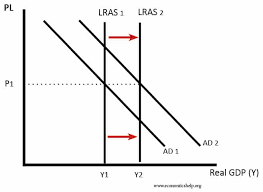
Long Run Aggregate Supply
1/12
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
13 Terms
LRAS
a curve that shows the relationship between price level and real GDP, that would be supplied if all prices, including nominal wages, were fully flexible
Factors of Production
in the long run, all factors of production are variable
Determinants of LRAS
state of technology
factor mobility
productivity
enterprise incentives
institutional structure of economy
attitudes
Factor mobility
OCCUPATIONAL MOBILITY (education: student loans for all)
GEOGRAPHICAL MOBILITY (transport: railways and investment in infrastructure such as HS railways)
Institutional structure of economy
Increased competition
Increased banking (more loans etc.)
Flexible working
HYBRID WORKING (working from home part time) - increases participation
LAND
increased land efficiency
permits to use new land
LABOUR
education/training/retraining
increase minimum wage to encourage participation
income tax lower to encourage participation
cutting benefits to encourage participation
childcare subsidies to allow employment (30hours free/ week)
CAPITAL
research and development grants
tax breaks on investment in capital goods
subsidies on capital (AI/Renewable energy)
technological advancement
ENTERPRISE
grants for energy store
grants for renewable energy
low corporation tax for small businesses (19% for profit under £250,000)
Economic incentives
13 investment zones (10yrs funding)
childcare subsidies
renewable subsidies
tax breaks on research and development
investment in research and development
AS CURVE
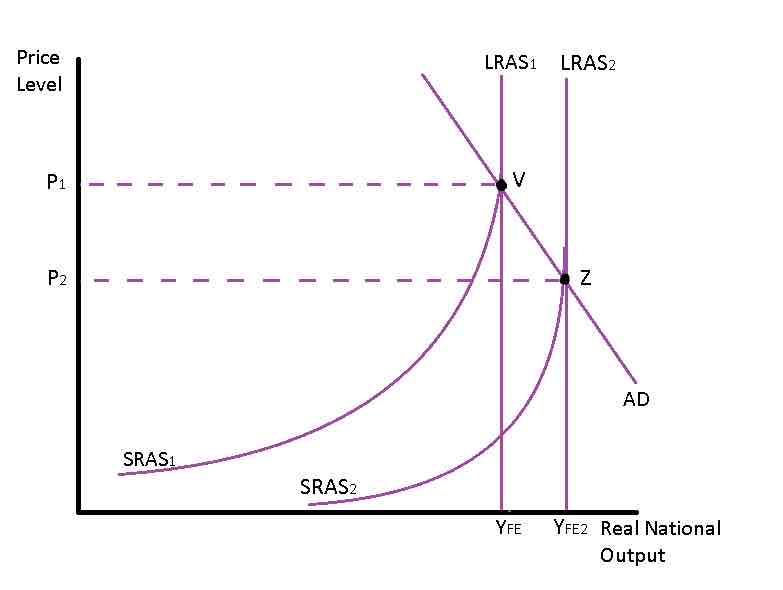
LRAS CURVE