BICD 110 Midterm 2
1/95
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
96 Terms
What is phagocytosis
an ancient, actin-dependent pathway that enables cells to engulf particles/cells/pathogens > 500nm (induced mechanism)
What are the steps of detection of opsonized target in phagocytosis?
pathogen that is tagged with Fab/Fc antibody is recognized by Fc region (constant) by Fc receptor on effector cell
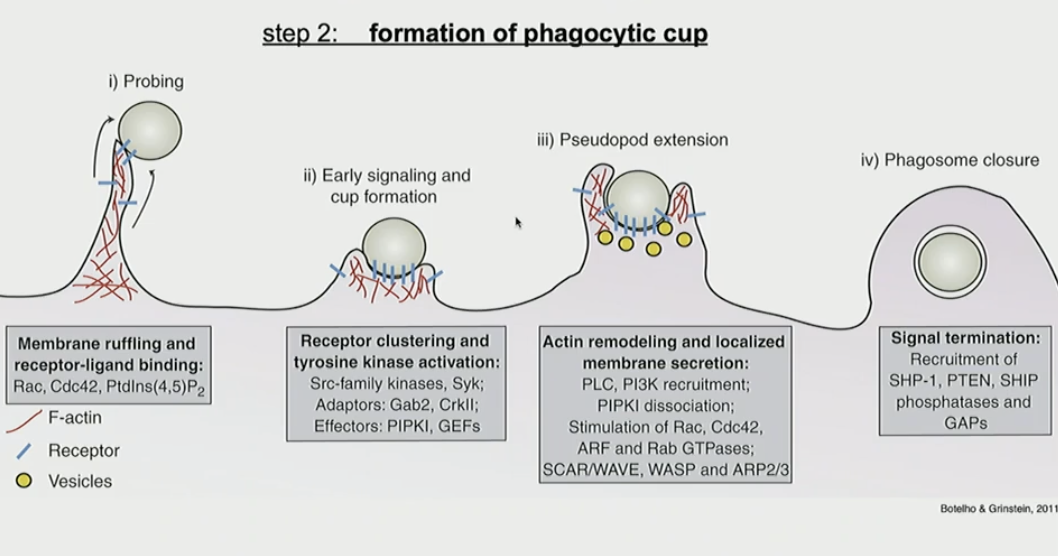
What are the steps of the formation of phagocytic cup in phagocytosis?
probing: membrane ruffles and extends to interact with tagged pathogen
early signaling and cup formation: once enough Fc receptors engage, cup forms and induces downstream signaling
pseudopod extension: extends even more to facilitate engulfment
phagosome closure: pathogen is fully enclosed
What are the steps of the phagosome maturation in phagocytosis?
engulfed bacteria acquires factors: Rab5 and GTPases
fuse with early endosome, where proton pump V-ATPase lowers pH to 5.5-6
conversion of Rab5-Rab7 + late endosome promotes conversion to late phagosome. pH dec to 4.5
fusion with lysosome brings degradative enzyme (now phagolysosome)
NADPH oxidase complex recruited to produce reactive oxygen species (ROS) to bleach interior of phagolysosome
after degradation, phagolysosome is exocytosed
What is macropinocytosis?
an ancient, actin dependent pathway that enables cell to engulf fluids. macropinosomes range from 200nm-10um. membrane “ruffles” can be induced by growth factors
Is phagocytosis and macropinocytosis induced or constitutive?
phagocytosis: induced
macropinocytosis: constitutive
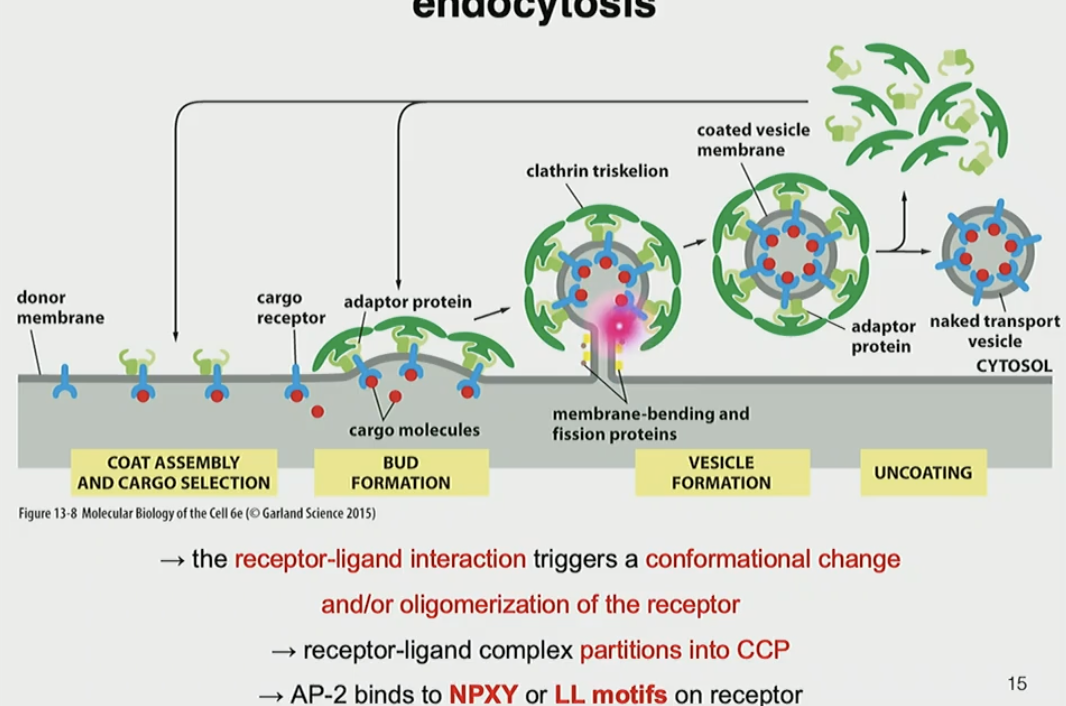
Steps for clatherin-dependent, receptor-mediated endocytosis
specific ligands bind to transmembrane receptors on PM
AP2 (locked) recognizes NPXY or LL motifs and binds to cargo receptor tails on PM and PIP2
AP2 recruits clatherin triskelion, which curves membrane into CCP (pit)
pit buds off into vesicle, AP and clathierin triskelion dissociate
What happens to lysosomal enzymes when the pH is 5 and why?
it becomes active, safeguarding mechanism
How do lysosomes decrease their pH
V-type ATPase are lysosomal membrane pumps, they pump protons (H+) into the lumen of the lysosome
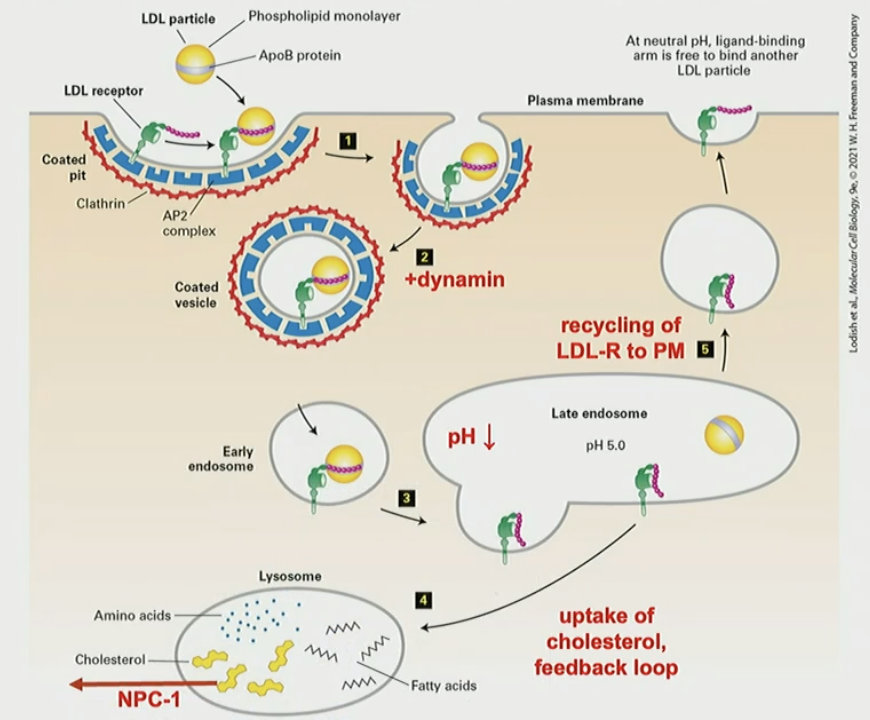
LDL particle structure
the shell is a single apolipoprotein wrapped around and phospholipid monolayer. the core is hydrophobic with neutral lipids. the particle, ApoB, is taken from the bloodstream and transported
Mechanism for receptor-mediated endocytosis of LDL
LDLr: B-propeller domain in PM, with NPXY sorting signal in cytosol. Cys-rich “hook” binds to ApoB (LDL) at pH 7. after endocytosis, pH 5 in late endosome weakens interaction (+ charged), and LDL is released. LDLr is recycled to PM
How does SRE-binding proteins monitor ER cholesterol levels?
when cholesterol levels are low, the ER sends SREBP in COPII vesicles to Golgi, which sends SREBP to nucleus. SREBP activates SRE on DNA and activates cholesterol synthesis pathways
What are mutivesicular bodies (MVB)
they degrade cytosolic portions of membrane proteins
Mechanism for degradation of PM receptor
lysosomal enzymes TGN → late endosome
endosome carrying PM receptor fuse with late endosome
vesicles containing PM receptor bud inward (MVB)
MVB fuse with lysosome. lysosomal enzyme activate and degrade PM receptor
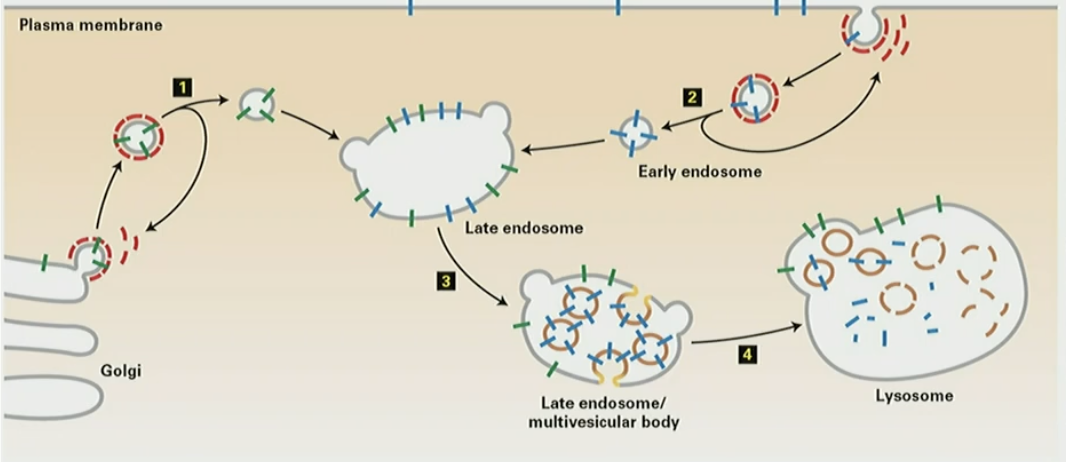
Mechanism for MVB formation
transmembrane proteins for degradation are ubiquitinated
Hrs protein sorts ubiquitinated cargo into inward buds
ubiquitin attracts ESCRT machinery and forms inward vesicles
ATP is invested into Vps4 to disassemble ESCRT from membrane
Mechanism for autophagy
ATG proteins induce formation of cup shaped structure around target in two bilayers
Atg8 specifies membrane growth
fusion of autophagosome and lysosome
degradation of target
What are caveolae?
stable membrane domains that depend on cholesterol (SDS PAGE cannot break apart) and contribute to exocytic and endocytic events
What is transcytosis?
the transfer of macromolecules from the apical to basolateral membrane and vise versa via endo and exocytosis.
What type of junction are apical and basolateral membrane separated by?
tight junction
What are the 5 major endocytic pathways?
phagocytosis, macropinocytosis, clatherin-dependent endocytosis, caveolae, clatherin/caveolin-indepdent
What does chemical and electrical gradients depend on?
chemical: concentration of molecules on either side of mem
electrical: ratio of ions (charge) on either side of mem
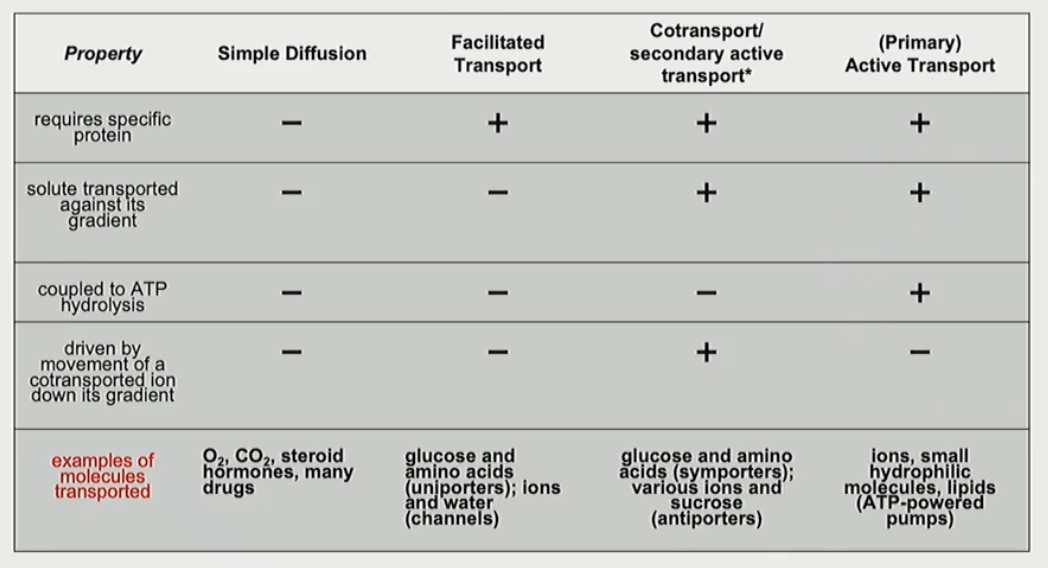
What is facilitated transport?
transport of a single type of molecule along its concentration gradient
What is co-transport, secondary active transport?
energy available from ion down an electrochemical gradient drives movement of a molecule against its concentration gradient
What is a ATP-powered pump?
energy released by ATP hydrolysis drives movement of specific ions or small molecules against their electrochemical gradient
What three transporters cooperate at the PM?
Na/K ATPase: 321 NOKIA
K+ channel: K out
Na/lysine symporter: Na in (down gradient), lysine in (up gradient)
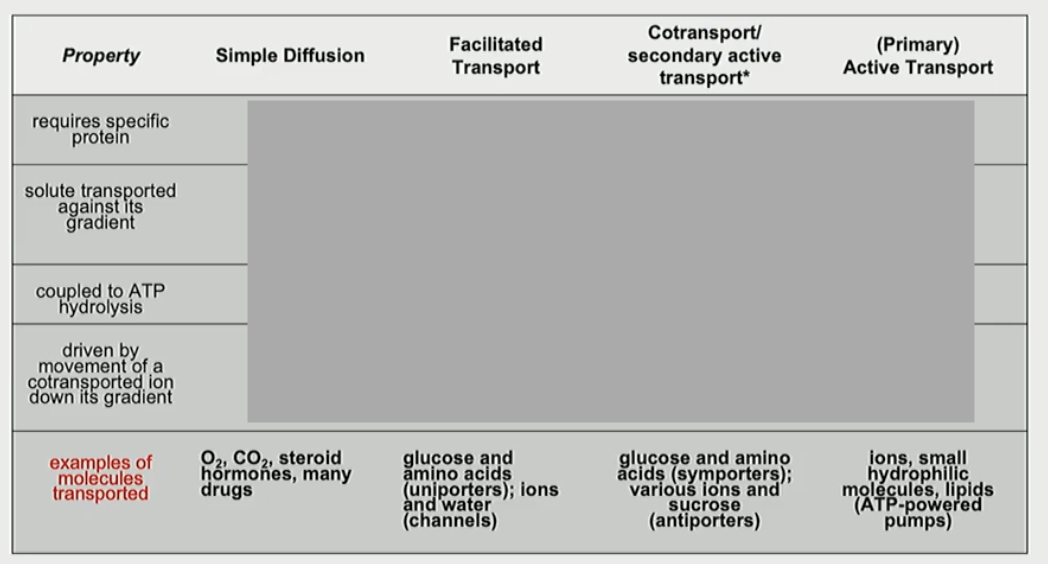
Fill in the table
Structure of aquaporin
homotetramer (4 identical subunits), highly conserved hydrophilic AA channel, arrangement of H-bonds and 0.28nm diameter pore, no conformational change during transport
What is Vmax and what is it dependent on?
maximum velocity at which you can transport a substrate across bilayer is dependent on the NUMBER of transporters that is working at max rate and the gradient is large
What is Km and what is it dependent on?
concentration at which rate of uptake is half-maximal (mM) is dependent on affinity of transporter
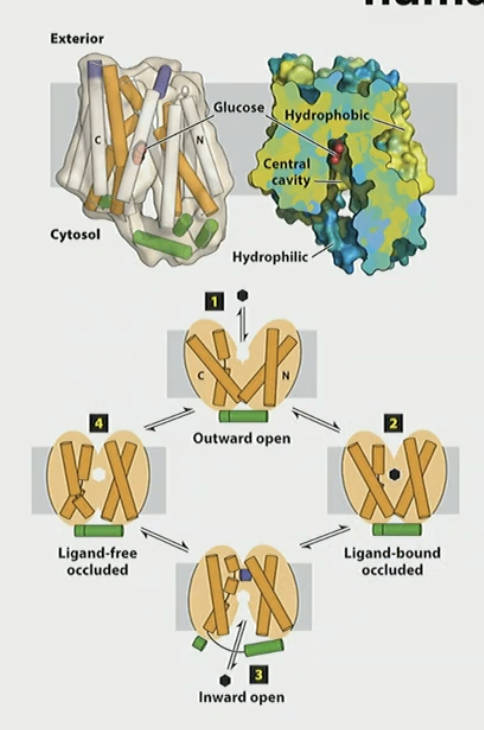
How does GLUT1 work in simple terms?
outward open conf binds glucose
ligand bound occluded conf
inward open conf releases glucose
ligand free occluded conf
cycle will work in reverse if conc changes
14 highly homologous GLUT proteins
What are P-class pumps?
type of ATP-powered pump
generate ion gradients across membranes
catalytic a subunit is phosphorylated
ex: Na/K ATPase
Mechanism for Na/K ATPase
high affinity for Na+, low aff for K, ATP binds
phosphorylation of Asp, D, ADP released
conformational change, Na+ low aff, released. high aff for K+
dephosphorylation of Asp, conformational change
low aff for K+, high aff for Na+
What are V-class pumps?
type of ATP-powered pump
couples ATP hydrolysis to transport protons against conc. gradient
general low pH of plant vacuole & lysosome
NOT phosphorylated
Mechanism of V-class pump
V1 subunit binds ATP
ATP hydrolysis triggers 120° rotation of V1
rotation of V0 drives proton binding from cytosol to lumen via de/protonation of glutamate and aspartate
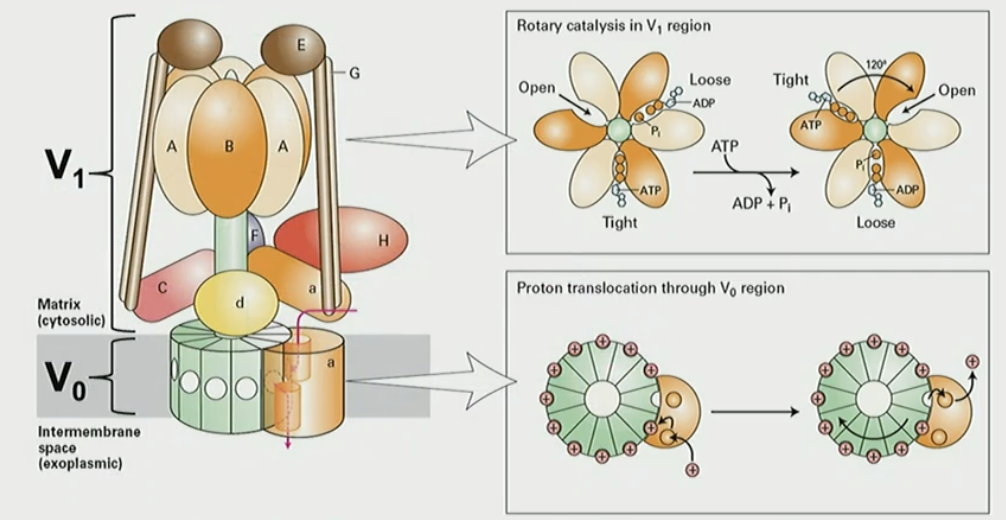
How do V-class pump + Cl- channels acidify cell
Cl- facilitated transport thru channel balances/neutralized pumped H+ so there is no electric potential. this allows for even more H+ to be pumped into lysosome to reach desired pH=5
What are F-class pumps?
most transport only H+
NO phosphoprotein intermediate
work in reverse to use energy in proton conc. or voltage gradient to drive ATP synthesis in mito or bacteria
What are ABC superfamily pumps?
have two transmembrane (T) domains + two cytosolic ATP-binding (A) domains
couple ATP hydrolysis to solute movement
each ABC protein is specific for single substrate
export wide variety of toxins and drugs
Mechanism for transcellular transport of glucose from intestinal lumen into blood
Na/K pump establishes concentration gradient so cell has negative membrane potential
glucose is taken from intestine lumen by 2xNa/glc symporter
glucose transported out of cell by low aff uniporter GLUT2
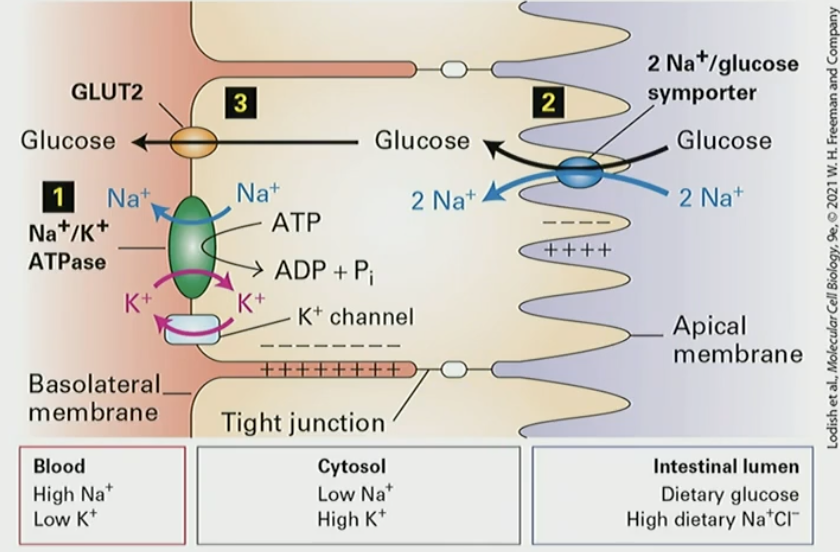
Which type of membrane transport proteins has the highest rate of transport: channels, uniporters, symporter/antiporter, ATP-powered pumps
channels
What is the 4 types of extracellular signaling?
endocrine
paracrine
autocrine
cell-cell (juxtacrine)
What is endocrine signaling?
signaling molecules are synthesized and secreted by signaling cells and transported thru circulatory system. affects distant target cells expressing specific receptor. ex. epinephrine, insulin
What is paracrine signaing?
signaling molecules are synthesized and secreted by cell and affect only nearby target cells expressing specific receptor. ex: NT, growth factor
What is autocrine signaling?
cells respond to signals they secrete (tumor cells may overproduce). ex: growth factors
What is cell-cell contacts (juxtacrine)?
direct contact with surface receptors of neighboring cells
Properties of hydrophobic signaling molecules
diffuse across PM
bind to cytosolic receptors
receptor-signal complex moves into nucleus
binds promoters in DNA to activate/repress gene exp
ex: steroids (testosterone, estrogen, cortisol)
Properties of hydrophilic signaling molecules
cannot cross PM
binds to cell surface receptor
activates downstream signal protein/secondary messenger
activate effector proteins
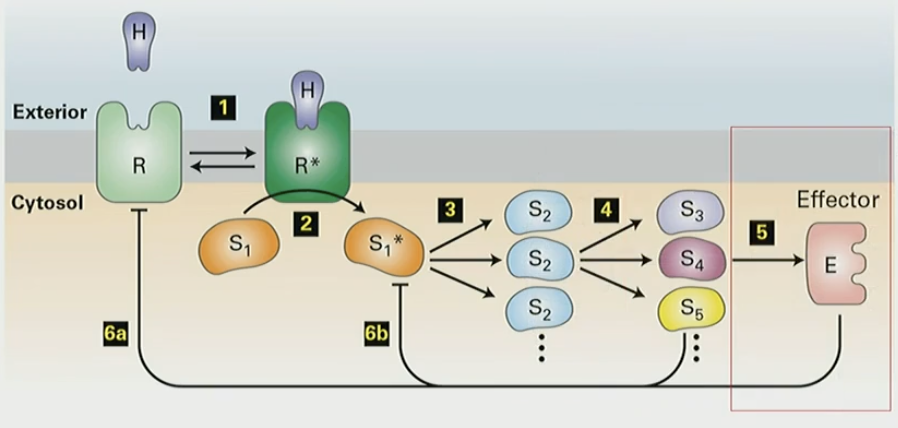
General mechanism of signal transduction pathway
receptor (R) binds ligand (H)
triggers conf change (R*), activated receptor binds signal transduction protein (S1)
amplification: S1 binds to other proteins S2, activates/inhibits
S2 activates more proteins S3-S5, different targets/locations in cell
signaling proteins bind and activate effector protein (E)
can be enzyme, trxn factor, ion channel etc
feedback loop: signal transduction proteins/effector can inhibit upstream mechanism
Structure of GPCR
N-term out, C term in cytosol
7 transmembrane domains
4 extracellular segments (E)
4 intracellular segments (C)
How does GPCR detect ligand and send signals inside?
use extracellular loops to detect ligand and send signals inside using intracellular loops
What does Family A of GPCR detect?
biological amines
light/odorants
peptides
purines
lipids
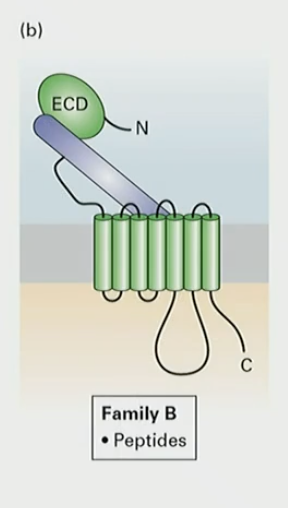
What does Family B of GPCR detect?
peptides (like glucagon)
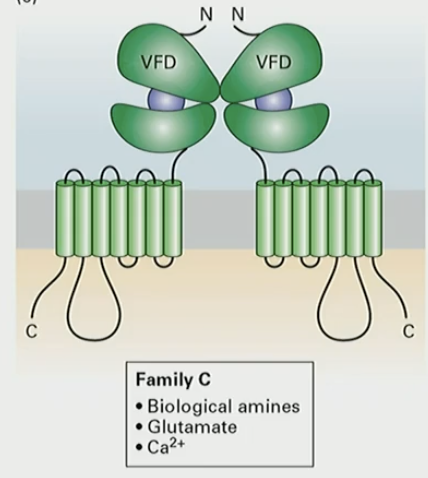
What does Family C of GPCR detect?
biological amines
glutamate
Ca2+
Mechanism for general GPCR signal transduction pathway
ligand binding induces receptor activation and conf change
activated receptor binds to trimeric G protein (alpha subunit)
GPCR GEF activity stimulate Ga to release GDP
GTP binding changes Ga conf and activates
Gby dissociates from Ga
Ga-GTP activates effector enzyme
Ga GTPase activity: GTP → GDP
Ga dissociates from effector enzyme (deactivates)
Adenylyl cyclase + ATP → ? → activates ?
cAMP → activates protein kinase A (PKA)
Guanylyl cyclase + GTP → ? → activates ?
cGMP → activates protein kinase G (PKG) and cation channels
phospholipase C + PIP2 → ?? → activates ??
DAG → +Ca2+, activates protein kinase C (PKC)
IP3 → opens Ca2+ channels in ER
How does cAMP active PKA?
cAMP releases inhibitory subunits
-cAMP: bind and inhibit catalytic subunit
+cAMP: release catalytic subunit
What does PKA do?
has two catalytic kinase subunits that catalyze phosphorylation of target specific Ser/Thr
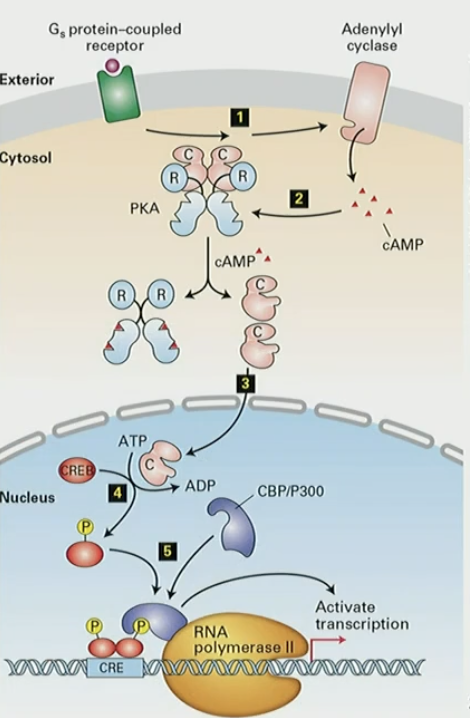
Mechanism for how PKA controls gene expression through CREB
GPCR activates Adenylyl cyclase, which produces cAMP
cAMP activates PKA
PKA catalytic subunits move to nucleus
PKA phosphorylates CREB transcription factor
CREB forms complex with co-activator CBP/P300, stimulates transcription of genes controlled by CRE (CREB responsive element)
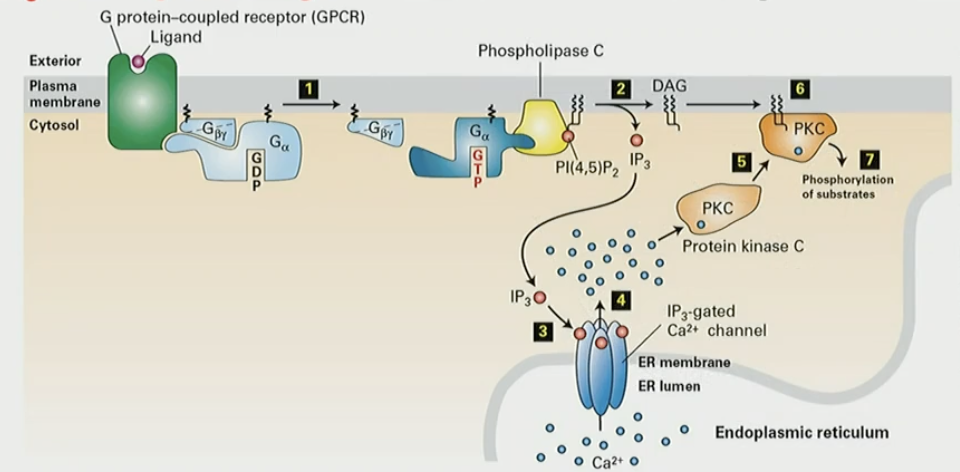
Mechanism for IP3/DAG pathway
GPCR activation activates PLC
PLC cleaves PIP2 → IP3 + DAG
IP3 diffuses through cytosol and opens Ca2+ ER channel
Ca2+ ions released, binds PKC, activation by DAG on PM
activated PKC leaves membrane to phosphorylate subcellular targets
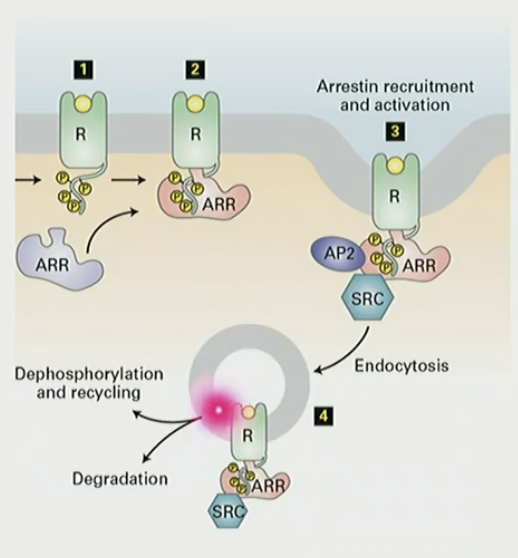
How does arrestin inactivate GPCR via endocytosis?
longer the signal, the more phosphorylation of GPCR. phosphorylated receptor binds arrestin, and AP2 is recruited for clatherin coated endocytosis. either dephosphorylated or degraded
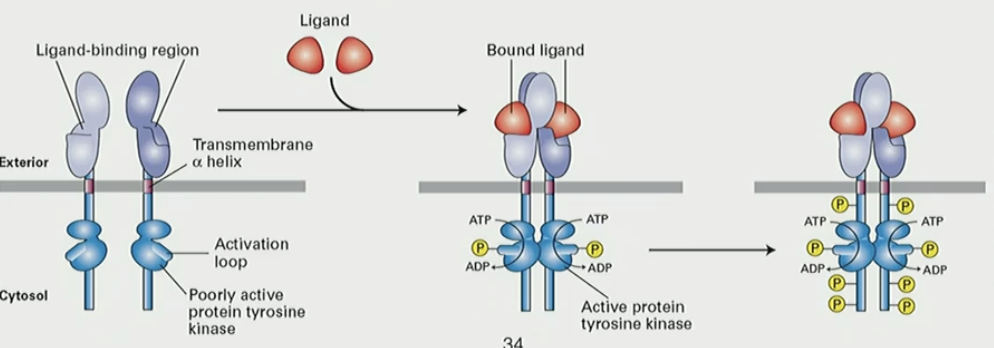
Mechanism for receptor tyrosine kinases (RTK)
+ ligand → RTK dimerizes
cytosolic domain kinases phosphorylate each other on Tyr
phosphorylated Tyr residues provide docking site for SH2 and other proteins
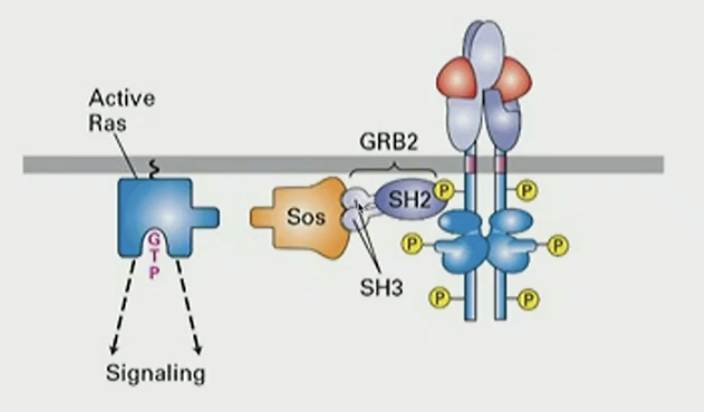
What does RTK do?
activate small GTPase Ras via adapter proteins by binding SH2 domain of GRB2, which binds to SH3, which binds to SOS, which has GEF activity towards Ras, forming active Ras-GTP
Mechanism for MAP Kinase cascade
after Ras is activated, Raf binds to Ras-GTP
Raf releases its 14-3-3 protein
Ras GTP hydrolysis to Ras-GDP releases active Raf
Raf phosphorylates and activates MEK
MEK phosphorylates MAP kinase on Tyr
MAP kinase phosphorylates transcription factors and others
Mechanism for induction of gene transcription by MAP kinase
1-3. dimeric MAP kinase phosphorylates p90RSK, which moves into nucleus, phosphorylating SRF
4-5. MAP kinase moves to nucleus, phosphorylates TCF
6. phosphorylated TCF, SRF stimulate transcription of c-fos and other genes
Hydrophobic signaling molecules require:
receptor at PM, receptor in cytosol, signal transduction mol, amplification via second messengers
receptor in cytosol
Cleavage of PIP2 gives rise to which second messenger?
cAMP, IP3, cGMP, IP4
IP3
Which subunit of trimeric G proteins bind GDP/GTP? alpha, beta, or gamma?
alpha
Activation of PKC requires: cAMP, cGMP, K+, Ca2+?
Ca2+
What are membraneless compartments?
coherent assembly of biological macromolecules
lack membrane
round/spherical shape (surface tension)
What phase is membraneless compartments most like?
liquid
Properties of liquids
short range positional order, high mobility
Properties of solids
long range positional order, molecules trapped, doesn’t rearrange
What % of all proteins have intrinsically disordered regions?
50%
Multivalent scaffolding proteins can undergo what process?
liquid-liquid phase separation
What is the implications of membraneless compartments?
reaction specificity: concentration of reactants inside condensates can inc rxn kinetics
reaction kinetics: increased viscosity can slow rxn kinetics
reaction inhibition by sequestration: prevent rxns
concentration buffer: buffer for molecules in bulk phase
Without energy input, condensates will?
harden out, turn into solid. to pry apart, use ATP dependent machinery (chaperone, disaggregases)
What are stress granules and their function?
ribonucleoprotein that is phase separated, membraneless that is formed due to stress on cell. they promote cell survival by condensing translocationally stalled mRNA, RBP, ribosomal components etc
Maturation of stress granule
SSRNA is released
dephosphorylated Ras GTPase-activating PBP1/2 (G3BP1/2) associates w/ released RNA and assembles into liquid condesates
caprin 1 and other RBP promote maturation of stress granule
Which factors impact the critical/saturation concentration of LLPS? PTM, chemical environment, time, all of the above
all of the above
What residues does SH2 on Grb2 recognize?
phospho-tyrosine residues
What residues does SH3 on Grb2 recognize?
poly-proline residues
What are the 3 distinct zones within nucleoli?
FC (fibrillar center): transcription of rDNA
DFC (dense fibrillar center): rRNA processing
GC (granular components): ribosome assembly, storage for unfolded proteins
What’s the mechanism to get through the nuclear pore complex (NPC) for proteins > 40kDa and <40kDa?
<40kDa: diffusion
>40kDa: nuclear localization/nuclear export signal or nuclear transport receptor
What fills the nucleoporin?
FG-repeat gel-like condensate that allows diffusion of small molecules
Mechanism for nuclear import
importin binds to NLS of cargo protein
importin-cargo diffuses thru NPC (work w/ FG-nucleoproins)
Ran-GDP releases GDP, binds GTP
Ran-GTP binds to importin, releases cargo
importin-Ran-GTP complex transported to cytoplasm
GTP hydrolysis, Ran-GDP conf change releases importin
GEF in nucleus, GAP in cytoplasm
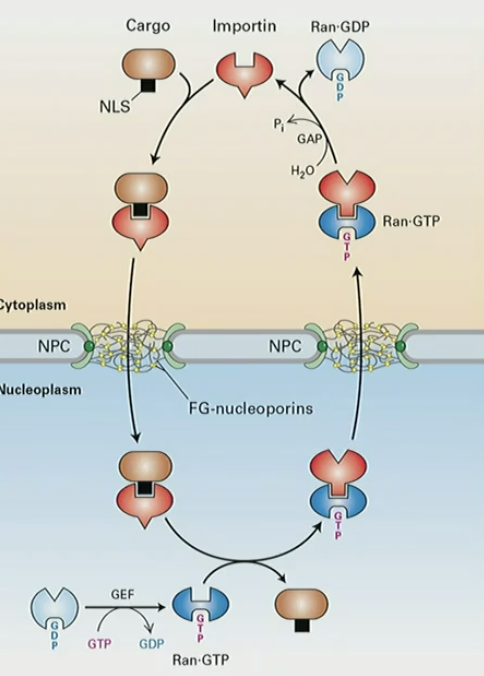
Mechanism for Ran-dependent nuclear export
exportin 1 binds to NES-cargo protein and Ran-GTP
complex diffuses through NPC
Ran-GTP → Ran-GDP conformational change releases NES cargo into cytosol
exportin 1 and Ran-GDP transported back into nucleus
What kind of amino acids are NES (nuclear export signals) rich in?
hydrophobic
Mechanism for Ran-indepdendent nuclear export
NXF1/NXT1 nuclear export receptor complex binds to mRNA protein complex
complex diffuses through NPC by interactions with FG
RNA helicase (Dbp5) located on cytoplasmic side uses ATP to remove NXF1/NXT1
NXF1/NXT diffuse back into nucleus
What % of human DNA encodes proteins? What does the rest do?
1.5%, the rest are regulatory sequences that control gene expression
What does the SMC complex do?
it clamps chromatin strands together
What structure stabilizes the nucleoporins
Y-complex
Is the concentration of Ran-GDP is higher in the cytosol or nucleoplasm?
cytosol, because more GAP in cytoplasmic filaments
Is nuclear localization signal (NLS) acidic, basic, hydrophobic?
basic
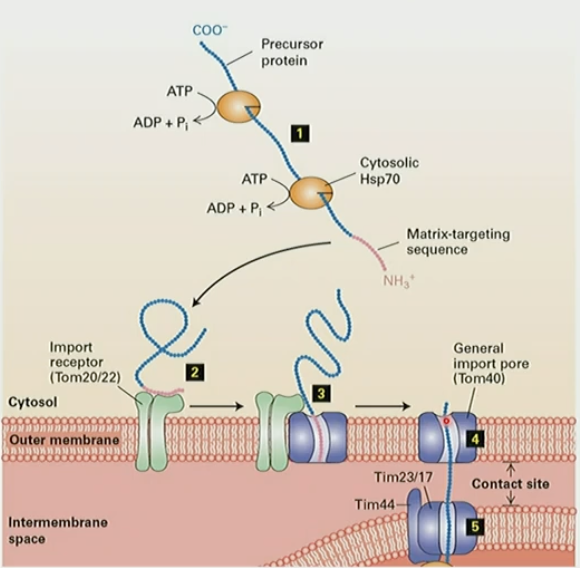
Mechanism for >500kDa proteins to mitochondrial matrix
amphipathic N-terminal targeting seq target proteins to mito matrix
Tom20/22 outer membrane import receptor binds to seq
target signal inserted into translocon Tom40
protein moves through Tom40 and inserts into inner membrane translocon Tim
protein binds to matrix Hsp70 to “pull” peptide through
Hsp70 ATP hydrolysis releases protein
protein folds
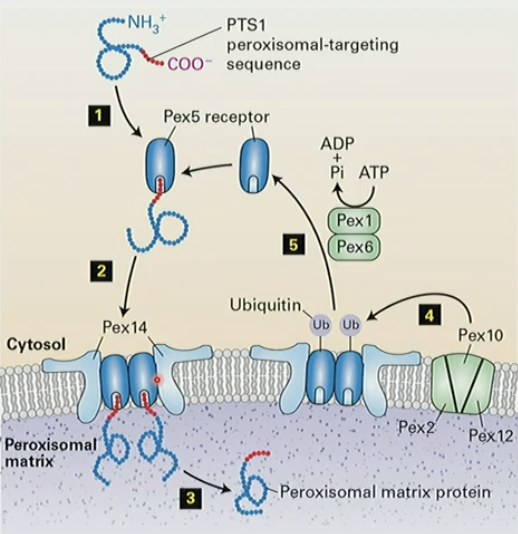
Mechanism of targeting proteins to peroxisomes
peroxisomal targeting seq PTS1 on C-term: S-K-L binds Pex5
complex binds to Pex14r in membrane
matrix protein dissociates into peroxsomal matrix
ubiquitinylation of Pex5 by Pex2/10/12 complex
ATP-dependent removal of Pex5 by Pex1/Pex6