acidity and basicity pt2
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
37 Terms
Lewis Acids and Bases
concept is based on the fact that acid–base reactions involve the transfer of electron
pairs from one substance to another
acid
is a substance accepts an electron pair; electron pair acceptor.
base
is a substance that donates an electron pair; electron pair donor.
covalent bond
The donated electron pair is shared between the acid and the base in a _.
Lewis acids
much broader definition of
acid
Lewis acids
not limited to those with
hydrogen
Lewis acids
substances that have unfilled
valence orbitals
H2O, HCl, HBr, HNO3, H2SO4 (neutral proton donors)
Carboxylic acid, Phenol, Alcohol
Li+, Mg2+ (cations)
AlCl3, TiCl4, FeCl3, ZnCl2 (metal compounds)
Some Lewis acids
Lewis bases
substances with a pair of
nonbonding electrons
alcohol, ether, aldehyde, ketone, acid chloride, carboxylic acid, ester, amide, amine, sulfide, organotriphosphate ion
Some Lewis bases
Curved arrows
show where
the electrons start from and
where they end up!
not from lewis acid to the lewis base
in any rxn we show the flow of electrons, and you start from lewis base and point it to the destination lewis acid. when u donate electrons from lb to la there will be a covalent bond
flow of electrons, not protons
curved arrows show the
Lewis Acids
also called electrophiles
Lewis Acids
also called electrophiles because they are attracted to electrons (electron
pair acceptor)
Lewis Bases
also called nucleophiles
Lewis Bases
also called nucleophiles because they are attracted to protons (electron
pair donor)
arrhenius acid
produce hydrogen or hydrroneum ions in aq solns
arrhenius bases
produce hydroide ions in aq solns
bronsted lowry acids
proton donors
bronsted lowry bases
proton acceptor
lewis acids
electron pair acceptors
lewis bases
electron pair donors
Organic Acids
Organic compounds that contain a hydrogen atom bonded to an electronegative oxygen
atom (O-H)
Organic Acids
Organic compounds that contain a hydrogen atom bonded to a carbon atom next to a
C=O bond (O=C-C-H)
15.54
methanol pKa
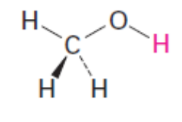
4.76
acetic acid pKa
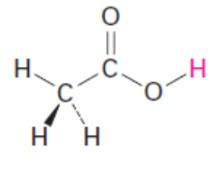
19.3
acetone pKa
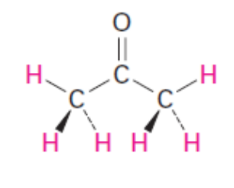
alcohol, phenol, carboxylic acids, acetic acid
or, (aromatic alcohols) can behave as acids because they contain hydrogen bonded to an electronegative oxygen
Organic Bases
org compounds that act as bases including Nitrogen-containing compounds
Organic Bases
Oxygen-containing compounds (if reacting with a sufficiently strong acid)
methylamine, methanol, acetone
org bases ex
carboxylic acid
most common ex org acid
amines
most common ex org base
methylamine
- may lone pair on nitrogen
methanol
- can act as acids, but since may lone pair sa oxygen if reacted sa strong acid
acetone
- lone pairs on oxygen