Intro to Biology 101 - Chapter 3
1/57
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Intro to Biology 101- Freshman year fall
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
58 Terms
What is Cell Theory?
All organism are made up of cells and cells comes from preexisting cells
What is a Cell
Fundamental unit of life
Whats are the characteristics of a Prokaryotic Cell?
It’s Bacteria
It’s Small and Simple
No nucleus
No Organelles surrounded by membrane
Has a cell membrane
What are the characteristics of a Eukaryotic Cell?
It’s All other organisms
More complex and larger
Has and Nucleus and Chromosomes are inside
Have organelles surrounded by membrane
Has cell membrane
What’s the differences of Eukaryotic Cells and Prokaryotic Cells?
Prokaryotic Cells are BACTERIA
Eukaryotic Cells are all other organisms
What surrounds the Cell?
Cell (Plasma) Membrane
What are the characteristics of the Cell membrane?
Spontaneously forming bilayers of Phospholipids
Fluid due to the movements of Phospholipids
Mosaic of lipids, proteins, and cholesterol found in/ on the membrane
Why do Membranes contain Cholesterol?
Helps maintains membrane fluidity amidst temperature changes
What kind of Proteins does the Cell Membrane Contain?
Integral and Peripheral Proteins
Where can you find Integral Proteins?
In the structures in the internal region of the cell membrane (inside)
Both Hydrophobic and Hydrophilic
Where can you find Peripheral Proteins?
attracted to structures on the surface of the cell membrane (outside)
only Hydrophilic
What are the different functions that Proteins do in the Cell membrane?
Transporter, Receptor, Enzyme, and Anchor
What are the Cell Membrane Functions?
Determines the cell shapes and size
Is Selectively Permeable
Maintains Homeostasis
What is Selective Permeable?
Allows for only some things to move into or out of the cell
What is Homeostasis?
A Constant environment
What is Passive Transport?
Does not require energy
Materiales move WITH the concentration gradient from High to Low
What is Active Transport?
Requires energy expenditure
Materials move AGAINST the concentration gradient from Low to High
How does Passive transport work in the Membrane?
Facilitated diffusion via Integral proteins through Channels and Carriers
Helps in Simple Diffusion and Omosis
What is Simple Diffusion?
Passive Movement Across a Permeable Membrane
How does Simple Diffusion work?
Movement of molecules from a high concentration area to a low concentration area
This helps it achieve equilibrium
Energy is not required
What is Osmosis?
Movement of water molecules from an area of high concentration to low concentration
What is Osmosis influenced by?
Osmolarity / Tonicity
What is Osmolarity/Tonicity?
The Solute in a solution
When are you doing for when you are looking at Osmolarity/Tonicity?
You are always comparing 2 solutions to one another
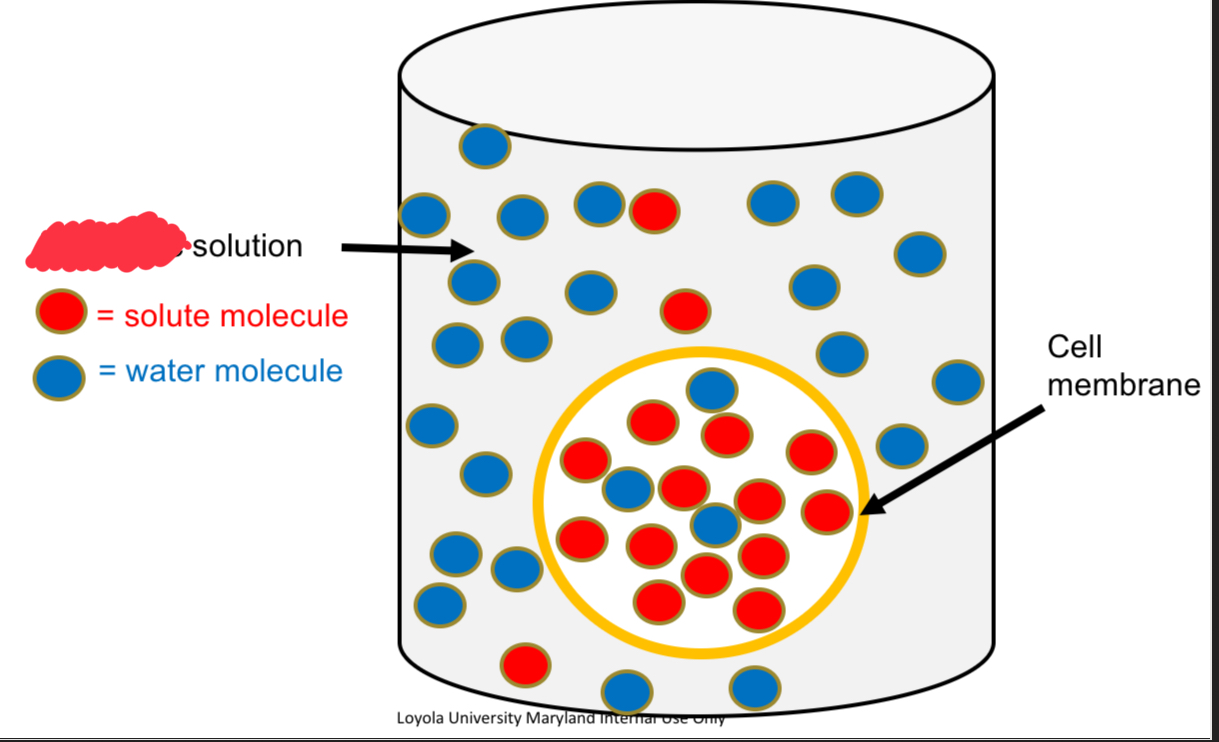
Hypertonic solution
↑ [Solute] and ↓ [Water] vs. other solution
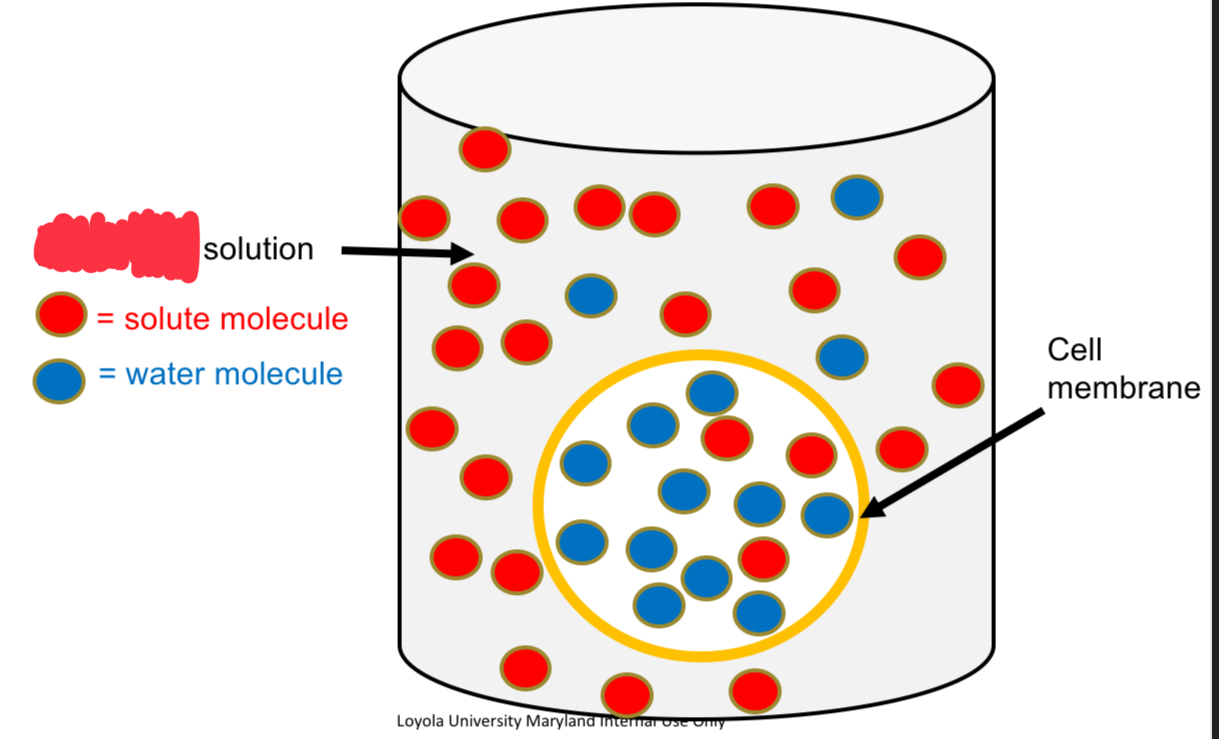
Hypotonic Solution
↓ [Solute] and ↑ [Water] vs. other solution
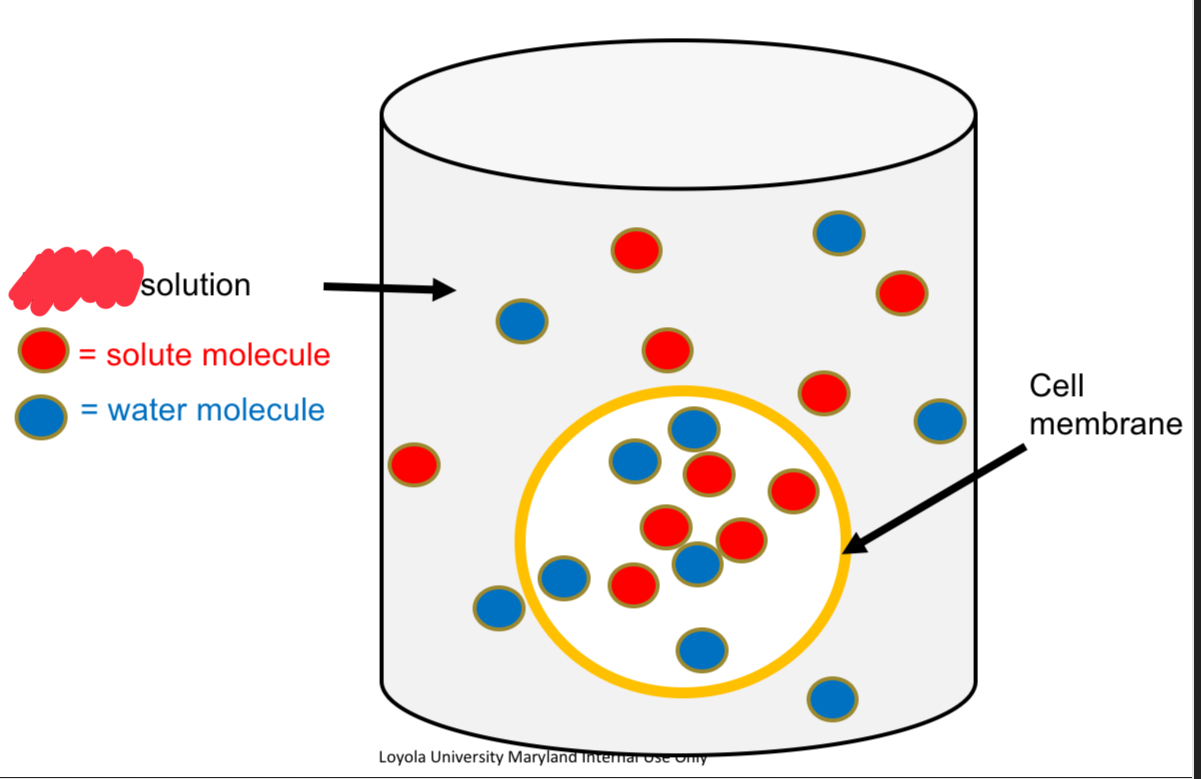
Isotonic Solution
Equal [Solute] and Equal [Water] vs. other solution
Why is Osmosis important to cells?
Affects the shape and size of cells due to the Solute concentration
What Happens to Red blood Cells when they are Isotonic?
They are at their normal shape
What Happens to Red blood Cells when they are Hypotonic?
They are Lysed (has been ruptured —> Low Concentration)
What Happens to Red blood Cells when they are Hypertonic?
They are Shrunken (High Concentration)
What Happens to Plant Cells they are Hypotonic?
They are Turgid
They want this to happen
What Happens to Plant Cells they are Hypertonic?
They are Flaccid
They do NOT want this to happen
What is the energy that Active Transport uses called?
ATP (Adenosine triphosphate)
What is Primary Transport?
A type of active transport that Creates an electrochemical gradient that drives the movement of other molecules
What is Electrochemical Gradient?
A difference in charge and concentration of ions across the membrane
What is an Example of Primary Active Transport
Pumps 3 sodium(NA+) ions OUT of the cell and 2 Potassium(K+) ions IN using ATP
NA+ and K+ are both moving against their Concentration
What is Secondary Transport?
A Type of active transport in which the movement of one substance against its concentration gradient is powered by the energy stored in the Electrochemical Gradient created by the Primary active transport.
Does not directly use ATP
What is an Example of Secondary Transport?
There’s more Na+ outside the cell, and Na+ wants to move back in
Na+ connects with a protein on the outside and using the energy of Na+ moving inward and pulls the protein into the cell at the same time. Even though glucose moves against its own gradient
Think about the protein as “hitches a ride” on the energy from Na+
What is the Endomembrane System?
Consist of the plasma (cell) membrane and internal organelles enclosed by membrane
Found in both plant and animal cells
What is the Endomembrane System Designed for?
To carry information for processing and products to where they are needed
How is the Endomembrane System Connected?
Via Bridges or indirectly by Vesicles that bud off one organelle and fuse to the next
What Processes that occur when vesicles fuse with the cell membrane?
Exocytosis and Endocytosis
What does the Exocytosis do?
Moves materials out of the Cell
What does the Endocytosis do?
Moves materials into the cell
What are the Organelles of the Endomembrane?
Nucleus
Endoplasmic Reticulum
Golgi apparatus
Lysosomes
What is the Nucleus?
Found in both Animal and Plant Cells
Found in the center of the endomembrane system
The Nuclear envelope contains pores that allows molecules to move into and out of the nucleus
Contains the cell’s DNA and produces RNA
What’s next to the Nucleus?
The Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER)
What is the Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum?
Found in both animal and plant cells
The outer membrane (next to the Nucleus)
It’s Rough
It contains ribosomes for producing proteins
What is the Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum?
Found in both animal and plant cells
Is an extension of the rough ER
It’s Smoother
It lacks ribosomes and is important in lipid and steroid synthesis
What are the Golgi Apparatus Functions?
synthesizing the cell’s carbohydrates
sorting proteins and lipids as they move to their final destinations
Modifying proteins and lipids produced in the ER
What is the Golgi Apparatus?
Found in both animal and plant cells
A series of flattened sacs called cisternae.
The edge of the cisternae bud off are vesicles that carry proteins or modified sugars to the cell membrane or organelles in the cell
Enzymes within here can chemically modify proteins and lipids as they pass through in a sequence of steps
Are part of the of the endomembrane system
What are Lysosomes?
Found only in Animal Cells
Are part of the endomembrane system
Small emebrane-bound sacs filled with digestive enzymes
Have a proton pump tjhat keeps its internal pH at a 5 (vs. a Ph of 7 in the rest of the cell)
Digest proteins, old/damged cell parts, defense the cell from bacteria and viruses
What does the mitochondria and chloroplasts have in common?
Both specialize in harness energy for the cell
What does the mitochondria and chloroplasts not have in common?
They grow and multiply independently and contain their own circular genomes
Theory of endosymbiosis
Suggest that mitochondria and chloroplasts were once independent prokaryotic that were engulfed by another cell
What is the Mitochondria?
Harnes energy from organic molecules such as sugars and coverts them to ATP in all Eukaryotic cells
What is the Chloroplast?
Captures the energy of sunlight to fix atmospheric carbon
Synthesize simple sugars in plant cells and photosynthetic organisms