Neuro-Environmental Considerations
1/76
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
77 Terms
What 3 factors can physical and virtual environments influence?
1. Human health
2. Well-being
3. Productive occupations
What must occupational therapists understand in order to provide client-centered care?
How people experience environments, places, and spaces
What 3 functional outcomes does occupational therapy practice consider the impact of environmental and contextual factors on?
1. Persons
2. Groups
3. Populations
Lifeworld
A person or group's everyday world of taken-for-grantedness normally unnoticed
What is a person or group's lifeworld hidden as?
Phenomenon
Place
Any environmental locus that gathers individual or group meanings, intentions, and actions spatially
Examples of Places
Furnishing
Room
Building (e.g. "this is where I went to school")
Neighborhood
City
Region
Environmental Embodiment
The various ways, sensorially and movement wise, that the lived body engages and coordinates with the world at hand, especially the physical aspects
Aging in Place
Dwelling that supports an individuals choice to occupy a home unit from childhood to old age unless illness or impairment are present
Home
A place of activity, identity, and memories
What does a home act as a center for?
Stability and continuity
5 Dimensions of a Home
1. Physical
2. Personal
3. Social
4. Cultural
5. Political
7 Key Pieces of Legislation for Accessibility and Design
1. Americans with Disabilities Act of 1990
2. American National Standards Institute
3. Architectural Barriers Act of 1968
4. Fair Housing Amendments Act of 1988
5. Hill-Burton Act of 1946
6. Rehabilitation Act of 1973
7. Uniform Federal Accessibility Standards
What legislative act protects the civil rights of persons with disabilities (e.g. physical or mental) access to public spaces?
Americans with Disabilities Act of 1990 (amended in 2008)
What 2 regulations did the Americans with Disabilities Act of 1990 implement in the United States?
1. Accessibility guidelines (2004)
2. Accessibility standards (2012)
What legislative act enforced standards for accessible design of buildings and facilities that are designed, built, or altered with federal funds after 1968?
Architectural Barriers Act of 1968
What legislative act prohibits housing discrimination on the basis of race, color, religion, sex, disability, familial status, and national origin?
Fair Housing Amendments Act of 1988
What type of tenants does the Fair Housing Amendments Act of 1988 require landlords to allow?
Tenants with disabilities to make reasonable access-related modifications to their private living space, as well as to common use spaces
What legislative act provided grants and loans to construct and modernize hospitals, nursing homes, and other health facilities?
Hill-Burton Act of 1946
What are hospitals receiving federal monies obligated to provide for their patients under the Hill-Burton Act of 1946?
Free or subsidized care to a portion of their indigent patients (e.g. charity care)
Charity Care
Medically necessary care for patients who can not afford to pay
What was the Hill-Burton Act of 1946 the driver of in hospitals?
Desegregation
When did the Hill-Burton Act of 1946 program stop providing funds?
1997
What legislative act provides grants to states for vocational rehabilitation services, with special emphasis on services to individuals with disabilities?
Rehabilitation Act of 1973
What legislative act describes standards for the design, construction, and alteration of buildings to be accessible to physically handicapped persons in accordance with the Architectural Barriers Act of 1968?
Uniform Federal Accessibility Standards
What do occupational therapists analyze?
Person
Environment
Performance skills
Functional demands
Environmental demands
What do occupational therapists develop based off their analysis?
Strategies to minimize barriers and optimize occupational performance
When are environmental modifications warranted?
Change in patient function
What do environmental modifications promote?
Productive aging (*specialty certification available*)
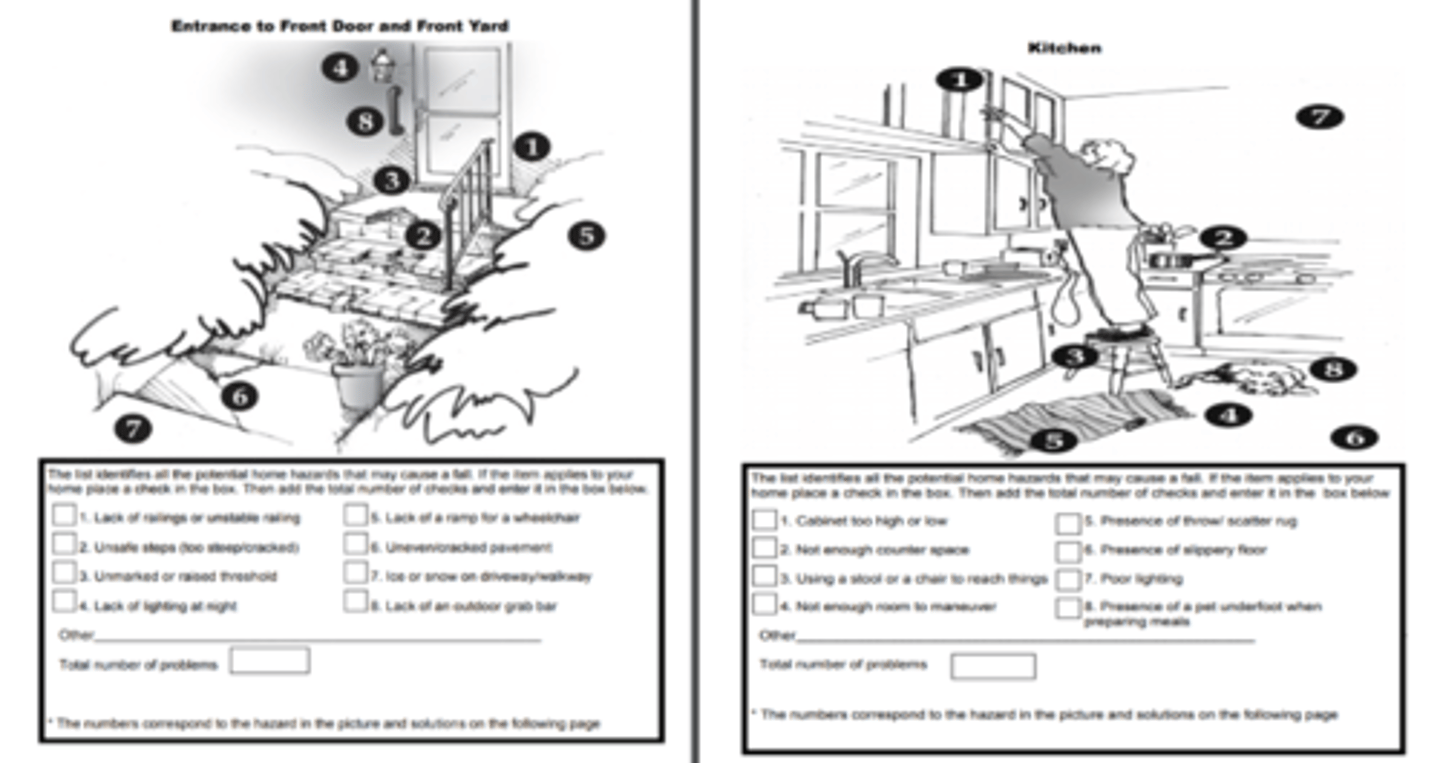
Who completes a home evaluation?
completed by examining architectural barriers in the exterior and interior of the home
When evaluating the home, what external things should you consider?
- Type of residence (apartment, duplex, townhome, single home, etc.) - assess elevator or stairs present, walkways, and railings
- Note weather protection - what surfaces does the client have to travel to access the home (concrete, gravel, bricks, mud, etc.)
- Examine driveway - width, slope, can the driveway accommodate a wheelchair van if needed?
- Surrounding area - trees, location of mailbox
What do you evaluate when assessing all entrances to and throughout the home?
width, height, thresholds, doorknobs, locks
Interior evaluation is organized room by room and should include what?
- Number of levels in a home
- Count and measure all steps and staircase dimensions
- Living Room
- Hallways
- Bedrooms
- Bathrooms
- Kitchen
- Laundry
- Basement
4 Strategies to Optimize Accessibility
1. Inclusive and universal design
2. Environmental modifications
3. Assistive technology
4. Task simplification strategy
5 Performance Skills
1. Vision
2. Hearing
3. Motor
4. Attention
5. Communication
What potential environmental modifications can be made for patients with visual deficits?
- Lighting
- Tactile indicators
- Raised surfaces
- Increase contrast
- Magnification/angled surfaces
- Medication management
- Modifying spaces to increase organization
- Decrease clutter
What potential environmental modifications can be made for patients with hearing deficits?
- Closed caption
- Minimize background noises
- Vibrating devices
What potential environmental modifications can be made for patients with motor deficits?
- Installation of grab bars
- Elevated chairs (to assist with sit to stand transfers)
- Modify surface heights
- Use of assistive technology (e.g. environmental control units)
What potential environmental modifications can be made for patients with attention deficits?
- Automated functions (e.g. medications)
- Decrease clutter
- Minimize distractions
What potential environmental modifications can be made for patients with communication deficits?
- Environmental control units
- Rearrange furniture (e.g. turn to face each other)
- Preprogrammed numbers
- In Home Occupational Performance Evaluation (I-HOPE)
- Safety Assessment of Function and the Environment for Rehabilitation - Health Outcome Measurement and Evaluation (SAFER-HOME)
- Home Falls and Accidents Screening Tool (Home- FAST)
- Westmead Home Safety Assessment
- Home Safety Self Assessment Tool (HSSAT v.5)
- Walkability Checklist
What are these OT assessments for?
environmental modifications
Home Safety Self-Assessment Tool (HSSAT v.5)
A patient-reported measure used to increase perceived knowledge of home safety and identify unsafe activities as well as develop a home safety plan to reduce the risk of falls
How wide should doorways be?
34-36 inches wide
How tall should door thresholds be?
No more than 1/2 inch
Are door levers or door knobs preferred?
Door levers
How wide should hallways be?
36 inches wide
How wide should hallways with decorations be?
48 inches wide
How many accessible entrances should there be? Why?
At least two in case of an emergency
What is the accessibility rule for ramps?
1 inch increase in height for every 1 foot increase in length (rise/run)
What is the measurement of a standard, nonslip ramp?
1 inch: 12 feet
How high should light switches be from the floor?
No more than 48 inches
Is tile, wood, or carpet flooring preferred?
Tile and wood
How high should towel rods be from the floor?
No more than 54 inches
How high should horizontal grab bars be from the floor?
33-36 inches
How tall should kitchen counters be?
34 inches
What should occupational therapists ensure there is under skinks and counters to prevent burns?
- Adequate space (for wheelchair)
- Pipe coverings
How does the Americans with Disabilities Act define disability?
As a physical or mental impairment that substantially limits one or more major life activities
What do job applicants or employees who have a mental health condition that meets this criteria have under the Americans with Disabilities Act?
Workplace rights
What standards does the American Disabilities Act for Accessible Design along with Title II and Title III regulations say is required for a building or facility to be physically accessible to people with disabilities?
- Newly constructed buildings and facilities
-Alterations/ renovations made to buildings and facilities
- Architectural changes to provide "program access"
- Removing architectural barriers that are easily accomplishable
Universal Design
The design and composition of an environment so that it can be accessed, understood, and used to the greatest extent possible by all people, regardless of their age, size, or disability
What places does universal design include?
- Public places in the built environment (e.g. buildings, streets)
- Spaces that the public has access to
- Products and services provided in those places
- Available systems (e.g. information communication technology)
7 Principles of Universal Design
1. Equitable use
2. Flexibility of use
3. Simple and intuitive use
4. Perceptible information
5. Tolerable for error
6. Low physical effort
7. Size and space for approach and use
Equitable Use
Useful and marketable to people with diverse abilities
What does equitable use not stigmatize or disadvantage?
Any group of users
Flexibility of Use
Accommodates a wide range of individual preferences and abilities
Simple and Intuitive Use
Easy to understand regardless of user's experience, knowledge, language skills, or concentration level
Perceptible Information
Communicates effectively to user regardless of encompassing conditions or sensory abilities
What does the tolerance for error minimize in Universal Design?
Hazards and adverse consequences of accidental or unintended actions
Low Physical Effort
Can be used efficiently, comfortably, and with minimum fatigue
Size and Space for Approach and Use
Can be used regardless of user's body size, posture, or mobility
4 Considerations of Environmental Modifications
1. Appropriation
2. Rootedness
3. Regeneration
4. Warmth
How can occupational therapists support personal autonomy?
By providing adequate human help and assistive technology (appropriation)
What do occupational therapists need to ensure meaningful daily occupations can be maintained through?
Retraining or environmental supports (rootedness)
What do occupational therapists need to consider when making environmental modifications?
How modifications may shift daily activities (regeneration)
Why should occupational therapists work with client's values when making environmental modifications?
To find compromises (warmth)
What funding and resources can patients use to make environmental modifications?
- Private insurance companies
- Medicaid waivers for home modifications
- Local independent living centers for additional grants or loans
- Rebuilding together
Rebuilding Together
Helps patients with disabilities live in their homes safely by changing different aspects of their environment