247 practical 4
1/205
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
206 Terms
gonads
produce gametes and hormones
females: ovaries, eggs
males: testes, sperm
ducts
receive and transport gametes
females: fallopian tubes and uterus
males: epididymis, vas deferens, ejaculatory ducts
epididymis function
sperm cells mature as travel through here to vas deferens
vas deferens function
sperm from epididymis to ejaculatory ducts
ejaculatory ducts function
formed by union vas deferens and seminal vesicle ducts, carry sperm through prostate gland into urethra
accessory glands
secrete fluids into ducts
males: seminal vesicles, prostate gland, bulbourethral gland
females: Bartholin’s glands and Skene’s glands
seminal vesicles function
sugar and vitamin rich fluid, nourish sperm in semen
prostate gland function
secretes alkaline fluid thats part of semen
bulbourethral gland function
secretes mucus that becomes part of semen
perineal structures
collectively, external genitalia
gamete production males vs females
females 1 per month, retain and nurture zygote
males produce 100 million sperm / day
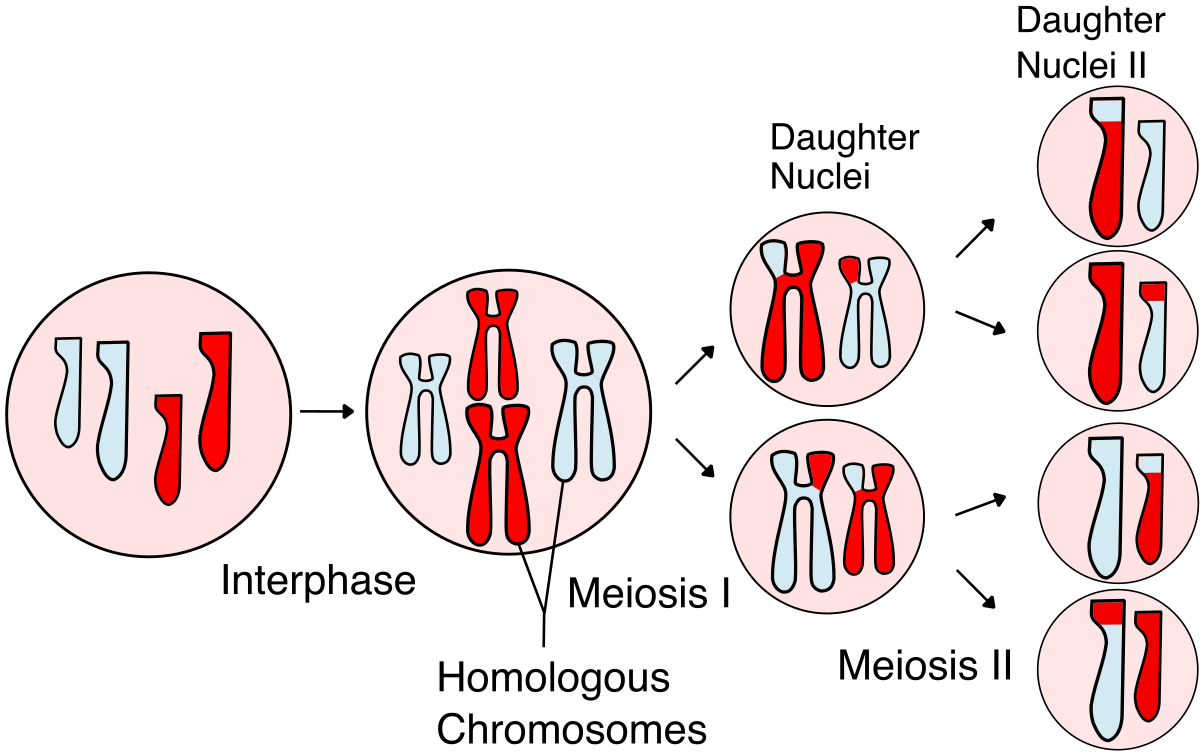
meiosis
produce sperm or eggs, cell splits twice, forming 4 daughter cells which have only ½ number of chromosomes as parent cell (haploid) hence egg + sperm = all 46 chromosomes
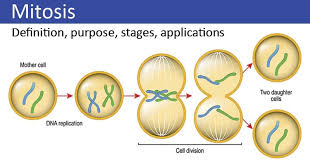
mitosis
single cell divides into 2 daughter cells, identical copies, new body cells
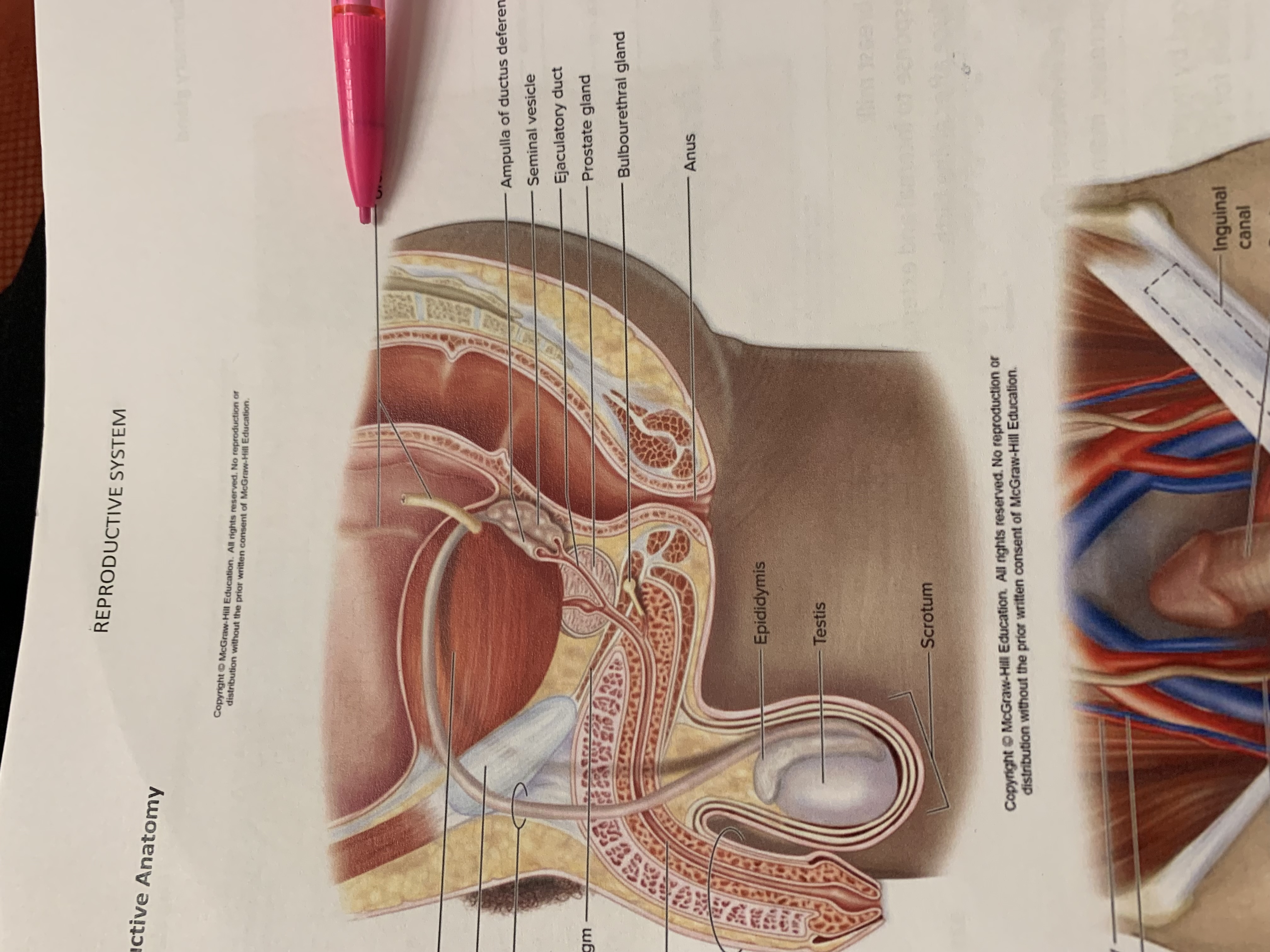
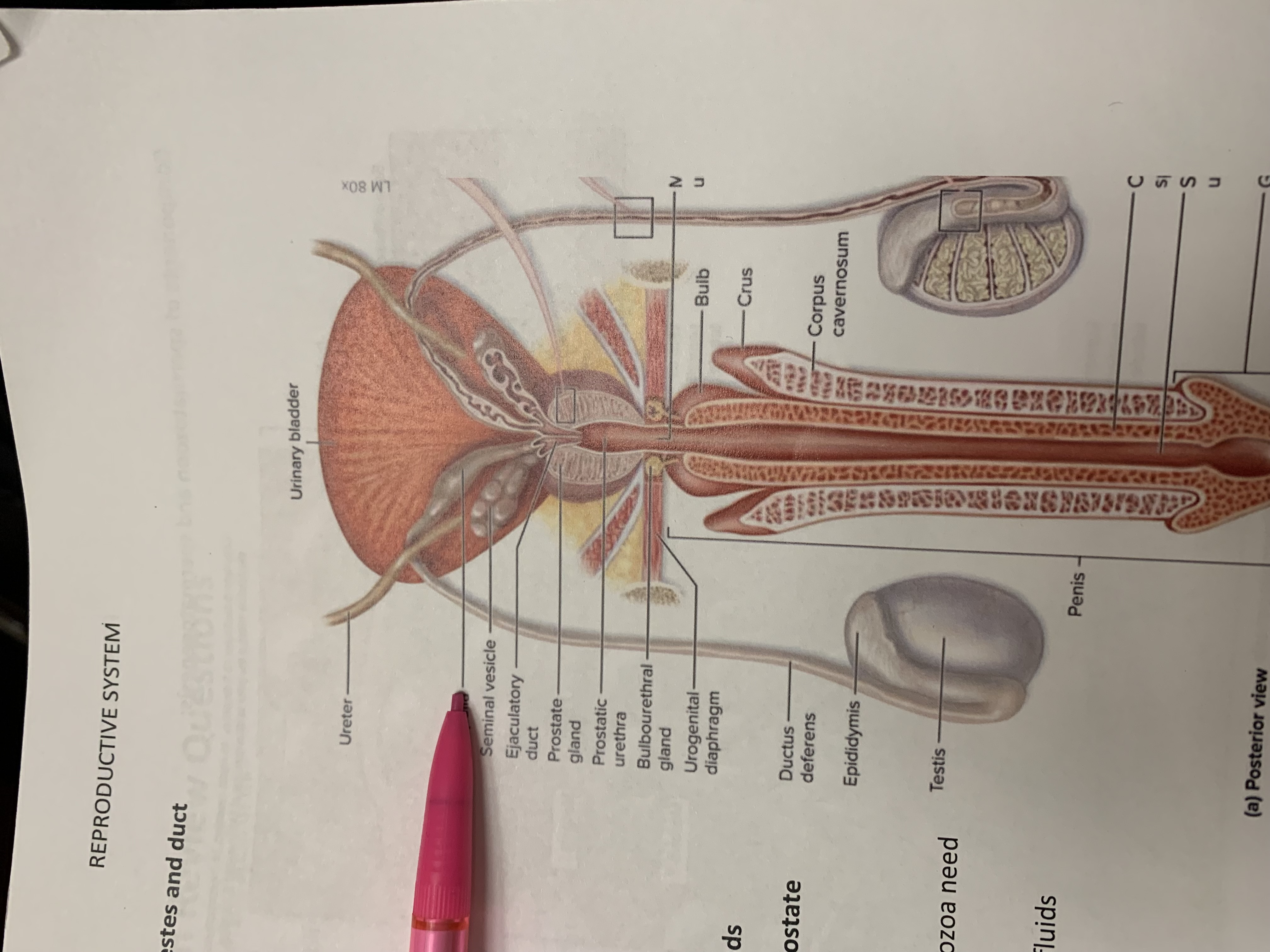
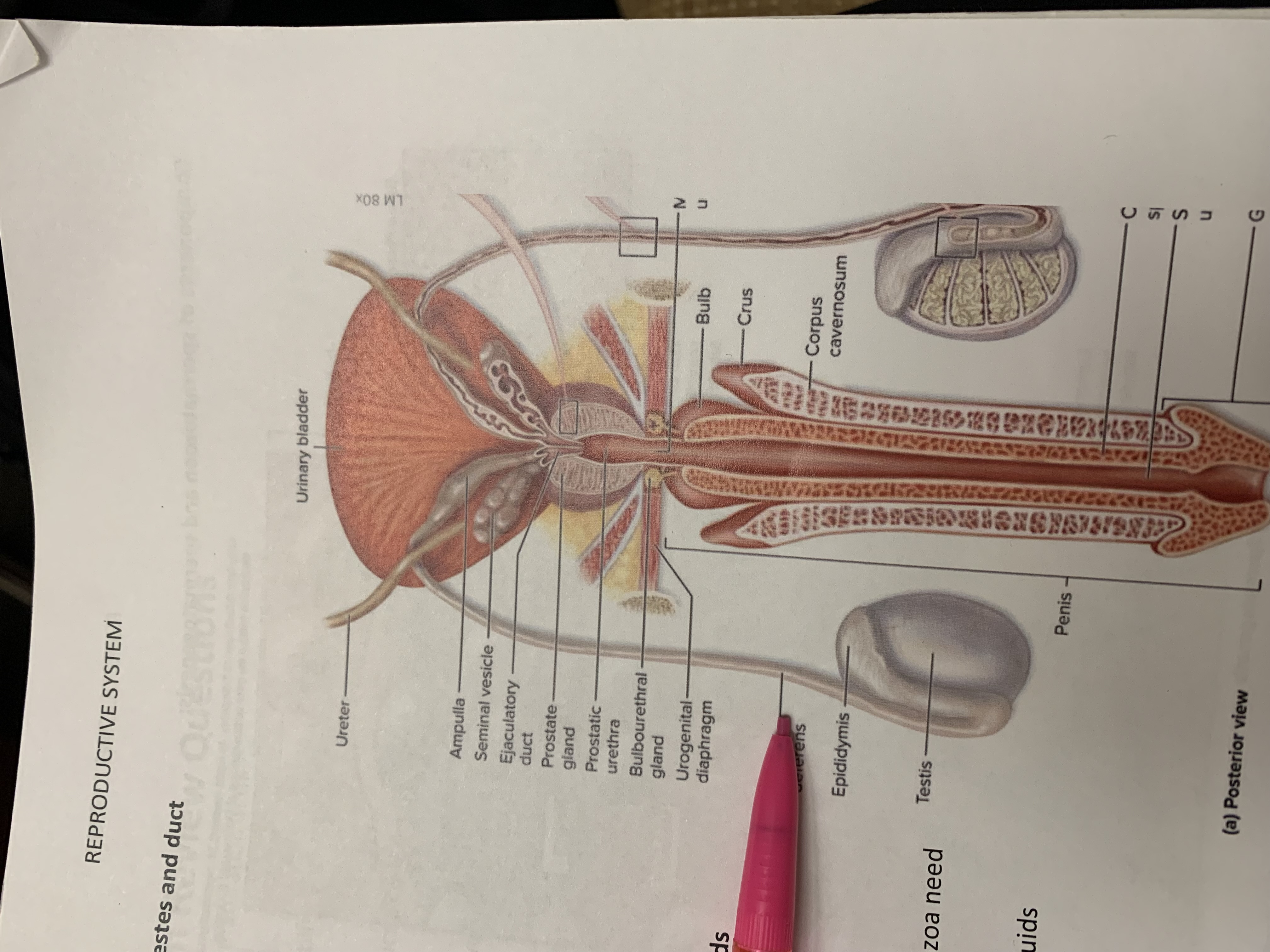
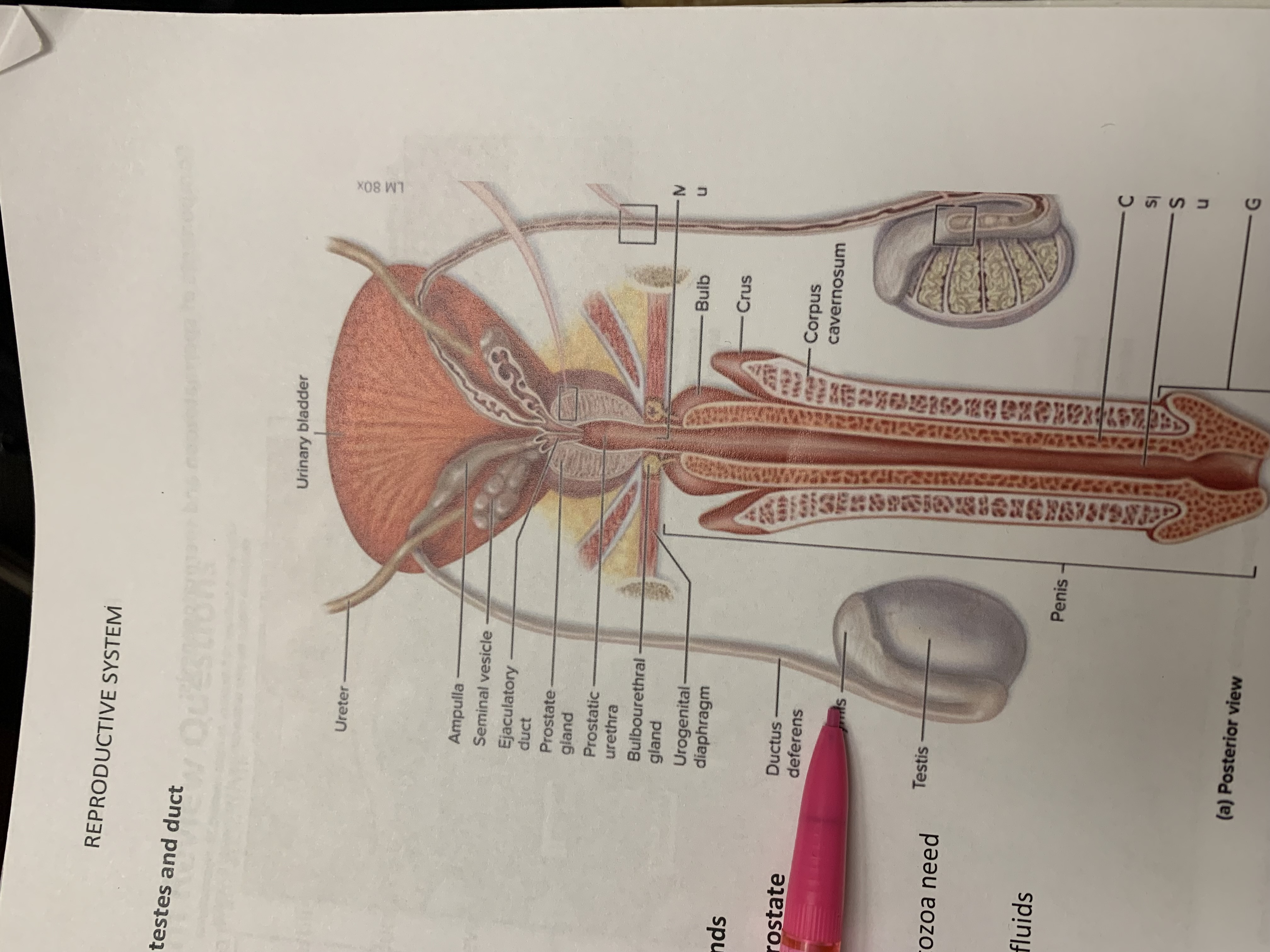
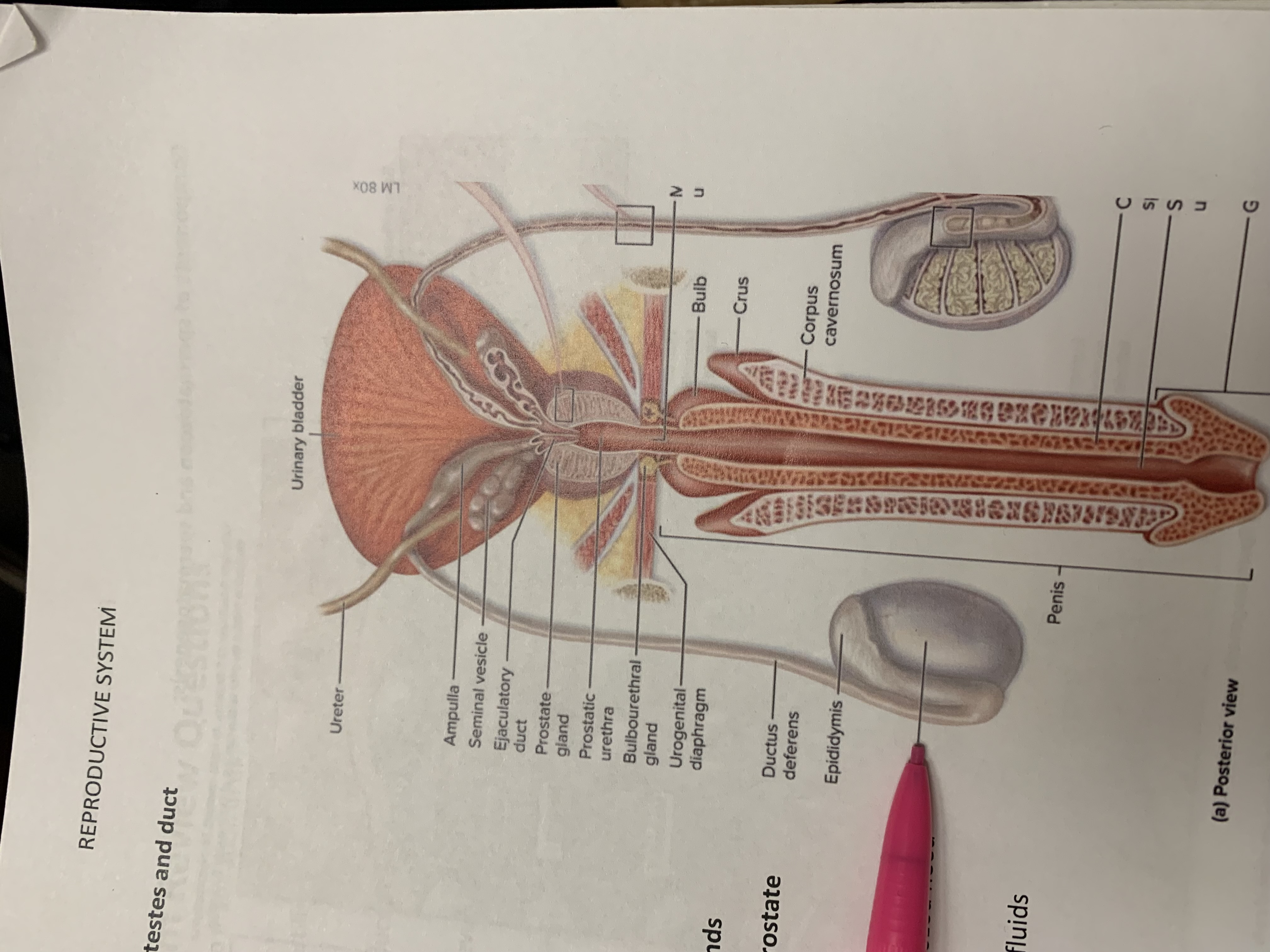
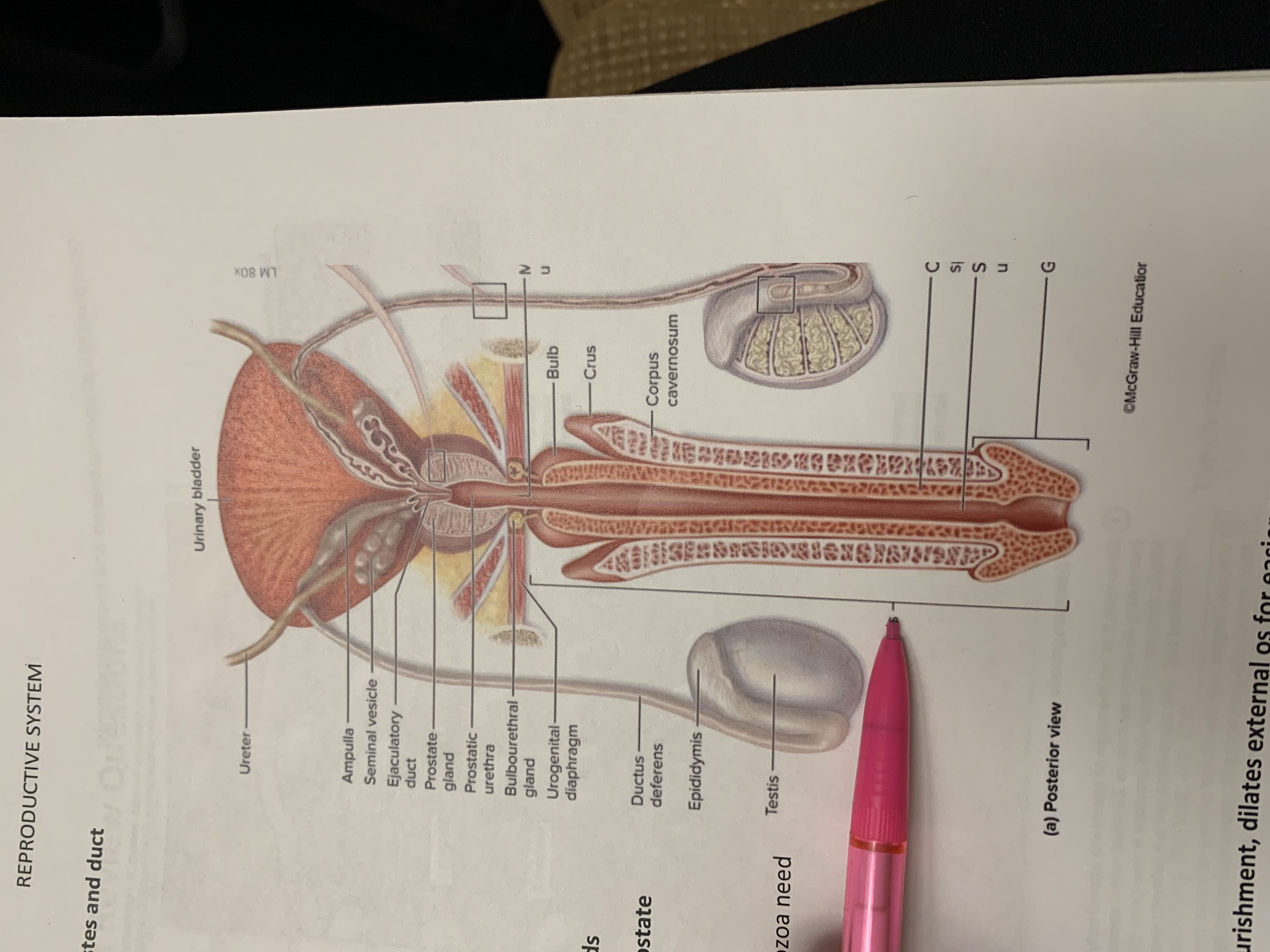
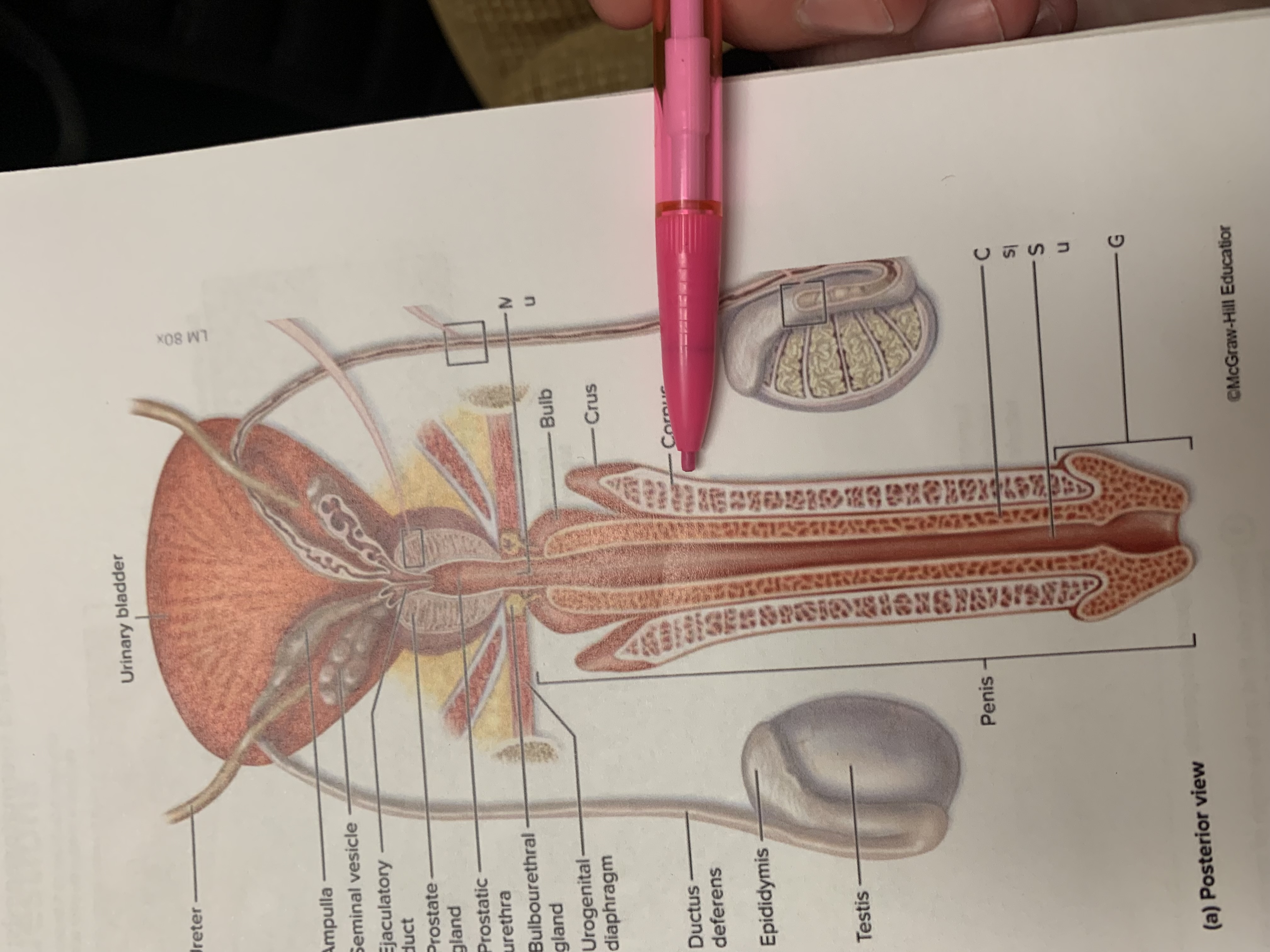
ureters
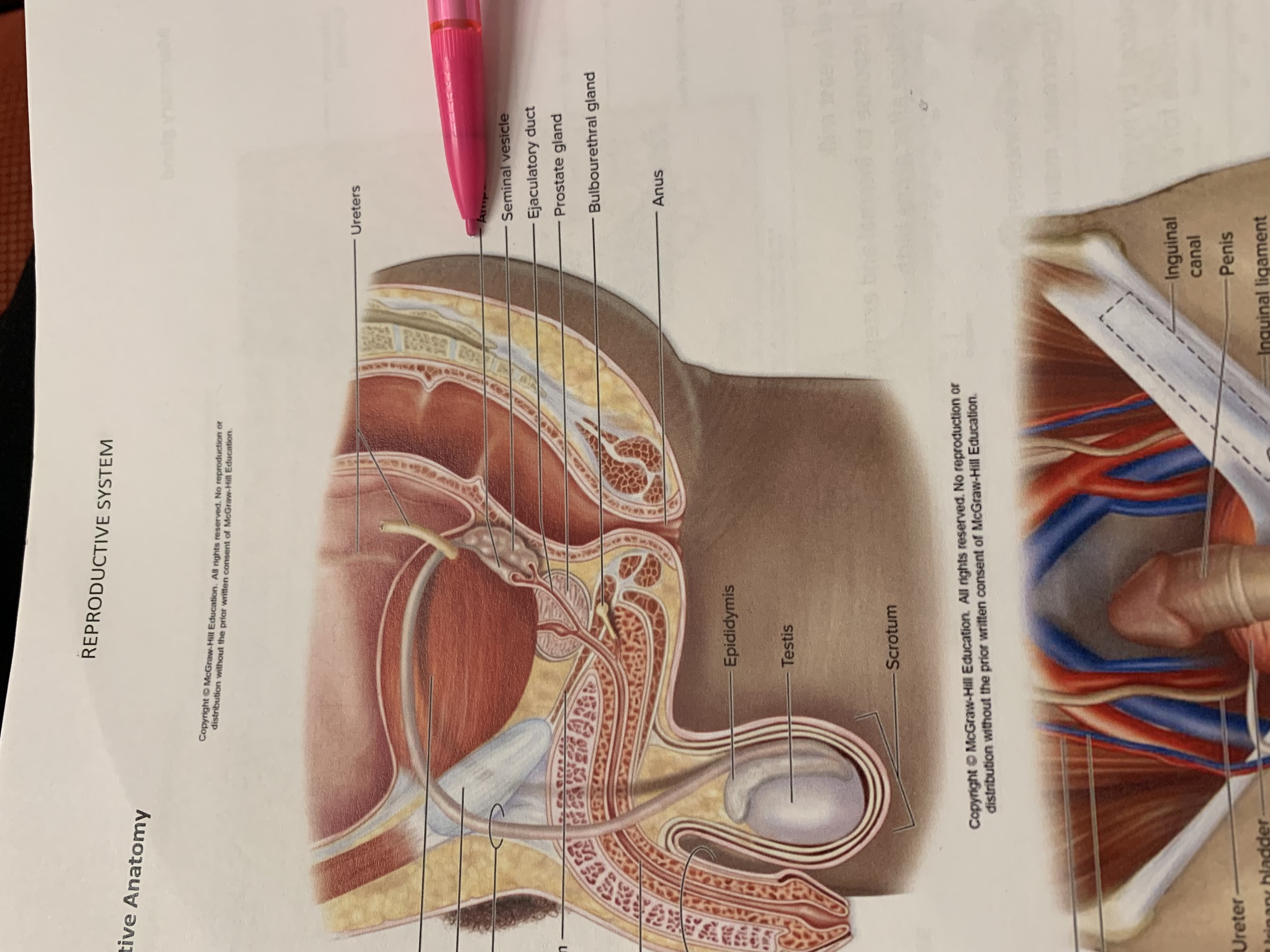
ampulla of ductus deferens
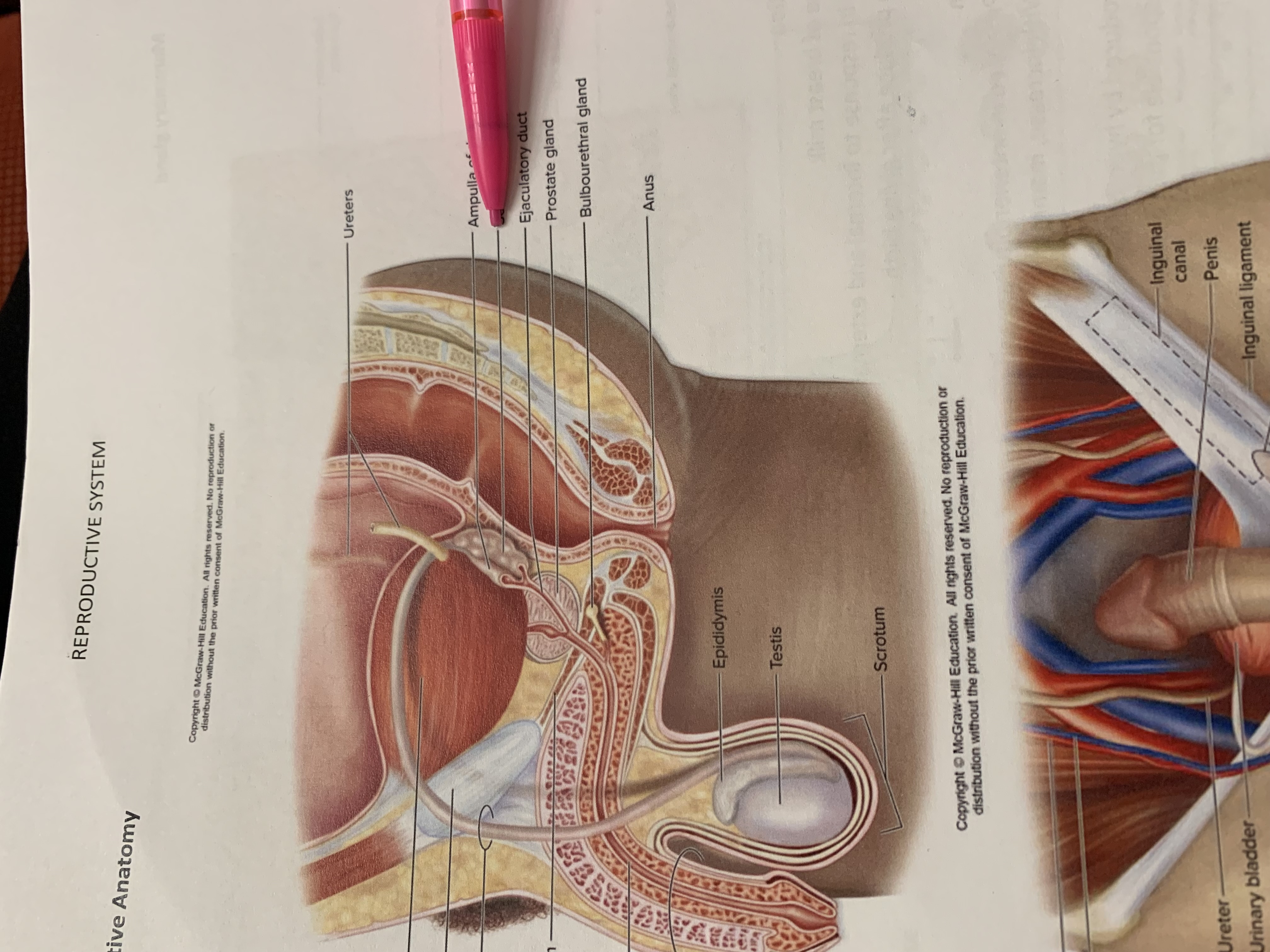
seminal vesicle
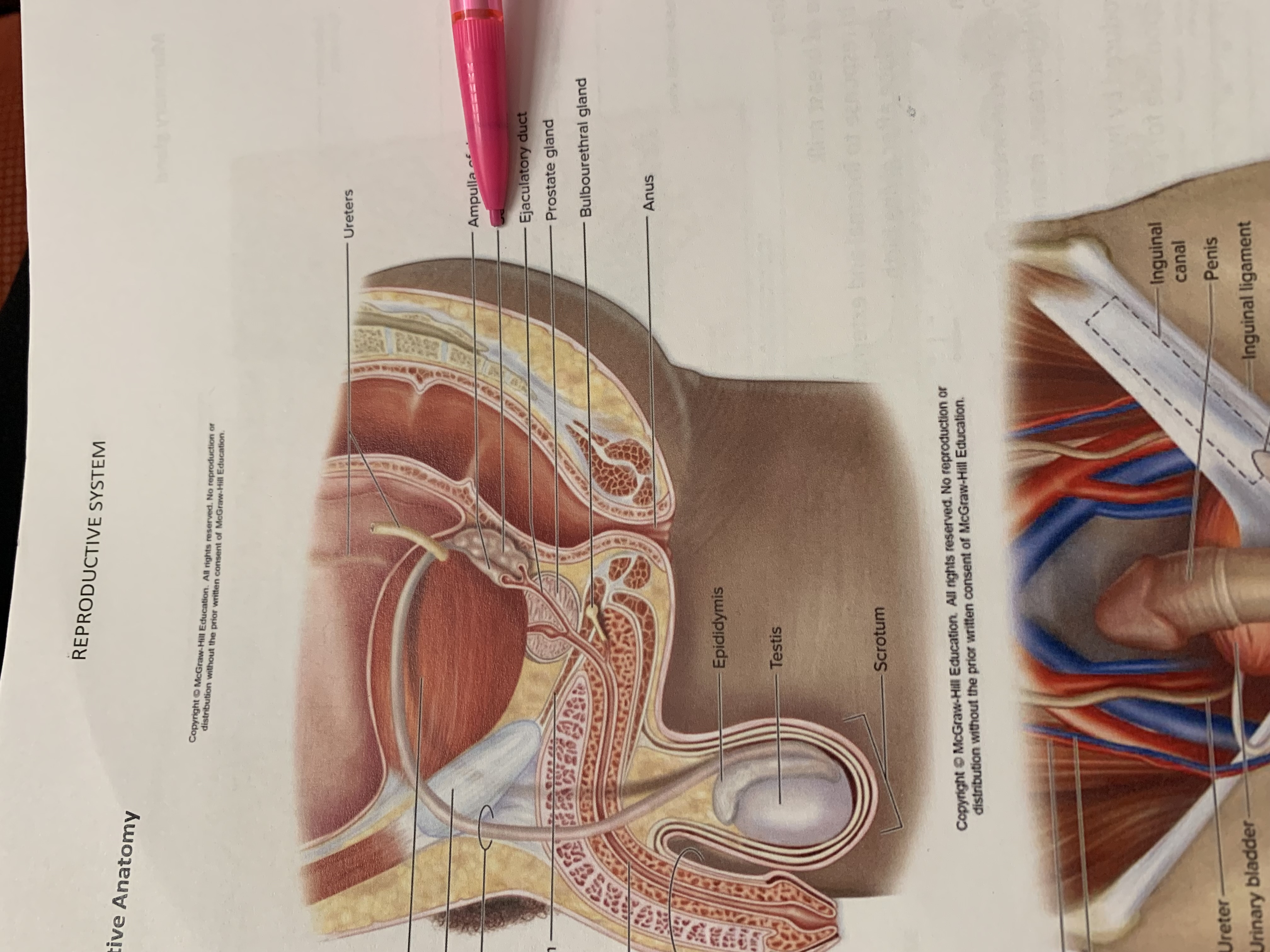
the one below pencil whoops
ejaculatory duct
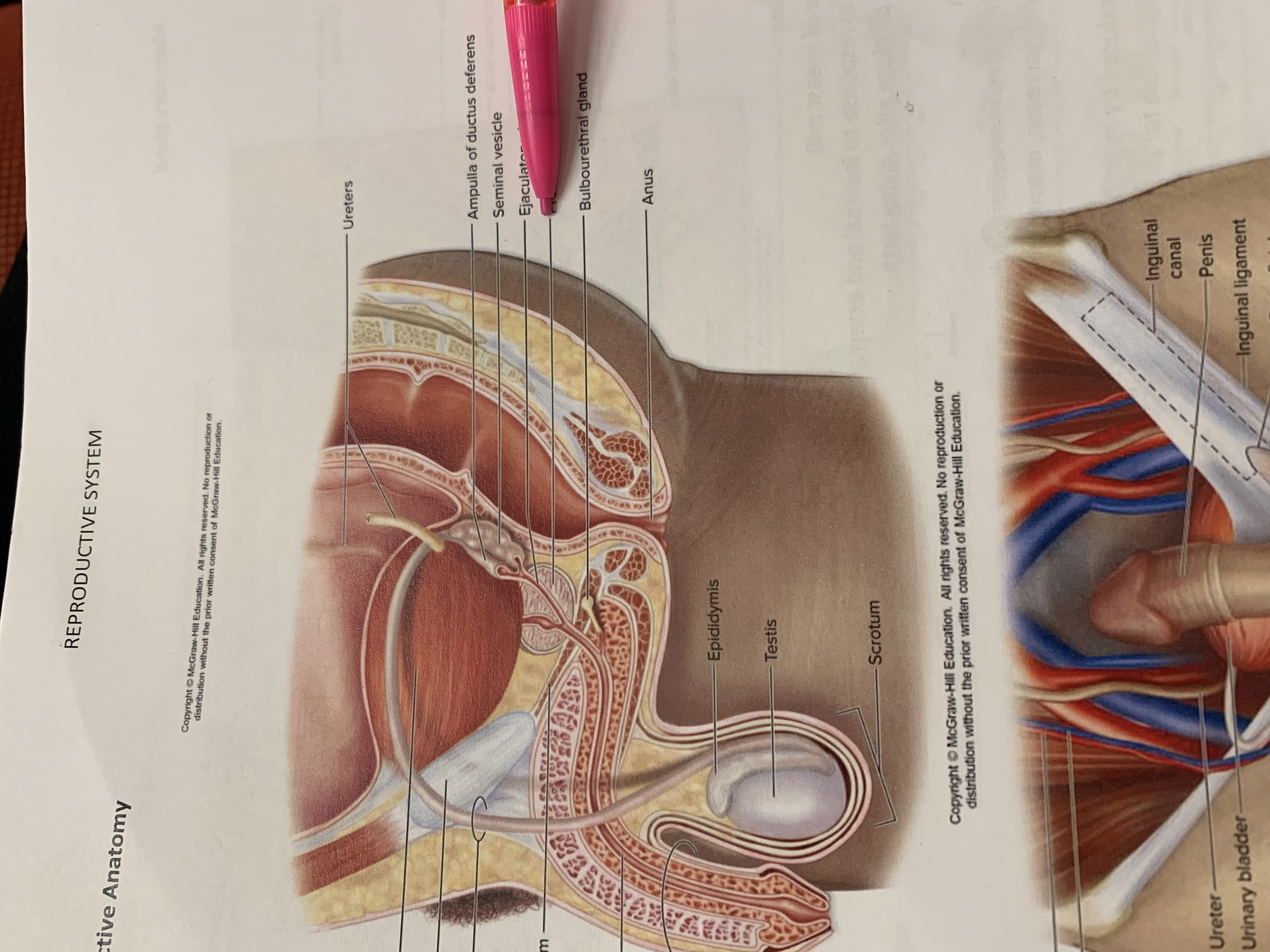
prostate gland
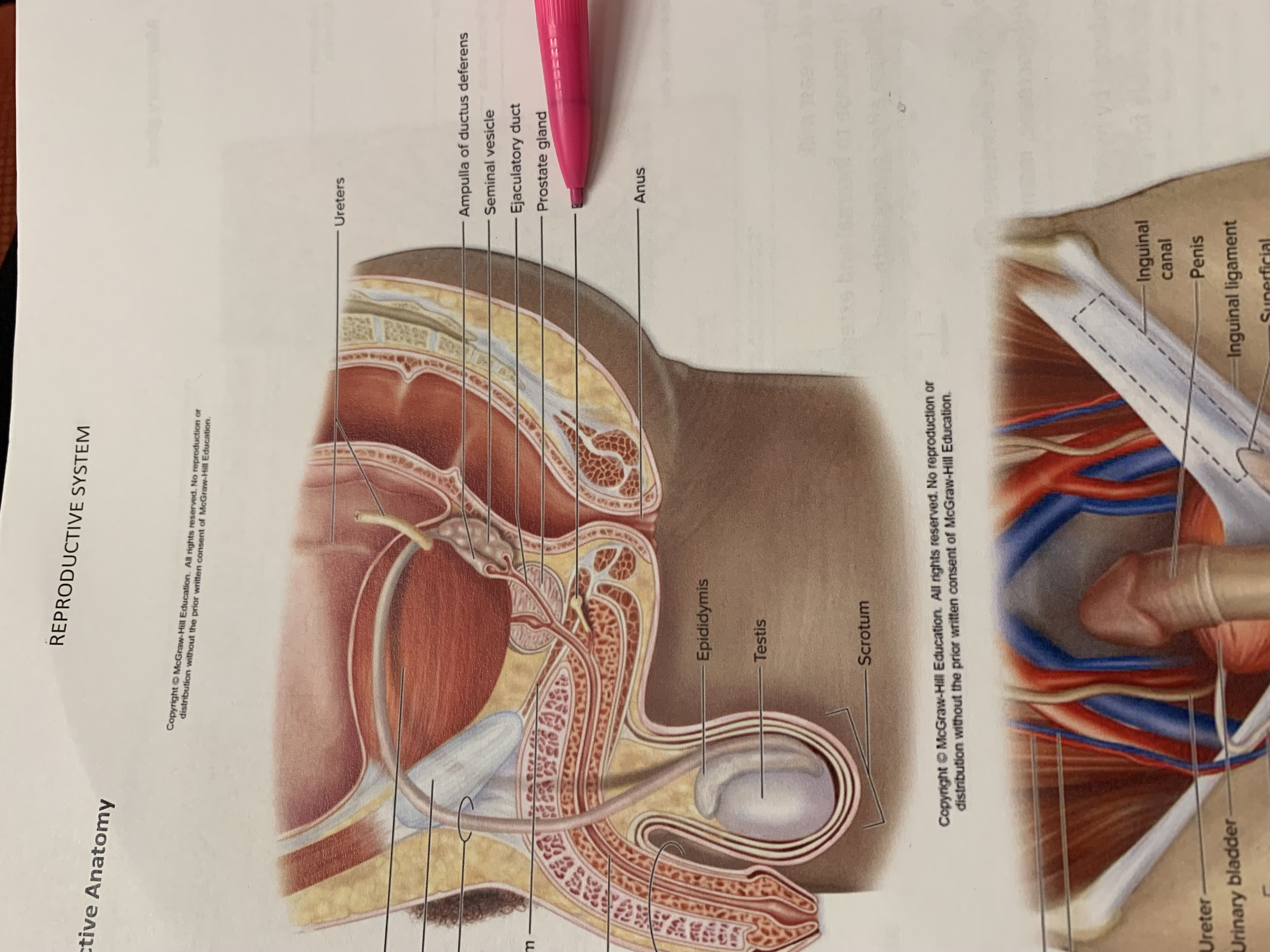
bulbourethral gland
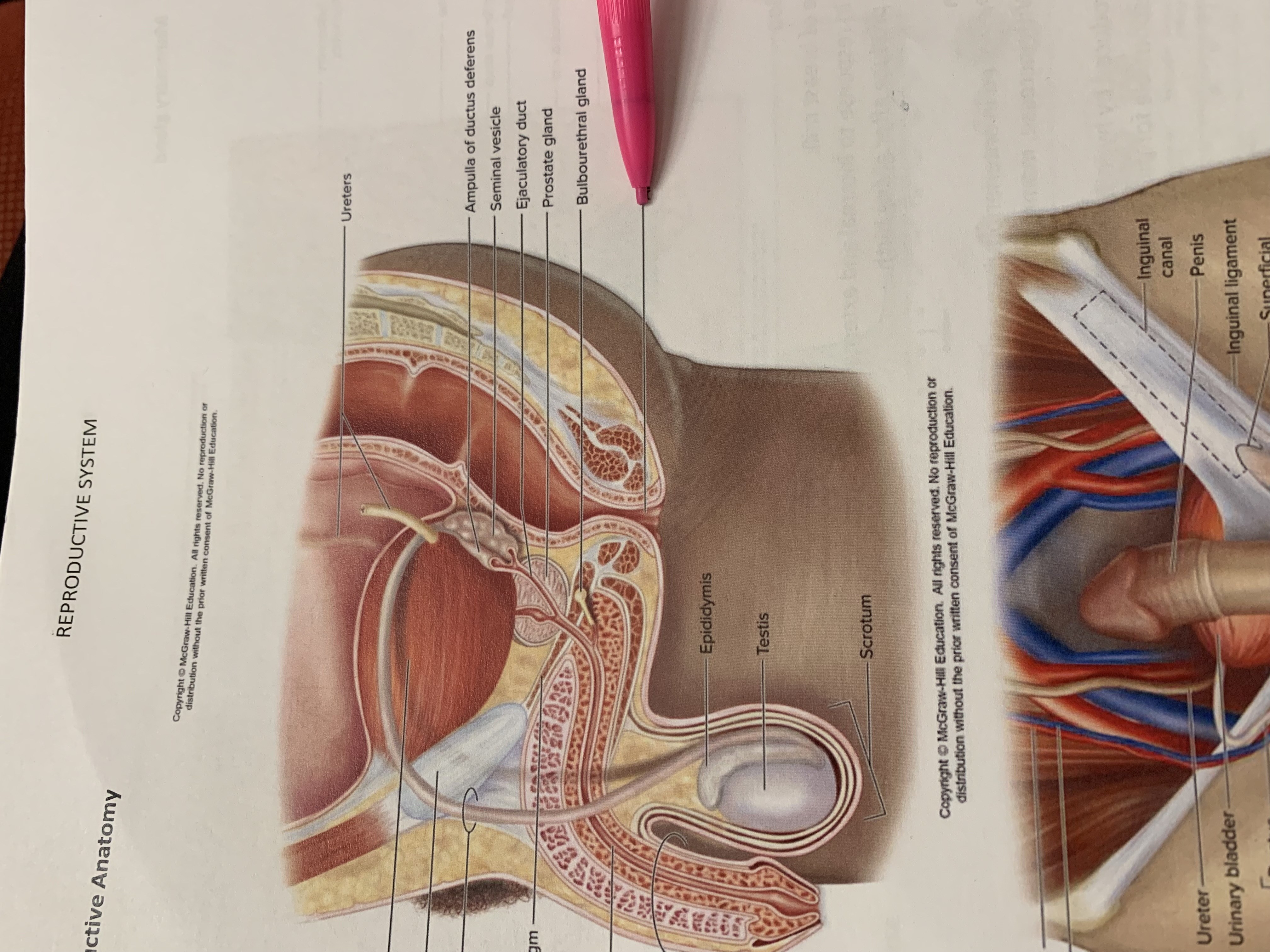
anus
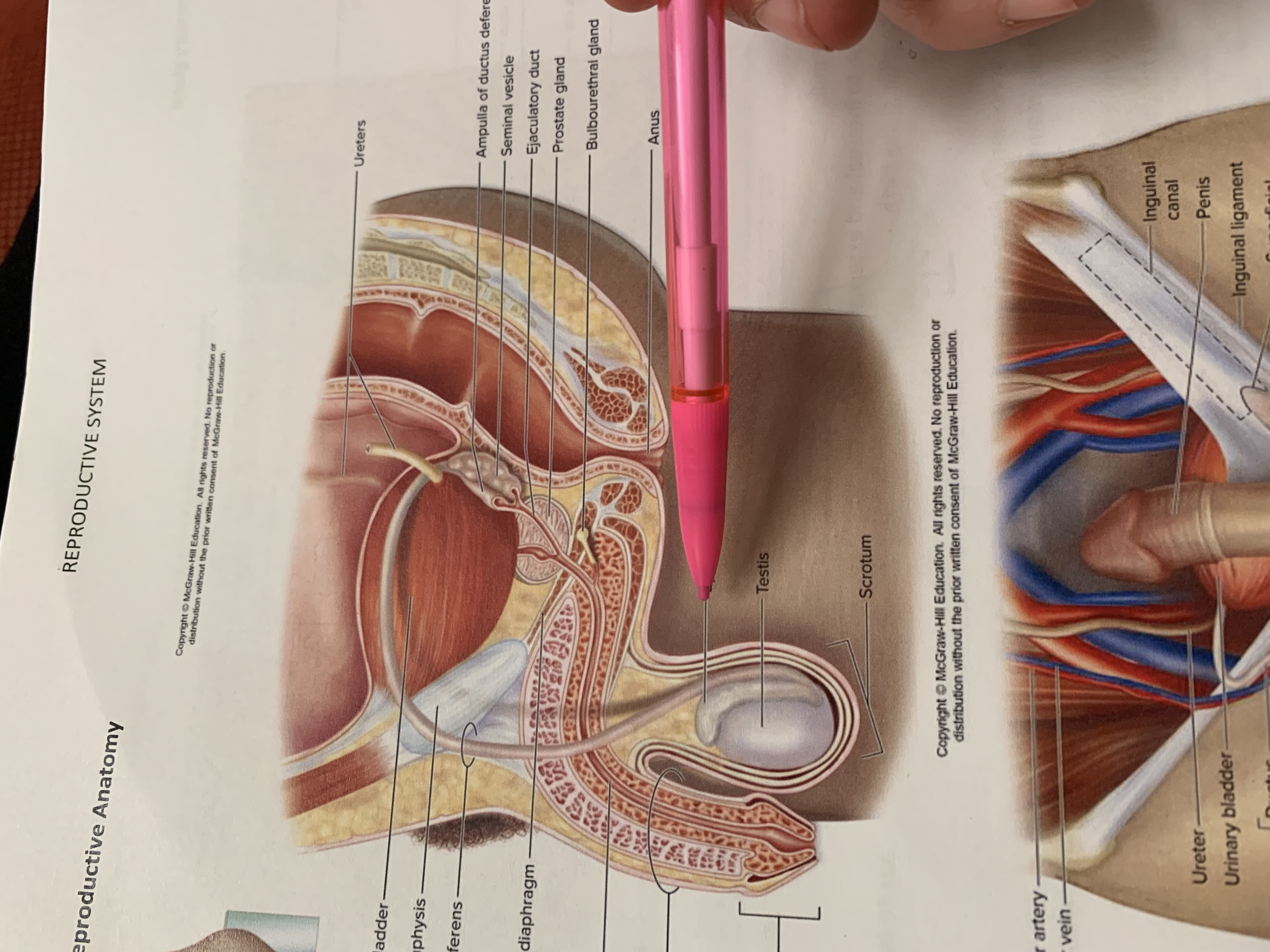
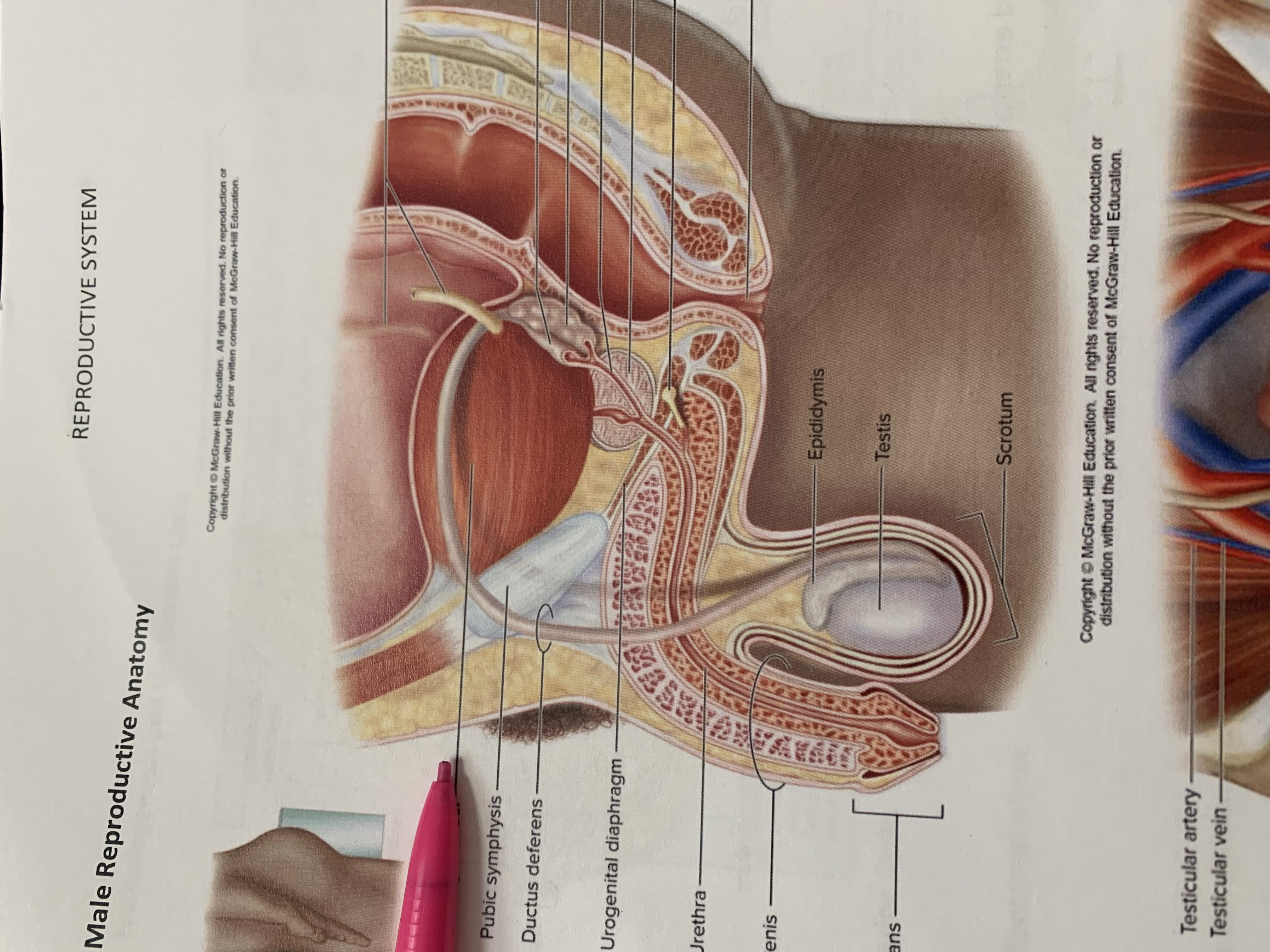
epididymis

testis
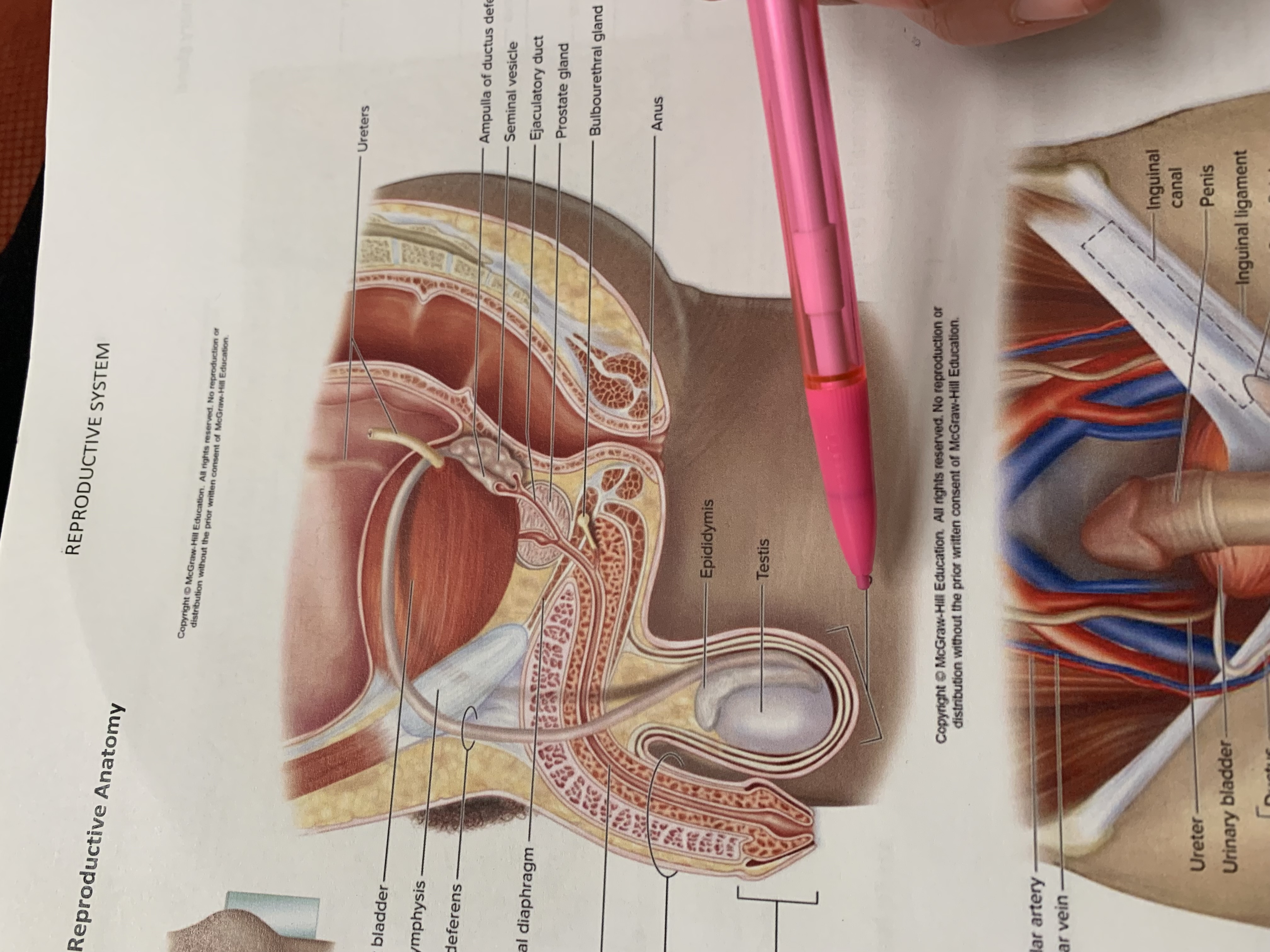
scrotum
urinary bladder
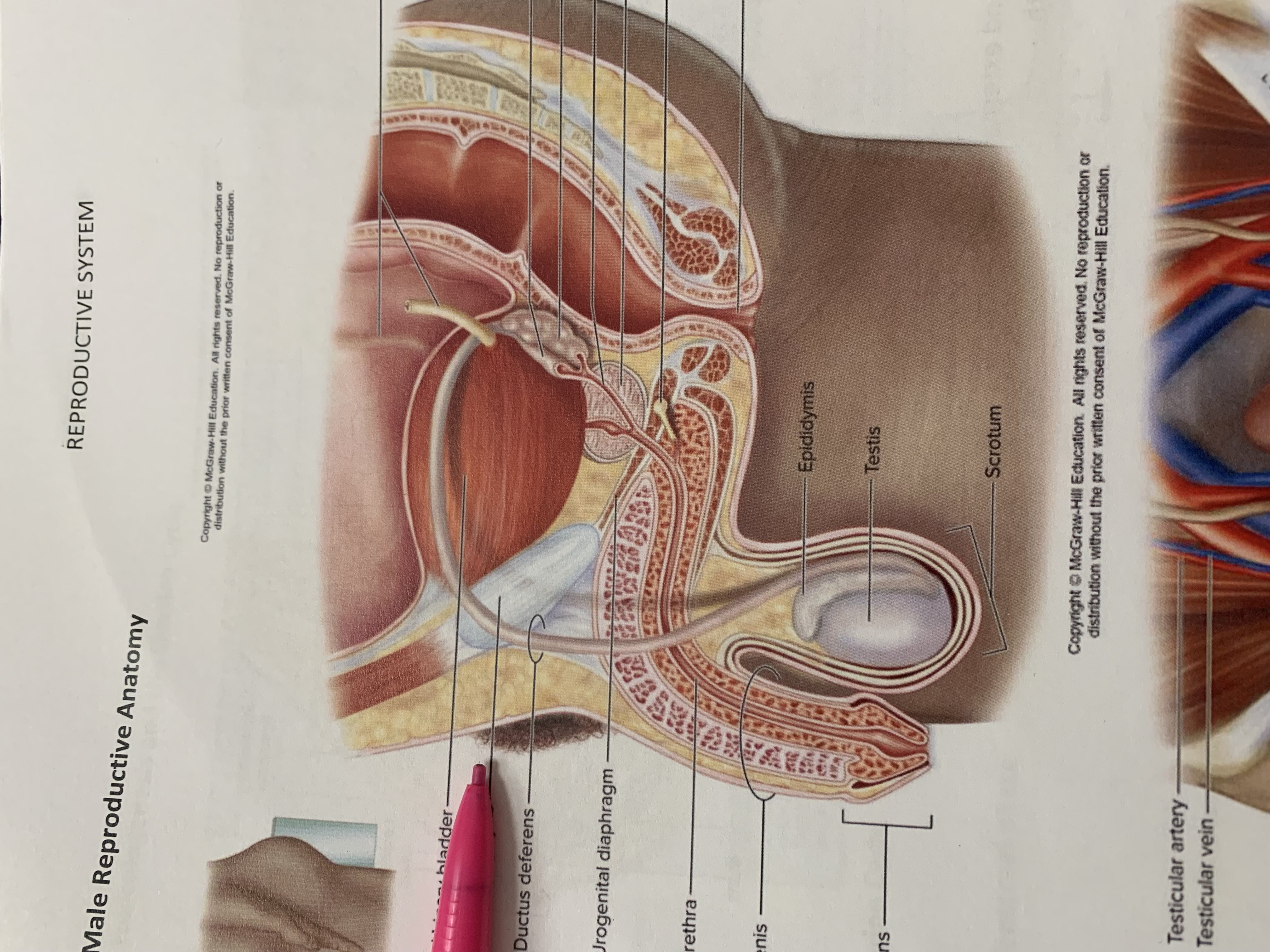
pubic symphysis
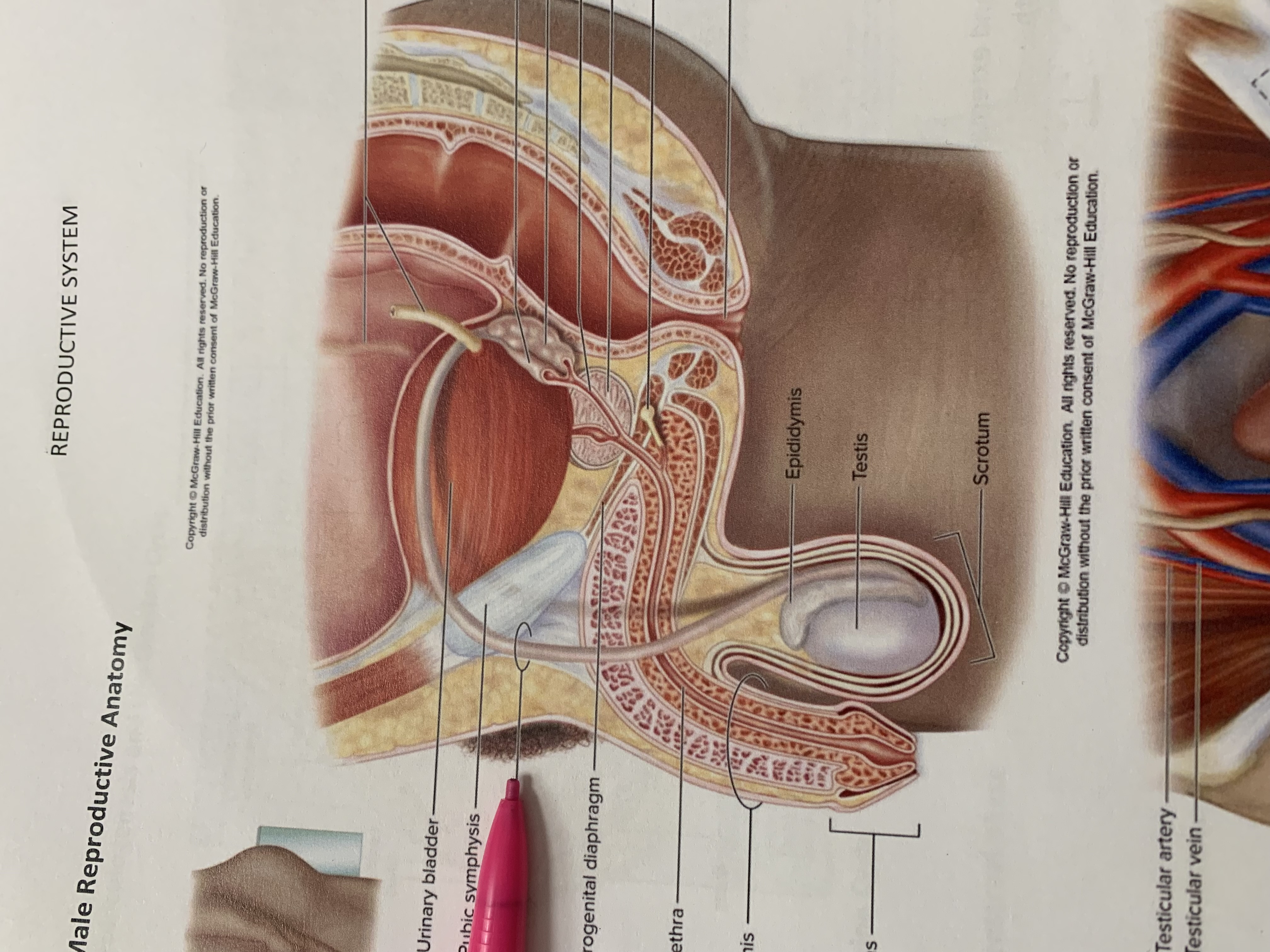
ductus deferens
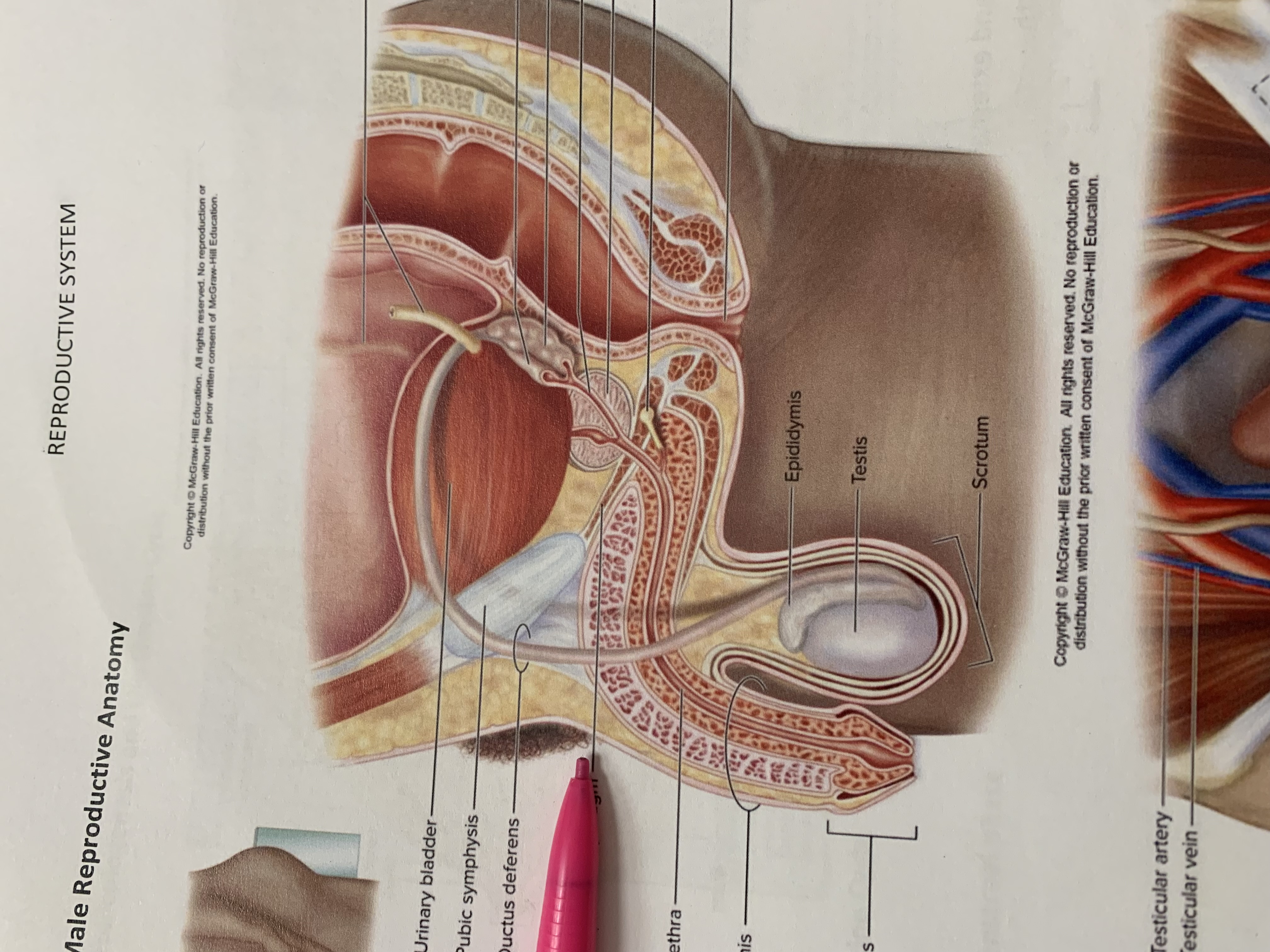
urogenital diaphragm
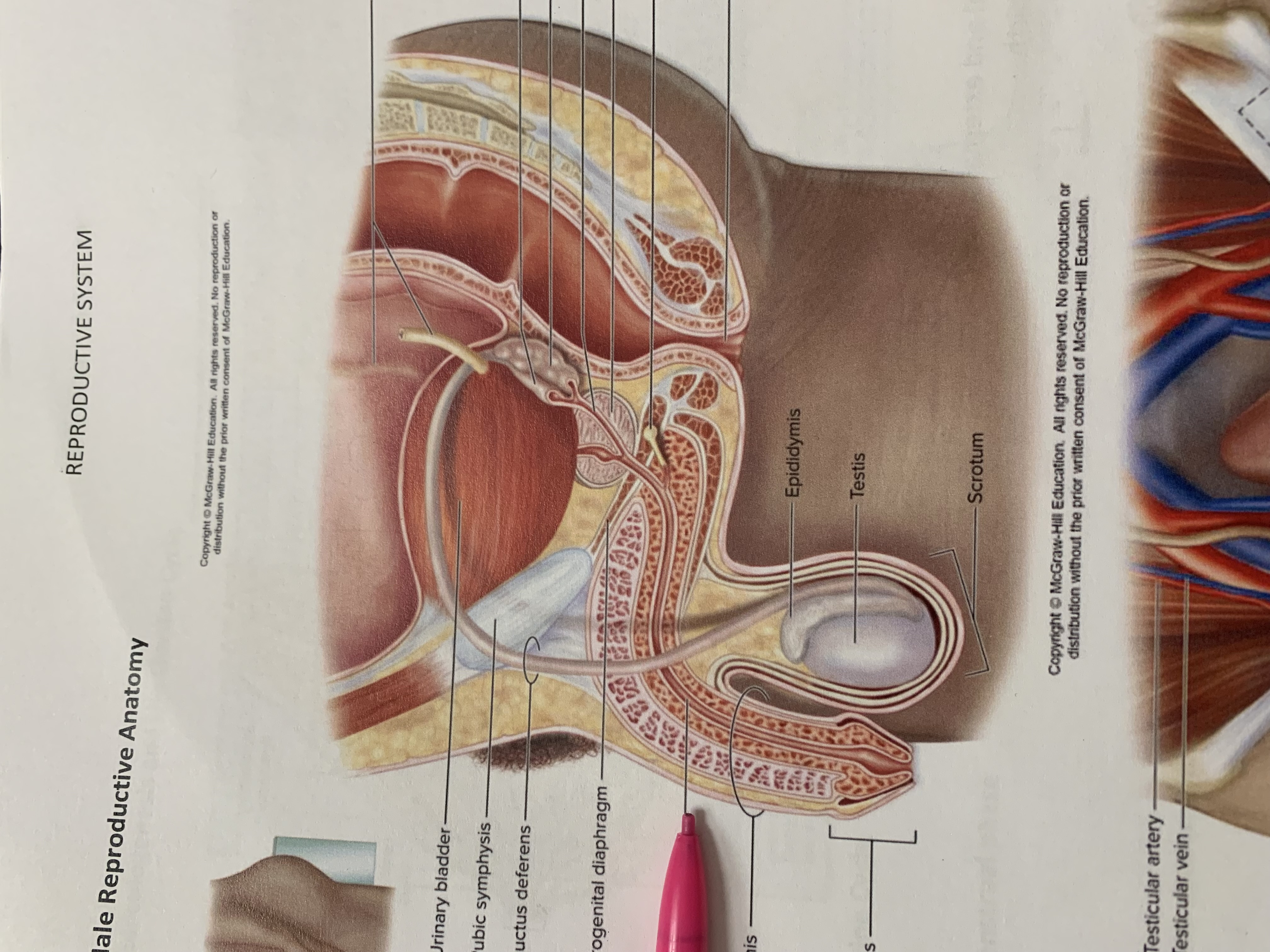
urethra
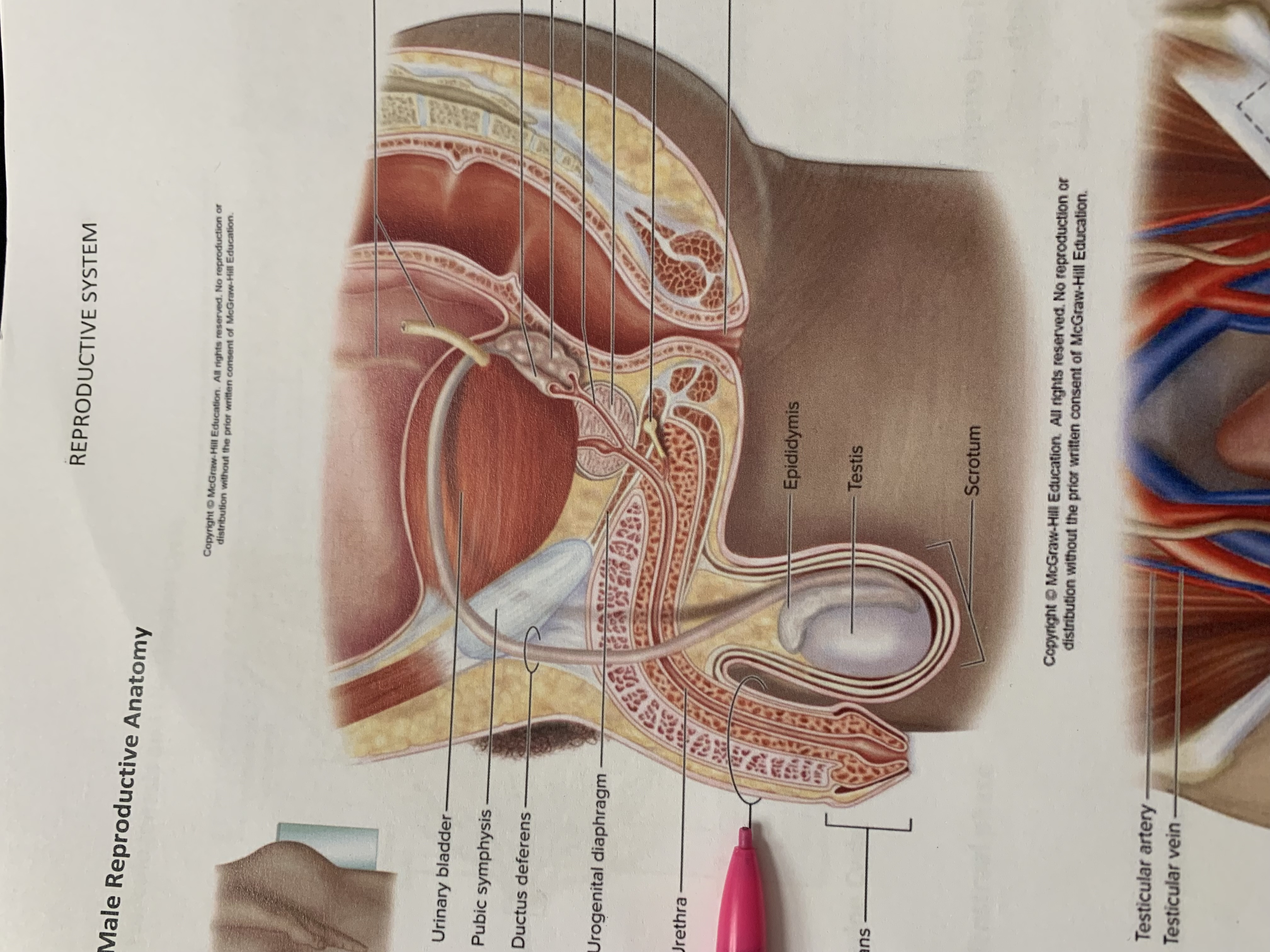
penis
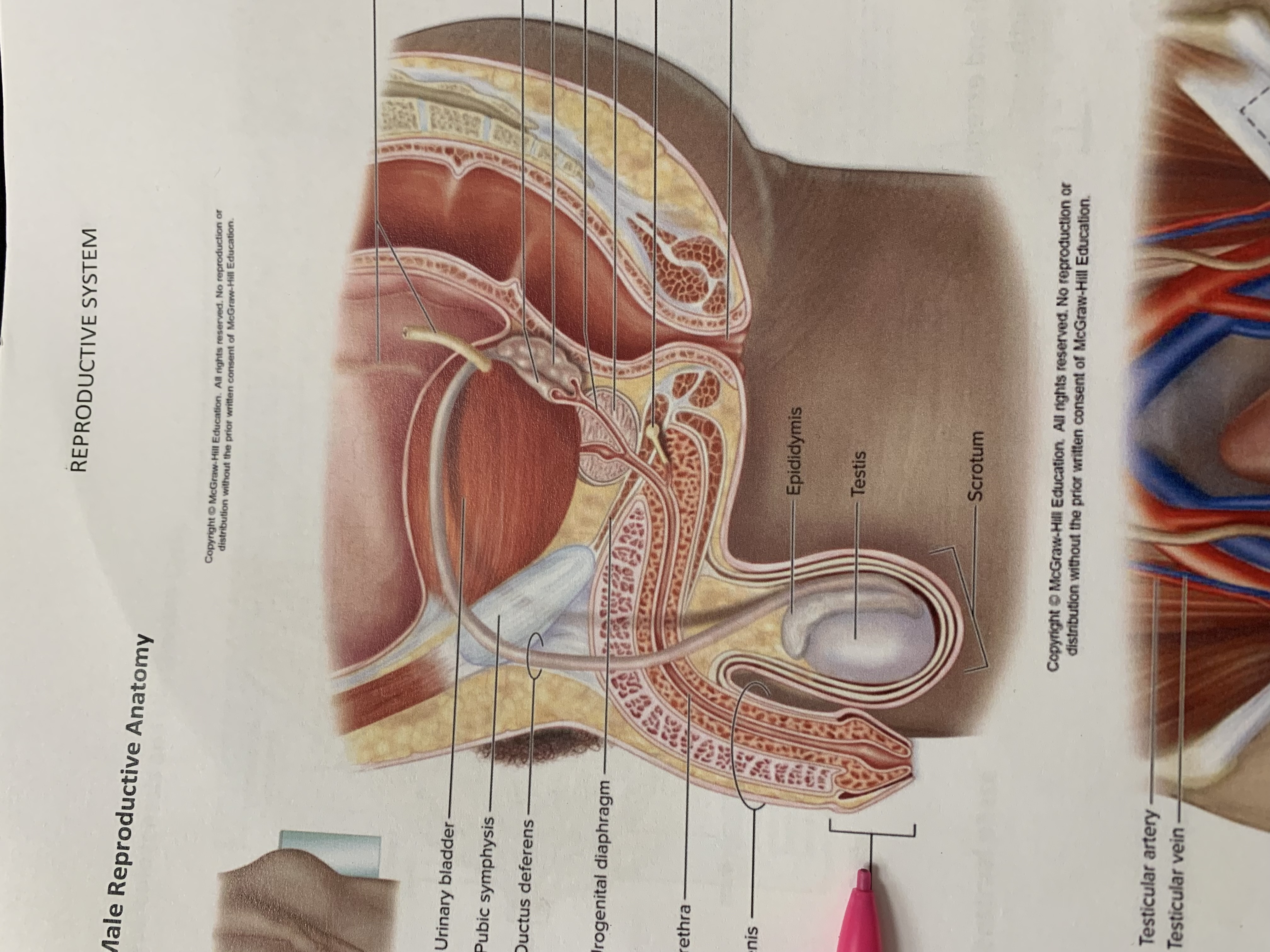
glans penis
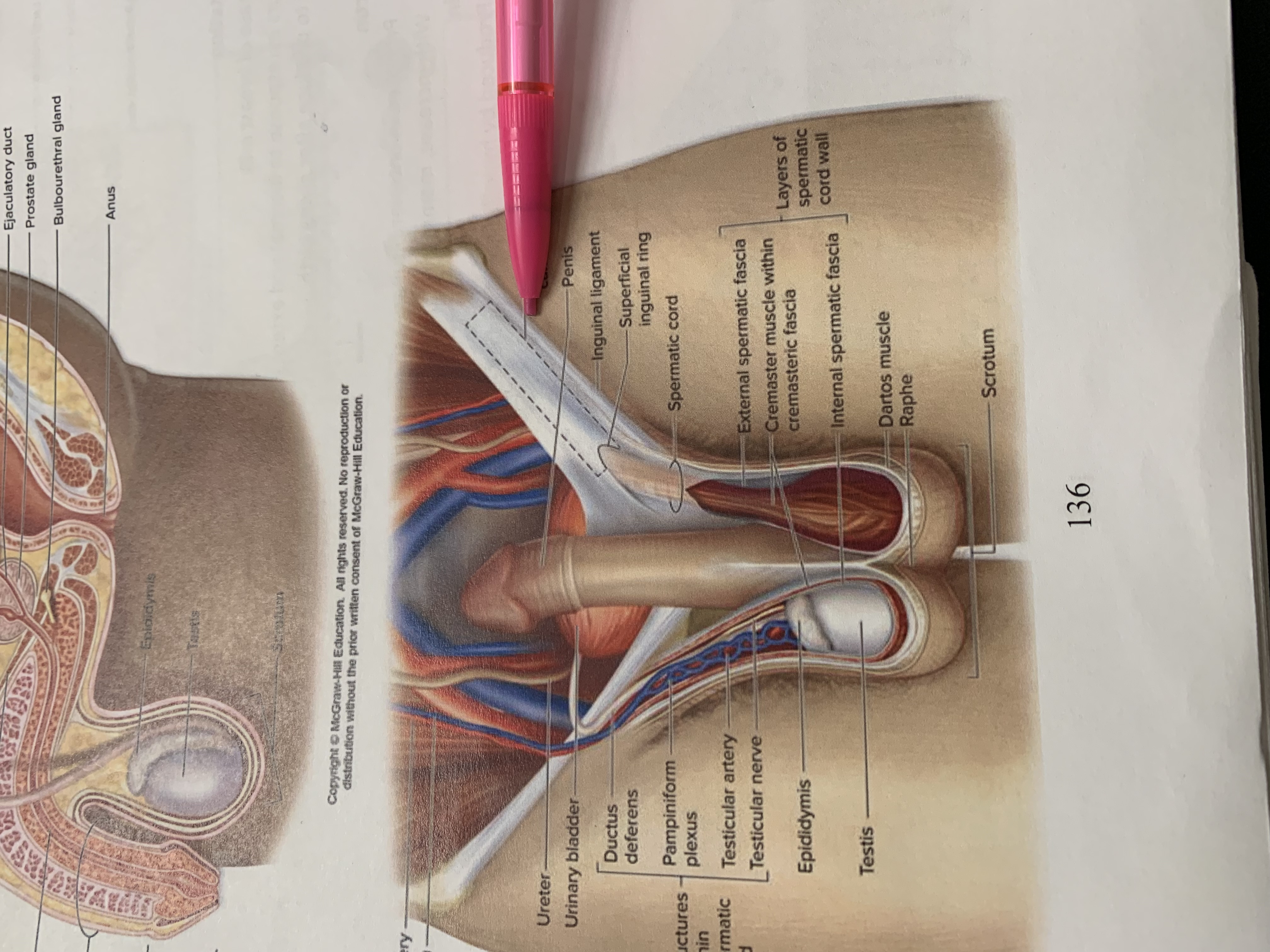
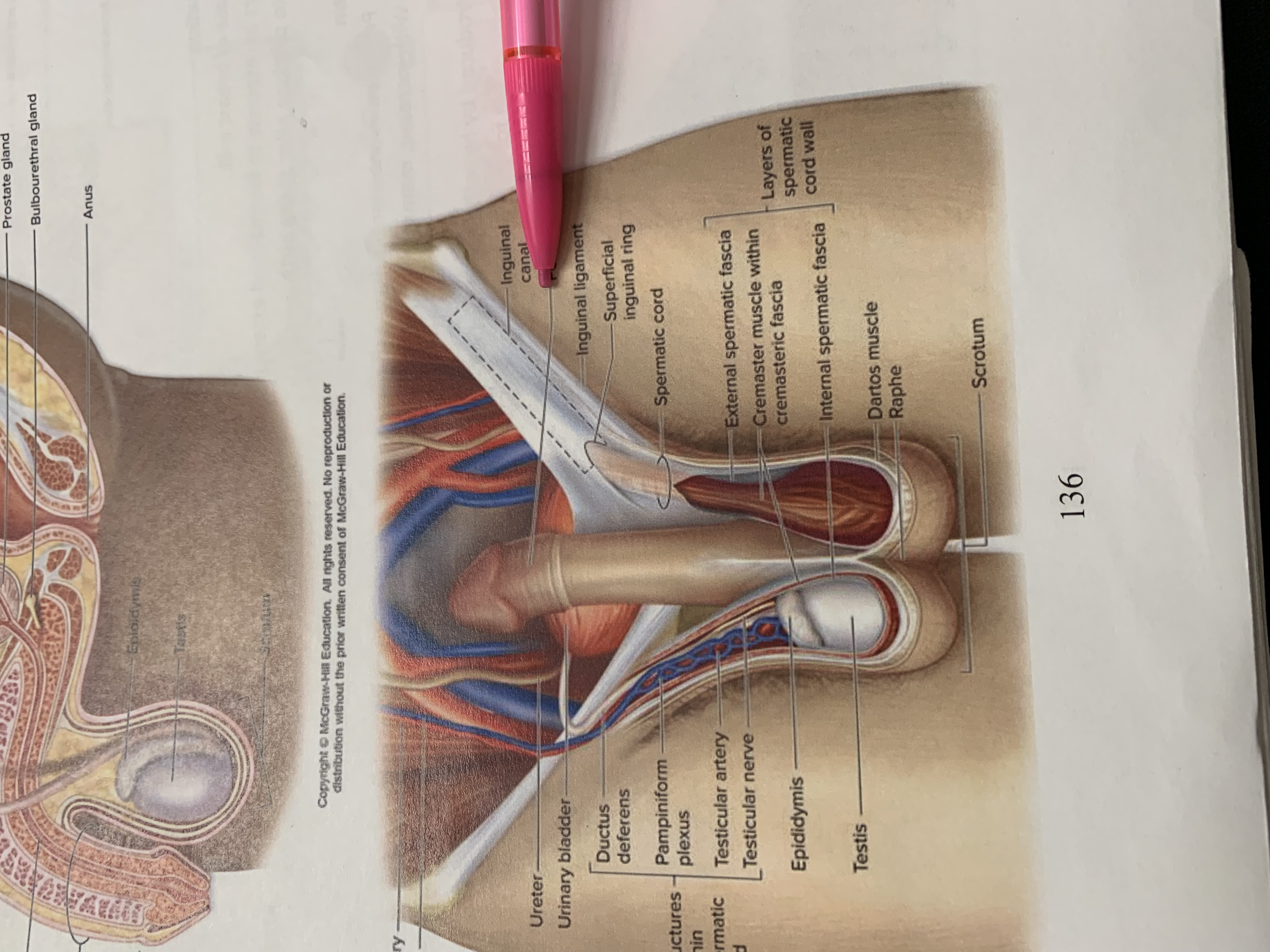
inguinal canal
penis
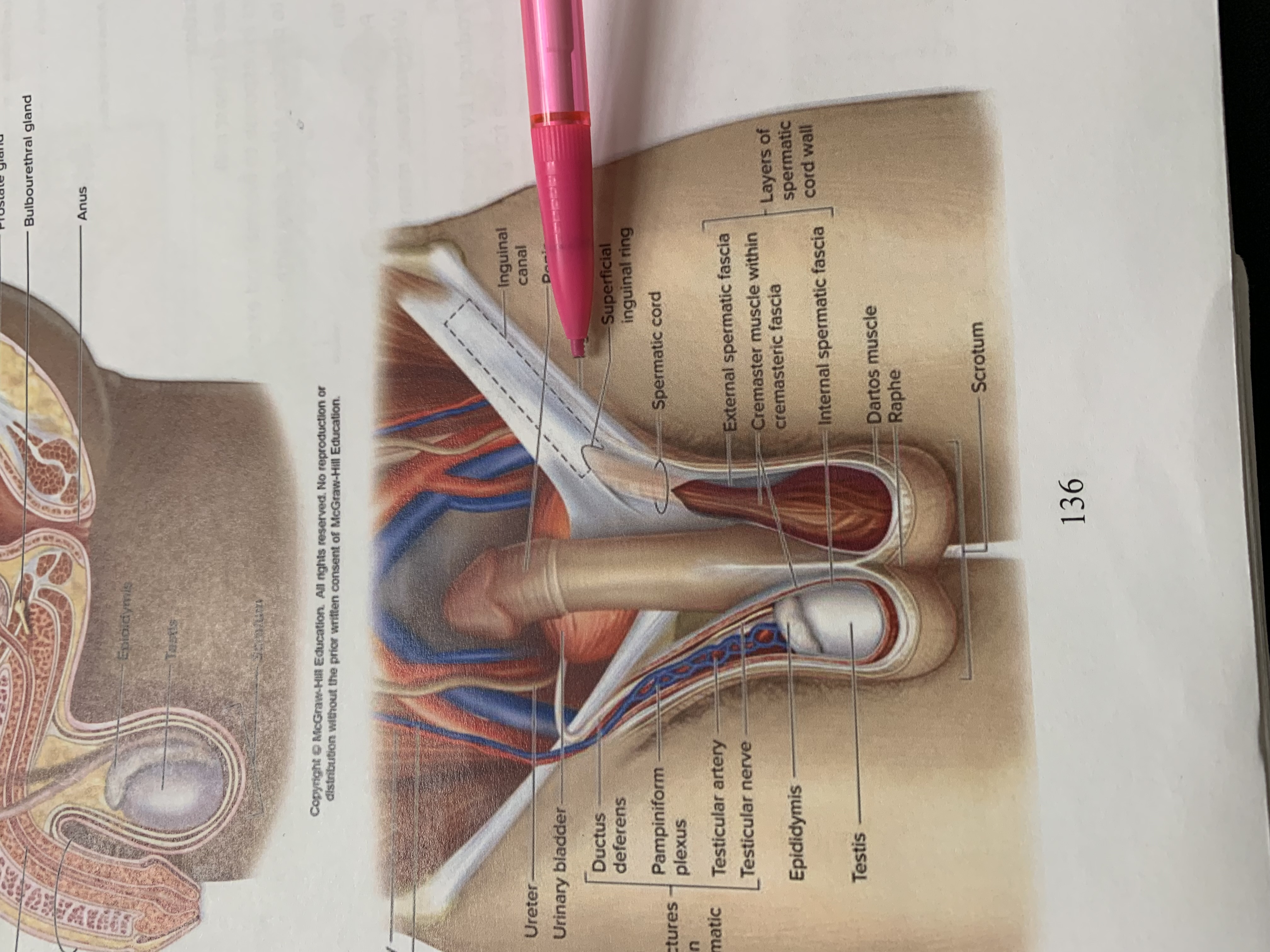
inguinal ligament
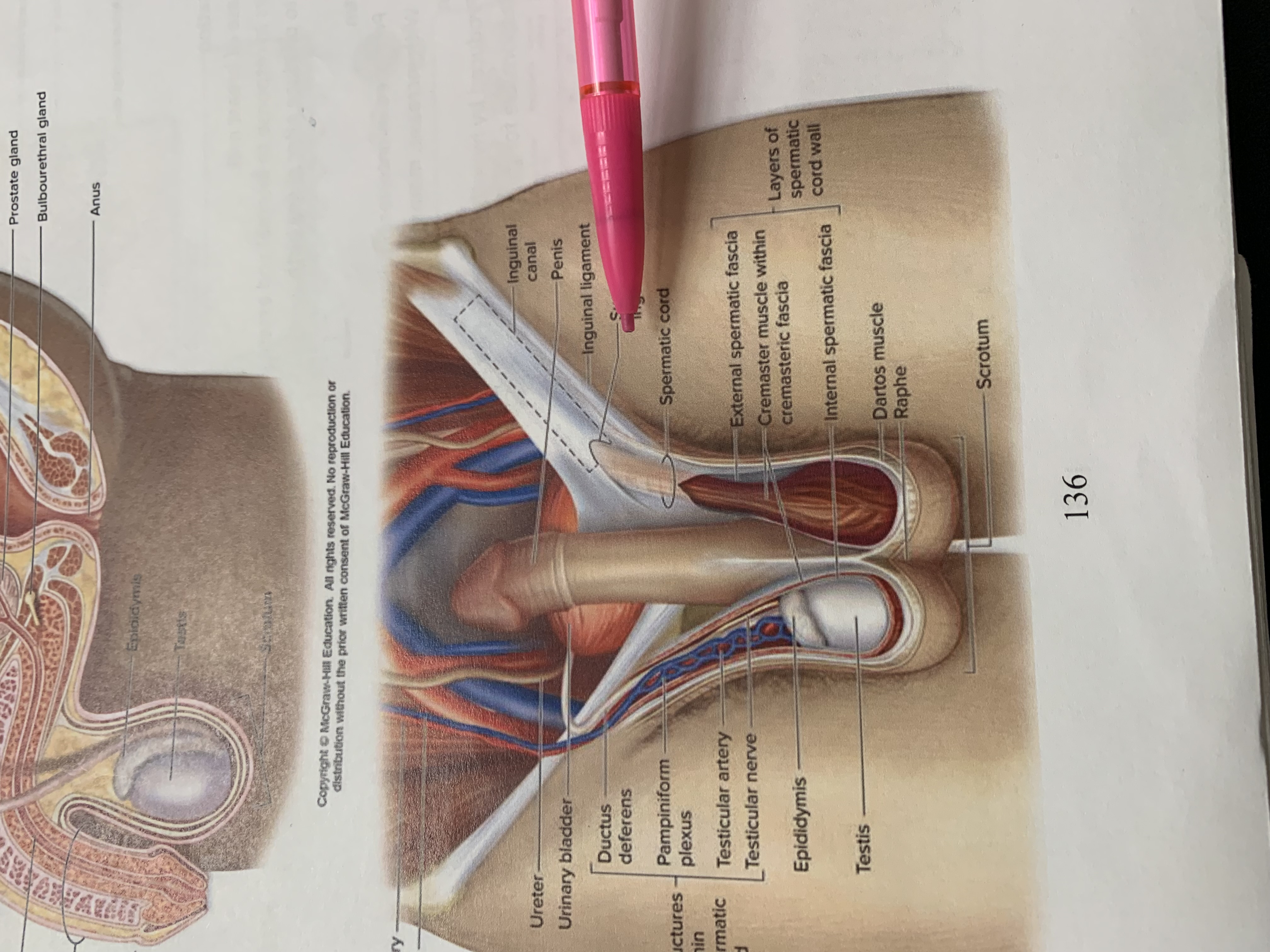
superficial inguinal ring
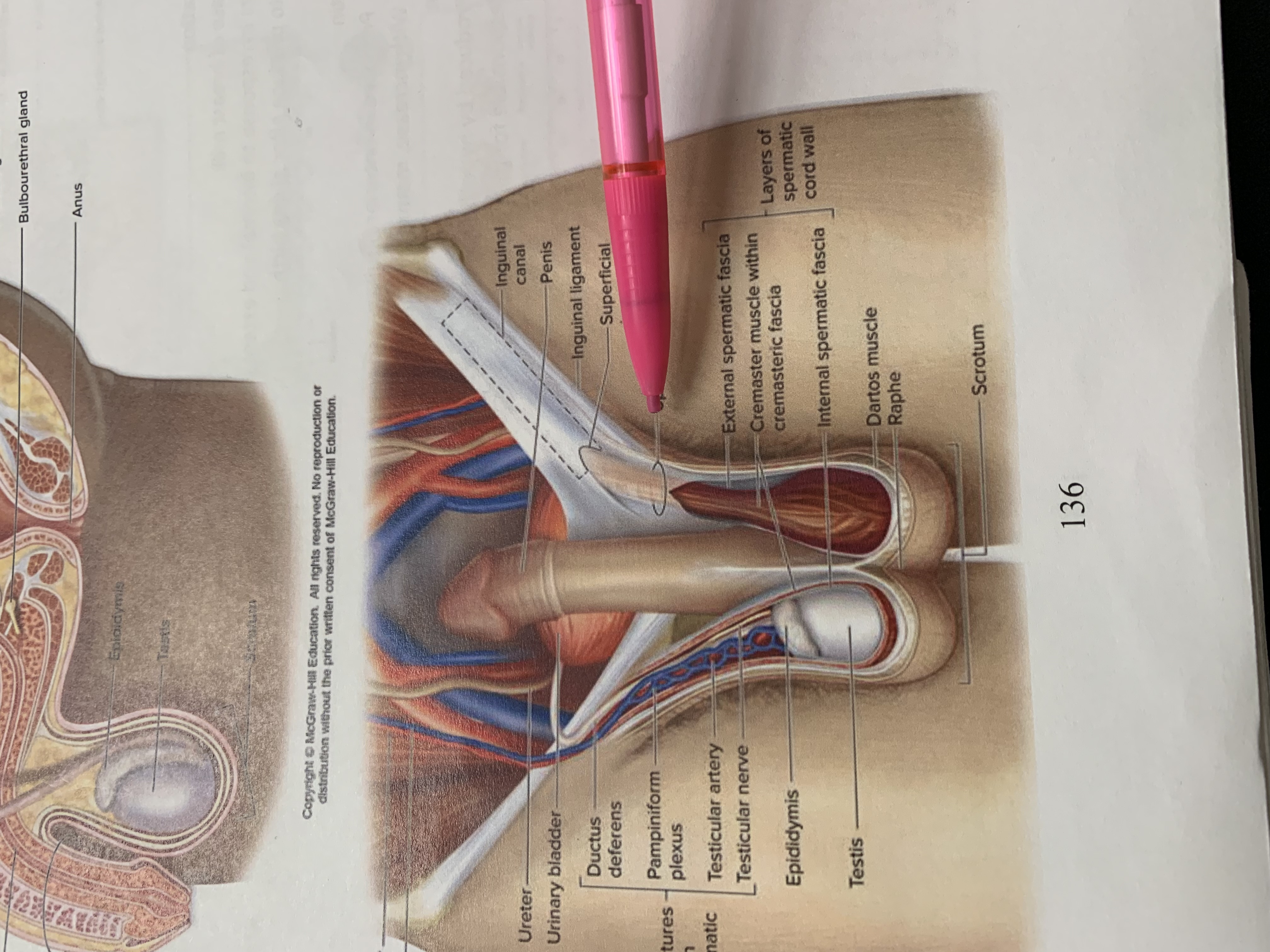
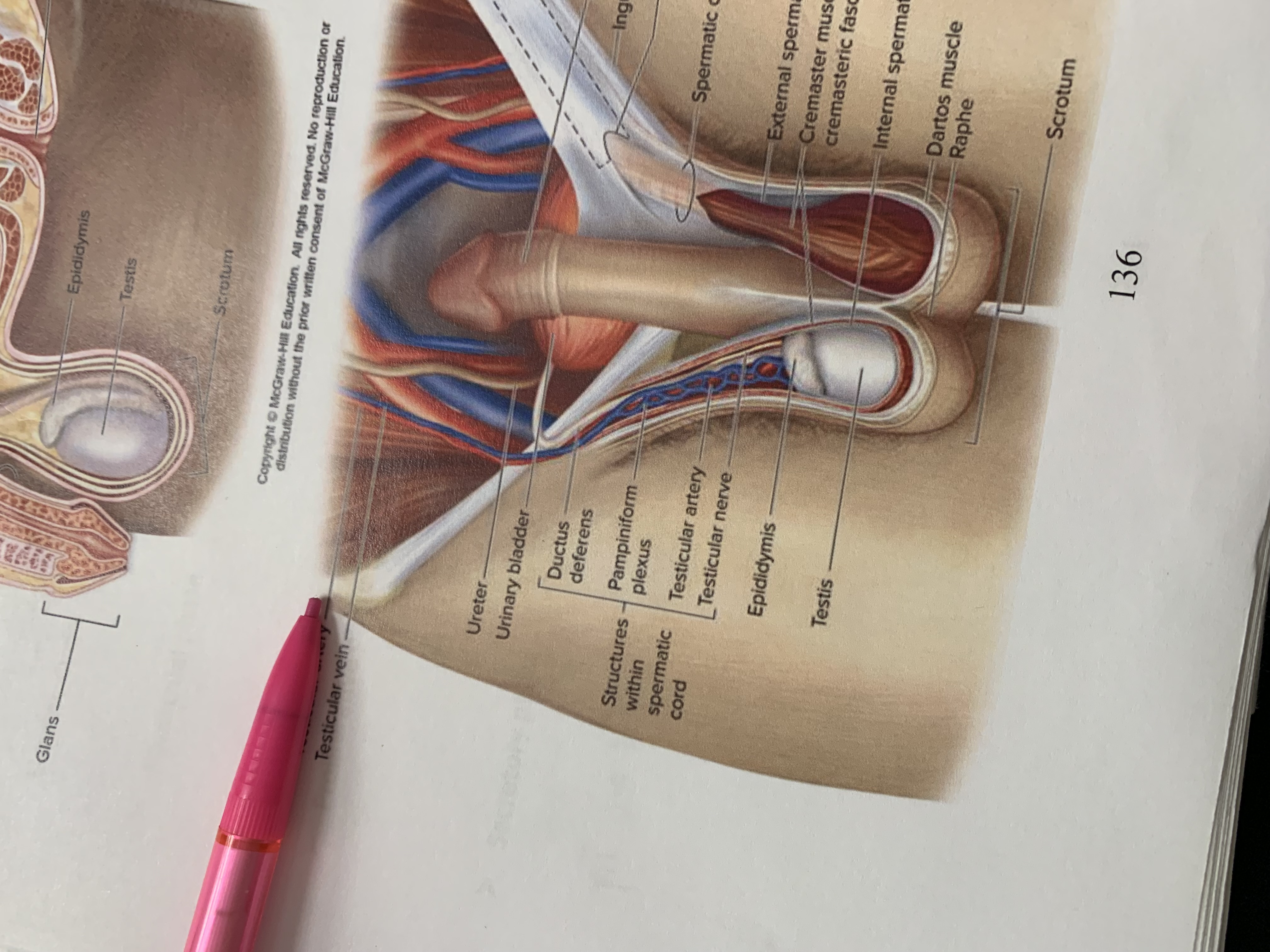
spermatic cord
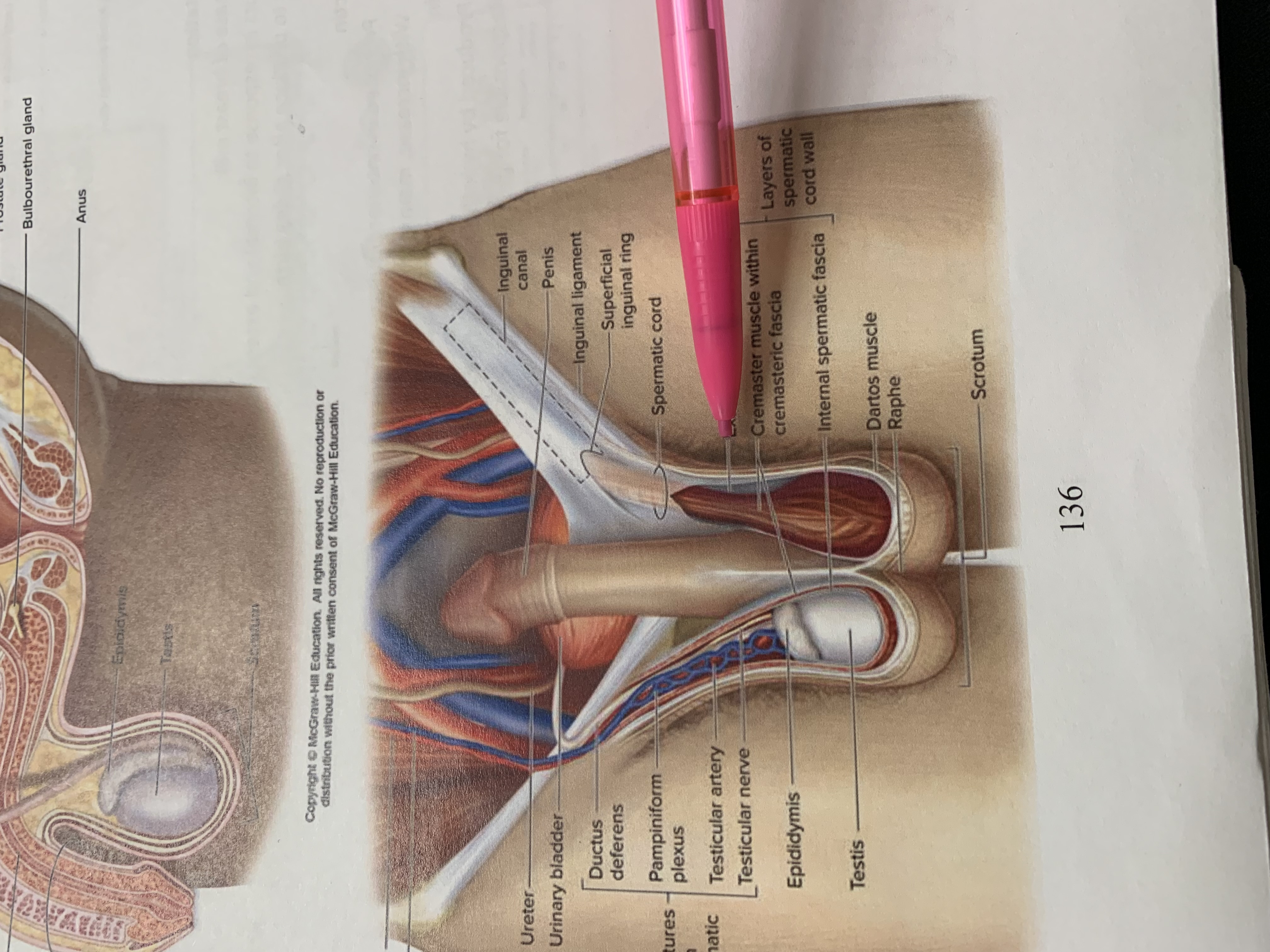
external spermatic fascia
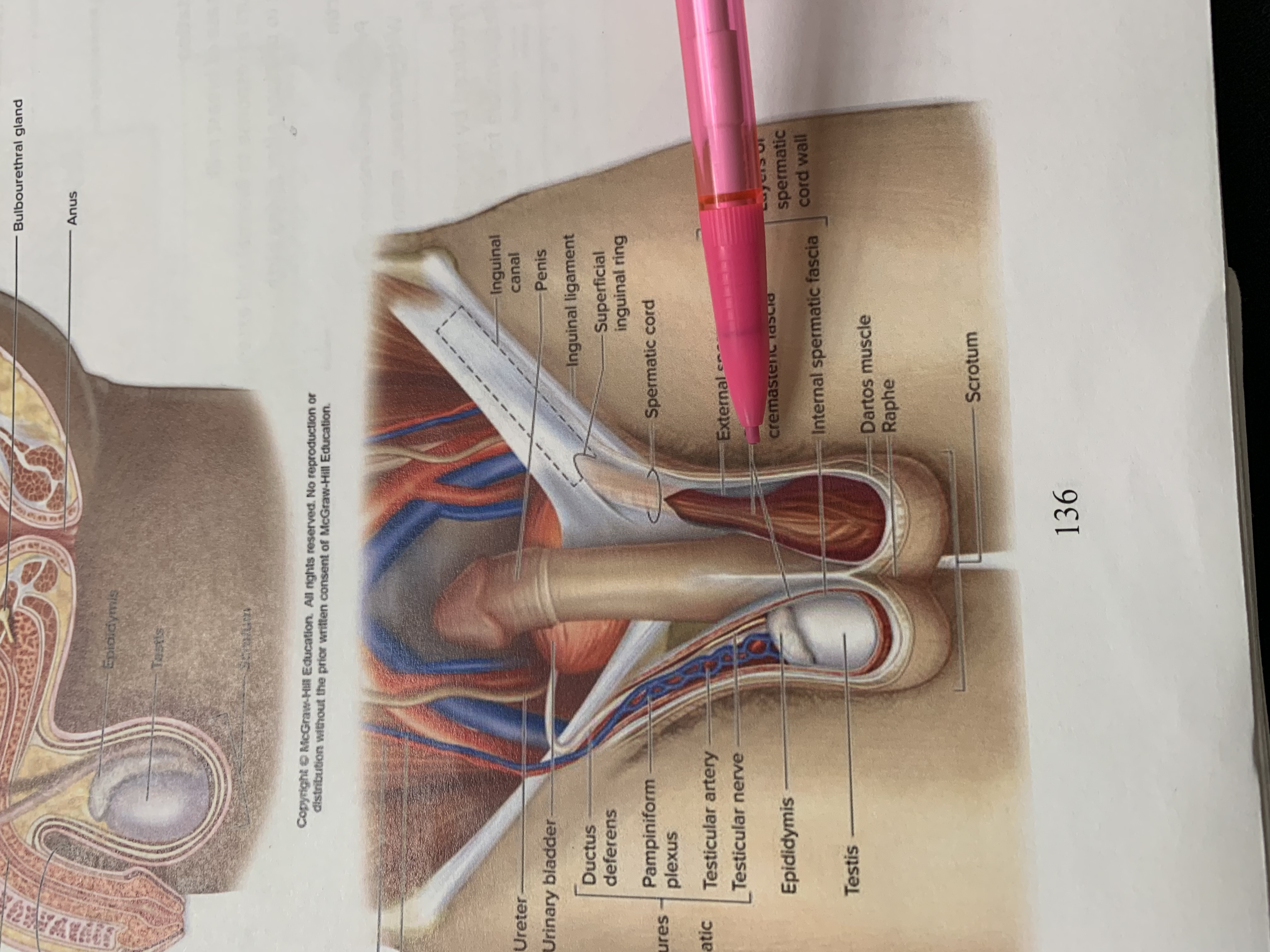
cremaster muscle wishing cremasteric fascia
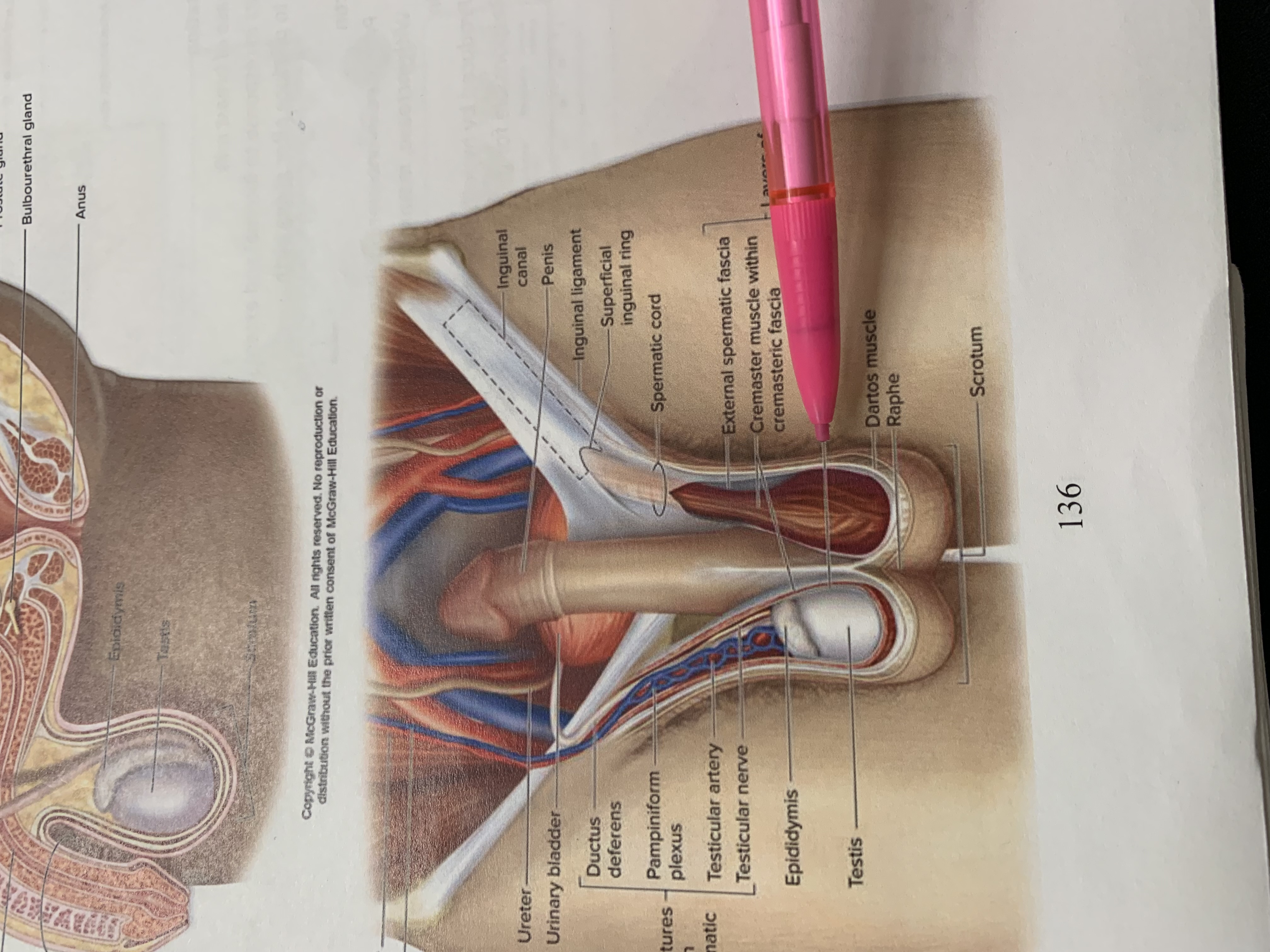
internal spermatic fascia
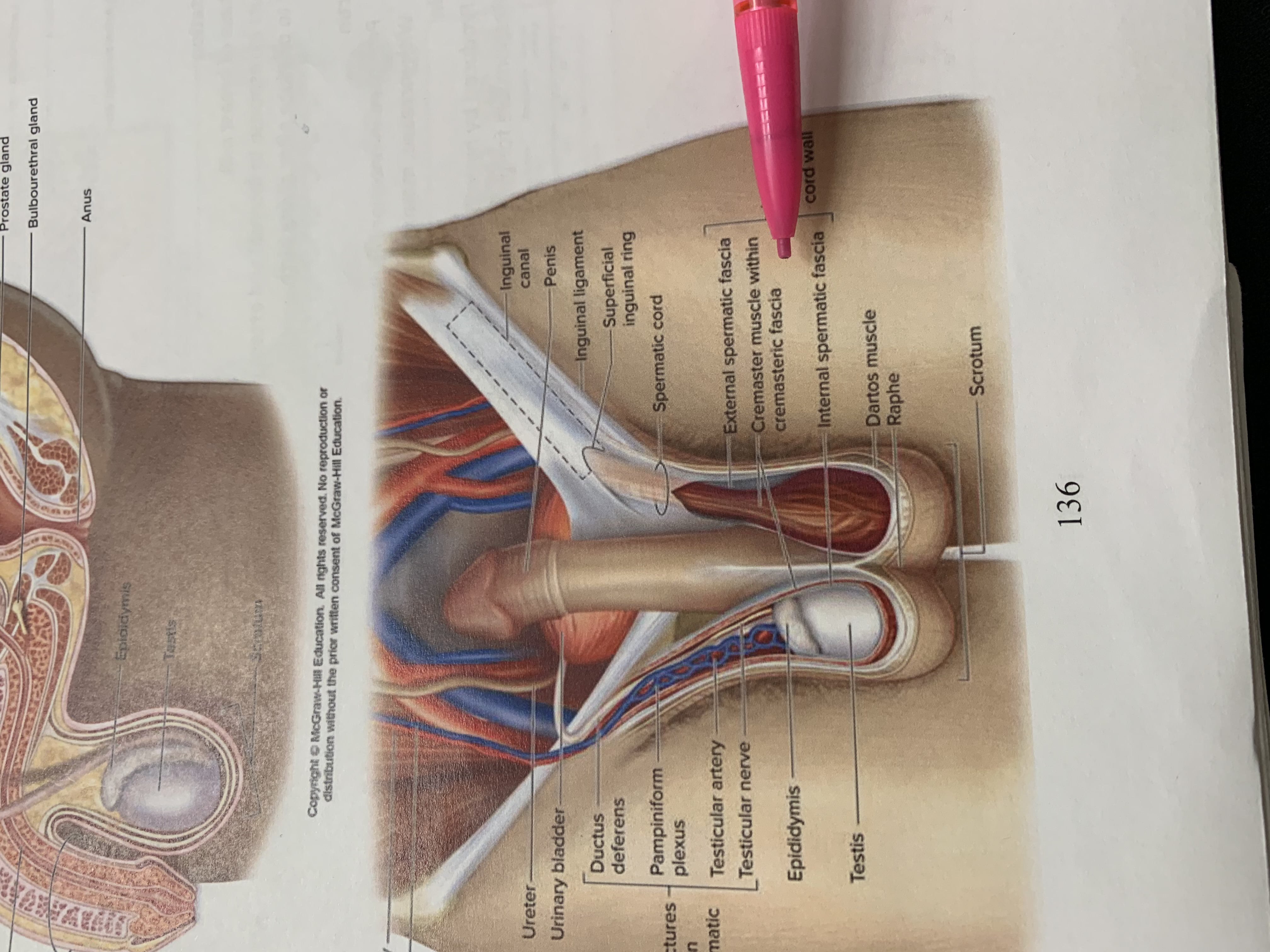
layers of spermatic cord wall
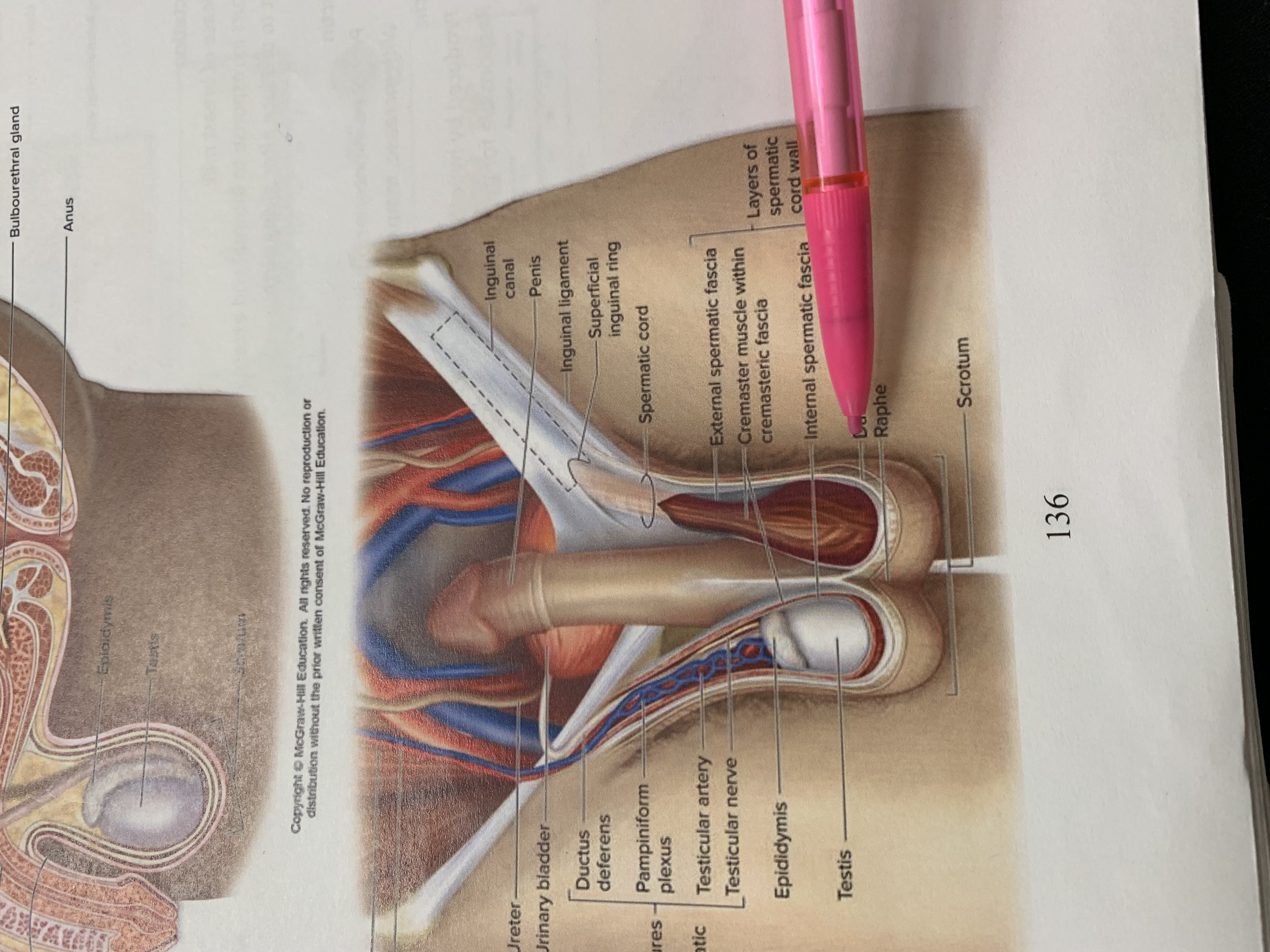
dartos muscle
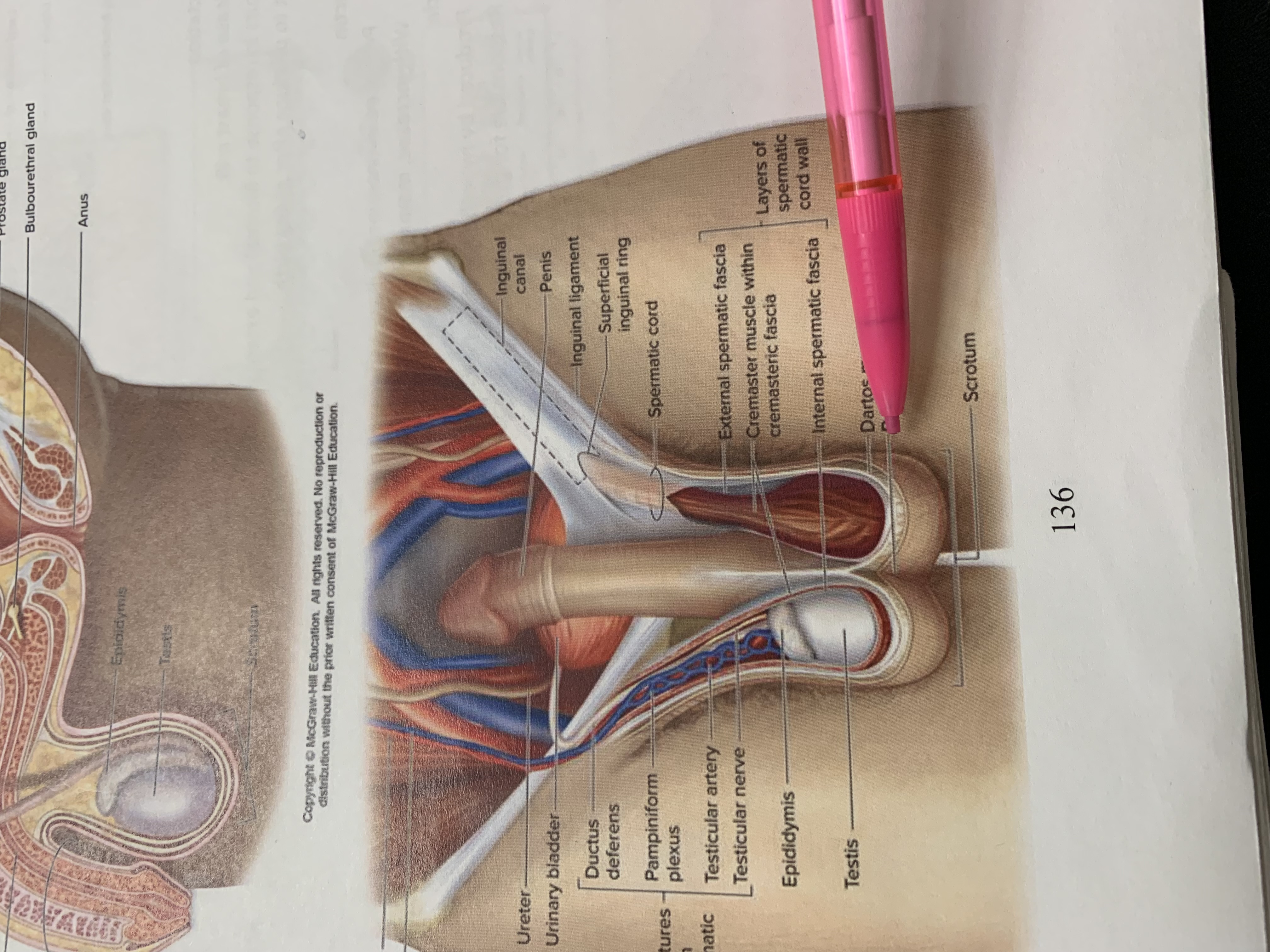
raphe
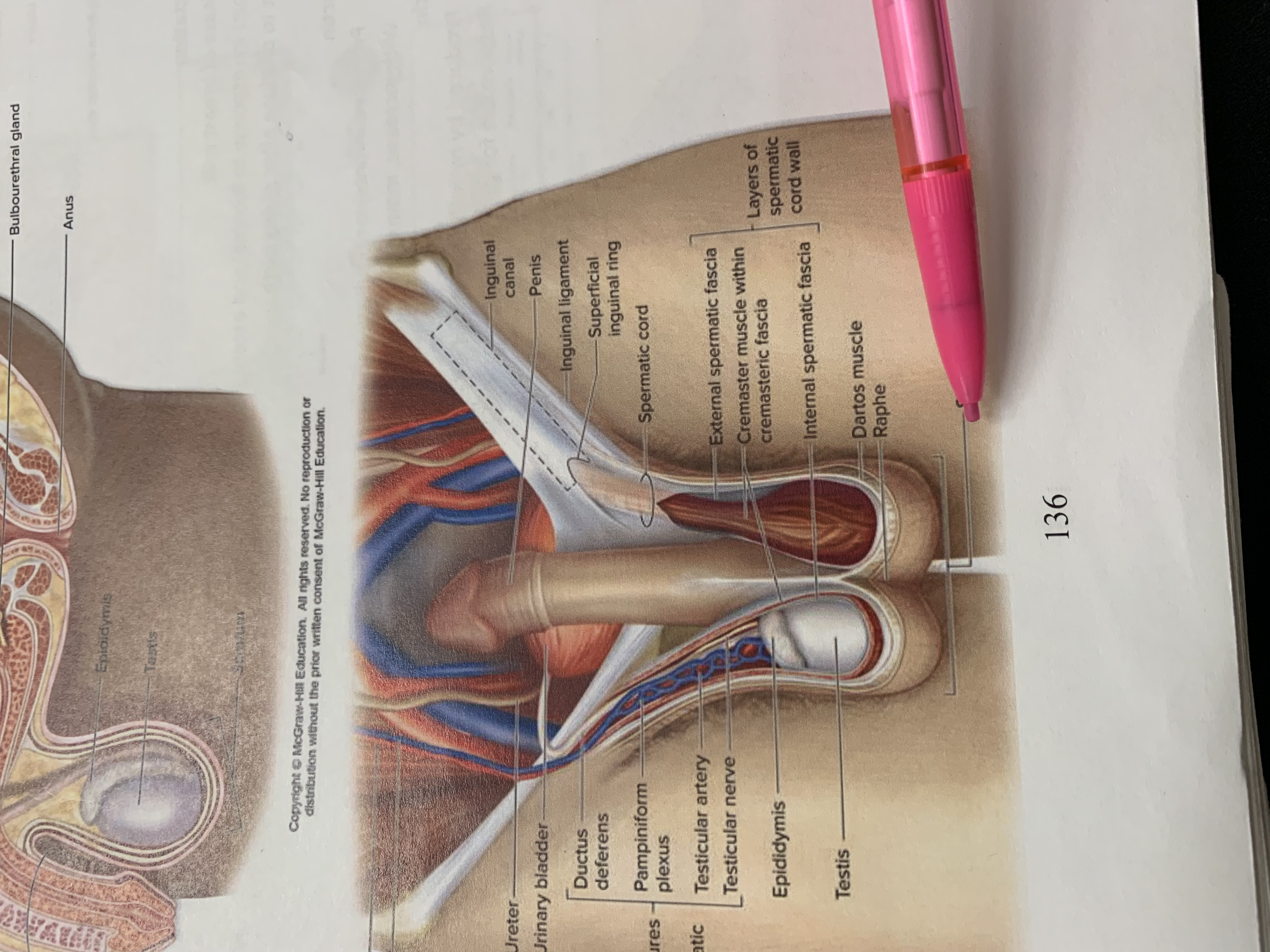
scrotum
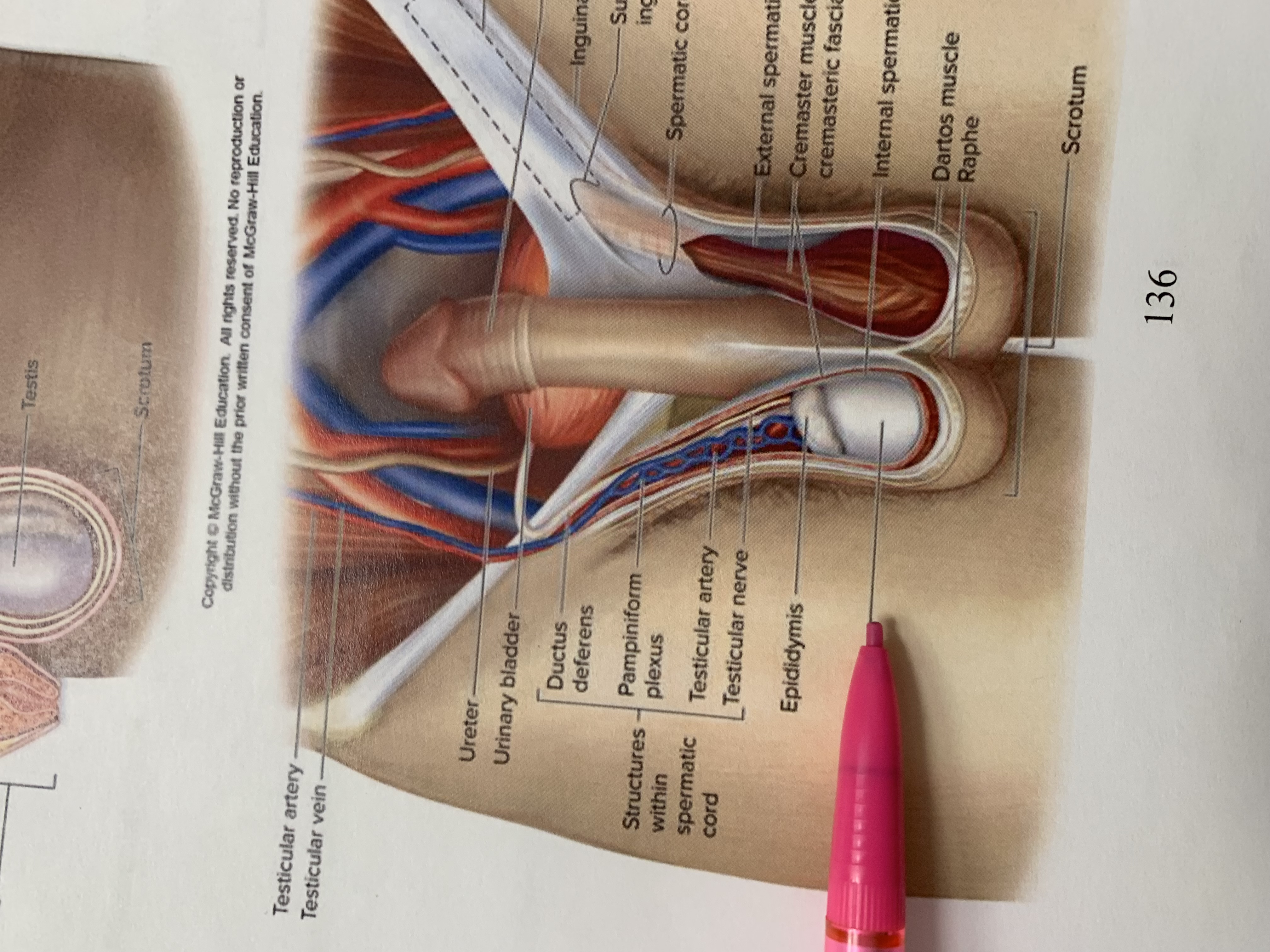
testis
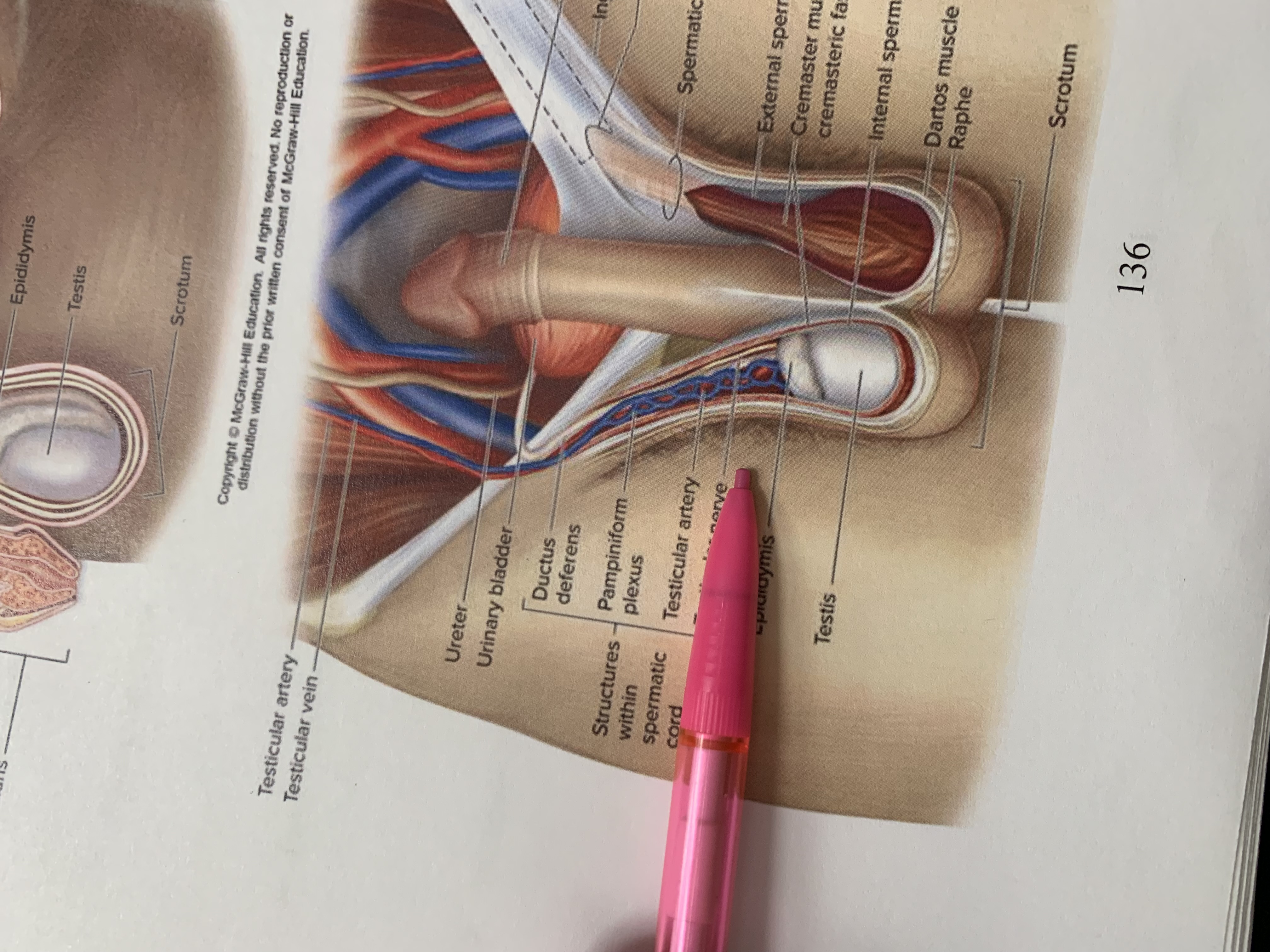
epididymis
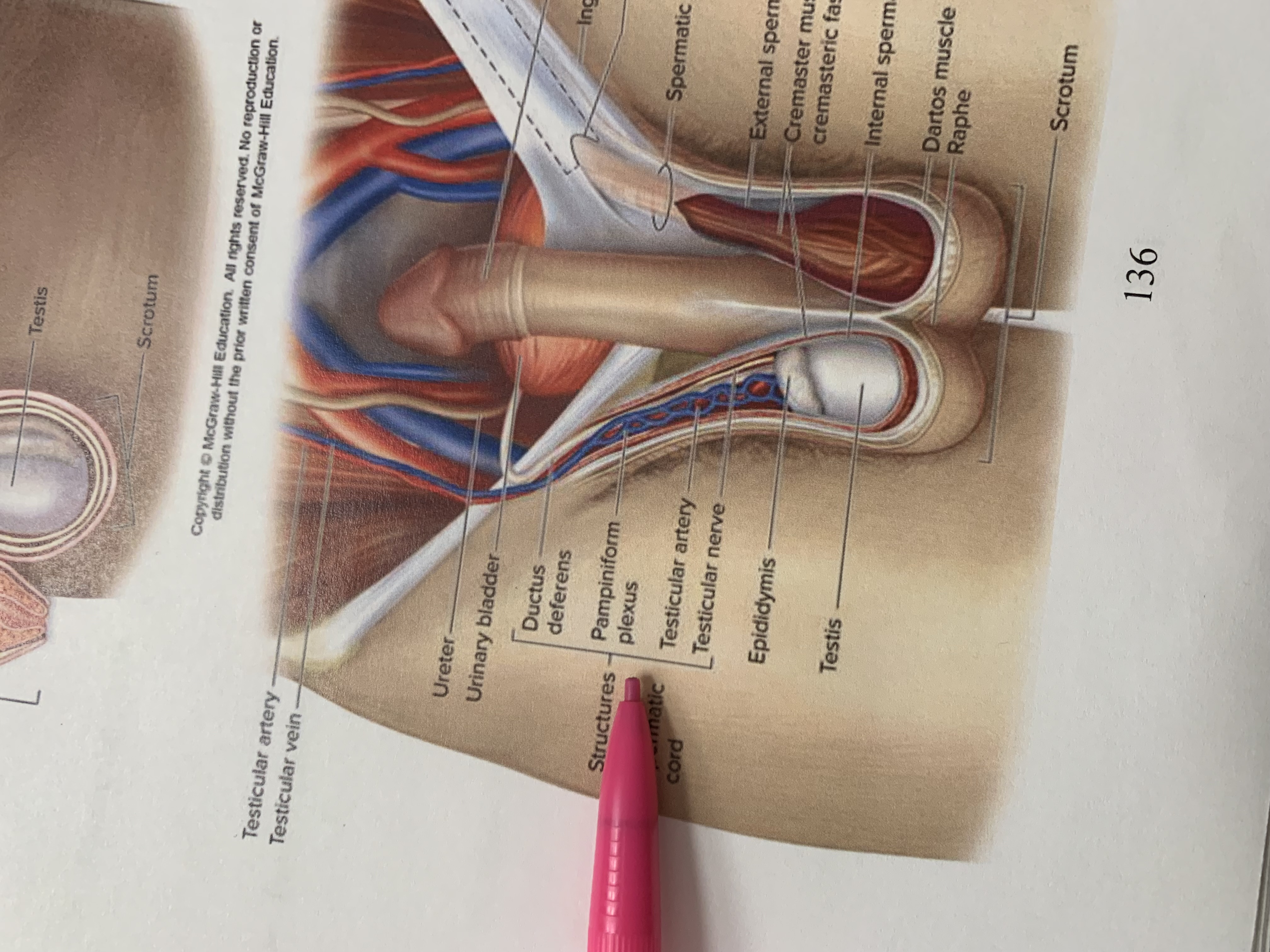
structures within spermatic cord
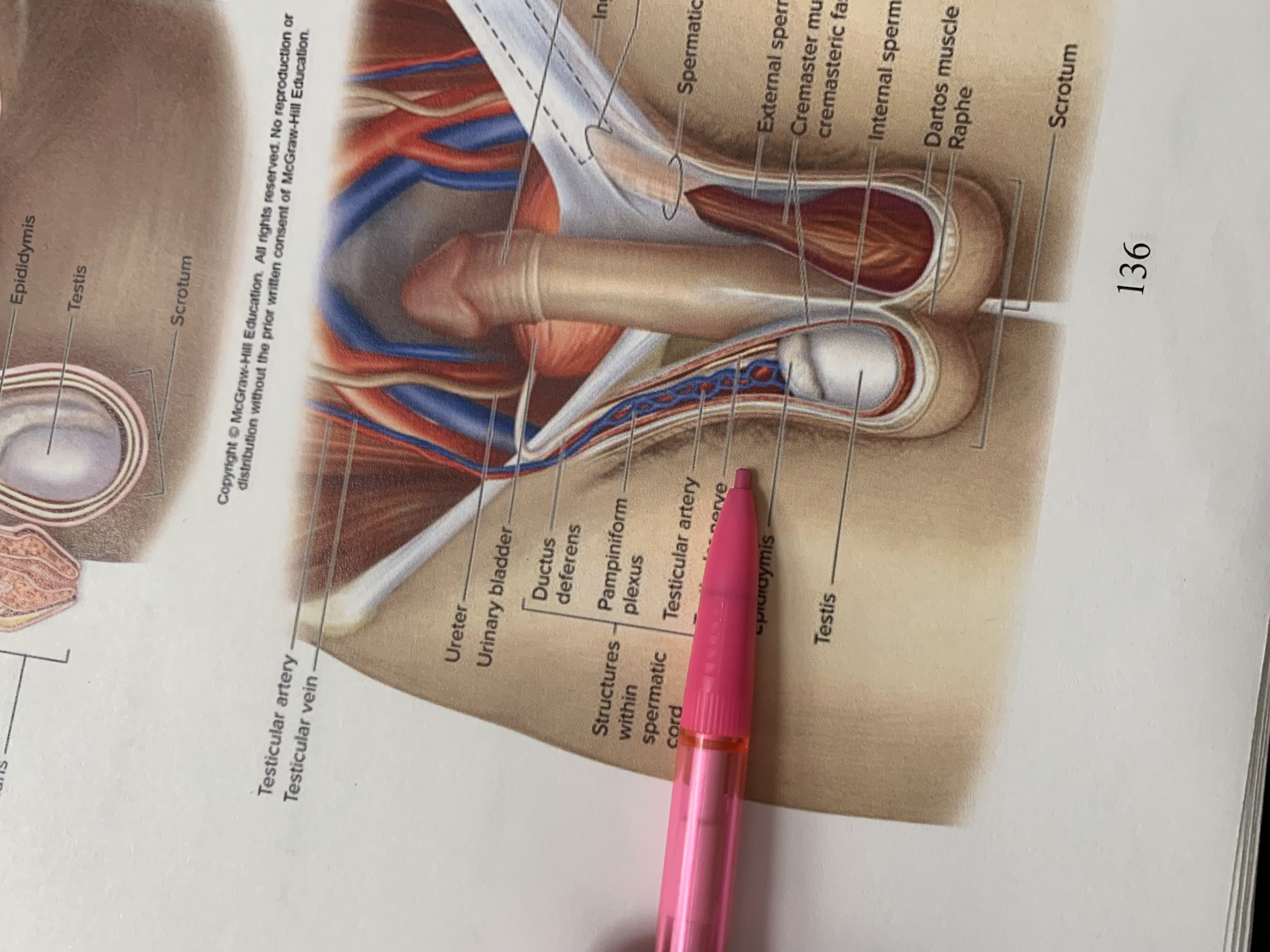
testicular nerve
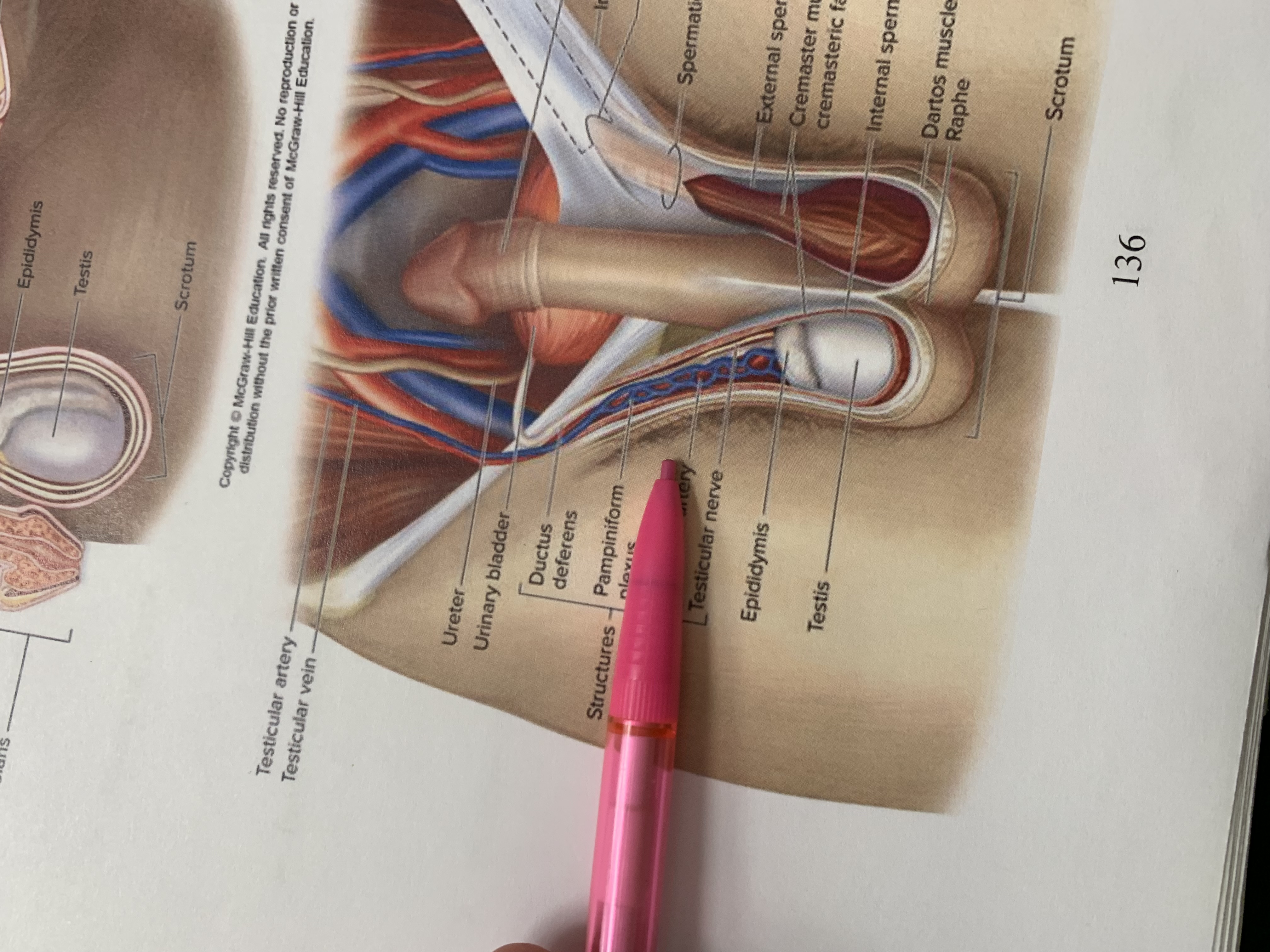
testicular artery
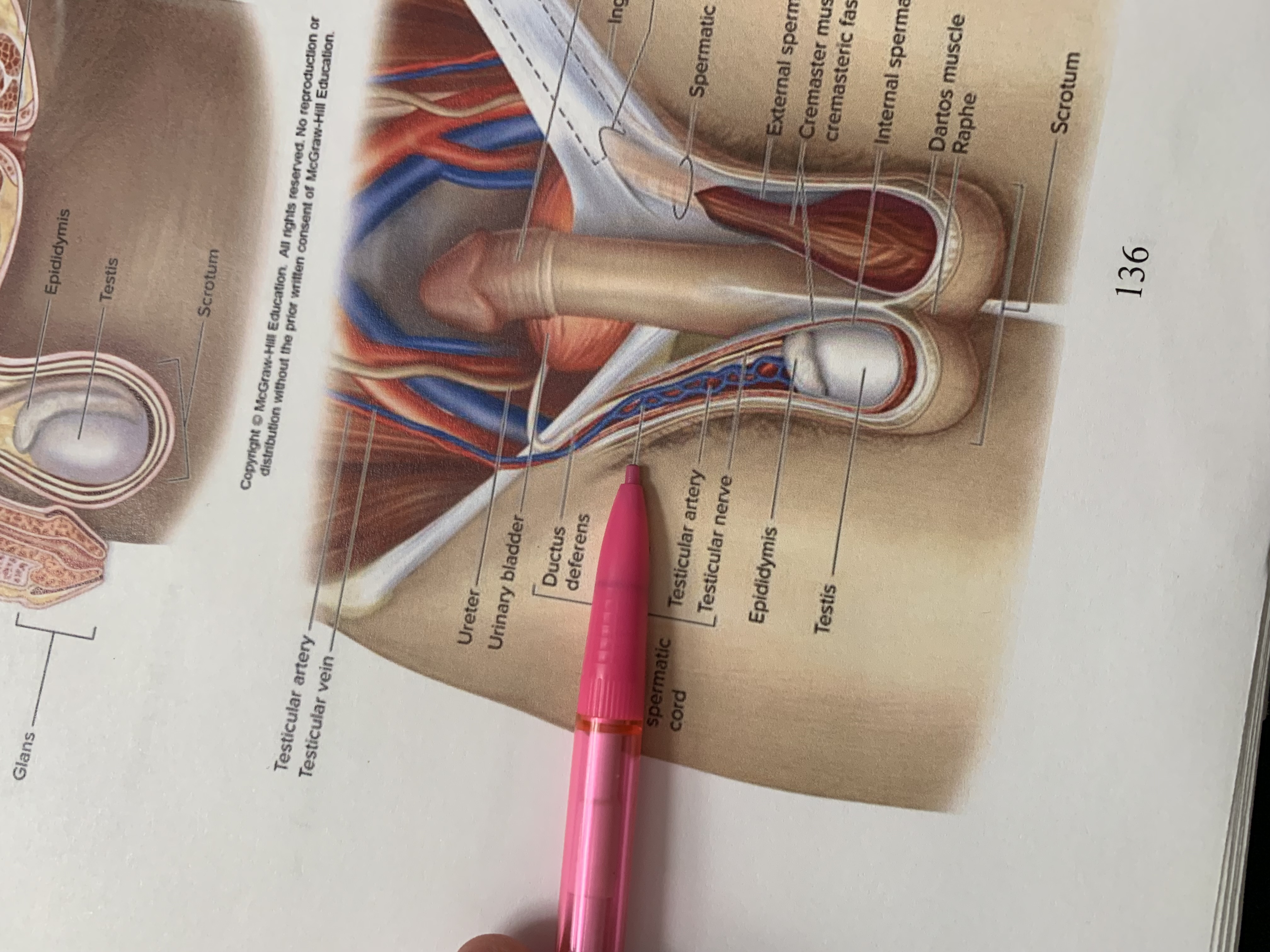
pampiniform plexus
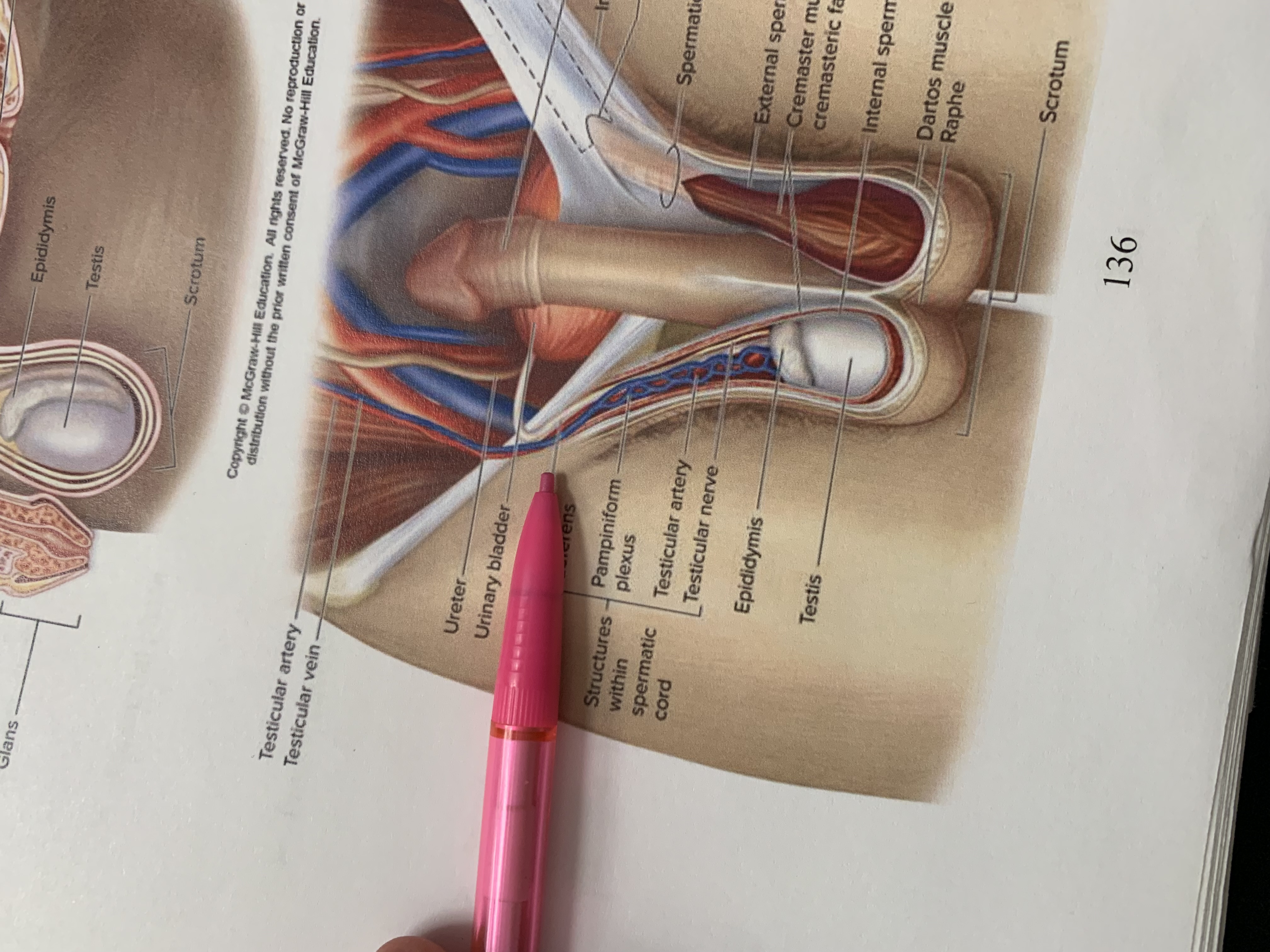
ductus deferens
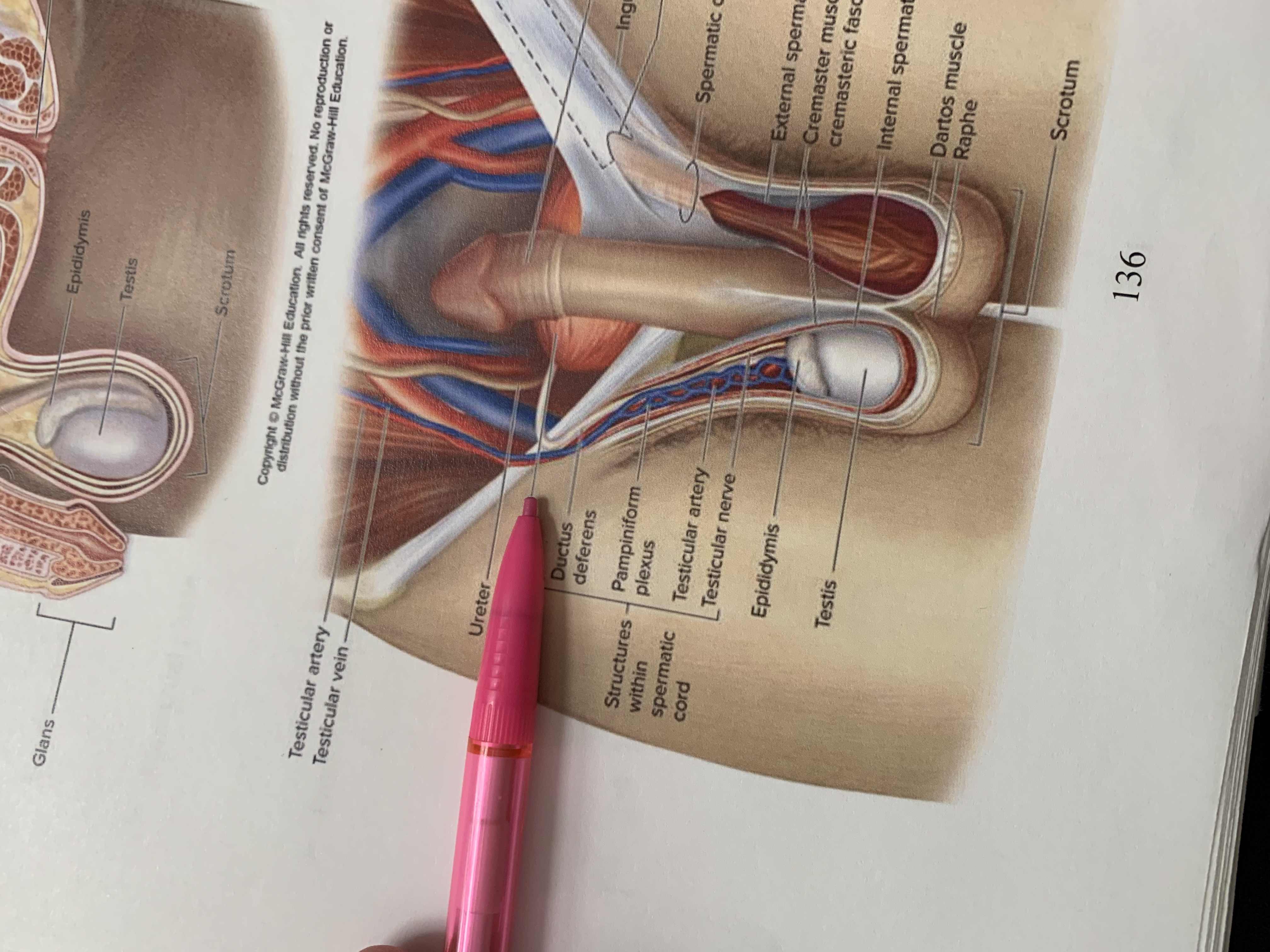
urinary bladder
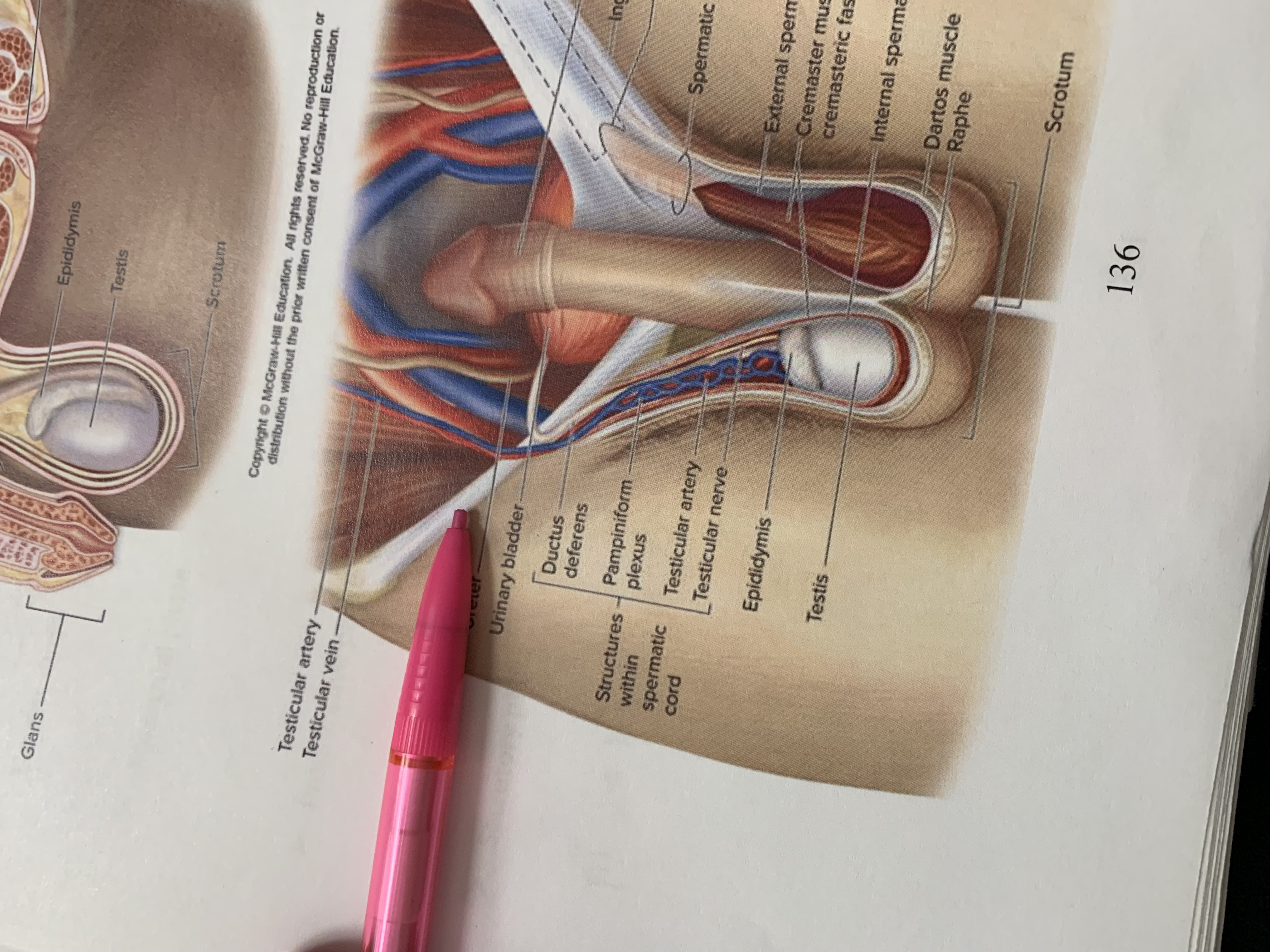
ureter
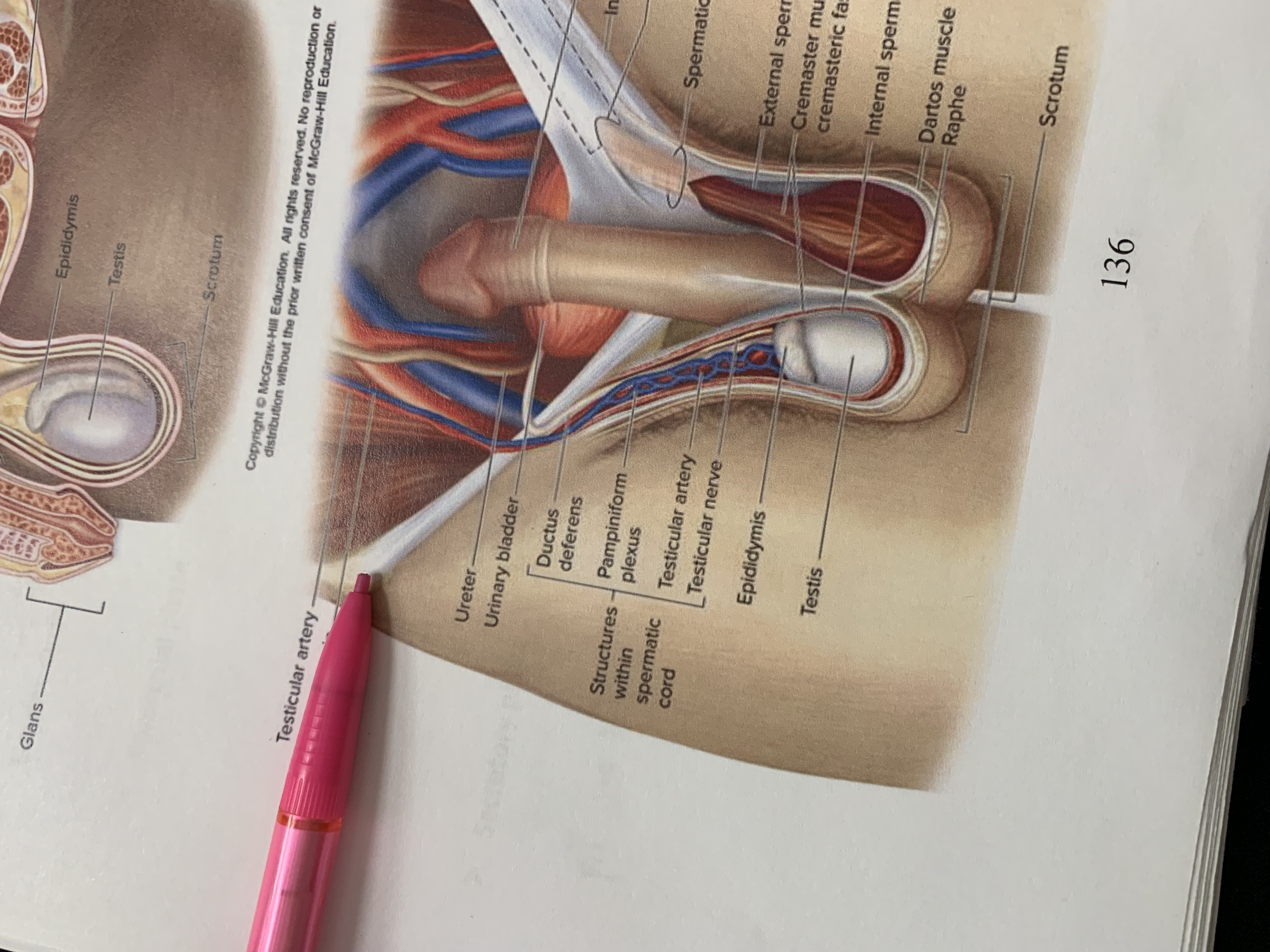
testicular vein
testicular artery
ampulla
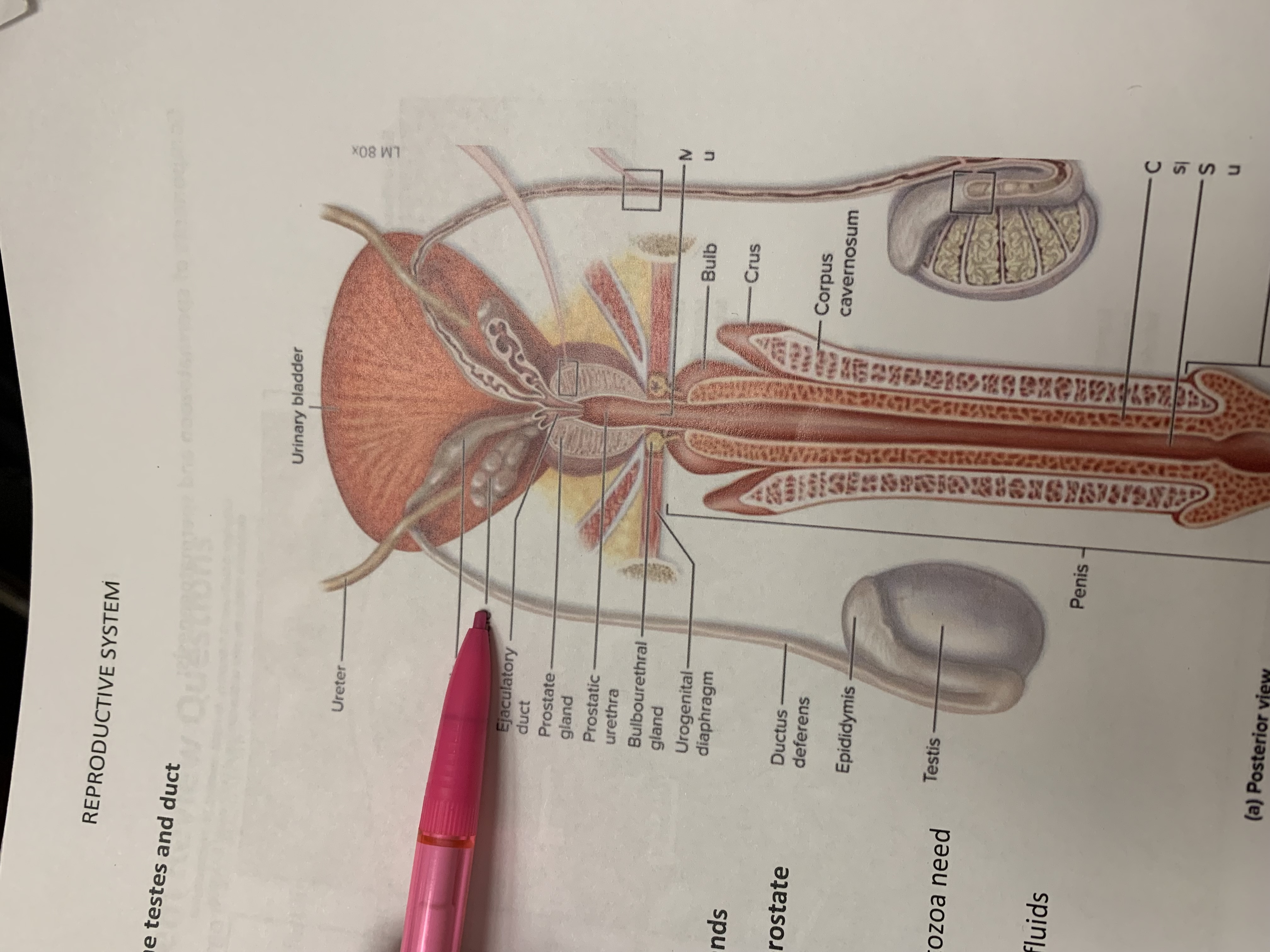
seminal vesicle
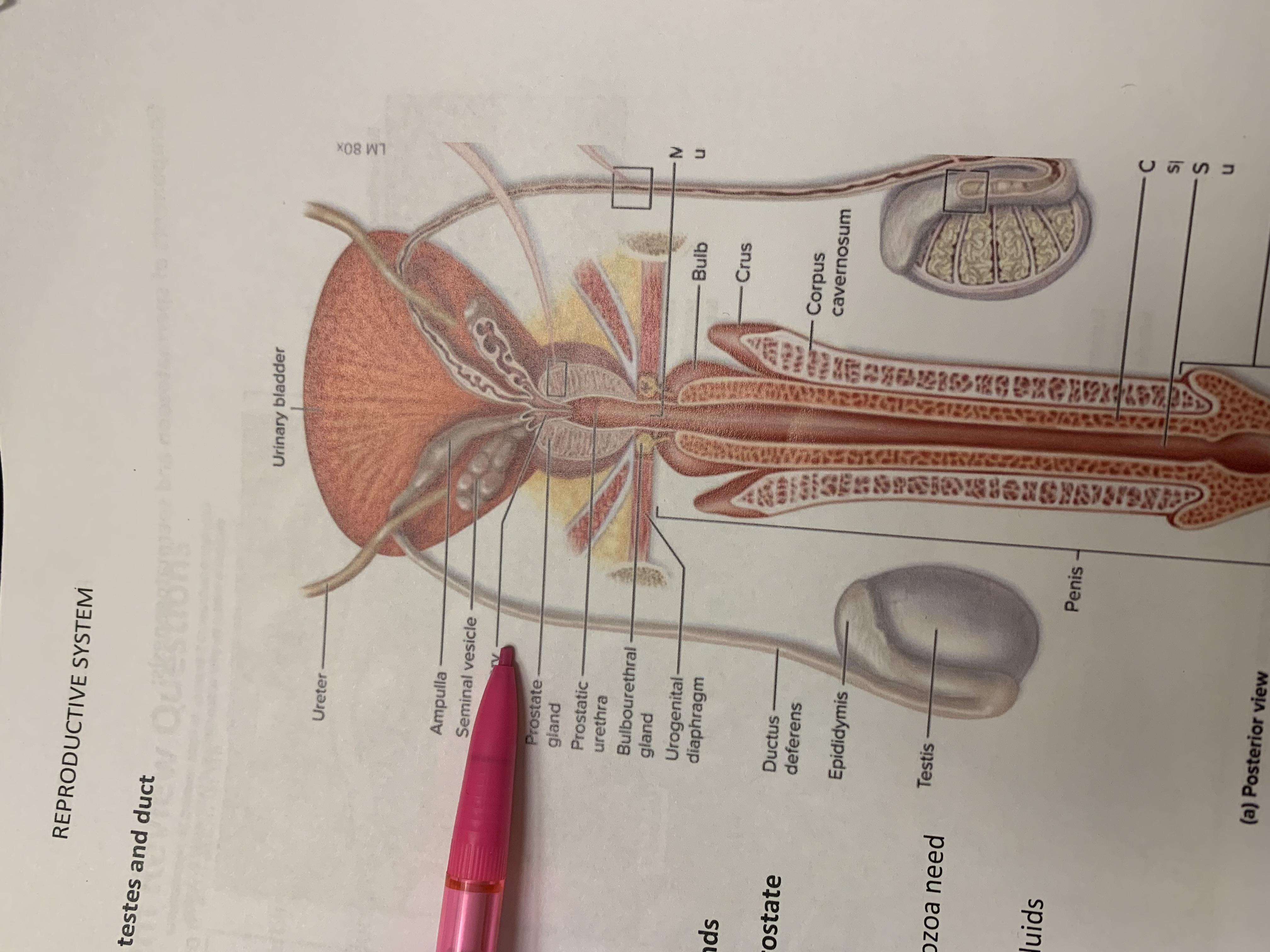
ejaculatory duct
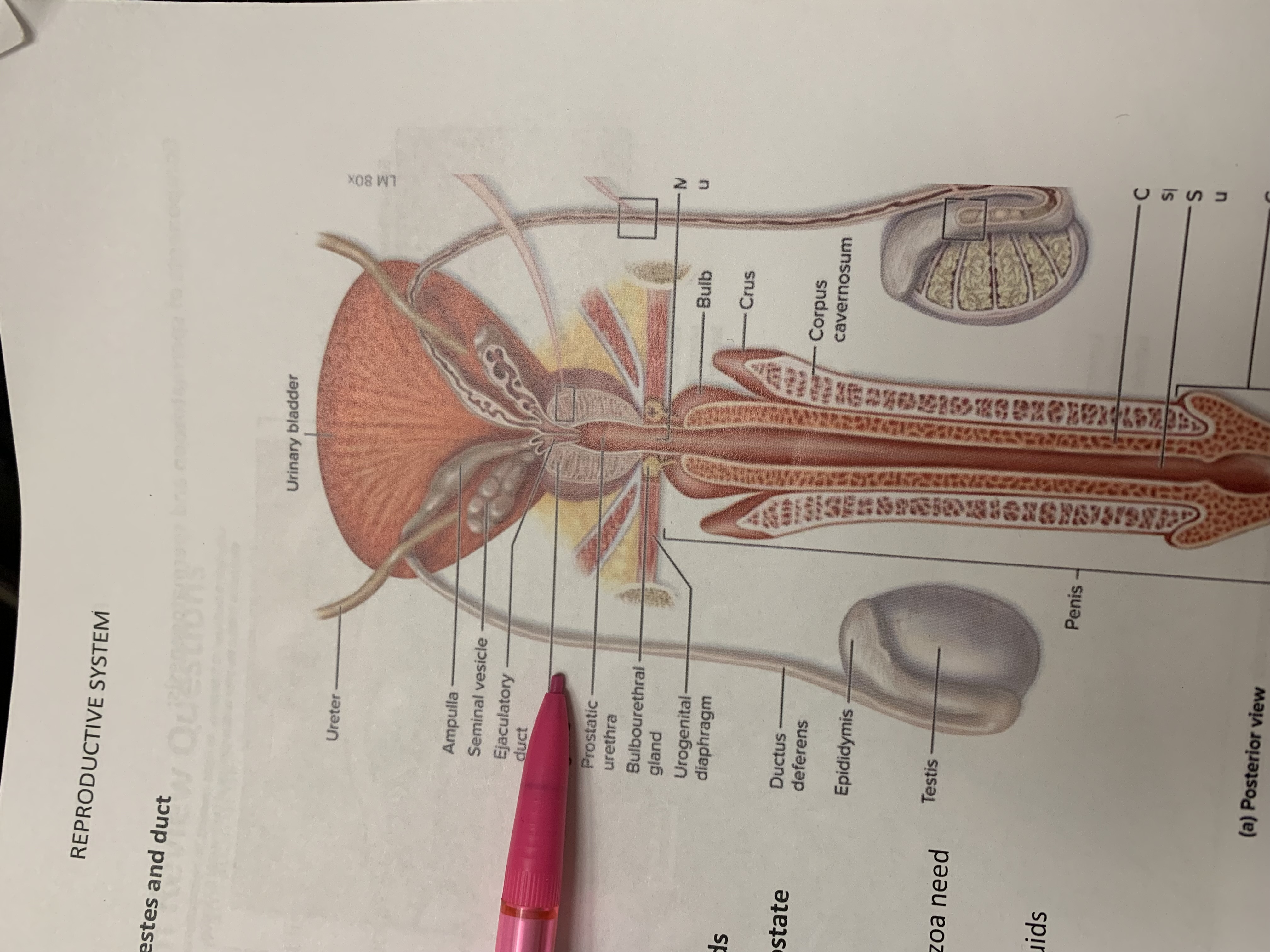
prostate gland
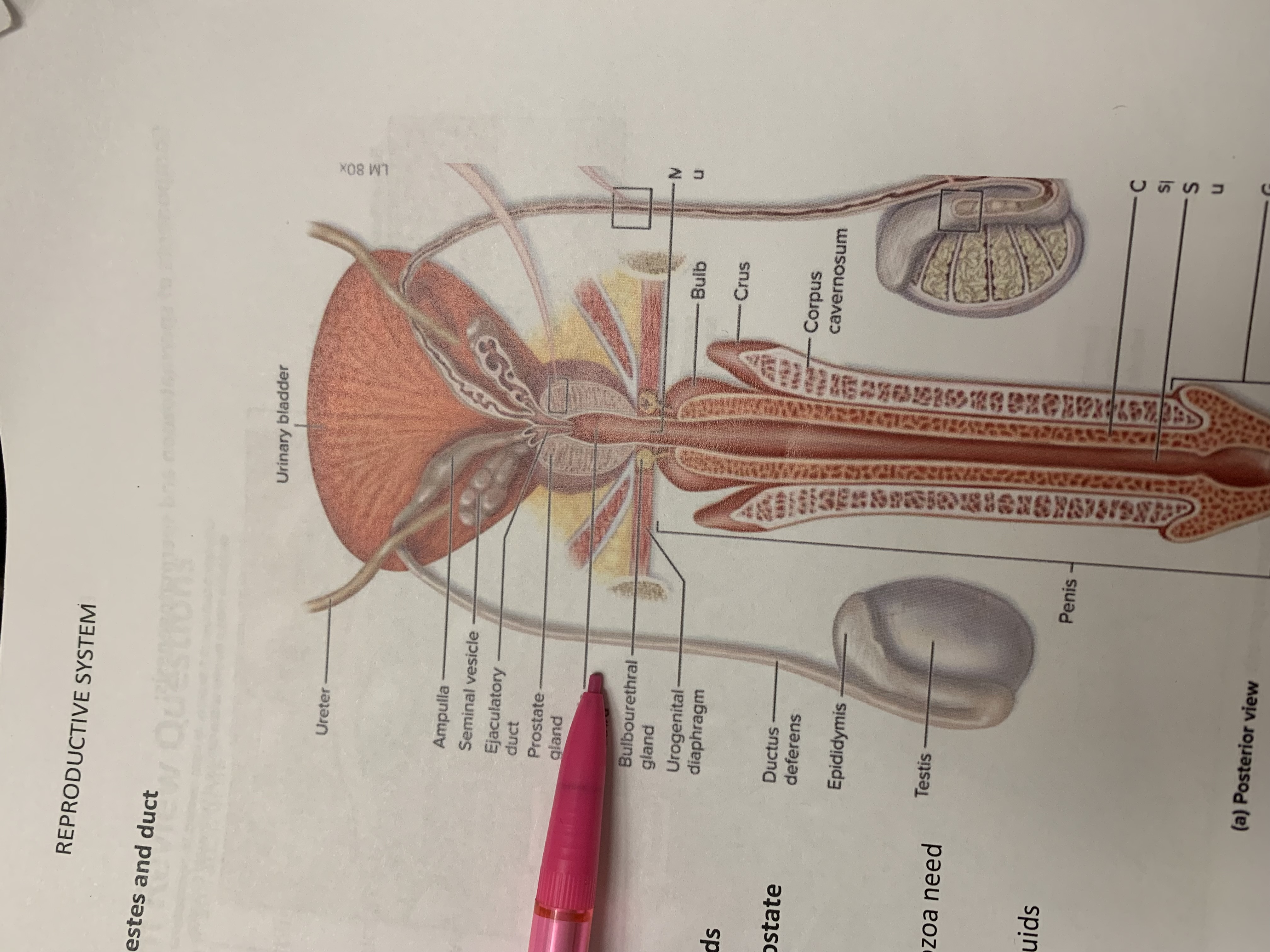
prostatic urethra
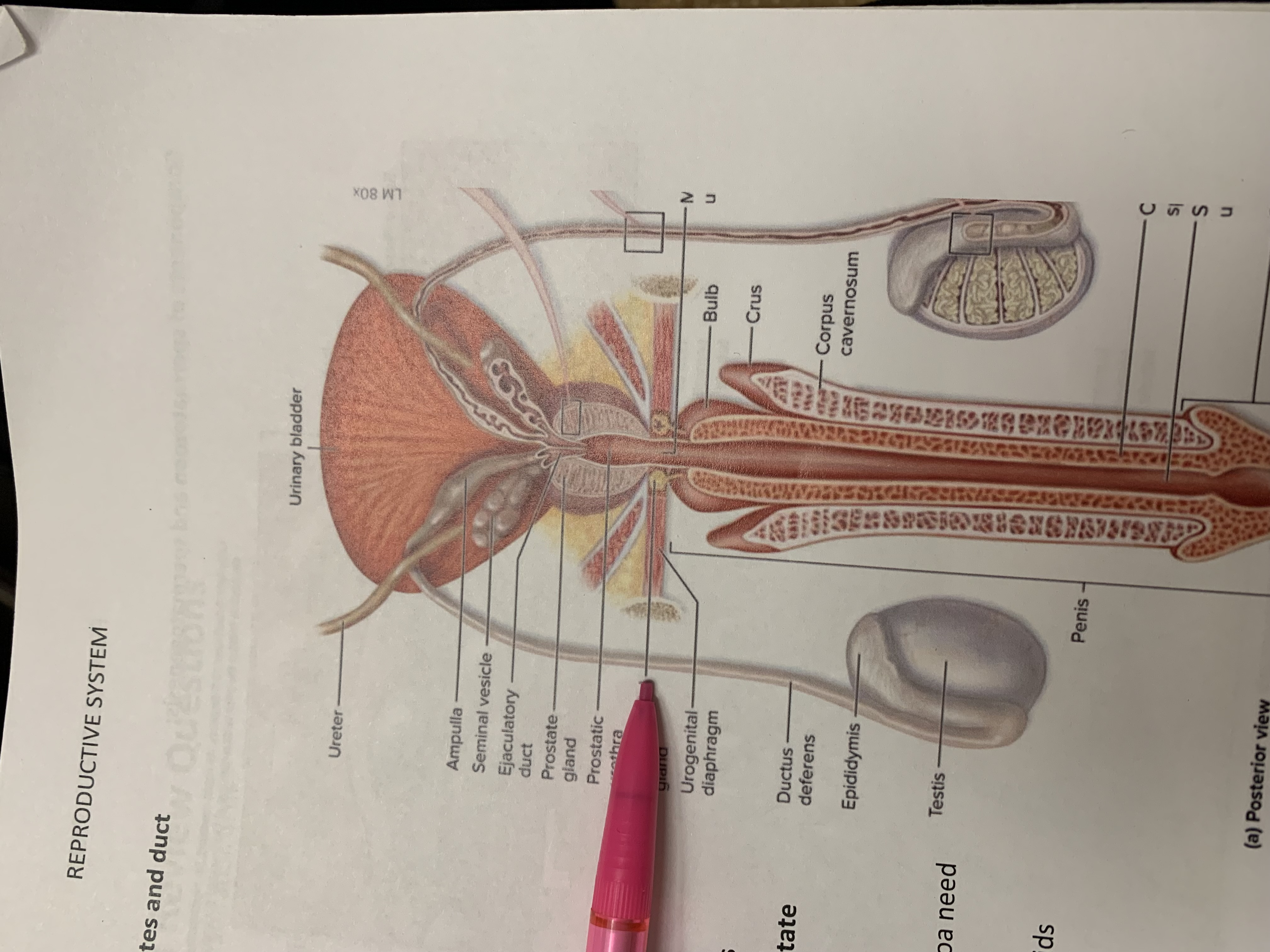
bulbourethral gland
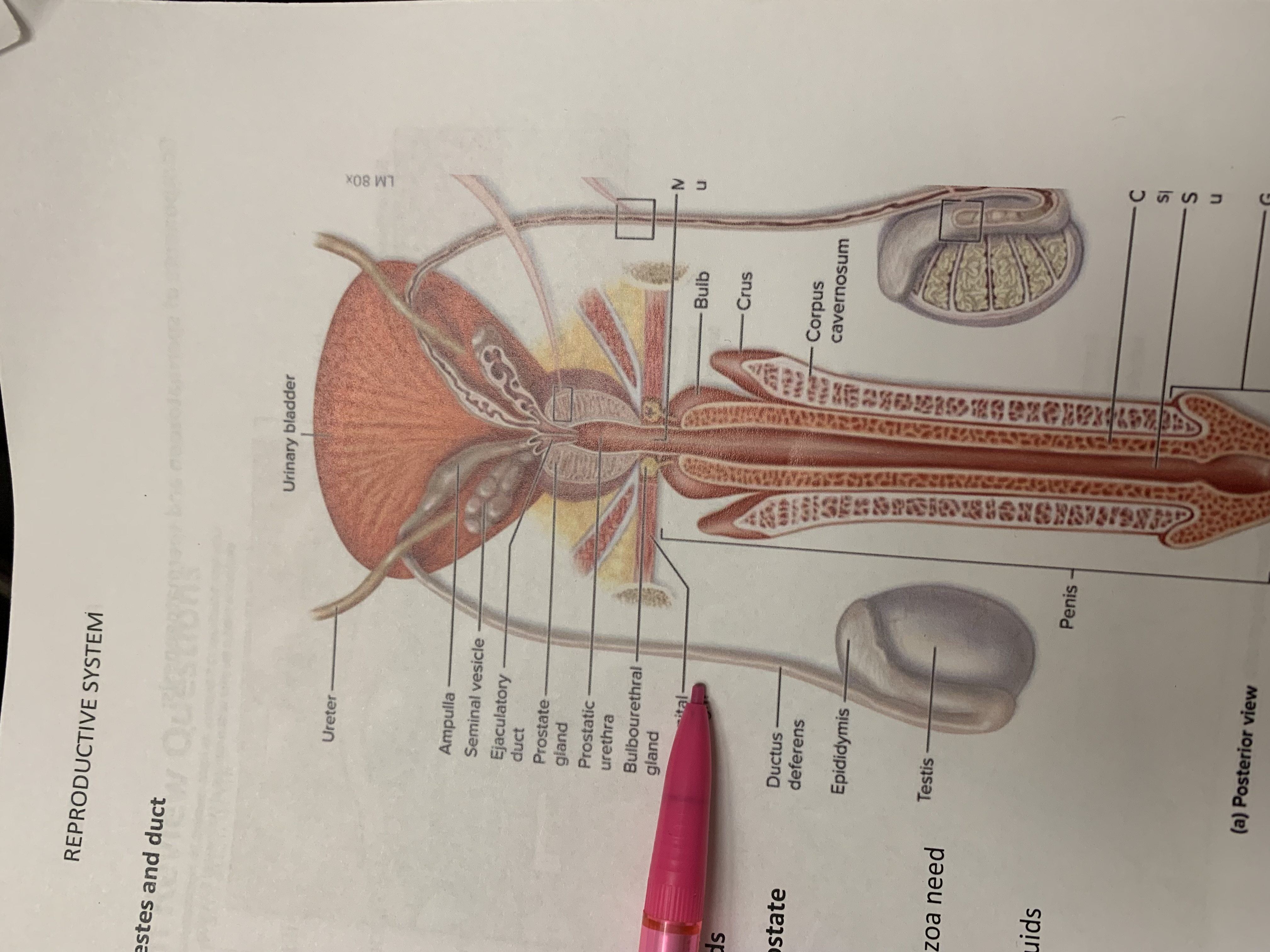
urogenital diaphragm
ductus deferens
epididymis
testis
penis
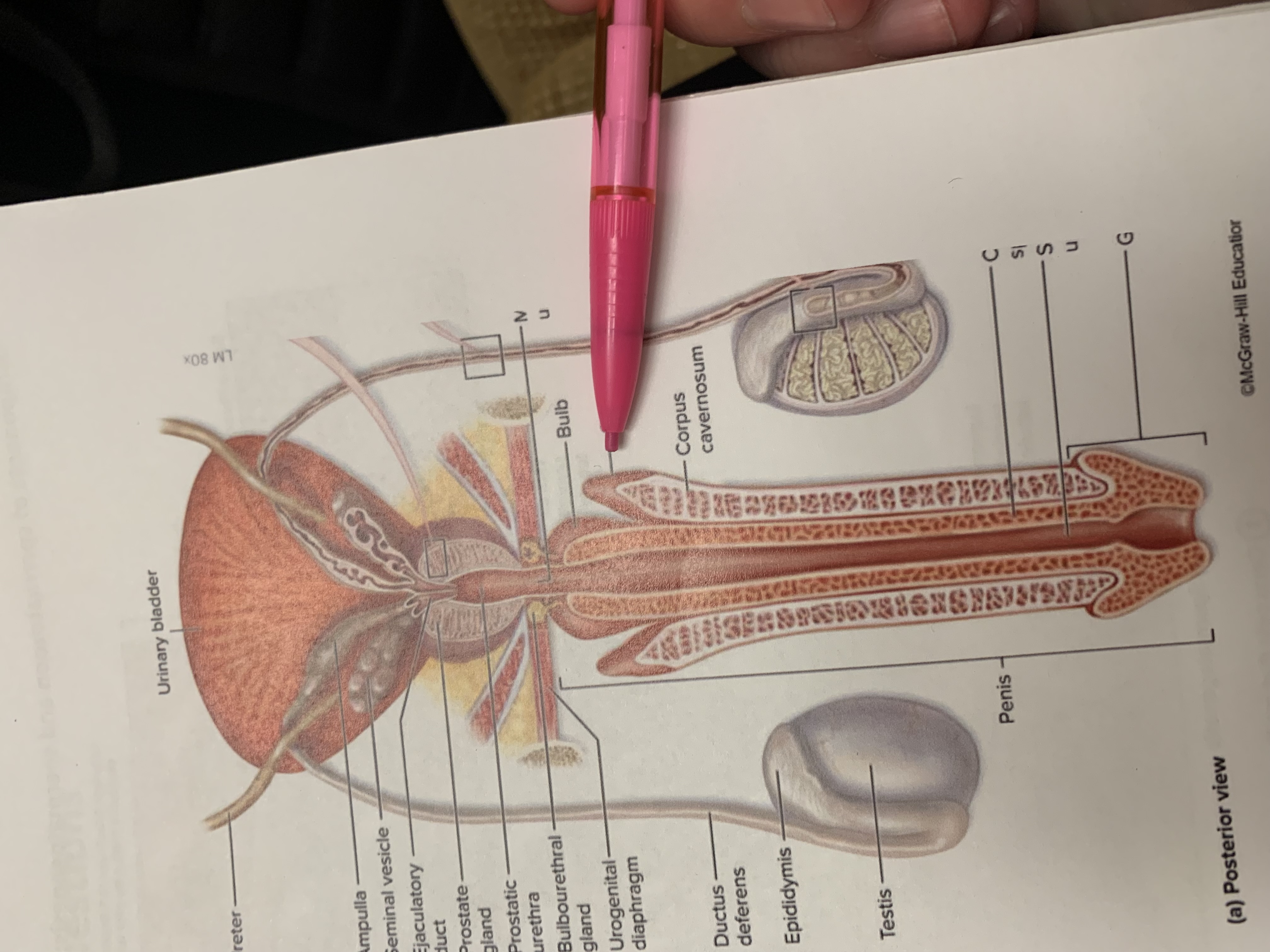
corpus cavernosum
crus
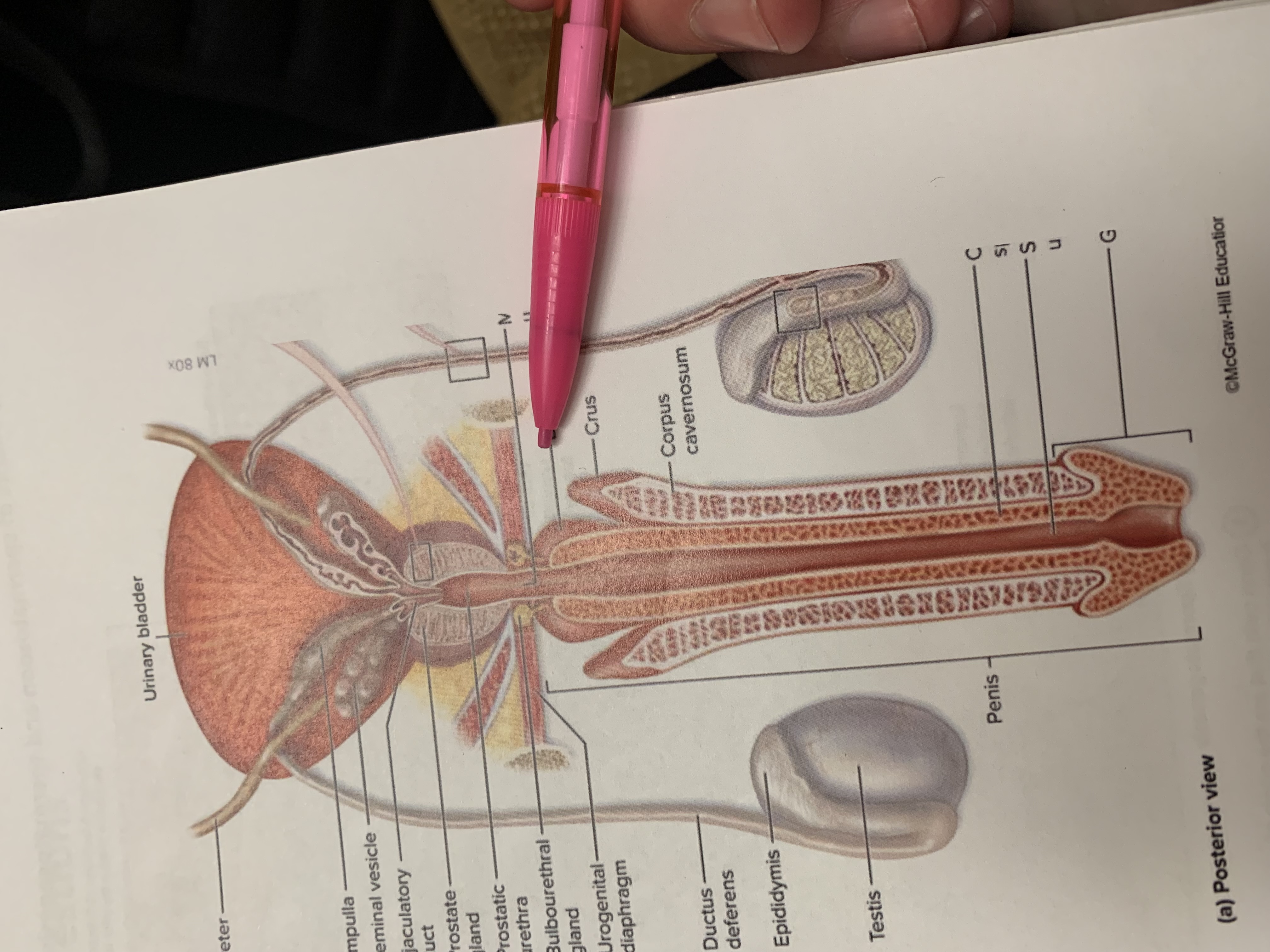
bulb
five cells of spermatogenesis
spermatogonia (stem cells) divide by mitosis to make 2 daughter cells. 1 stays as spermatogonium, other differentiates to primary spermatocyte
primary spermatocytes being meiois and form 2ndary spermatocytes
2ndary spermatocytes differentiate into spermatids (immature gametes)
spermatids diff to spermatozoa
spermatozoa enter fluid in lumen, lose contact w wall seminiferous tubules
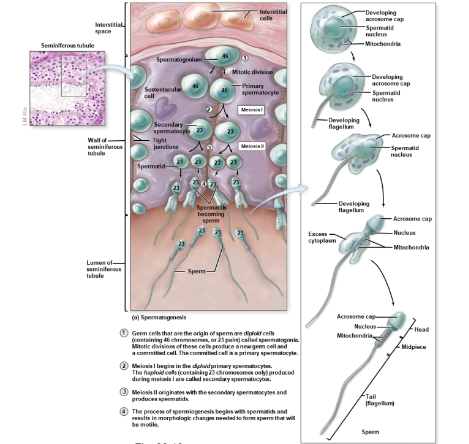
sperm pathway through testes and ducts
seminiferous tubules
rete testis
efferent ductules
epididymis
ductus deferens
ejaculatory duct
urethra
major functions male accessory glands
activate spermatozoa
provide nutrients to spermatozoa for motility
propel spermatozoa and fluids along reproductive tract (peristaltic contractions)
product buffers (counteract acidity of urethra and vagina)
components of ejaculate
spermatozoa
seminal fluid
60% seminal glands, buffer, nourish, dilate so easy to uterus
30% prostate, nourish and semen thinning so sperm mobile
5% epididymis, proteins so sperm infertil til activated in female
5% Bulbourethral glands, lube urethra and vagina
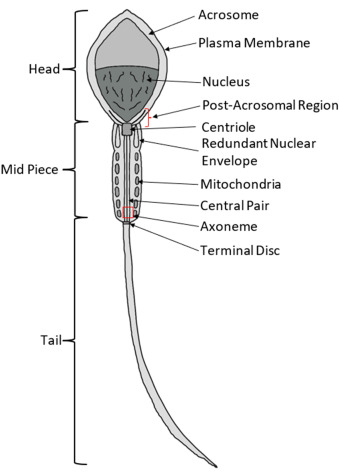
structure of sperm cells
head with acrosome cap, mid piece, tail (flagellum)
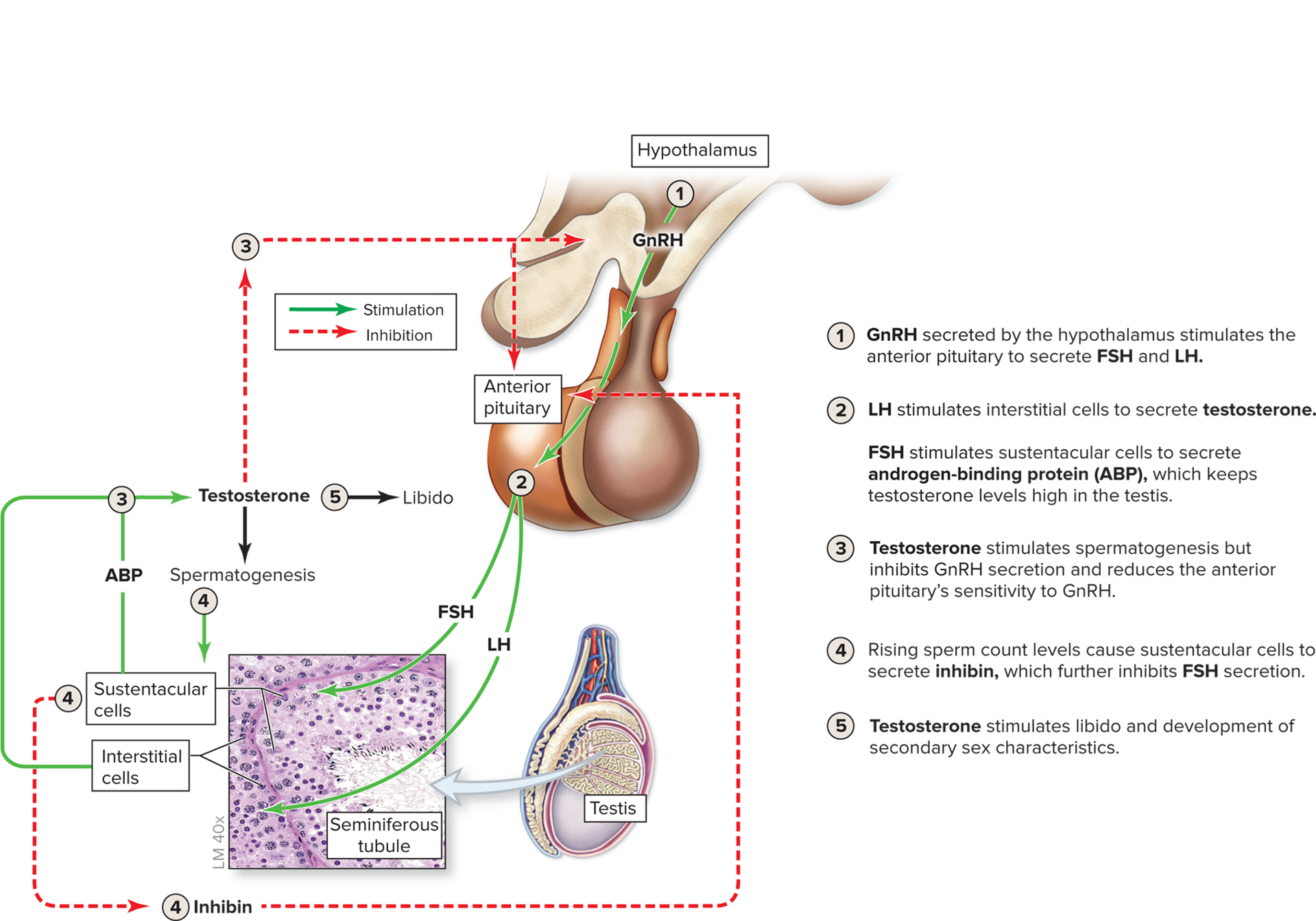
male hormone pathway
GnRH by hypothalamus, ant pituitary secretes FSH and LH
LH stim interstitial cells to secrete testosterone, FSH stims ABP so testosterone in testis high
testosterone stim spermatogensis, inhibit GnRH
rising sperm count levels = sustentacular cells secrete inhibin so less FSH
testosterone stim libido and development of 2ndary sex characteristics
ejaculation physiology
Peristalsis: Rhythmic contractions of smooth muscle in the male reproductive ducts (ductus deferens), which are triggered by a burst of oxytocin from the posterior pituitary.
Seminal fluid formation: Accessory glands secrete fluids that mix with sperm to form semen.
Internal urethral sphincter: Contracts to prevent urine from entering the urethra during ejaculation.
Sympathetic innervation (from the lumbar splanchnic nerves): Coordinates the contractions of smooth muscle in the urethra wall to expel semen. This innervation is essential for ejaculation.
andropause
“male menopause” when men age, testosterone levels decrease. can lead to reduced testicular function
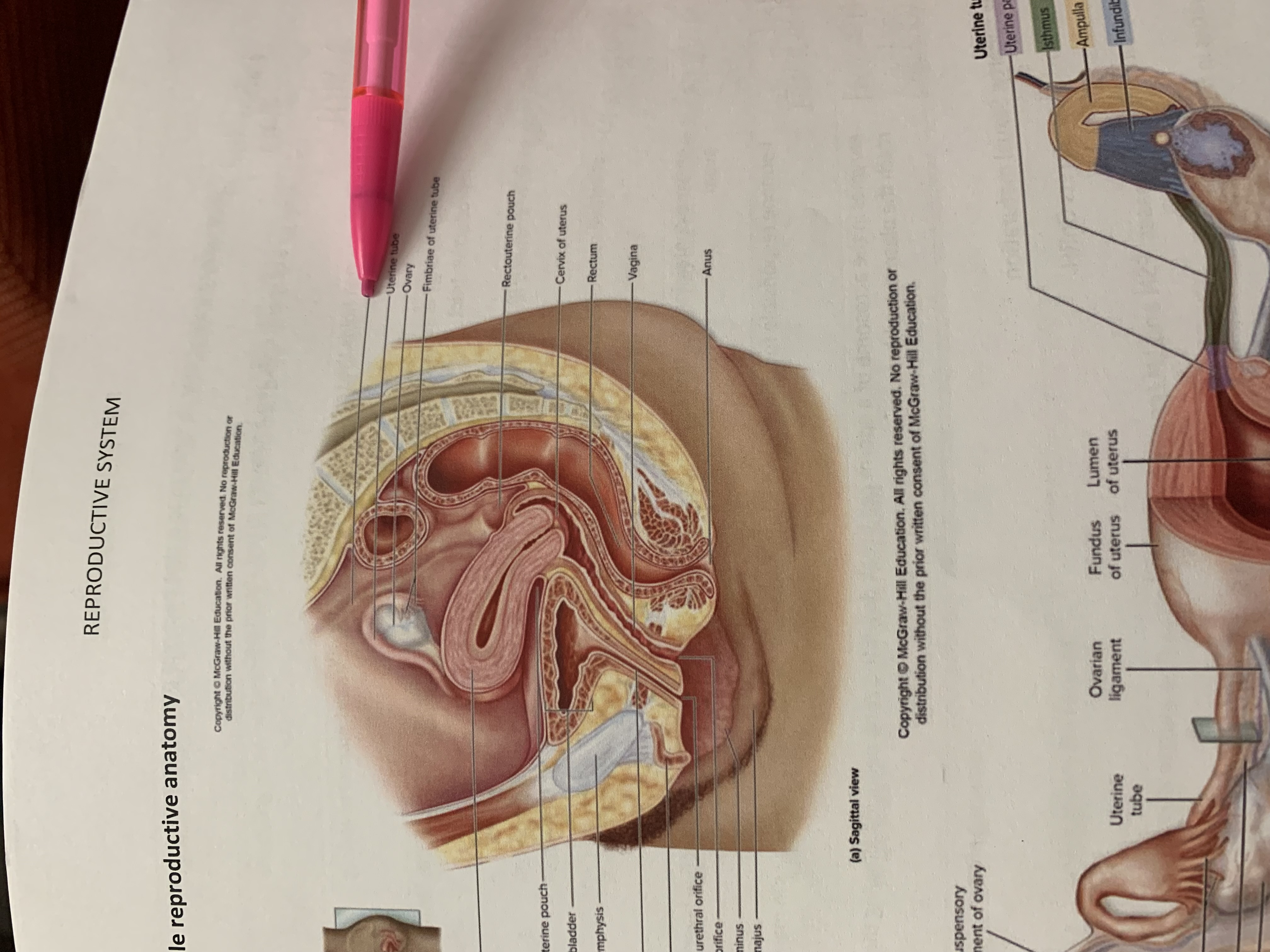
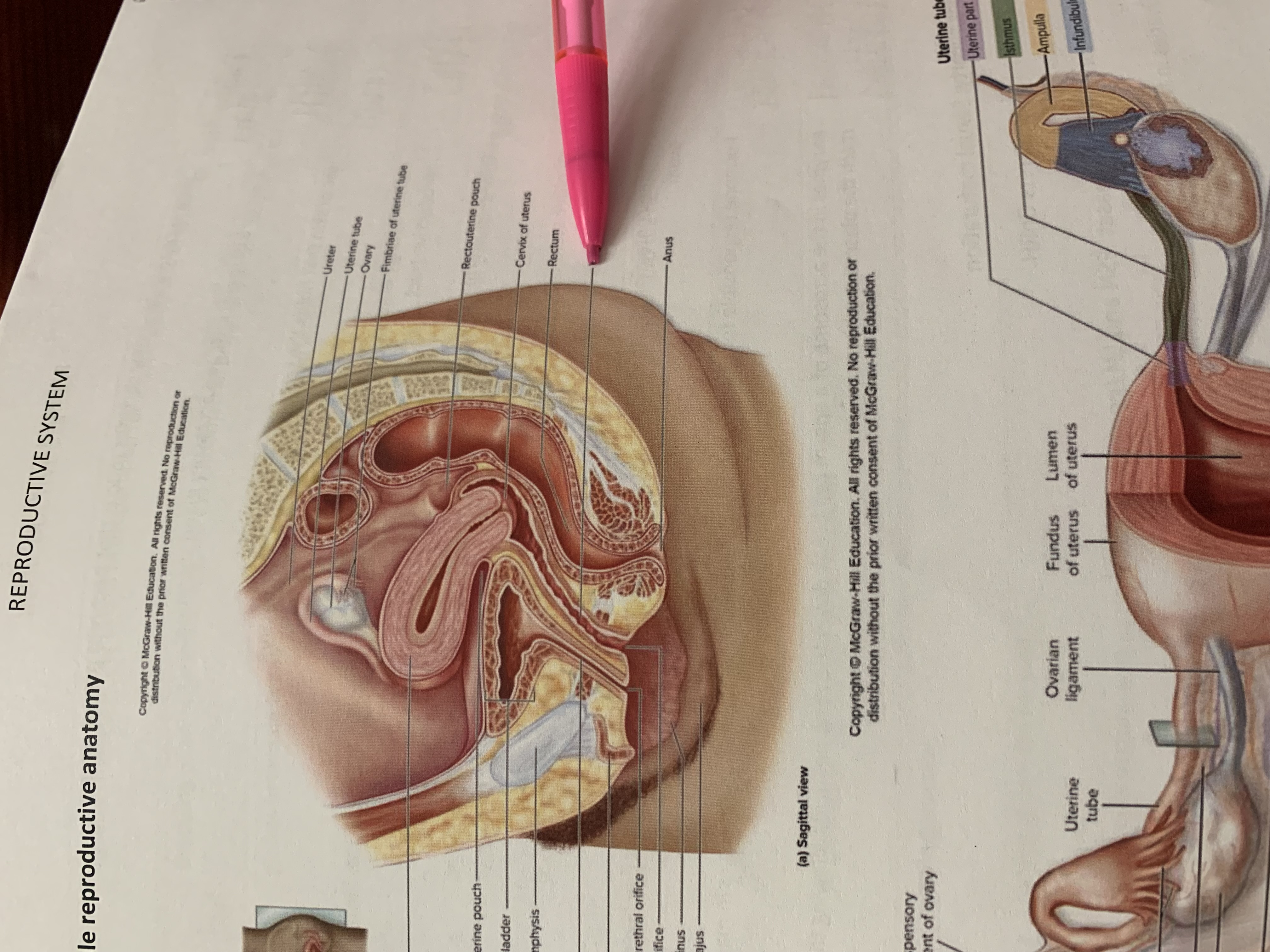
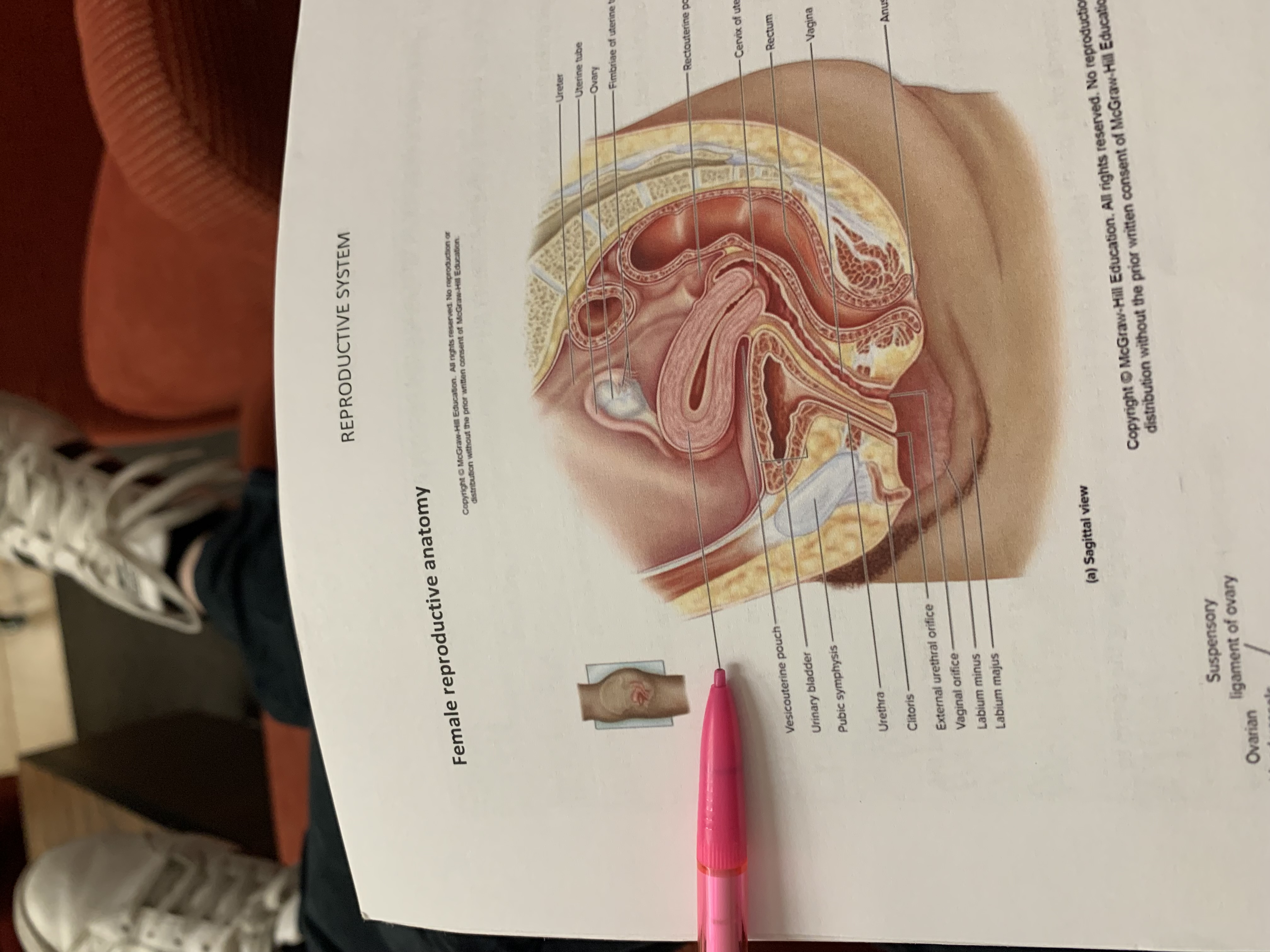
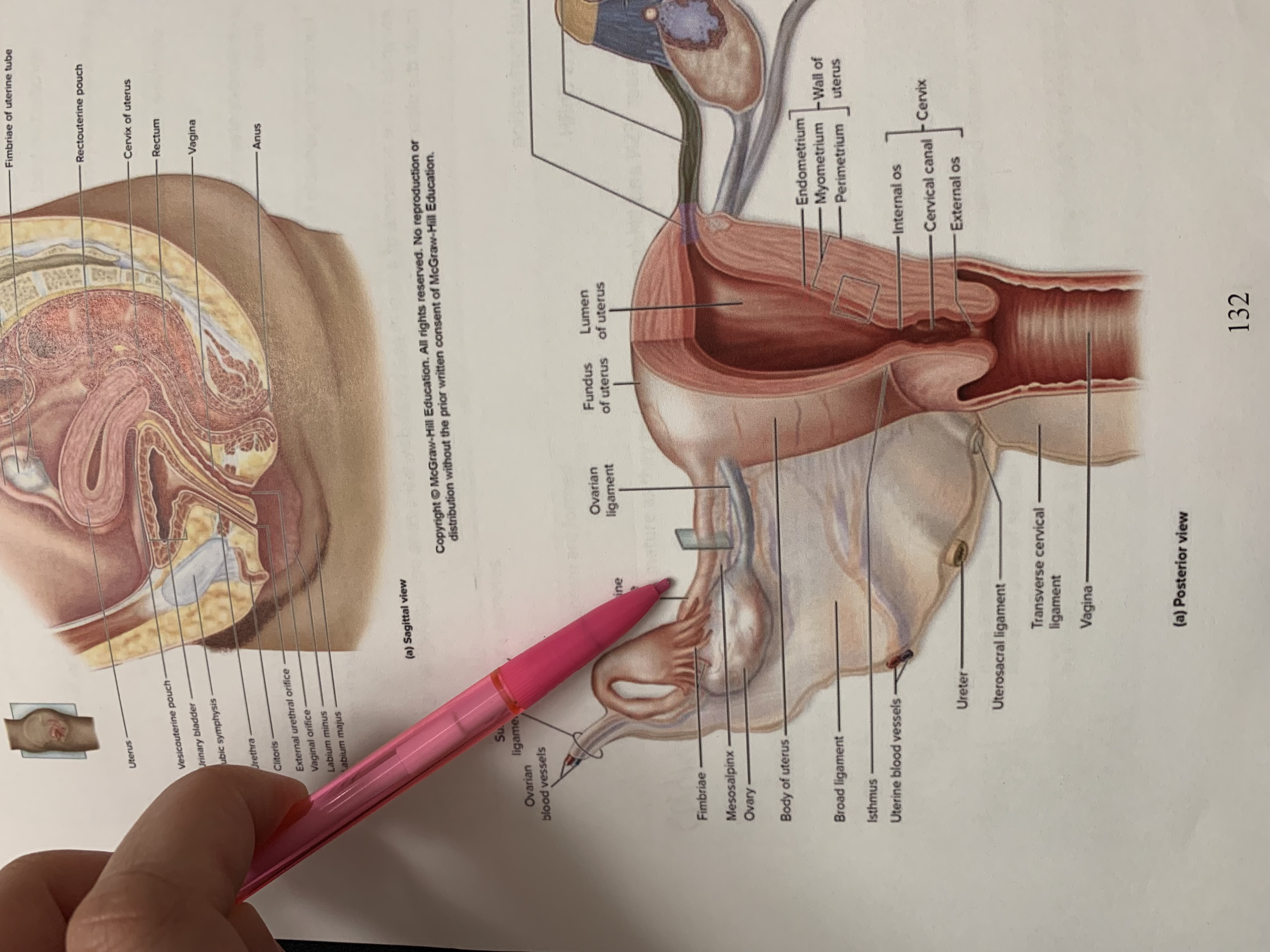
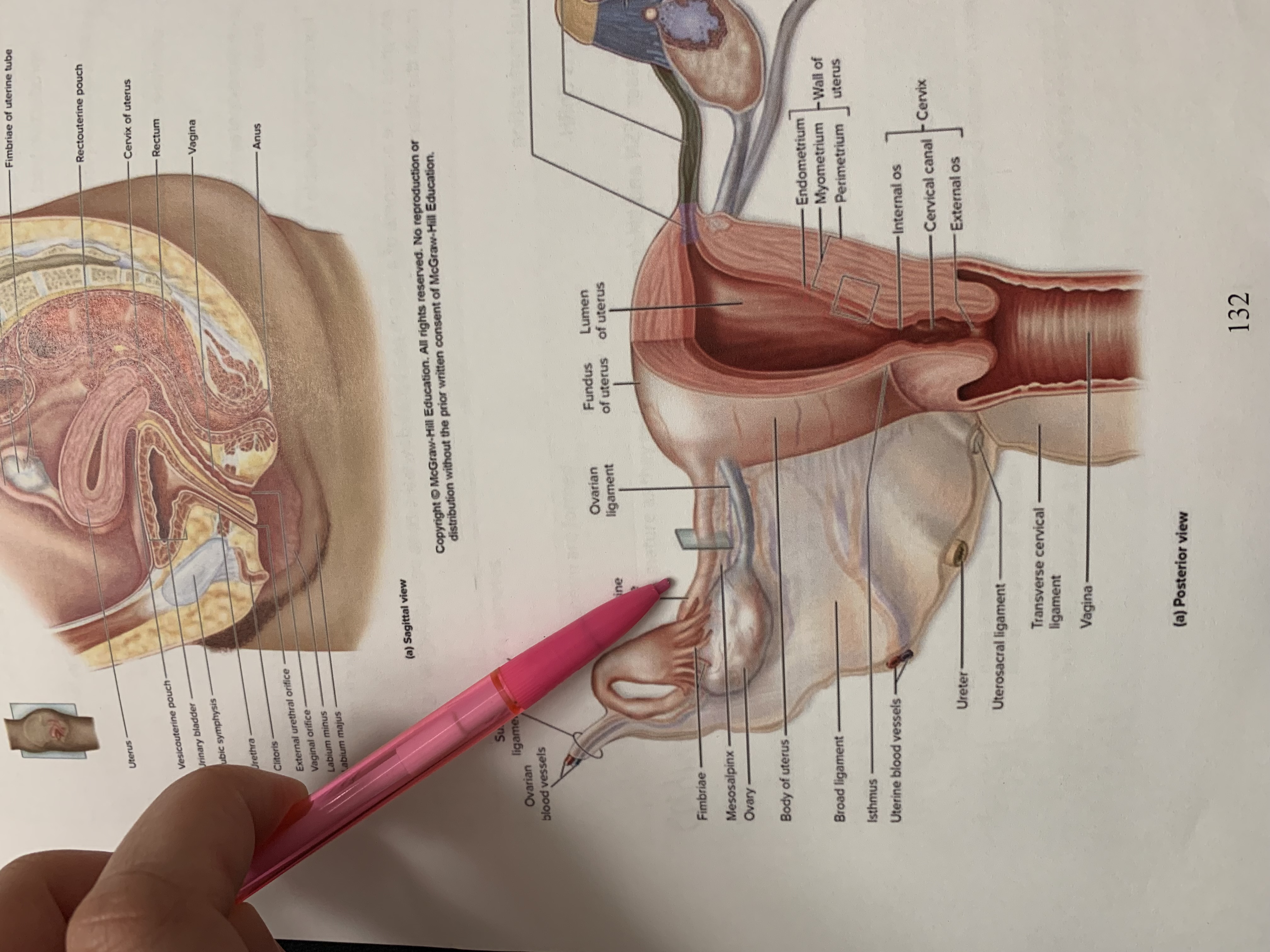
ureter
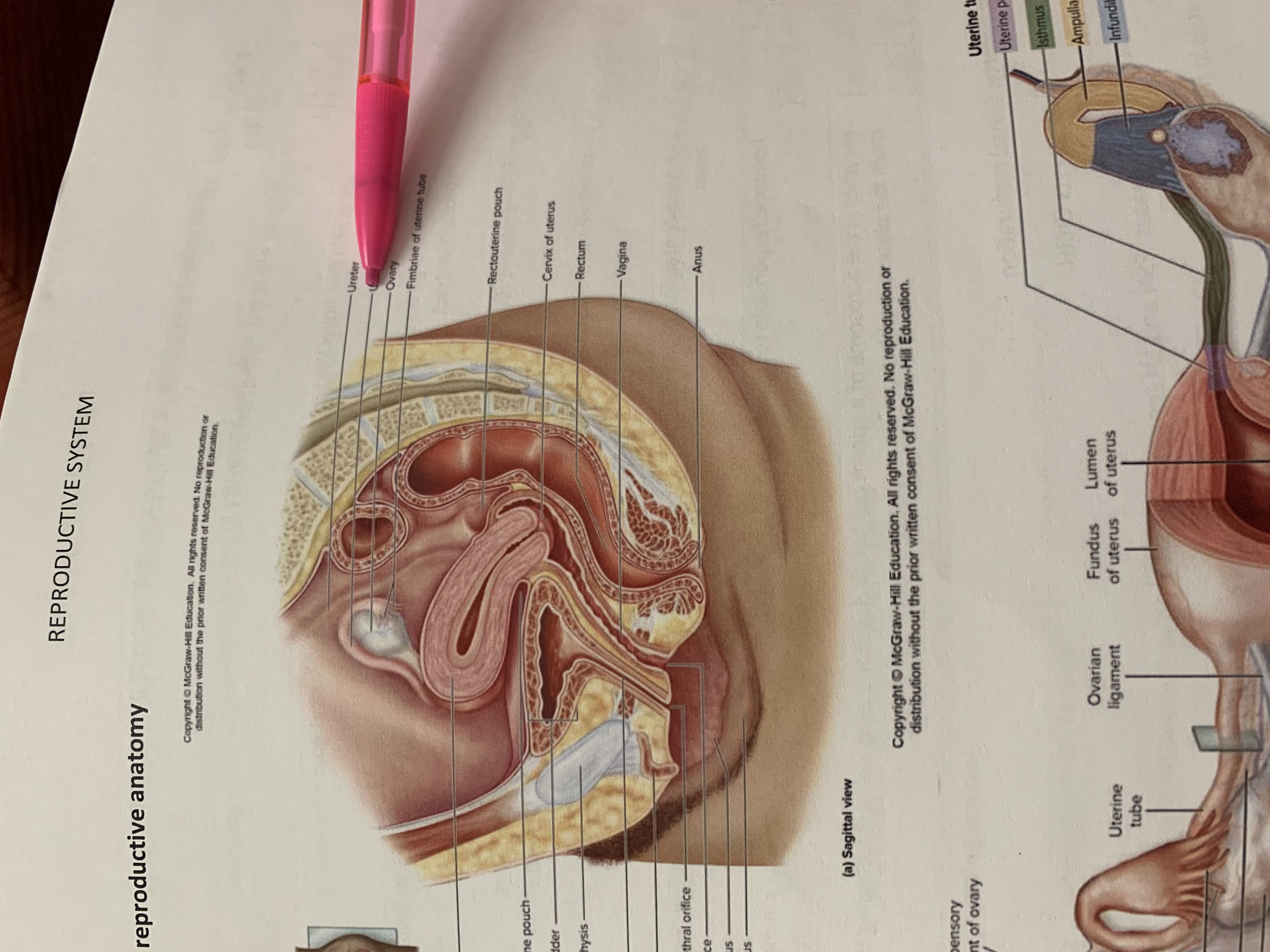
uterine tube

ovary
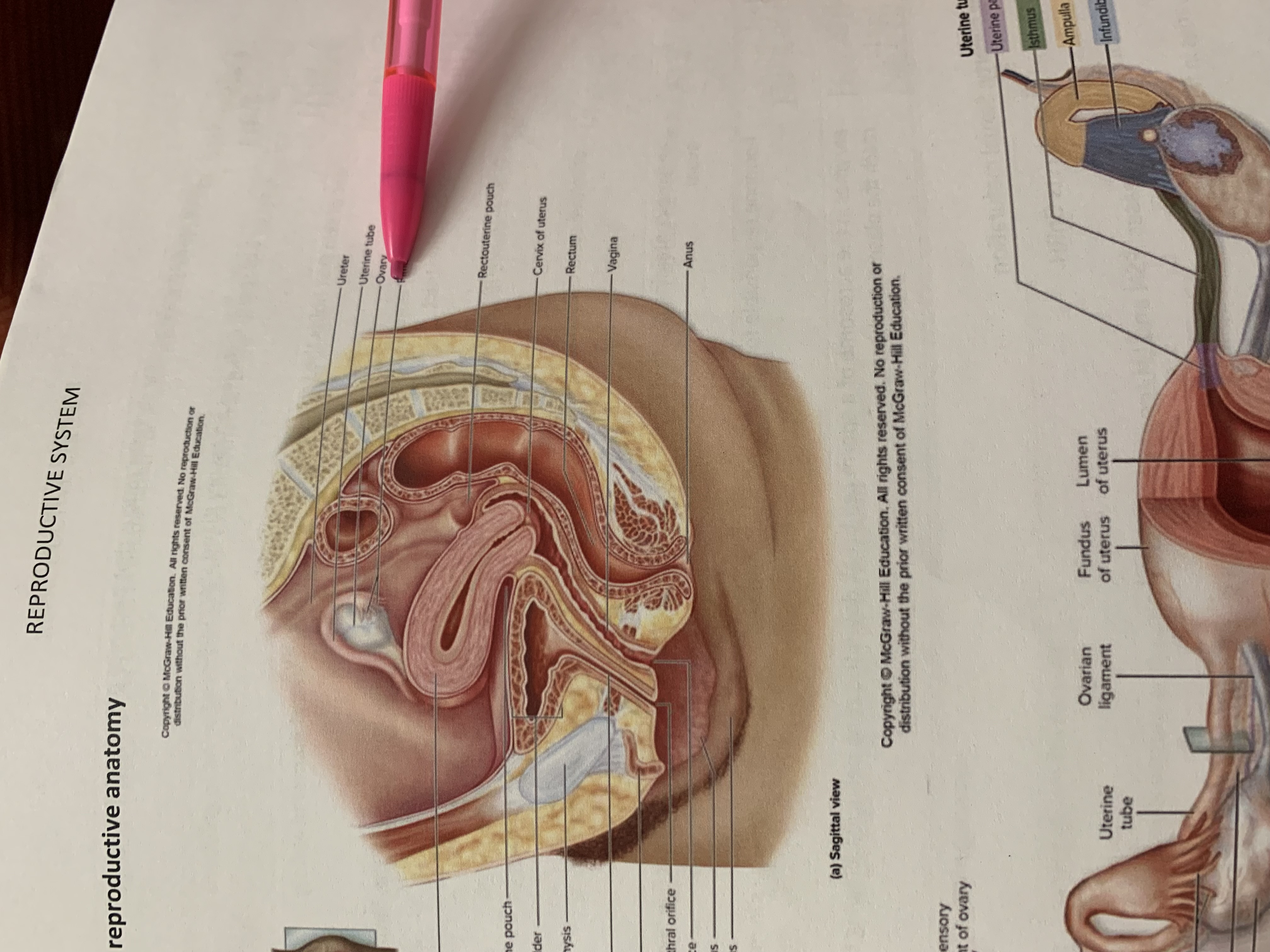
fimbriae of uterine tube
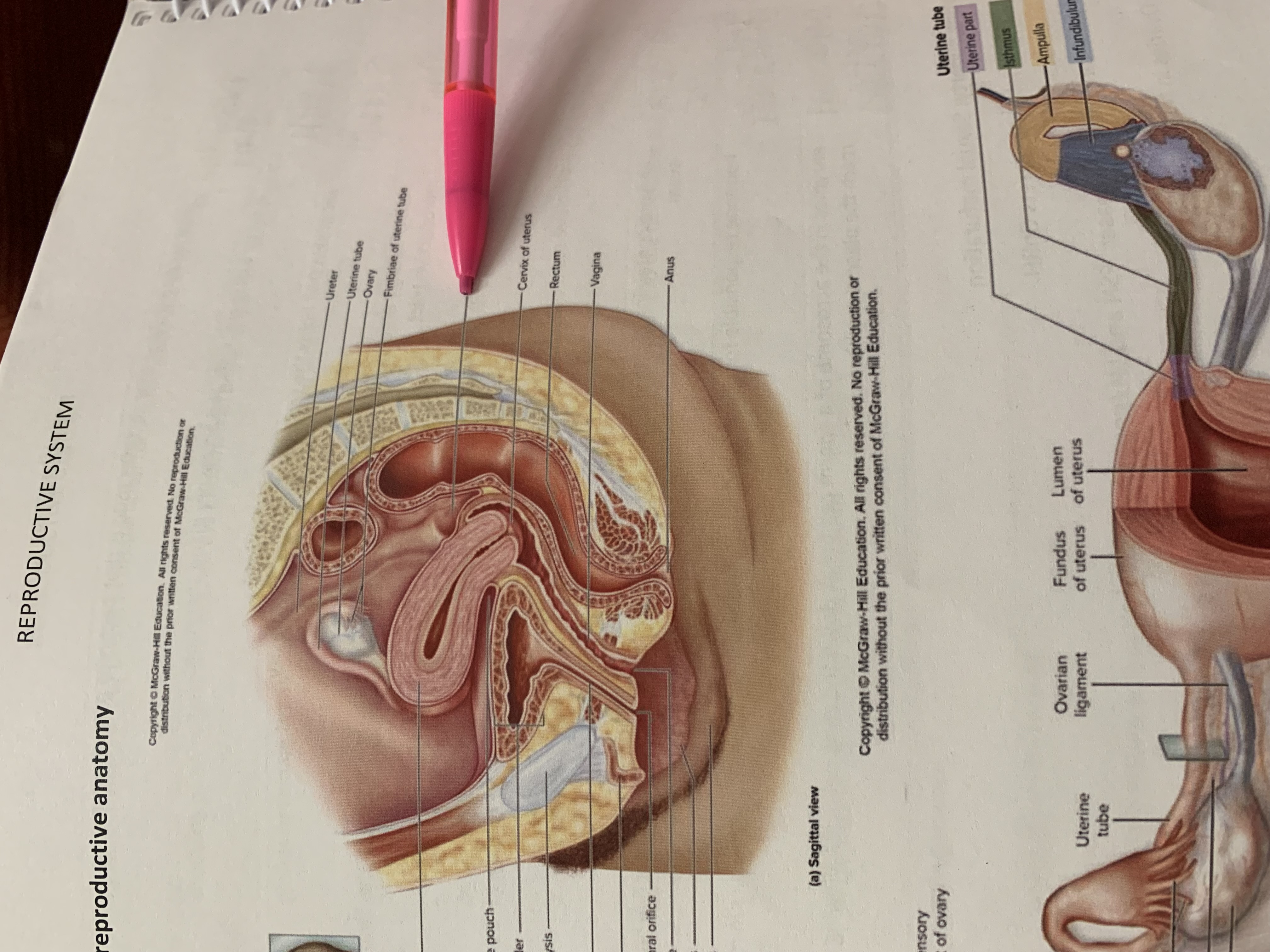
rectouterine pouch
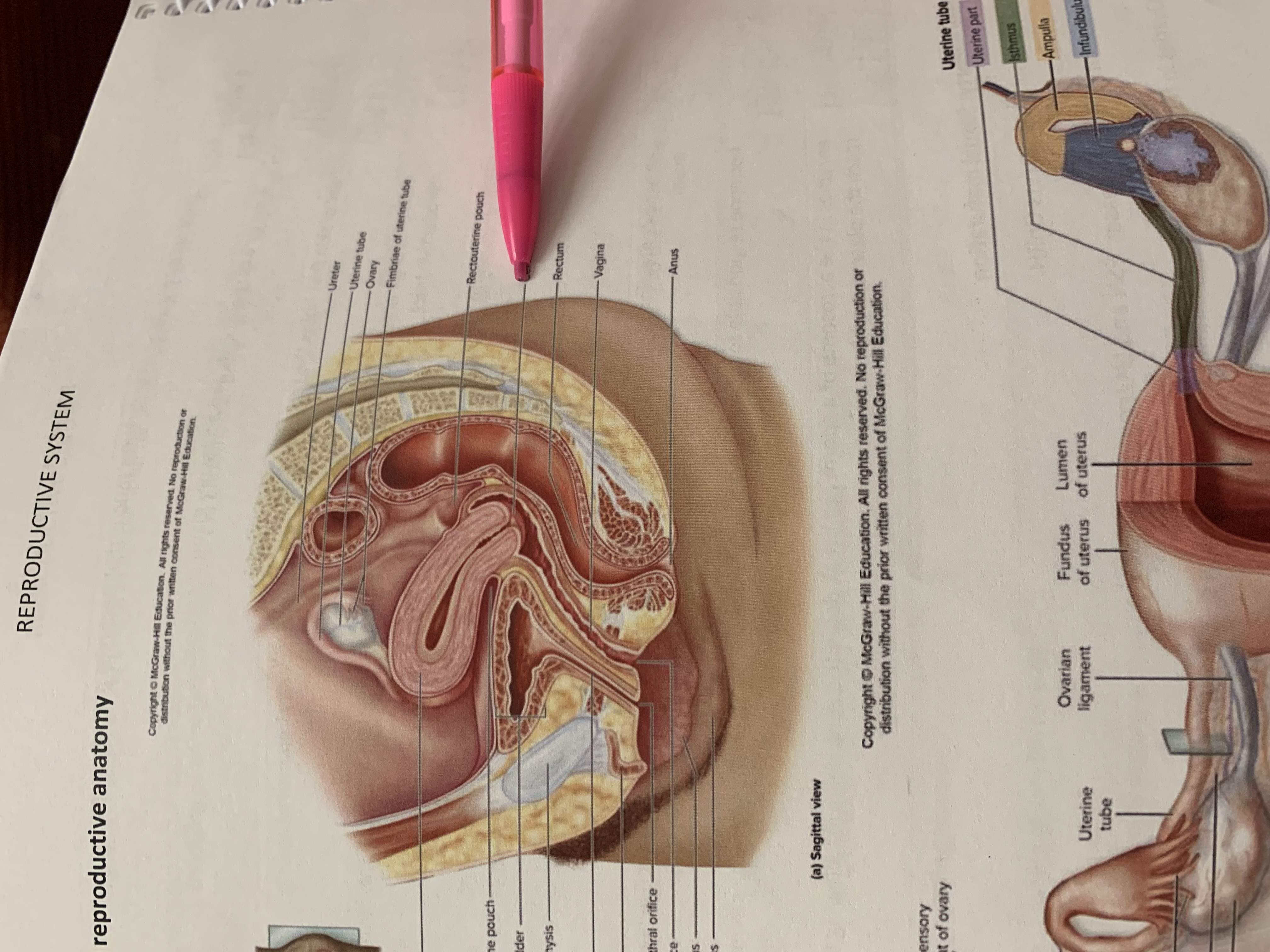
cervix of uterus
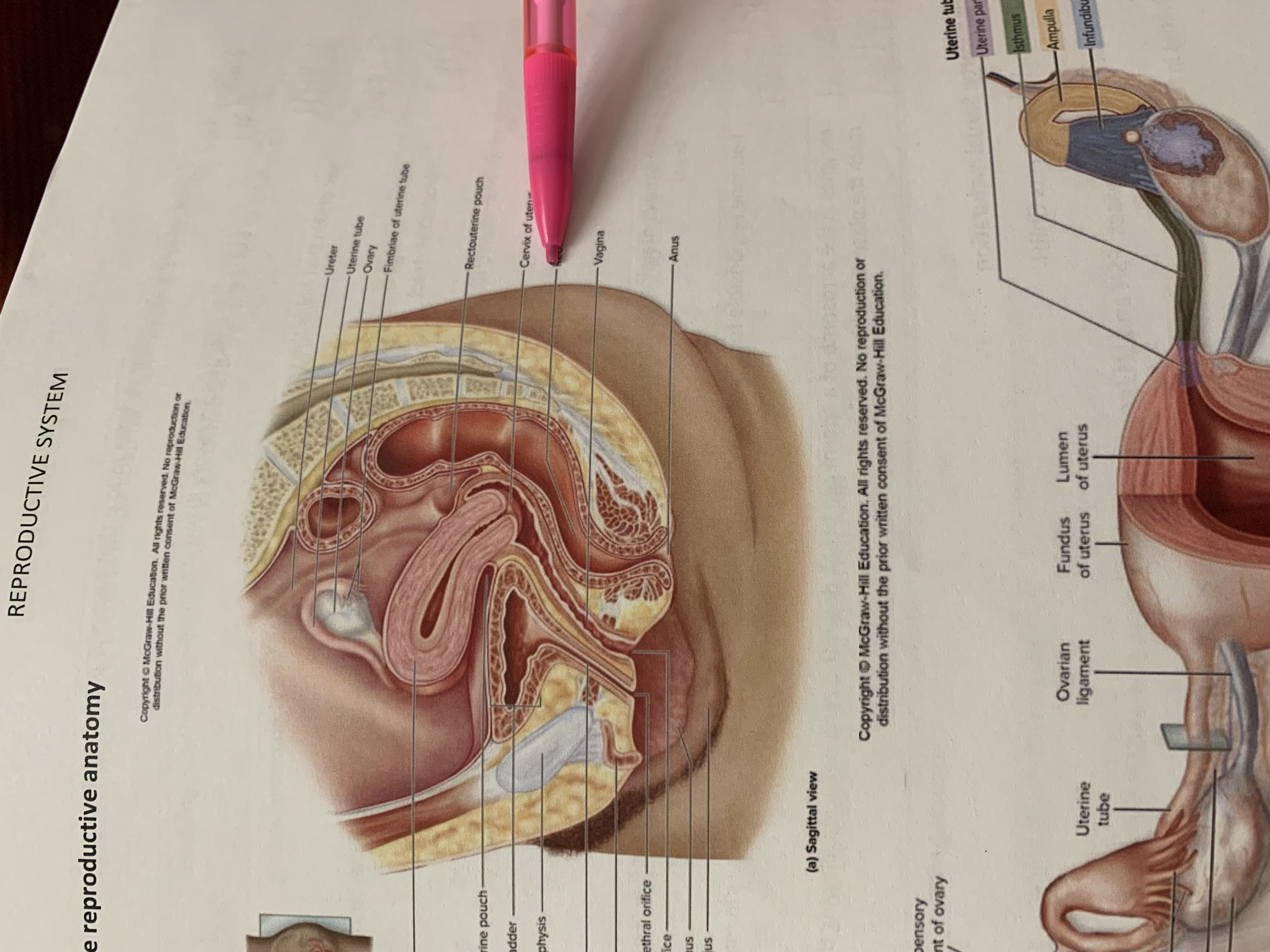
rectum
vagina
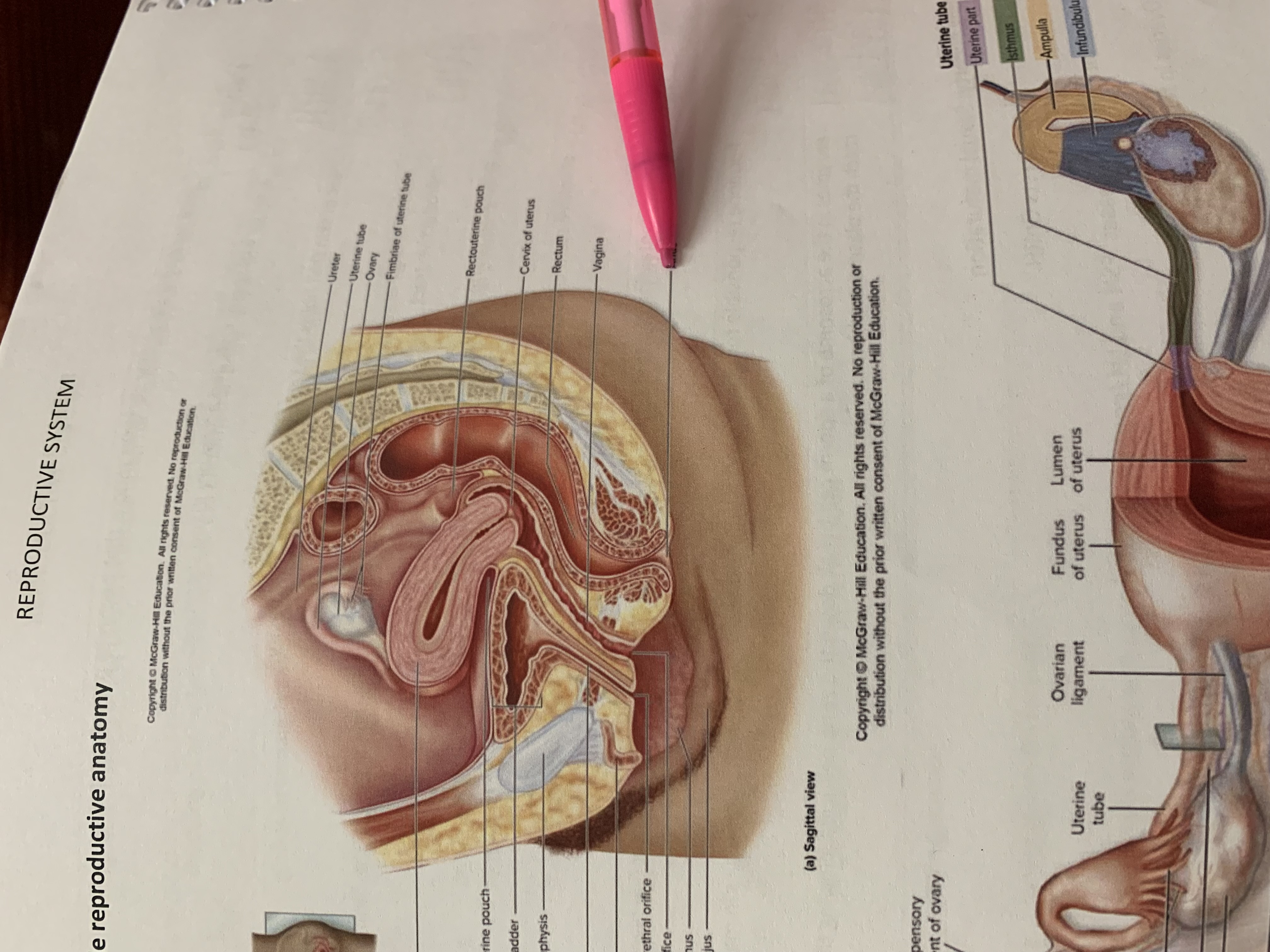
anus
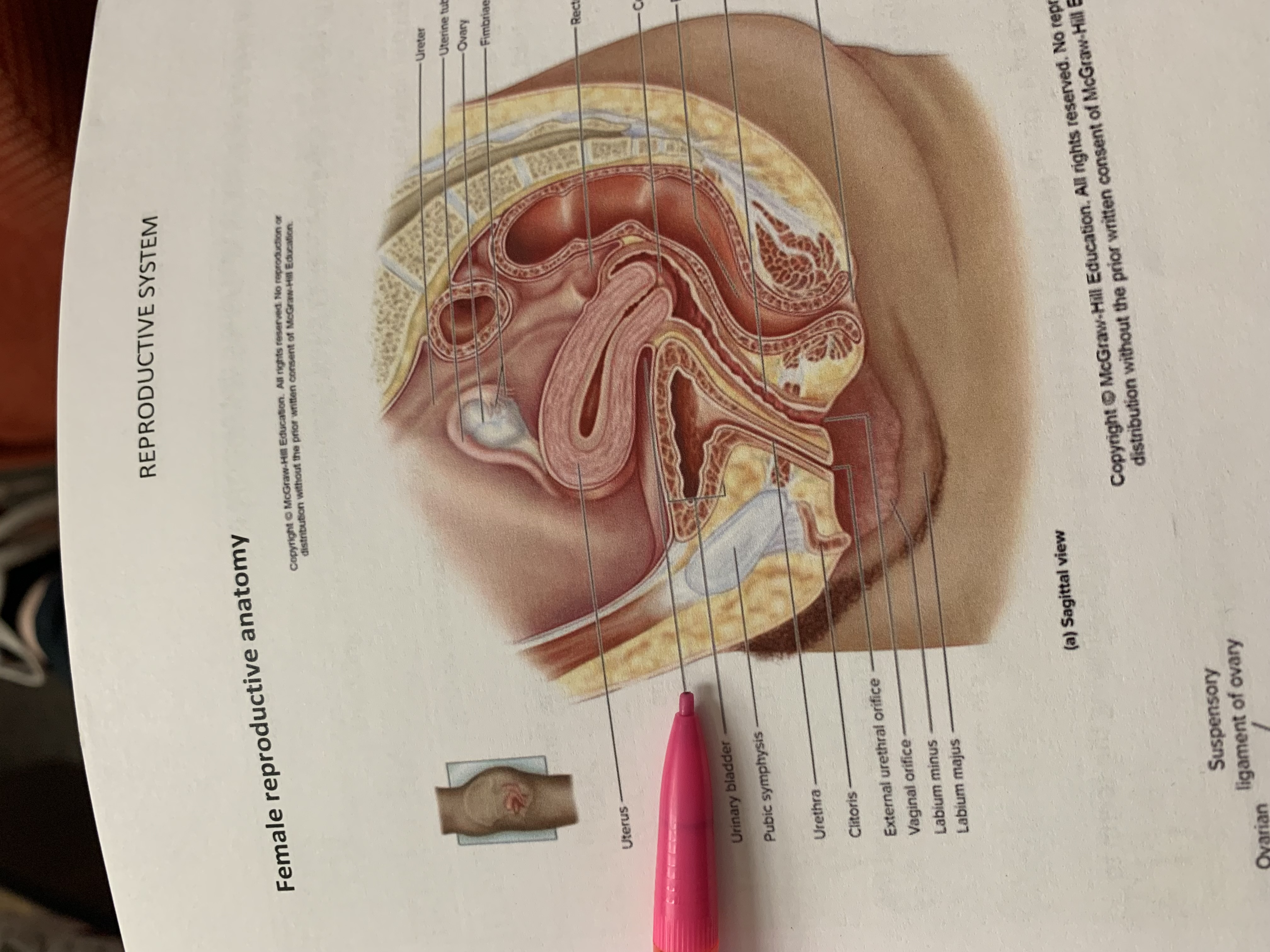
uterus
vesicouterine pouch
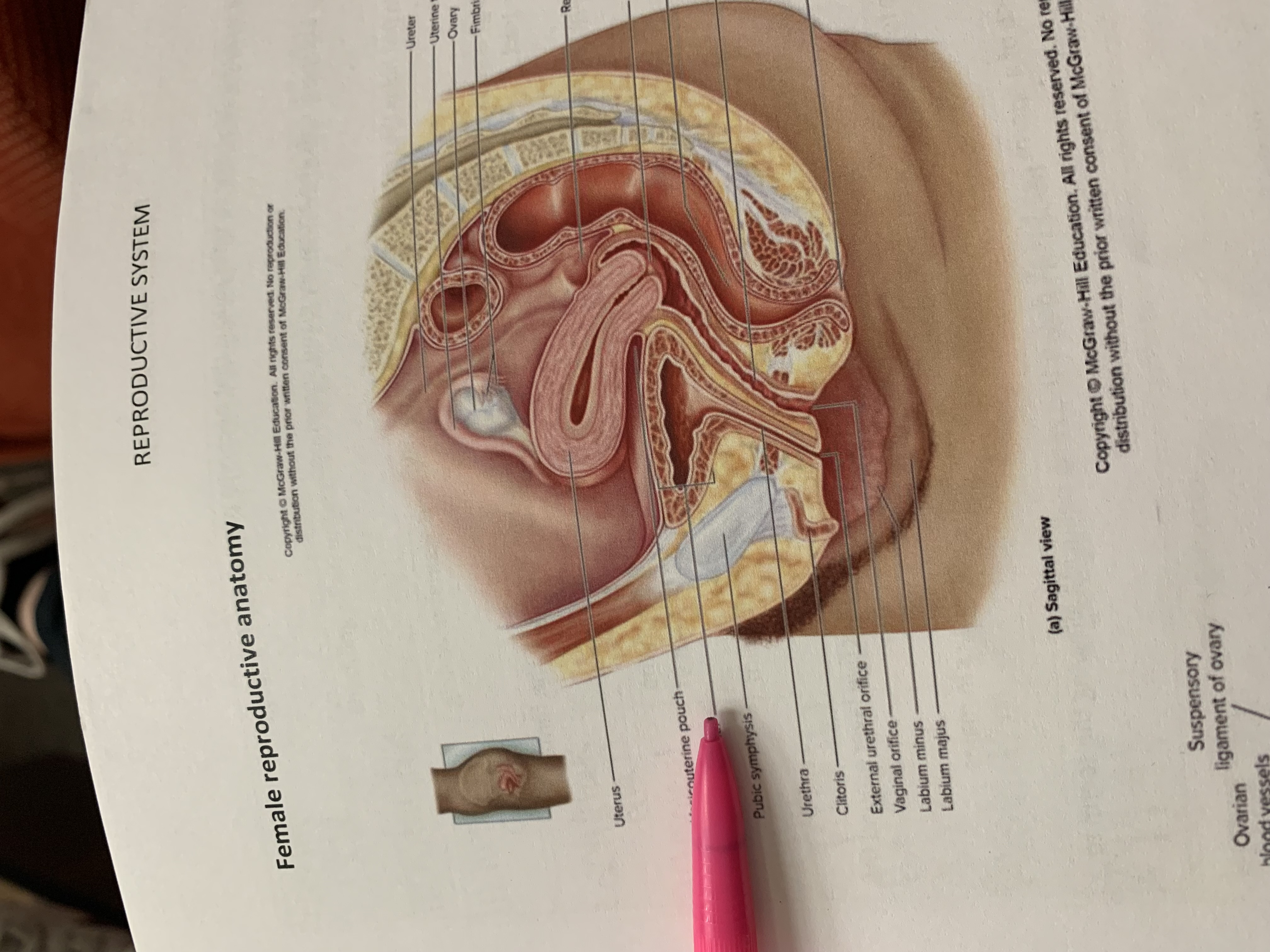
urinary bladder
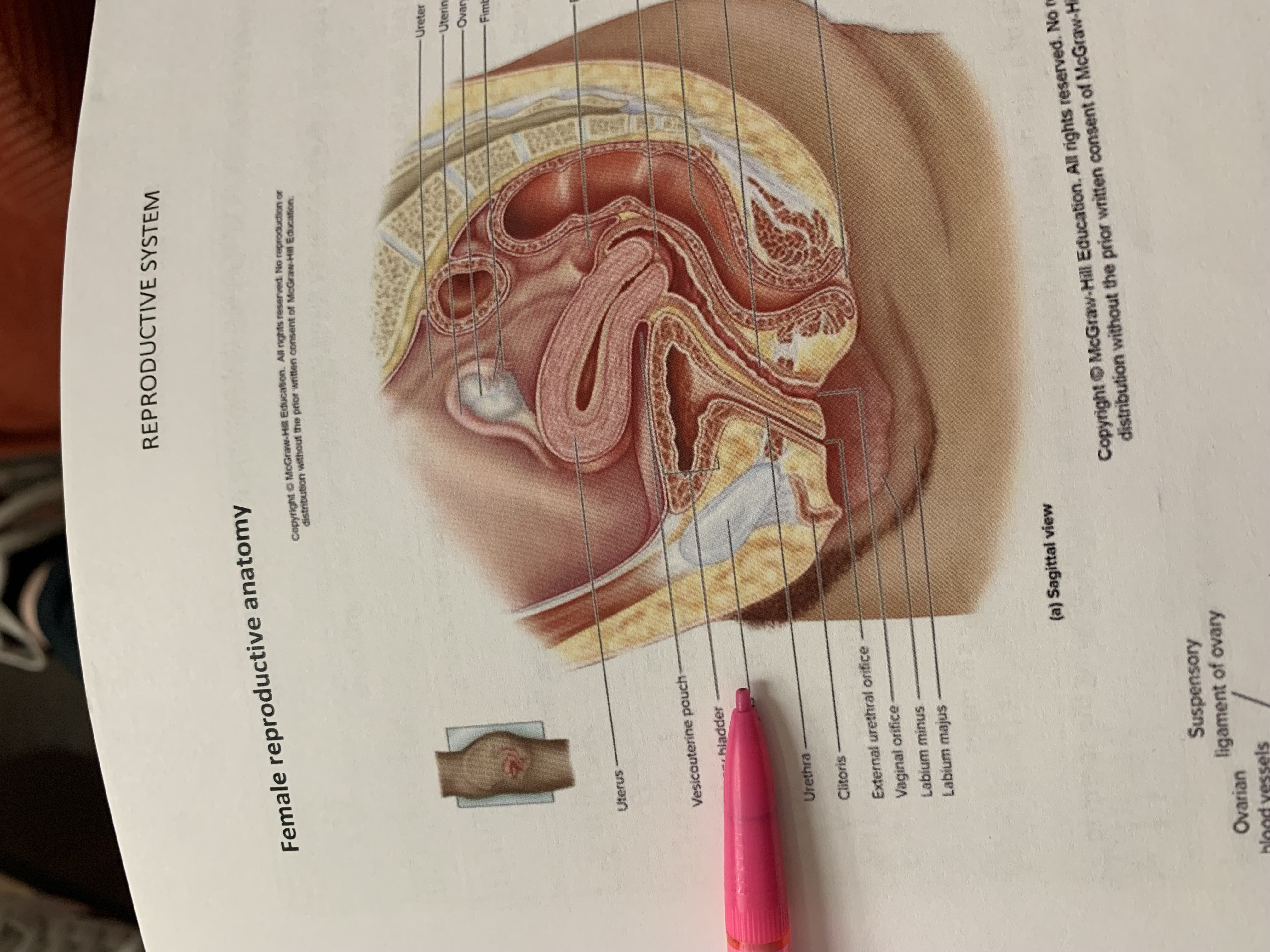
pubic symphysis
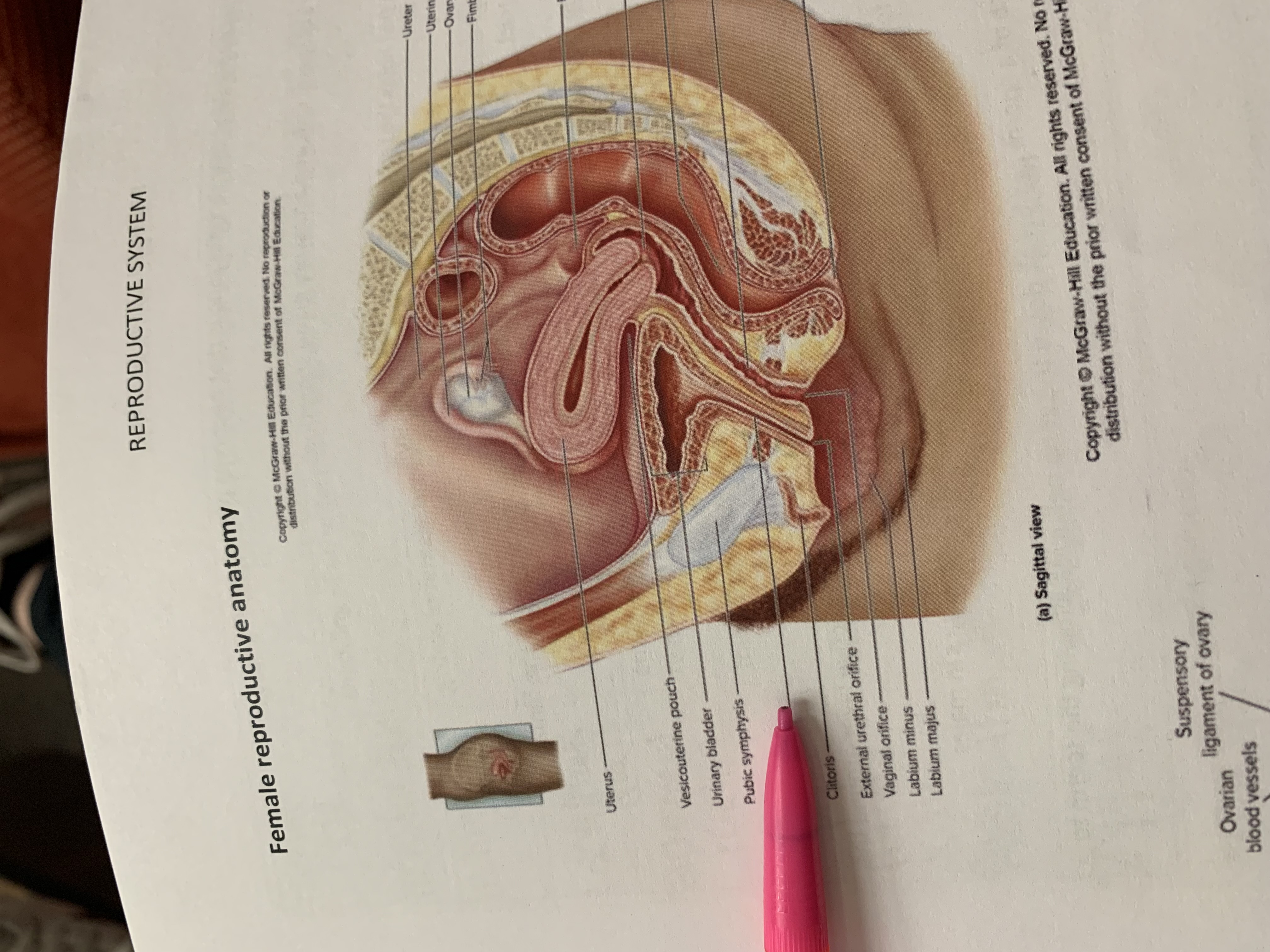
urethra
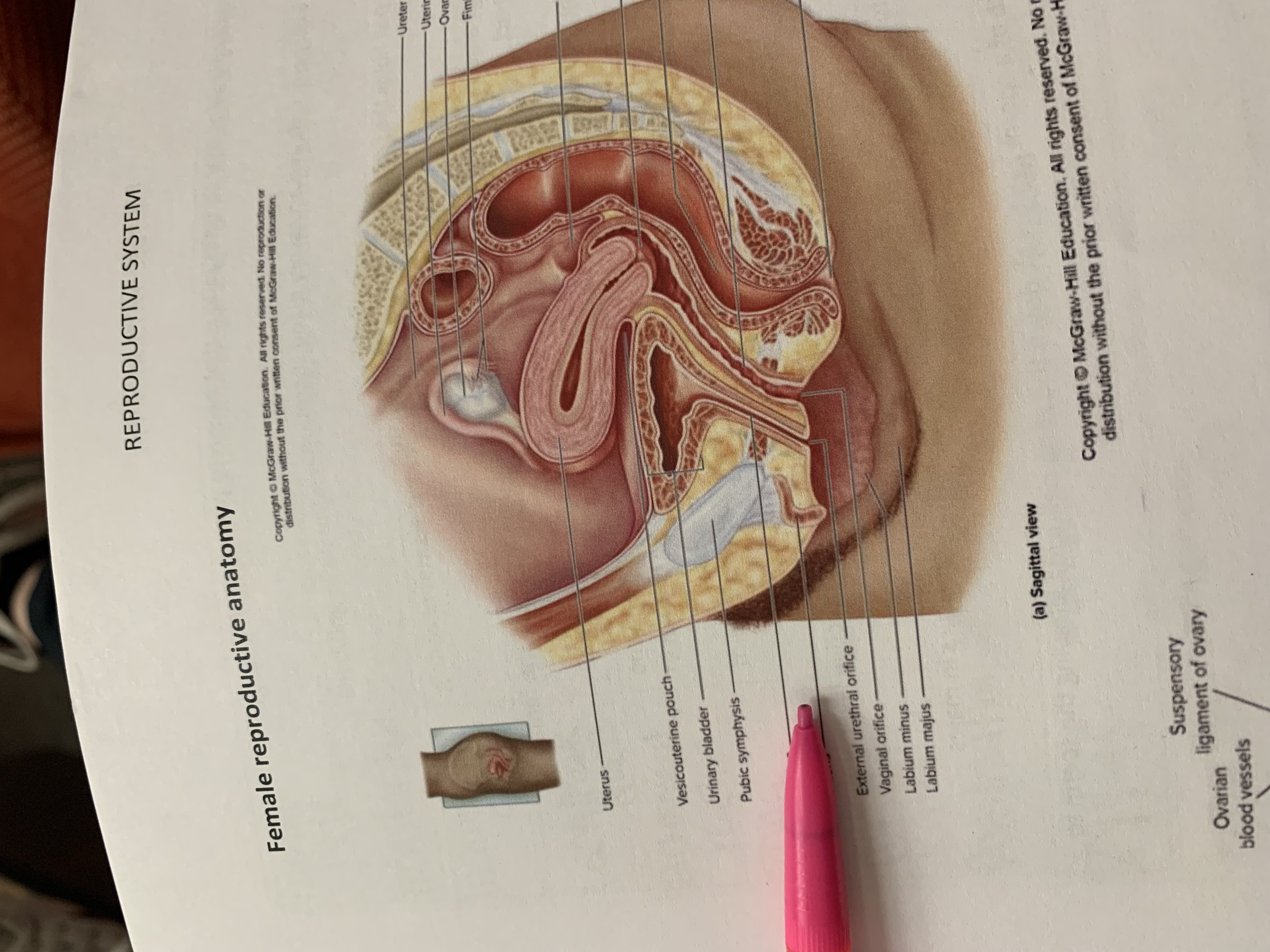
clitoris
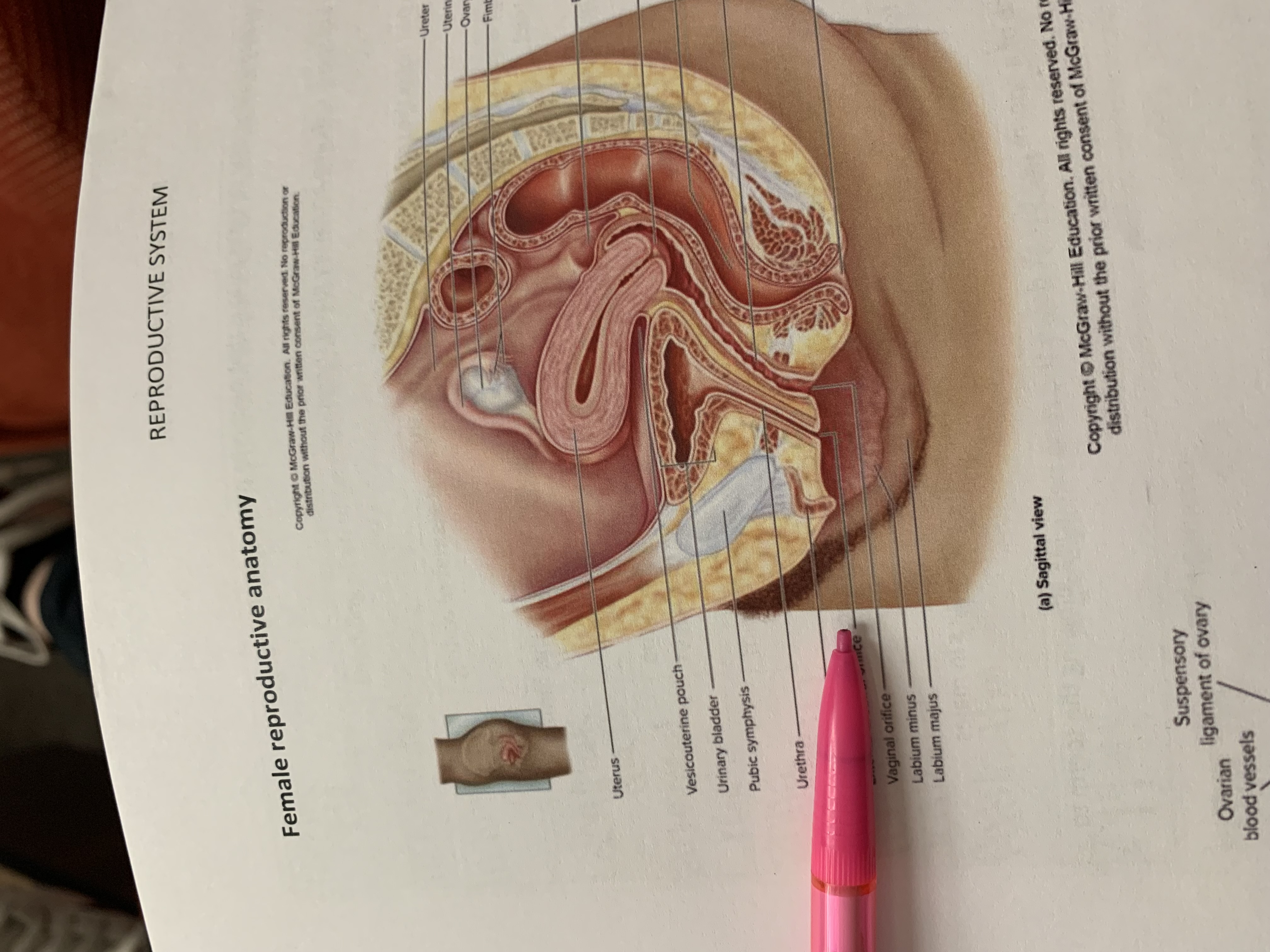
external urethral orifice
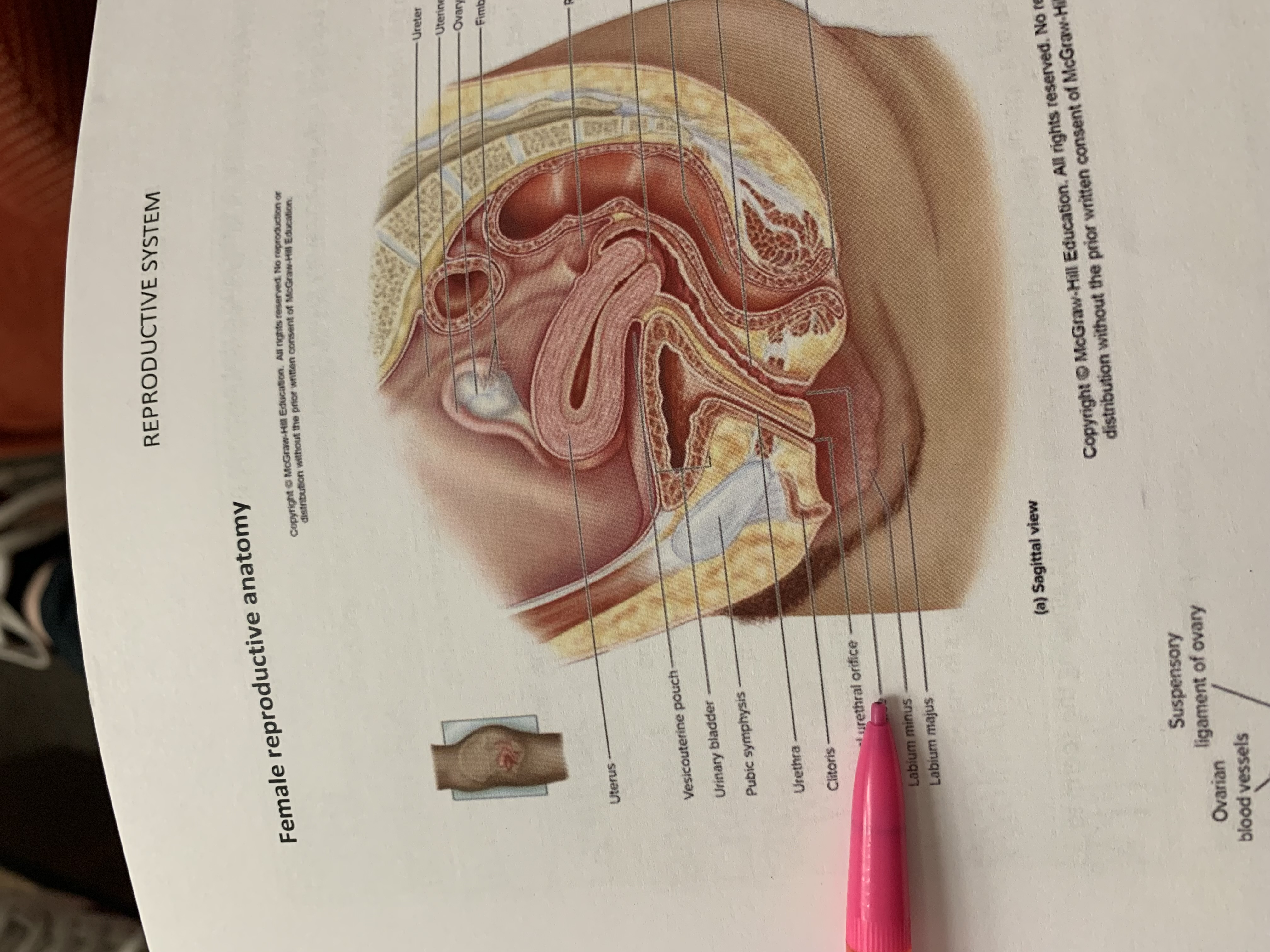
vaginal orifice
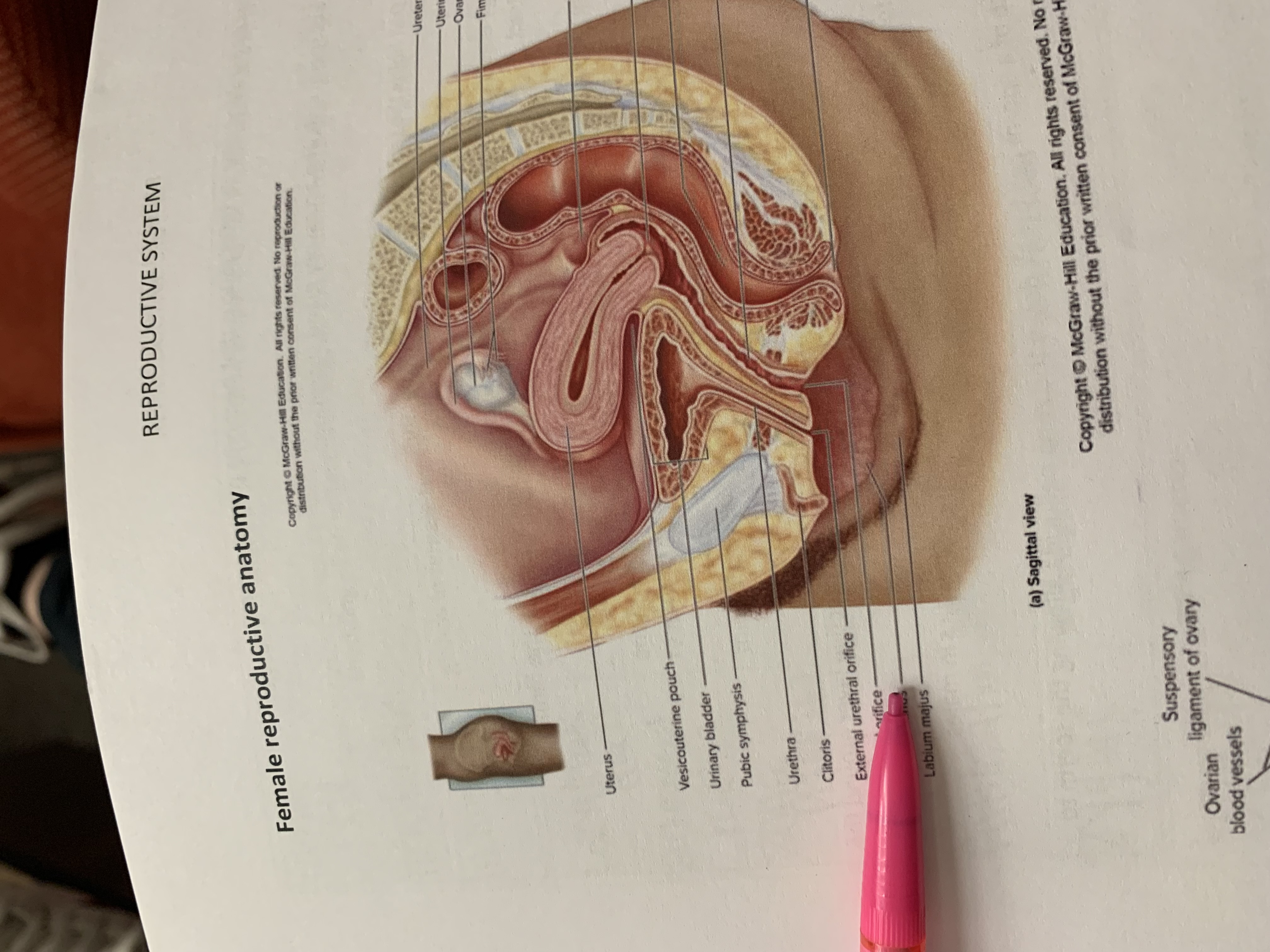
labium minus
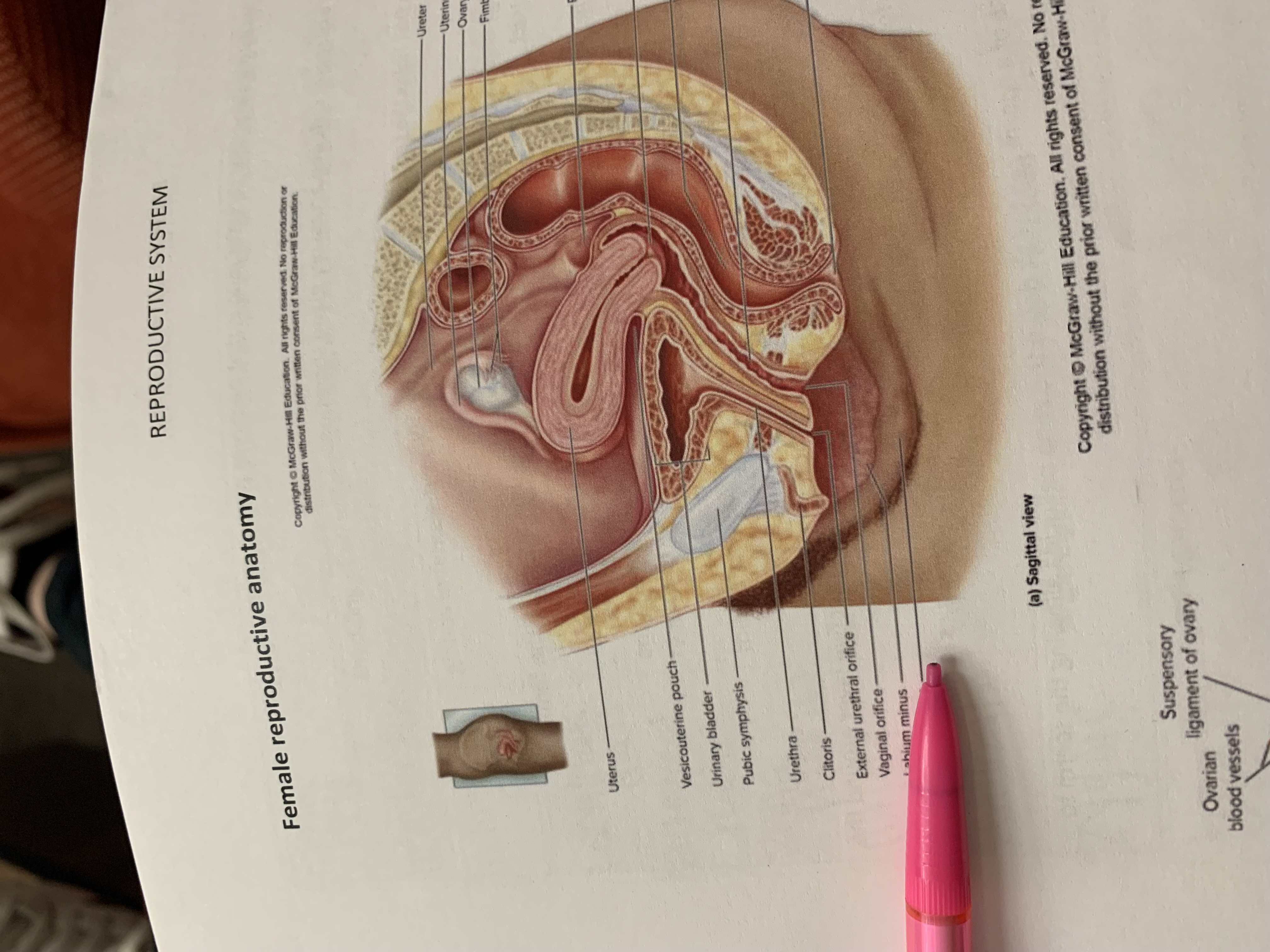
labium majus
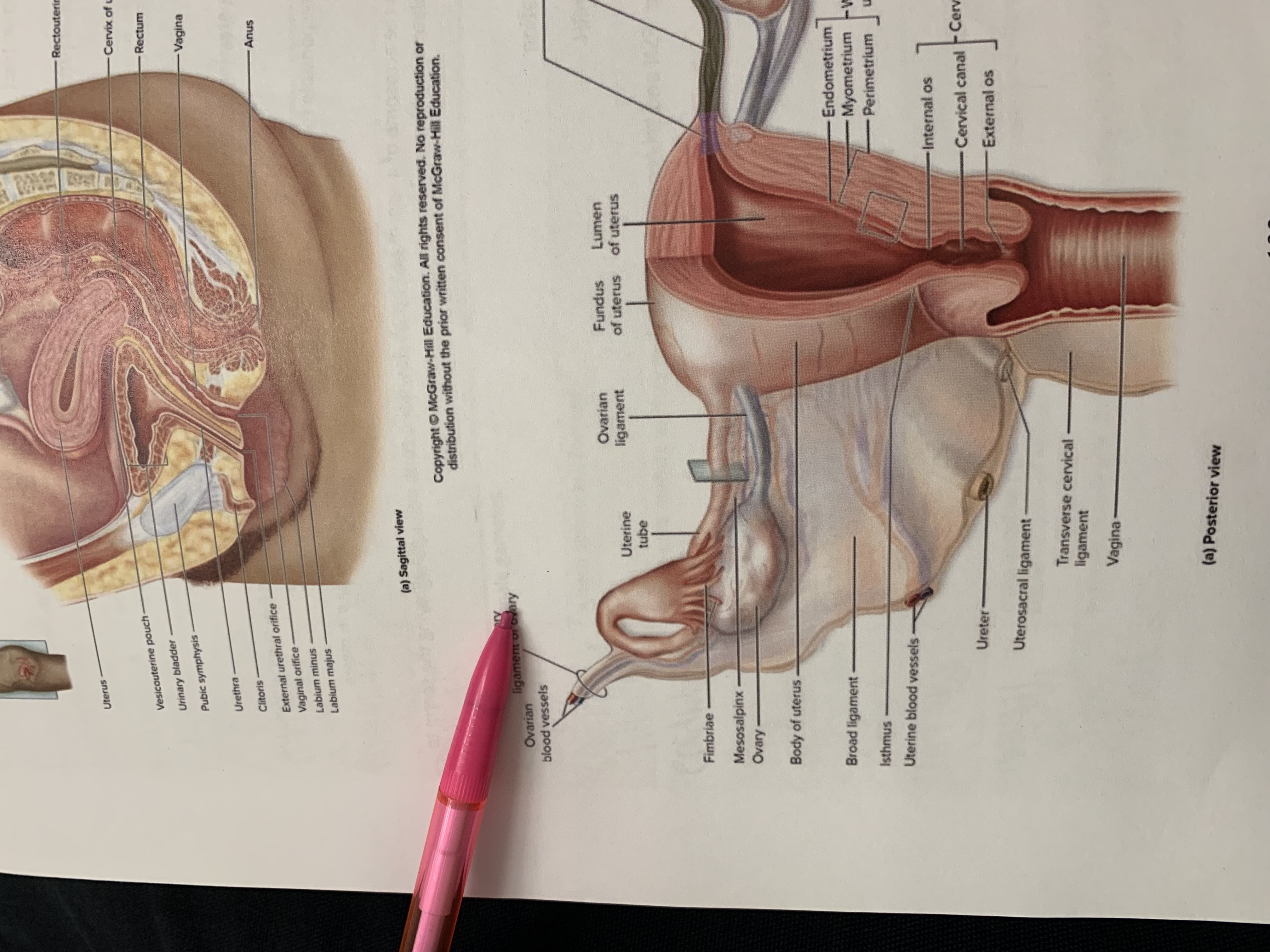
suspensory ligament of ovary
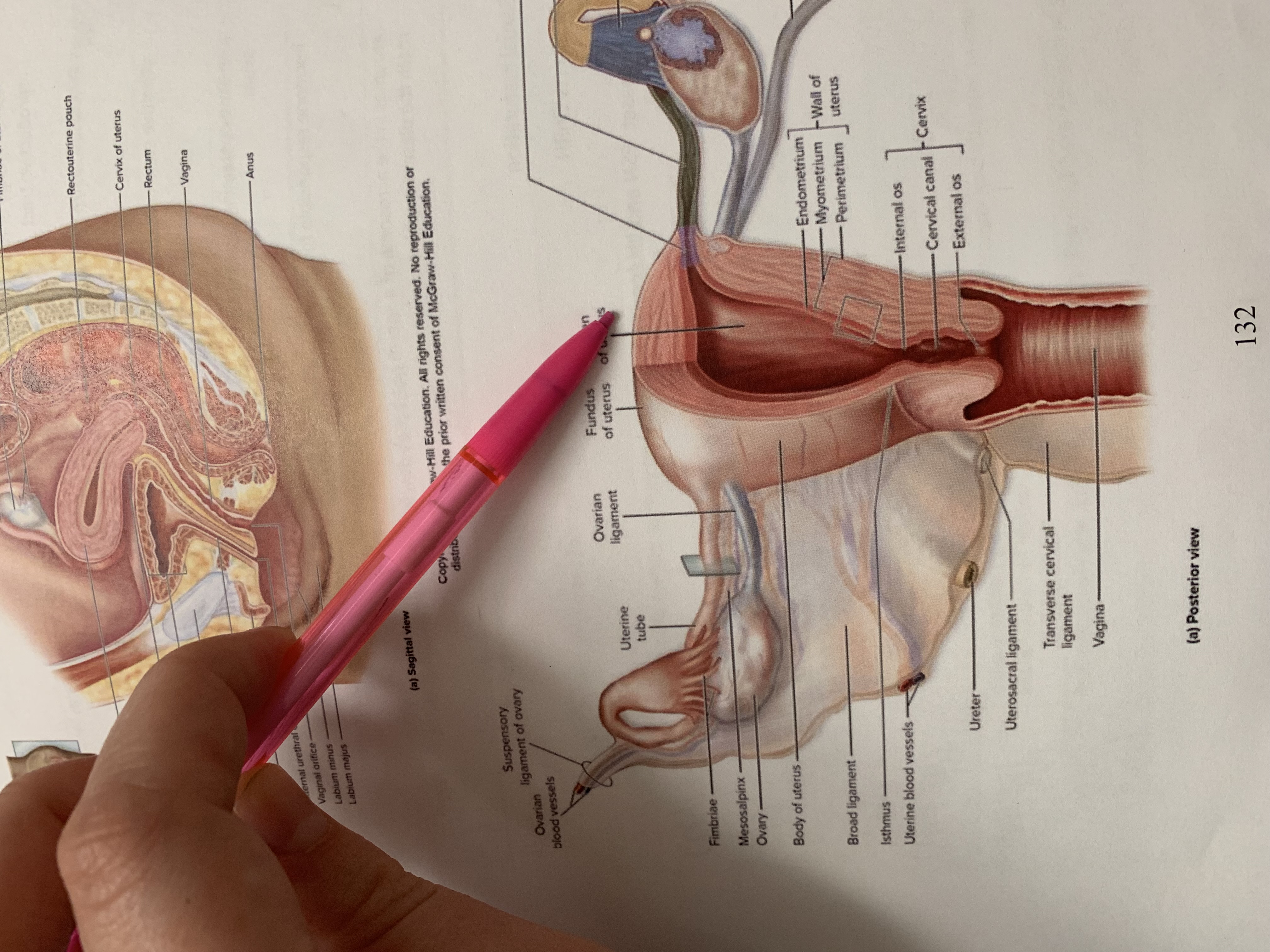
lumen of uterus
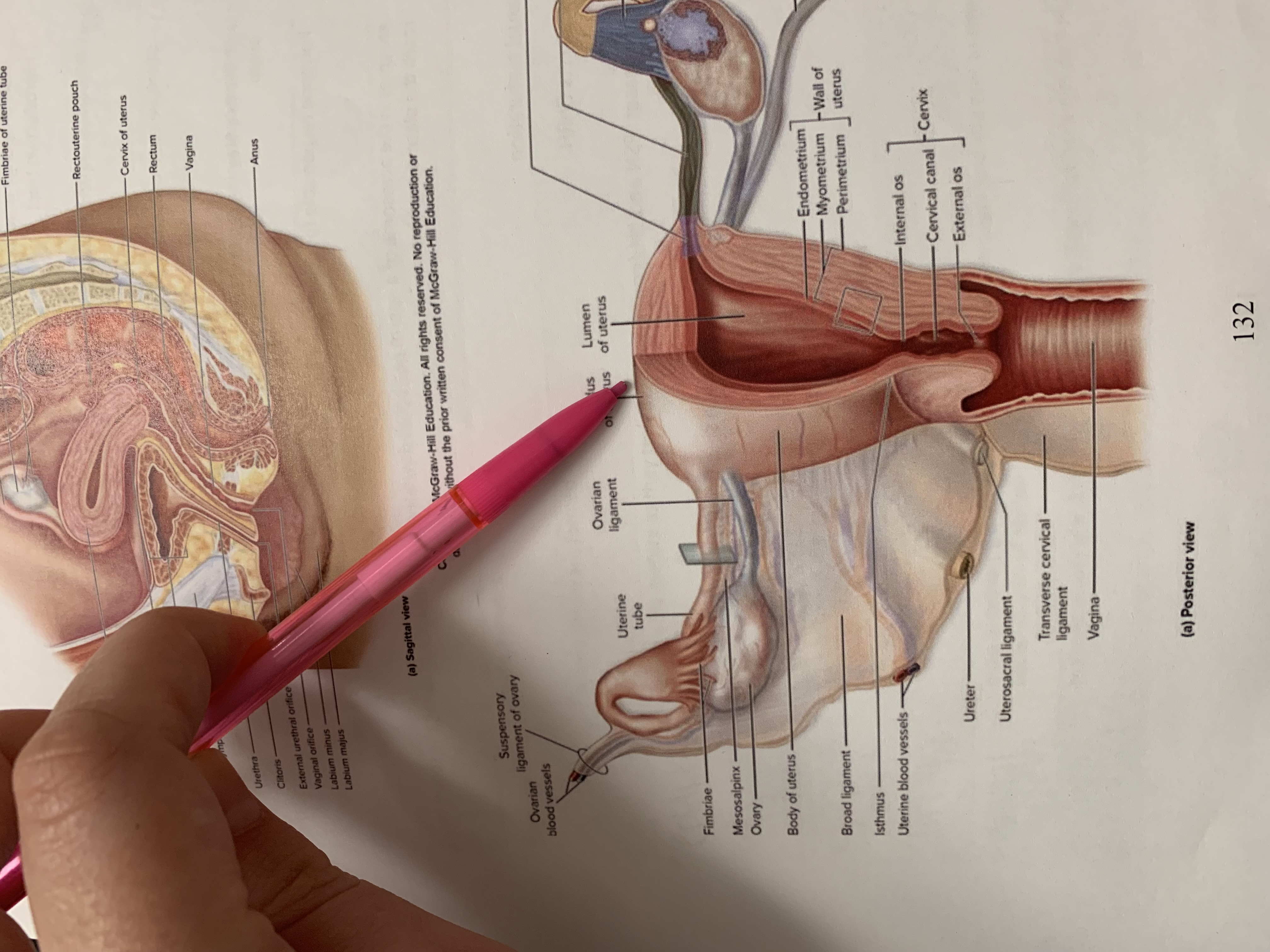
fundus of uterus
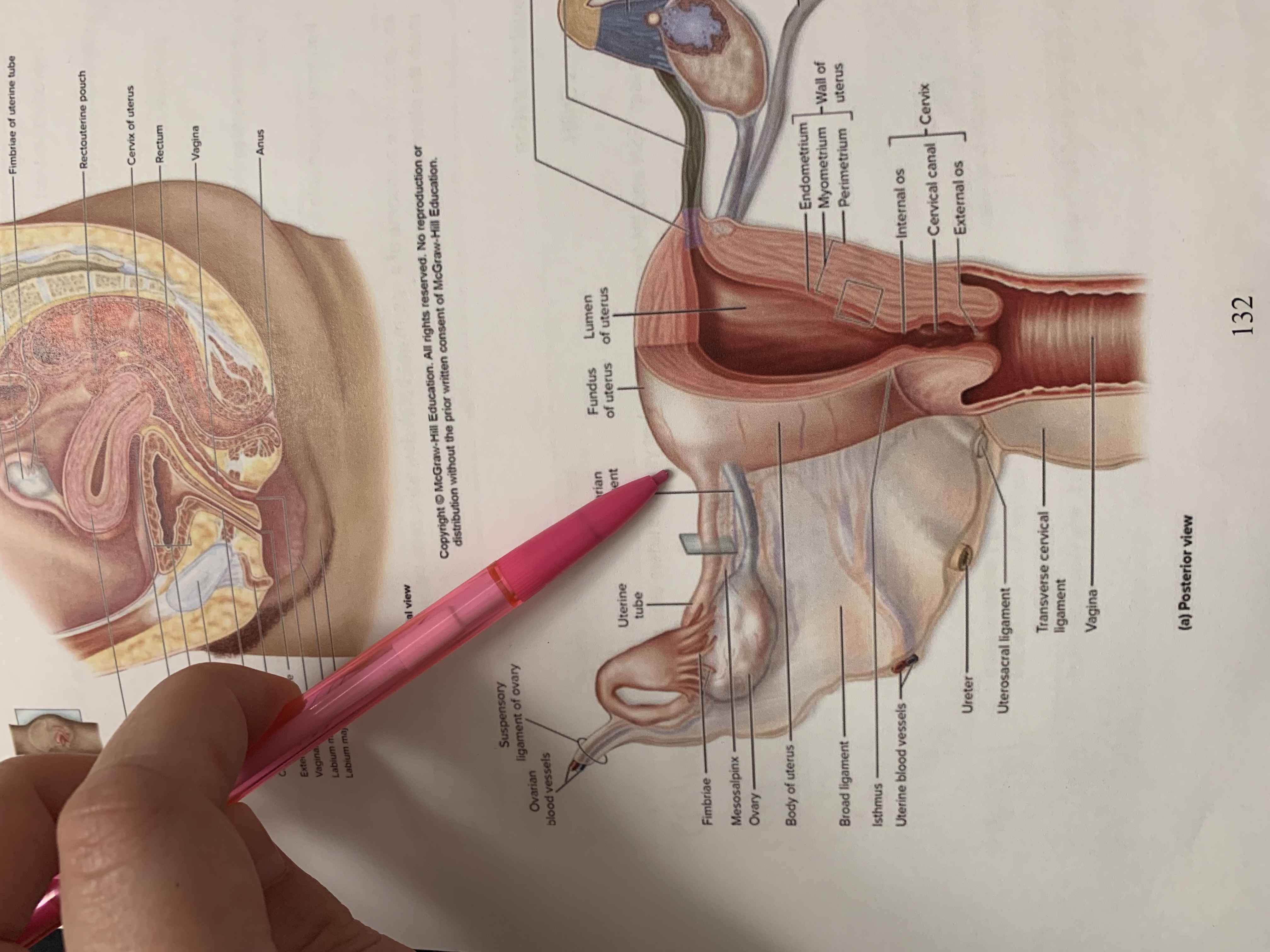
ovarian ligament
uterine tube
uterine tube