Blood Supply
1/140
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
141 Terms
what does external carotid artery do
provides blood to superficial areas of head and neck
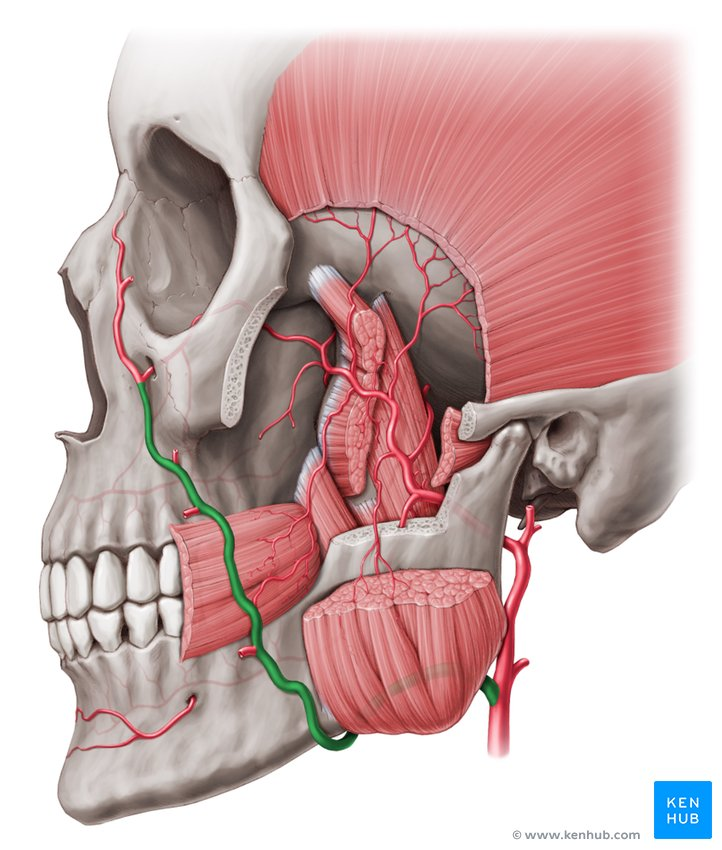
important external carotid artery branches
facial artery, maxillary artery, superficial temporal artery
where does the facial artery branch and where does it go
branches at the mandible
goes across the cheek to the medial canthus of the eye
what is the terminal branch of the facial artery
angular artery
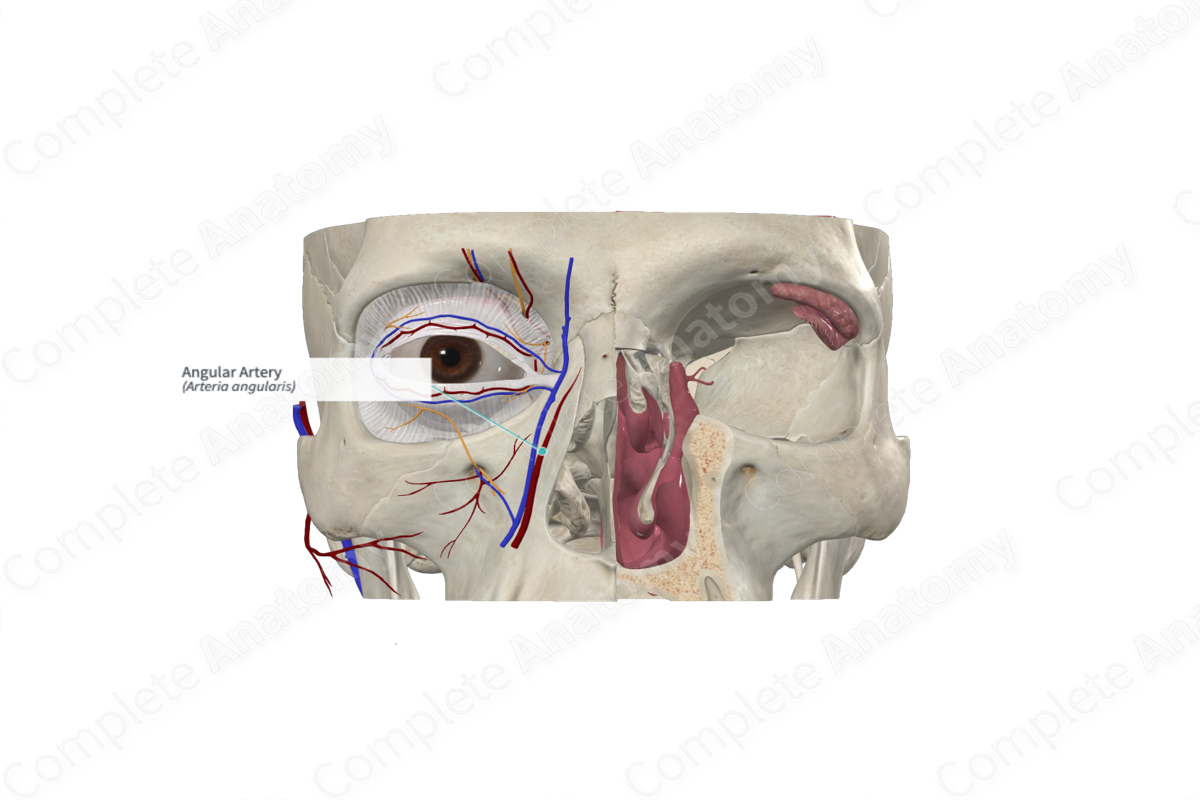
function of angular artery
supplies medial canthus
communicates with the dorsal nasal artery (from the ophthalmic artery)
where does the maxillary artery start
in front of the ear in the parotid gland
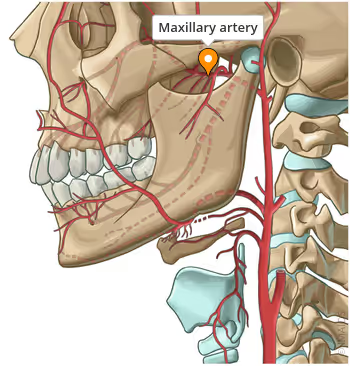
what branch of the maxillary artery enters the orbit
infraorbital artery
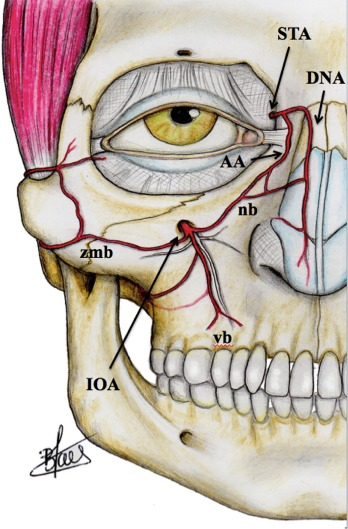
where does the infraorbital branch of the maxillary artery enter and leave the orbit
enters the orbit through the inferior orbital fissure
leaves the orbit through the infraorbital foramen
what does the infraorbital branch of the maxillary artery supply
when it enters the orbit: IO, IR
when it leaves the orbit: lower lid, lacrimal sac
where does the infraorbital branch of the maxillary artery go when it leaves the orbit
joins the angular artery and the dorsal nasal artery
where does the superficial temporal artery start
parotid gland
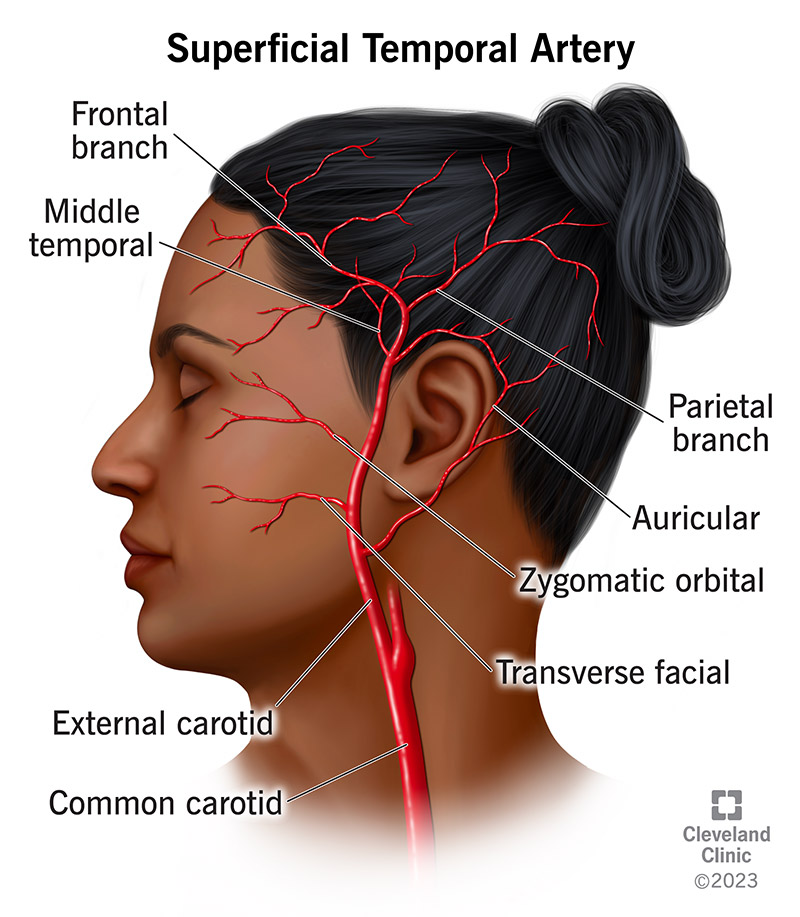
what does the superficial temporal artery supply
skin, muscles, and soft tissue of the face and orbit
what artery does the superficial temporal artery communicate with
ophthalmic artery (supraorbital branch)
what ocular arteries are damaged in giant cell arteritis (GCA)
short posterior ciliary arteries (in the circle of Zinn) are damaged
causes damage and suffocation of the ON leading to irreversible vision loss
superficial temporal artery becomes inflamed in GCA
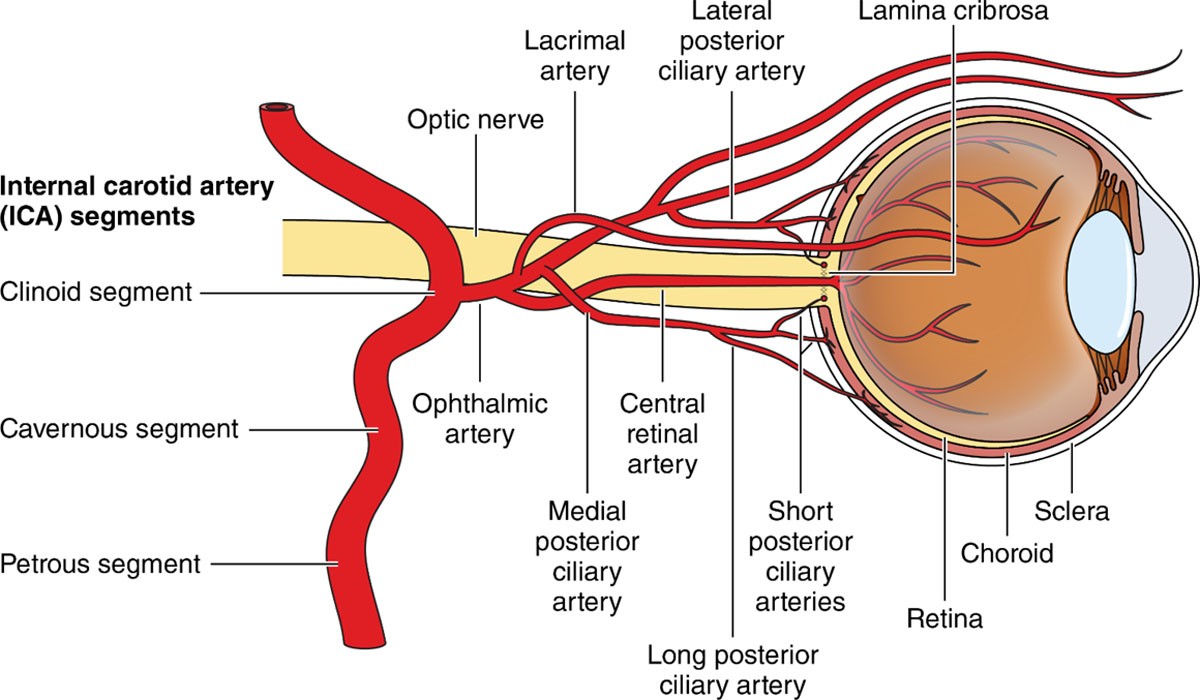
what does the internal carotid artery do
provides blood to structures in the cranium
what part of the internal carotid artery helps the external carotid artery supply areas of the superficial face and orbit
terminal branches of ophthalmic nerve
what happens if the supraorbital artery (branch of ophthalmic artery) is obstructed and cannot provide blood to the orbit
the supraorbital artery (of the ophthalmic artery) anastomoses with the superficial temporal artery
if the SOA is obstructed, the STA will temporarily provide a low level of circulation to the orbit
where does the ICA enter the skull and where does it go
enters through the petrous part of the temporal bone
travels through the cavernous sinus
what travels alongside the ICA in the cavernous sinus
CN VI
where are CN II and CN III located in relation to the ICA in the cavernous sinus
CN II is medial to the ICA as it exits the sinus
CN III is lateral to the ICA as it exits the sinus
what is the first branch of the ICA towards the orbit
ophthalmic artery
what would most likely be affected if there was an aneurysm of the ICA within the cavernous sinus
CN VI
where does the ophthalmic artery enter the orbit
optic nerve sheath
where does the ophthalmic artery travel after leaving the ON sheath
near medial wall of orbit between the LR and SO
what does the ophthalmic artery travel with after leaving the ON sheath
nasociliary nerve
branches of the ophthalmic artery
central retinal artery, lacrimal artery, muscular artery, short posterior ciliary artery, long posterior ciliary artery, supraorbital artery, ethmoid artery
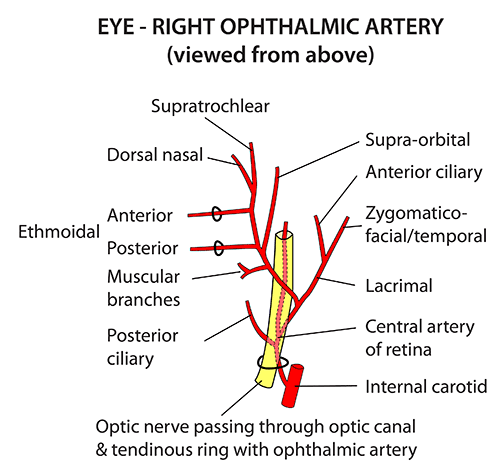
what is the first branch of the ophthalmic artery
central retinal artery
path of CRA
travels in ON, enters optic disc nasally, divides into multiple superior and inferior branches
what does the CRA supply
optic nerve and surrounding pia mater that it is traveling through
inner 2/3 of retina
lacrimal artery path
travels along lateral wall of orbit with lacrimal nerve
branches and terminates into lateral palpebral artery
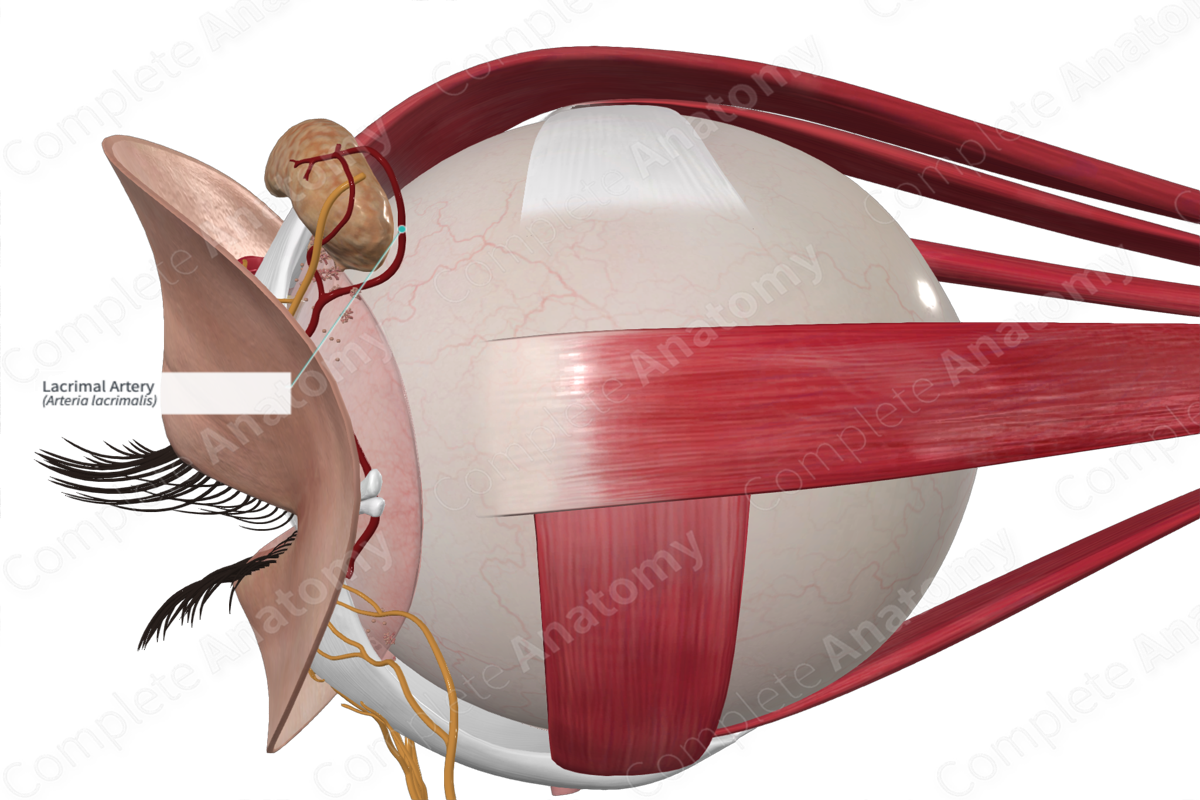
what does lacrimal artery supply
lateral rectus & lacrimal gland
what does lacrimal artery terminate into
lateral palpebral artery
what does the lateral palpebral artery supply
lateral inferior and superior lids
what forms the palpebral arcades
lateral (lacrimal artery branch) and medial (dorsal nasal artery branch) palpebral arteries anastomose to form palpebral arcades of the eyelids
what does the muscular artery supply
EOMs
name of 2 branches of the muscular artery
superior lateral and inferior medial
what does the superior lateral muscular artery supply
LR, SR, SO
what does the inferior medial muscular artery supply
MR, IR, IO
what are the anterior ciliary arteries made up of
branches of the muscular artery that supply the four recti muscles
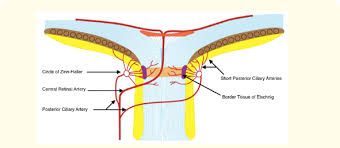
pathway of short posterior ciliary arteries
1-2 large branches enter the eye on either side of the ON and branch 10-20 times within the choroidal stroma
in the choroidal stroma, SPCA branches form the arterial network that supplies the ON head known as the circle of zinn
what do the SPCAs supply
posterior choroid and macula
what is the circle of zinn
branches of SPCAs that form a network in the choroidal stroma to provide blood to the optic disc
pathway of long posterior ciliary arteries
2 arteries enter the eye on either side of the ON and travel between the choroid and sclera, joining the SPCAs to supply blood to the choroid
they continue traveling forward to the ciliary body to join the anterior ciliary arteries and form the major arterial circle of the iris
what do the LPCAs supply
anterior choroid, ciliary body, iris
blood supply of the choroid
SPCAs supply posterior choroid (post seg)
LPCAs supply anterior choroid (ant seg)
what makes up the major arterial circle of the iris
anterior ciliary arteries from the muscular artery that supplies the recti
LPCAs
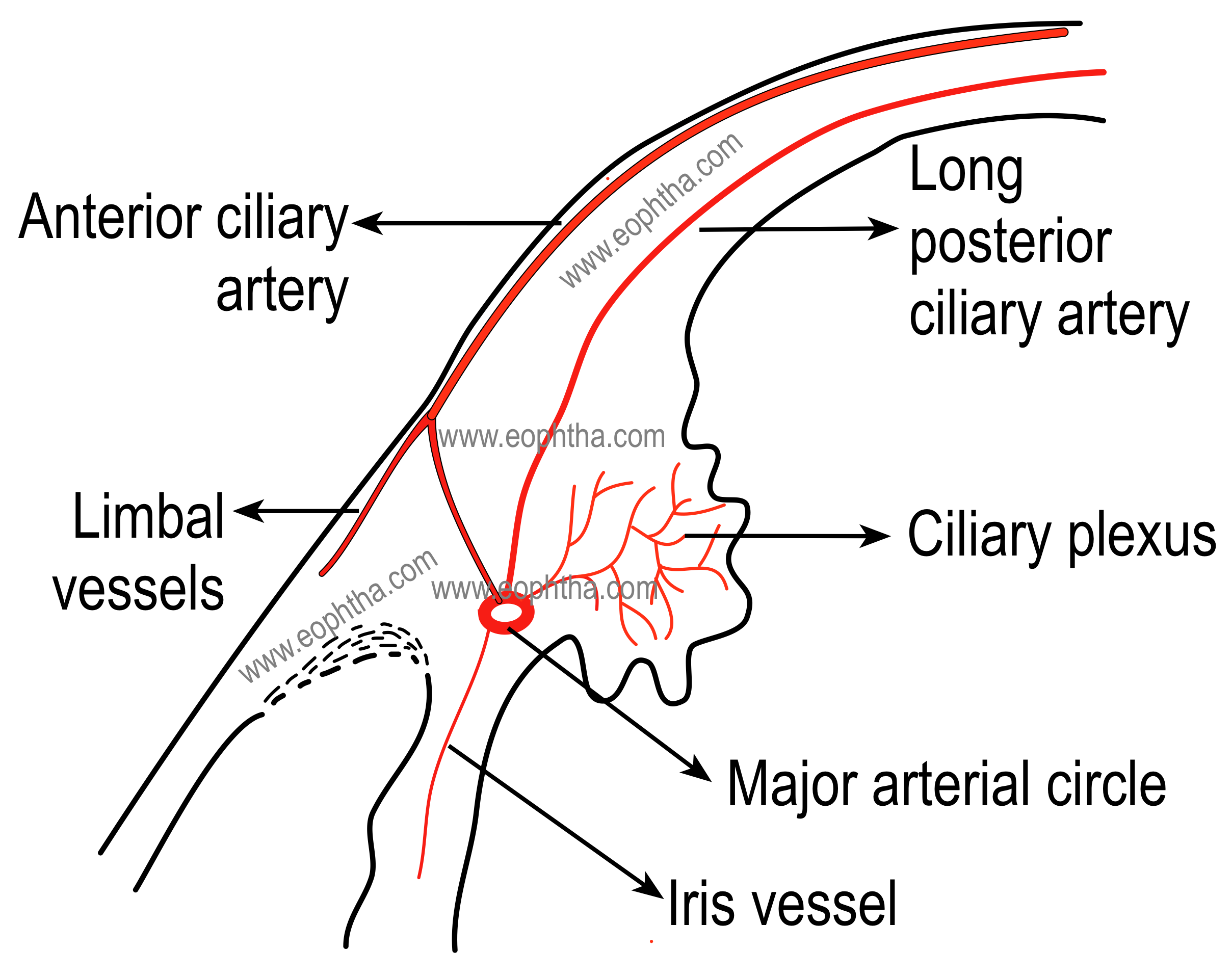
what is the major arterial circle of the iris
fenestrated capillaries in the ciliary body that leak out plasma, allowing aqueous humor to form
made up of anterior CAs and LPCAs
path of the supraorbital artery
goes into the orbit and exits the orbit through the supraorbital notch
what does the supraorbital artery supply
in the orbit: SR, SO, levator
once it exits the orbit, it supplies the superficial scalp and forehead alongside the superficial temporal artery of the ECA
what does the ethmoid artery supply
sphenoid, frontal, and ethmoid sinuses
what are the 2 terminal branches of the ophthalmic artery
supratrochlear artery & dorsal nasal artery
what does the supratrochlear artery supply
skin of the forehead and scalp, muscles of the forehead
pathways of dorsal nasal artery
supplies lacrimal sac and travels down side of nose to join angular artery (of facial artery of ECA) and later infraorbital artery (of maxillary artery of ECA)
what does the dorsal nasal artery supply
lacrimal sac
what does the dorsal nasal artery branch into
medial palpebral arteries that supply medial upper and lower lids and form palpebral arcades
ocular ischemic syndrome is the occlusion of the ________________
internal carotid or ophthalmic artery
how are orbital veins similar to veins in the head and neck (unlike the rest of the body)
do not contain valves
venous drainage does not correspond to arterial supply
central retinal vein pathway
exits the eye through the ON and enters the cavernous sinus (alone or with superior ophthalmic vein)
where does central retinal vein drain from
inner 6 layers of the retina supplied by the CRA
anterior ciliary vein pathway
follow path of anterior ciliary arteries across the recti and drain into superior and inferior ophthalmic veins
what do anterior ciliary veins drain
blood from anterior parts of the eye: ciliary body, conjunctiva, Schlemm’s canal
what do vortex veins drain
blood from choroid, at least 1 vein in each quadrant
largest vein in the orbit
superior ophthalmic vein
veins that drain into the superior ophthalmic vein
central retinal vein, superior vortex veins, muscular veins from the SR, SO, & MR (anterior ciliary veins), lacrimal vein
origin of the superior root of the superior ophthalmic vein
branches of the supraorbital and supratrochlear
where in the orbit does the superior root of the superior ophthalmic vein originate
superomedial orbital rim
origin of the inferior root of the superior ophthalmic vein
branches of the angular vein (of the facial vein)
what 2 roots form the superior ophthalmic vein and where
superior and inferior root of superior ophthalmic vein
join together behind the trochlea and medial to the superior rectus
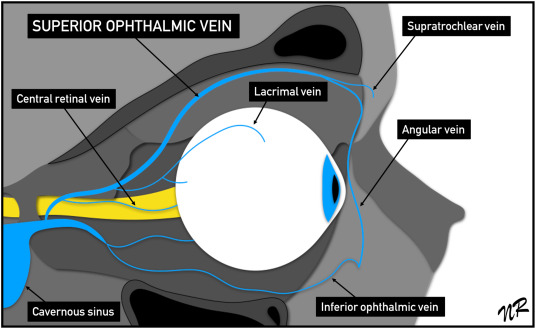
where does the inferior ophthalmic vein originate
network of veins along the anterior medial orbital floor between the globe and IR
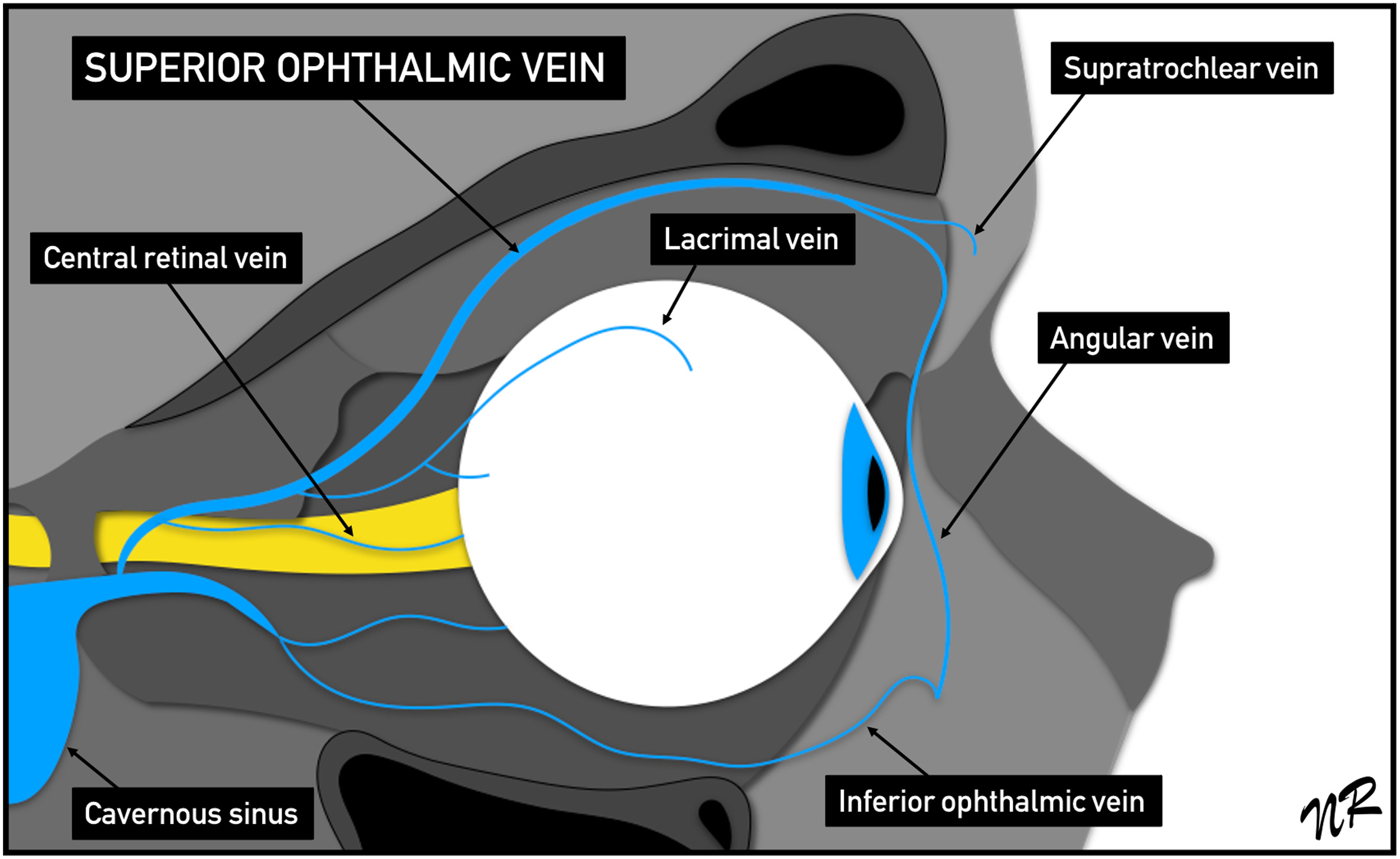
veins that drain into the inferior ophthalmic vein
muscular veins (drain the IR, IO, LR), inferior vortex veins, small veins (drain inferior conjunctiva, lower lid, lacrimal sac)
where do the 2 branches formed by the inferior ophthalmic vein exit the orbit
inferior branch: inferior orbital fissure
superior branch: superior orbital fissure
where do the inferior and superior branches of the IOV drain
inferior: pterygoid plexus to communicate with facial veins
superior: cavernous sinus, joining superior ophthalmic vein
where does the supraorbital vein originate
forehead
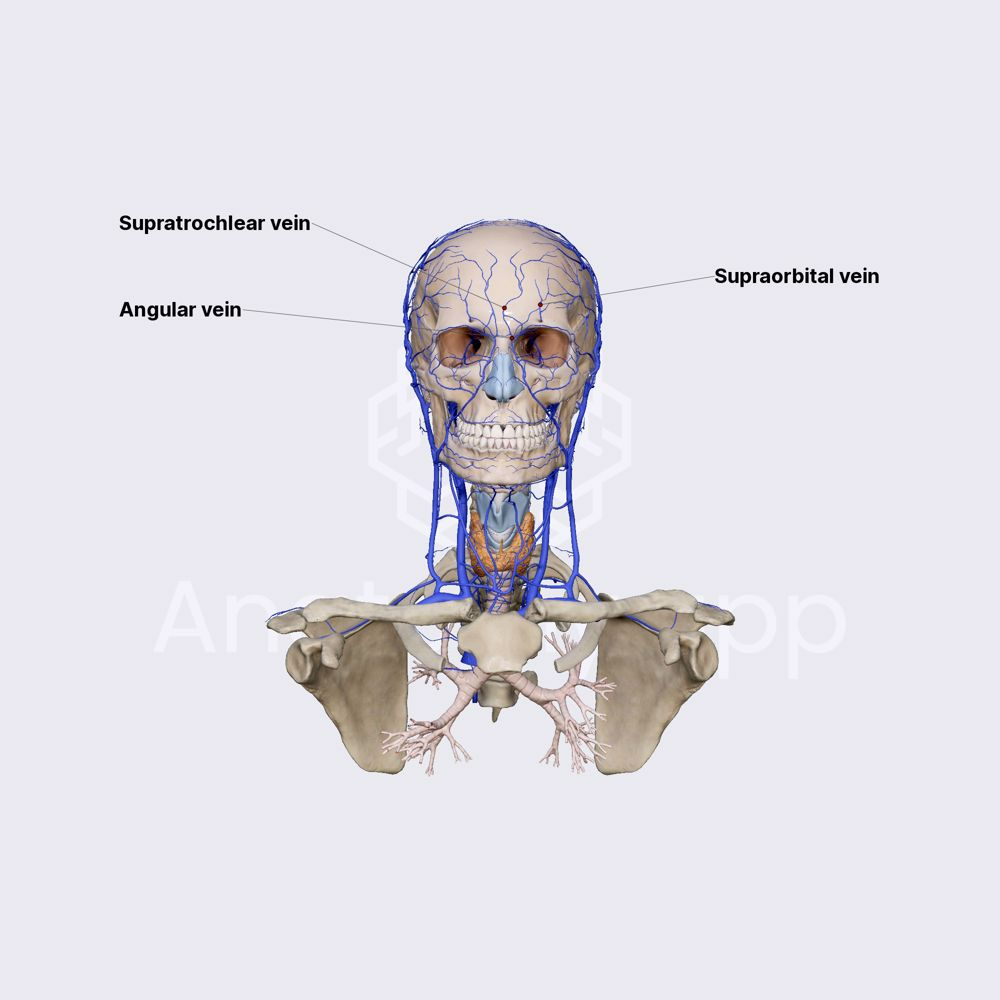
the supraorbital vein sends a branch through the ____________ to help form the ____________
supraorbital notch; superior ophthalmic vein
where does the frontal vein originate
venous plexus on the forehead
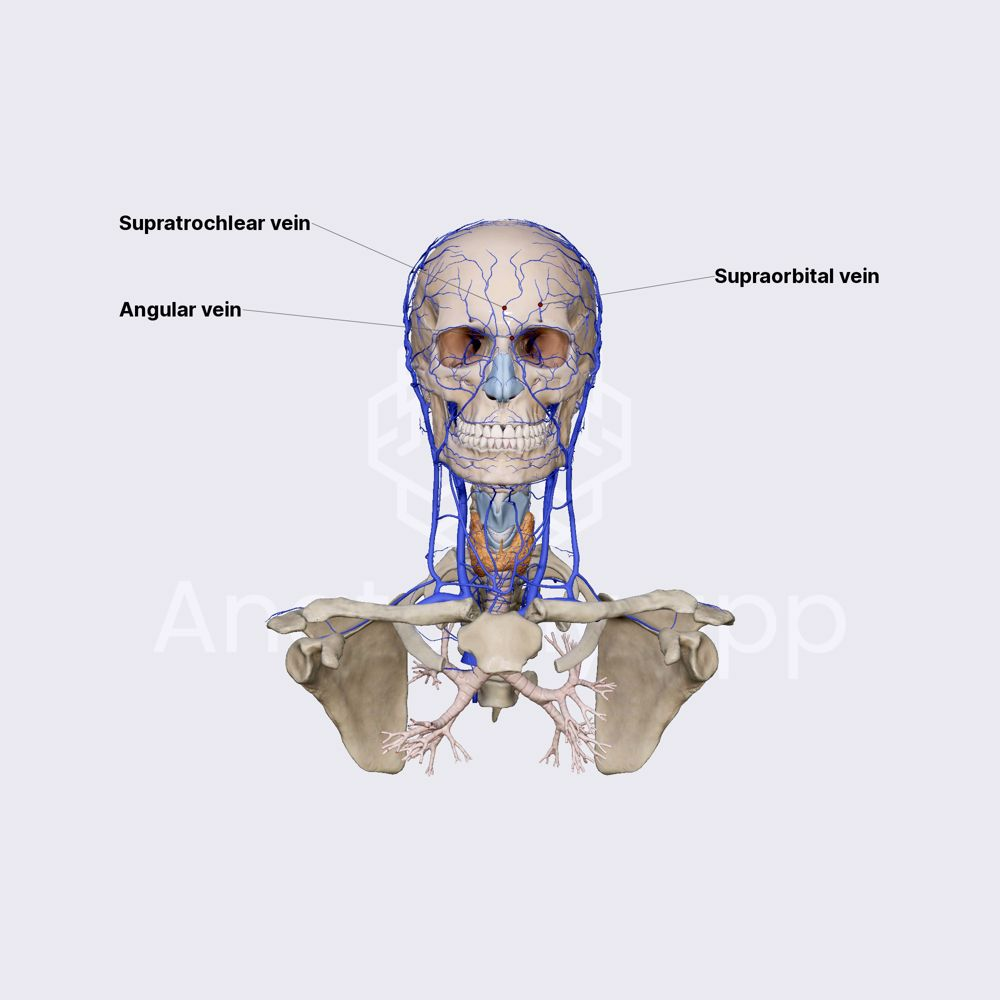
what 2 veins form the angular vein
supraorbital vein and frontal vein
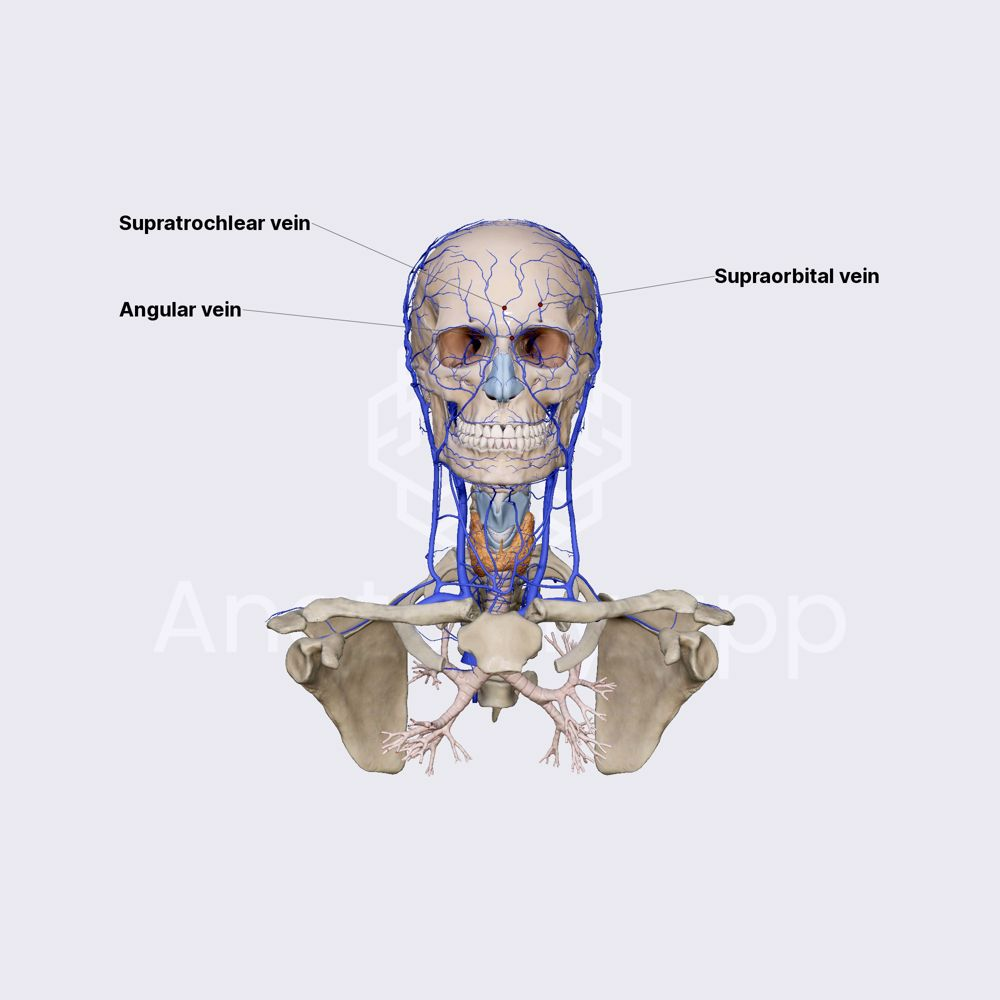
where does the angular vein originate
side of nose at the medial angle of the orbit
what 2 anterior vein branches help form the SOV
supraorbital branch of supraorbital vein and nasofrontal branch of angular veins
what vein does the angular vein form into and where
anterior facial vein at the inferior orbit margin
where does the anterior facial vein get blood from
superior and inferior palpebral veins, pterygoid venous plexus branch
what forms the common facial vein
anterior facial vein travels from the side of the nose to the masseter and joins the posterior facial vein forming the common facial vein
where does the common facial vein drain
internal jugular vein
what drains into the infraorbital vein
small superficial veins that drain the inferior orbit
where does the infraorbital vein enter the orbit and travel
enters the infraorbital foramen
travels along orbital floor in infraorbital groove
where does the infraorbital vein empty
pterygoid venous plexus
where is the pterygoid plexus located
infratemporal fossa
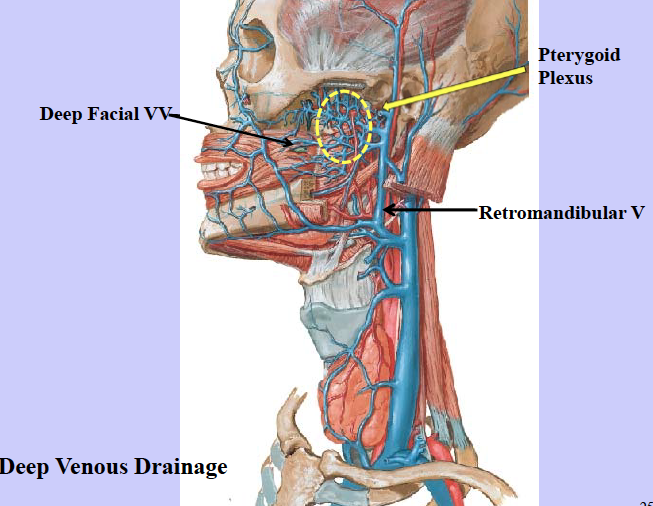
what does pterygoid plexus communicate with
anterior facial veins and cavernous sinus
what does the pterygoid venous plexus form
maxillary vein
what forms the posterior facial vein
superficial temporal vein and maxillary vein
what forms the superficial temporal vein
frontal and parietal branches of venous plexus
what vein originates from lateral palpebral venous branches
orbital vein
where does the orbital vein drain
middle temporal vein
where is the posterior facial vein formed
parotid gland
what does the anterior branch of the posterior facial vein do
joins anterior facial vein to form common facial vein and drains into internal jugular vein
what does the posterior branch of the posterior facial vein do
joins the posterior auricular vein to form the external jugular vein
where does the occipital vein originate
posterior vertex of the skull
where does occipital vein drain
internal jugular vein or posterior auricular vein to go to external jugular vein
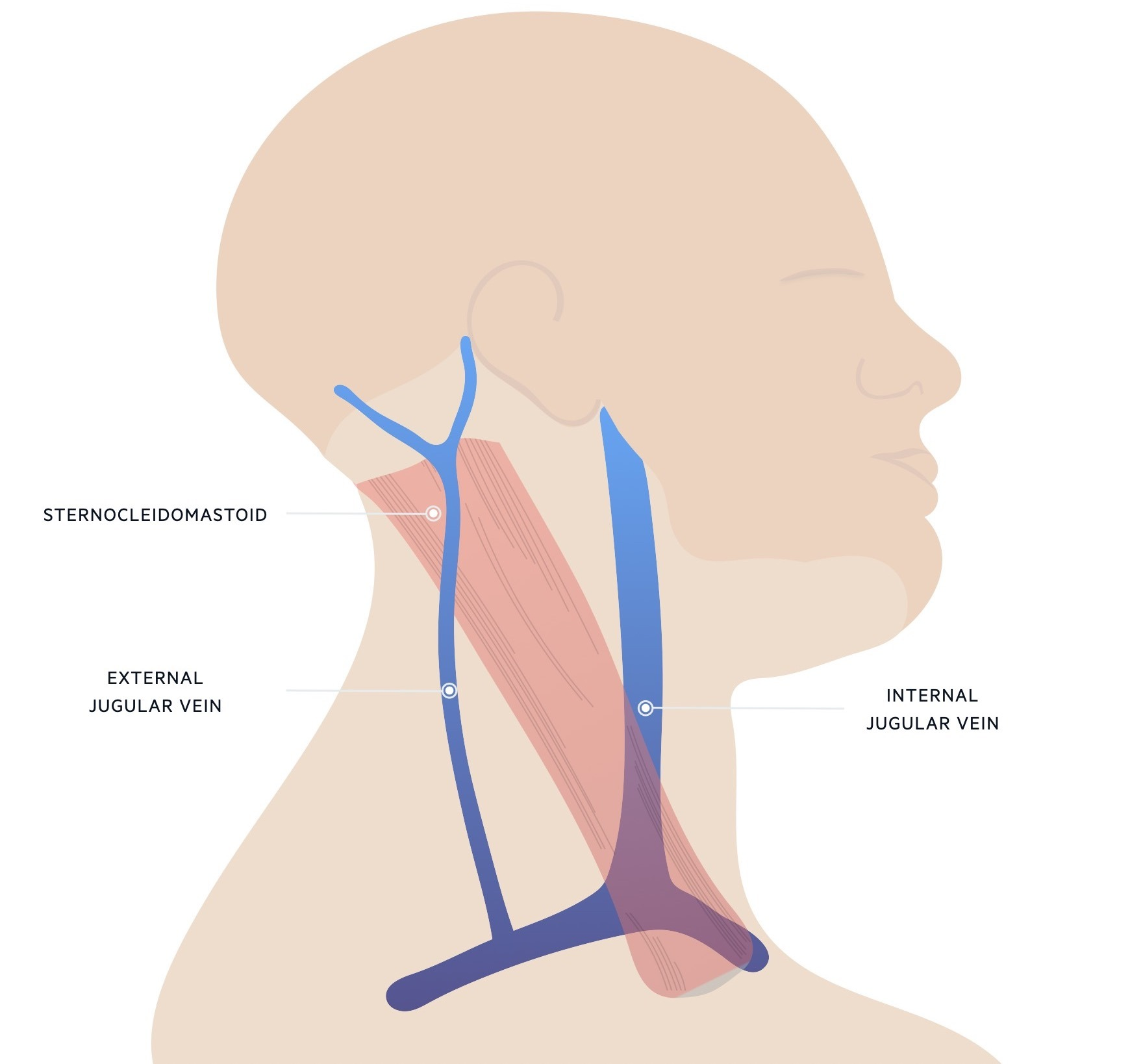
what is the external jugular vein
formed by retromandibular and posterior auricular veins, drains blood from superficial face
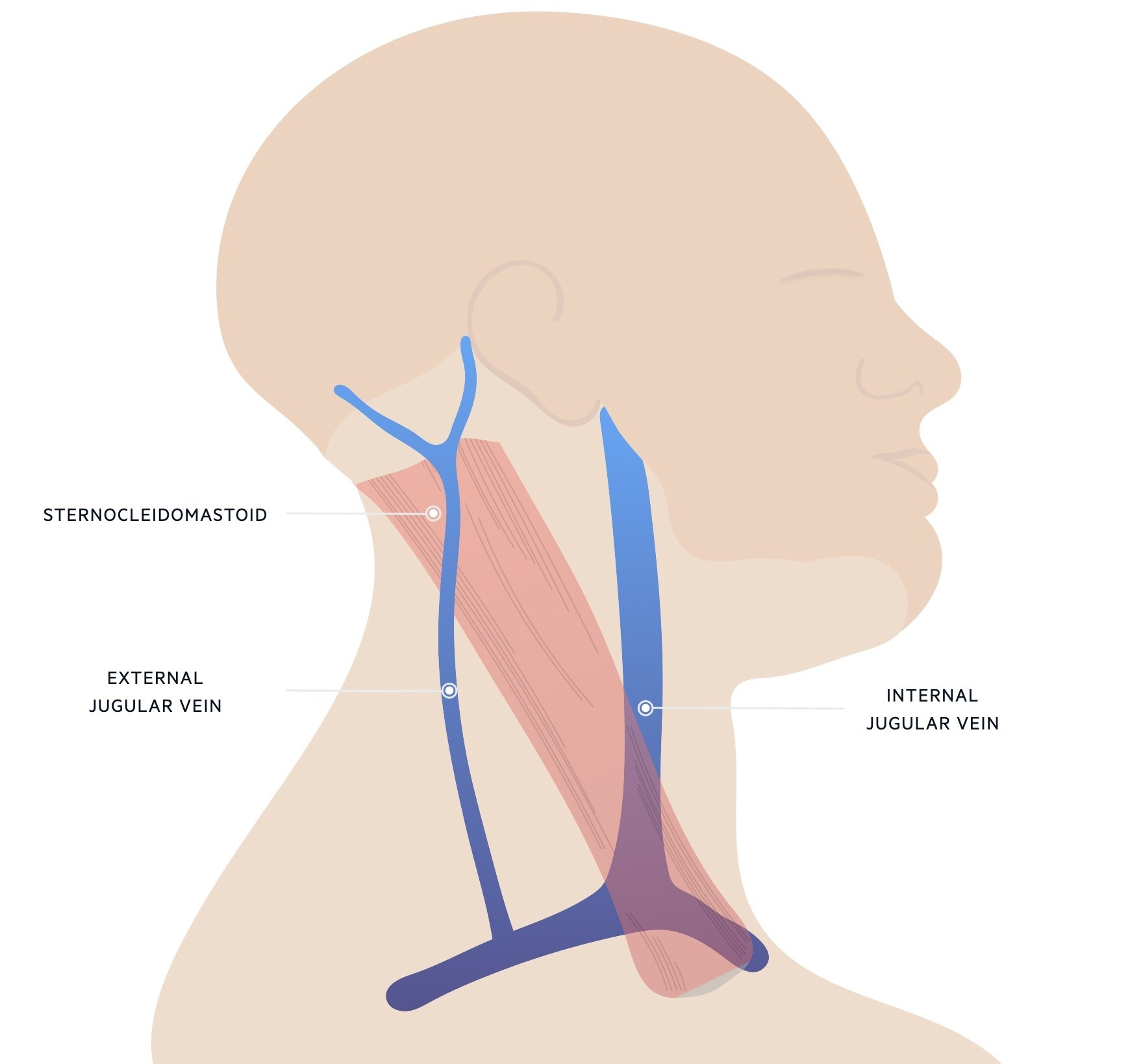
what is the internal jugular vein
continuation of sigmoid sinus, drains blood from internal facial veins
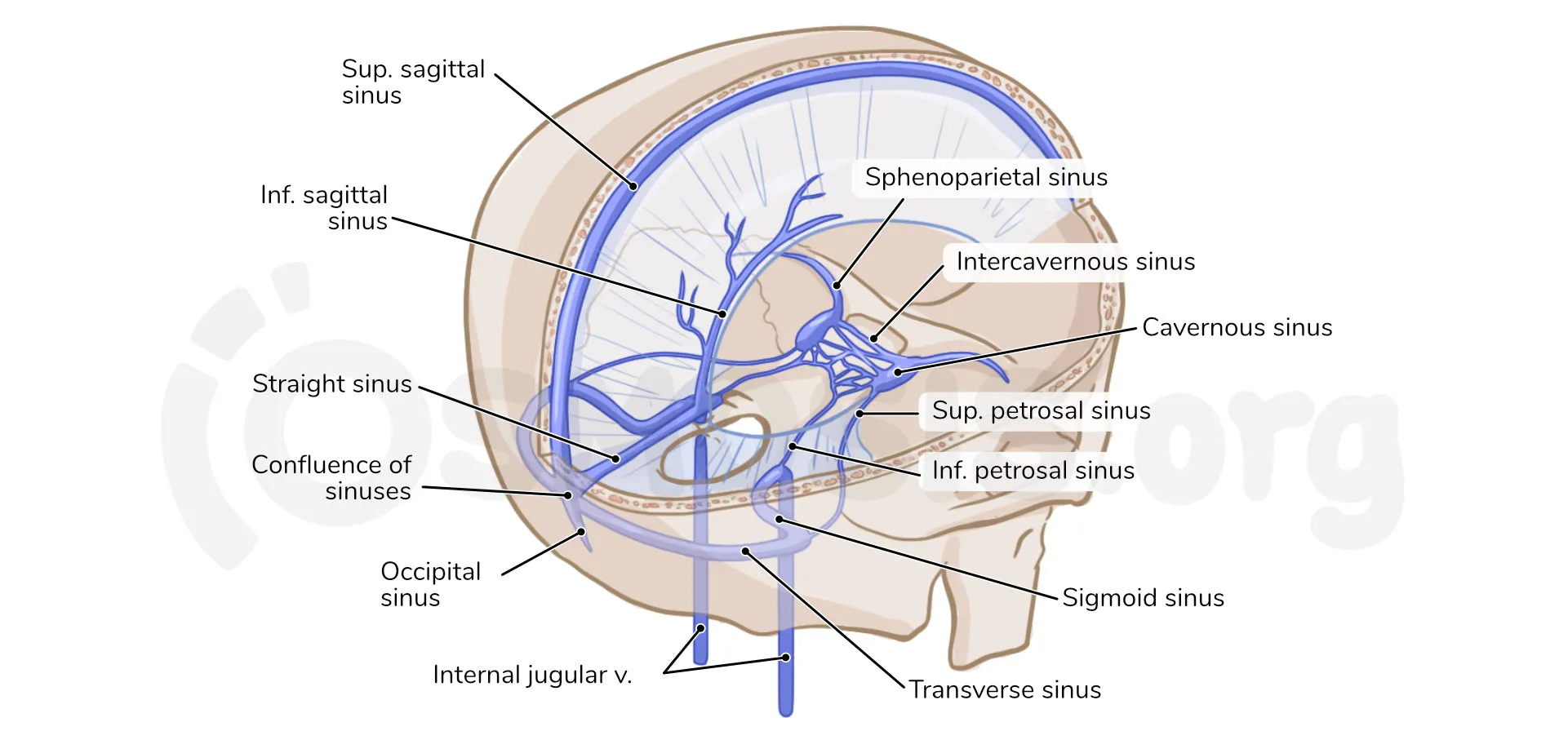
what are dural sinuses
venous channels in the dura mater of the brain that drain blood from the head back to the heart