8.1 RECOMBINANT DNA
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
20 Terms
what is biotechnology
technology that uses cellular processes to make products that are of use to humans.
what is artificial selection/selective breeding
A process where humans deliberately choose which organisms to reproduce to enhance or reduce specific traits in off spring. This involves selecting individuals with desired characteristics and mating them to produce new generations with those traits more pronounced.
why do we use alternative processes
because artificial selection is a slow and inefficient process. Genes are passed on by chance and it is necessary to wait for the next generation to mature before knowing the outcome.
what is genetic engineering/recombinant DNA technology
it involves the artificial modification of DNA, where DNA is either added or removed from a cell.
the dna produced is called the?
recombinant DNA
and the organism is the?
genetically modified organism (GMO)
what are the possible uses of recombinant DNA technology
introducing desired traits into organisms
using harmless bacteria to produce proteins
replacing faulty genes
introducing DNA from a species into another species
what is the organism produced from introducing DNA from a species into another species?
transgenic organism
what is the aim of transgenic organisms
to introduce a trait that is not normally present.
All transgenic organism are GMO’s but not all GMOs are transgenic.
One example is golden rice, developed to address vitamin A deficiency
who and how did a person invent the recombinant DNA technique
Stanley Norman Cohen and Herbert Boyer invented the technique in 1973.
technique was to isolate and amplify genes or DNA segment and insert them into a bacterial cell
the introduced genes became part of the transgenic organisms DNA and could be passed on from one generation to the next.
what must be done for a genetic engineering to be possible
the gene for the desired trait must be identified then isolated
next the DNA gene must be “opened'“ and the gene is then added to the recipient and joins it’s DNA
what is a recognition site/recognition sequence
certain enzymes in bacteria are able to resist the duplication of bacteriophages by cutting up the viral DNA.
these enzymes always cut the DNA at a point where there is a certain sequence of bases.
what is a restriction enzyme
the enzyme that cuts the DNA, restricting the duplication of bacteriophages
what is a restriction enzyme an example of
endonucleases, enzymes that cut within a DNA molecule by separating two nucleotides.
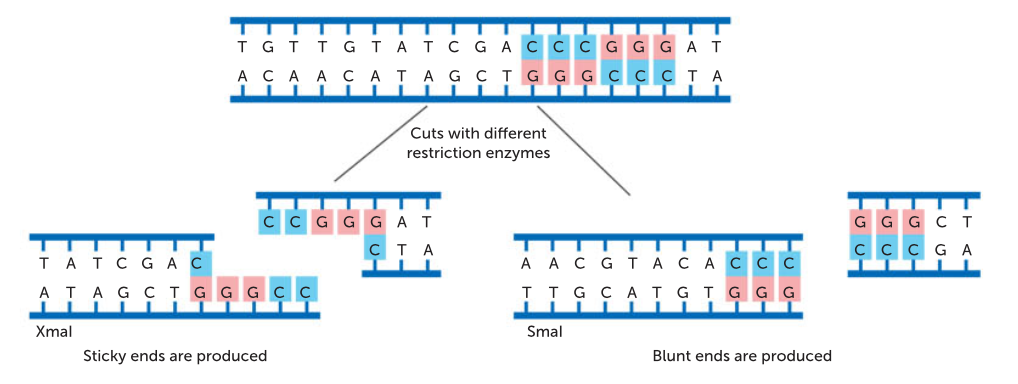
some restriction enzymes produce different types of cuts, what are these?
straight cut
blunt end
staggered cut
sticky end
straight cut
when the restriction enzyme makes a clean break across the two strands of DNA to produce a blunt end.
a blunt end is when both strands terminate in a base pair
staggered cut
results in fragments with sticky ends
a sticky end is a stretch of unpaired nucleotides in the DNA molecule that overhang at the break in the strands
recognition sites are -
four to eight base pairs long and are palindromic
which means that they have the same sequence when read both forwards and backwards.
this means that the same sequence occurs on both strands within the recognition site, therefore both strands will be cut, forming two segments.
what factors contribute to the type of cut a restriction enzyme will do
the recognition of a certain base sequence
the cut at a certain point