Lecture 9: Touch and Sensory
1/50
Earn XP
Description and Tags
imma touch you
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
51 Terms
What results in perception?
The cerebral cortex analyzes the sensory information
Tactile sensation includes
Touch
Vibration
Pressure
Proprioception
Pain and Temperature sensation includes
Pain
Itch
Warm and Cool
What is the “3-neuron pathway”?
The pathway of perception
Reflexes are…
Immediate responses to stimuli
Axons conduct
Action potentials
Cell body (nuclei) synapses
Integrate activity
Cell Body and Axon of path 1
Dorsal Root ganglion, Spinal cord
Cell body and Axon for pathway 2
Spinal cord/brainstem, decussates on CNS
Cell body and axon of pathway 3
Thalamus, Internal capsule Corona Radiata synapses
Nerve endings of neuron #1 are modified to what ?
Transduce sensory stimuli
Different types of receptors respond to…
Different types of tactile stimuli
Meissner’s corpuscle responds to
Touch, low frequency vibration
Merkel Disk responds to
Touch
Pacinian corpuscle responds to
High frequency vibration
Ruffini ending responds to
Pressure
Hair folicle responds to
Bending
Muscle spindles golgi tendon organs responds
Proprioception
Receptors vary in
Shape
Position in skin/body
Density many more on fingers and face
Physiological properties
Muscles spindles respond to…
Muscle stretch
Nerve endings contain
mechanosensitive ion channels
Membrane is deformed
The axon is depolarized and action potentials are conducted along a pathway
Axons conducting tactile information are ____ and ____ fibers
Large, myelinated
Axons conducting pain/temperature information are small ______ or small ________ fibers
myelinated, unmyelinated
A tactile stimulus at my finger would travel to my spinal cord in about _____
8msec
A pain stimulus at my finger would travel to my spinal cord in about _____
1sec
Dermatomes
The spinal nerve from each spinal cord segment supplies a specific region of body surface
Body dermatomes are key to identifying what?
Sensory deficits
Lower body dermatomes are below __ and axons enter through _
T6, Fasciculus gracilis
Upper body dermatomes are at/above __ and enter what?
T6, enters fascilcus cuneatus
Fasciculus gracilis and fasciculus cuneatus travel the length of what? On which side?
The spinal cord and dorsal (posterior) surface
Sensory info enters the spinal cord, it is used for
Reflexes
What is the basis of stretch reflexes?
Spinal cord
Axons make local connections in what? And then onto what?
Spinal cord, onto the motoneurons before continuing to cortex
Tactile Sensory Pathway FIRST HALF
Dorsal root ganglion → Dorsal root → Fasciculus Gracilis → Nucleus Gracilis → THE CHECKPOINT
Tactile Sensory Pathway (second half?)
Medial Lemniscus → VPL → Internal Capsule → Corona Radiata → Postcentral Gyrus
Nucleus Gracilis and Cuneatus are in the ____ ____ on the what surface?
Caudal medulla the dorsal surface
What are the two bumps on the caudal medulla?
The nucleus gracilis and cuneatus ON THE DORSAL SURFACE
The axon of neuron 3 travels through the _________ and then to _______ to reach the ______
Internal capsule, corona radiata, Postcentral gyrus
The internal capsule is between these 3 structures
Thalamus, caudate nucleus, and lentiform nucleus
What is the corona radiata?
The radiating crown
Beyond the internal capsule, axons spread out into what?
The corona radiata then to the cortex
Neuron 3 terminates in the _______ and _______
Postcentral Gyrus, Paracentral Lobule
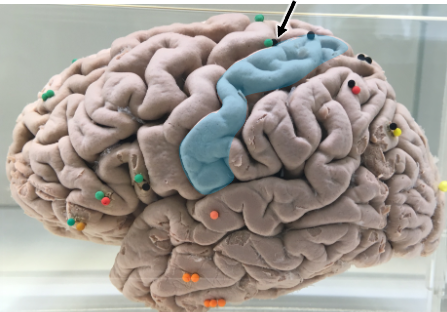
What is the highlighted area?
The postcentral gyrus
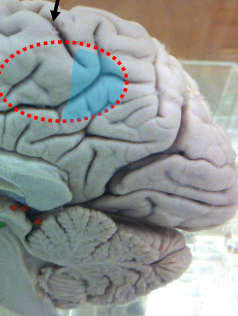
What is this highlighted area?
Paracentral lobule
Cortex, in relation to sensory, is for
Somatotopic orientation
Posterior part of paracentral lobule is responsible for
Sensory information from the leg and foot
Vitamin B12 deficiency and Tabes Dorsalis are examples of…
Disorders involving demylination of axons in the fasciculus gracilis and cuneatus
Tactile Pathway Part 1
Dorsal Root Ganglion → Dorsal Root → Fasciculus Gracilis/Cuneatus
Tactile Pathway Part 2
Nucleus Gracilis/Cuneatus → Medial Lemniscus
Tactile Pathway Part 3
VPL → Internal Capsule → Corona Radiata → Paracentral Gyrus/Paracentral Lobule