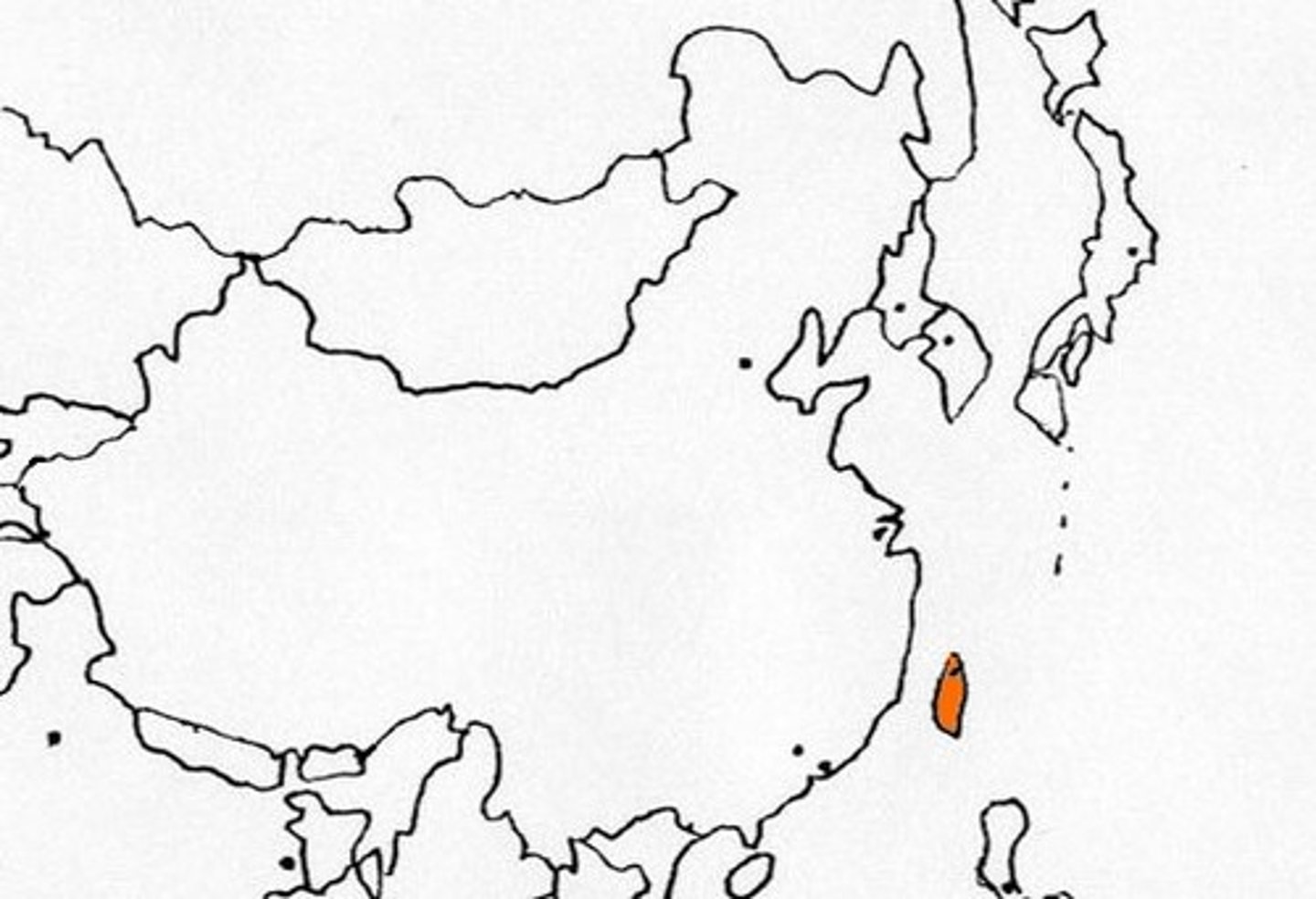
Taiwan
an island to the east of mainland China; NOT recognized as a state; Chinese nationalists
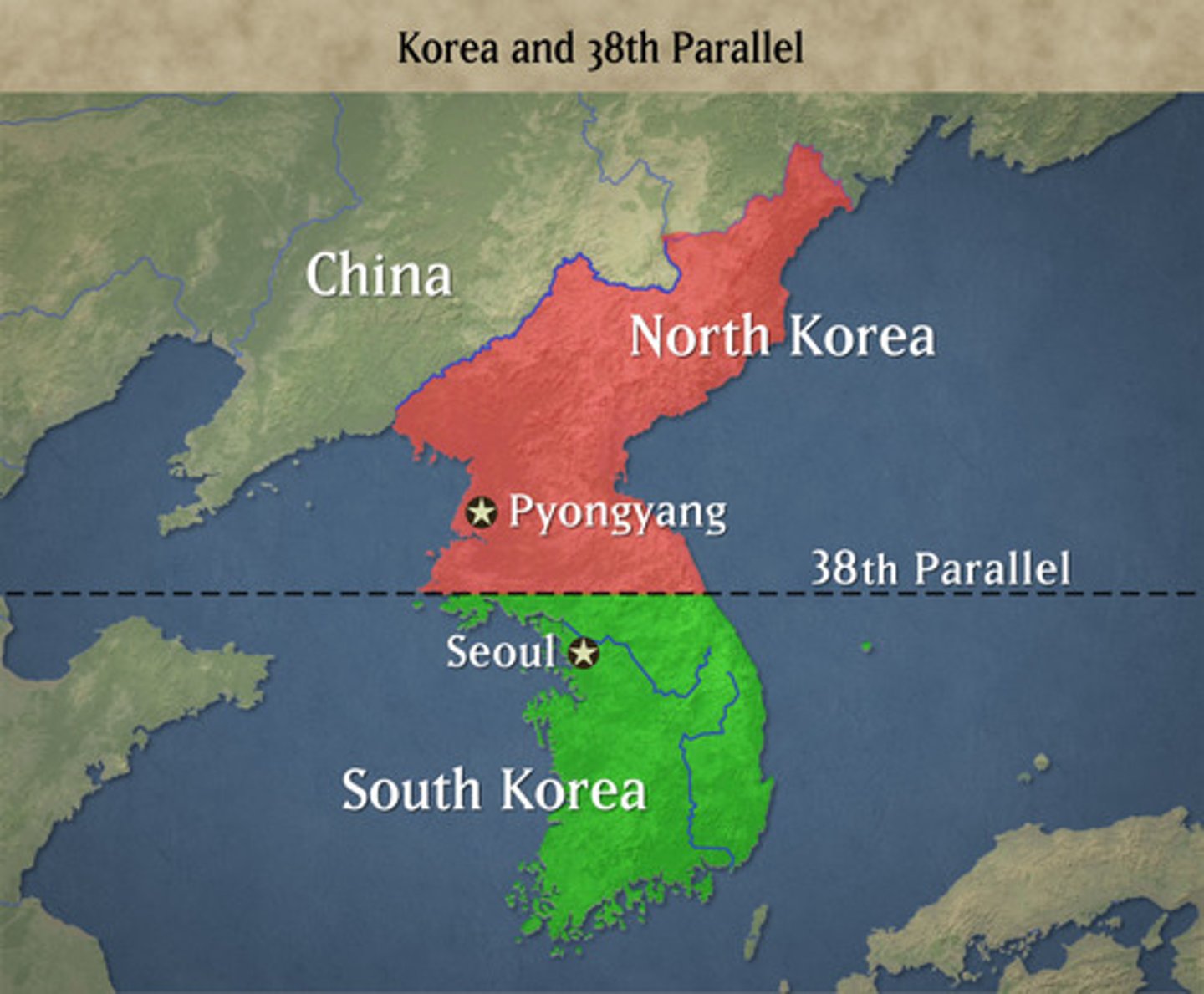
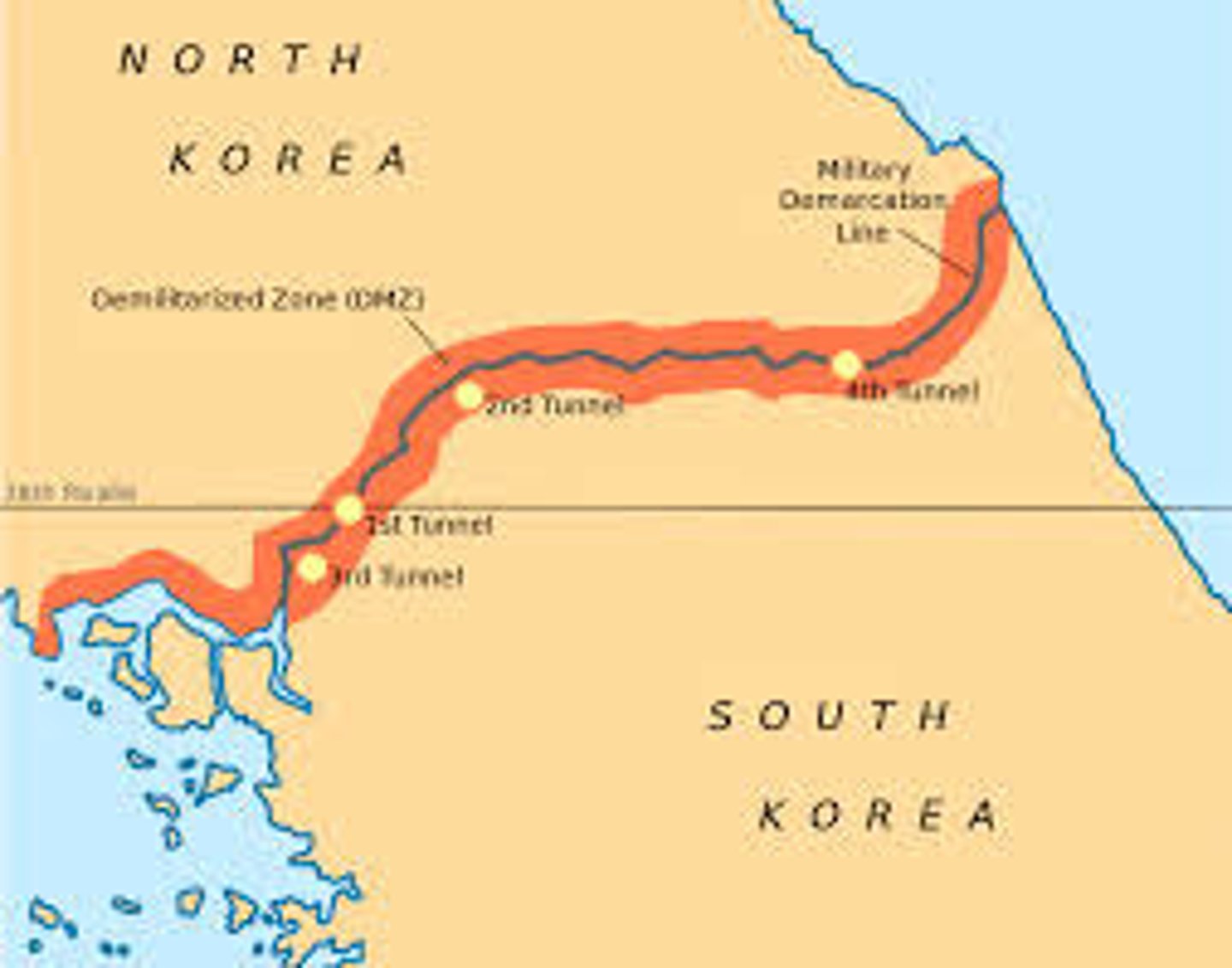
DMZ
A zone from which military forces or operations or installations are prohibited; 38th parallel between North and South Korea
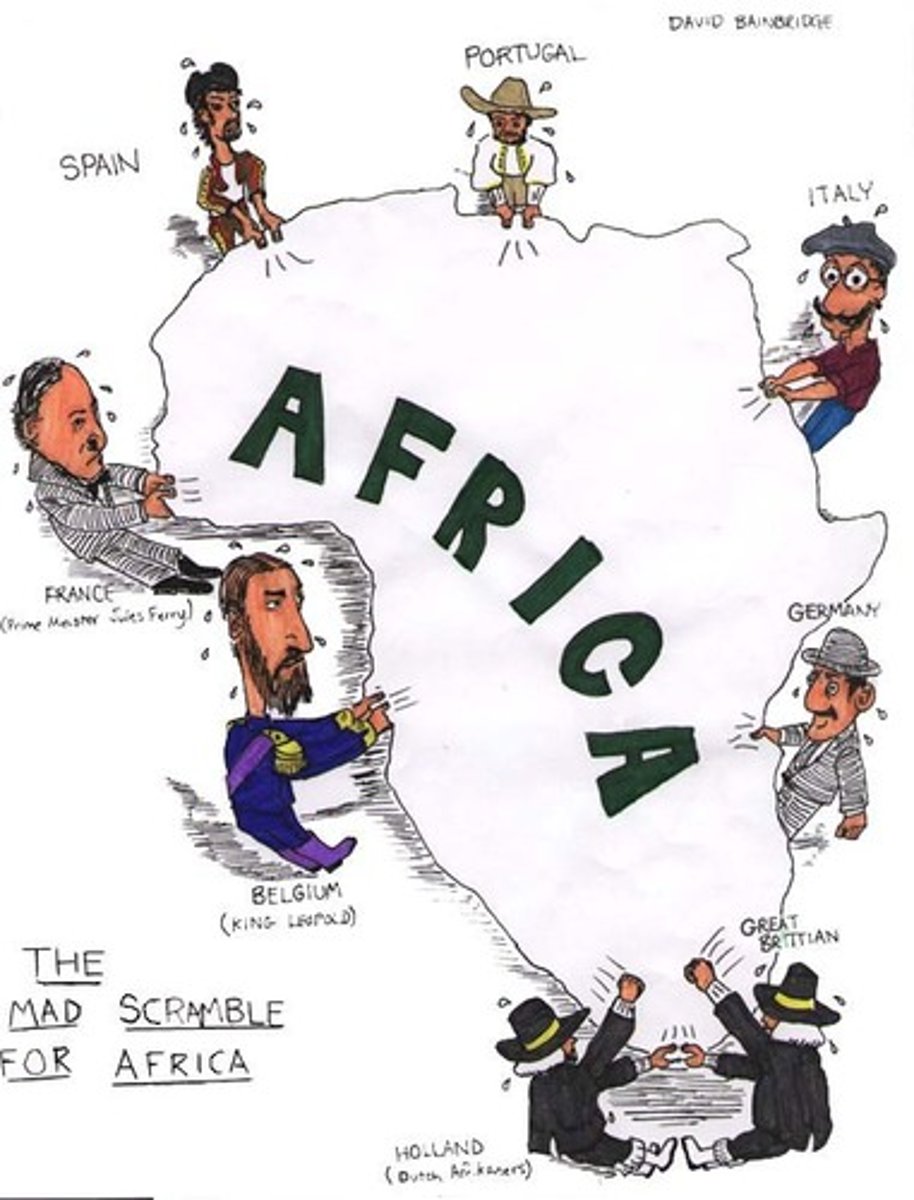
Berlin Conference
A meeting from 1884-1885 at which representatives of European nations agreed on rules colonization of Africa
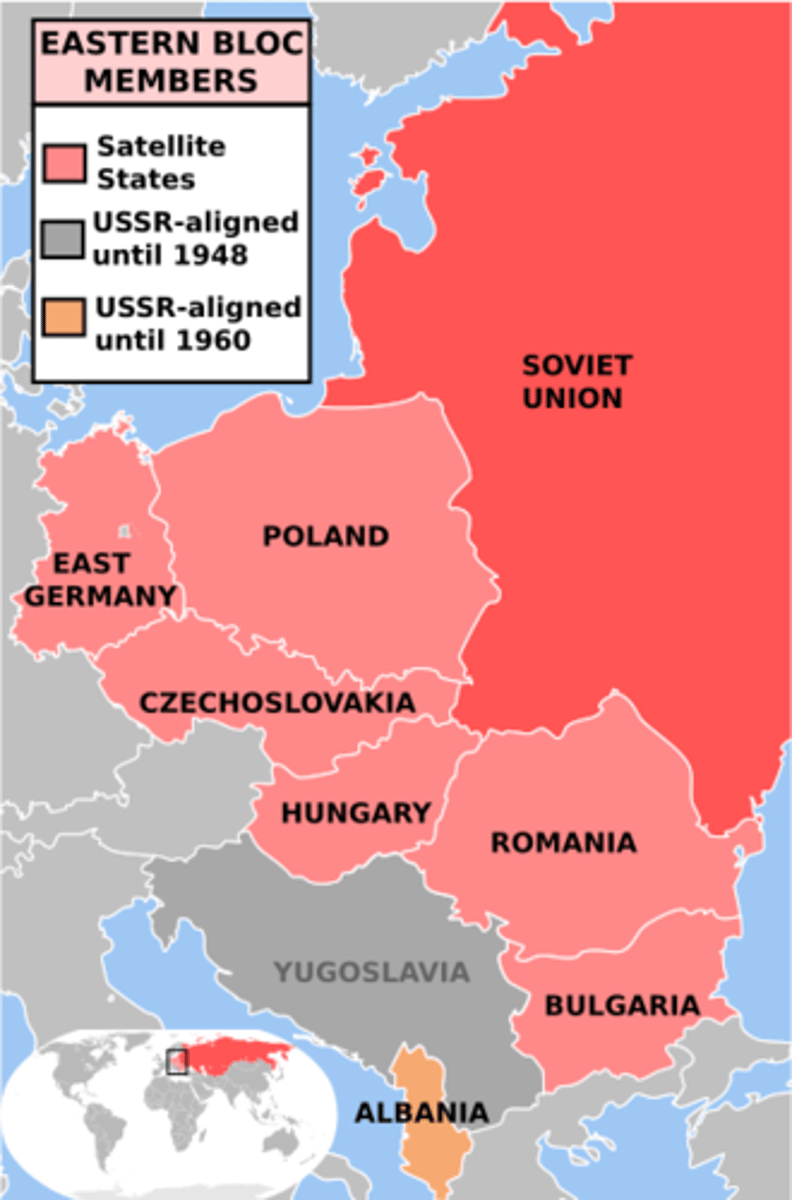
Satellite States
Countries in Eastern Europe that were independent but became politically and economically influenced/dependent on the Soviet Union. Also known as the Eastern Bloc.
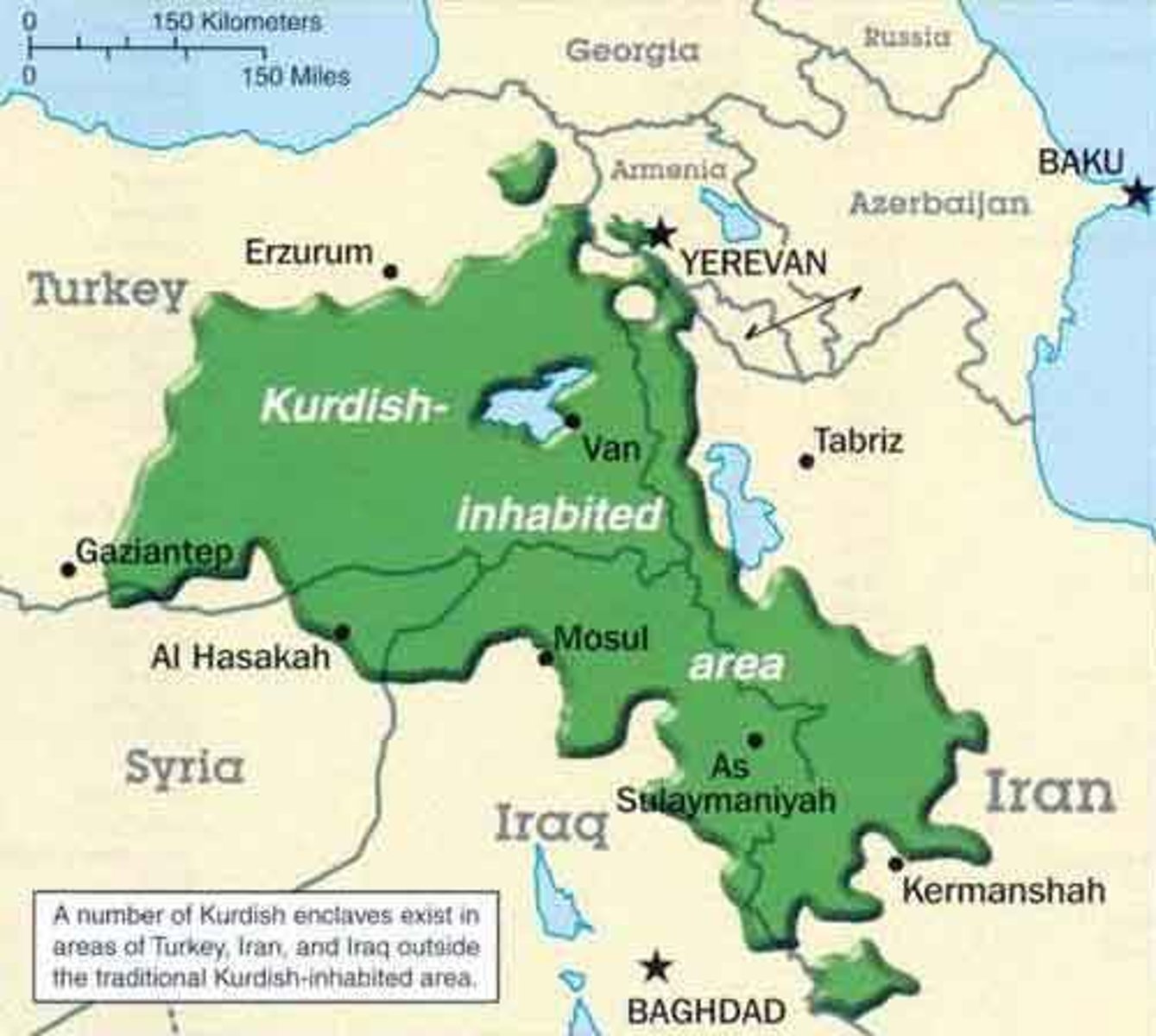
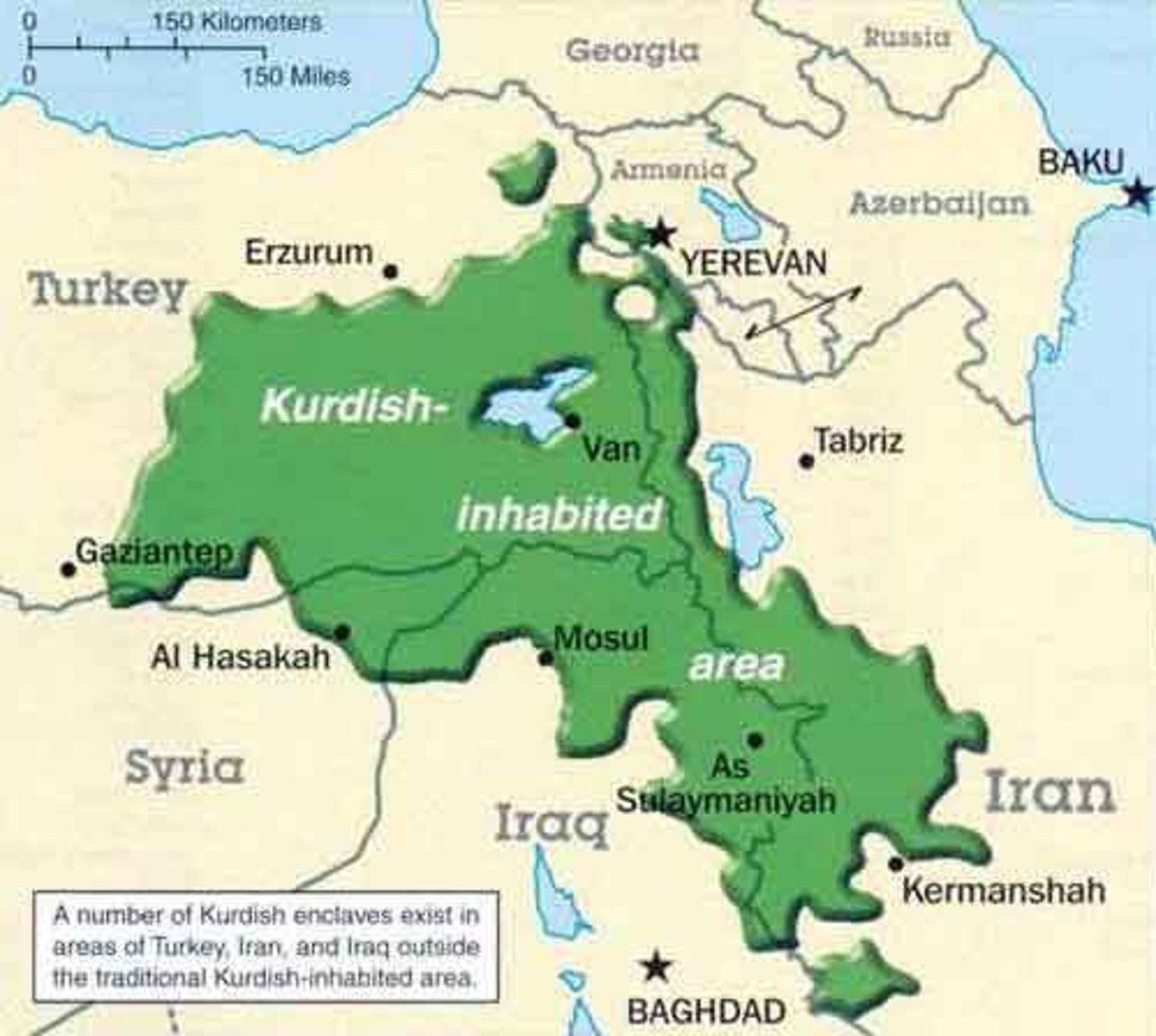
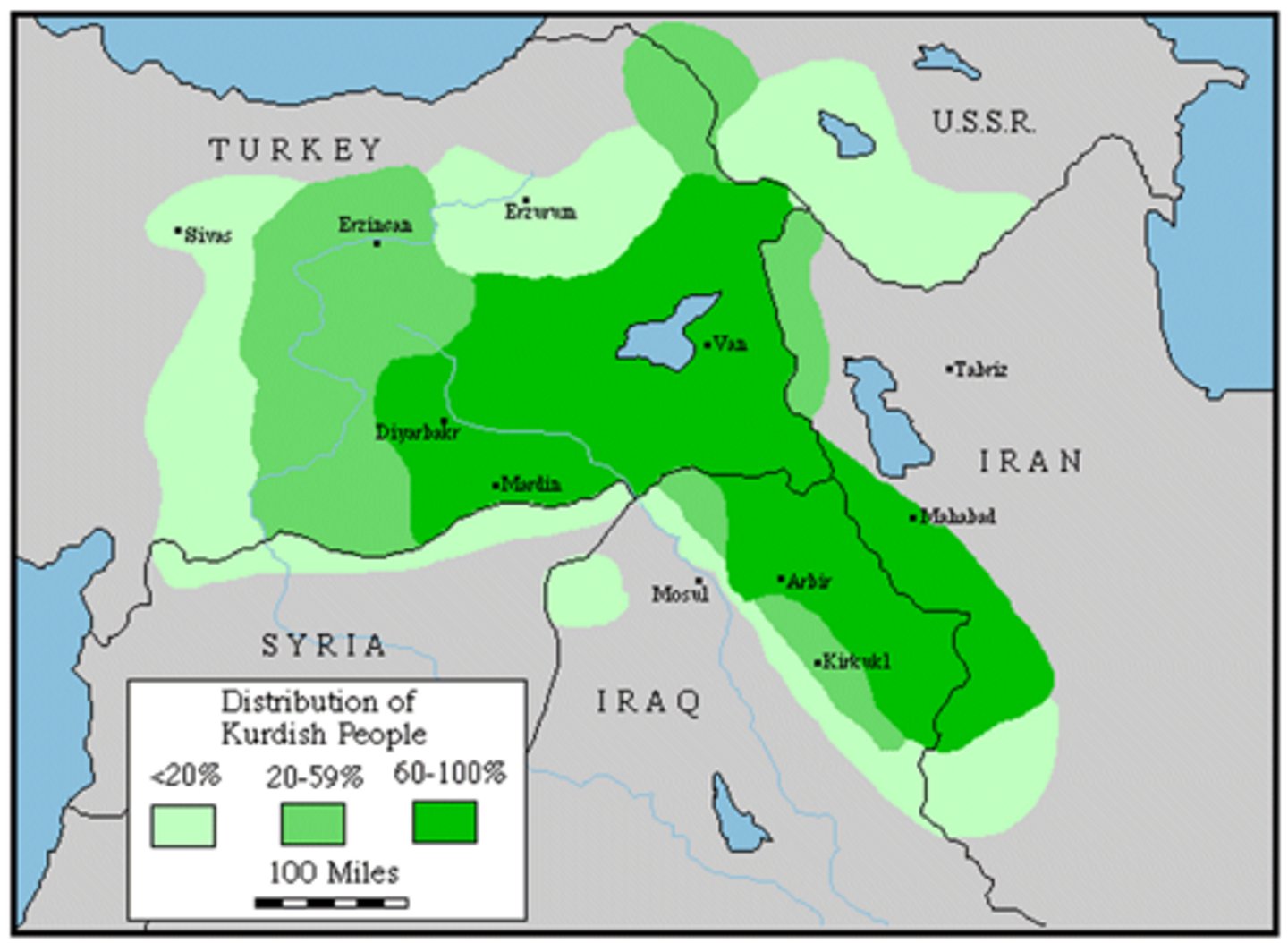
Kurdistan
a stateless nation that is spread throughout Turkey, Iraq and Syria
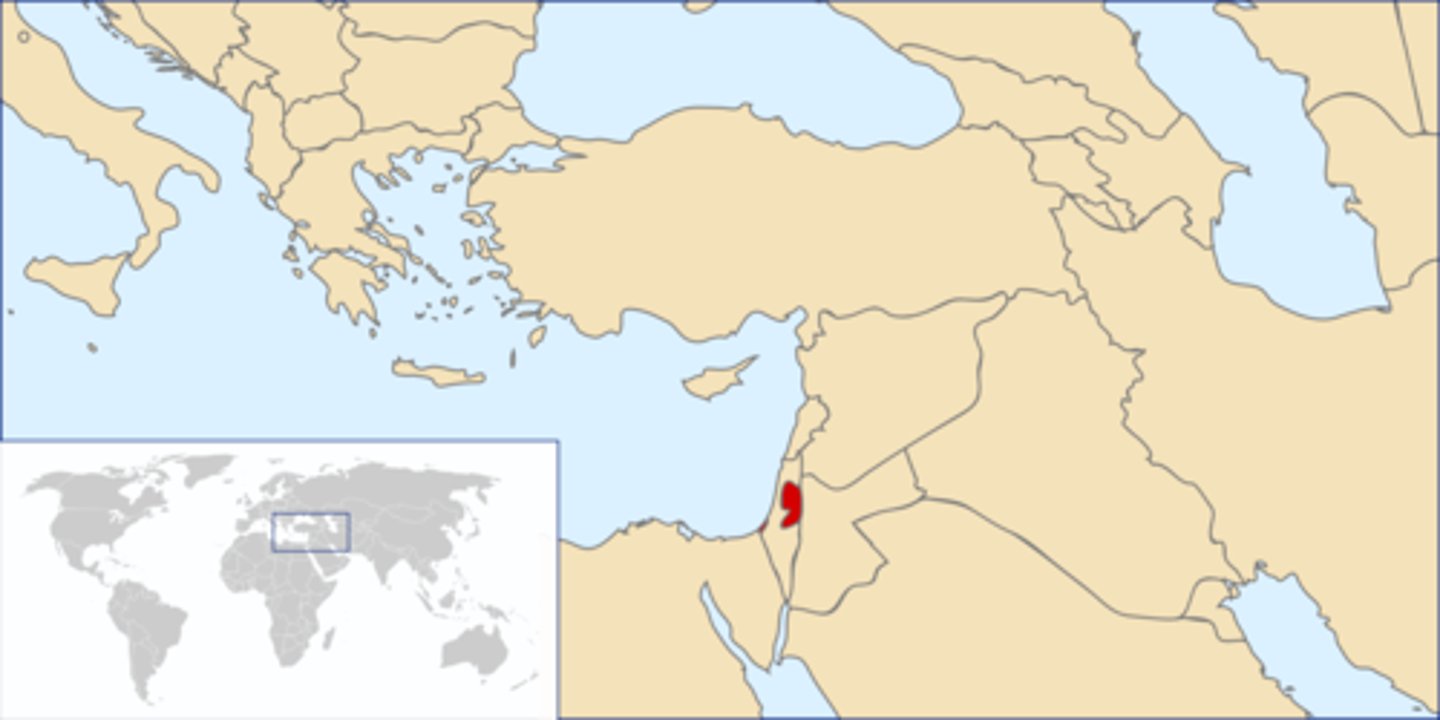
Palestine
stateless nation feuding with territory with Israel
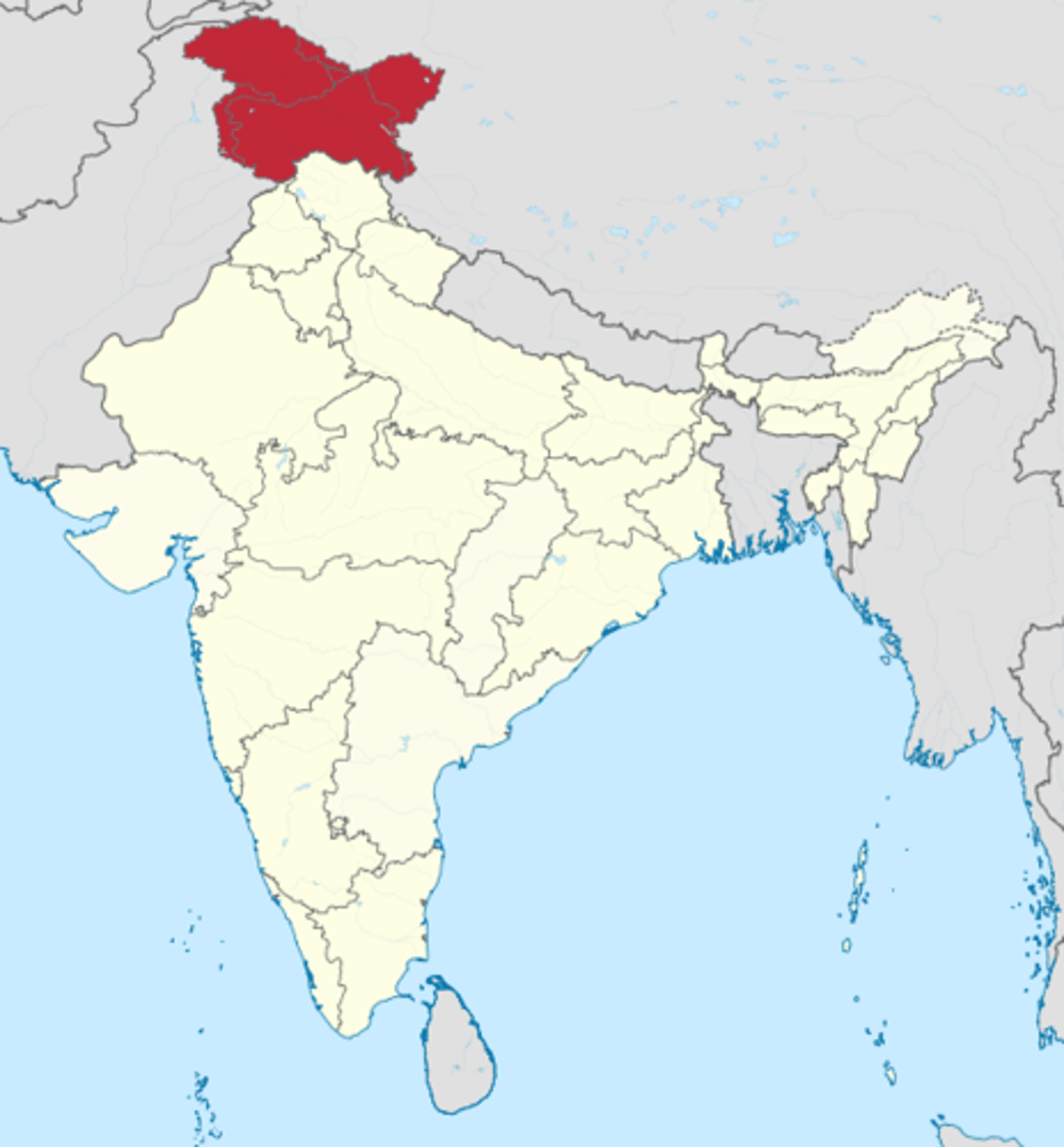
Kashmir
A region in the northwestern part of the Indian subcontinent; India and Pakistan dispute control of it. Predominantly Muslim.
stateless nation
A nationality that is not represented by a state.
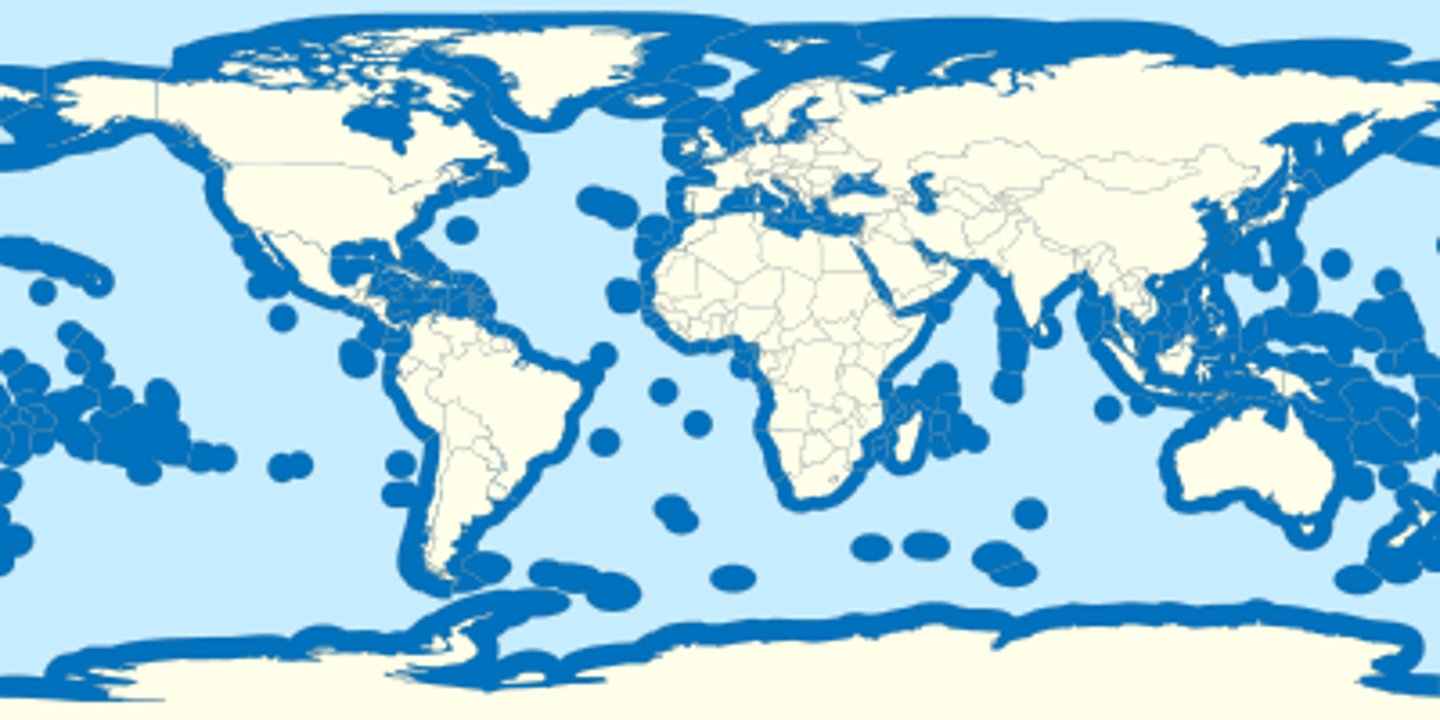
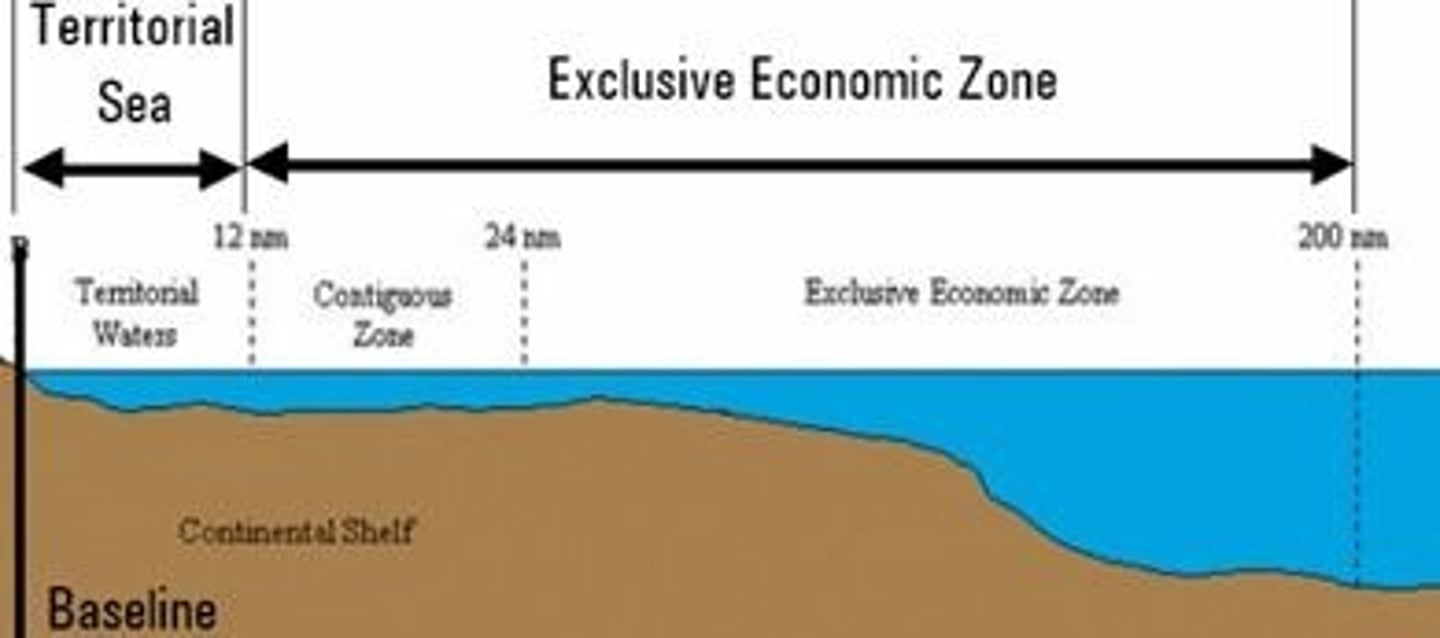
UNCLOS
A code of maritime law approved by the United Nations in 1982 that authorizes, among other provisions, territorial waters extending 12 nautical miles (22km) from shore and 200-nautical-mile-wide (370-km-wide) exclusive economic zones.
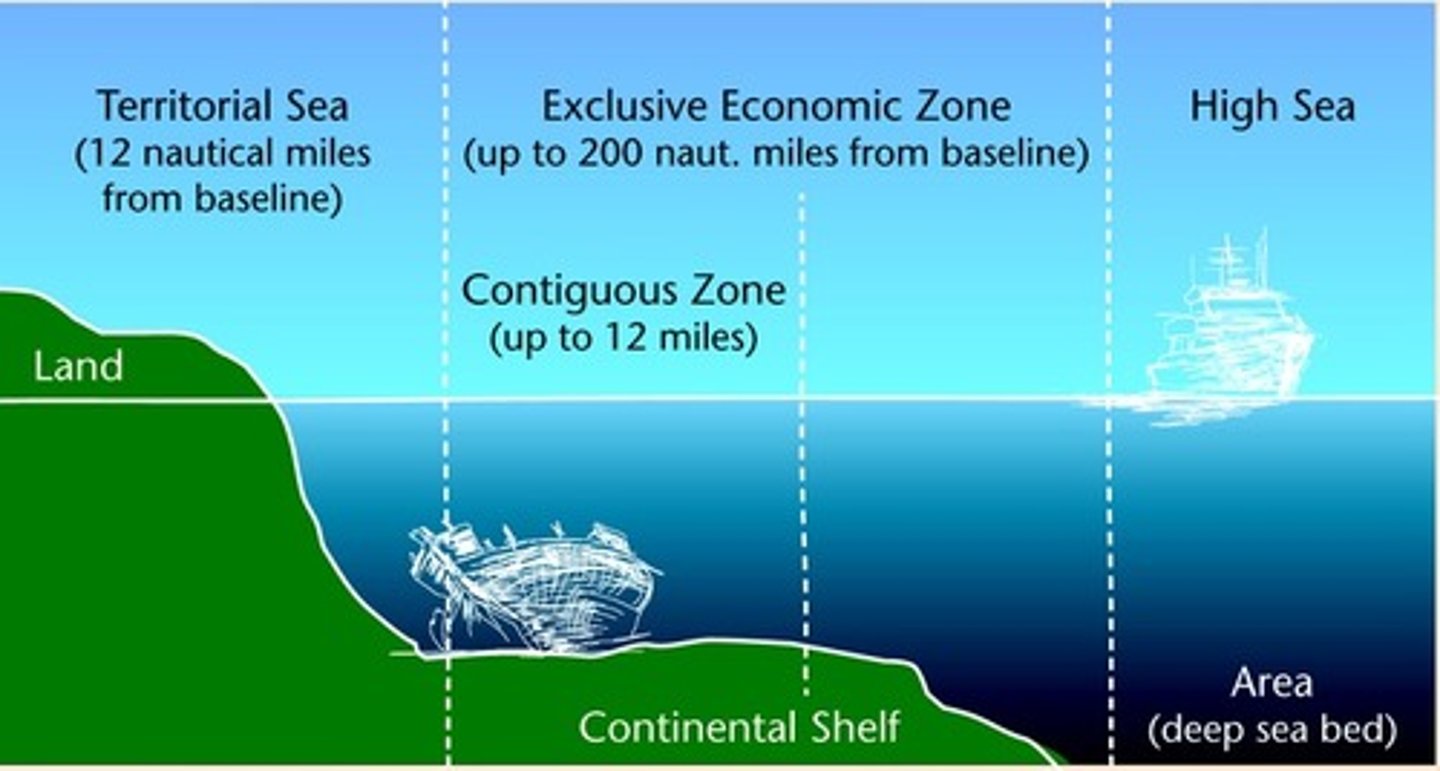
Exclusive Economic Zone (EEZ)
the seazone extending 200 nautical miles from the coast over which a state has special rights as to the exploration and use of marine resources
Territorial Zone
12 mile zone belonging to a nation that no one may enter without permission
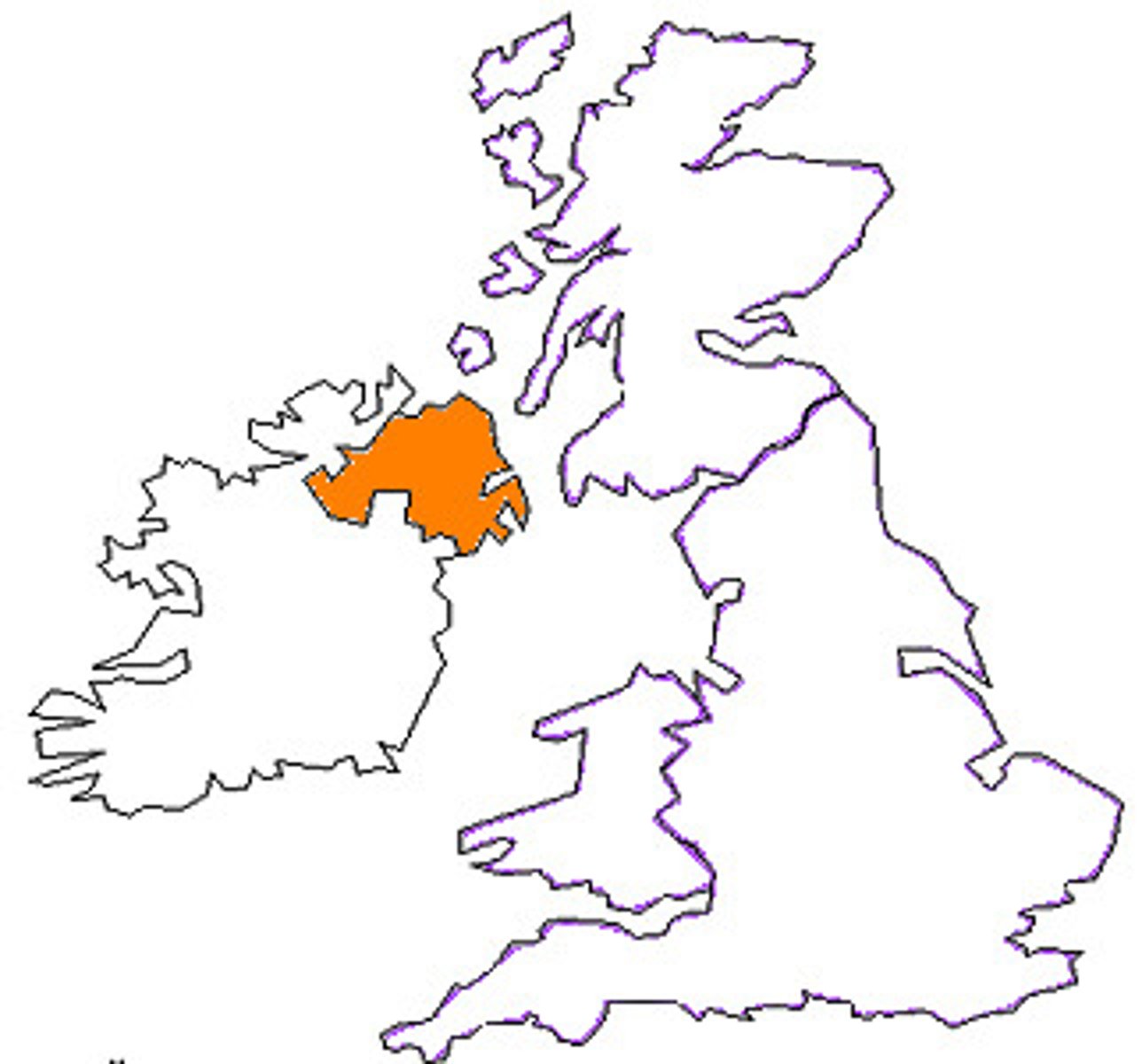
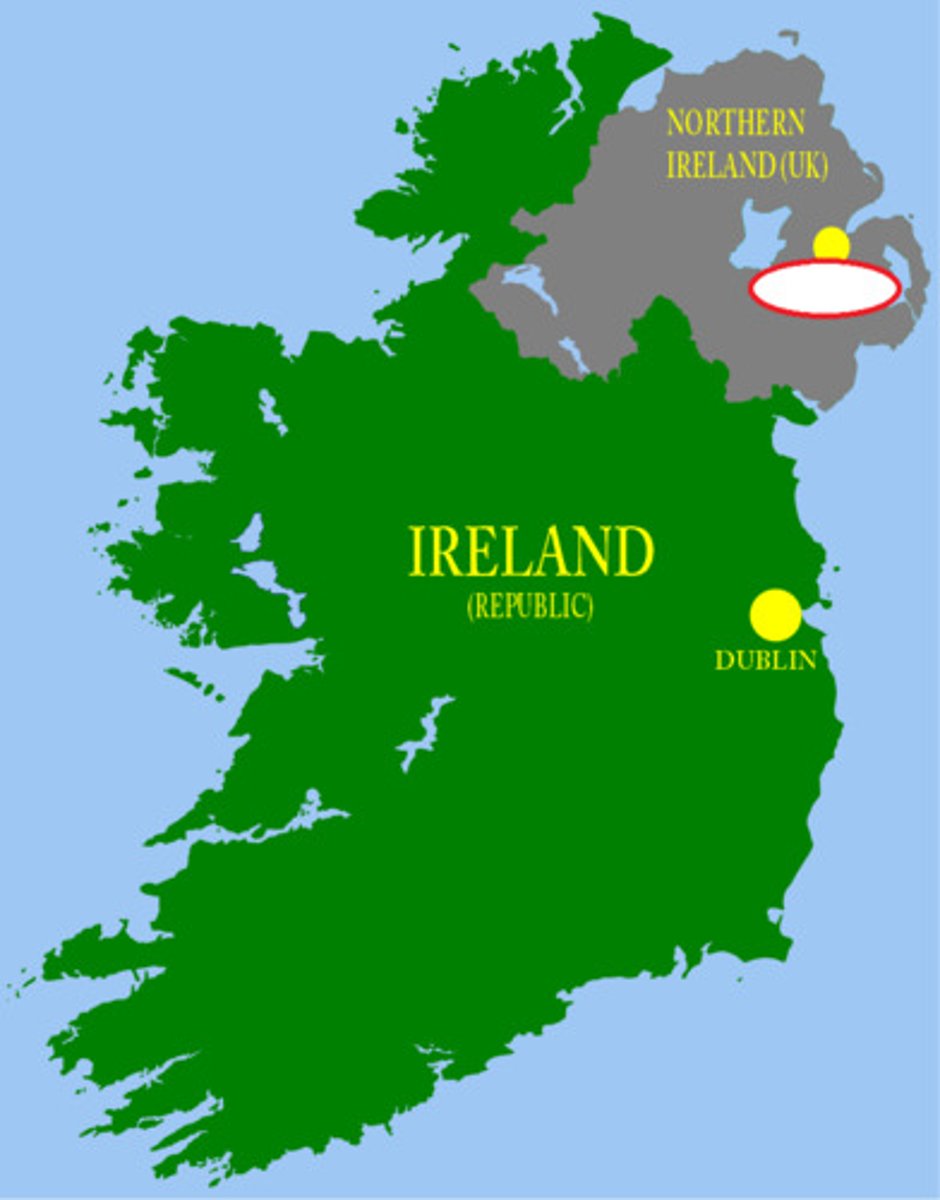
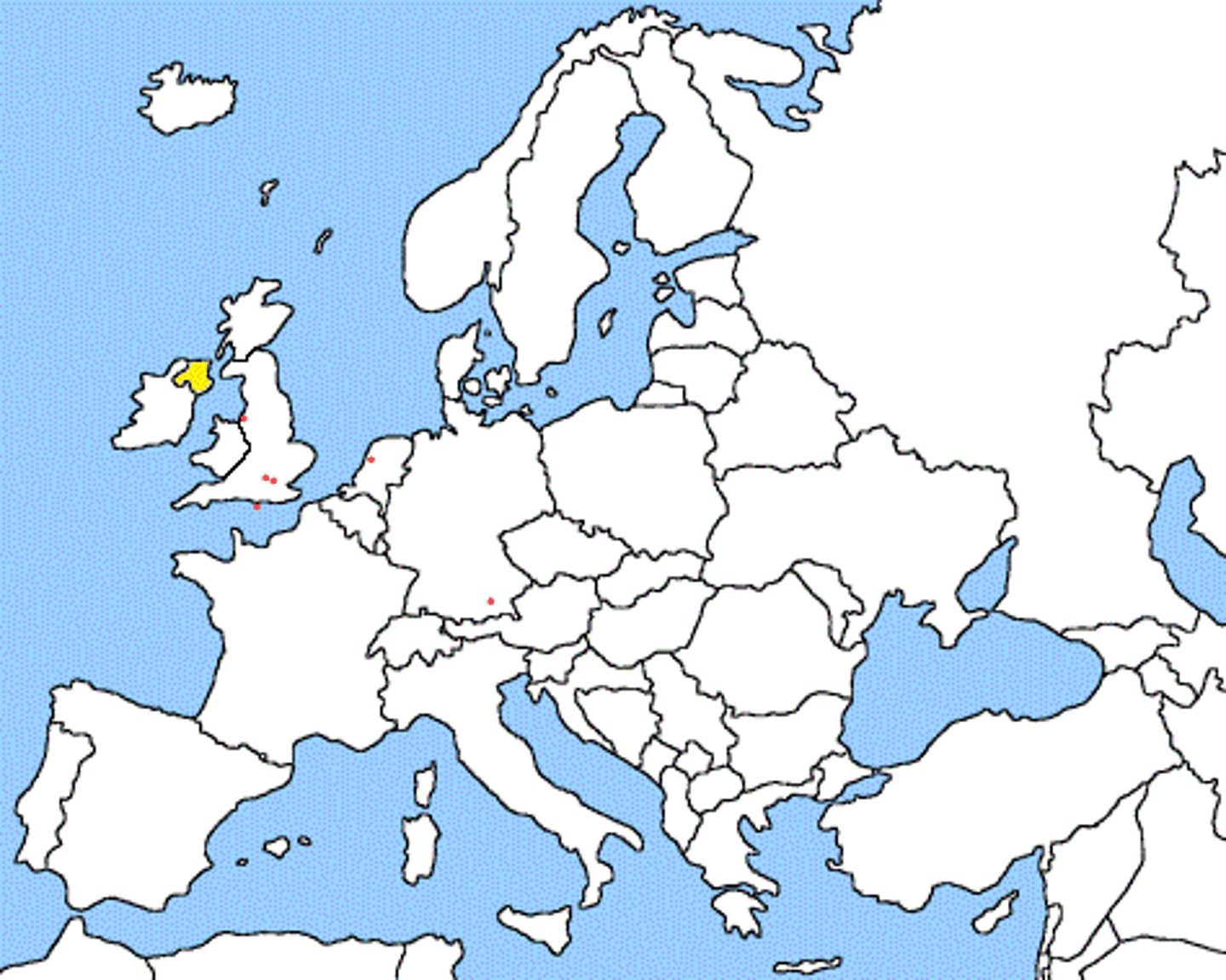
Northern Ireland/ Ireland
countries are separated by Catholicism and Protestantism
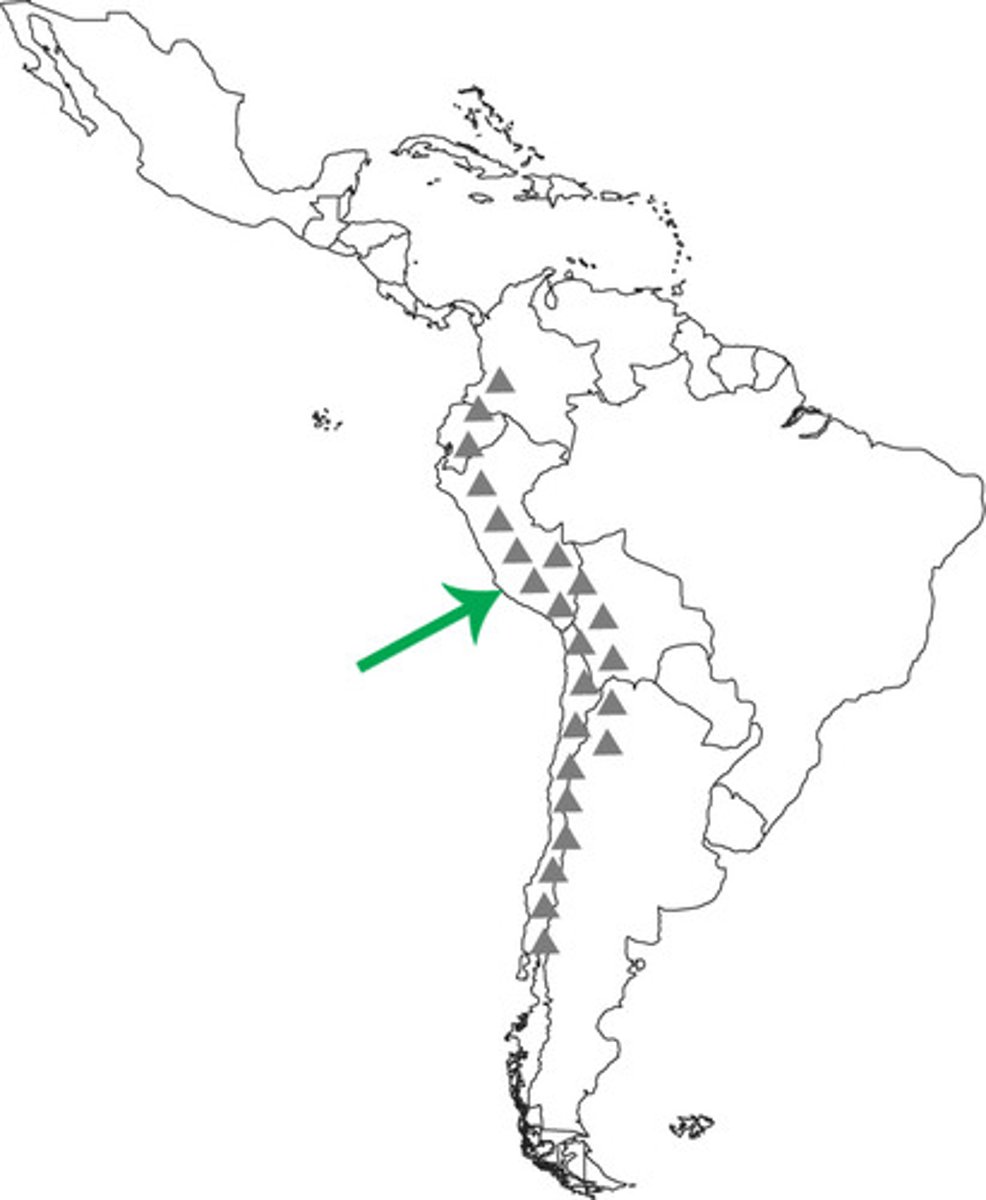
Argentina/ Chile
has the Andes mountain as a physical boundary.
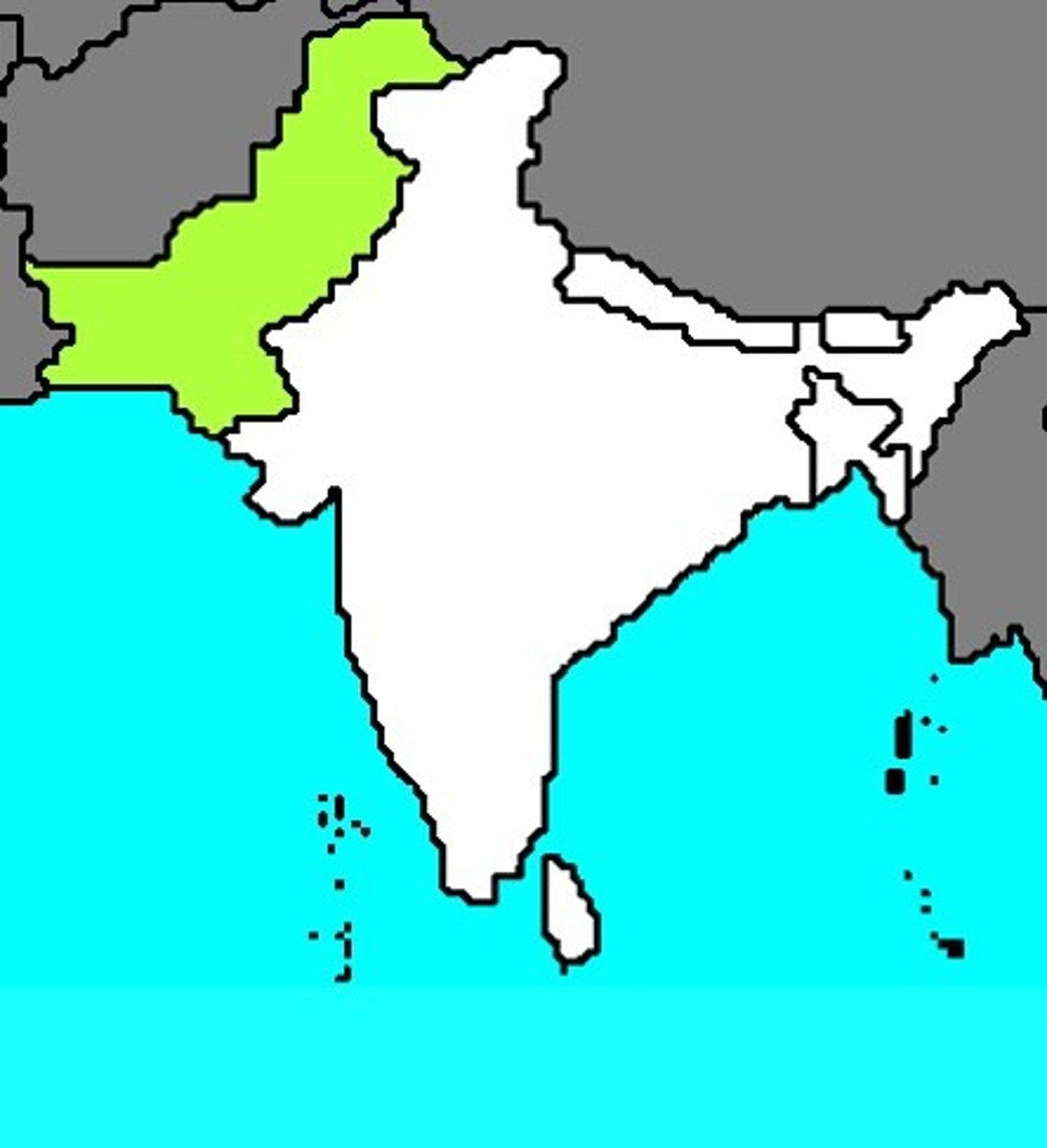
India/Pakistan
countries are separated by religion Hinduism and Islam
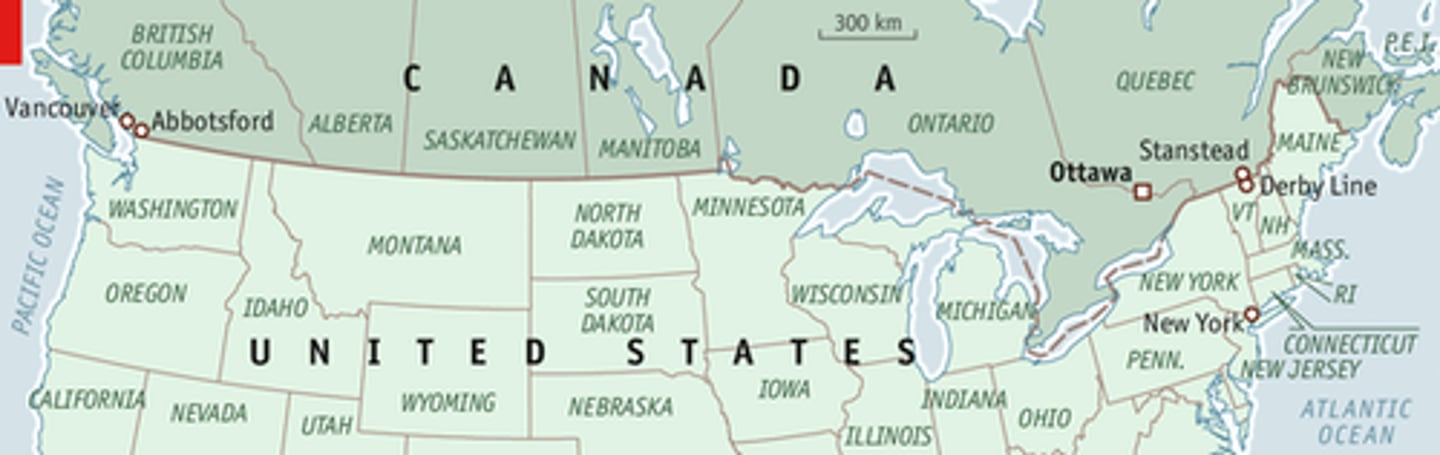
USA/ Canada
countries are separated by a line of latitude for a portion which is a geometric boundary
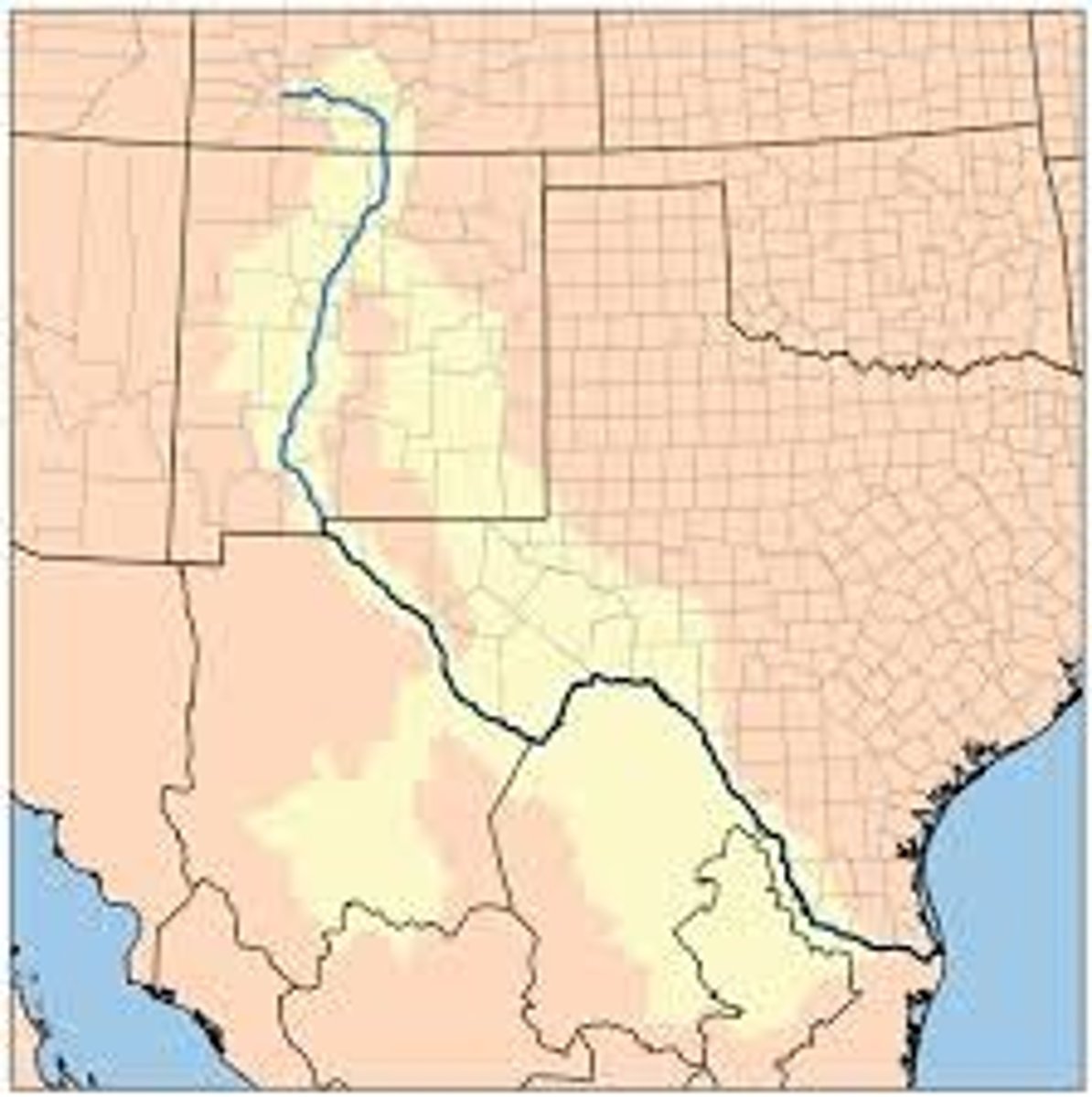
USA/ Mexico
countries are separated by a physical boundary the Rio Grande for a portion
autonomous region
an area of a country that has a degree of autonomy, or has freedom from an external authority
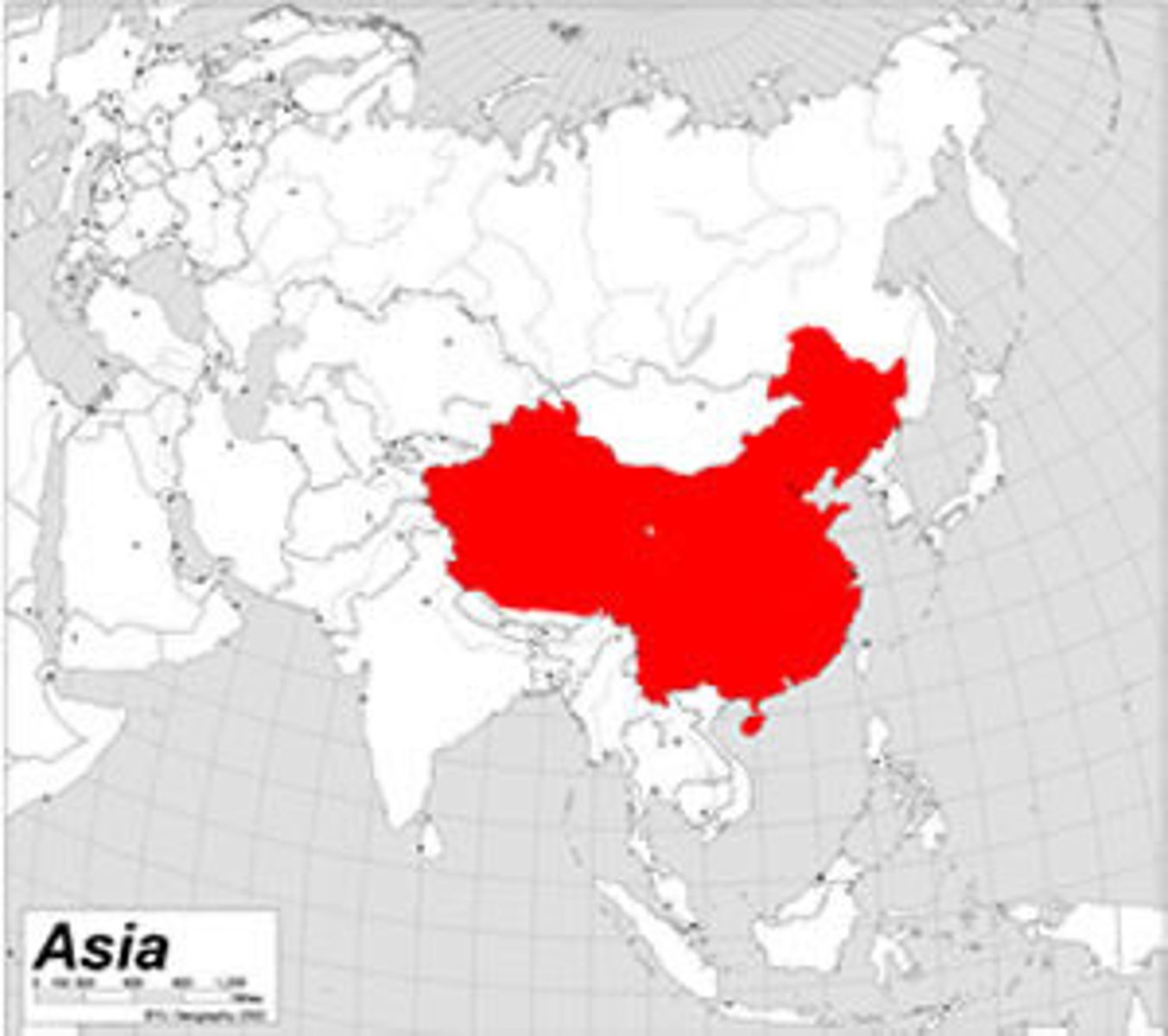
This country is an example of a unitary state
China
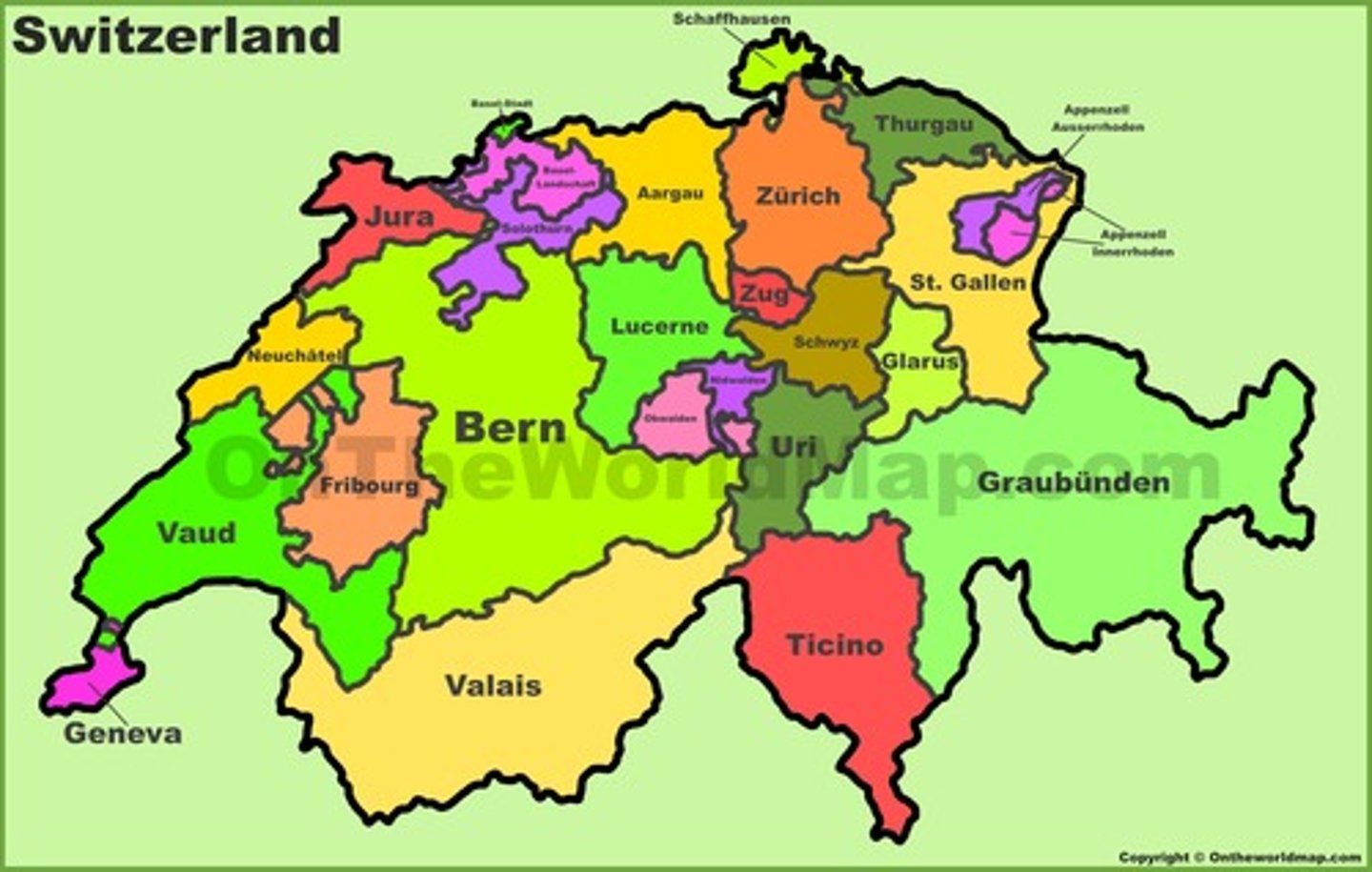
This country is an example of a federal state
Switzerland
ethnic cleansing
Process in which more powerful ethnic group forcibly removes a less powerful one in order to create an ethnically homogeneous region

Arctic boundary
five maritime boundaries between Russia, USA, Canada, Norway, and Denmark (Greenland)
Haiti and Dominican Republic
borderline is a product of French and Spanish colonialism