CH 31-33: alternative diagnostic tests, medical therapies, surgical and endovascular therapies
1/147
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
148 Terms
Alternative diagnostic tests related to venous diseases fall into 2 main categories.
What are they?
Diagnostic tests for possible venous thrombosis or venous reflux
Evaluation for a pulmonary embolism (PE)
Which 2 factors are considered when ruling out a venous thrombosis and/or reflux?
D-dimer
Contrast venography
D-dimer is a…
Lab value
What does ‘PE’ stand for?
Pulmonary embolism
Describe what ‘D-dimer’ is.
Protein fragment that is produced when a blood clot dissolves in the body
Name the lab:
“Protein fragment produced when a blood clot dissolves in the body”
D-dimer
D-dimer is normally __________ in the blood.
Undetectable
When is D-dimer measurable?
When a clot is breaking down
When there is an increase in clot breakdown, what can that result in?
Rise in D-dimer levels in the blood
High levels of D-Dimer can suggest what?
Presence of a thrombus
A high level of which lab can suggest the presence of a thrombus?
D-Dimer
Positive D-Dimer lab results have little (1)__________, but points to the need for (2)_____________________.
Specificity
Additional testing
Because D-Dimer does not specify if there is a (1)______, what can it be an indicator for instead(2)?
Clot
Extra testing
Which 2 factors does D-Dimer lack?
Specificity
Positive Predictive Value (PPV)
What does ‘PPV’ stand for?
Positive predictive value
List the 5 conditions/pathologies/procedures that D-Dimer elevation will be seen in.
Pregnancy
Liver disease
Renal disease
Cancer/Any thrombotic processes
Recent surgery
A positive D-Dimer result is consistent with which 2 pathologies?
Lysis
Breakdown of thrombus
A negative D-Dimer will imply, but not be conclusive, for what pathology?
Absence of a thrombus process
What imaging modality is considered the gold standard in regards to DVTs/Venous Testing?
Ultrasound
Which procedure’s use has decreased due to the accuracy of venous ultrasound exams?
Contrast venography
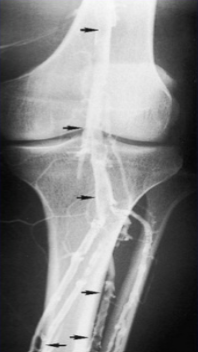
Which imaging modality is seen here?
Contrast venography
Contrast venography is capable of…
Helping in the evaluation of ___________.
Evaluates congenital _________ disease and/or __________.
Assists in the evaluation of ________________ changes.
Can detect and quantify _________________.
Acute DVT
Venous, Anomalies
Chronic venous
Reversed flow
Reversed flow is essentially…
Reflux
List the 2 types of venograms that are performed.
Ascending
Descending
Ascending venograms images veins from _________ to _________.
Distal to Proximal
Descending venograms images veins from _________ to _________.
Proximal to Distal
Which venogram images veins from distal to proximal?
Ascending
Which venogram images veins from proximal to distal?
Descending
An ascending venogram detects which 2 abnormalities?
Venous abnormalities
DVT
A descending venogram assesses which 2 factors?
Valve function
Venous reflux
Which venogram detects venous abnormalities, including a DVT?
Ascending
Which venogram assesses valve function and venous reflux?
Descending
Which venogram requires contrast to be injected into a distal superficial vein and directed into the deep system?
Ascending
An ascending venogram requires contrast to be injected into a (1)_______________________ and directed into the (2)_______________.
Distal superficial vein
Deep system
If contrast is injected into the lower extremity for an ascending venogram, which vein is used?
A vein on the dorsum of the foot
If contrast is injected into the upper extremity for an ascending venogram, which 2 veins can be used?
Basilic vein
Cephalic vein
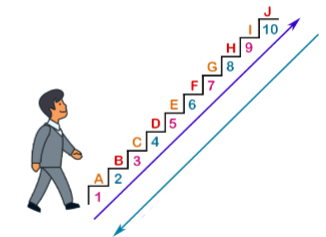
Label which arrow is ascending and descending.
Purple = Ascending
Blue = Descending
Which venogram only evaluates the lower extremity?
Descending
If contrast is injected into the lower extremity for an descending venogram, which vein is it usually injected into?
Common femoral vein (CFV)
Any deviation of normal is evidence of ___________ as seen on ascending venography.
Obstruction
On an ascending venogram, a filling defect can indicate the (1)____________ of contrast material by (2)_________.
Displacement
Thrombus
On descending venography…
What pathology is evidence of reflux?
It is evidence of reflux in what vessels?
Retrograde filling
Common femoral vein (CFV) / Femoral vein (FV)
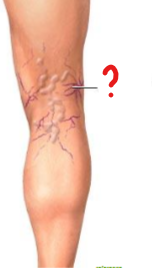
What pathology is seen here?
Varicose veins
Does this vein look normal or abnormal?
If abnormal, what pathology would it be?
Normal
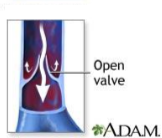
Does this vein look normal or abnormal?
If abnormal, what pathology would it be?
Abnormal
Varicose veins
List the 3 procedures used to evaluate pulmonary embolisms.
Lung ventilation / Perfusion scan / V/Q scan
Pulmonary angiography
Computed tomographic angiography (CTA) of the chest
What does ‘V/Q’ stand for?
Ventilation quotient
Lung ventilation / perfusion scan / V/Q scan is from what imaging modality?
Nuclear medicine
Lung ventilation / perfusion scan / V/Q scan measures for which 2 factors in the lungs?
Air
Blood flow
Lung ventilation / perfusion scan / V/Q scan is a screening test for the detection of _________ defects of the lungs.
Perfusion
Which procedure measures air and blood flow in the lungs?
Lung ventilation / perfusion scan / V/Q scan
Which procedure is a screening test for the detection of perfusion defects in the lungs?
Lung ventilation / perfusion scan / V/Q scan
Pulmonary angiography is from what imaging modality?
Flouroscopy
Pulmonary angiography is used to evaluate the (1)__________ arteries for a (2)____________________.
Pulmonary
Pulmonary embolism
Which procedure is used to evaluate the pulmonary arteries for pulmonary embolism?
Pulmonary angiography
Which procedure is the study of choice to evaluate pulmonary embolisms?
Computed tomographic angiography (CTA)
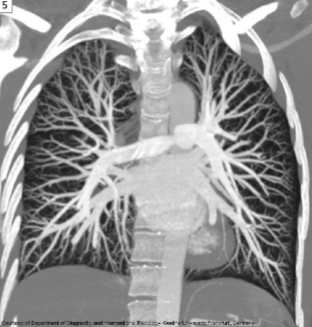
Which imaging modality is used for this image?
This modality can be used to look for what pathology?
Computer tomographic angiography (CTA)
Pulmonary embolism
List the 3 causes of venous thrombosis.
What is the name of all 3 factors combined?
Venous stasis
Trauma
Hypercoagulability
Virchow’s Triad
Which 2 factors decrease the chance of venous stasis?
Limit long periods of inactivity / bed rest
Promote venous drainage when patient is inactive
List 4 techniques that helps promote venous drainage/decreases venous stasis.
Leg elevation
Support stockings
Pneumatic compression devices
Weight management
How can trauma be controlled before becoming a venous thrombosis?
By preventing injury or infection of the extremity
To prevent venous thrombosis, the sonographer should be aware of hypercoagulability ______/______.
States/Factors
Virchow’s triad is associated with which pathology?
Venous thrombosis

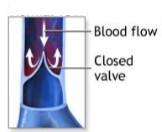
What is seen in this image?
What can this promote?
What can it help prevent?
Support stockings
Promotes venous drainage
Venous stasis (Venous thrombosis)
What treatment is used to decrease the risk of venous thrombosis in a high risk population?
Medications
Anticoagulation therapy can be used for what 3 pathologies?
Disease
Acute DVT
Pulmonary embolism
What kind of medication is Lovenox?
Low molecular weight heparin
What kind of medication is Arixtra?
Low molecular weight heparin
Which 2 medications are used to decrease the risk of venous thrombosis in high risk populations?
Unfractioned heparin
Low molecular weight heparin
List the 2 types of low molecular weight heparin that are commonly in use today.
Lovenox
Arixtra
When using heparin to treat acute DVT and pulmonary embolism, continuous (1)________ until oral (2)____________ is deemed (3)_________, usually in (4)__-__ days.
Infusion
Anticoagulation
Therapeutic
4-5
List the 2 anticoagulation therapies used to treat acute DVT and pulmonary embolisms.
Heparin
Oral anticoagulation (Warfarin/Coumadin)
What is the brand name of Coumadin that is typically administered?
Warfarin
Dosage of Warfarin/Coumadin is regulated to ensure that the patient’s (1)_____________ is (2)____-____ times more normal.
Prothrombin time (PT)
1.5-2
With surgical and endovascular therapies, list the 3 sonographer role and clinical preparations.
Role of the sonographer
Clinical information
Informed consent
The 3 roles of the sonographer for surgical and endovascular therapies…
Assist physician with real time imaging guidance during _________ procedures (e.g., biopsies, vascular access, thrombin injection)
Optimize imaging _______ and transducer _________
Maintain patient _______ and ________
Vascular
Settings, Selection
Safety, Comfort
The 3 points of clinical information that should be taken down for surgical and endovascular therapies are…
Review relevant patient ________ (e.g., coagulability, allergies, prior interventions)
Verify procedure ______ and ___________
Know __________ and variations of ___________
History
Order, Indication
Anatomy, Anatomy
The 3 points of informed consent that should be taken down for surgical and endovascular therapies are…
To ensure _______________ is obtained by providers performing the procedure
Confirm consent is ________, _________, and includes procedure specific risks
Be prepared to answer basic patient ________ or refer to the provider for more detail
Informed
Signed, accurate
Questions
With surgical and endovascular therapies, the safety protocols and sterile techniques to keep in mind are…
Procedural _________
______ technique
Time out
Sterile
What is performed immediately before a procedure begins?
Procedural time out
A procedural time out will include which 3 things?
Correct patient identity
Correct procedure
Correct site and side
A procedural timeout must be (1)___________ and (2)________ confirmed by the team.
Documented
Verbally
List the 5 tips to keep in mind for sterile techniques? (Including PPE)
Sterile gloves
Sterile gel and probe cover if contacting sterile field
Disinfect skin
Maintain sterile field throughout procedure
Avoid crossing over sterile field or contaminating instruments
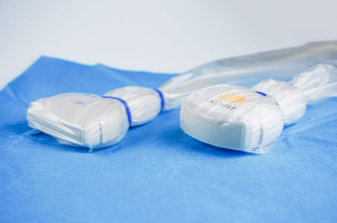
Why does the probe appear this way?
What materials are on it?
To maintain sterile field
Probe cover and sterile gel
With surgical and endovascular therapies, list the 2 documentation and post procedure care documentations.
Pre-procedure documentation
Post-procedure documentation
With pre-procedure documentations, the sonographer should confirm and document…
Patient _______ and ________
Pre-procedure _________ findings
___________ (if applicable)
Identity and consent
Imaging
Site marking
With post-procedure documentations, the sonographer should record…
Any ___________ or __________
Immediate ________ (e.g., successful access or hematoma)
Post-procedure _________ or ________ (if applicable)
Complications or observations
Outcomes
Imaging or compression
Remember, clear and accurate documentation is essential for what 3 purposes?
Legal
Clinical
Quality assurance
Varicose veins are a result of…
Chronic _______________________
____ pressure in the veins due to loss of ______ function or _________
Ambulatory venous hypertension
High, Valve, Obstruction
Which pathology is a result of chronic ambulatory venous hypertension?
Varicose veins
Which pathology is a result of high pressure in the veins due to loss of valve function or obstruction?
Varicose veins
Varicose veins are associated with what 6 risk factors?
Pregnancy
Heredity
Prolonged standing
Trauma
Age
Obesity
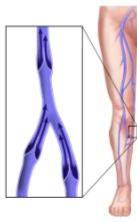
Are these veins normal or abnormal?
If abnormal, what pathology is seen here?
Normal
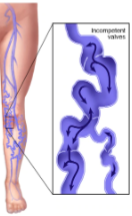
Are these veins normal or abnormal?
If abnormal, what pathology is seen here?
Abnormal
Varicose veins
Define ‘ablation.’
Destruction of a body part’s function
What procedure uses heat energy to close off the diseased vein?
Superficial venous ablation
What does superficial venous ablation use to close off the diseased vein?
Heat energy
If a superficial venous ablation cannot be performed, what other procedure can be considered?
Microphlebectomy
Define ‘microphlebectomy.’
Surgical removal of the diseased vein
What is the most common cause of varicose veins?
Incompetence of the great saphenous veins (GSV)