Female Reproductive System Anatomy
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
46 Terms
production, gametes, estrogen, ovaries, uterus
The Female Reproductive System
-The female reproductive system includes all organs that take part in the ___________ of an offspring
-Ovaries → female gonads
Produce female _________ (ova)
Secrete female sex hormones, _________ (estradiol, estrone, estriol), and progesterone
-Internal genitalia → located in the pelvic cavity, including _________ and duct system (uterine tubes, _______, and vagina)
-External genitalia → external sex organs
-Mammary glands
oocytes, hormones, maturation, fertilization, milk
Functions of the Female Reproductive System
-Produce secondary _________
-Produce __________
-Ensure sexual _____________
-Provide site of ____________, implantation, and development of fetus/embryo
-Synthesize, secrete, and eject ____ for newborn nourishment
pubic symphysis, coccyx, urethra, anus
Female Perineum
-Diamond-shaped area between the thighs
Anterior border → _____ ___________
Lateral border → ischial tuberosities
Posterior border → ______
-Contains 2 distinct triangles
Anterior triangle → urogenital triangle → contains ________ and vagina
Posterior triangle → anal triangle → contains _____
Urogenital triangle
#1
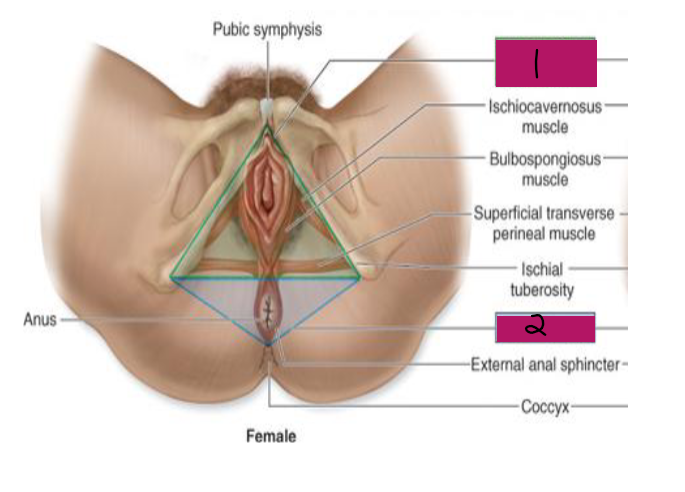
Anal triangle
#2
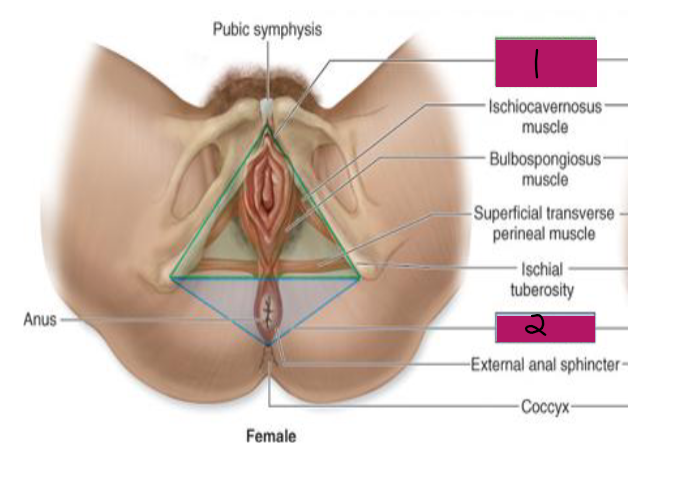
uterus, bladder, uterus, rectum
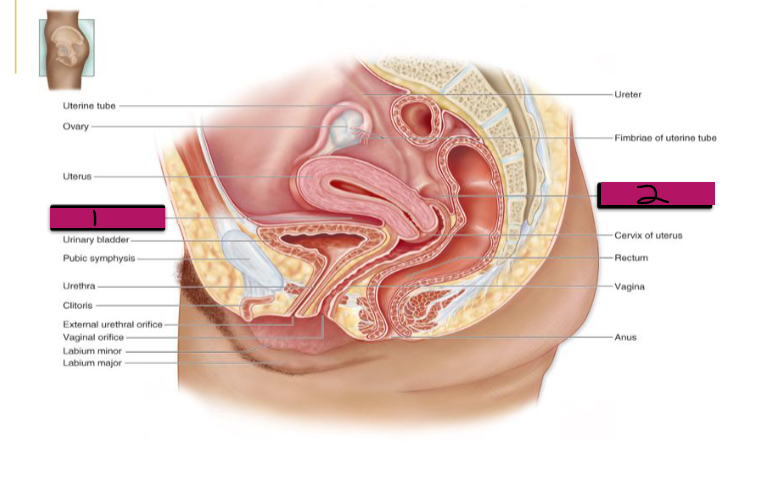
Pouches of the Female Reproductive System
-Due to folds in the peritoneum, there are two major pouches created in the pelvic cavity in the female anatomy
(1) Anterior Vesicouterine Pouch → forms space between ________ and urinary _______
(2) Posterior Rectouterine Pouch → forms the space between the _______ and _________
Vesicouterine pouch
#1
-Important anatomical landmark for c-sections
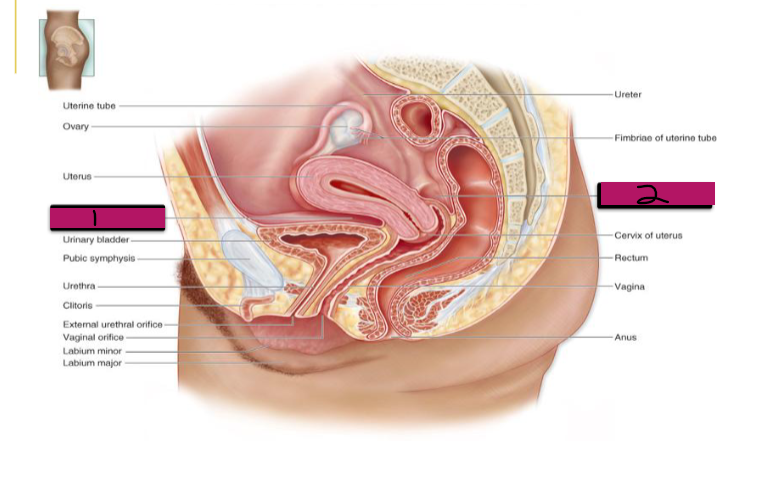
Rectouterine pouch
#2
-Very important landmark for the pelvic exam. Need to feel for a tumor or other abnormalities
-Normally very minimal fluid in this region, so feeling fluid could be indicative of bleeding or an infection
-Endometriosis lesions can be detected here
uterus, pelvic wall, uterus, fallopian, vagina, broad, uterus
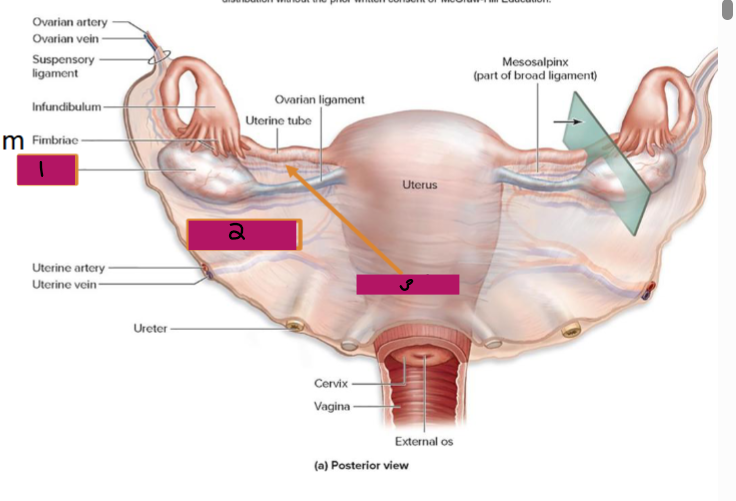
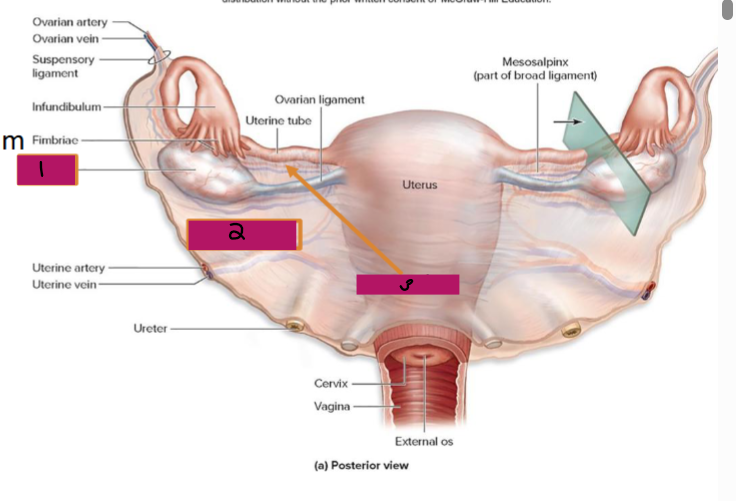
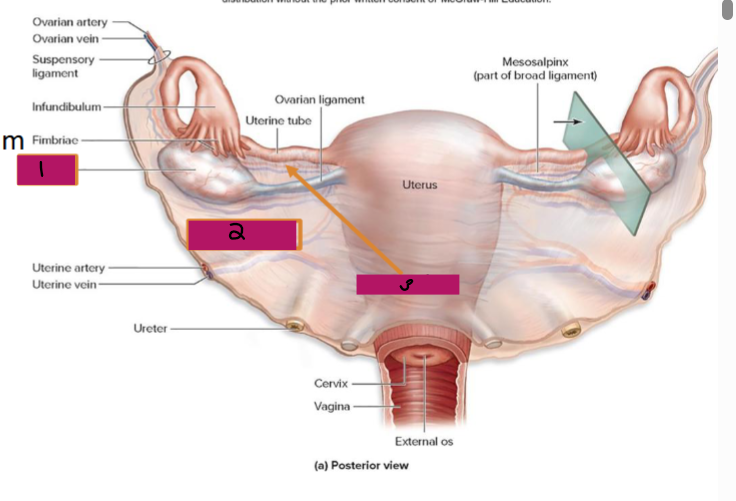
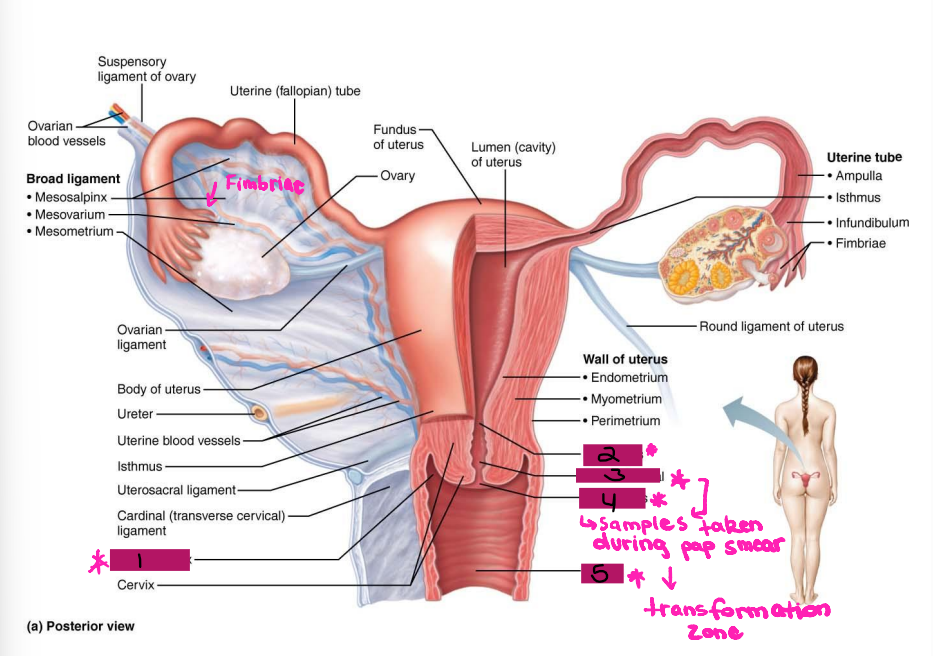
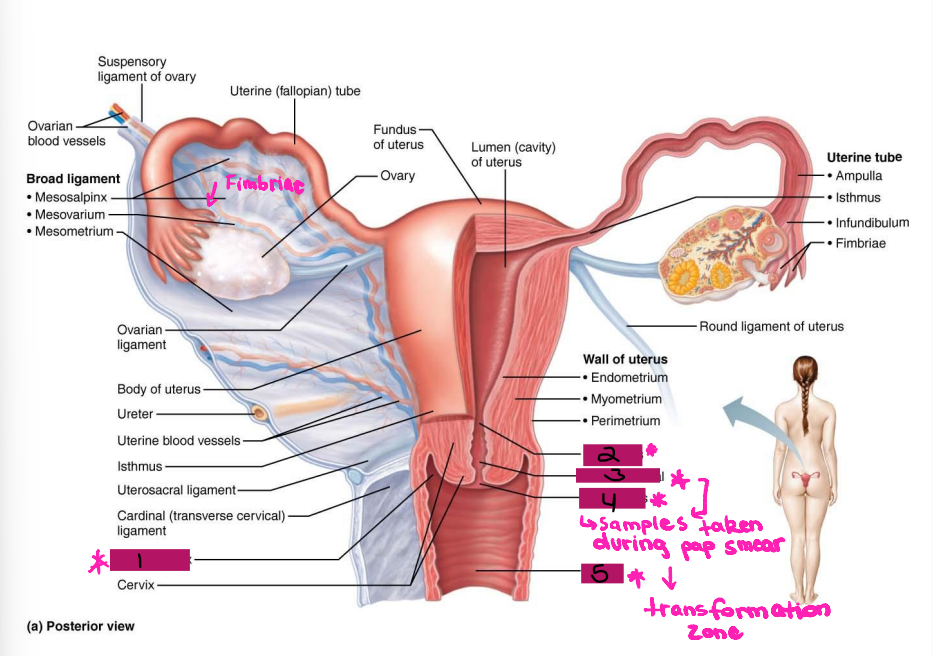
Ligamentous Support of Female Reproductive System
-Ovarian ligament → anchors ovary to the ________, medially
-Suspensory ligament → anchors ovary to the ______ ____, laterally
-Mesovarium → suspends ovary
-Broad ligament → tent-like structure that covers the _______ and helps to provide it with support, along with support to the ________ tubes and ______
-Suspensory ligament and mesovarium are part of the _____ ligament that supports uterine tubes, ______, and vagina
mesovarium, peritoneum, hilum, broad
Reproductive Organs
-Ovaries anchored within the pelvic cavity by the ____________
Meso = related to the mesentery
A double fold of ____________
Attaches to the ovary at the _____
Secures the ovary to the _____ ligament → sheet of peritoneum that hangs over the uterus
Ovary
#1
Broad ligament
#2
Mesovarium
#3
cervix, anterior, labia majora, sacrum
Uterus Ligaments
-Cardinal ligament → attaches the ______ portion of the uterus to the lateral pelvic wall
-Round ligament → binds uterus to _______ body wall by attaching it to subcutaneous tissue of _____ ______
-Uterosacral ligaments → anchors uterus to ______, posteriorly
-Become very loose during menopause, which can lead to prolapse
Suspensory ligament
#1
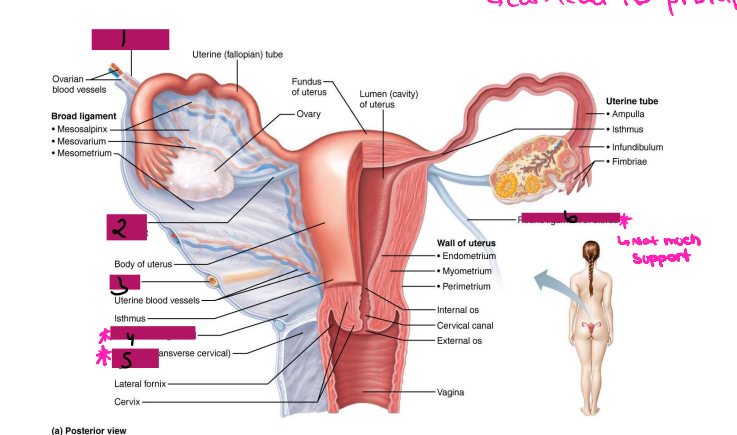
Ovarian ligament
#2
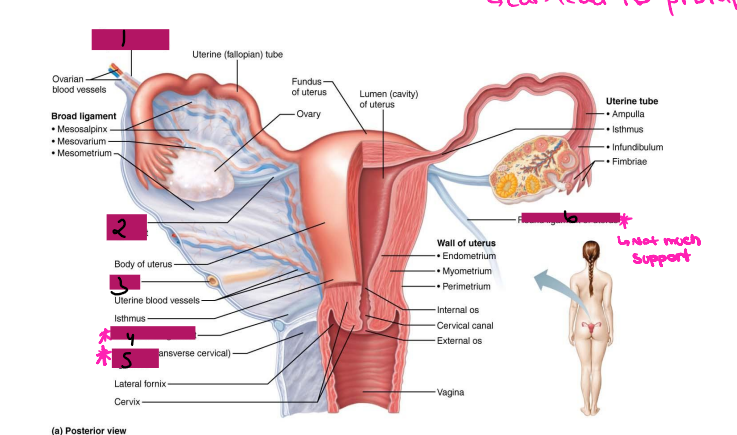
Ureter
#3
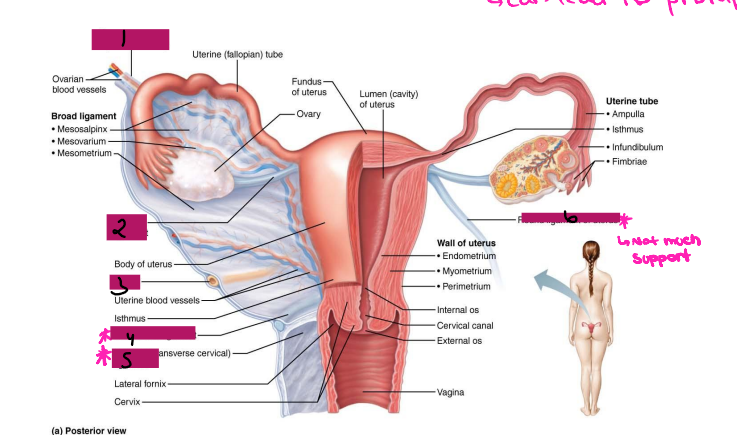
Uterosacral ligament
#4
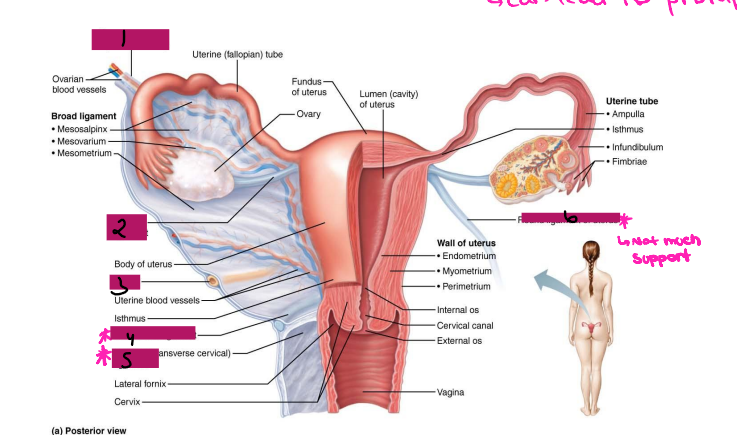
Cardinal ligament
#5
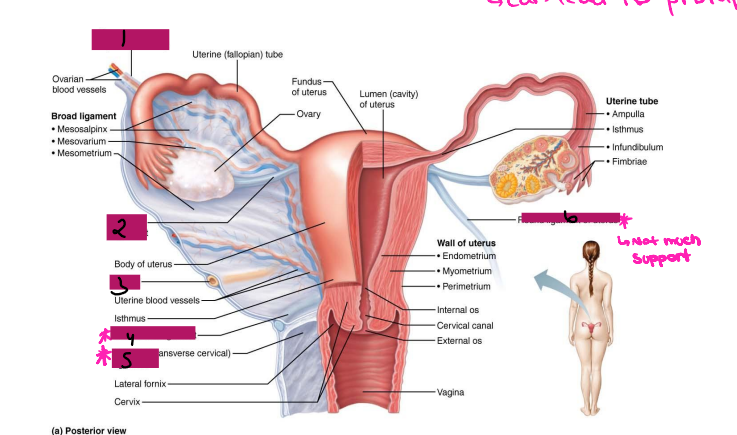
Round ligament
#6
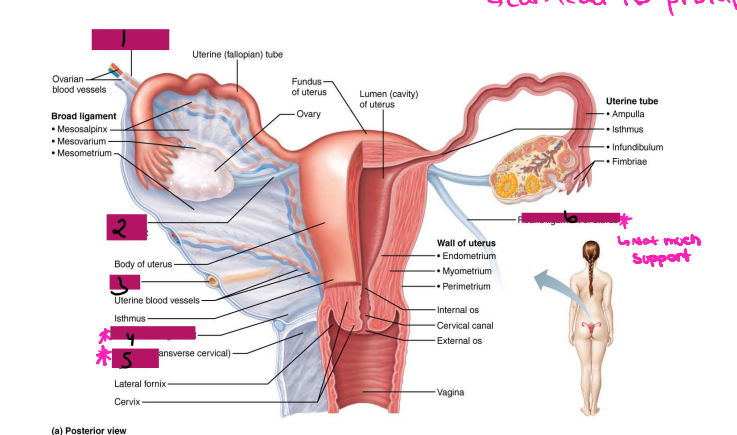
cortex, medulla, gametes, vessels, nerves, cortex, oocyte, ovulation, progesterone
Ovaries
-Paired, female gonads that are almond shape and twice as large in size
-Has two layers → ______ (outer layer) and _______ (inner layer). The cortex contains forming _________, while the medulla contains large blood ________ and ______
-Ovarian follicles → tiny saclike structures embedded in _______. It contains immature eggs (_________) encased by one or more layers of very different cells
-Each month, a ripened follicle ejects oocyte in an event called __________
-The ovaries produce gametes, _____________, and estrogen
ovaries, peritoneal, uterus
Female Duct System
-Uterine tube system does not have direct contact with __________
-Ovulated oocyte is released into ___________ cavity, where some oocytes never make it to the tube system
-Tube system includes uterine tubes, ________, and vagina
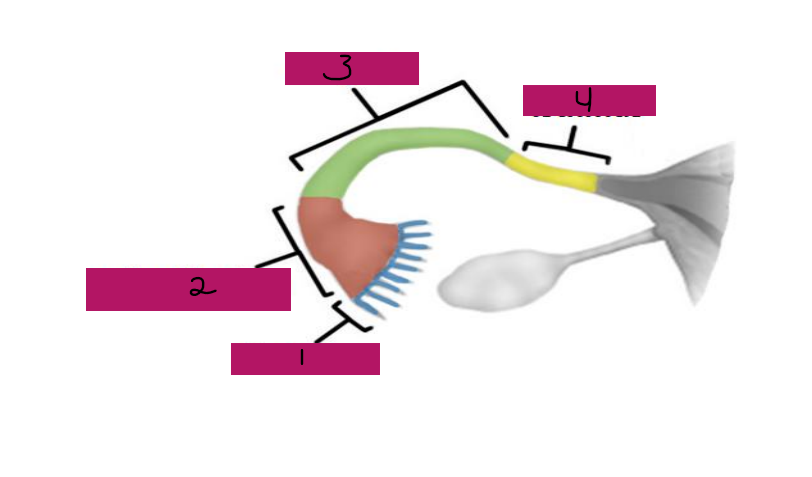
Fallopian, superior, oocytes, peristaltic, ciliated, fertilization, ampulla, isthmus
Uterine Tubes (AKA _________ tubes)
-Each tube is approximately 4 in long and extends from area of ovary to _________ region of the uterus, transporting secondary ___________ that were released by the ovaries to the uterus through ___________ contractions and movement of _________ cells
-If ___________ occurs, it typically occurs in the fallopian tubes, specifically, the ________ portion
-The fallopian tube has different regions including fimbrae, infundibulum, ampulla, and _______
Fimbrae
#1
-Feather-like projections off of the most distal aspect of the fallopian tubes
-Pick up egg once it has been released, no direct contact with the ovary
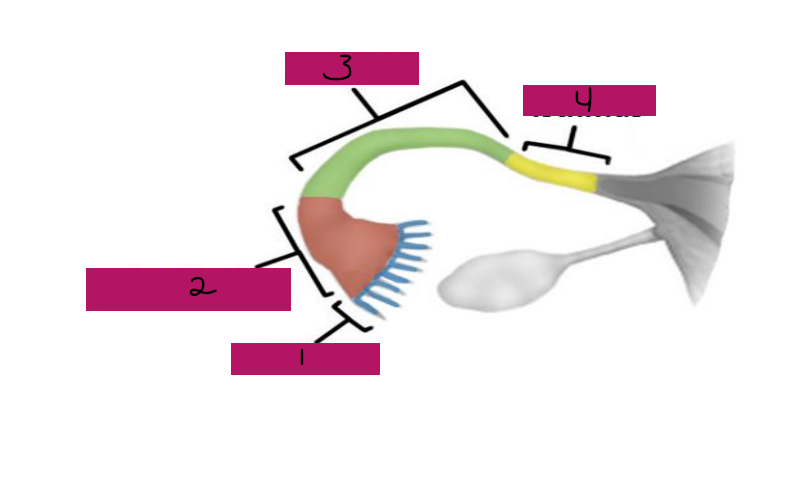
Infundibulum
#2
-Distal-most aspect of the fallopian tubes, trumpet shaped in appearance
-Egg goes here after being picked up by the fimbrae
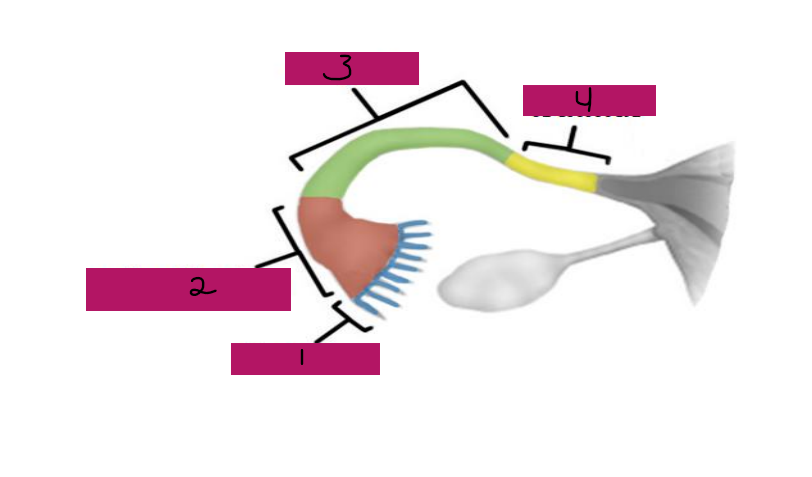
Ampulla
#3
-Middle and longest part of the fallopian tubes
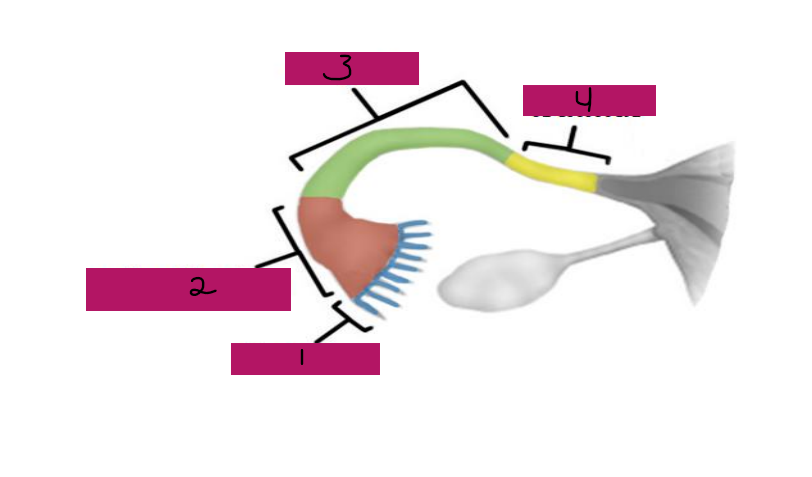
Isthmus
#4
-Narrow region closest to the uterus
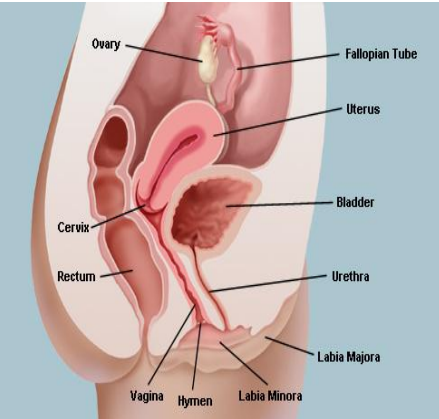
Lateral fornix
#1
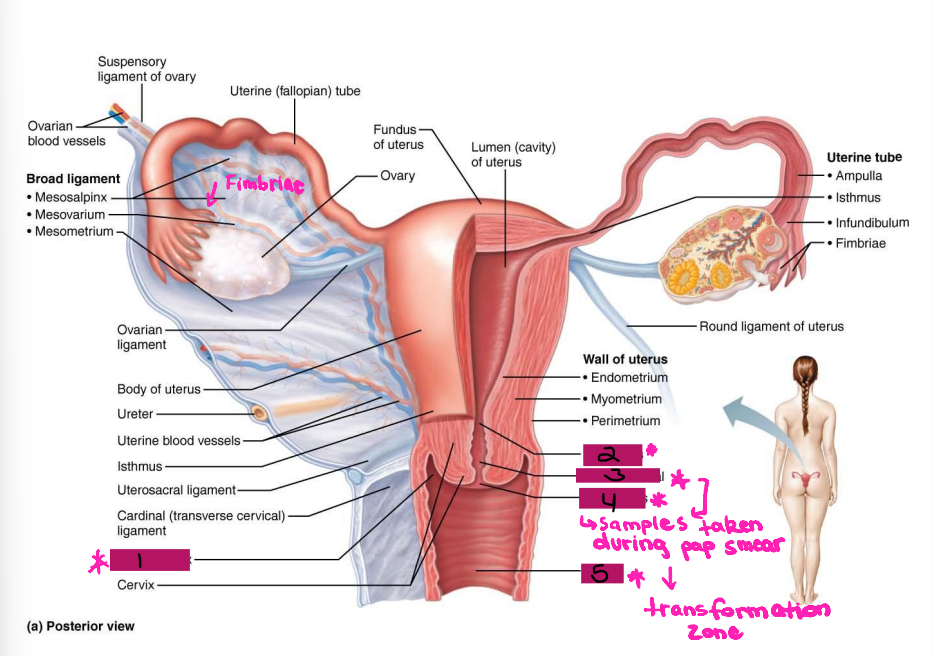
Internal os
#2
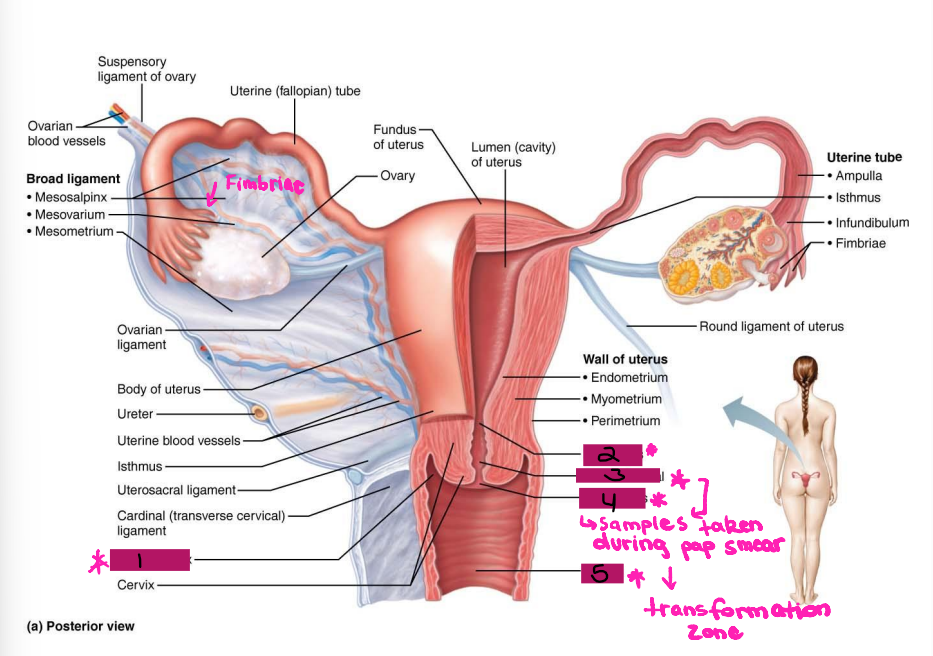
Cervical canal
#3
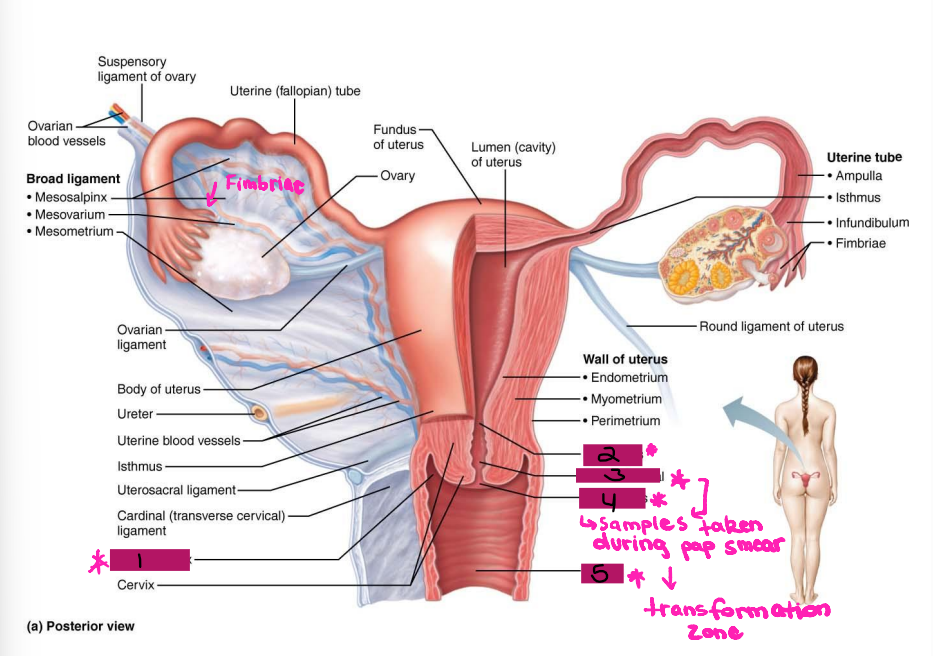
External os
#4
Vagina
#5
anteverted, implantation, sperm, fundus, mucus, sperm
Uterus
-Hollow, thick-walled, muscular organ
-Position of the uterus
____________ → inclined forward (normal position)
Retroverted → inclined backward
-Site of ____________, sustains embryo/fetus, forms placenta, transports _____ to fallopian tubes and in times of no egg fertilization, is the source of menstrual flow
-Regions of the uterus → body, _______, isthmus, cervix, and cervical canal
-Cervical glands secrete ______ that blocks _____ entry except midcycle
outermost, visceral, middle, muscle, mucosal, columnar
Uterus
-The uterine wall consists of three layers:
(1) Perimetrium → ___________ serous layer (______ peritoneum)
(2) Myometrium → bulky _______ layer consisting of interlacing layers of smooth _______
(3) Endometrium → _______ lining. Made of simple ________ epithelium on top of a thick lamina propria. Fertilized egg burrows into endometrium and resides there during development
functionalis, hormone, shed, new, hormones
Endometrium
-Stratum ____________ (functional layer) → changes in response to ovarian ________ cycles, _____ during menstruation
-Stratum basalis (basal layer) → forms ____ stratum functionalis after menstruation. Unresponsive to ovarian ______________. Remains steady
internal, myometrium, endometrium, spiral, spasms, menstruation
Blood Supply: Uterine Wall
-Vascular supply plays key role in cyclic changes
-Uterine arteries → arise from _______ iliacs and branch into….
-Arcuate arteries → ____________, branch into …
-Radial arteries → in ____________, branch into …
Straight arteries in stratum basalis and
_______ arteries in stratum functionalis, which degenerate and regenerate. ______ cause shedding of functionalis layer during ____________
birth canal, rugae, squamous, acidic, hymen, fornix
Vagina
-Outlet for menstrual flow, also the site to receive sperm
-Connects uterus with outside world and functions as _____ _____, approximately 8-10 cm in length
-Contains ______. Tissue there is stratified ___________ epithelium, which secretes an _______ fluid
-The _________ partially covers the vaginal opening
-The _______ is a narrow space between the wall of the cervix and wall of the vagina
vulva, clitoris, majora
External Genitalia
-Collectively known as the _____
-Consists of the mons pubis, __________, labia ________, and labia minora
Mons pubis
#1
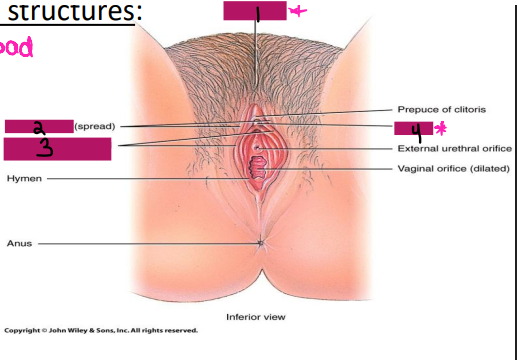
Labia majora
#2
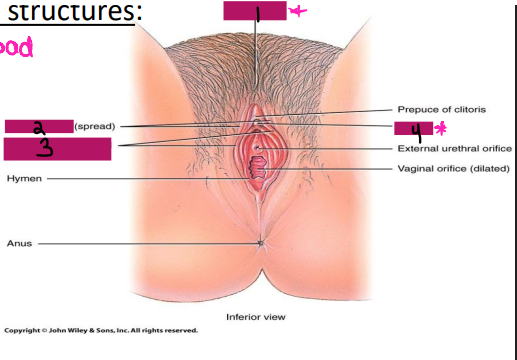
Labia minora
#3
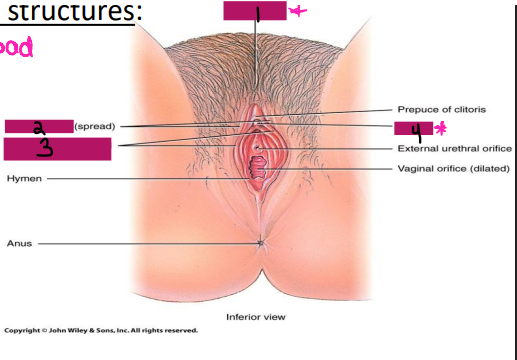
Clitoris
#4
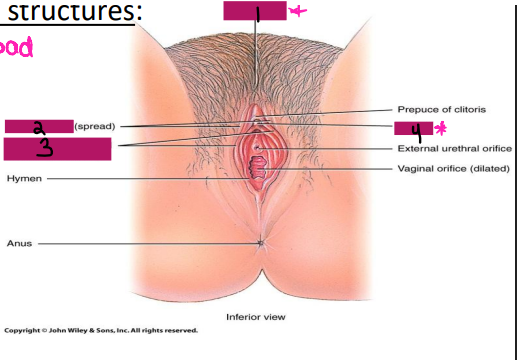
symphysis, pubic hair, adipose, external, scrotum, vestibular, mucus, sexual
Mons Pubis and Labia
-Mons Pubis
Rounded are overlying the pubic __________
Covered with _____ ____ in post-pubescent women
Consists mostly of adipose tissue
-Labia
Elongated, fatty folds which enclose the _________ openings of the urethra and vagina
The labia majora is the equivalent of the _________, for they come from the same embryonic tissue e
The labia minor contains the __________ glands, which secrete _____ into the area during ________ stimulation
minora, posterior, opening, mucus, sexual
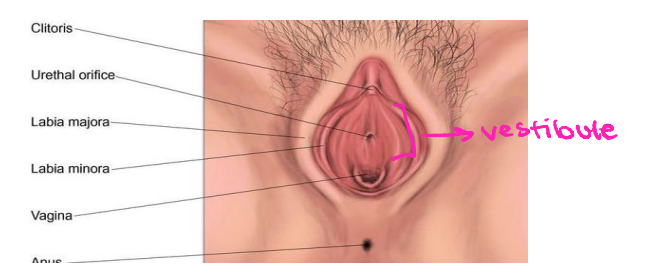
Vestibule
-Vestibule → recess within labia _______
-Fourchette → ridge formed by joining of __________ vestibule and labia minora
-Greater vestibular glands → flank vaginal ________, homologous to bulbo-urethral glands, and release ______ into vestibule for lubrication
-Bulbs of the vestibule → lie along each side of the orifice that engorge with blood during ________ stimulation
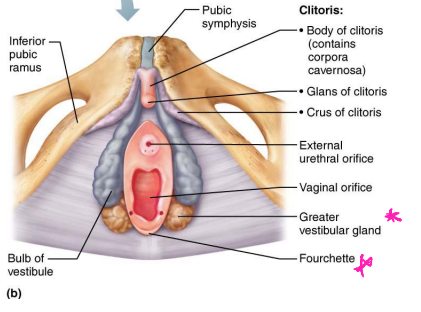
erectile, prepuce, sensory
Clitoris
-Found anterior to vestibule
-Protrusion of ________ tissue anterior to external urethral orifice and vagina, which is covered by a fold of tissue called the ________
-Contains a large number of ________ nerve endings
sweat, milk, nutrients, immature, nipple, oil, sebaceous, inhibits, production, alveoli, lactiferous, sinuses
Breasts and Mammary Glands
-Mammary glands → modified ______ glands found within the breast tissue that produce and secrete ____ in pregnant and nursing mothers
-Milk contains proteins, fats, and sugar → provides ________ to infants
-Both females and males have mammary glands, but males have __________ ones
-______ → cylindrical projection in the center of the breast, containing multiple tiny openings for breast milk to leave the mammary gland
-The areola is pigmented skin around the nipple → contains numerous ____ glands, normally a rose-pink to brown color
-Progesterone → causes development of alveolar ___________ glands, also ______ milk production in early months of pregnancy
-Prolactin → released toward end of pregnancy and after to cause milk __________
-Lobules within lobes contain glandular _______ that produce milk, which is passed into ___________ ducts and then into lactiferous __________