Histology Set (Epithelium, Connective Tissue, Membrane Slides BC D3)
1/105
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
106 Terms
What 4 basic tissues make up all the organs of the body?
Epithelial
Connective
Muscular
Nervous
What is an epithelium?
Sheet of closely apposed cells that separates a lumen from underlying tissue
If you compared epithelial and lumen to a watering hose which structure would correspond with the part of the hose that you hold?
Epithelium (surrounds the inside of the hose that actually is hollow and carries water)
If you compared epithelial and lumen to a watering hose which structure would correspond with the inside of the hose where water flows?
Lumen (free space of hose where water flows)
What is the name of the epithelium that is the covering of the skin?
Epidermis
What is the epidermis?
Epithelial layer of skin that covers the body
What is the name of the epithelium that lines blood vessels?
Endothelium
What are the 5 common features of all epithelia?
Close apposition of cells
Free surface of epithelial cells is adjacent to the space that is limited
Basal surface is adjacent to connective tissue
Absence of blood vessels inside epithelial layer
Sheets of epithelial cells may be modified into tubes forming glands
What is the name for the side of an epithelial layer that borders the lumen?
Apical side
What is the name for the side of an epithelial layer that borders the connective tissue?
Basal side
What are the 7 functions of epithelia?
Protection against abrasion and desiccation
Lubrication
Secretion
Absorption
Sensory reception
Gas transfer
Ion transport
What/where is an example of epithelial executing protection?
Epidermis
What/where is an example of epithelial executing Lubrication?
Mesothelia
What/where is an example of epithelial executing secretion?
Glands
What/where is an example of epithelial executing Absorption?
Intestine
What/where is an example of epithelial executing Sensory reception?
Ear, epidermis, etc.
What/where is an example of epithelial executing Gas transfer?
Lungs
What/where is an example of epithelial executing Ion transport?
Kidney
What are the two ways to classify epithelia?
Number of cells
Shape of superficial cells
How are simple epithelial cells described?
Only one layer of cells
How are stratified epithelial cells described?
Two or more cell layers
For stratified epithelial cells how many and layer(s) contact connective tissue?
Only cells at the basal surface contact connective tissue, so 1 layer
How are pseudostratified epithelia described?
Epithelial cells that have their nuclei arranged at different levels in the epithelium that gives off a stratified appearance
In terms of connection to the connective tissue, how do stratified and pseudostratified epithelia differ?
All the cells of pseudostratified epithelia contact the basal lamina, while for stratified epithelia only cells at the basal contact connective tissue
How are squamous epithelium cells described?
Flattened in the plane of the epithelium
How are cuboidal epithelial cells described?
Cells have heights approximately equal to width
How are columnar epithelial cells described?
Cells are “taller” than they are wide
How are transitional epithelia described?
Epithelia that are capable of changing shape
Where would you find examples of simple squamous epithelia?
Endothelium and mesothelioma
Where would you find examples of Simple cuboidal epithelia?
Glands and ducts
Where would you find examples of Simple columnar epithelia?
GI tract and collecting ducts
Where would you find examples of Pseudostratified columnar epithelia?
Respiratory epithelium
Where would you find examples of Transitional epithelia?
Urinary tract
What does a goblet cell do?
Secretes mucus
Where would you typically find goblet cells in the body and surrounded by what kind of epithelia?
Found in regions of the GI tract and respiratory tracts; surrounded by simple columnar epithelium
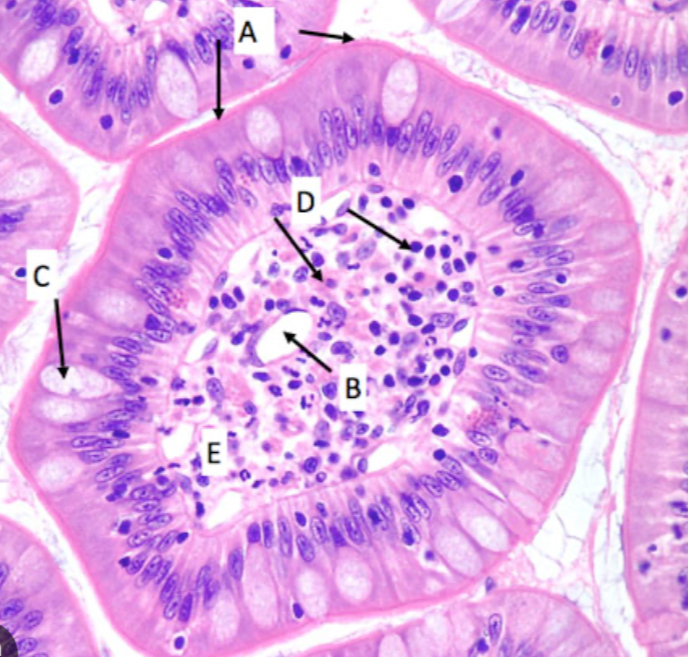
In this sample of the GI tract, what does letter “C” point to?
Goblet cells
Although epithelial cells are typically packed tightly together, what characteristic of the binding allows for absorption and secretion to still occur?
Tight junctions are formed near the apical surface while the lateral surfaces between epithelial cells have some free intercellular space that allows for secretion and absorption to occur
What is the difference between secretion and absorption?
Secretion is the releasing of products from the connective tissue through the epithelial cells then into the lumen, while absorption works the opposite way where products move from the lumen through the epithelial cells then into the connective tissue
Why can’t microvilli be seen under a light microscope?
Their diameter is too small, so they appear to form uniform borders
What two terms are typically used to describe the boarders made by microvilli when observed under a light microscope?
Brush-like
Striated
How are cilia described?
Longer than microvilli and have a greater diameter that allows them to be seen with a light microscope
How are stereocilia described?
Long microvilli r-like structures that are found in the epididymis of the male reproductive tract and some special sensory epithelia like the inner ear
What are the 4 free surface (apical) specializations we discussed?
Microvilli
Cilia
Stereocilia
Keratin
How is keratin described?
Specialization of stratified squamous epithelia that are subject to abrasion or desiccation
What two ways are stratified squamous epithelia usually described?
Keratinized
Non-keratinized
Where are two examples of keratin epithelium?
Epithelium covering the skin
Epidermis
How are glandular epithelia described?
Glands formed by epithelial cells that secrete a fluid of different composition than blood or intercellular fluid
What are examples substances that are secreted by glandular epithelia?
Ions, secretory polypeptides/proteins, lipids, or glycoproteins
What is the difference between endocrine glands and exocrine glands?
Endocrine glands do not have a connection (ductless) to the surface from which they originated and therefore they secrete their hormones directly into the blood stream; exocrine glands retain their connection (ductless) to the surface and their secretions are transported to the surface via epithelial cells then into-lined ducts
What are the 3 glandular epithelia modes of secretion?
Merocrine
Apocrine
Holocene
How are merocrine secretions described?
Secretory granules leave by exocytosis with no loss of cytoplasm or part of cell itself
How are apocrine secretions described?
Secretory product and a portion of the apical cytoplasm of the gland cells are secreted
How are holocrine secretions described?
Whole cell is secreted into lumen of gland
Name the three types of glandular epithelia and an example of each
Merocrine//secretion of sweat
Apocrine//mammary glands during milk production
Holocrine//hair follicles
What are the two type of exocrine gland cells?
Serous cells
Mucus-secreting cells
How are serous cells described?
Often triangular shaped cells that have rounded nuclei towards the base of them; when stained and viewed the central portion is less stained due to the lack of ribosomes and nuclei acids
How are mucus-secreting cells typically described?
Cells are often columnarly shaped; when stained and viewed nuclei usually flattened at the base of the cell while the majority of the cell is pale due to the mucin content
What are some of the functions attributed to connective tissues?
they’re supportive in nature
Provide support for overlying epithelia of organs and provide tensile strength to areas of the body that experience mechanical stress
Act as packing materials filling spaces and encapsulating other tissues
What are the three basic ingredients of all connective tissues?
Cells
Fibers
Ground substance
What re the 2 functions of the intercellular maxtrix?
Storage site for water, ions, and inorganic material
Transport of these substances from circulatory system to various tissues in the body
How do the different types of connective tissues differ from each other?
differ in cell types
Amount and types of fibers
Amount and type of ground substance
How are fibroblasts described?
Cells that produce fibers and intercellular material in ordinary connective tissue
What kind of structure do fibroblasts show when stained?
Large oval-shaped nucleus with a hard to discern cytoplasm
What other cell types may be found wandering in loose connective tissue?
eosinophils
Neutrophils
Lymphocytes
What are the 3 different types of fibers discussed?
Collagen
Elastic fibers
Reticular fibers
Going from smallest unit to largest unit, what makes a up a collagen bundle?
Collagen Fibril—>Group of Fibrils = Collagen Fiber—>Group of Fibers = Collagen Bundle
What is probably the most common protein in the body and what produces it?
Collagen most abundant and is made by fibroblasts
What two unusual amino acids are integrated in the composition of elastic fibers that give them their rubber like qualities?
Desmosine and isodesmosine
How do reticular fibers differ from collagen fibers?
They lack periodicity and are smaller in diameter
How is the storm as of reticular fibers described?
Flexible network of support in areas that are subject to changes in form or volume
What kind of cells are reticular fibers that give most commonly associated with?
Lymphatic cell and the immune system
How is ground substance described?
Product of fibroblasts that fills in the spaces between fibers and cells
What is the ground substance important for in terms of intercellular spaces?
Retention of water and ions
What determines the diffusion rate through loose connective tissue?
D the state of the large molecules comprising the ground substance
What are the 9 different classifications of connective tissue discussed?
Mesenchymal
Mucoid
Loose (areolar)
Dense irregular
Dense regular
Reticular
Elastic
Adipose tissue
Hard
How is Mesenchymal connective tissue described?
Connective tissue derived from mesoderm in early embryo that fills the space between other structures
How do the Mesenchymal cells of the Mesenchymal connective tissue change in the embryo as it moves forward in development?
The Mesenchymal cells will migrate and differentiate into different cell types depending on their final destination
How is mucoid connective tissues differ described?
Connective tissue found in the umbilical cord that acts as a packing material around the two umbilical arteries and one umbilical vein
What is Wharton’s jelly?
Intercellular gelatinous matrix associated with mucoid connective tissue
What is the intercellular gelatinous matrix associated with the mucoid connective tissue called?
Wharton’s jelly
What is another name for loose connective tissue?
Areolar connective tissue
How is areolar connective tissue described?
Flexible but non-resistant to mechanical stress
Where is areolar connective tissue commonly found?
Underlying the epithelium of the trachea, esophagus, and GI tract
How is dense irregular connective tissue described?
Connective tissue fibers that are r arranged in an irregular fashion where an increase in the amount and arrangement of the fibers gives the tissue more strength to withstand mechanical stress
Where is dense irregular connective tissue commonly found?
Found in dermis of skin and deep fascia surrounding tendons and nerves
How is dense regular connective tissue described?
Fibers are arranged in an irregular very regular and parallel fashion that can handle a great deal of mechanical stress
Where is dense regular connective tissue commonly found?
Tendons (attachments from muscles to bones) and ligaments ( attachments of bone to bone)
How is reticular connective tissue described?
Similar to fibroblasts connective tissue but has a more delicate nature while providing structural support
Where are reticular connective tissues found?
Supporting lymph nodes, spleen ,liver, and many glands
How is hard connective tissue described?
Consisting of bone and types of cartilage
How is adipose connective tissue described?
Serves as a great means of packing to soften mechanical stress and acts as storage site for fat
How is elastic connective tissue described?
Being found in areas of the body where the mechanical stresses require pliability and resiliency
Where is elastic connective tissue commonly found?
Walls of arteries and vocal cords
What are the three types of surface lining membranes?
Mucous
Serous
Cutaneous
How are mucous membranes described?
Membranes that’s line the internal surfaces of visceral (hollow) organs that are kept moist by secretions or other bodily fluids
What are the two layers of mucous membranes referred as?
Top layer = epithelium
Lower layer = laminate propia
Which membrane is the laminate propia associated with?
Mucous membranes
How are the mucous membranes associated with the exterior of the body?
All the organs and associated organ systems lined by a mucous membrane are continuous with the external body; digestive (lips and anus), respiratory (nostrils and lips), urogenital (genital area)
How are the serous membranes described?
Smooth membranes consisting of a thin layer of epithelial cells which secrete serous fluid, overlying a loose connective tissue layer
What is the serous membrane’s associate with the ventral organs?
Serous membrane lines and encloses the ventral body cavities secreting a lubricating fluid to reduce friction from muscle movement