Module 5 - Maxillary Incisors
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
18 Terms
Permanent Anterior Teeth Characteristics & Terms
Developmental Depressions
Triangular
Contact Area
CEJ Curvature
Cingulum & Marginal Ridge
Fossa
Grooves & Pits
Single Rooted
Esthetic Concerns
General Features of Permanent Maxillary Incisors (Central & Lateral Incisors #7-10)
Size
Maxillary incisors larger than mandibular incisors
Maxillary central incisor larger than lateral, however, they resemble each other
Wider mesiodistally versus labiolingually
Shape
Labial surfaces are rounded and tapered toward lingual
Incisal edge more toward labial when looking at proximal view
Other Features
Lingual surface features more pronounced compared to mandibular incisors
Roots are short compared to other maxillary teeth
Usually without root concavities
Permanent Maxillary Central Incisors (#8 and #9)
Erupt between 7-8 years
Most prominent tooth in the permanent dentition because of their large size and anterior position
Root Features - Central Incisors
Root completely forms at age 10
Single conical root with blunt apex
Root length about the same length (or shorter) but wider than lateral
Pulp cavity mirrors shape of tooth
3 horns in pulp chamber
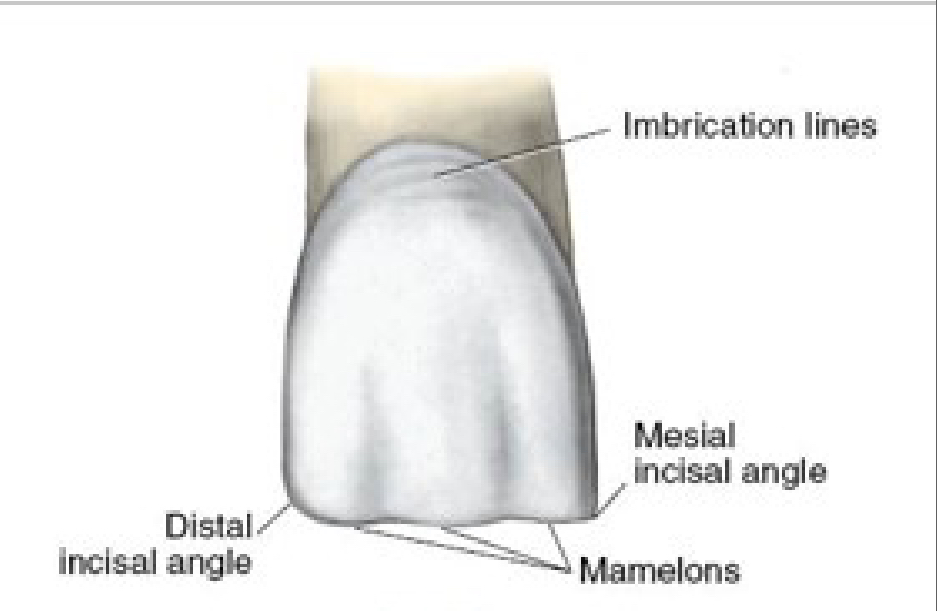
Labial View Features - Central Incisors
Trapezoidal in shape
Developmental depressions
Imbrication lines
Perikymata
Sharper mesio-incisal angle
The distal contact is located farther cervically than the mesial contact
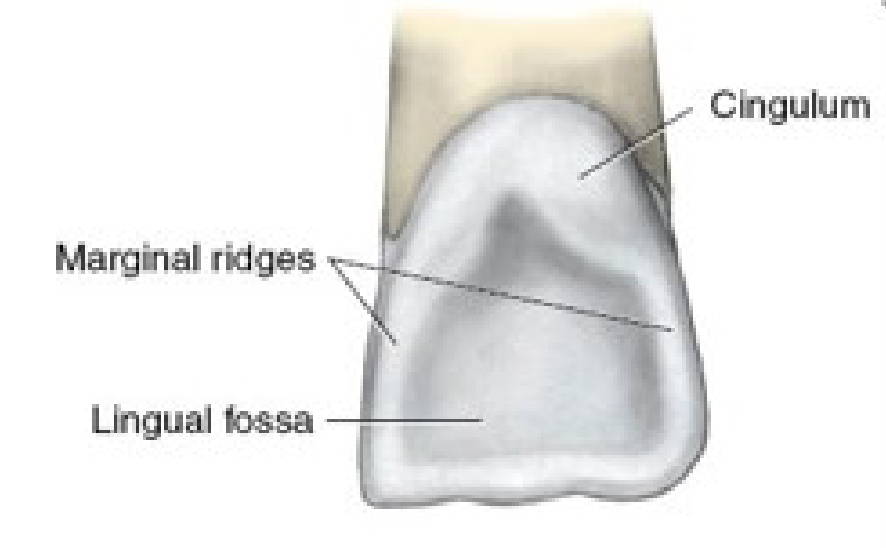
Lingual View Features - Central Incisors
Cingulum
Fossa
Ridges
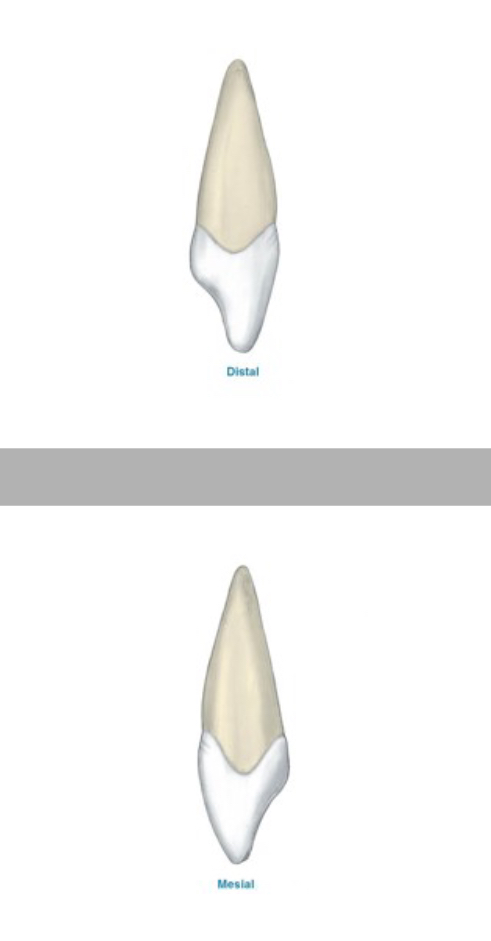
Proximal View Features - Central Incisors
The incisal edge is located slightly labial to the long axis of the tooth
The incisal edge is sloped toward the lingual
Mesial CEJ curvature greater than any other tooth
Height of contour at cervical third
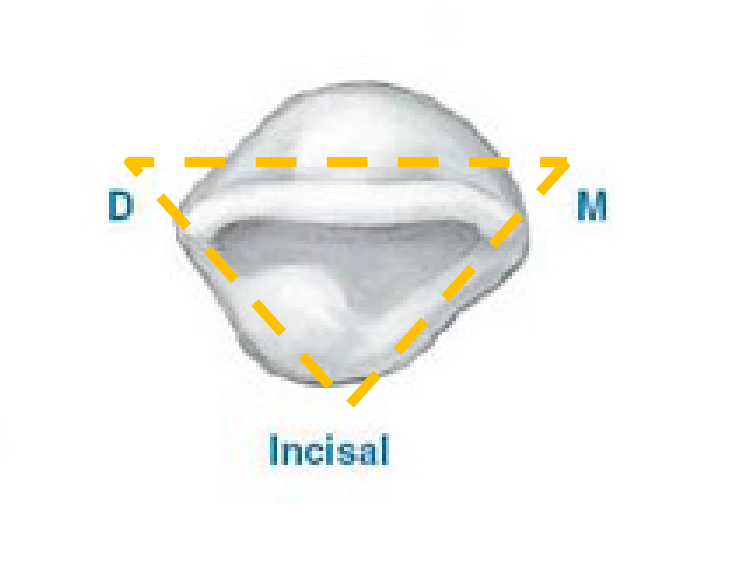
Incisal View Features - Central Incisors
The overall shape of the crown from the incisal view is triangular
Cingulum toward the distal
Mesial marginal ridge appears longer than distal
Incisal edge located toward labial side of tooth
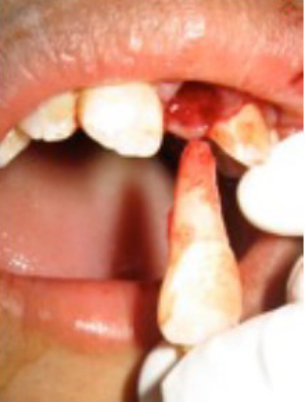
Avulsion
Displacement of tooth from socket
Maxillary central more at risk due to anterior and labial position

Diastema
Space between teeth, open contact
Common between maxillary centrals
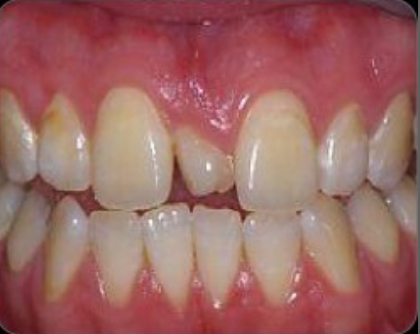
Mesiodens
Extra tooth (supernumerary tooth) between #8,9 forms during tooth development

Permanent Maxillary Lateral Incisors (#7 and #10) Crown Features
Erupt between age 8-9
Very similar to central, just smaller
Greatest degree of variation in form of any permanent tooth (except 3rd molars)
Root Features - Lateral Incisors
Root completion at age 11
Single conical root that may curve slightly to the distal
Apex of the root is more sharp, not rounded like maxillary central incisor
About the same length of root as central (possible longer)
Thinner than central
Linguogingival groove may be present on root
Pulp cavity has single pulp canal and single pulp chamber

Labial View Features - Lateral Incisors
Labial development depressions and imbrication lines are less common than on the maxillary central incisor
Crown is smaller and less symmetrical
Mesial contact is at the incisal third
Distal contact is at the middle third
Mesioincisal angle is sharper than the distoincisal angle
Incisal angles more rounded compared to centrals
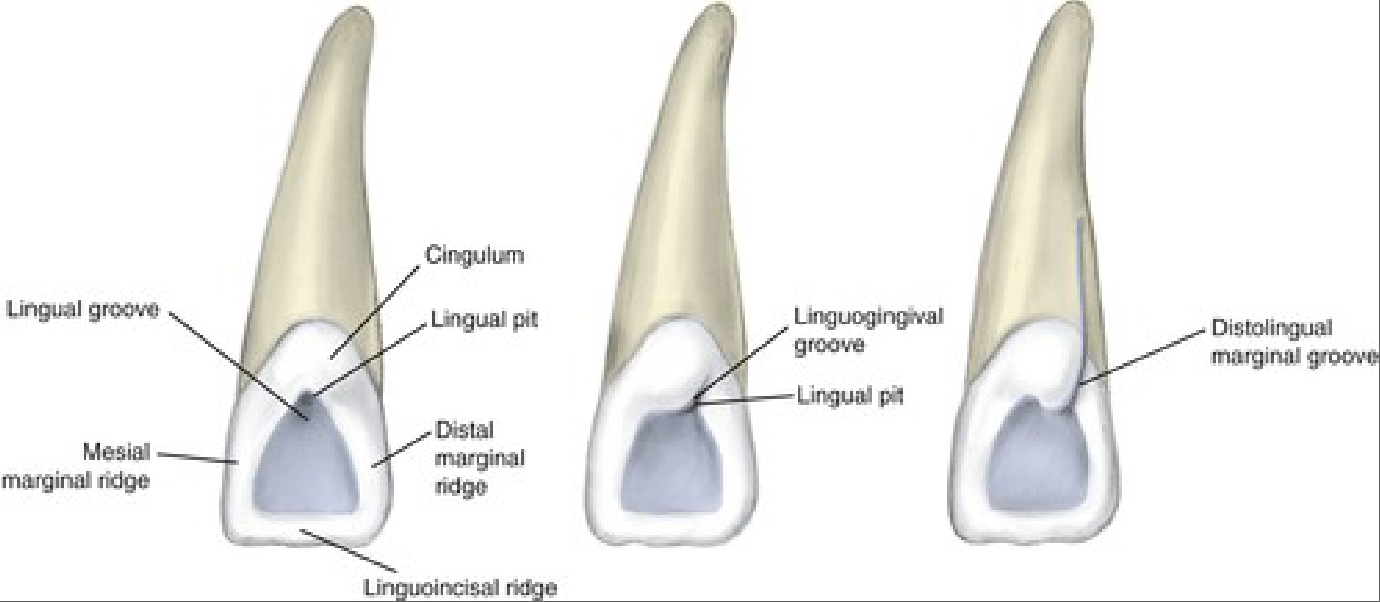
Lingual View Features - Lateral Incisors
More prominent cingulum compared to central incisor
Deeper lingual fossa compared to central
Pronounced marginal ridges
Lingual pit more common on lateral versus central
Linguogingival groove may be present, more common on lateral compared to central
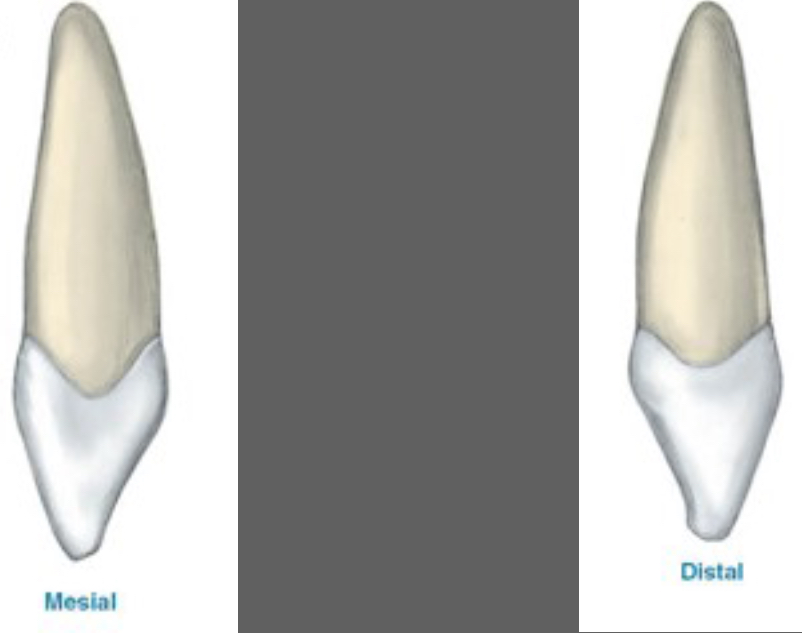
Proximal View Features - Lateral Incisors
Crown triangular
CEJ like central but less curvy
CEJ more curved on mesial versus the distal
Incisal edge usually labial to long axis of the tooth
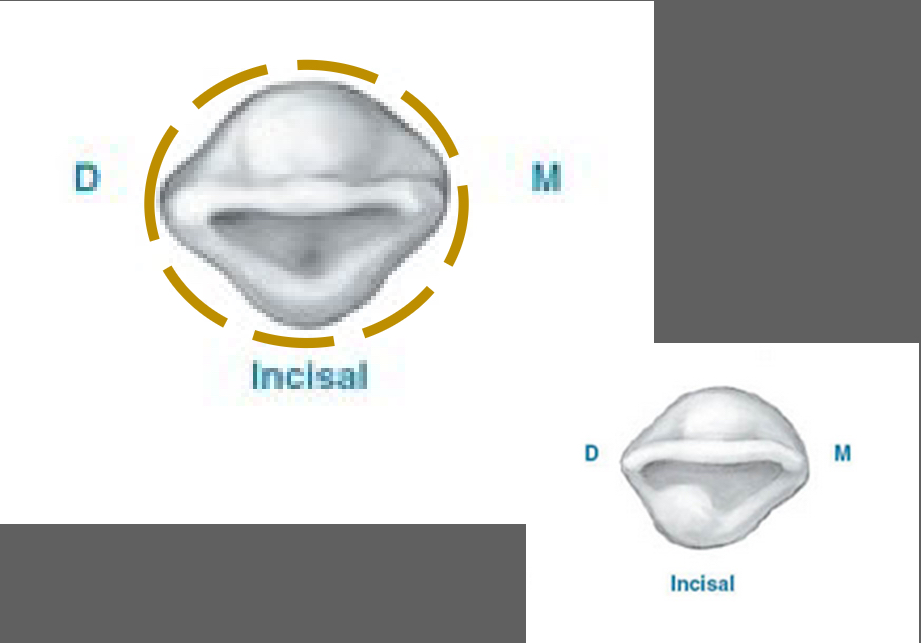
Incisal View Features - Lateral Incisors
Crown from incisal view is round or oval not triangular like the central
Mesiodistal measurement is wider than the labiolingual measurement
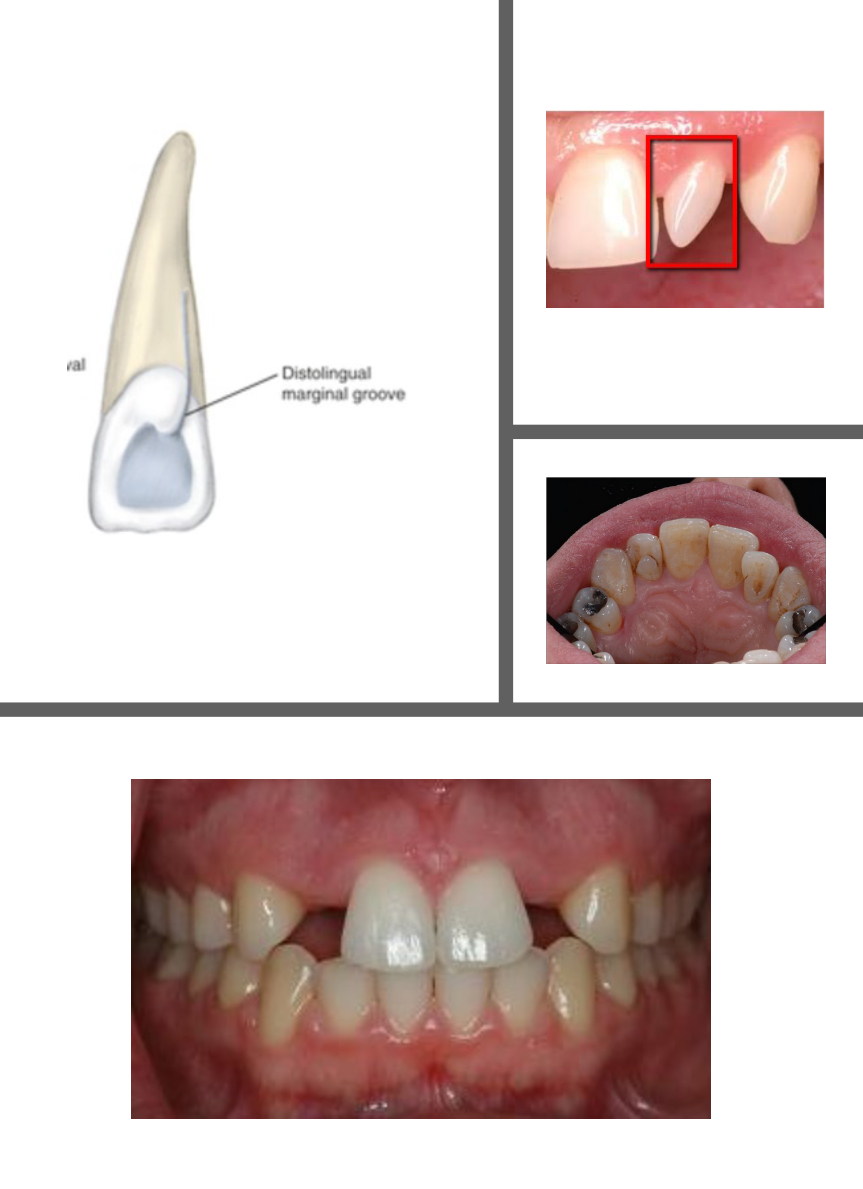
Developmental Disturbances of Maxillary Lateral Incisors
Linguogingival groove
Peg lateral
Partial anodontia
Tubercle/Talon cusp