Middle Ear Anatomy
1/31
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
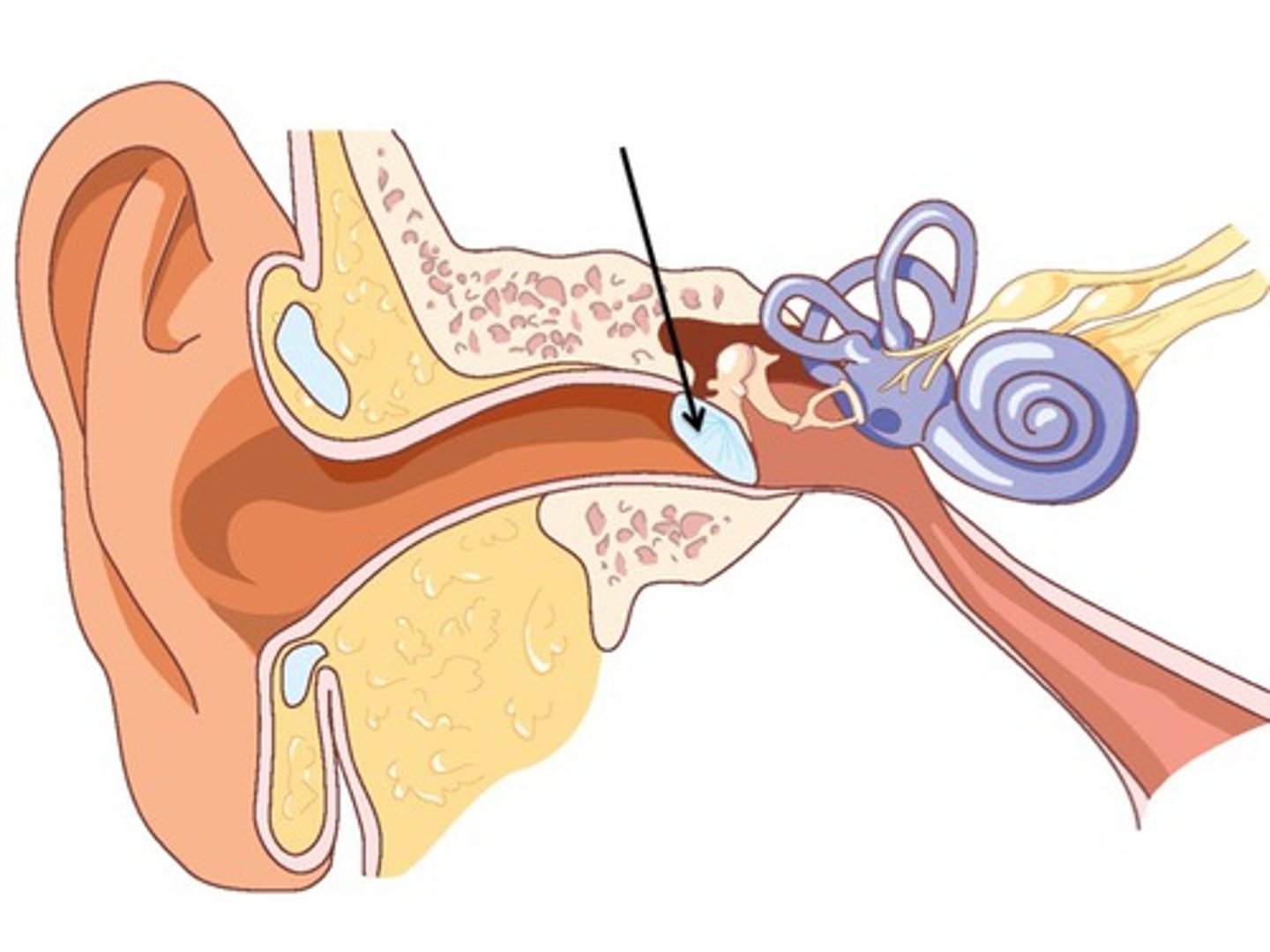
Tympanic Membrane
The eardrum. thin, semi-transparent membrane separating the outer ear from the middle ear. vibrates in response to sound waves.
Tympanic Membrane Outer Layer
Cuticular. thin layer continuous with the lining of the external auditory meatus. allows elasticity. protective layer
Tympanic Membrane Intermediate Layer
Fibrous. keeps tension/stiffness
Tympanic Membrane Inner Layer
Mucosal. produces fluid, protects, heals damage
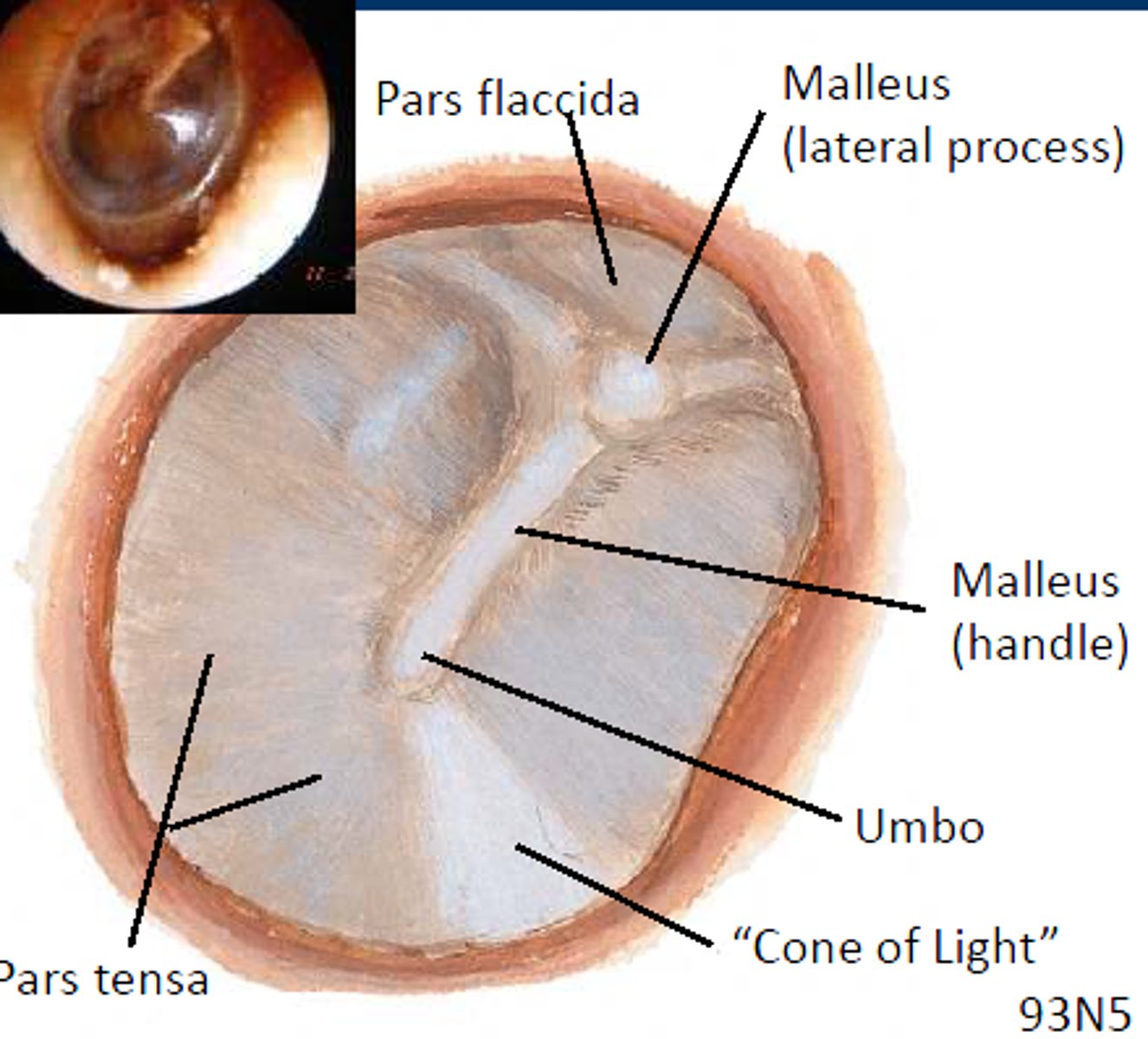
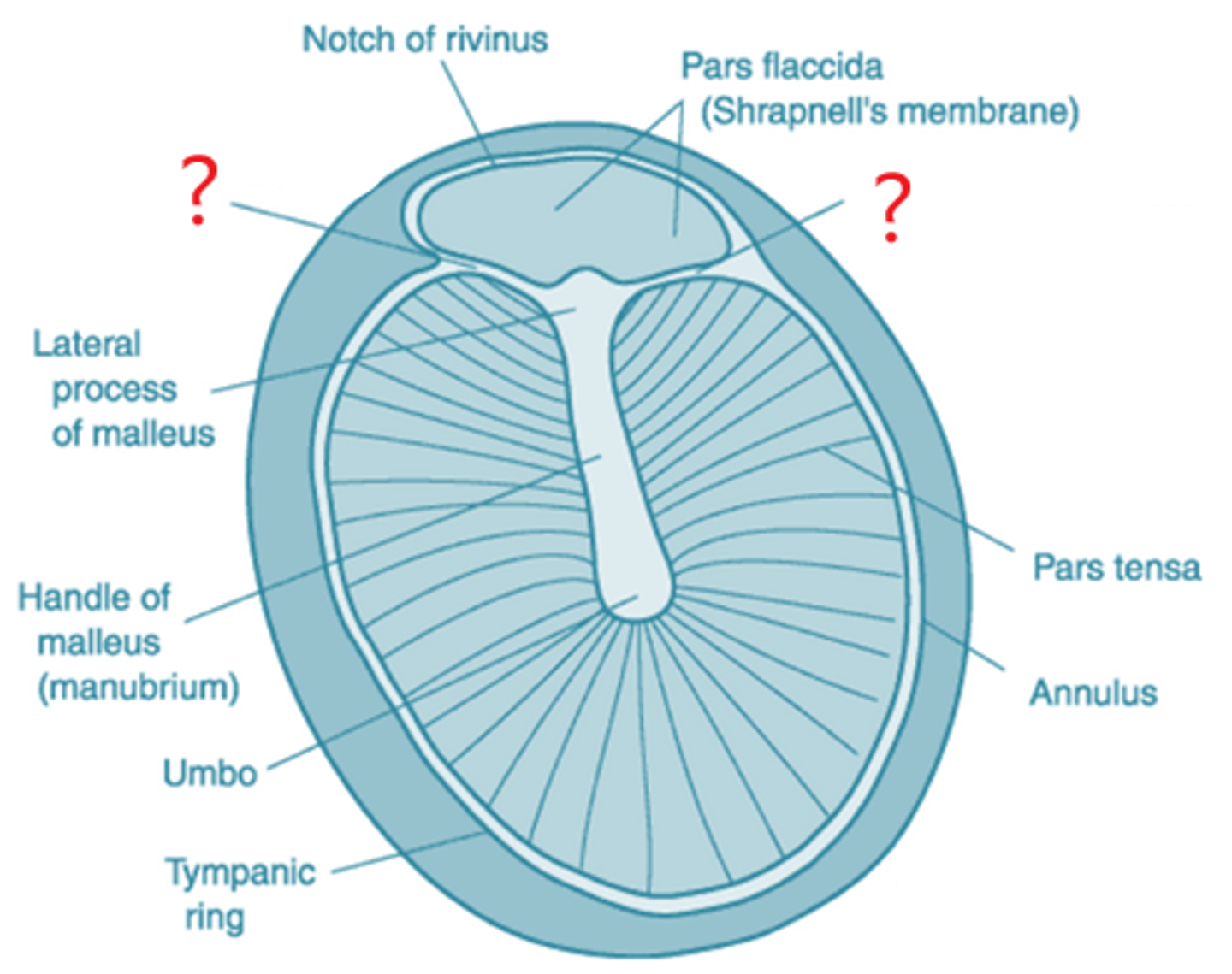
Malleolar Stria
light-coloured stripe on the outer surface of the tympanic membrane, caused by the malleus
Umbo
where handle of the malleus attaches to tympanic membrane, drawing the eardrum slightly inward in a cone shape
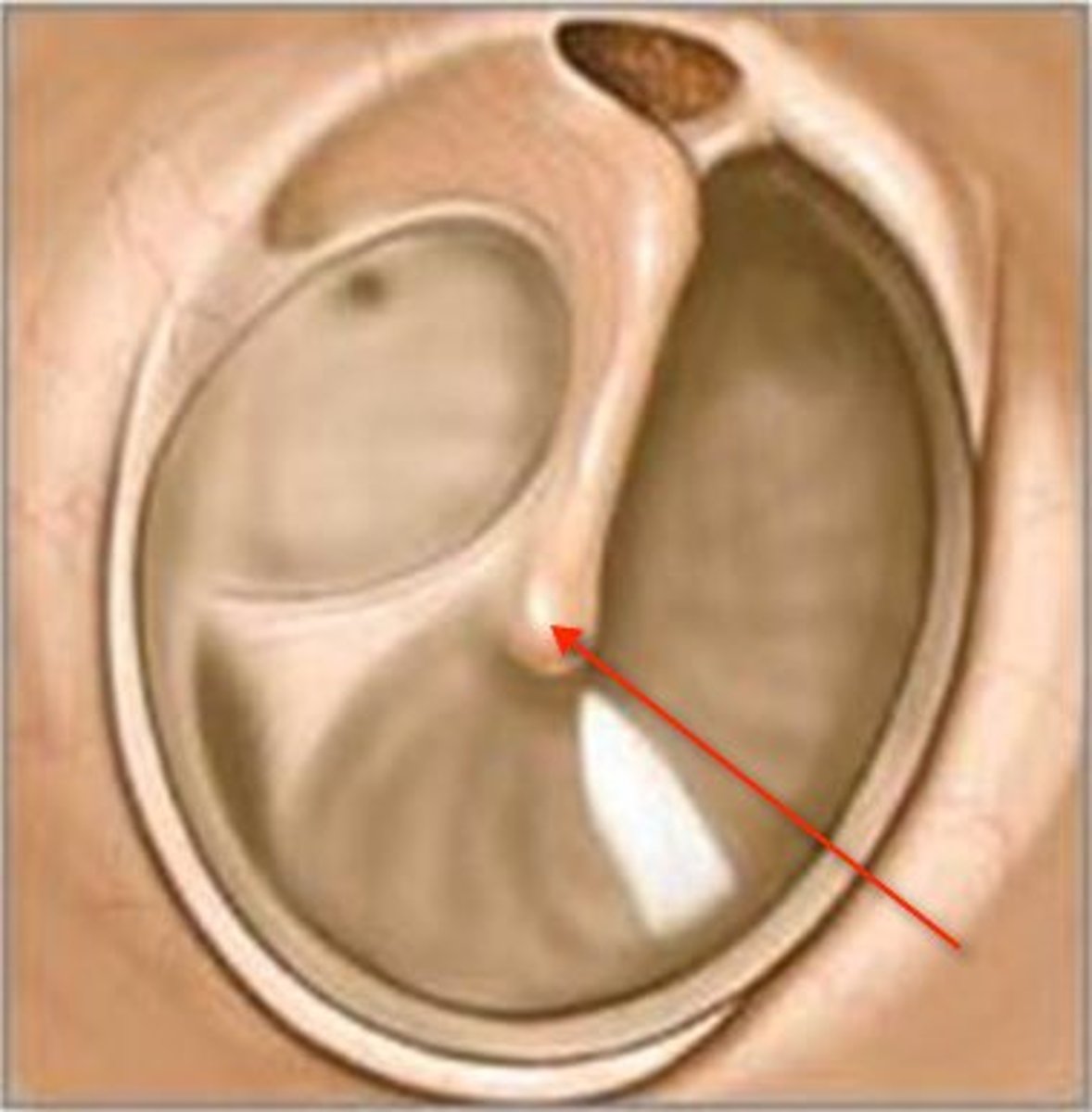
cone of light
reflection of light from otoscope. means a healthy eardrum
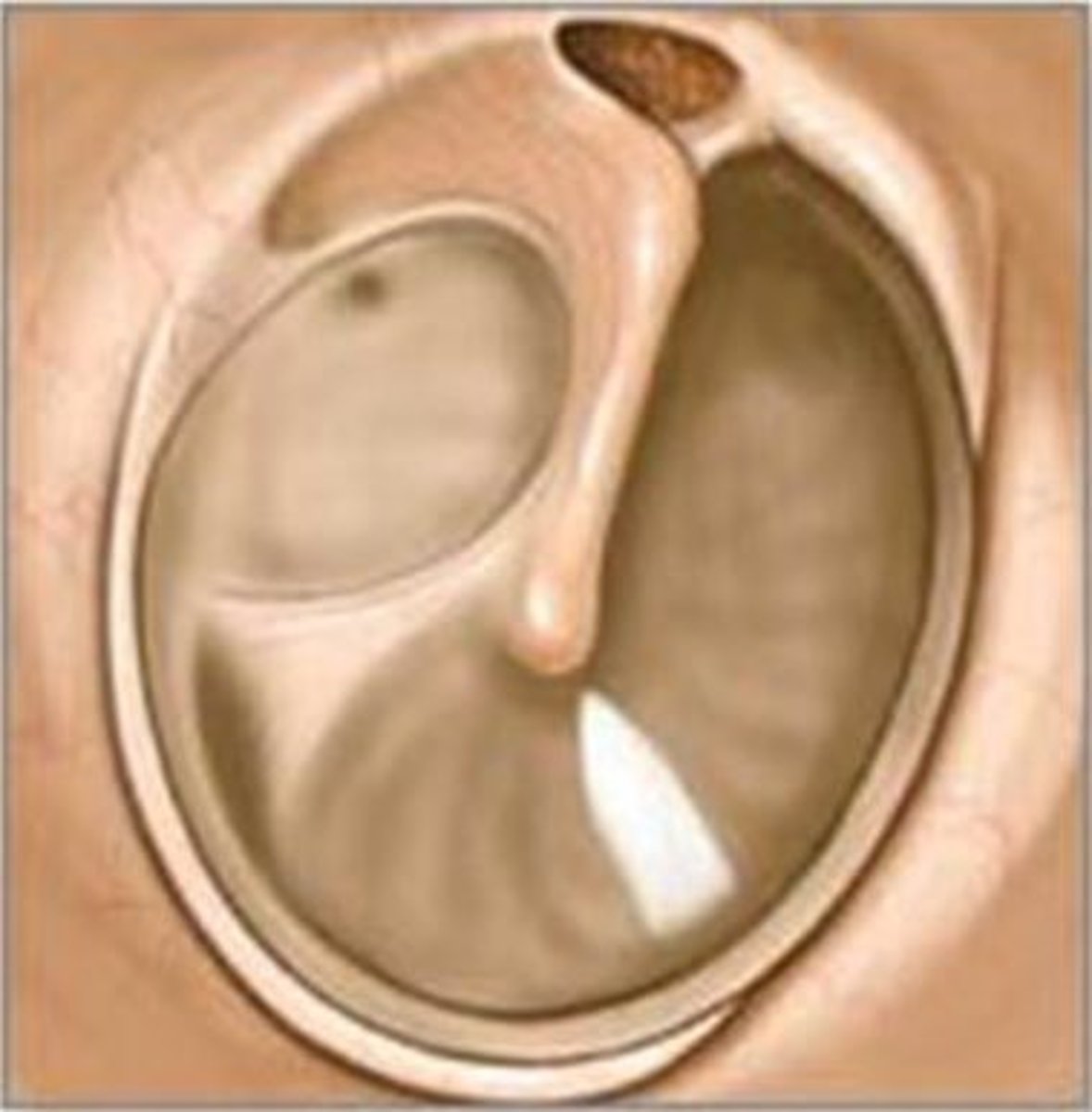
pars tensa
larger, thicker and more taut portion of the tympanic membrane
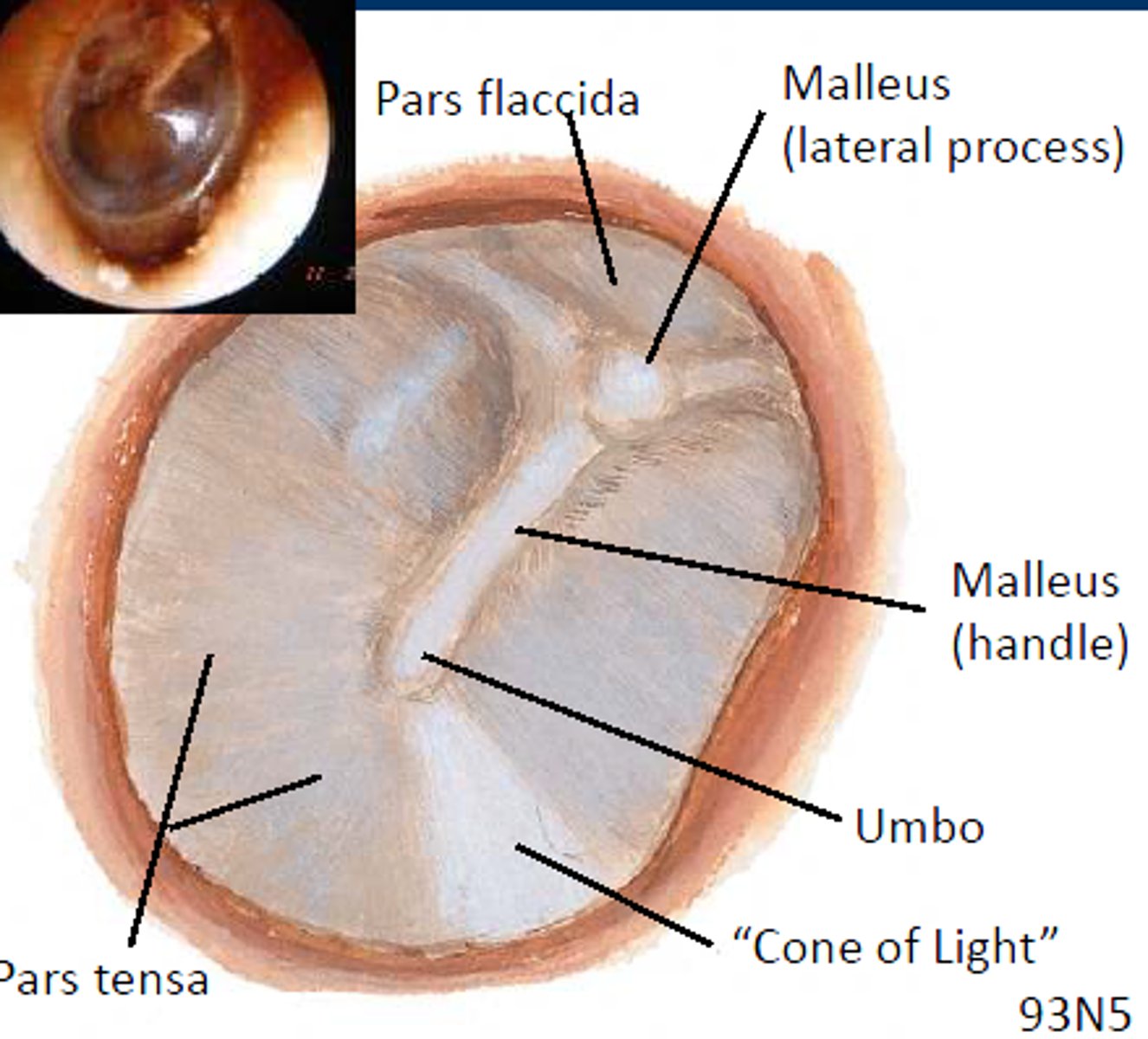
pars flaccida
small, flaccid, superior section of tympanic membrane, separated from the pars tensa by the malleolar folds.
malleolar folds
lines of separation between the pars flaccida and pars tensa
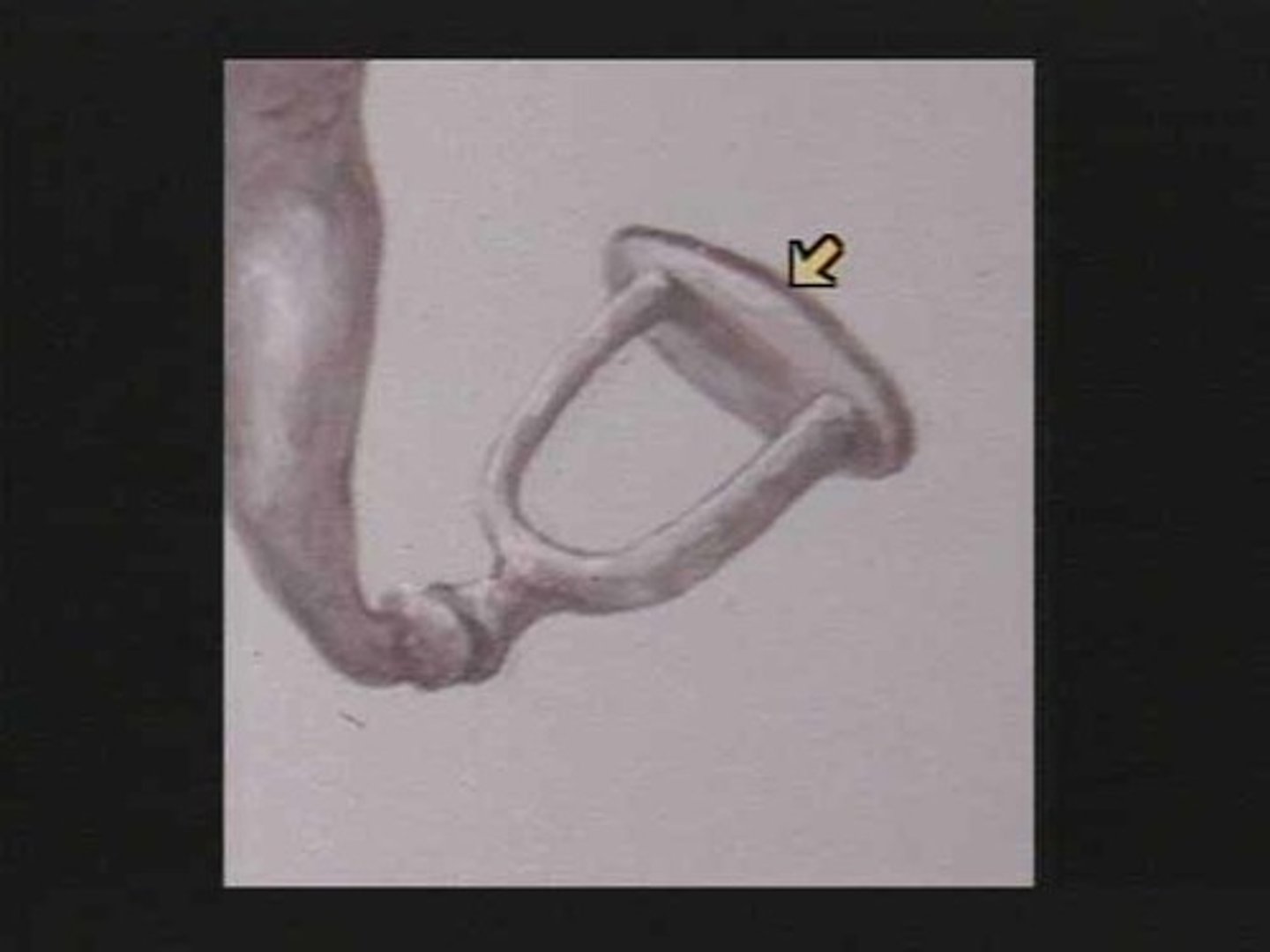
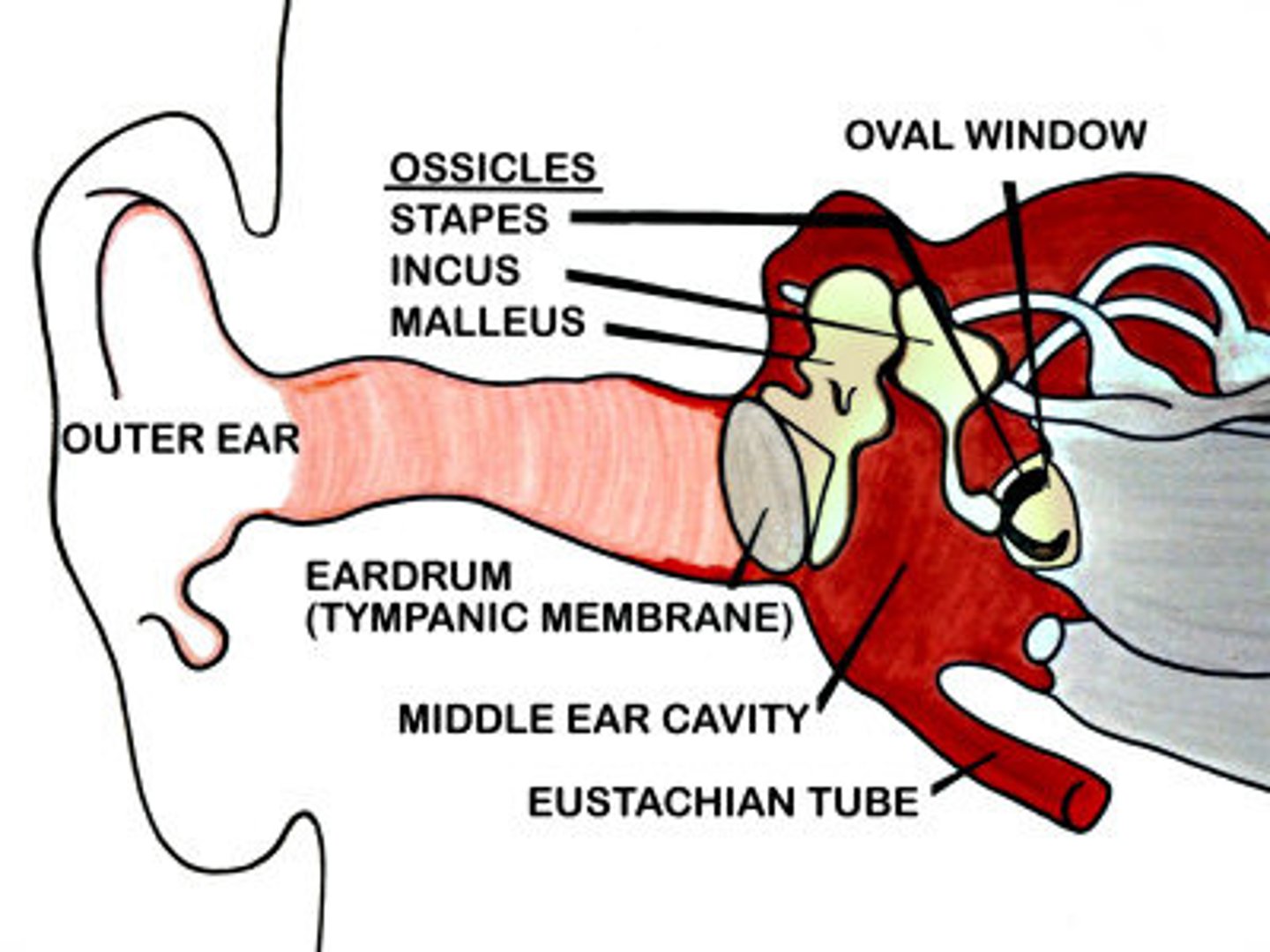
name the 3 auditory ossicles
malleus (hammer), incus (anvil), stapes (stirrup)
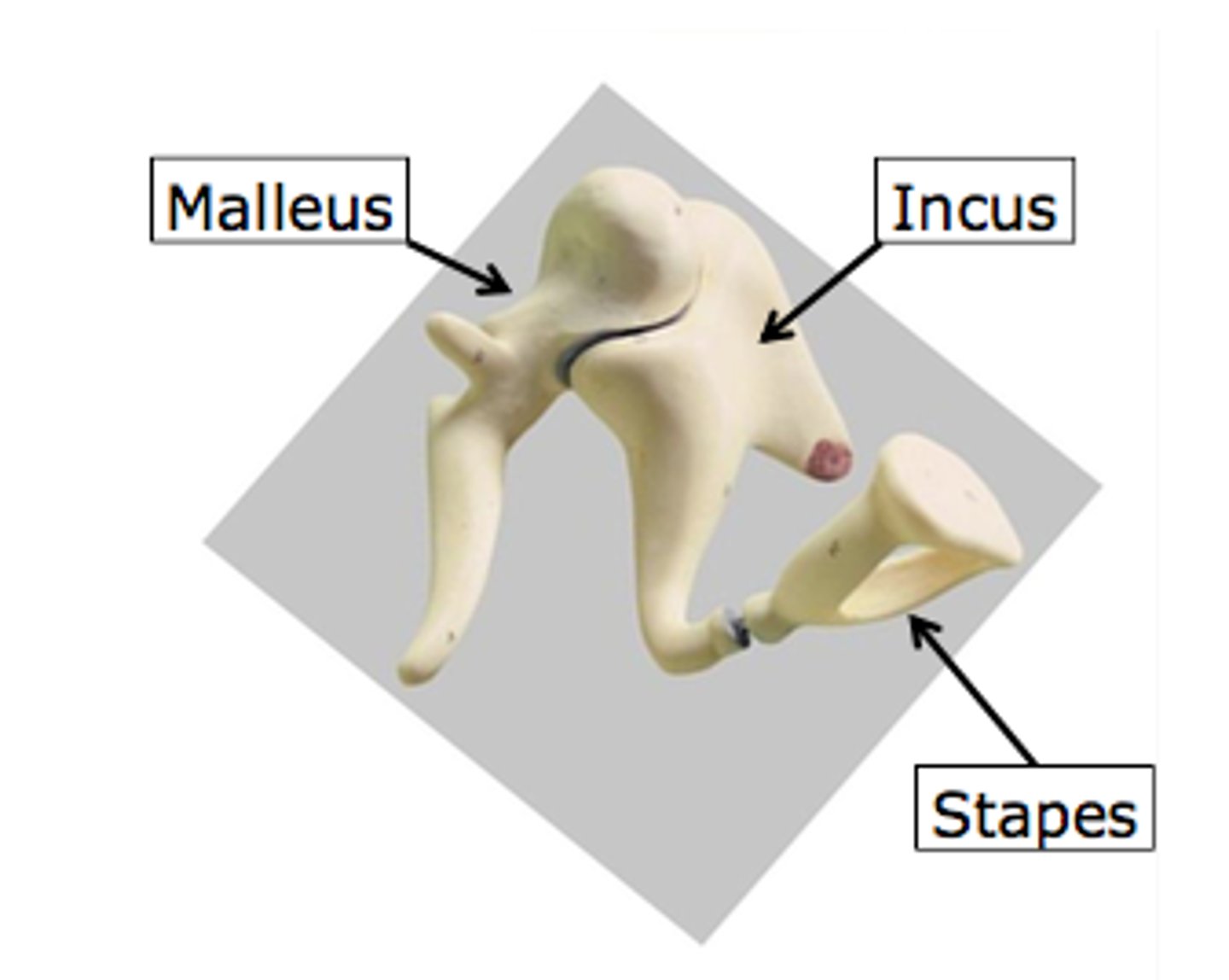
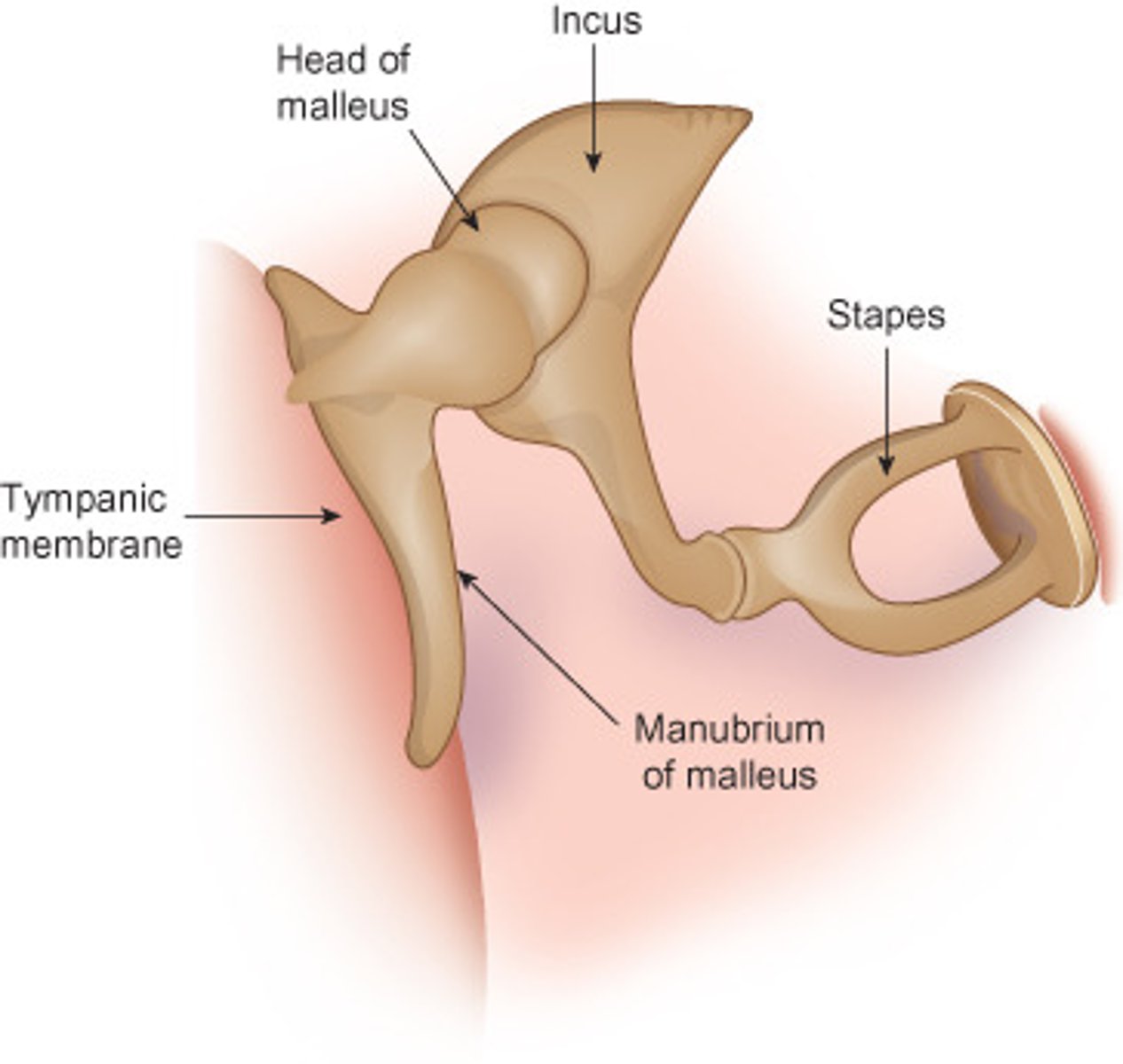
malleus
hammer. attached to inner surface of eardrum and connects with the incus. transmits sound vibrations from eardrum to incus
incus
anvil. connected to malleus and stapes. transmits vibrations from malleus to stapes
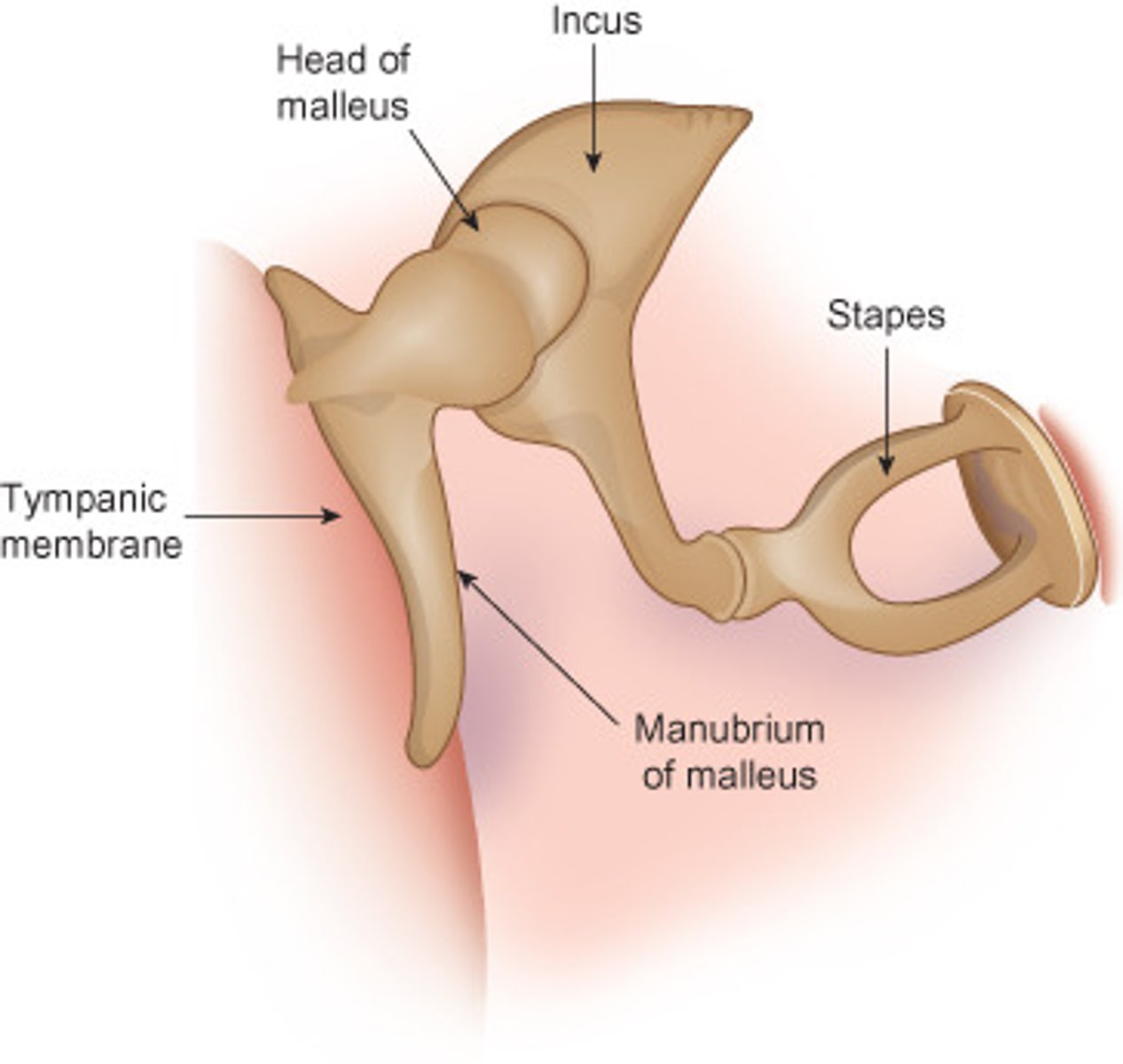
stapes
stirrup. connected to incus via the lenticular process. transmits vibrations from incus to the oval window
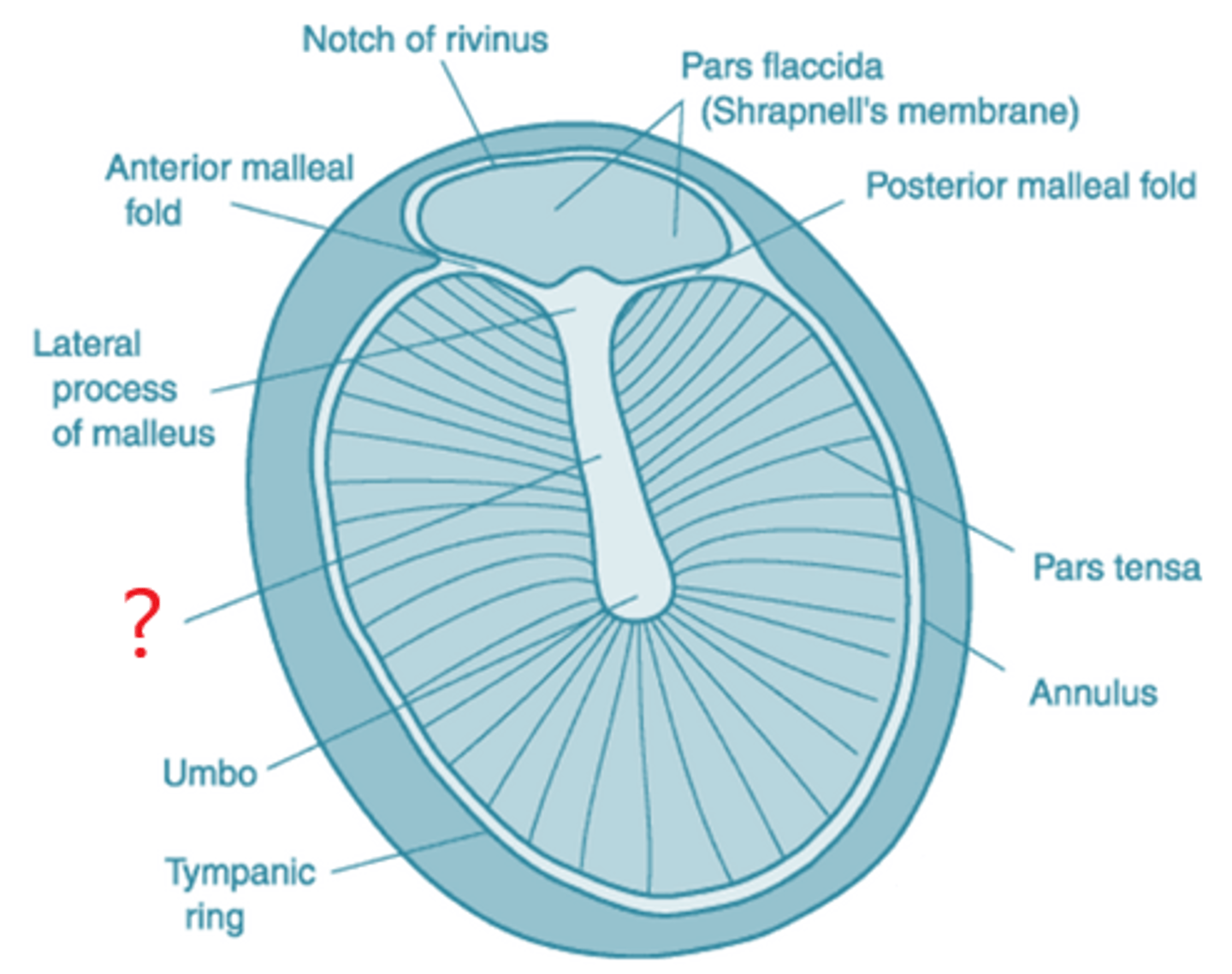
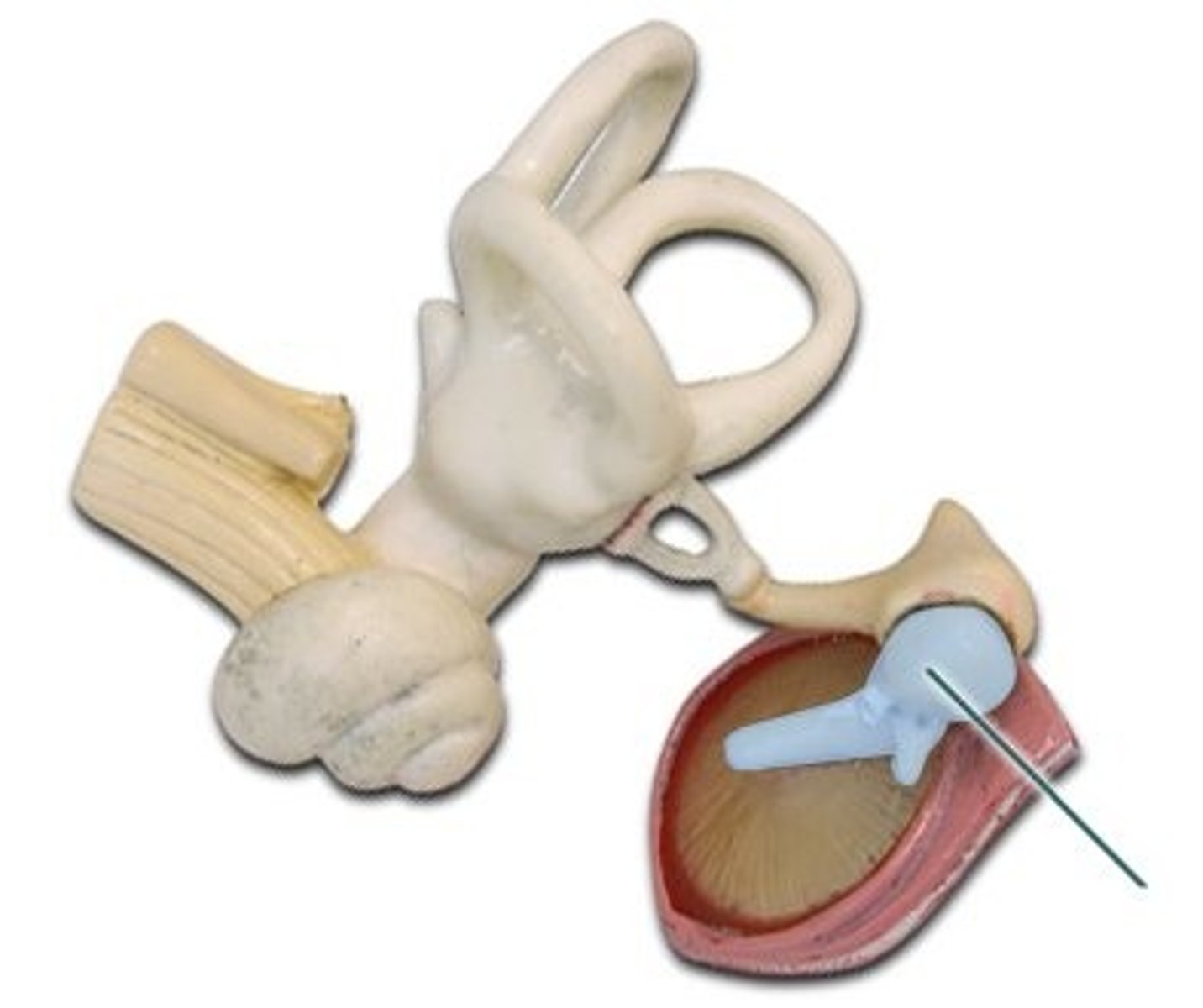
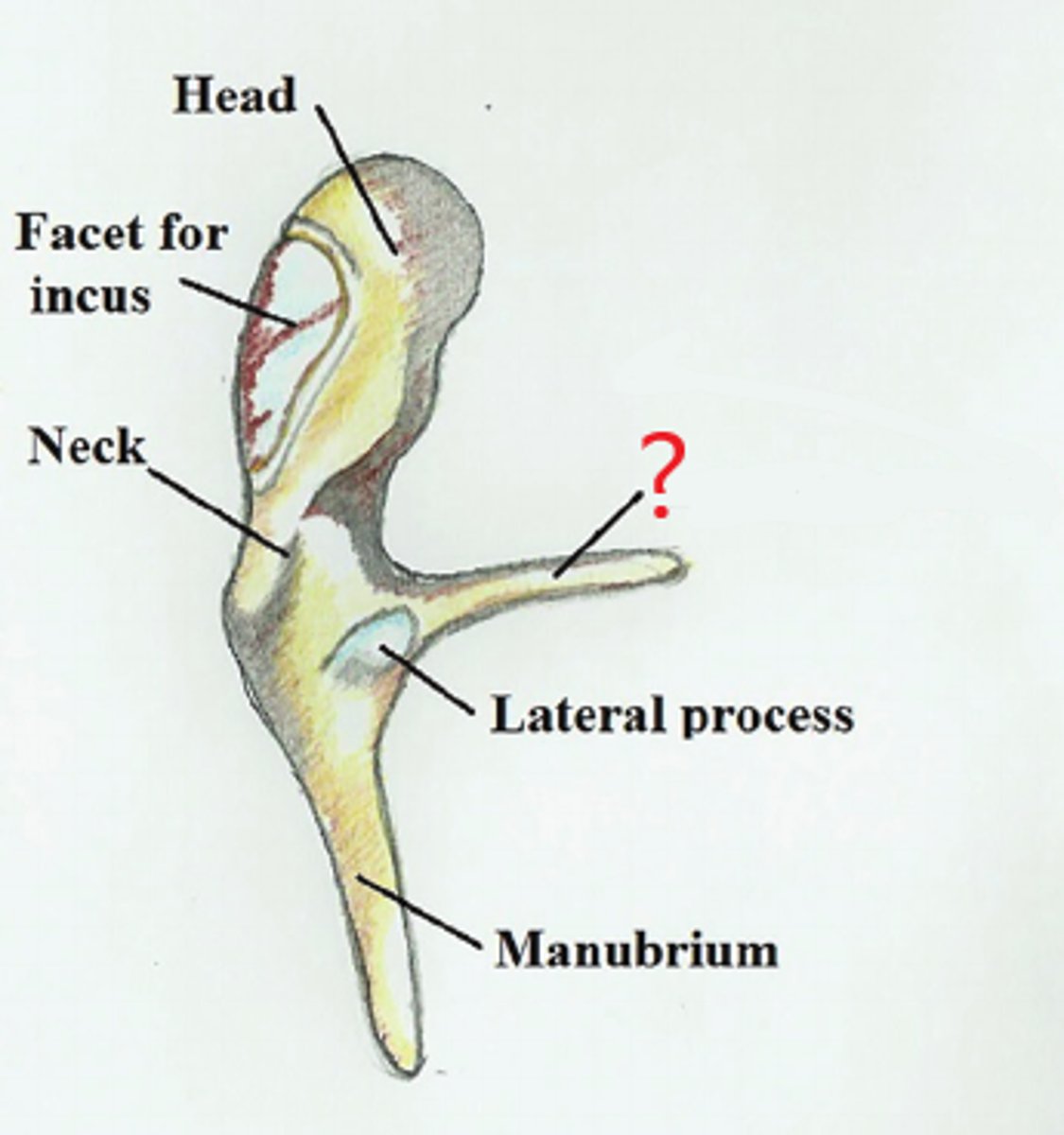
lateral process
protrusion from the base of the malleus's handle that attaches to the upper portion of the tympanic membrane
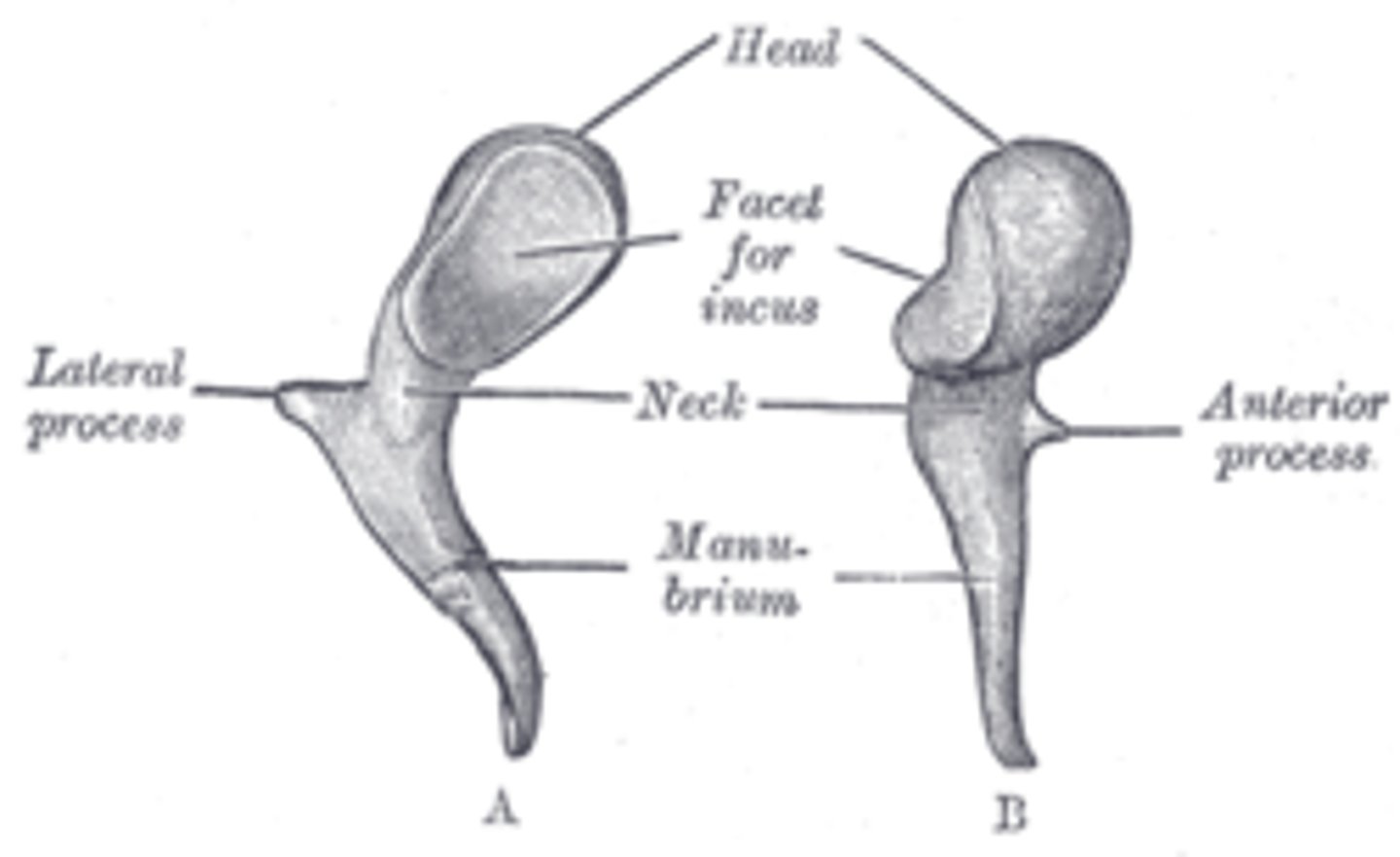
anterior process
protrusion of the malleus attached to the anterior wall of the tympanic cavity
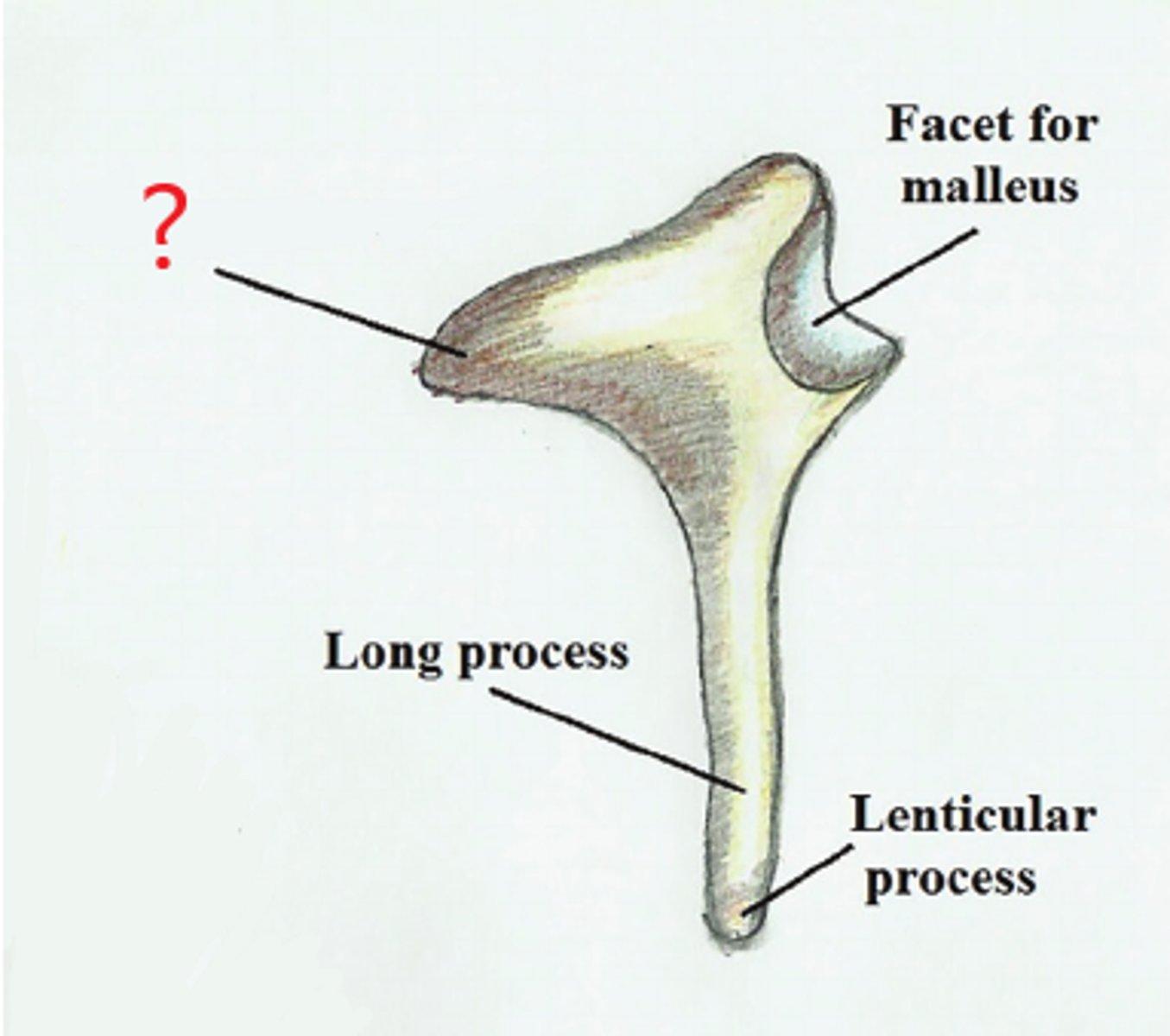
lenticular process
egg-shaped end of the incus. transmits vibrations from the incus to the stapes
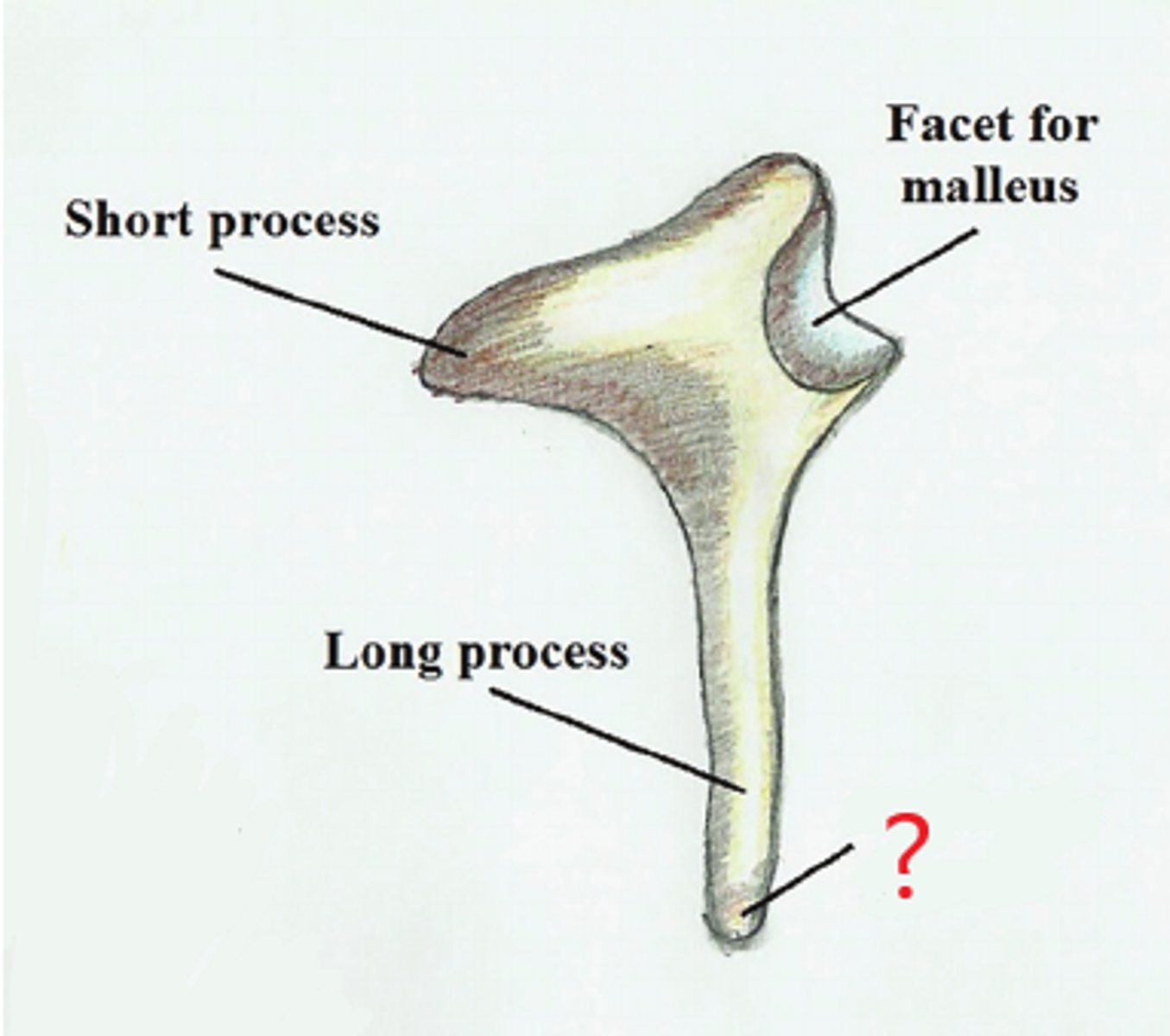
short process/short crus
short tapered horn of incus.
long process/long crus
extends from body of incus and attaches to head of stapes via lenticular process.
manubrium of malleus
handle of malleus, attaches to inner surface of tympanic membrane
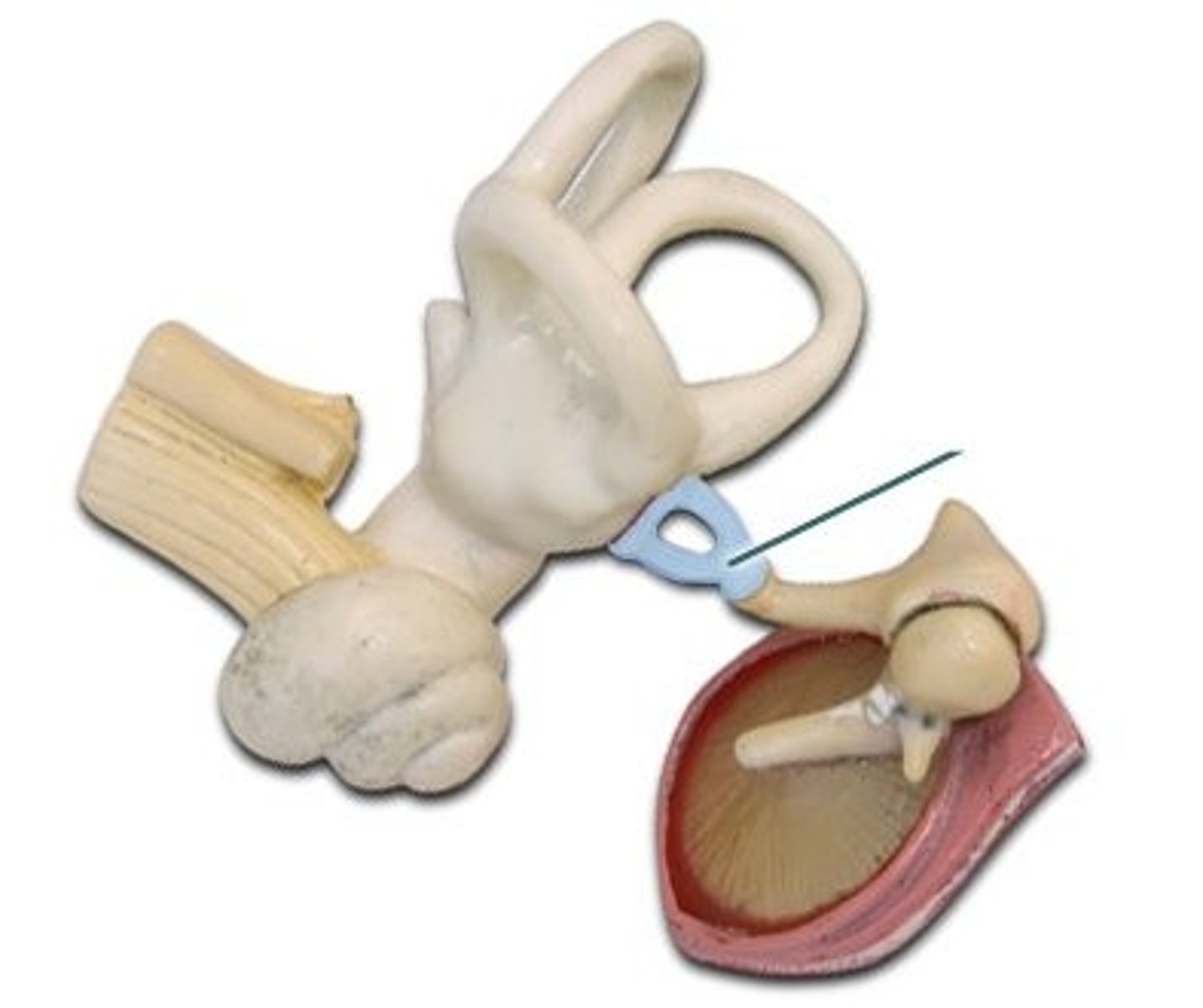
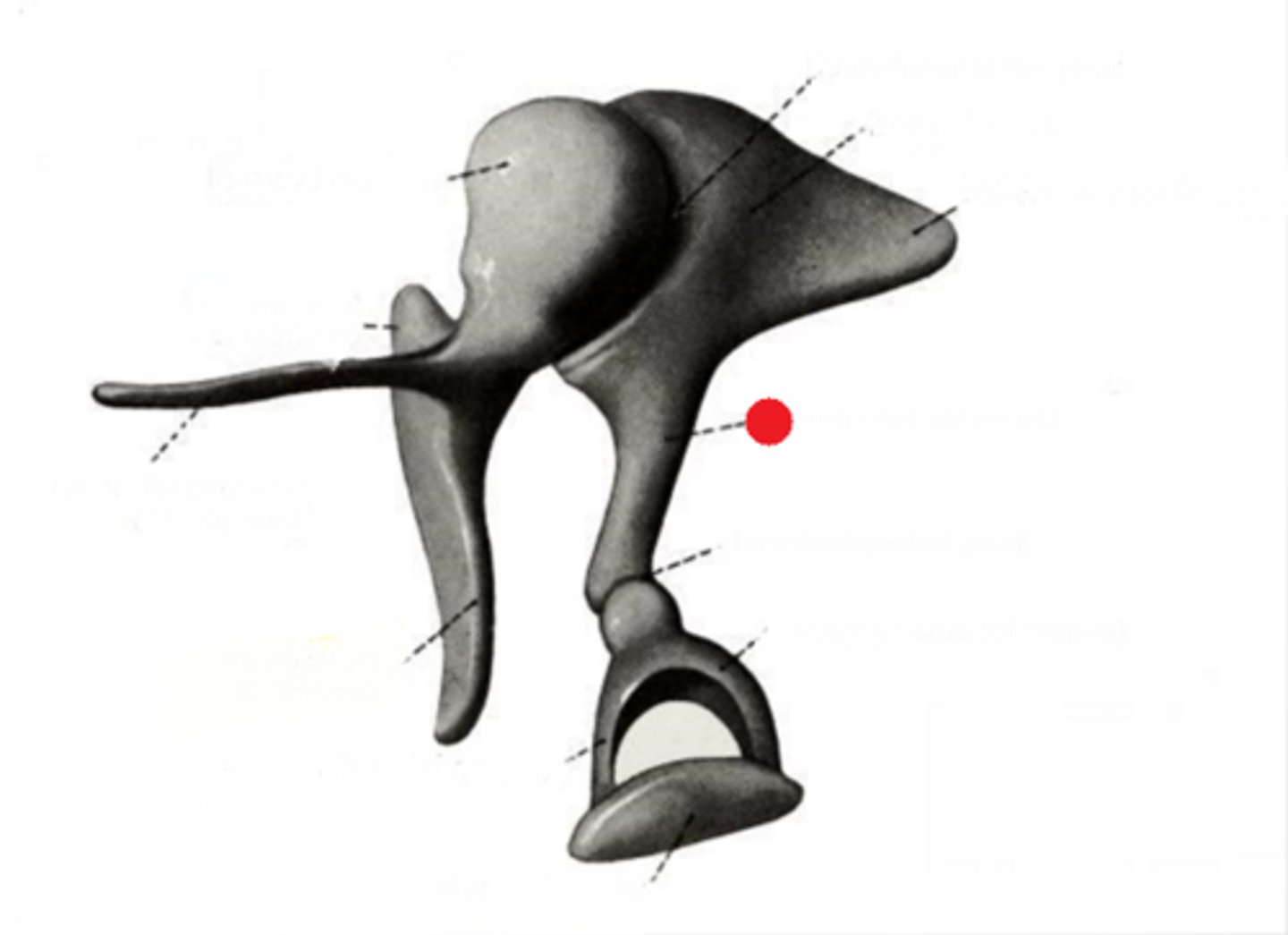
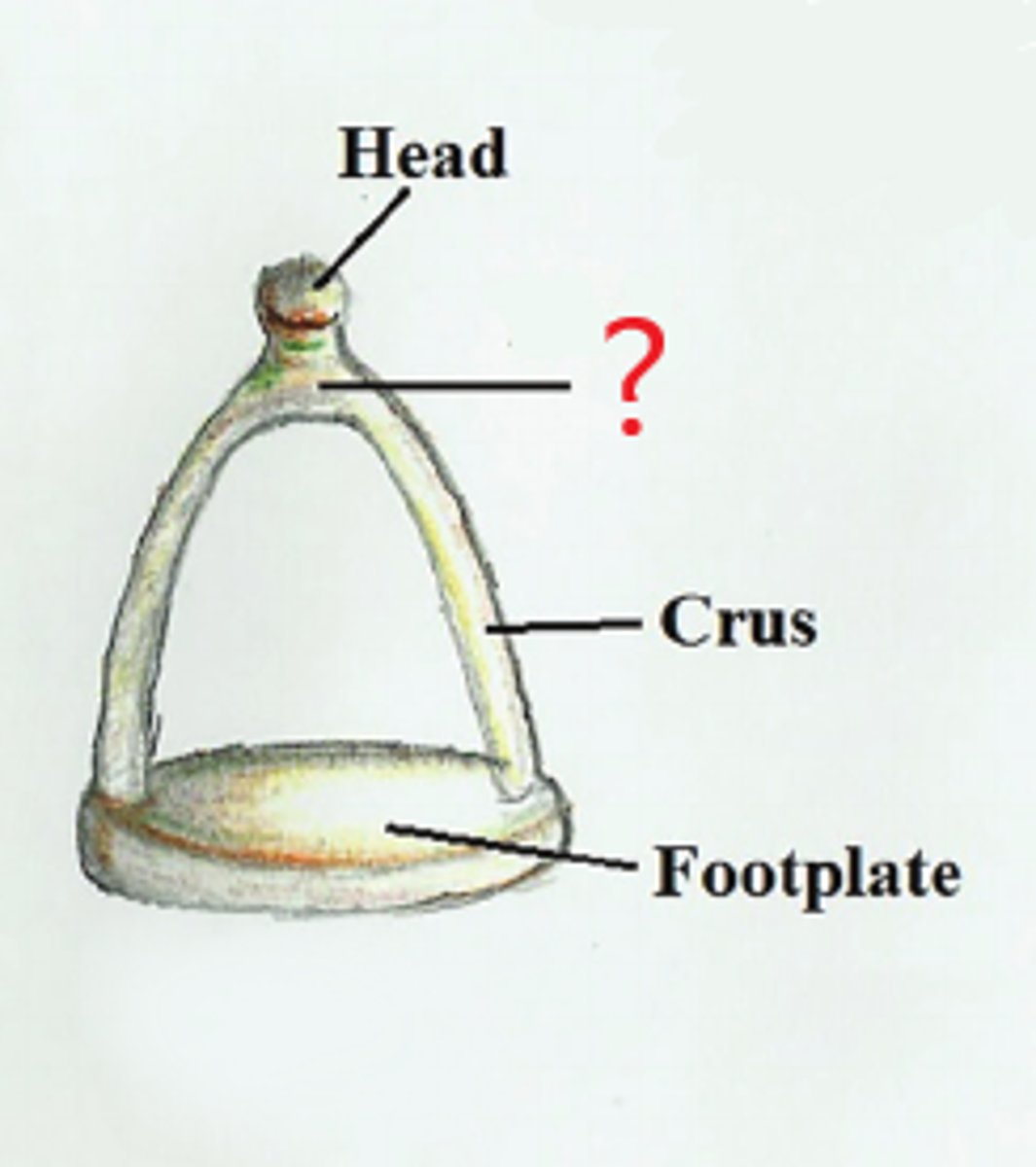
neck of stapes
connects head to the two crura (limbs). attachment point of stapedius muscle
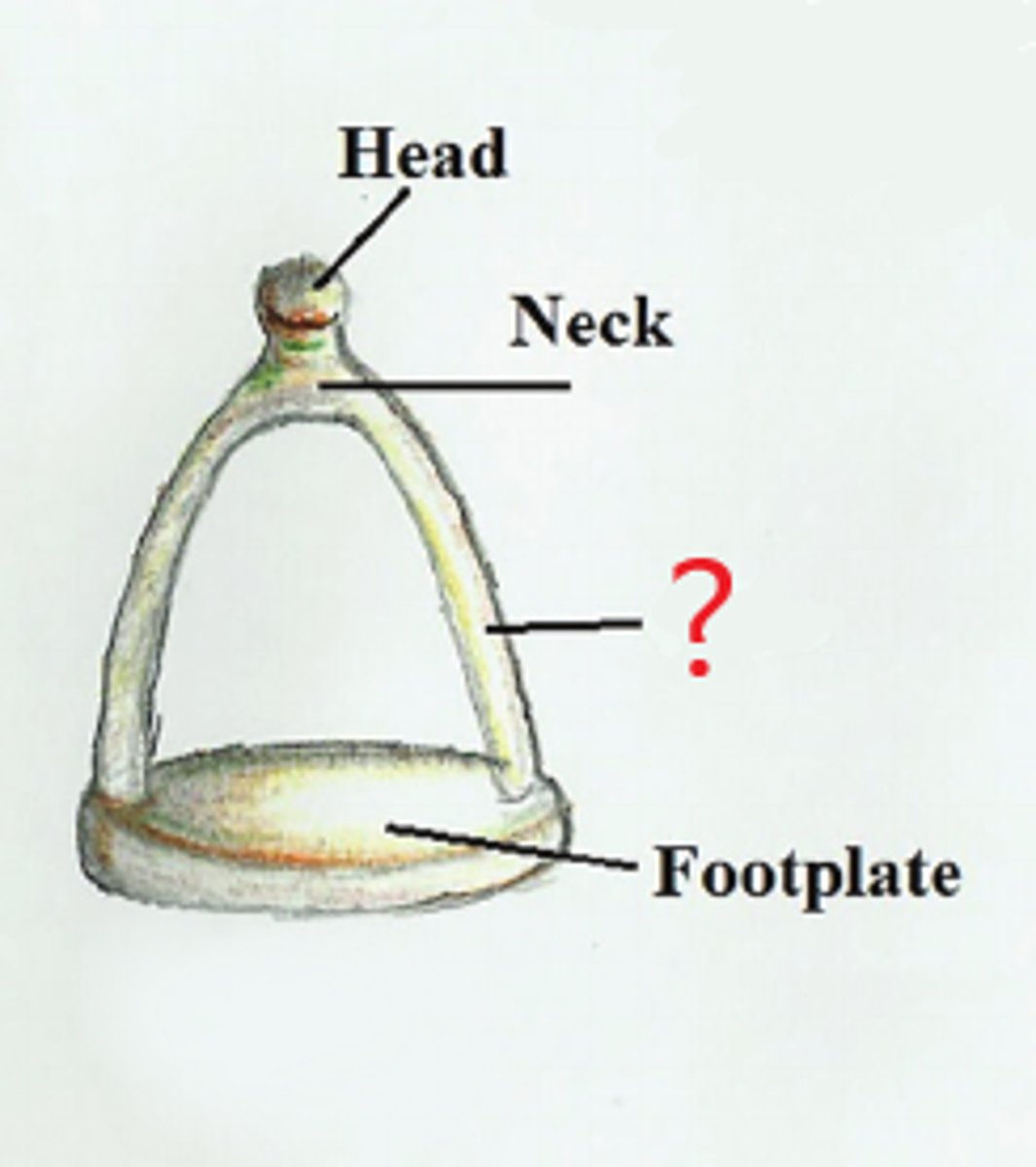
crura of stapes
two limbs/arches connected to footplate & neck
footplate of stapes
rests on oval window. transfers vibrations through oval window into the perilymph, creating fluid waves.
tensor tympani muscle
muscle in the middle ear that attaches to malleus and tenses the eardrum to dampen loud/unpleasant sounds (rumbling sound)
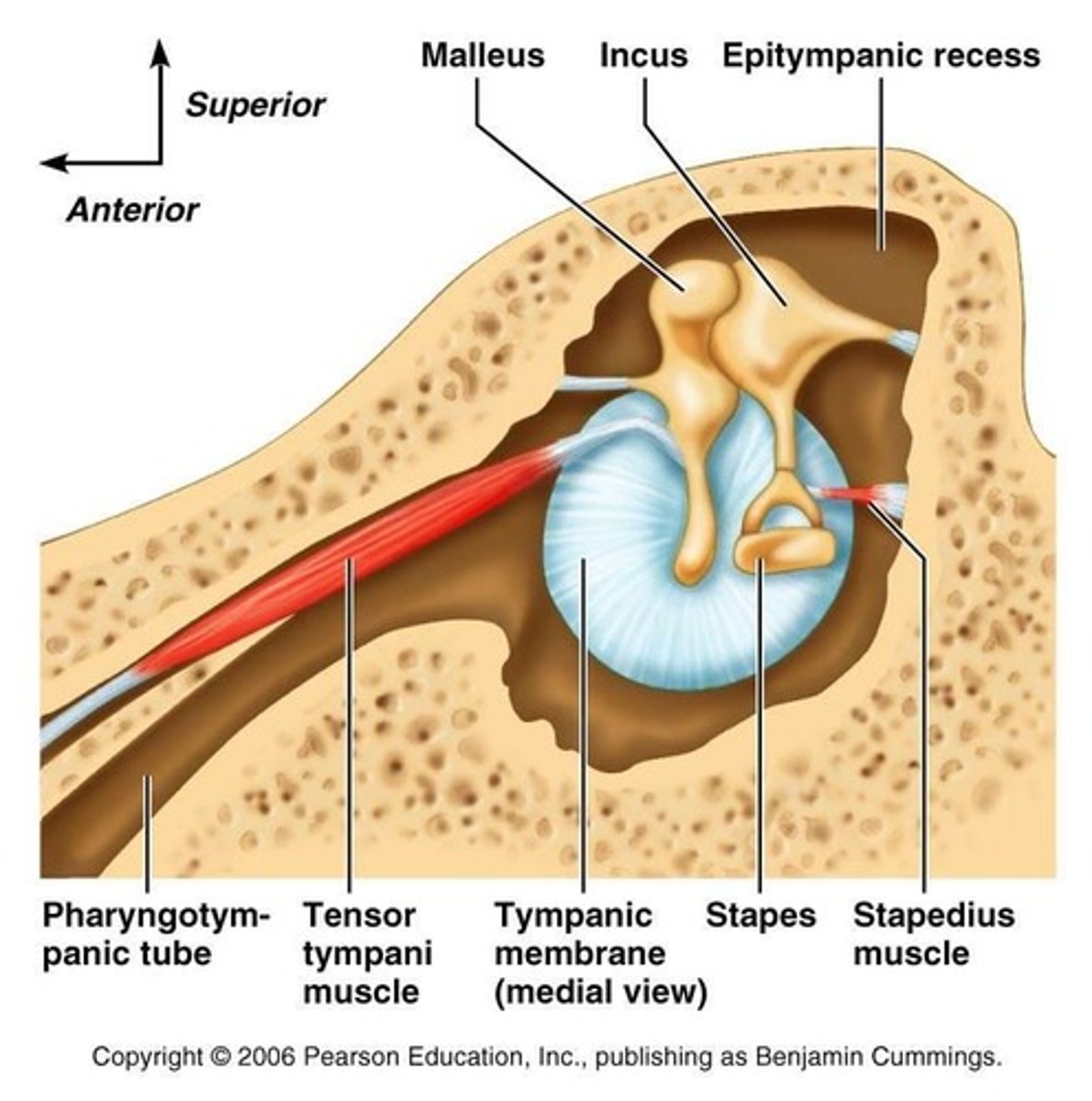
stapedial pyramid/pyramidal eminence
small, hollow, cone-shaped bony prominence on the posterior wall of the middle ear. houses stapedius muscle
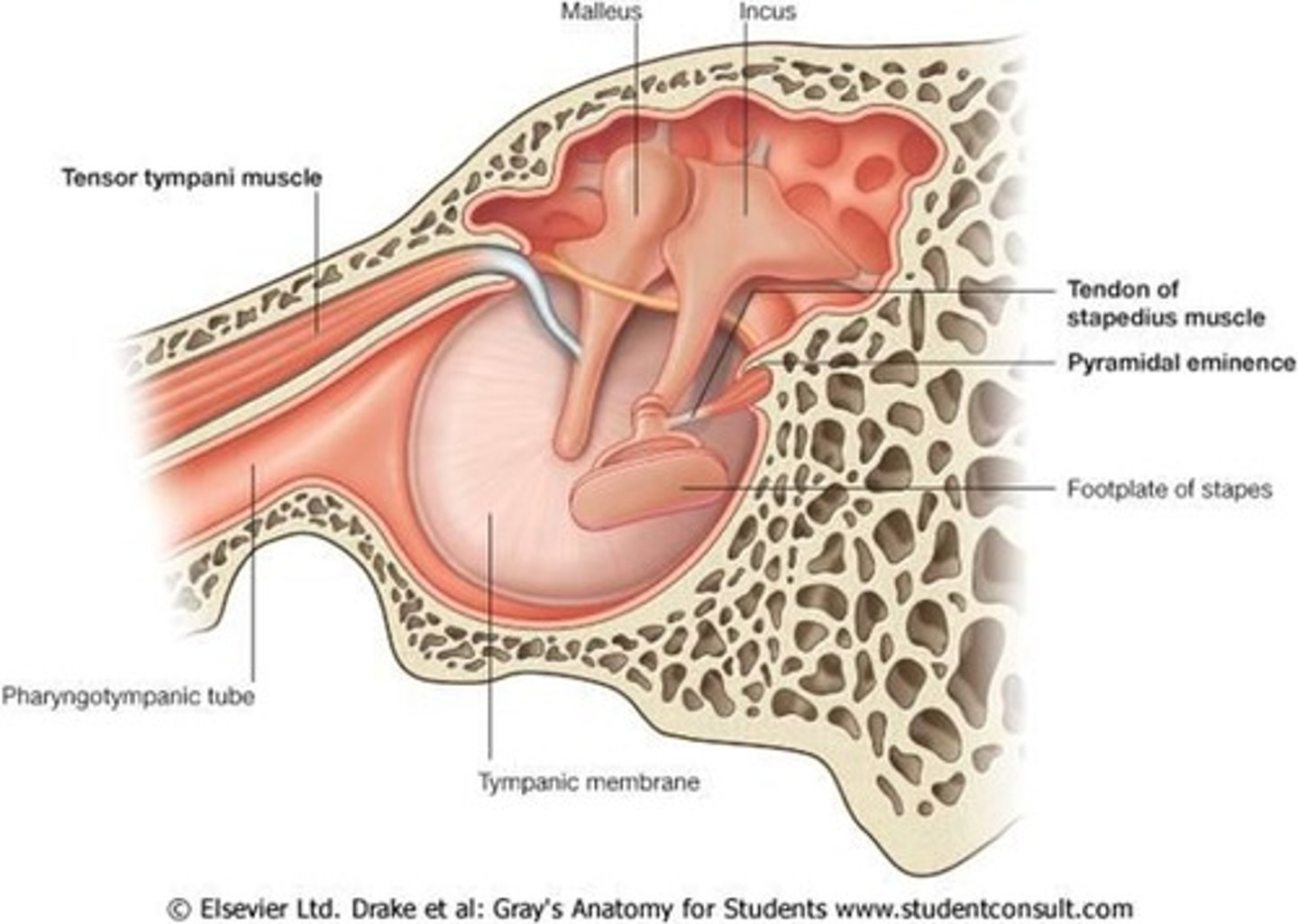
stapedius muscle
contracts reflexively in response to loud sounds to dampen sound vibrations and protect the inner ear.
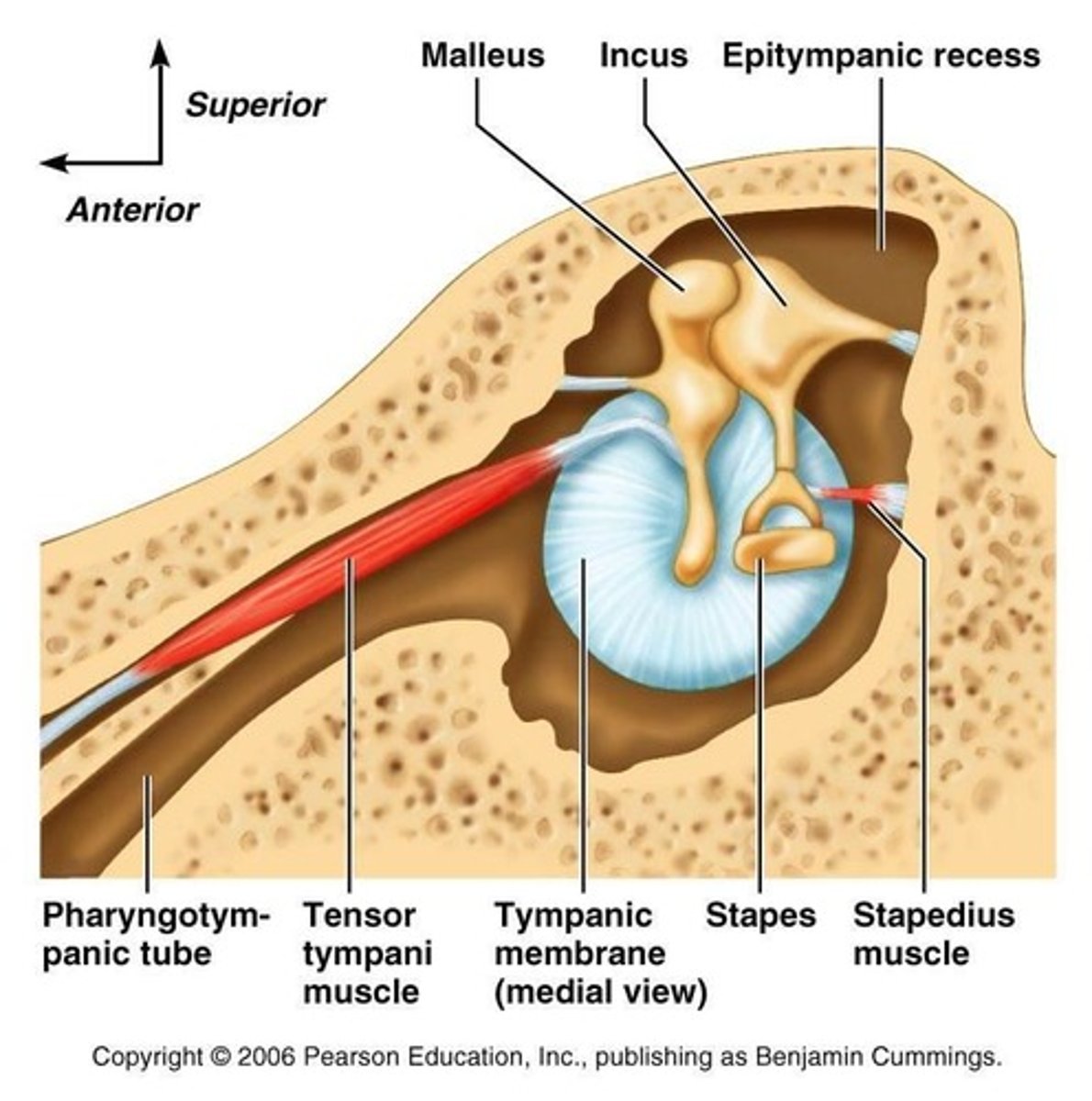
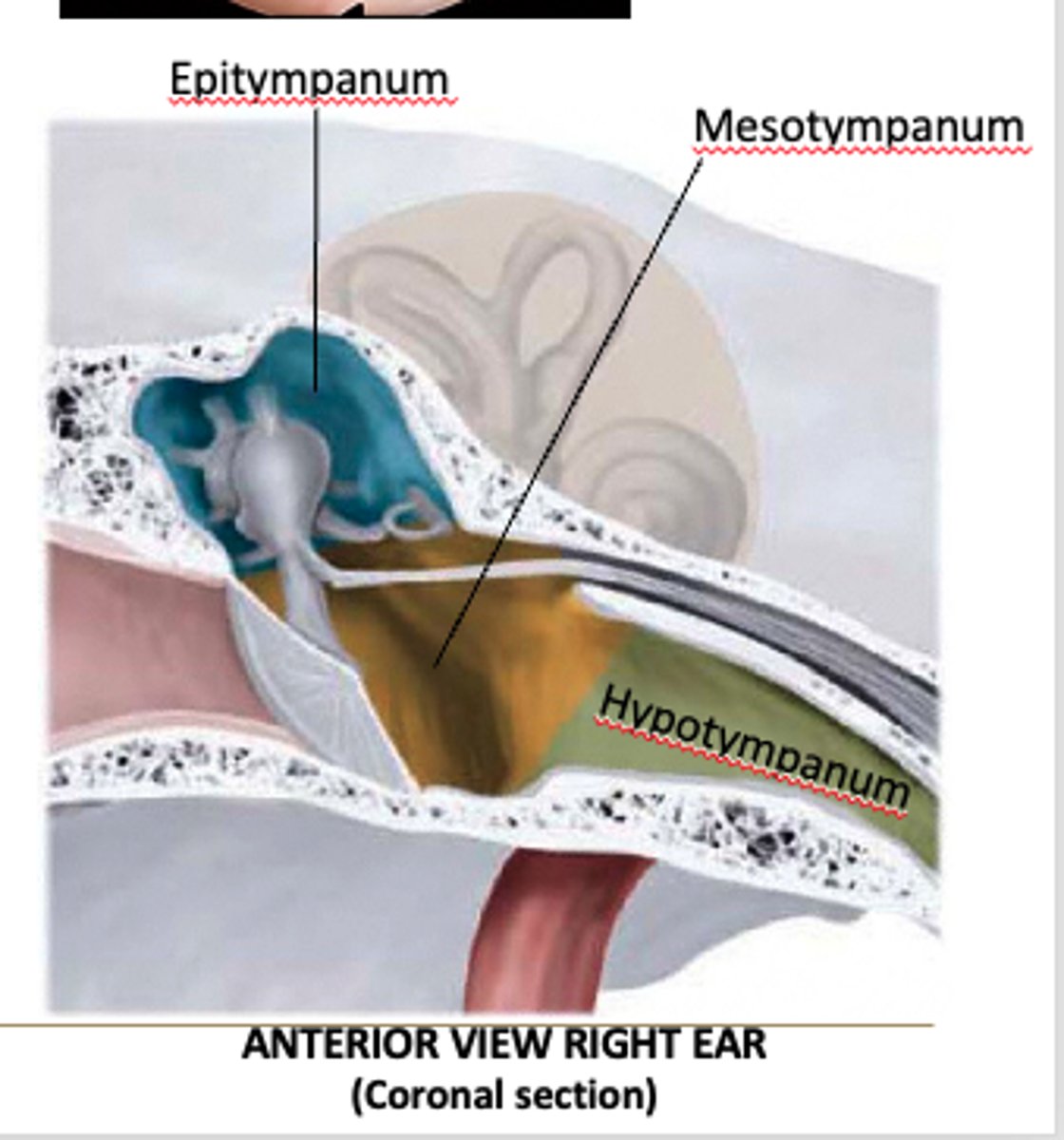
attic recess/epitympanum
superior area of the middle ear, above the tympanic membrane, containing the head of the malleus and part of the incus
cochlear promontory
bony projection on the inner wall of the middle ear cavity, formed by the first turn of the cochlea. between oval window & round window
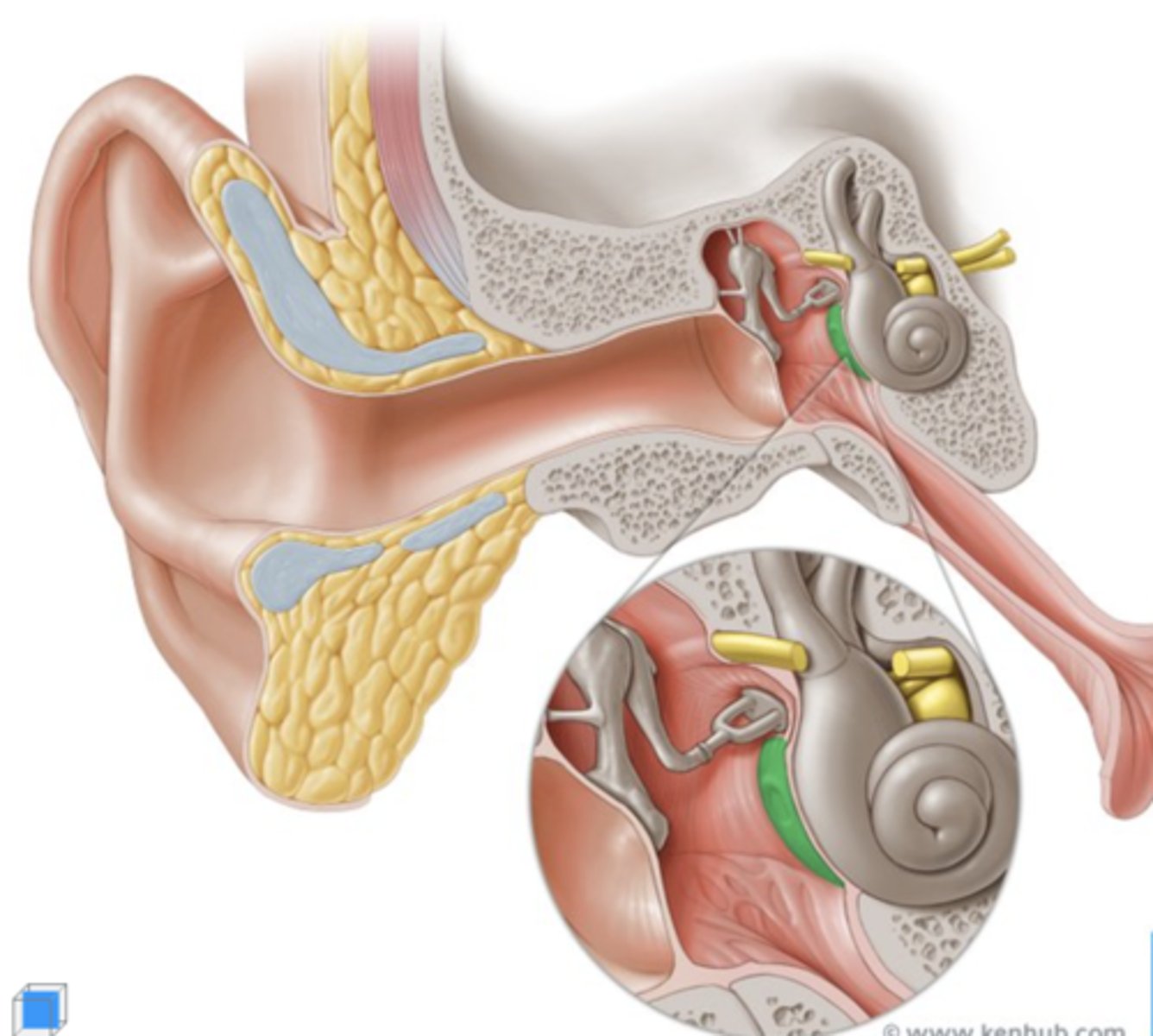
Pharyngotympanic (Eustachian/auditory/PT) tube
a bony and cartilaginous passage that connects the middle ear to the nasopharynx. opens when swallowing
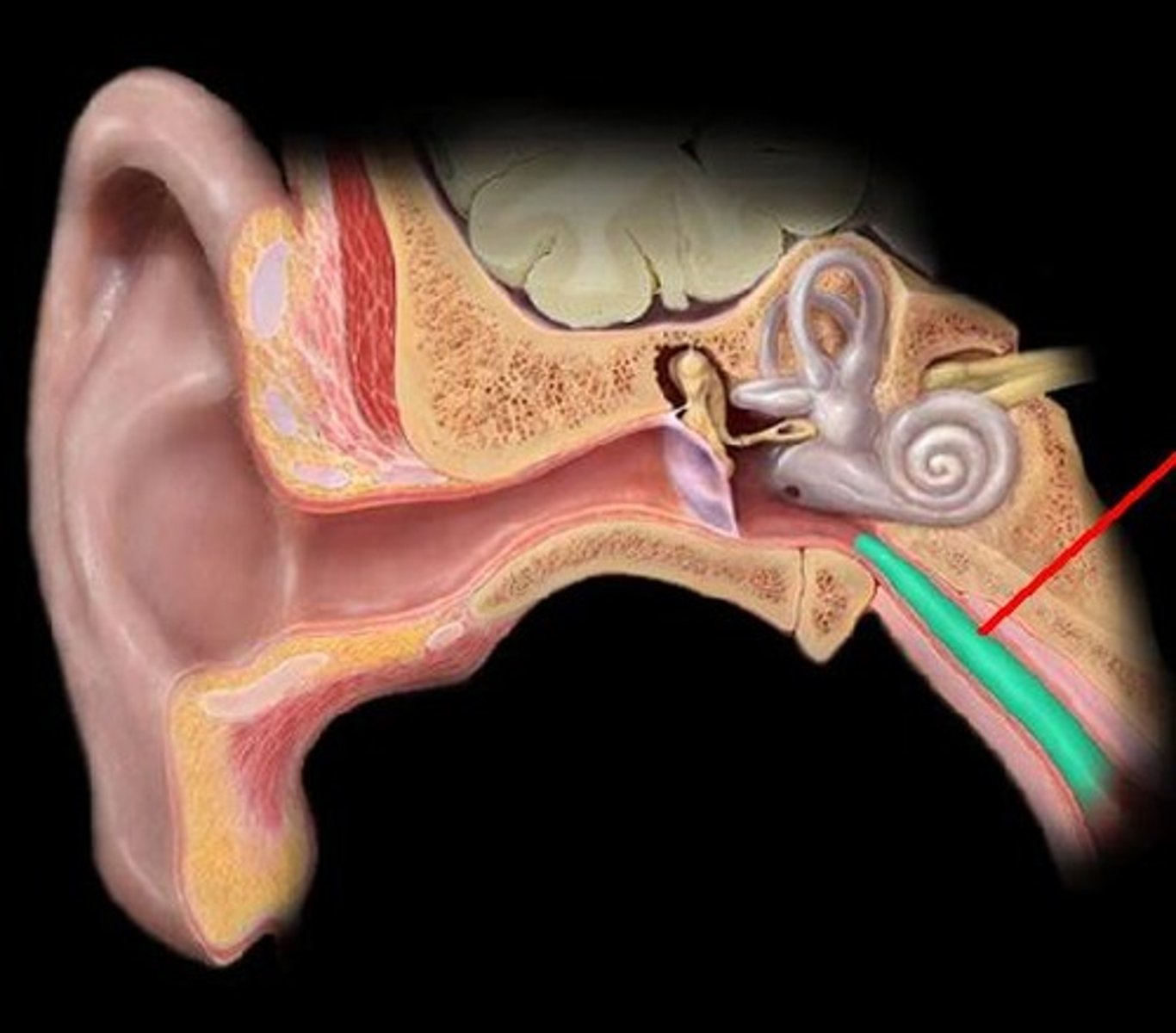
oval window
membrane-covered opening connecting the middle ear to the cochlea of the inner ear. transmits vibrations from stapes to cochlea
round window
A membrane-covered opening separating cochlea from the middle ear. acts as a pressure release valve for energy entering the cochlea via oval window
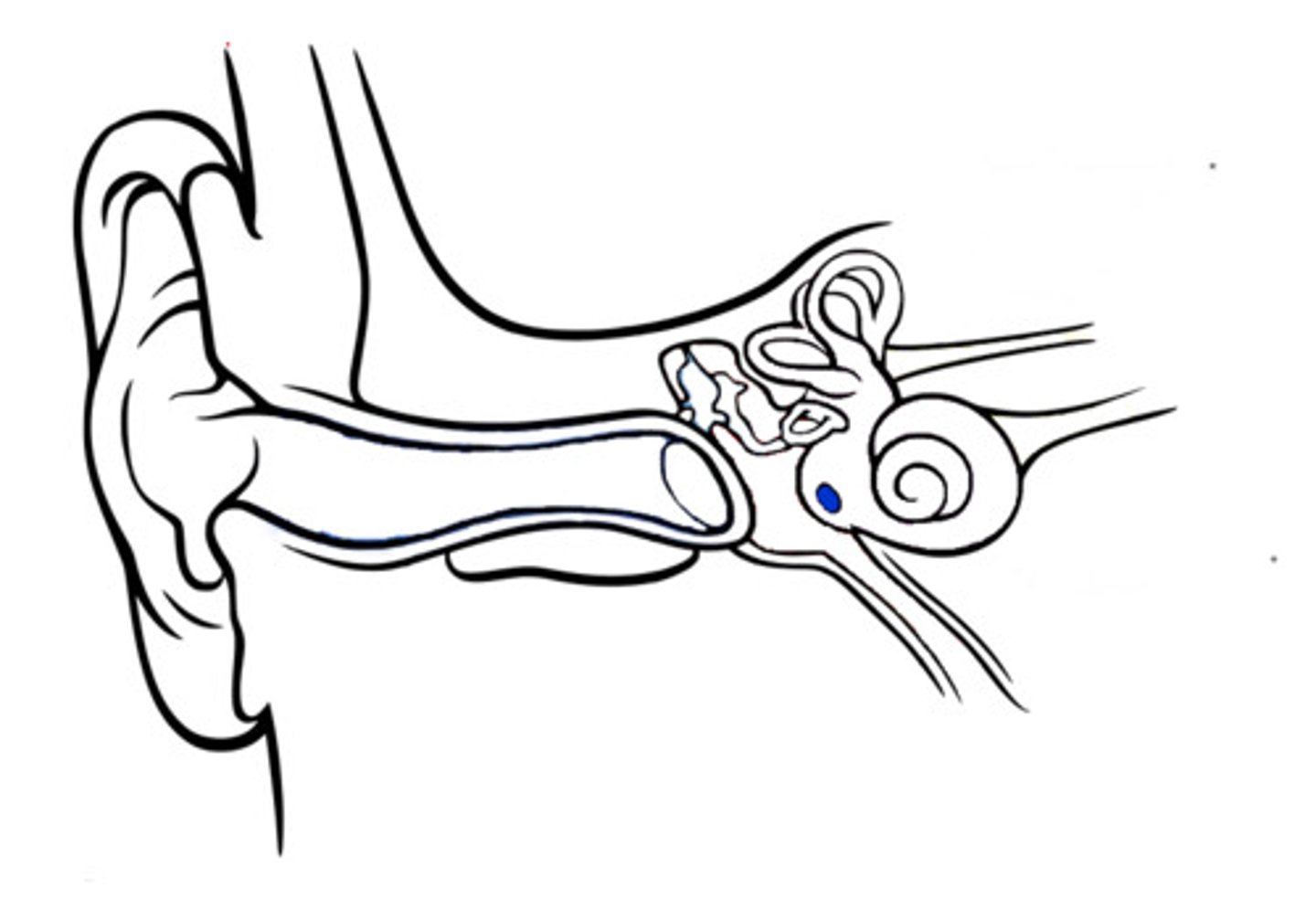
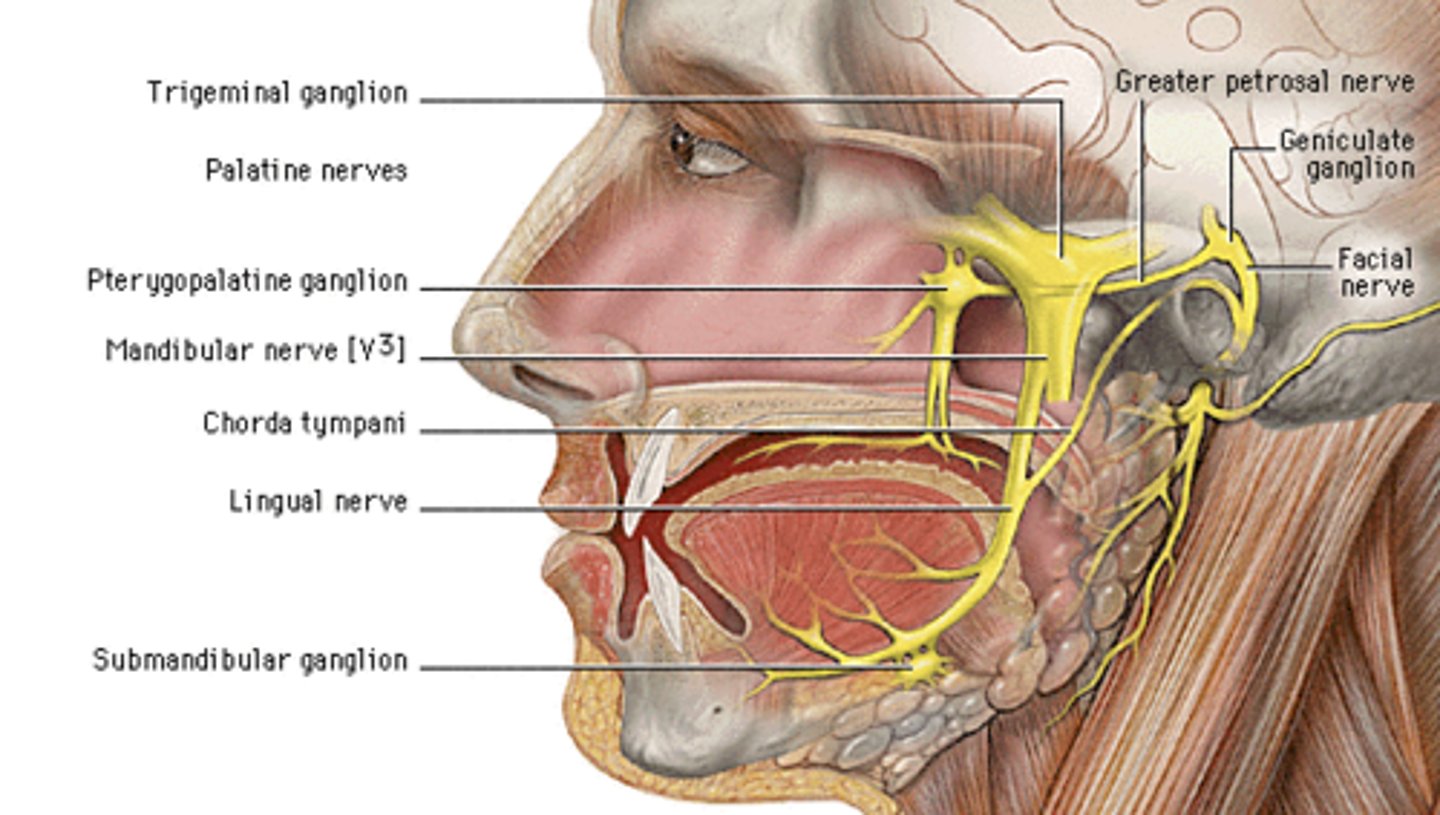
chorda tympani
a nerve branch of the facial nerve that travels through the middle ear