Radiographic Procedures 2 (155) Cranium Exam
1/64
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
65 Terms
PA/PA axial (Caldwell) skull
patient position:
seated upright or prone
MSP centered to midline
forehead and nose resting on Bucky
part position:
MSP and OML perpendicular to IR
respiration suspended
CR:
PA: perpendicular to IR, exiting nasion
PA axial: 15 degrees caudad, exiting nasion
collimation:
1 inch beyond skin line of the skull
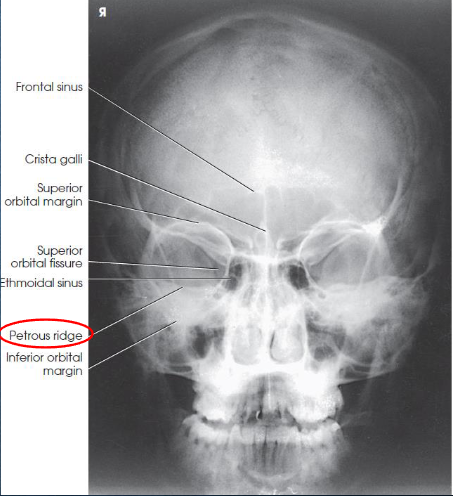
PA skull image criteria
evidence of proper collimation
entire cranial perimeter showing three tables of squamous bone
no rotation:
equal distance from lateral borders of skull to lateral border of orbits
symmetric petrous ridges
petrous ridges fill orbits
penetration of frontal bone without excessive density of lateral borders of skull
PA axial (Caldwell) skull image criteria
petrous ridges demonstrated in lower third of orbits
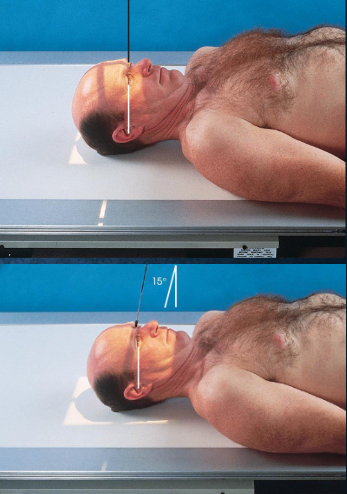
AP/AP axial (Reverse Caldwell) skull
a similar but magnified image when patient cannot be positioned for PA or PA axial
patient and position part:
supine
MSP centered to midline
MSP and OML perpendicular to IR
respiration suspended
CR:
AP: perpendicular, enters nasion
AP axial: 15 degrees cephalad, enters nasion
collimation:
1 inch beyond the skin line of the skull
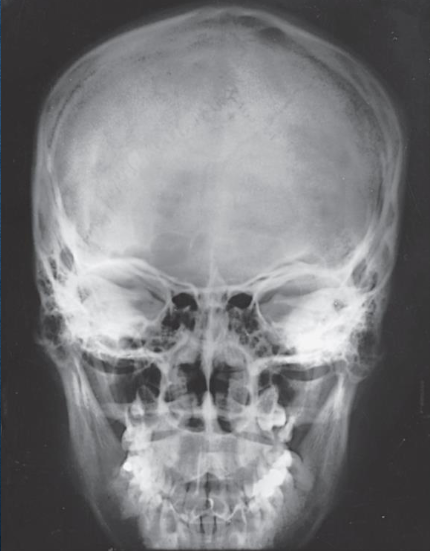
AP/AP axial (Reverse Caldwell) skull image criteria
shows the same as PA and PA axial projections
evidence of proper collimation
entire cranial perimeter showing three tables of squamous bone
no rotation:
equal distance from lateral borders of skull to lateral border of orbits
symmetric petrous ridges
anatomy is more magnified
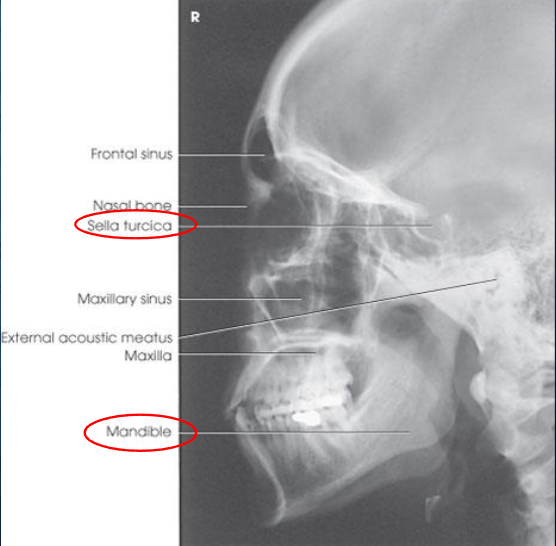
Lateral skull
patient position:
upright or semiprone
part position:
MSP of head parallel to IR
IPL perpendicular
IOML perpendicular to front edge of IR
respiration suspended
CR:
perpendicular to IR
enters 2 inches above EAM
collimation:
1 inch beyond skin line of the skull

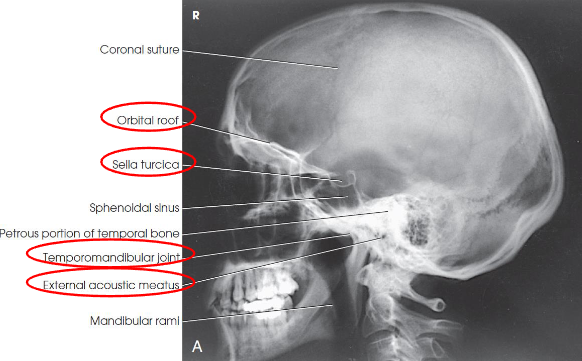
Lateral skull image criteria
entire cranium without rotation or tilt
superimposed orbital roofs and greater wings of sphenoid
superimposed mastoid regions, EAMs, and TMJs
sella turcica in profile
penetration of parietal region
no overlap of c-spine by mandible
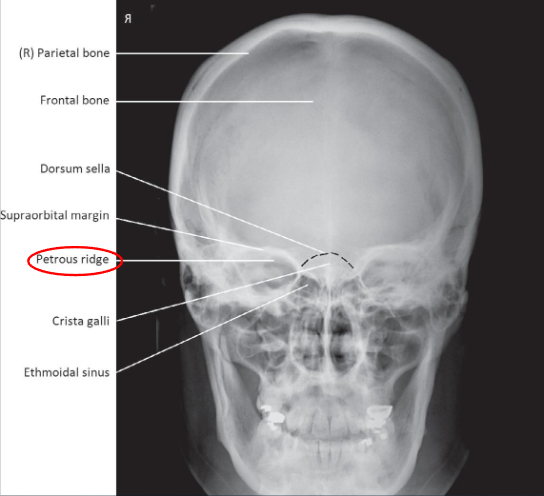
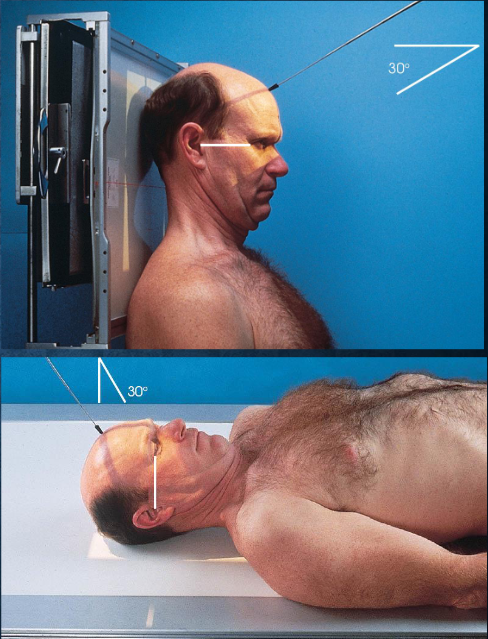
AP axial (Towne) skull
patient and part position:
supine or upright, seated
MSP centered to midline
MSP perpendicular
OML perpendicular to IR
IOML perpendicular if patient cannot flex neck enough
top border of IR level with vertex
IR centered at or near foramen magnum
respiration suspended
CR:
directed through foramen magnum
OML: 30 degrees cacudal
IOML: 37 degrees caudal
collimation:
1 inch beyond the skin line of the skull
AP axial (Towne) skull image criteria
no rotation:
equal distance from lateral border of skull to lateral margin of foramen magnum
symmetric petrous ridges
dorsum sellae and posterior clinoid process visible within foramen magnum
penetration of occipital bone without excessive density at parietals
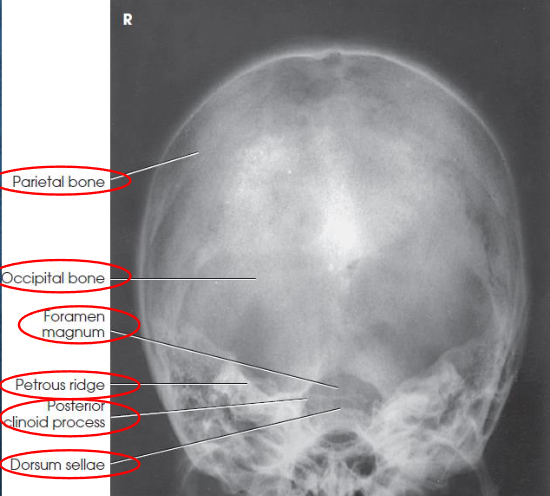
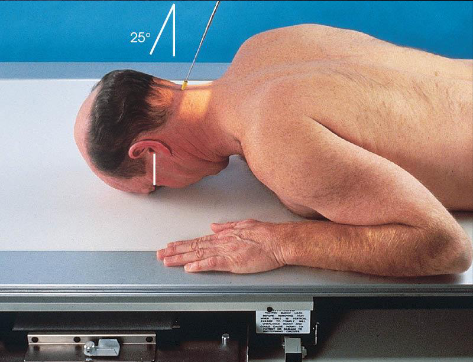
PA axial (Haas) skull
patient position:
prone or upright
MSP centered to midline
shoulders in same horizontal plane
part position:
forehead and nose resting on Bucky/table
MSP perpendicular to IR
OML perpendicular to IR
respiration suspended
CR:
25 degrees cephalad to OML
enters 1 ½ inches below external occipital protuberance
exits 1 ½ inches superior to nasion
collimation:
1 inch beyond the skin line of the skull
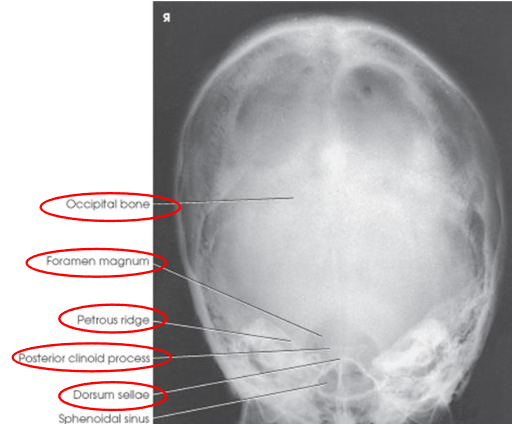
PA axial (Haas) skull image criteria
projection of dorsum sellae and posterior clinoid processes within foramen magnum
equal distance from lateral border of skull and lateral margin of foramen magnum
symmetric petrous pyramids
entire cranium
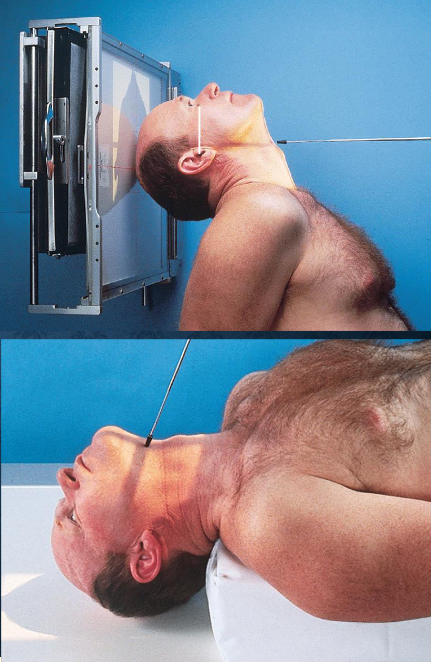
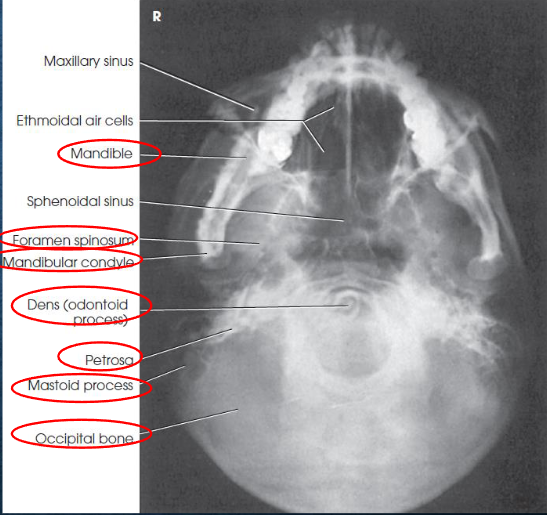
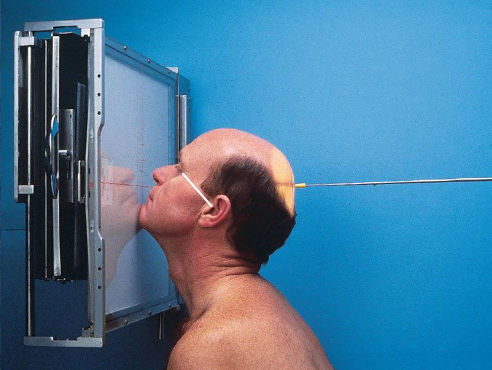
SMV (Schuller) skull
patient position:
upright (seated) or supine (torso elevated)
part position:
MSP centered to midline
MSP perpendicular to IR
IOML parallel with IR
patient hyperextends neck and rests head on vertex
respiration suspended
CR:
perpendicular through sella turcica and IOML
enters MSP of throat between angles of mandible (gonion)
passes through a point ¾ inch anterior to the level of the EAM
collimation:
½ inch beyond the shadow of the tip of the nose and 1 inch beyond the lateral borders
SMV (Schuller) skull image criteria
no rotation or tilt:
equal distance from lateral border of skull to mandibular condyles
symmetric petrous pyramids
penetration sufficient to demonstrate structures of cranial base
superimposition of mental protuberance over anterior frontal bone, indicating full neck extension
mandibular condyles anterior to petrous pyramids
Lateral facial bones
patient position:
upright or recumbent anterior oblique position
part position:
MSP of head parallel with IR
IPL perpendicular to IR
IOML perpendicular to front edge of the IR
zygomatic bone centered to grid
respiration suspended
CR:
perpendicular to IR
enters zygomatic bone halfway between outer canthus and EAM
collimation:
1 inch beyond shadow of the tip of the nose, superior to ½ inch above supraorbital margins, inferiorly to the gonion, and posteriorly to the EAM
no larger than 6 × 10 inches

Lateral facial bones image criteria
right and left sides superimposed
all facial bones in entirety with zygomatic bone centered
no rotation or tilt:
almost perfectly superimposed mandibular rami
superimposed orbital roofs
sella turcica in profile
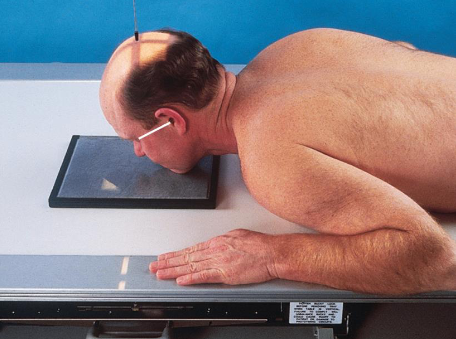
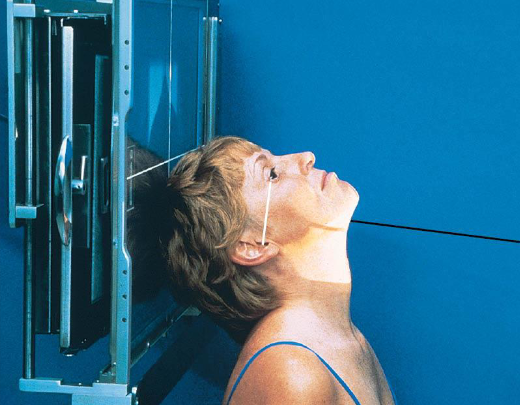
Parietoacanthial (Waters) facial bones
patient position:
prone or upright
center MSP to midline
part position:
rest head on tip of extended chin
nose slightly off IR
OML adjust to form 37 degree angle with IR plane
MML perpendicular to IR
MSP perpendicular to IR
IR centered to level of acanthion
respiration suspended
CR:
perpendicular, exits acanthion
collimation:
1 inch beyond the shadows of the lateral sides of the face, superiory to include the supraorbital margins, and inferiorly to the level of the chin
no larger than 8 × 10 inches
Parietoacanthial (Waters) facial bones image criteria
shows orbits, maxillae, and zygomatic arches
entire orbits and facial bones
no rotation or tilt:
distances between the lateral borders of the skull and the orbits
MSP of head aligned with long axis of collimated field
petrous ridges projected just below maxillary sinuses
Modified parietoacanthial (modified Waters) facial bones
head positioned as described using Water’s method
less extension of the patient’s neck to increase angulation of OML
OML is more perpendicular to IR plane
good to demonstrate blowout fractures
patient position:
prone or upright
MSP centered
part position:
rest head on tip of extended chin
nose touhcing IR
less extension of neck
OML forms 55 degree angle with IR plane
MML perpendicular to IR
MSP perpendicular to IR
IR centered at level of acanthion
respiration suspended
CR:
perpendicular, exiting acanthion
collimation:
1 inch beyond the shadows of the lateral sides of the face, superiory to include the supraorbital margins, and inferiorly to the level of the chin
no larger than 8 × 10 inches
Modified parietoacanthial (modified Waters) facial bones image criteria
facial bones with less axial angulation than Waters method
petrous ridges projected just below the inferior border of the orbits at a level midway through the maxillary sinuses
orbital floor seen perpendicular to the IR and parallel to the CR
demonstrates inferior displacement of the orbital flooropacified maxillary sinus
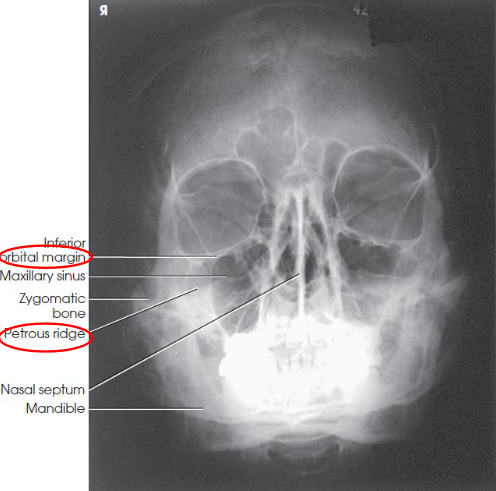
Acanthioparietal (Reverse Waters) facial bones
patient position:
supine
MSP centered to midline
part position:
extend chin and neck so OML forms a 37 degree angle with the IR plane
MML almost perpendicular
MSP perpendicular to IR
respiration suspended
CR:
perpendicular, enters acanthion
collimation:
1 inch beyond the lateral sides of the face, superiorly just to the skin shadow, and inferiorly to the chin
no larger than 8 ×10 inches
Acanthioparietal (Reverse Waters) facial bones image criteria
shows orbits, maxillae, and zygomatic arches
entire orbits and facial bones
no rotation or tilt:
distances between the lateral borders of the skull and the orbits
MSP of head aligned with long axis of collimated field
petrous ridges just below maxillary sinuses
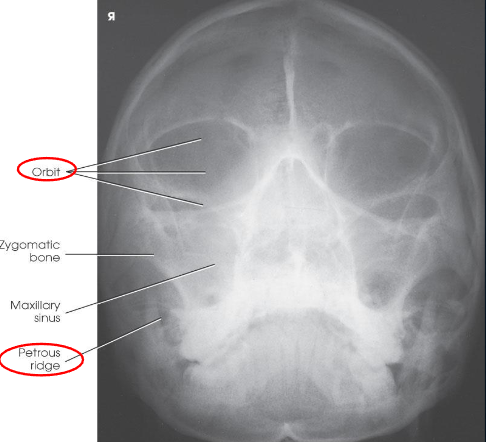
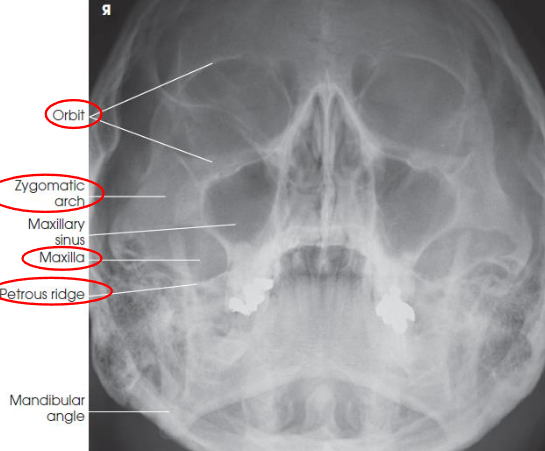
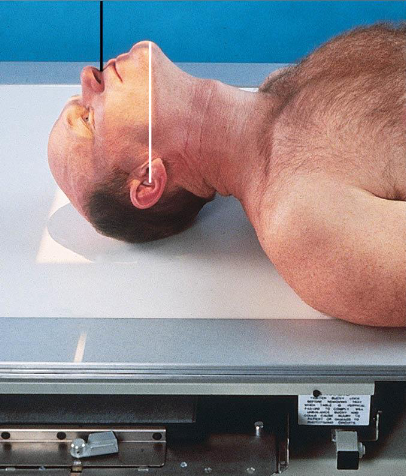
PA axial (Caldwell) facial bones
patient position:
upright (seated) or prone
MSP centered to midline
forehead and nose resting on Bucky/table
part position:
OML perpendicular to IR
MSP perpendicular to IR
IR centered to nasion
respiration suspended
CR:
15 degrees caudad, exiting nasion
collimation:
1 inch betond the lateral sides of the face, superiorly to include the supraorbital margins, and inferiorly to the chin
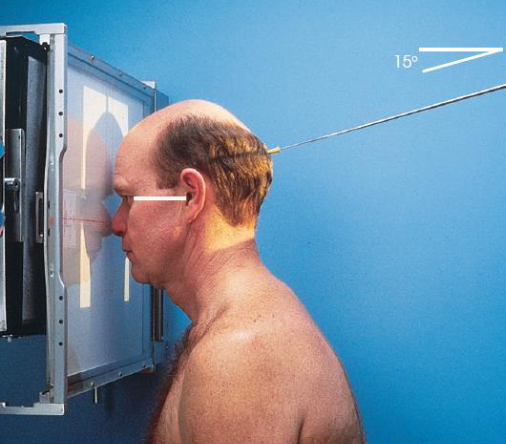
PA axial (Caldwell) facial bones image criteria
shows:
orbital rims
maxillae
nasal septum
zygomatic bones
anterior nasal spine
petrous ridges in lower third of orbits (caused be 15 degree caudal angle)
entire orbits and facial bones
no rotation or tilt:
equal distances from lateral borders of skull and lateral borders of orbits
MSP of head alligned with long axis of collimated field
symmetric petrous ridges
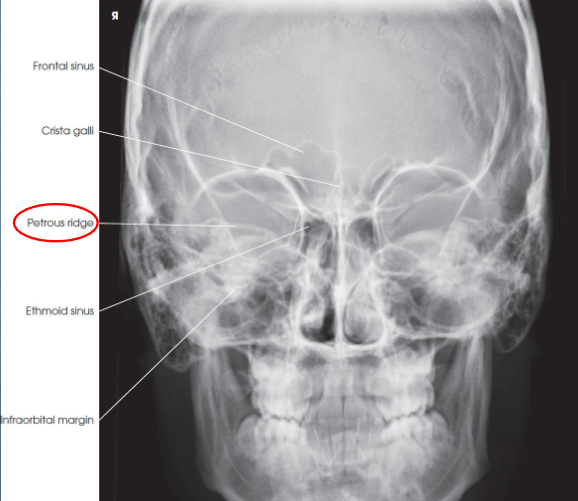
Lateral nasal bones
patient position:
upright or recumbent anterior oblique position
MSP parallel with IR
part position:
IPL perpendicular
flex neck to place IOML parallel to transverse axis of IR
respiration suspended
CR:
perpendicular
enters 1 inch distal to nasion
collimation:
extends from the glabella to 1 inch inferior to the acanthion and ½ inch beyond the tip of the nose
should be no larger than 3 × 3 inches
both sides done for comparison

Lateral nasal bones image criteria
shows:
nasal bone and soft tissues of the nose
anterior nasal spine
frontonasal suture
no rotation
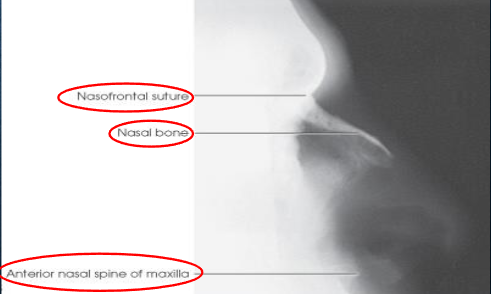
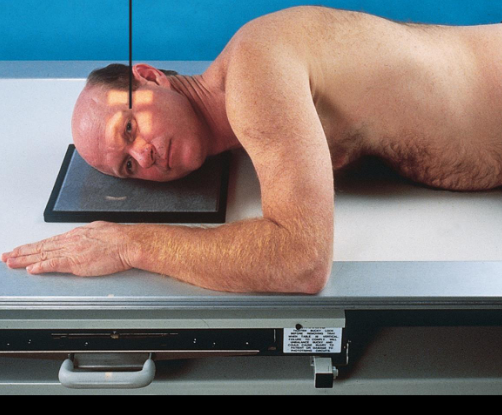
Lateral orbits
patient position:
upright or recumbent anterior oblique position
part position:
outer canthus of affected eye adjacent and centered to IR
adjust patient’s head to place MSP parallel with IR
IPL perpendicular to IR
flex neck to place IOML perpendicular to front edge of IR
respiration suspended
CR:
perpendicular through outer canthus

Lateral orbits image criteria
entire orbit(s)
no rotation
superimposed orbital roofs
close beam restruction centered to orbital region
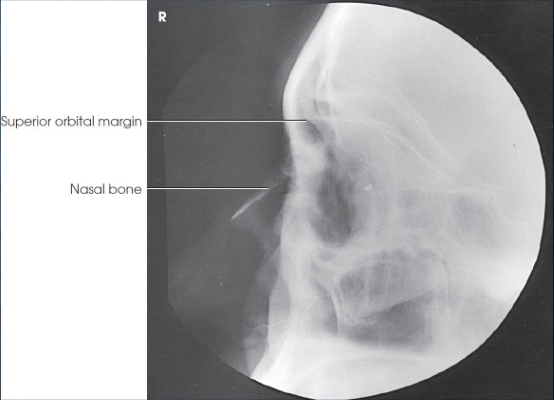
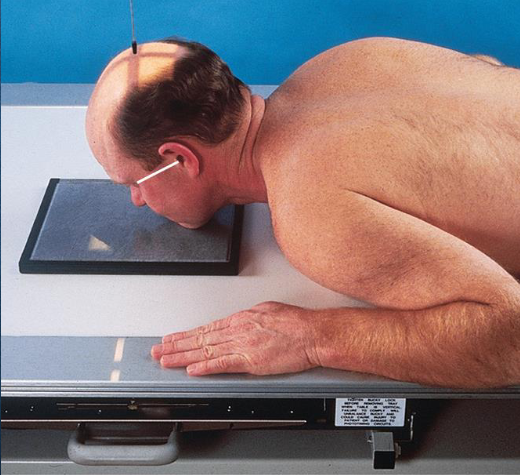
PA axial (exaggerated Caldwell) orbits
patient position:
upright or recumbent
part position:
rest forehead and nose on IR
IR centered ¾ inches distal to nasion
adjust head to place MSP and OML perpendicular to IR
respiration suspended
CR:
30 degrees caudad, through center of orbits
non-grid technique recommended to reduce magnification and eliminate possible artificats

PA axial (exaggerated Caldwell) orbits image criteria
entire orbit(s)
petrous pyramids lying below orbital shadows
no rotation:
symmetric orbits
close beam restriction to orbital region
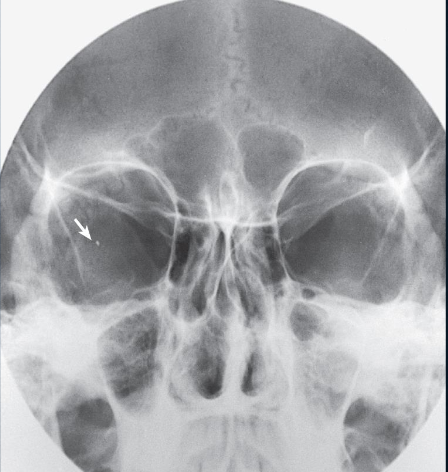
Parietoacanthial (modified Waters) orbits
patient position:
upright or recumbent
part position:
IR centered at level of the center of the orbits
rest chin on IR
nose lifted way off IR
MSP perpendicular to IR
flex neck to form 50 degree angle between OML and IR
respiration suspended
CR:
perpendicular, through mid-orbits
Parietoacanthial (modified Waters) orbits image criteria
entire orbit(s)
no rotation:
symmetric orbits
close beam restriction to orbital region
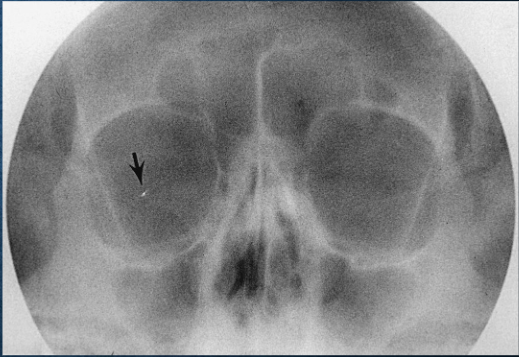
SMV zygomatic arches
patient position:
upright (seated) or supine (torso elevated)
part position:
hyperextend neck to place IOML parallel as much as possible with IR
rest head on vertex
MSP perpendicular to IR
respiration suspended
CR:
perpendicular to IOML
enters MSP of throat 1 inch posterior to outer canthi
collimation:
1 inch beyond the lateral sides of the face, superiorly to the chin, and inferiorly to the gonions
no larger than 8 × 10 inches
SMV zygomatic arches image criteria
bilateral symmetric zygomatic arches
arches free from overlying structures
no foreshortening of arches
no rotation or tilt of head
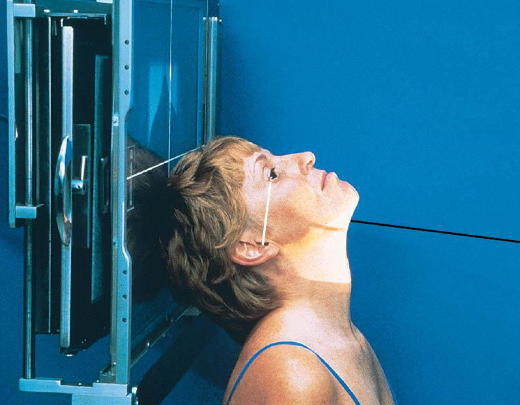
Tangential zygomatic arches
patient position:
upright (seated) or supine (torso elevated)
part position:
hyperextend neck and rest head on vertex
IOML as parallel with IR as possible
rotate MSP of head 15 degrees toward side being examined
tilt top of head 15 degrees away from side being examined
center zygomatic arch to IR
respiration suspended
CR:
perpendicular to IOML
centered to zygomatic arch 1 inch posterior to outer canthus
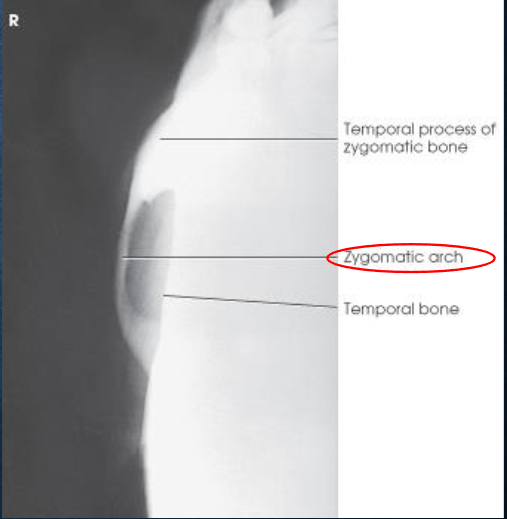
Tangential zygomatic arches image criteria
one zygomatic arch free of superimposition
arch not overexposed
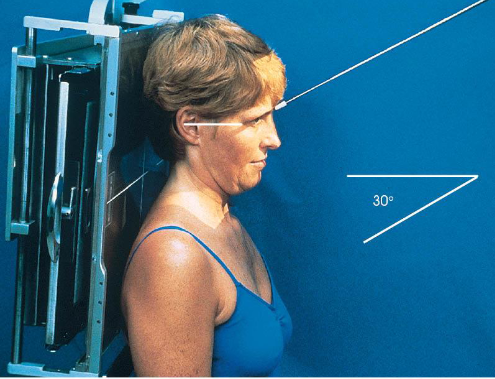
AP axial (modified Towne) zygomatic arches
patient position:
upright or supine
part position:
MSP perpendicular to midline
OML perpendicular to IR
may use IOML if patient can’t flex neck enough
increase in CR angle
respiration suspended
CR:
OML: 30 degrees caudad, enters glabella 1 inch above the nasion
IOML: 37 degrees caudad
collimation:
1 inch beyond the lateral sides of the face, superiorly to the top of the forehead, and inferiorly to the chin
AP axial (modified Towne) zygomatic arches image criteria
both zygomatic arches, free of superimposition
no overlap of arches by mandible
no rotation
symmetric arches
arches projected lateral to mandibular rami
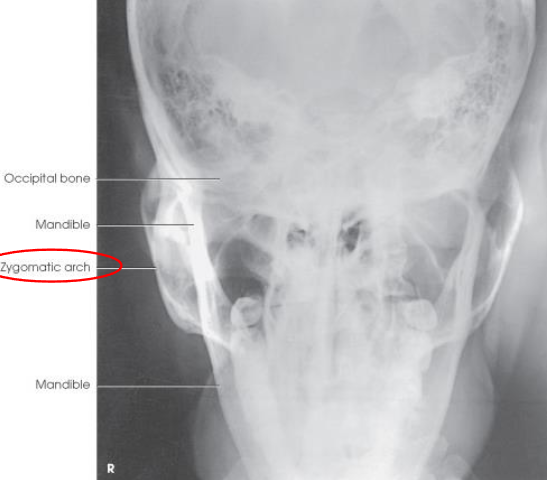
PA mandibular rami
patient position:
prone or upright
part position:
forehead and nose resting on IR
OML perpendicular to IR
MSP perpendicular to Ir
respiration suspended
CR:
perpendicular, exits acanthion
collimation:
1 inch beytond the lateral sides, above the TMJs, and below the chin
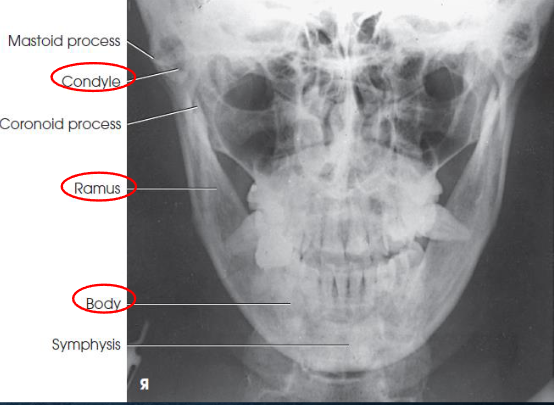
PA mandibular rami image criteria
mandibular body and rami
central part of body not well shown due to superimposition
shows medial or lateral displacement of fragments in fractures of the rami
no rotation or tilt:
symmetric mandibular body and rami
MSP of head aligned with long axis of collimated field
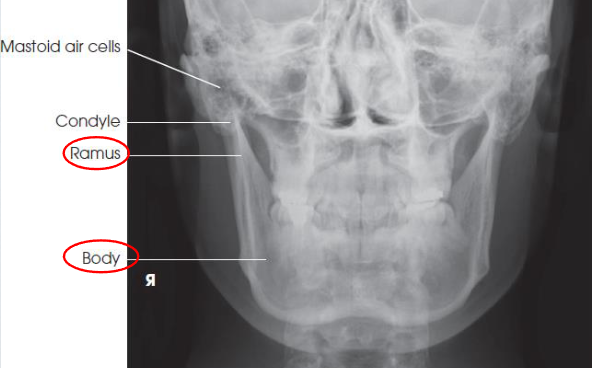
PA axial mandibular rami
patient position:
prone or upright
part position:
forehead and nose resting on Bucky/table
OML perpendicular to IR
MSP perpendicular to IR
respiration suspended
CR:
20-25 degrees cephalad, exits acanthion
collimation:
1 inch beyond the lateral sides, above the TMJs, and below the chin

PA axial mandibular rami image criteria
mandibular body and rami
central part of body not well shown due to superimposed spine
demonstrates medial or lateral displace ment of fragments in fractures of the rami
no rotation or tilt:
symmetric mandibular body and rami
MSP of head aligned with long axis of collimated field
condylar processes
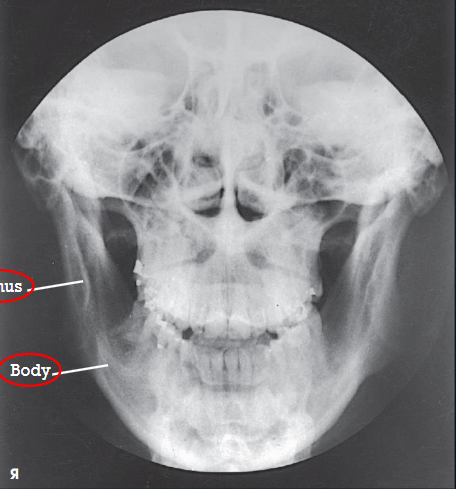
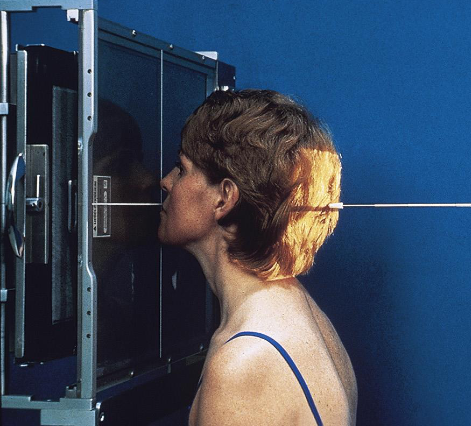
PA mandibular body
patient position:
prone or upright
part position:
rest nose and chin on IR
anterior surface of the mandibular symphysis parallel to IR'
AML nearly perpendicular to IR
MSP perpendicular to Ir
respiration suspended
CR:
perpendicular to level of lips
collimation:
1 inch beyond the lateral sides, above the TMJs, and below the chin
PA mandibular body image criteria
shows mandibular body
no rotation or tilt
symmetric mandibular body
MSP of head aligned with long axis of collimated field
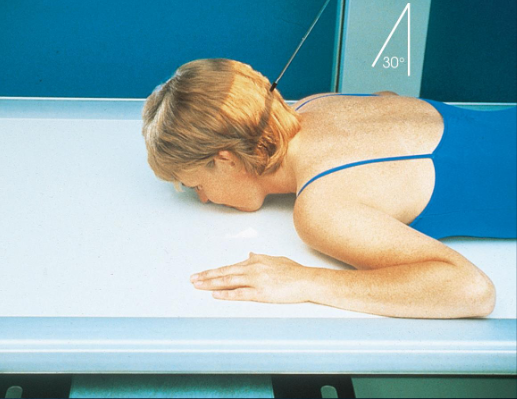
PA axial mandibular body
patient position:
prone or upright
part position:
rest nose and chin on Bucky/table
anterior surface of the mandibular surface parallel to IR
AML nearly perpendicular to IR
MSP centered and perpendicular to IR
respiration suspended
CR:
30 degrees caudad, midway between TMJs
collimation:
1 inch beyond the lateral sides, above the TMJs, and below the chin
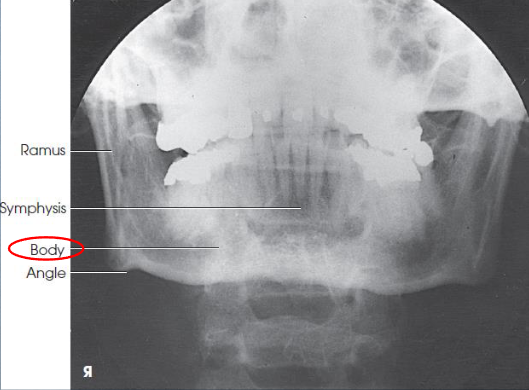
PA axial mandibular body image criteria
mandibular body and TMJs (condyles)
TMJs just inferior to the mastoid process
no rotation or tilt
symmetric rami
MSP of head aligned with axis of collimated field
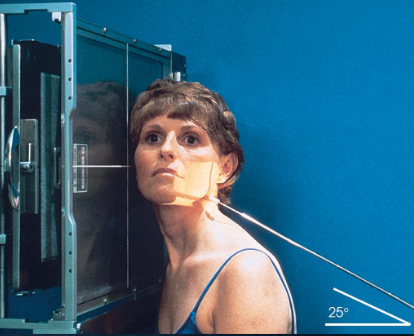
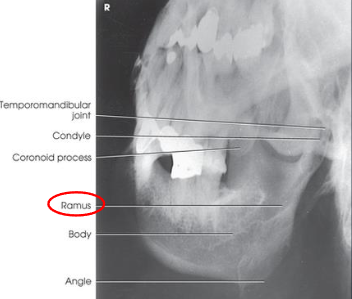
Axiolateral and axiolateral oblique mandible
goal is to place desired portion of the madible parallel with the IR
patient position:
upright in anterior oblique position, semiprone, or semisupine
part position:
head lateral with IPL perpendicular to IR
mouth closed with teeth together
extend neck to place mandibular body parallel with transverse axis of IR
adjust rotation of head to place area of interest parallel to IR
ramus: head in true lateral
body: rotate head 30 degrees toward IR
symphysis: rotate head 45 degrees toward IR
respiration suspended
CR:
25 degrees cephalad, passes directly through mandibular region of interest
collimation:
1 inch beyond the anterior and inferior skin shadows and above the TMJ
Axiolateral and axiolateral oblique mandible image criteria
shows region of the mandible that was parallel with the IR: ramus, body, or symphysis
ramus and body:
no overlap of the ramu sby opposite side of mandible
no elongation or foreshortening of ramus or body
no superimposition of the ramus by the cervivcal spine
symphysis:
no overlap of the mentum region by the opposite side of the mandible
no foreshortening of the mentum region
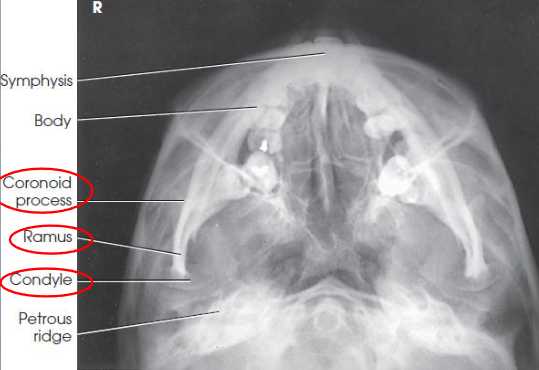
SMV mandible
patient position:
upright or supine
part position:
MSP centered to midline
neck fully extended
head resting on its vertex
MSP vertical
IOML as parallel as possible with IR
if neck cannot be flexed enough, angle the grid device and place it parallel to IOML
respiration suspended
CR:
perpendicular to IOML
centered midway between mandibular angles
if neck cannot be flexed enough, angle the tube to be parallel to IOML
collimation:
1 inch beyond the loateral sides and above the tip of the nose

SMV mandible image criteria
coronoid and condyloid processes of the rami
no rotation or tilt
equidistant lateral border of skull and mandible
MSP of head aligned to long axis of collimated field
condyles of mandible anterior to pars petrosal
symphysis extending almost to anterior border of the face
mandible not foreshortened
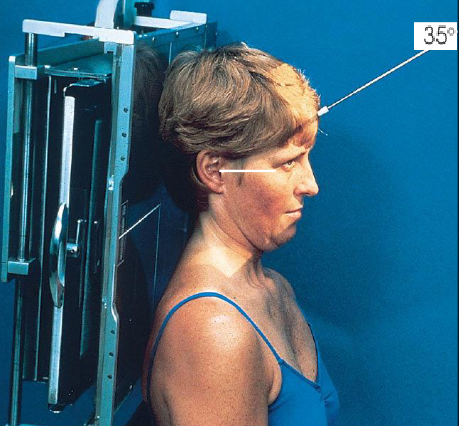
AP axial TMJs
patient position:
supine or upright
posterior skull in contact with Bucky/table
part position:
MSP of head perpendicular
flex neck to place OML perpendicular to IR
one exposure taken with mouth closed
one exposure taken with mouth open, if not contraindicated
respiration suspended
CR:
35 degrees caudad
midway between TMJs, 3 inches above nasion
collimation:
1 inch beyond the lateral sides, superiorly to the glabella, and inferiorly to the lips
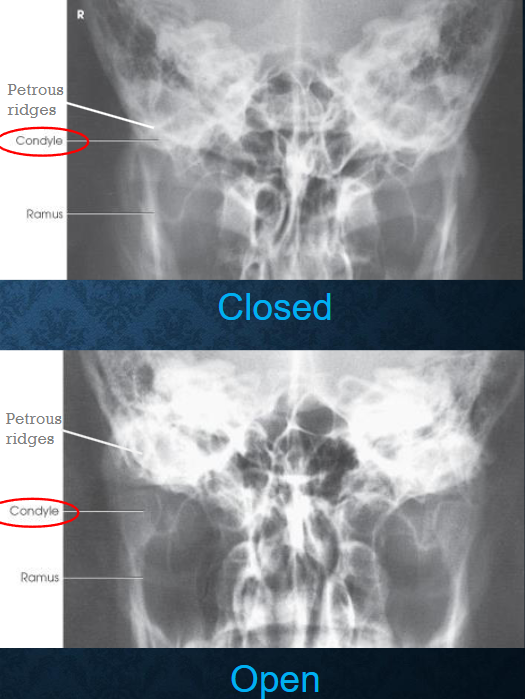
AP axial TMJs image criteria
mandibular condyles and fossae of the temportal bones
no rotation of head
closed mouth: minimal superimposition of petrosa on the condyle
open mouth: condyle and TMJ below pars petrosa
Axiolateral (modified Schuller) TMJs
patient position:
right or left lateral, both sides done for comparison
semiprone or upright
part position:
center ½ inch anterior to the EAM to the IR
head in true lateral
MSP parallel with IR
IPL perpendicular
one exposure with the mouth closed, and a second with the mouth open (if not contraindicated
respiration suspended
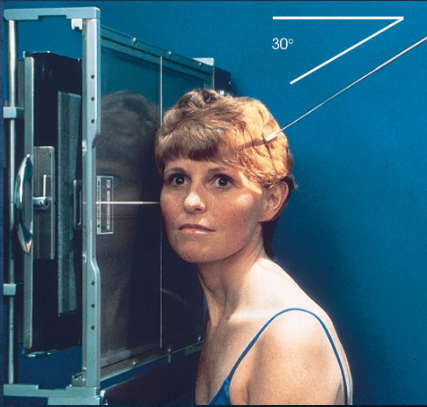
CR:
25-30 caudad
enters ½ inch anterior and 2 inches superior to upside EAM
collimation:
1 inch betond the anterior skin line, posteior and inferior to the TMJs
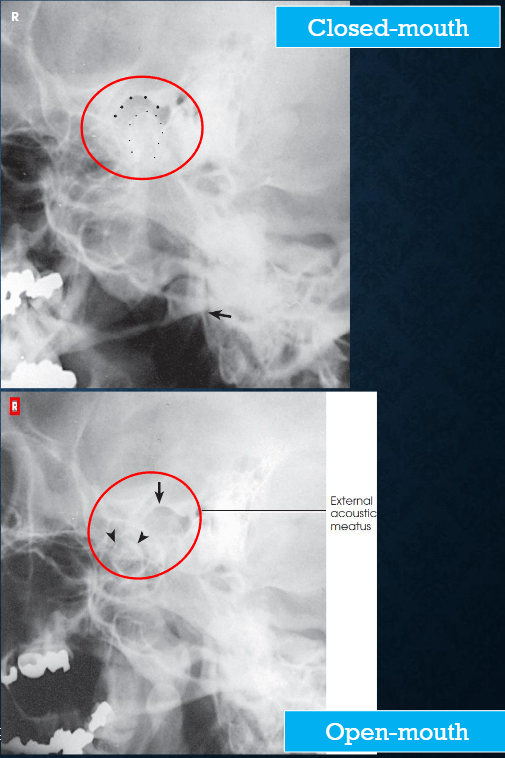
Axiolateral (modified Schuller) TMJs image criteria
TMJ with mouth open and closed
both sides done for comparison
TMJ anterior to EAM
closed mouth: condyle in mandibular fossa
open mouth: condule inferior to the articular tubercle
Axiolateral oblique (modified Law) TMJs
patient position:
semiprone or upright
both sides for comparison
one exposure made with mouth closed, and one made with the mouth open, if not contraindicated
part position:
center ½ anterior to EAM on the side closest to IR
rest cheek against IR
rotate MSP of head 15 degrees toward IR
IPL perpendicular to IR
AML parallel with transverse axis of IR
respiration suspended
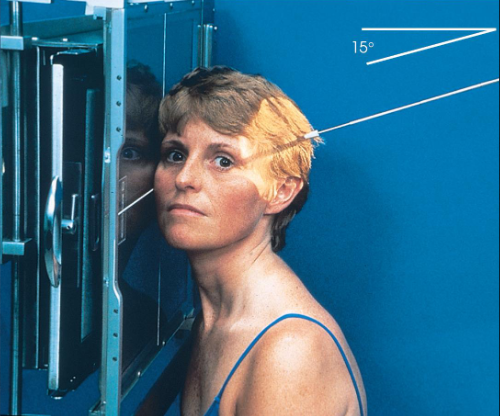
CR:
15 degreees caudad
exits through TMJ closer to IR
enters 1 ½ inches superior to upside EAM
collimation:
from the outer canthus to the posterior edge of the auricle and from the midparietal region to the inferior edge of the auricle
Axiolateral oblique (modifed Law) TMJs image criteria
condyles and necks of the mandible
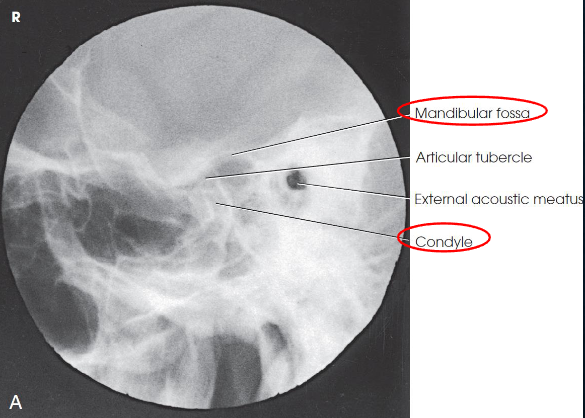
relationship between mandibular fossa and condyle
closed mouth: fractures of the neck and condyle of the ramus
open mouth: mandibular fossa and inferior and anterior excursion of the condyle
TMJ articulation
condyle lying in mandibular fossa in closed-mouth
condyyle lying inferior to articular tubercle in open-mouth
Lateral sinuses
patient position:
upright anterior oblique
can be done in dorsal decubitus position
part position:
head in true lateral
MSP parallel to IR
IPL perpendicular
extend neck so that IOML horizontal and parallel to transverse axis of IR
respiration suspended
CR:
horizontal and perpendicular
enters 1 inch posterior to outer canthus
collimation:
1 inch beyond the tip of the nose, 3 inches above the nasion, inferior to the occlusal plane, and posteriorly to the auricle
SID of 72” recommened for preoperative measurements
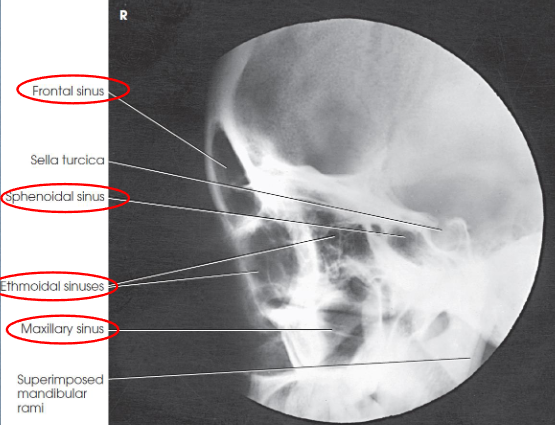
Lateral sinuses image criteria
demonstrates:
all four sets of sinuses
anteroposterior (AP) and superoinferior dimensions of paranasal sinuses
thickness of frontal bone
detail of side closer to IR
sphenoidal sinus best demonstrated
no rotation or tilt
sella turcica in profile
superimposed orbital roofs
superimposed mandibular rami
air-fluid levels, if present
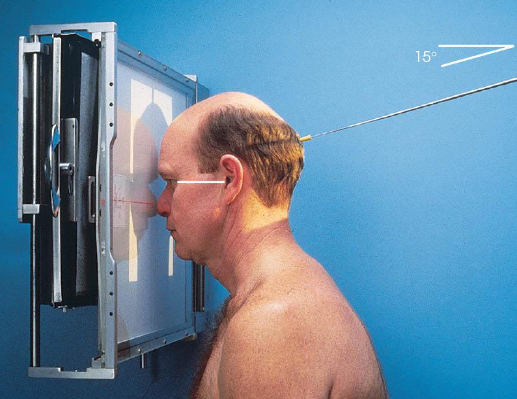
PA axial (Caldwell) sinuses
patient position:
upright
MSP centered to midline
part position, angled grid technique:
tilt vertical Bucky down 15 degrees (horizontal CR)
rest forehead and nose on IR
center nasion to IR
MSP and OML perpendicular to IR
part position, vertical grid technique:
extend neck to rest tip of nose on Bucky
OML 15 degrees to horizontal IR
sponge can be used to support forehead
center nasion to IR
MSP perpendicular to IR
not preferred because of an increased OID, which results in decreased resolution
respiration suspended
CR:
horizontal, exits nasion
15 degree relationship between CR and OML
collimation:
1 inch beyond the lateral skin shadows, superiorly to include just the shadow of the top of the head, and inferiorly to the occlusal plane

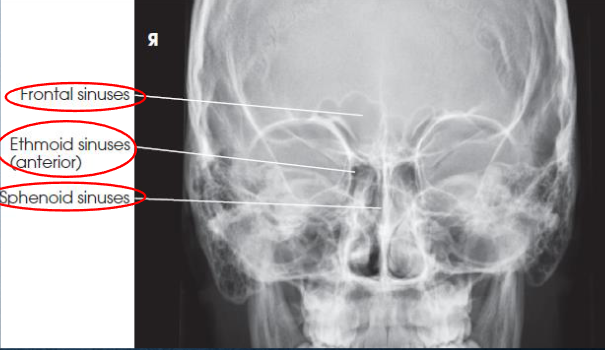
PA axial (Caldwell) sinuses image criteria
demonstrates:
frontal sinuses above frontonasal suture
anterior ethmoidal air cells
sphenoid sinuses seen through nasal fossa below or between ethmoids
petrous pyramodis lower third of orbits
primarily demonstrates the frontal sinuses and anterior ethmoidal air cells
anterior ethmoidal air cells above petrous ridges
no rotation or tilt
equidistant lateral borders of the skull and lateral borders of the orbits
symmetric petrous ridges
MSP of head aligned with long axis of collimated field
air-fluid levels, if present
Parietoacanthial (Waters) sinuses
patient position:
upright
MSP centered to midline
part position:
rest chin on vertical grid devie
hyperextend neck to place OML at 37 degree angle from IR
MSP and MML perpendicular to IR
center IR to acanthion
respiration suspended
CR:
horizontal, exits acanthion
collimation:
1 inch beyond the lateral skin shadows, superiorly to include just the shadow of the top of the head, and inferiorly to the occulsal plane

Parietoacanthial (Waters) sinuses image criteria
demonstrates:
maxillary sinuses
petrous pyramids lying inferior to maxillary floor
frontal and ethmoid sinuses are distorted
insufficient extension: petrosa are projected over the inferior portions of the maxillary sinuses
overextension: maxillary sinuses are foreshortened, and antral floors are not shown
OML in proper position:
petrous pyramids lying immediately inferior to floor of maxillary sinsues
symmetric orbits and maxillary sinuses
MSP of head aligned with long axis of collimated field
air-fluid levels, if present
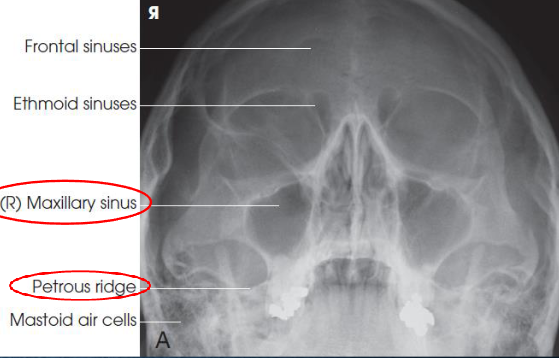
Parietoacanthial (open-mouth Waters) sinuses
patient position:
upright
MSP centered to midline
part position:
rest chin on IR
hyperextend neck to place OML at 37 degree angle from IR
MSP perpendicular to IR
open mouth
respiration suspended
CR:
horizontal, exits acanthion
collimation:
1 inch beyond the lateral skin shadows, superiorly to include just the shadow of the top of the head, and inferiorly to the occlusal plane

Parietoacanthial (open-mouth Waters) sinuses image criteria
demonstrates:
sphenoid sinuses through open mouth
maxillary sinuses
petrous pyramids lying inferior to maxillary floor
(OML in proper position)
no rotation or tilt
equidistant lateral borders of skull to lateral border of the orbits
summetric orbits and maxillary sinuses
MSP of head aligned with long axis of collimated field
air-fluid levels, if present
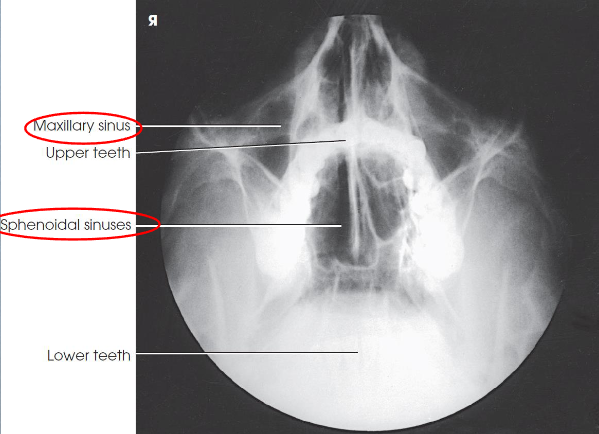
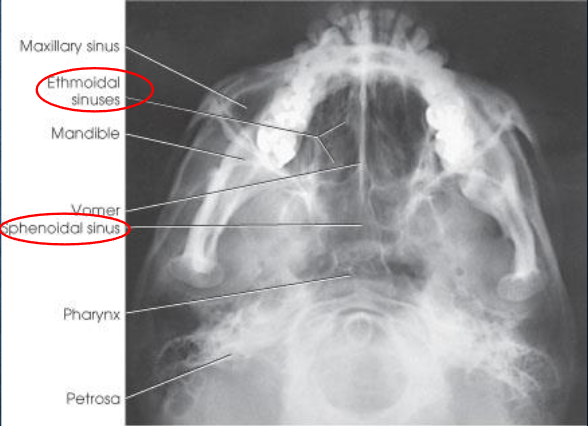
SMV sinuses
patient position:
upright
part position:
hyperextend neck and rest vertex of head on Bucky
adjust head to place MSP perpendicular to IR plane
IOML parallel to IR
respiration suspended
CR:
horizontal and perpendicular to IOML
enters MSP ¾ inch anterior to level of EAM
collimation:
1 inch beyond the tip of the nose and on the lateral sides
SMV sinuses image criteria
demonstrates:
sphenoid and ethmoid sinuses
mandible
bony nasal septum
no tilt:
equidistant lateral border of skull to mandibular condyles
IOML parallel to IR:
superimposition of anterior frontal bone by mental protuberancce
insufficient neck extension will cause mandible to superimpose ethomoid sinuses
mandible condyles anterior to petrous pyramids
air-fluid levels, if present