Concrete, Masonry & Steel – Vocabulary Review
1/75
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Vocabulary flashcards covering key terms, materials, tests, and systems related to concrete, masonry, and associated steel topics from Chapters 13–15 and related study-guide content.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
76 Terms
Concrete
A manufactured stone-like construction material made of Portland cement, water, fine aggregate (sand), and coarse aggregate (gravel, limestone, or granite).
Portland Cement
The binding agent in concrete that reacts chemically with water to harden and gain strength.
Fine Aggregate
Small-sized particles such as sand used in concrete mixes to fill voids between coarse aggregate. (SAND)
Coarse Aggregate
Larger particles, typically gravel, crushed limestone, or granite, providing bulk and strength to concrete.
Concrete Mix (1 : 2 : 3)
Proportion of one part cement, two parts sand, and three parts coarse aggregate, with water added for workability.
Water-Cement Ratio
The weight ratio of mixing water to cement; principal factor controlling concrete strength.
Fly Ash
Fine powder from coal-fired power plants used as a concrete admixture to increase strength, improve workability, and enhance sustainability.
Ground Blast-Furnace Slag
Granulated by-product of iron production added to concrete for strength and durability.
Microsilica (Silica Fume)
Very fine silica powder used to increase concrete strength and reduce permeability.
Air-Entraining Admixture
Additive that forms microscopic air bubbles in concrete to resist freeze-thaw damage and improve workability.
Laitance
Surface accumulation of cement fines caused by upward water movement in fresh concrete; must be removed before placing new concrete.
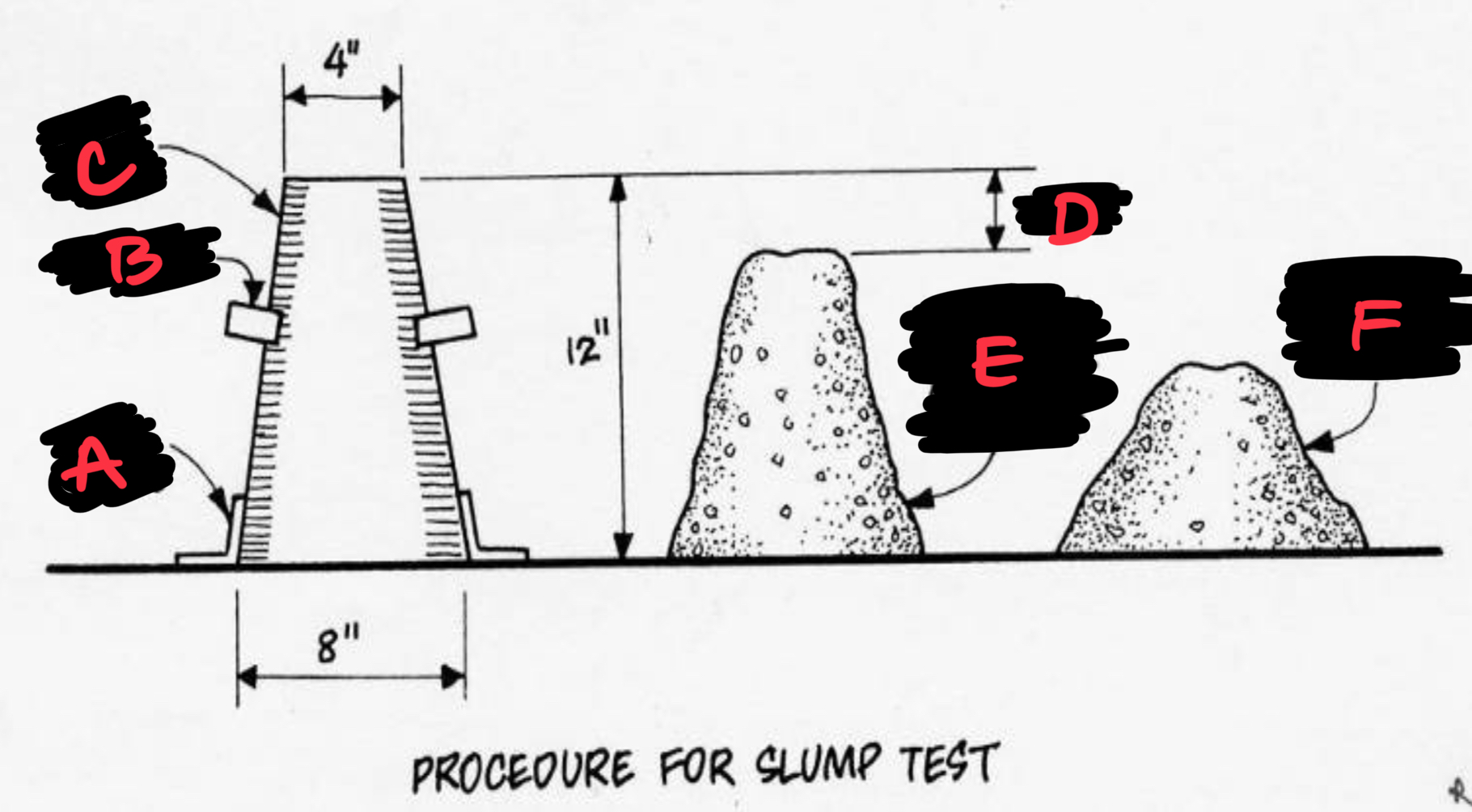
Slump Test
Field test measuring the consistency and workability of fresh concrete by the subsidence of a cone-shaped sample.
Cylinder Test
Laboratory test of concrete compressive strength using 28-day-cured cylindrical specimens.
Impact Hammer Test
Non-destructive test estimating in-place concrete strength by the rebound of a spring-loaded hammer.
28-Day Compressive Strength
Standard age at which concrete’s specified compressive strength (e.g., 3,000 psi) is cured
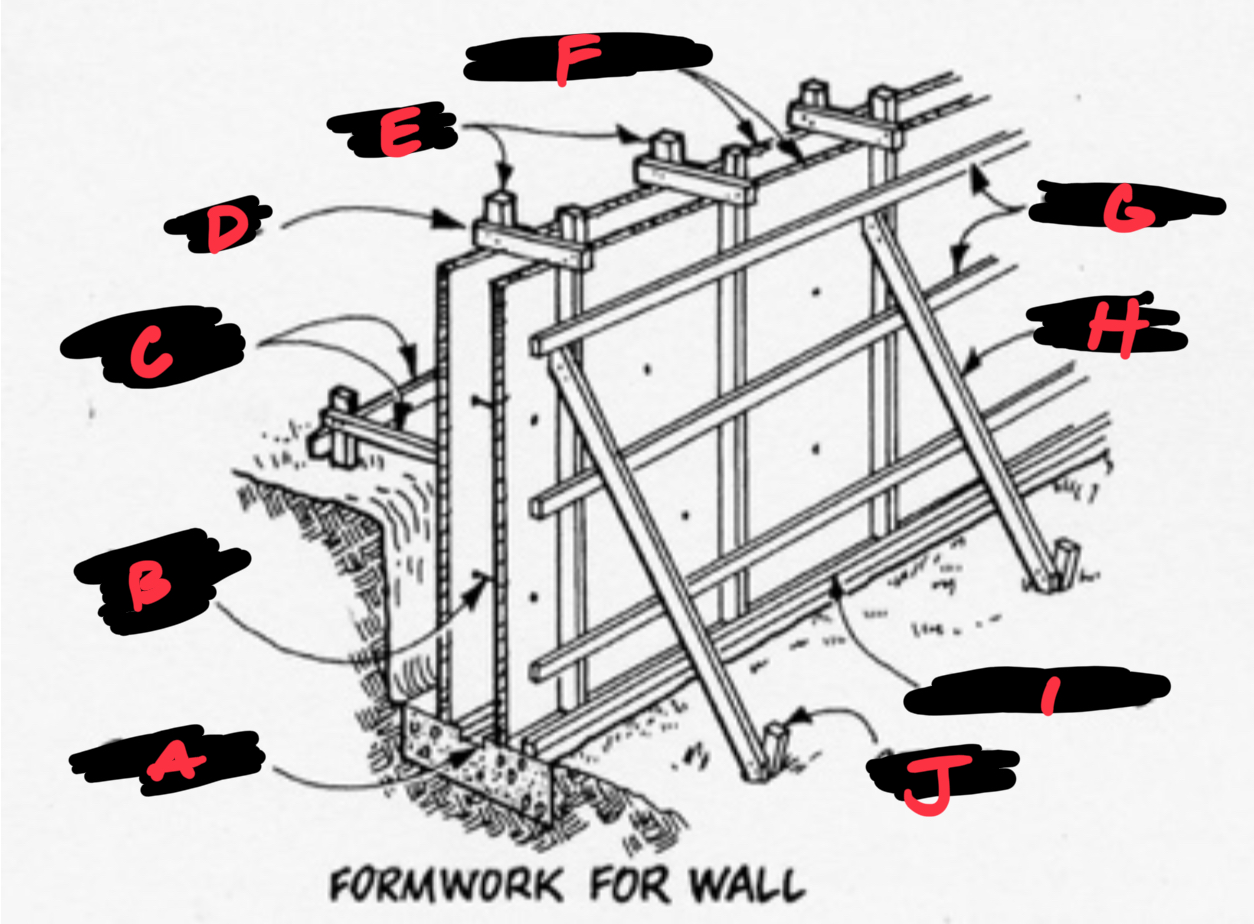
Formwork
Temporary molds used to shape cast-in-place concrete; major cost factor of concrete construction.
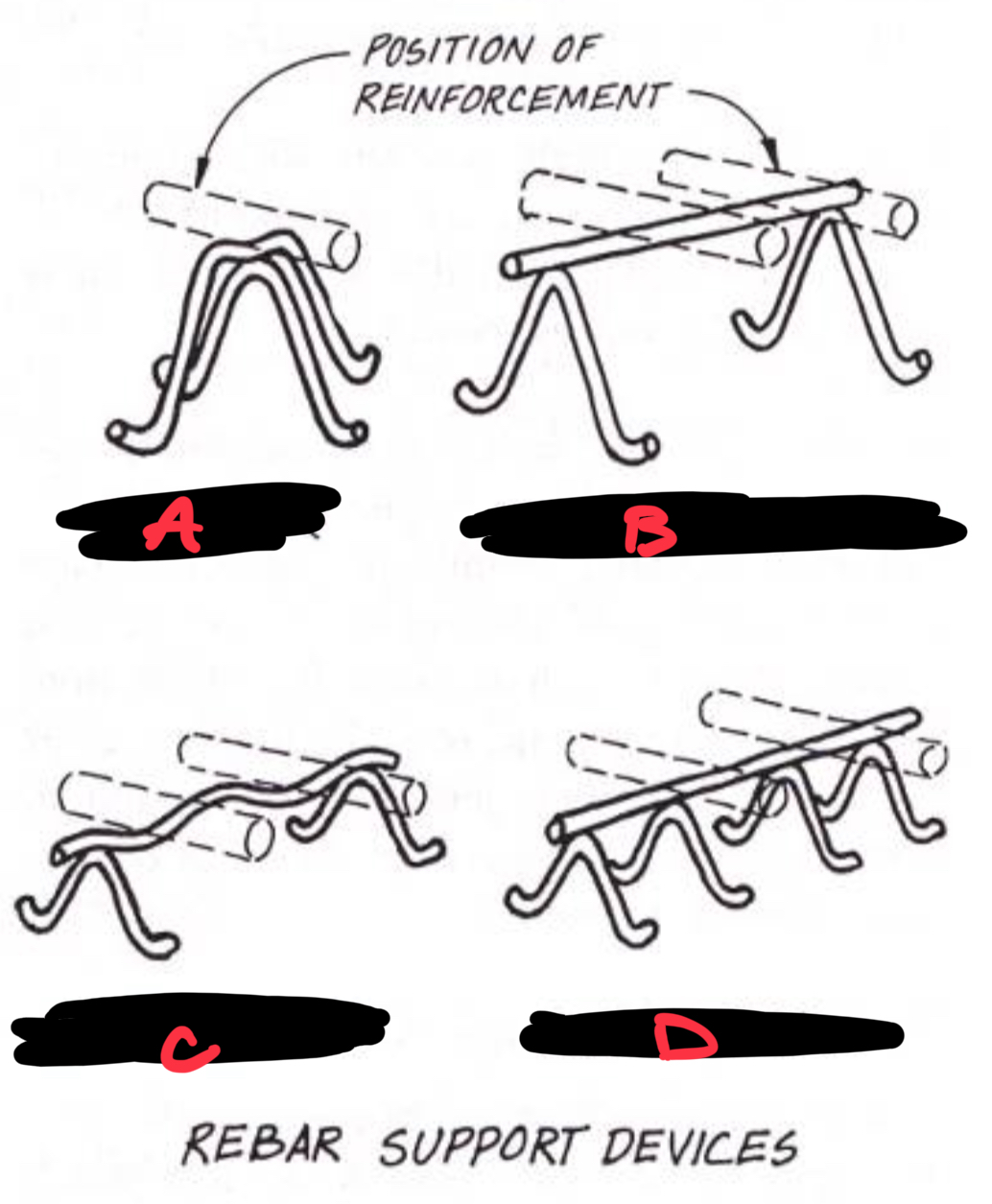
Rebar
Steel reinforcing bars placed in concrete to provide tensile strength.
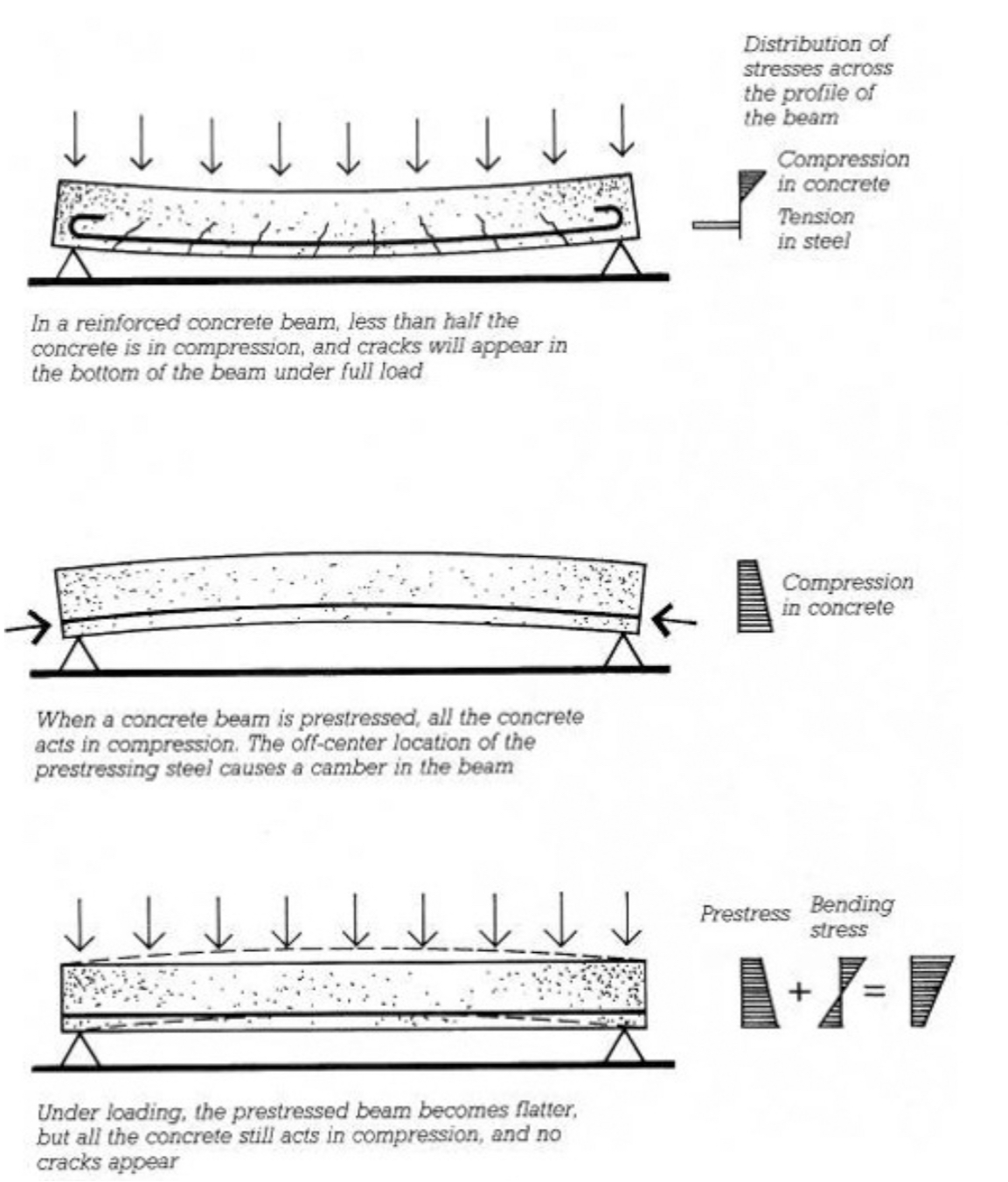
Reinforced Concrete
Concrete strengthened with embedded steel reinforcement to resist tensile stresses.
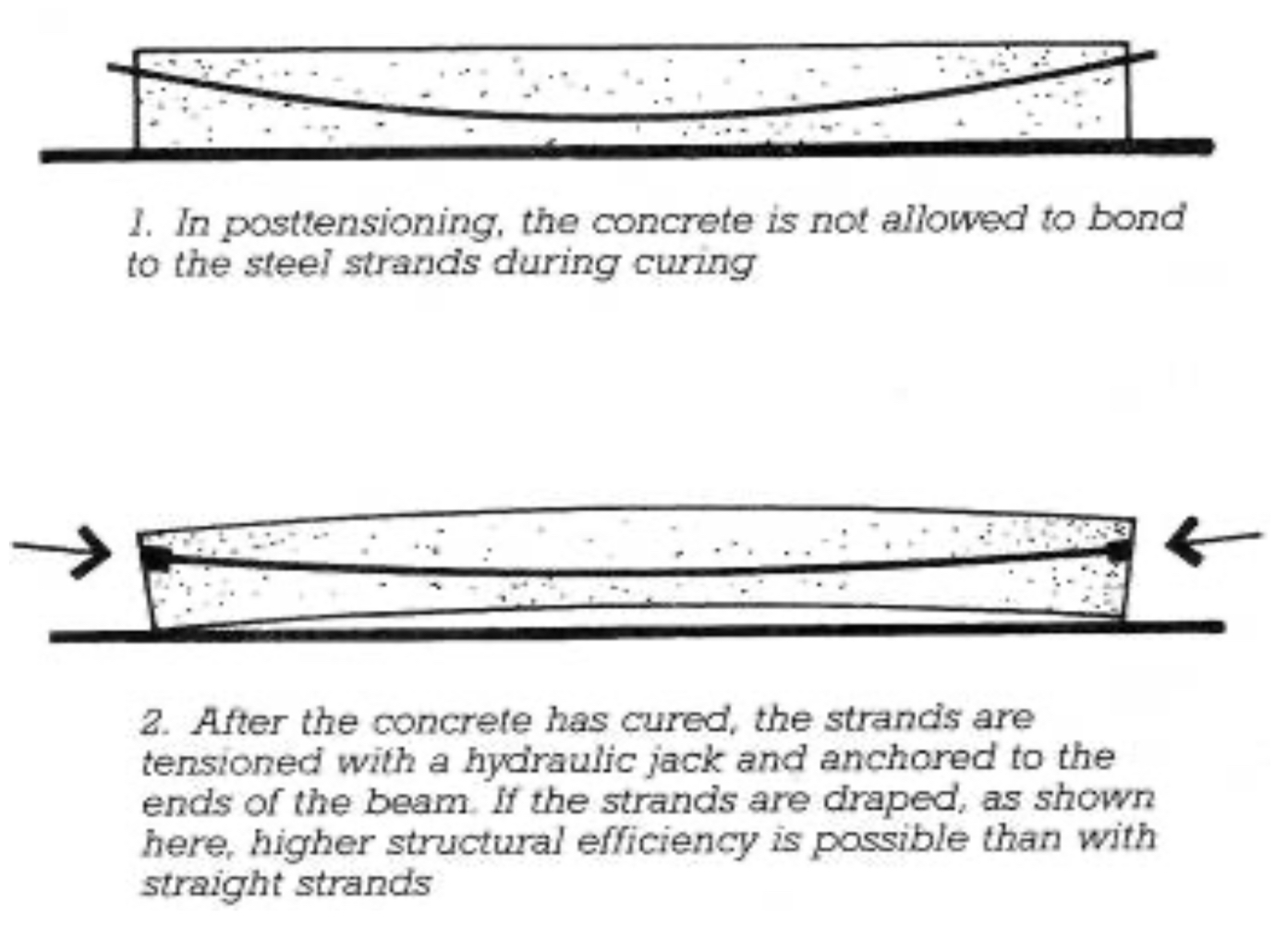
Prestressed Concrete
Concrete in which steel tendons are tensioned before (pre-tensioning) or after (post-tensioning) casting to reduce tensile cracking and increase capacity.
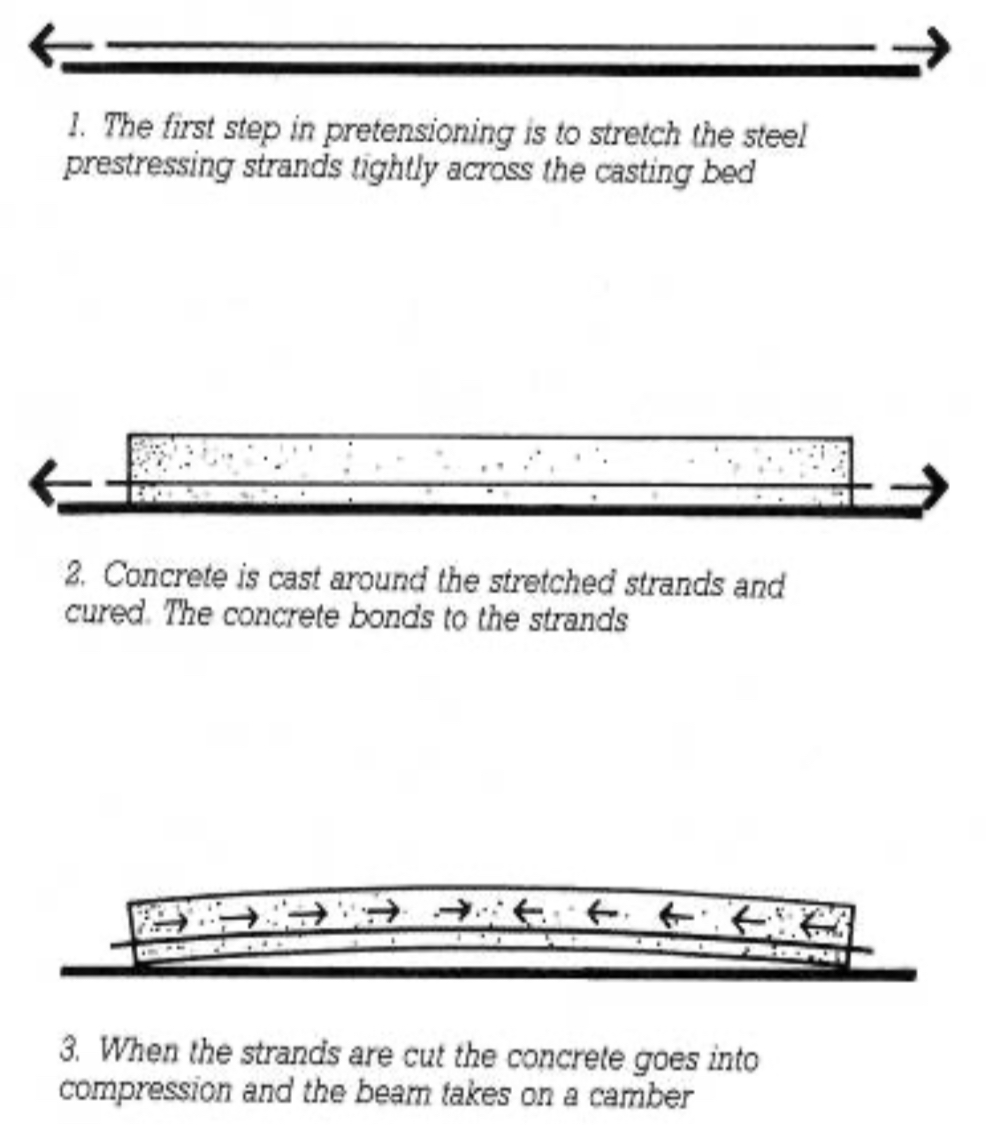
Pre-Tensioning
Method of prestressing where tendons are tensioned before concrete is placed and bond as it cures.
Post-Tensioning
Method of prestressing where ducts are cast, and tendons are tensioned after concrete has hardened.
Thermal Mass
Ability of a material like concrete to absorb and store heat, moderating indoor temperature swings.
Mortar
Cementitious paste of cement, lime, sand, and water used to bond masonry units.
Type M Mortar
High-strength mortar (about 2,500 psi) with high cement content for load-bearing masonry and below-grade walls.
Type S Mortar
Medium-high-strength mortar (about 1,800 psi) suitable for structural walls and exterior applications subject to wind or seismic loads.
Type N Mortar
General-purpose mortar (about 750 psi) used for above-grade, non-load-bearing masonry.
Type O Mortar
Low-strength mortar (about 350 psi) for interior, non-load-bearing walls and restoration work.
Grout (Masonry)
Flowable mixture similar to mortar but with higher water content, poured into CMU cores or cavities for strength and reinforcement bond.
Efflorescence
White crystalline deposit on masonry surfaces caused by water-soluble salts migrating and crystallizing upon evaporation.
Masonry Mortar Joint Tooling
Compacting and shaping of fresh mortar joints to make them watertight and give a finished appearance.
CMU (Concrete Masonry Unit)
Standardized concrete block used in reinforced or load-bearing masonry construction.
Solid Flat Slab
Precast concrete floor element with uniform thickness and flat soffit; relies on shear reinforcement or drop panels for punching resistance.
Hollow Core Slab
Precast floor plank 2–4 ft wide with continuous voids to reduce weight and provide conduit space.
Double-Tee Slab
Precast concrete member shaped like two letter T’s joined, 8–10 ft wide, offering long spans and high load capacity.
Single-Tee Slab
Precast slab shaped like one letter T, used similarly to double-tees but narrower.
Waffle Slab
Cast-in-place concrete floor with a grid of ribs forming coffers, providing strength with reduced weight.
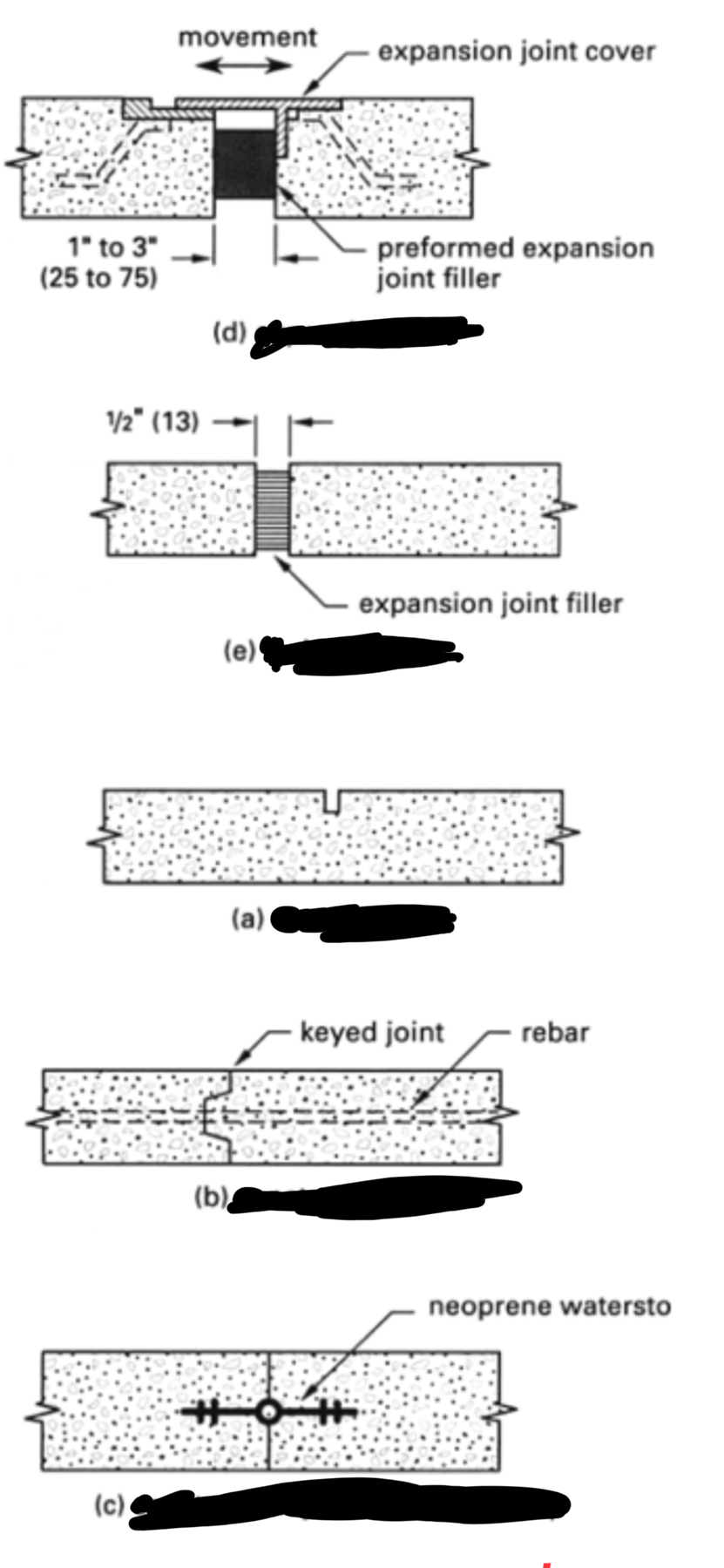
Control Joint
Planned groove or weakened plane that allows shrinkage cracking to occur in a controlled location.
Isolation Joint
Joint separating slabs from columns or walls to allow independent movement and avoid restraint cracking.
Steel (Carbon Steel)
Iron-based alloy with less than 2 % carbon; stronger and less brittle than cast iron.
ASTM
American Society for Testing and Materials; publishes standards for materials, tests, and construction methods.
AISC
American Institute of Steel Construction; develops steel design specifications, codes, and research.
Allowable Stress Design (ASD)
Design method limiting service stresses in steel members; basis for K-series open-web steel joist tables.
Hot Weather
Greatest environmental factor + concern when pouring concrete
Steel
Metal alloy whose major component is iron, with less than 2% carbon content
Increasing Carbon Content in Steel
Can be made harder and stronger than iron, but also more brittle
Cast Iron
Alloys with higher carbon content greater than two percent [2%]
Carbon
most cost-effective alloying material for iron, but many other alloying elements is also used… carbon and other elements act as hardening agents
Steel Reinforcing
Rebar Mesh ETC ] used in reinforced concrete, provide tensile strength in structural concrete
How does concrete cure?
through a chemical reaction
How does concrete resist tension?
using steel reinforcing
basic material properties of reinforced concrete:
reinforced concrete is great in thermal mass and is good in thermal insulation
§ reinforced concrete has better resistance to fire than steel
§ reinforced concrete has a sustainable long-term life cycle and durability with minimum maintenance
§ reinforced concrete has a relatively high compressive strength compared to steel
Advantages of Pre-Stressed Concrete over Reinforced Concrete
pre-stressed concrete will reduce and eliminate tension cracks
pre-stressed concrete provides economy in repetitive applications
A HORIZONTAL TIES
B WEEP HOLES
C FLASHING
D SEALANT
E COMPRESSIBLE JOINT
F STEEL SHELF ANGLE ANCHORED TO STRUCTURE
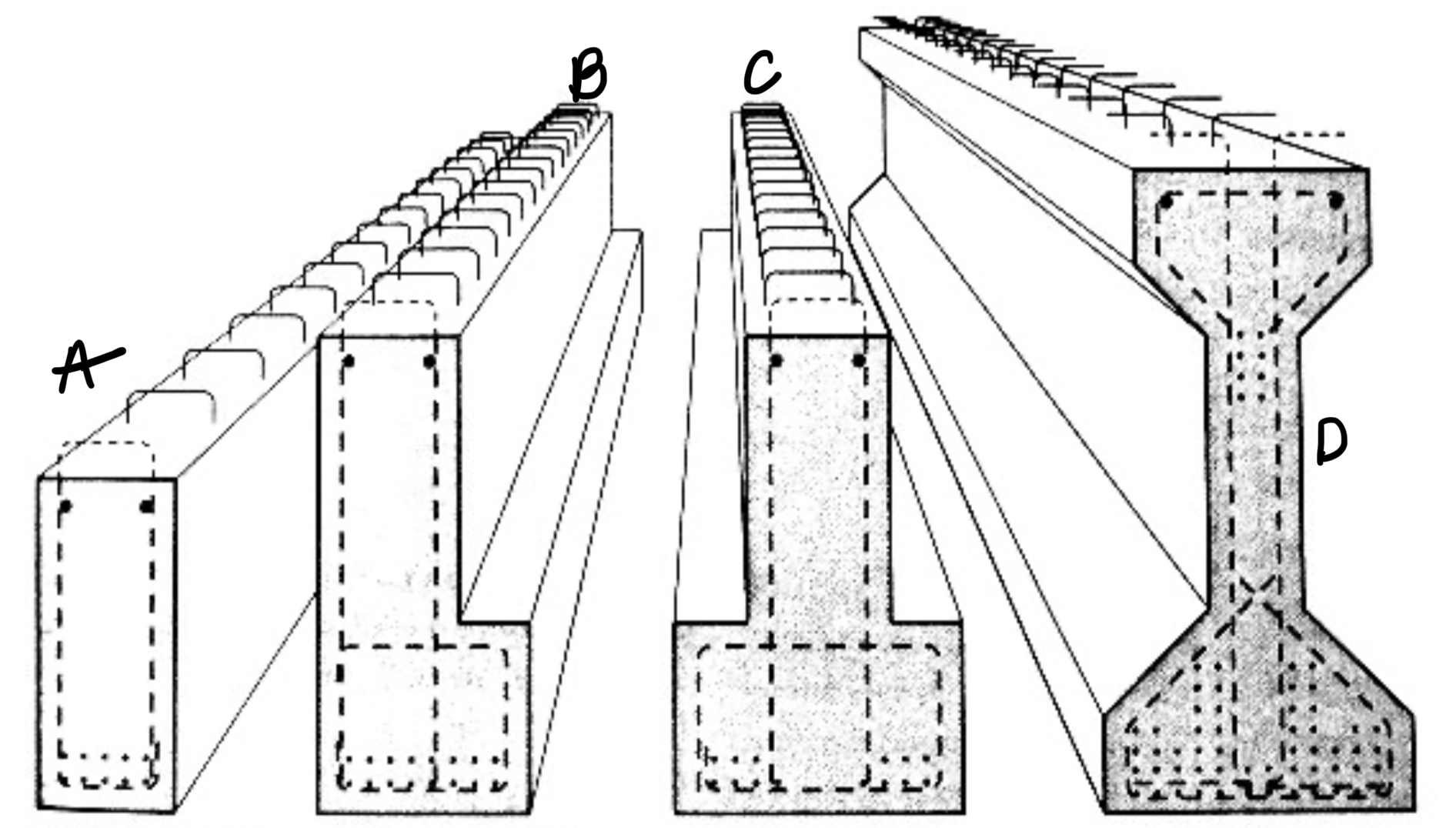
A RECTANGULAR BEAM
B L-SHAPED BEAM
C INVERTED TEE BEAM
D AASHTO BEAM
A RECTANGULAR BEAM
B L-SHAPED BEAM
C INVERTED TEE BEAM
D AASHTO BEAM
A FOOTING
B METAL TIE
C BRACES
D TIE
E STUDS
F SHEATHING
G WALERS
H BRACE
I SOLE PLATE
J STAKE
A SHORE POST
B SCAB
C BRACE
D T-HEAD ASSEMBLY
E 2X BOTTOM
F KNEE BRACE
G BEAM SIDE
H CONCRETE SLAB
I PLYWOOD DECK
J WOOD JOISTS
K LEDGER
L TOE PLATE
A HIGH CHAIR
B CONTINUOUS HIGH CHAIR
C SLAB BOLSTER
D BEAM BOLSTER
A FOOT HOLDS
B HANDLES
C CONE MOLDS
D SLUMP
E CONCRETE MIX AFTER MOLD IS REMOVED
F CONCRETE MIX AFTER TAPPING
A CONTROL JOINT
B FUTURE ISOLATION JOINT
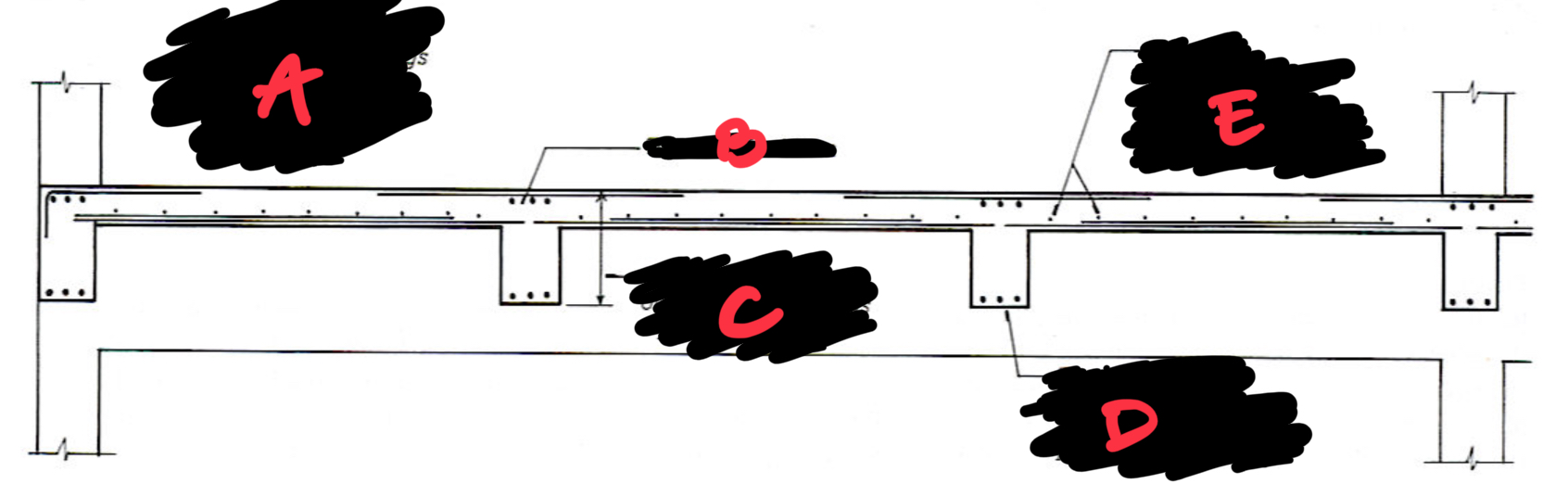
A THE THICKNESS OF THE SLAB IN THESE DRAWINGS IS EXAGGERATED IN ORDER TO SHOW THE REINFORCING BETTER
B TOP STEEL FOR BEAM
C THE ENTIRE THICKNESS OF THR CONCRETE ACTS AS A PART OF THE BEAMS;
D THE STIRRUPS HAVE BEEN OMITTED FROM THE BEAMS IN THIS DRAWING FOR THE SAKE OF CLARITY
E SHRINKAGE TEMPERATURE BARS REINFORCE AGAINST PARALLEL TO THE MAIN REINFORCING BARS
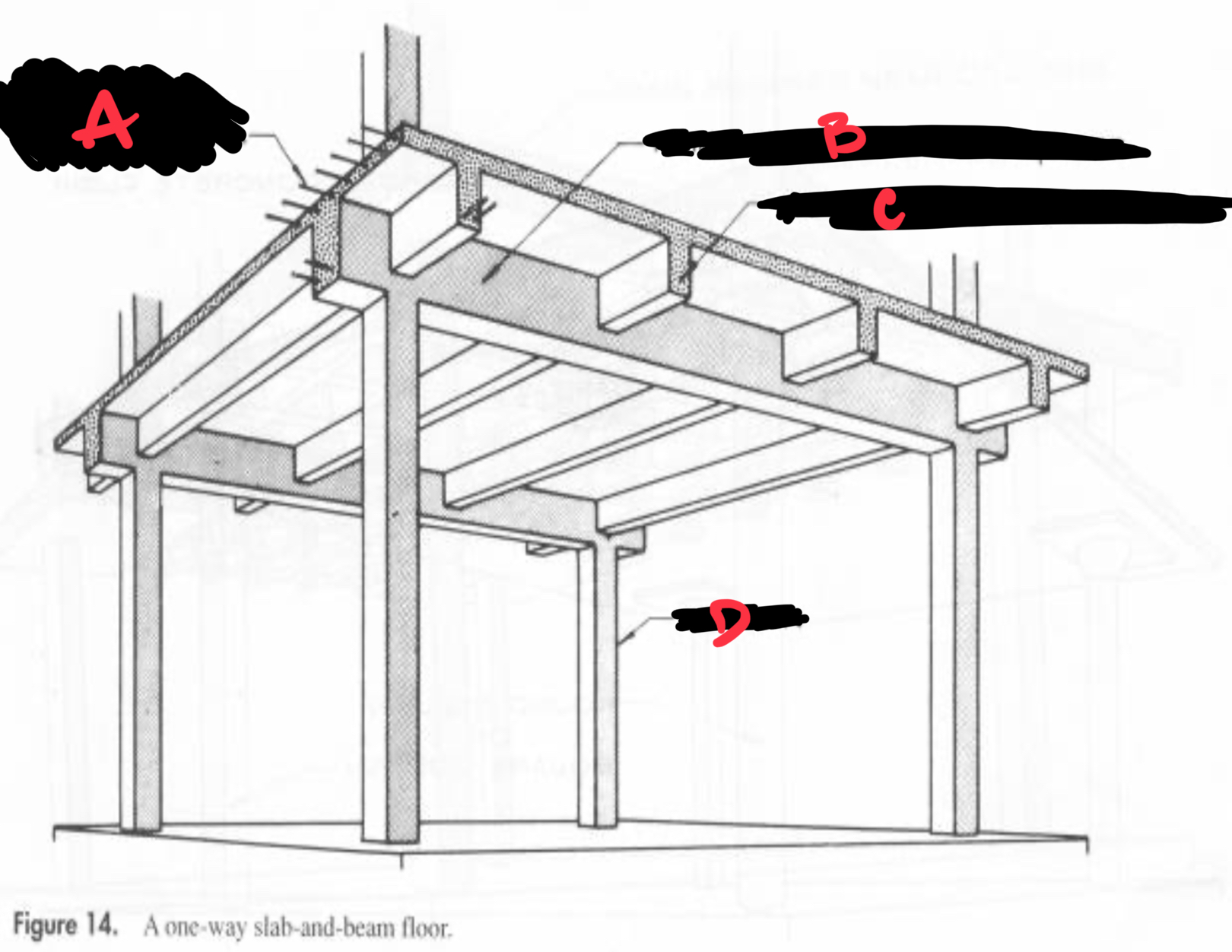
A REBARS FROM BEAM TO BEAM
B REINFORCED CONCRETE GIRDER
C REINFORCED CONCRETE BEAM
D COLUMN
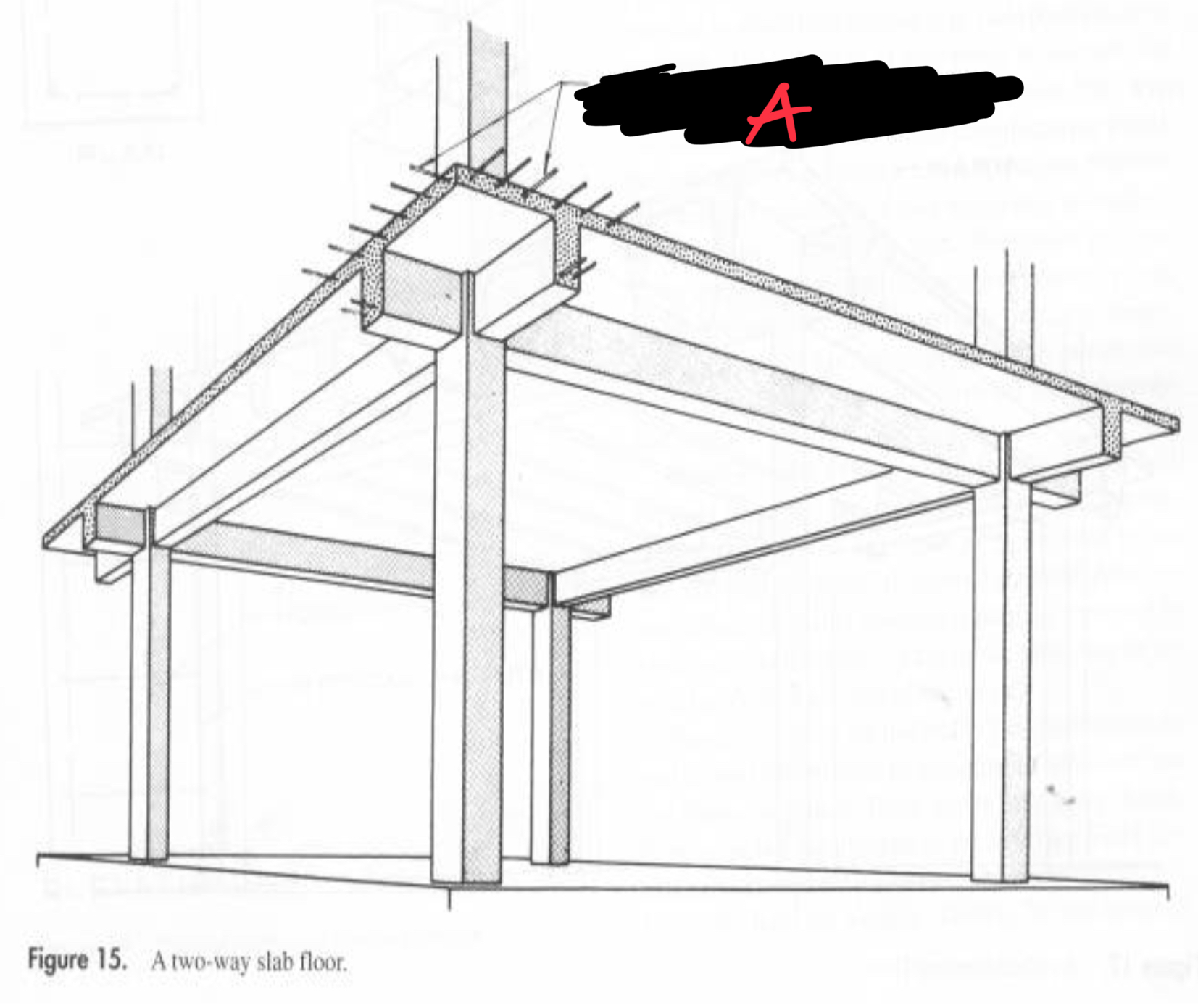
A REBARS BETWEEN BEAMS IN BOTH DIRECTIONS
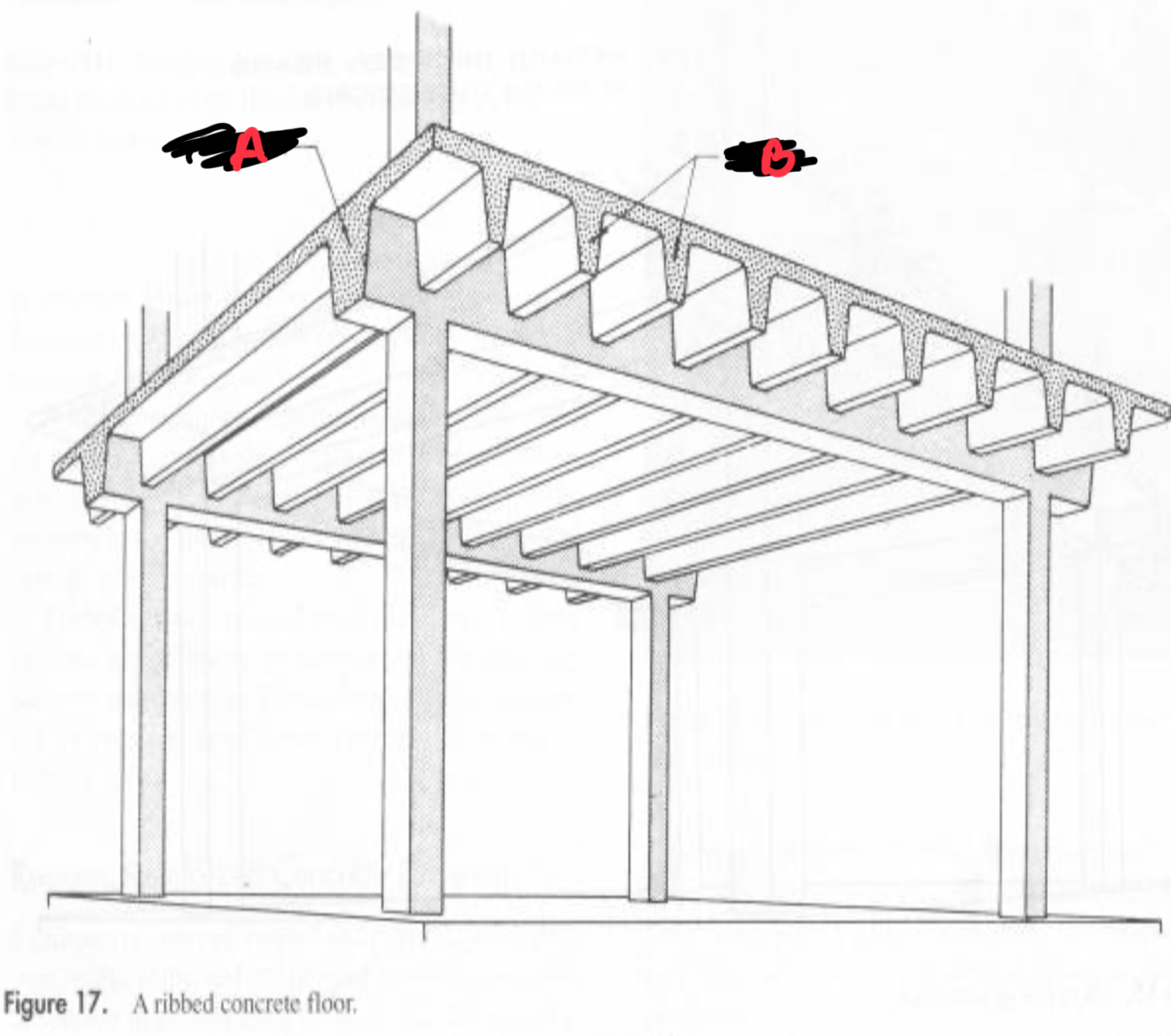
A BEAM
B RIBS
A PANS REMOVED NEAR COLUMNS
B WAFFLE RIBS
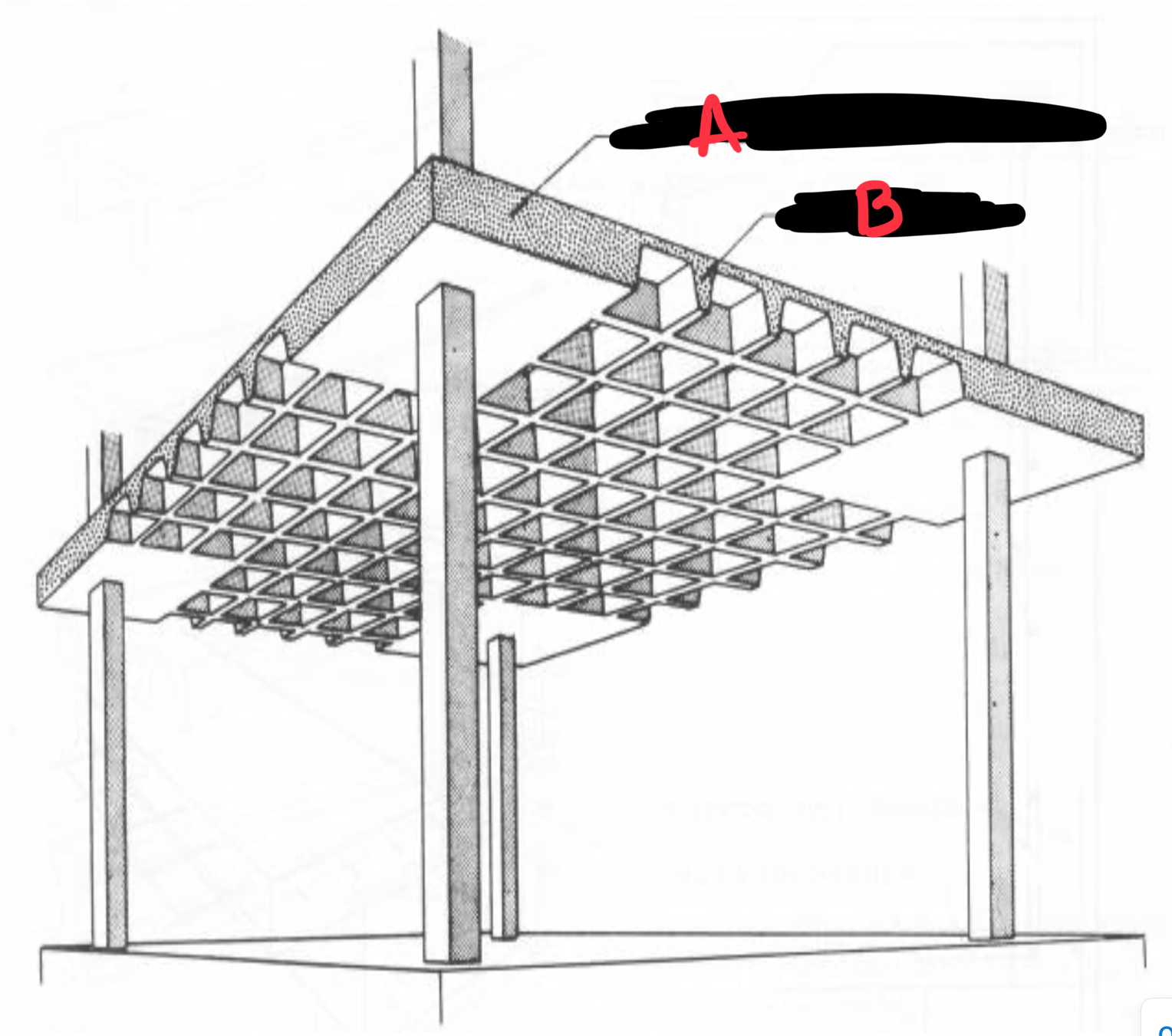
A COLUMNS
B PERIMETER BEAM
C ½ COLUMN STRIP
D & F MIDDLE STRIP
E COLUMN STRIP
G EDGE PANEL
H INTERIOR PANEL
I HEAD
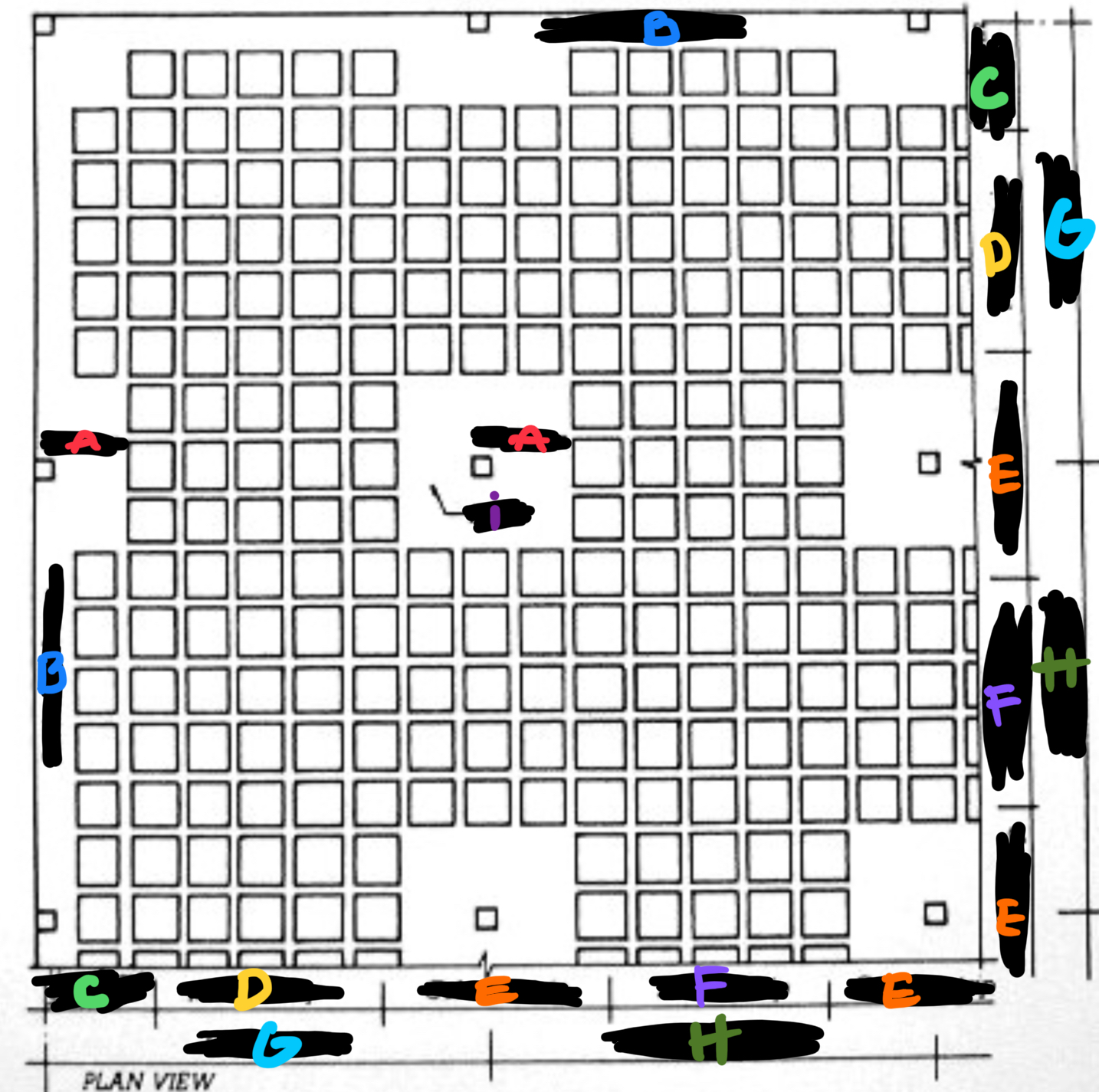
A STRETCHER BOND AKA RUNNING BOND
B COMMON BOND
C ENGLISH BOND
D CROSS BOND
E FLEMISH BOND
F STACK BOND
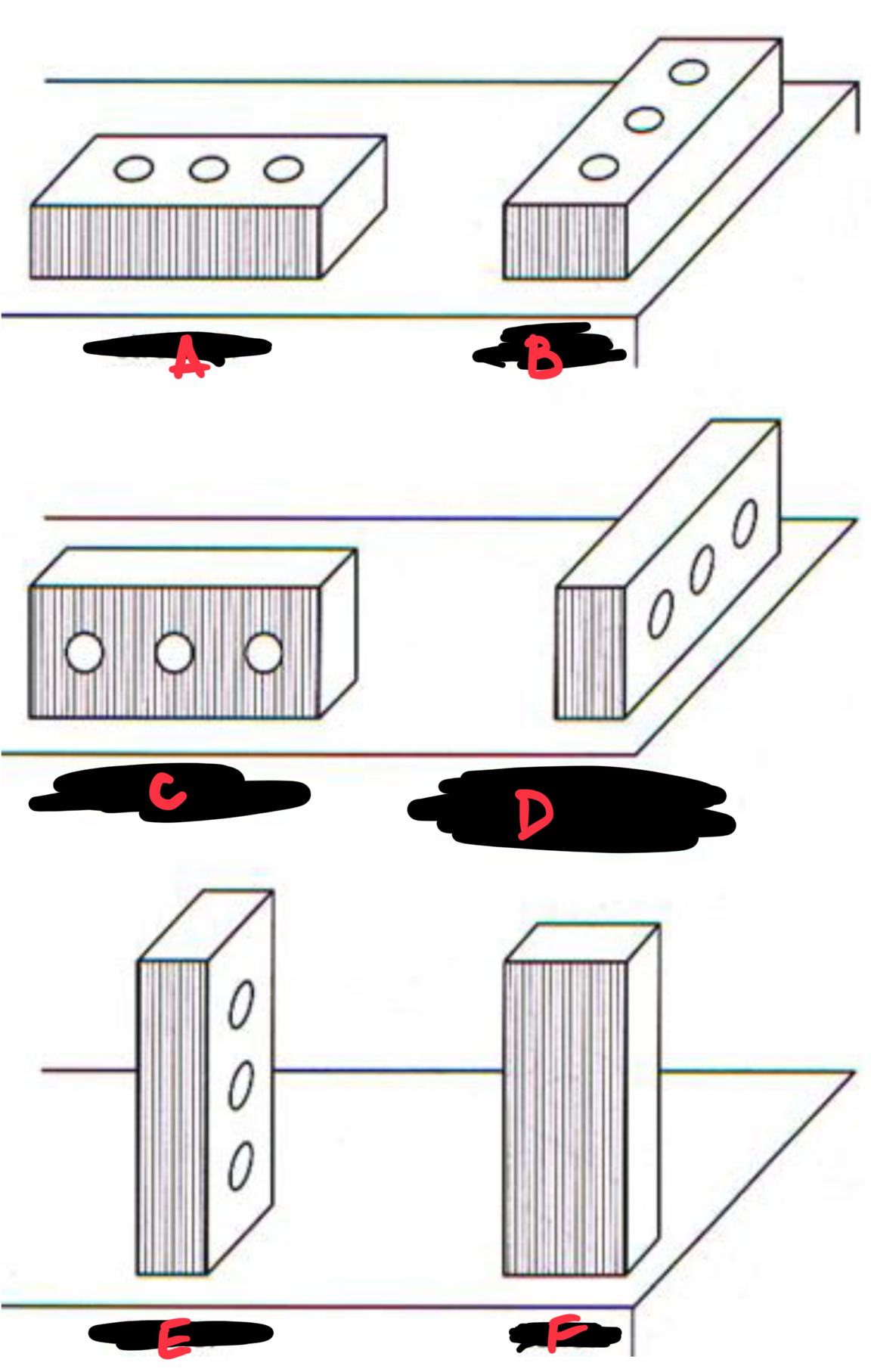
A STRETCHER
B HEADER
C BULL STRETCHER
D BULL HEADER (ROWLOCK COURSE)
E SOLDIER
F SAILOR
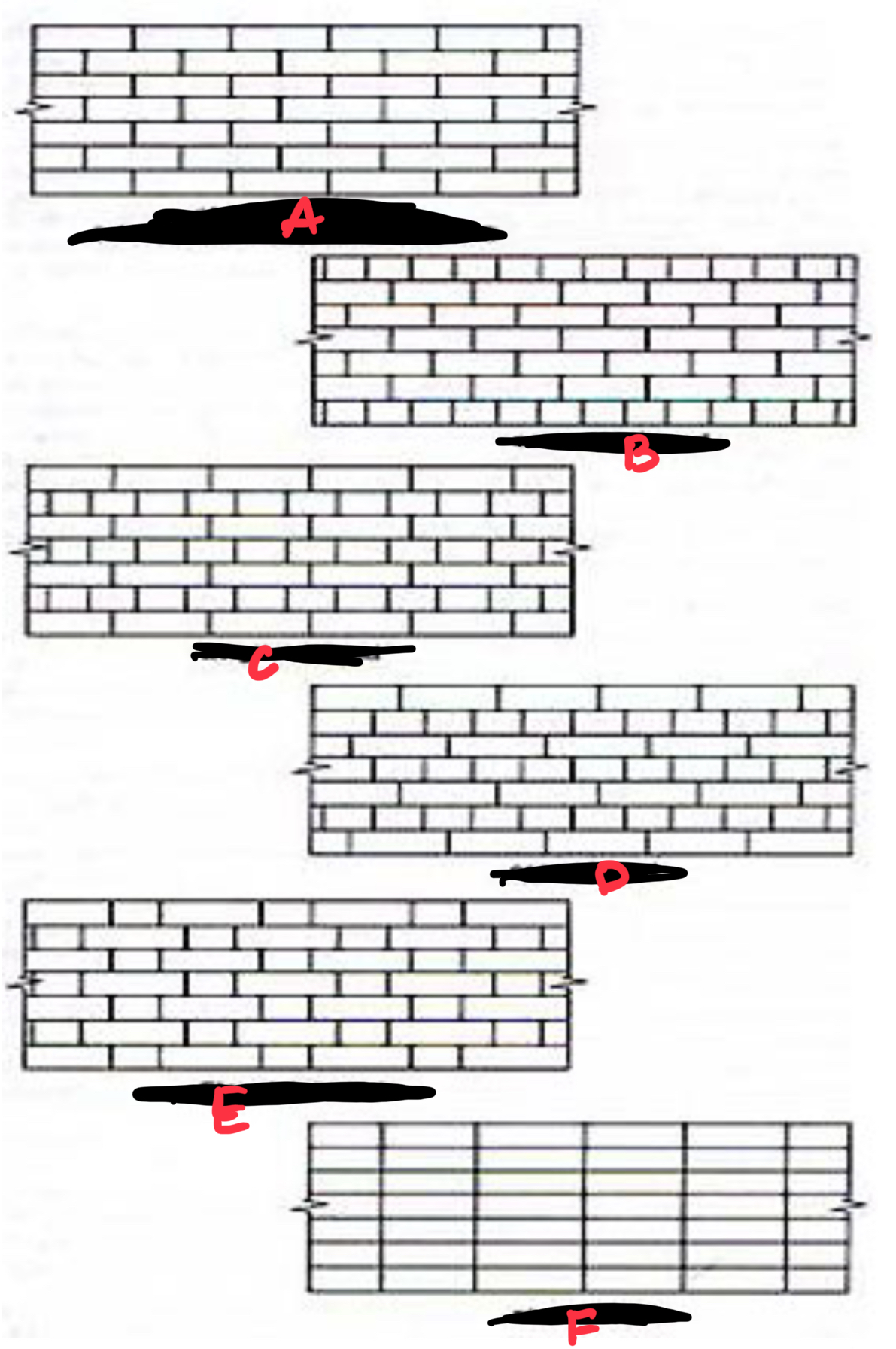
A CONCAVE
B VEE
C WEATHER STRUCK
D FLUSH
E RAKED
F TROWEL STRUCK
G BEADED
H EXTRUDED
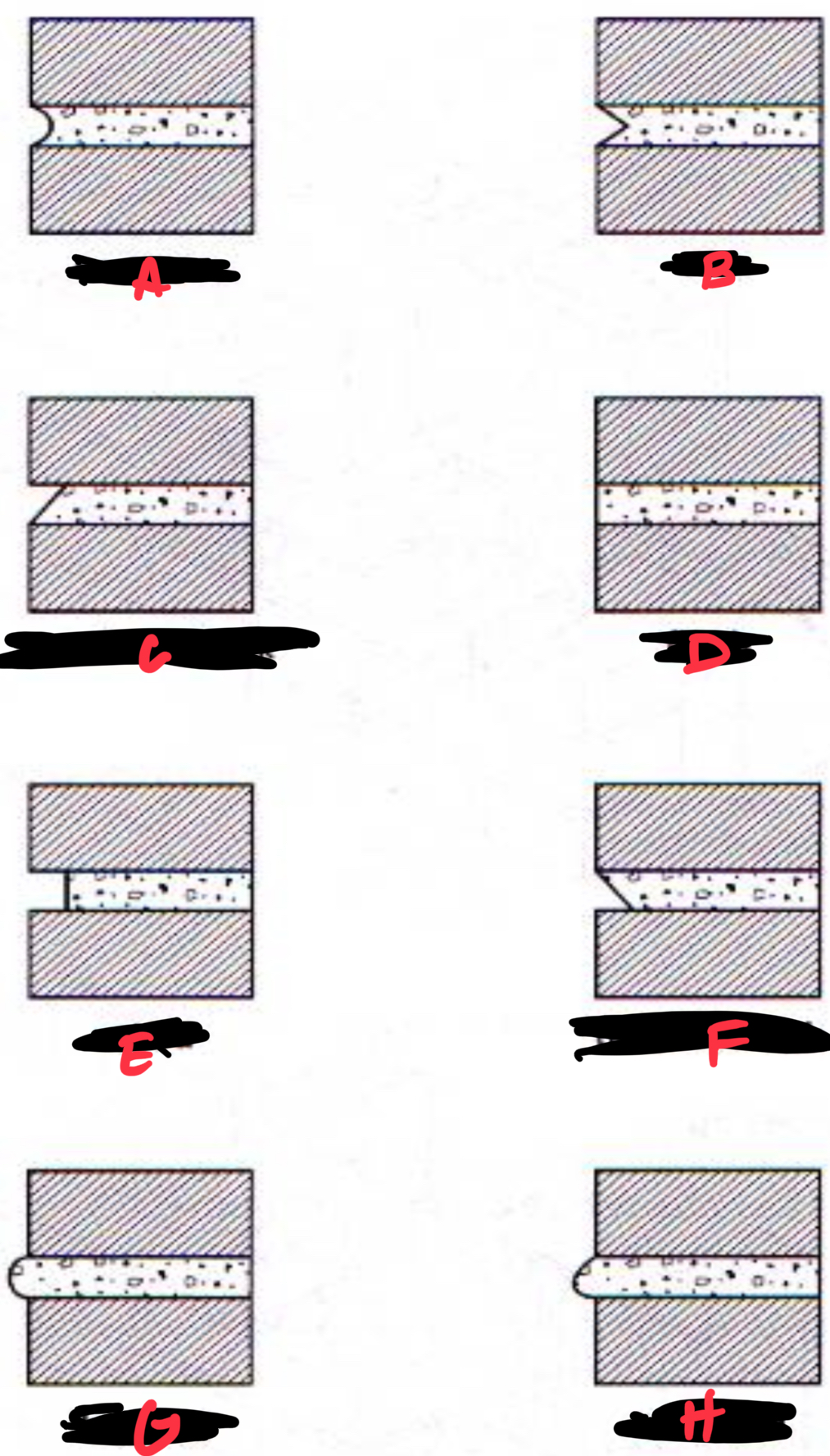
D EXPANSION JOINT
E ISOLATION JOINT
A CONTROL JOINT
B CONSTRUCTION JOINT
C CONSTRUCTION JOINT WITH WATER STOP
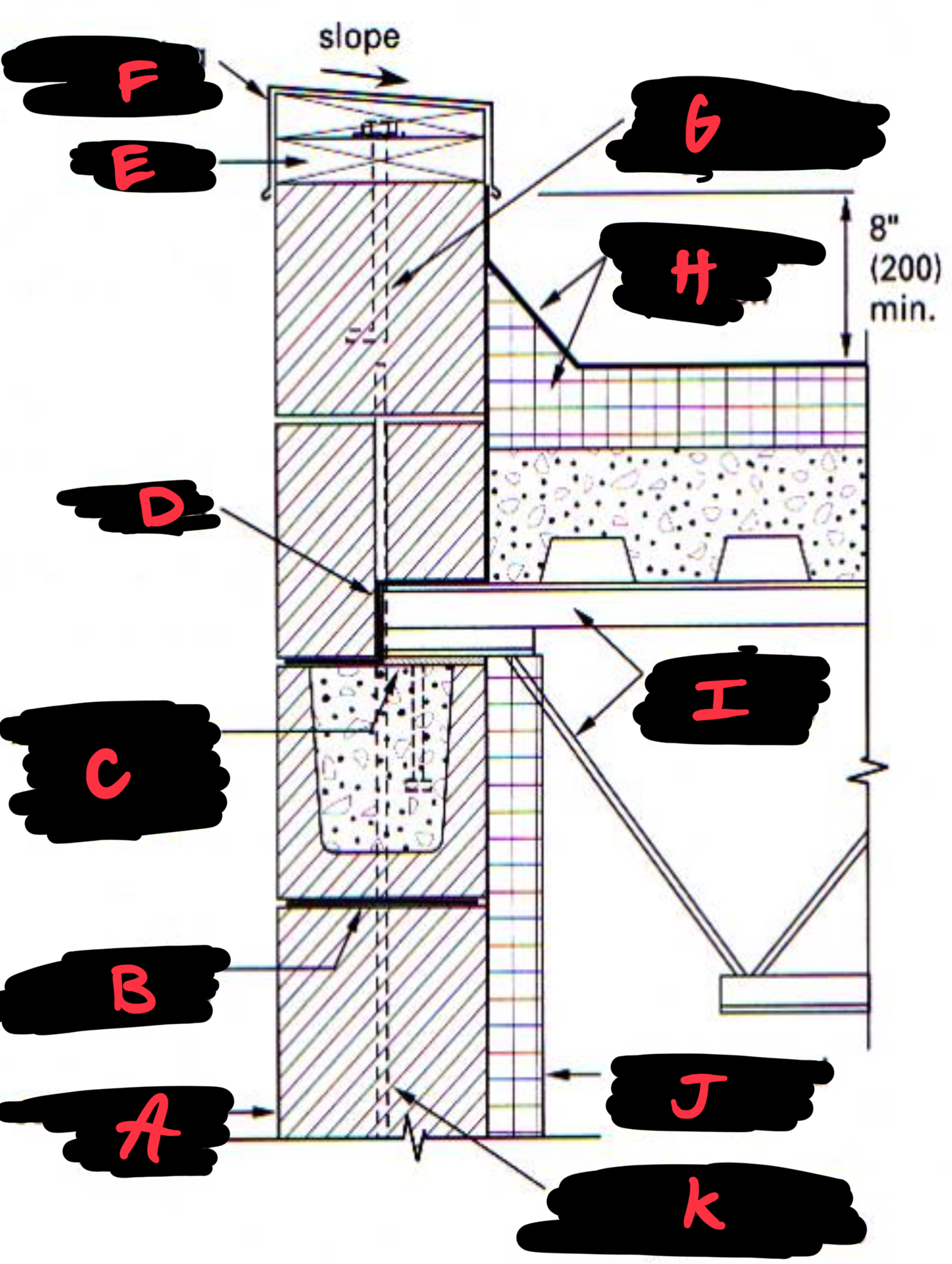
A CONCRETE MASONRY UNIT
B JOINT REINFORCEMENT
C BEARING PLATE ANCHORED IN BOND BEAM
D FLASHING
E BLOCKING
F METAL COPING WITH DRIPS
G ANCHOR BOLT SET IN GROUTED CELL
H ROOFING AND INSULATION
I OPENING-WEB STEEL JOISTS
J INSULATION AND WALL FINISH
K VERTICAL REINFORCING IN FULLY GROUTED CELLS
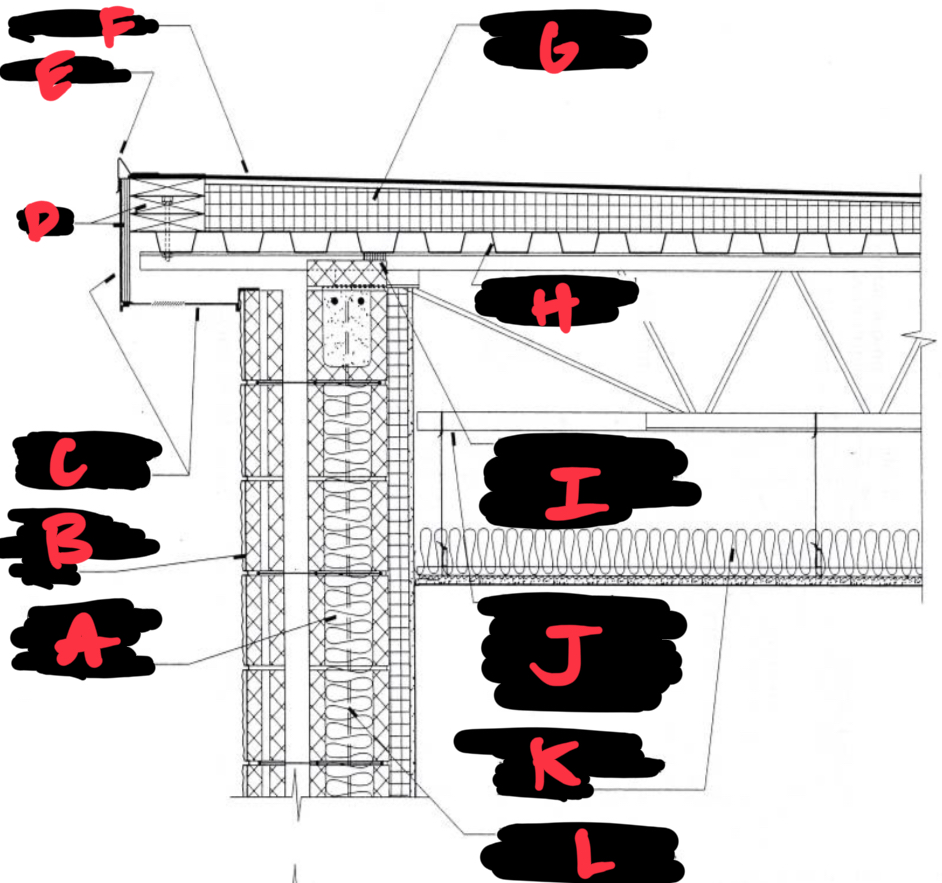
A CONCRETE BLOCK BACKUP WITH INSULATED CORES
B TEXTURE CONCRETE BLOCK FACING
C METAL FASCIA AND VENTILATED SOFFIT
D WOOD
E GRAVEL STOP
F ROOF MEMBRANES
G TAPERED RIGID INSULATION BOARDS
H CORRUGATED STEEL ROOF DECKING
I FOAM RUBBER FILLER GASKET CLOSES BETWEEN THE STEEL DECK AND THE MASONRY WALL
J A LOWER CHORD EXTENSION ON THE OPEN WEB STEEL ROOF JOISTS SUPPORTS THE EDGE OF A SUSPENDED CEILING
K GLADS FIBER BATT INSULATION AND VAPOR RETARDER
L VERTICAL REINFORCING BARS IN GROUTED CORES
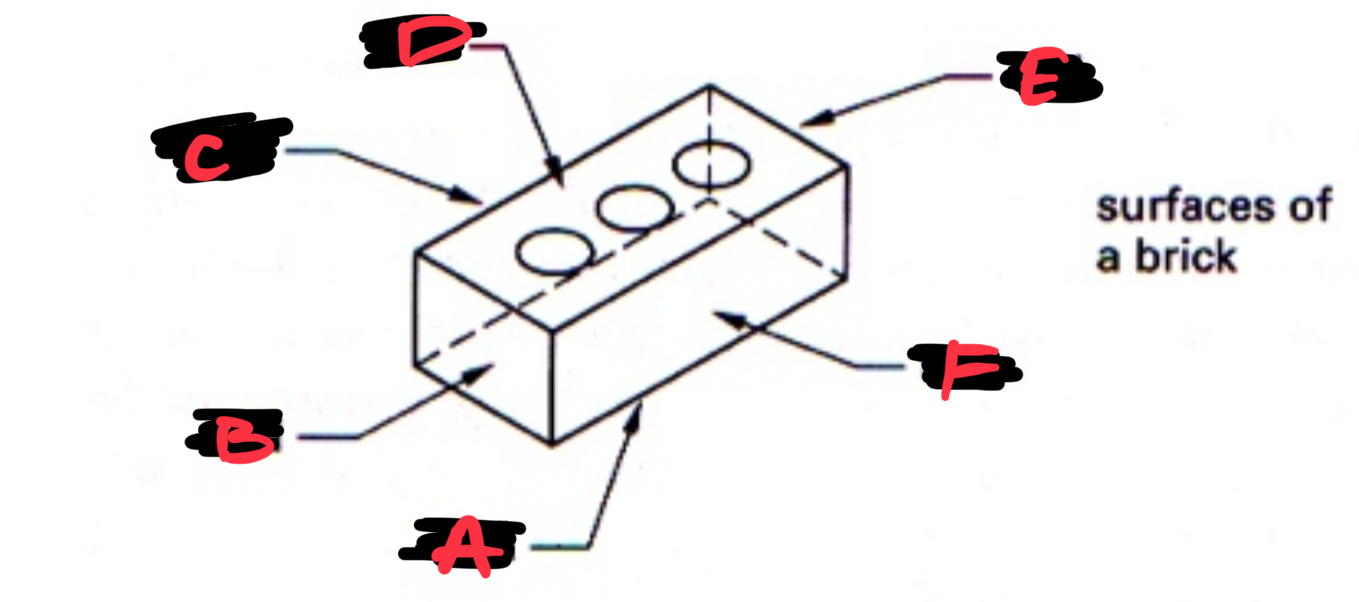
A BED
B END
C SIDE
D BED
E CULL
F FACE
PRE TENSIONING A CONCRETE BEAM DIAGRAM
PRE-STRESSING A CONCRETE BEAM DIAGRAM
POST-TENSIONING A CONCRETE BEAM DIAGRAM