Unit 6: Classification of Matter
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
36 Terms
Matter
Anything that has mass and takes up space
Mass
This is the amount of matter or "stuff" something has and is measured in grams or kilograms.
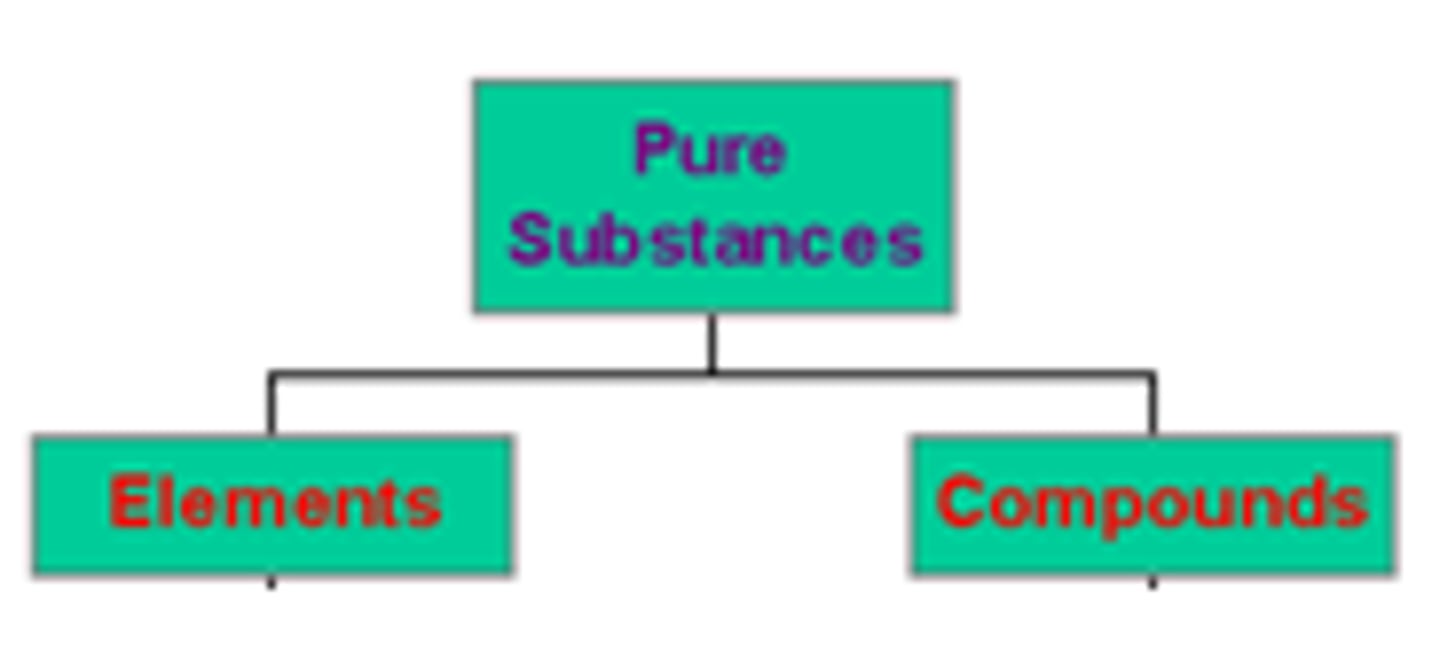
Element
All of the atoms in a substance are of the same same type or identify.
Pure Substance
A type of substance with a fixed composition or ratio. It can either be an element or a compound.
Compound
A pure substance in which atoms of two or more elements are bonded in a fixed proportion or ratio. One example would be H2O or water.
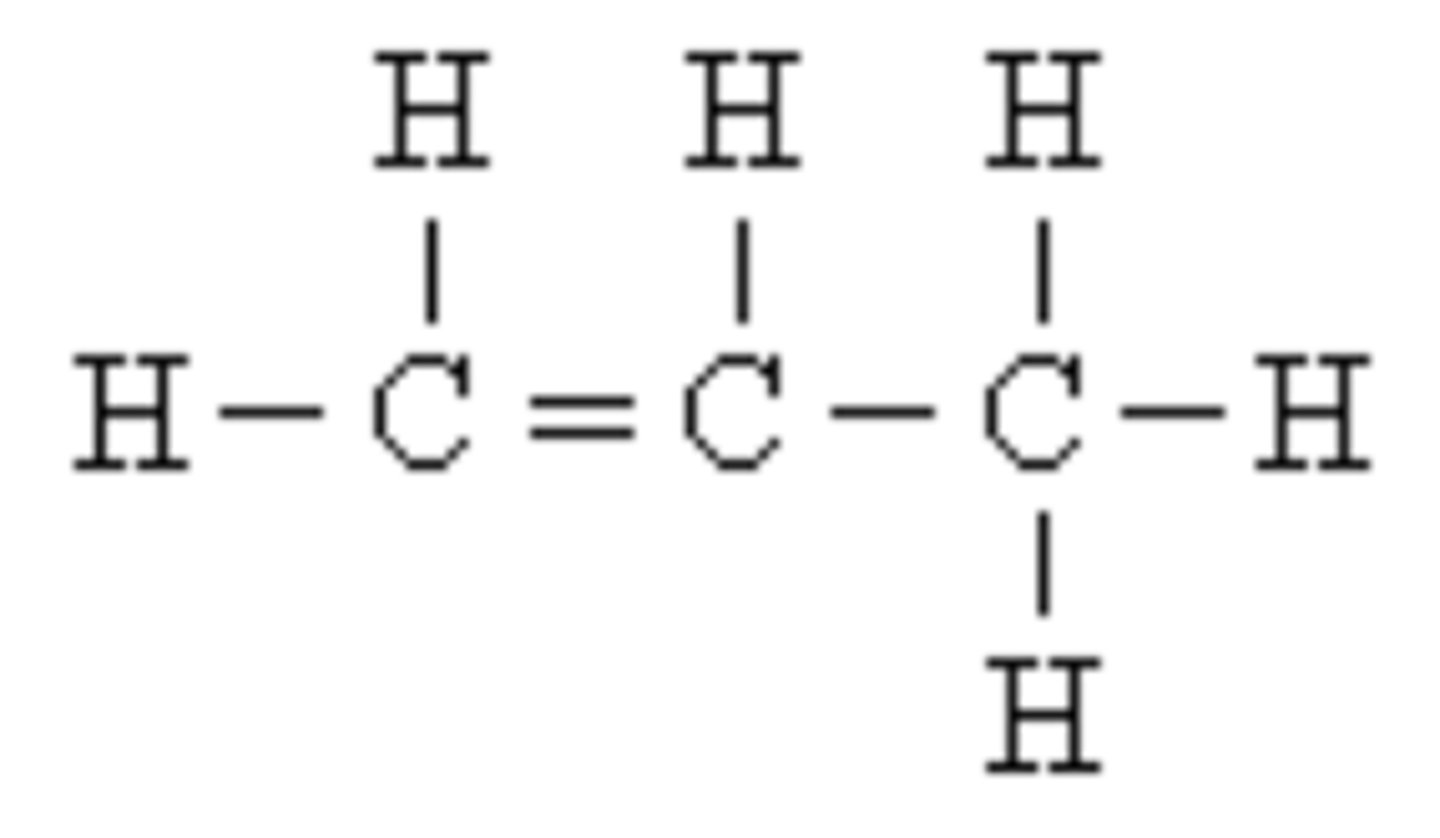
Mixture
A material that contains two or more substances that can be separated fairly easily by physical means.
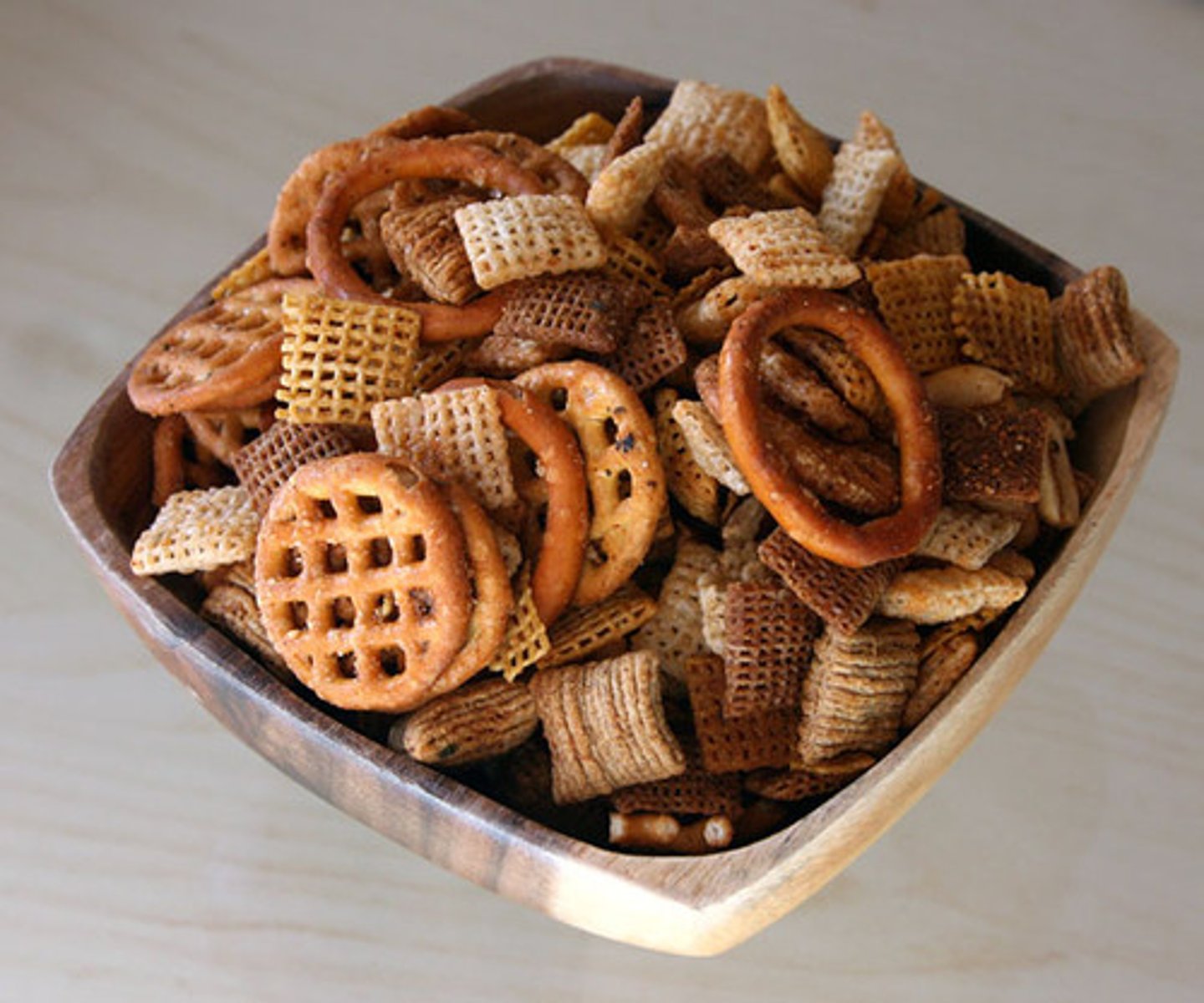

Heterogeneous
A type of mixture in which different substances can be easily distinguished.
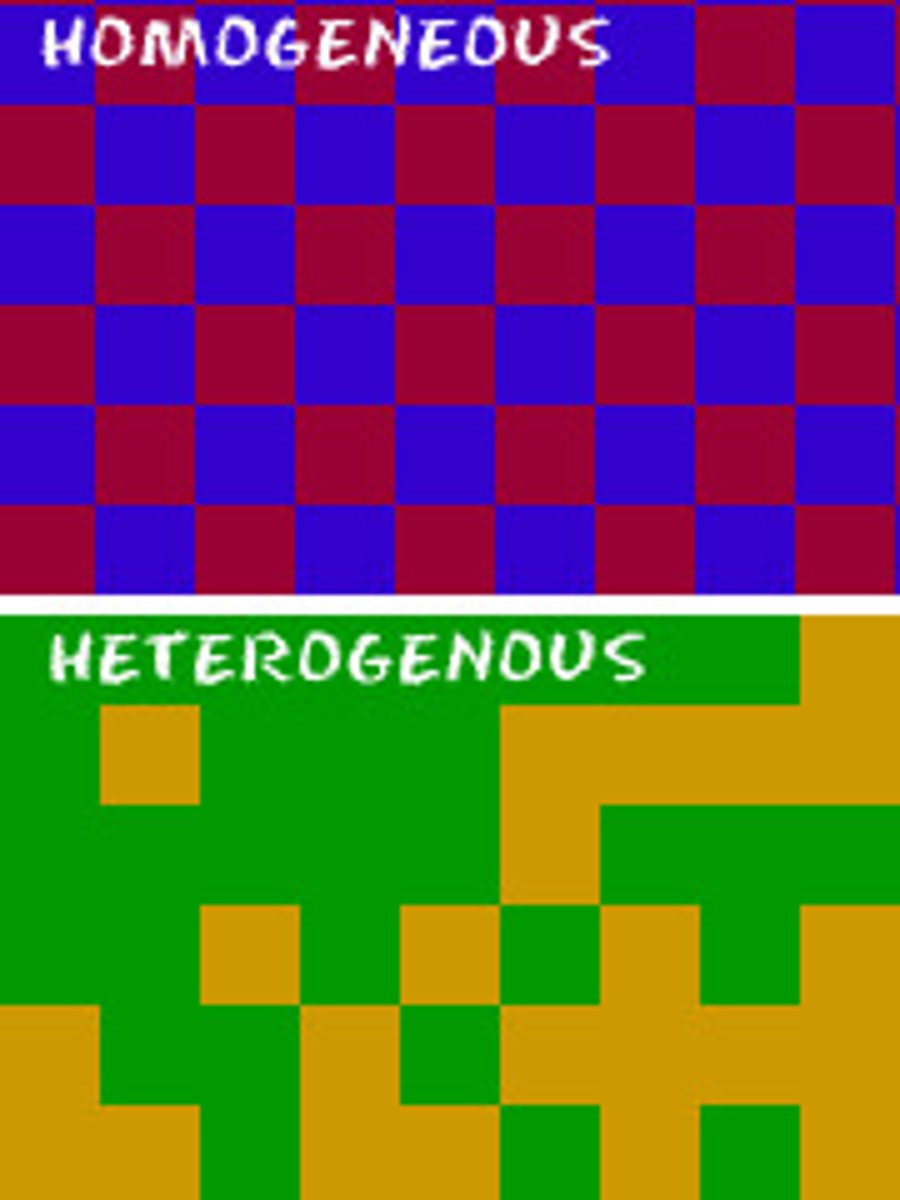

Homogeneous
A type of mixture that appears to be easily blended but is actually made up of two or more substances.

Solution
A special of homogenous mixture that consists of a solvent and a solute.
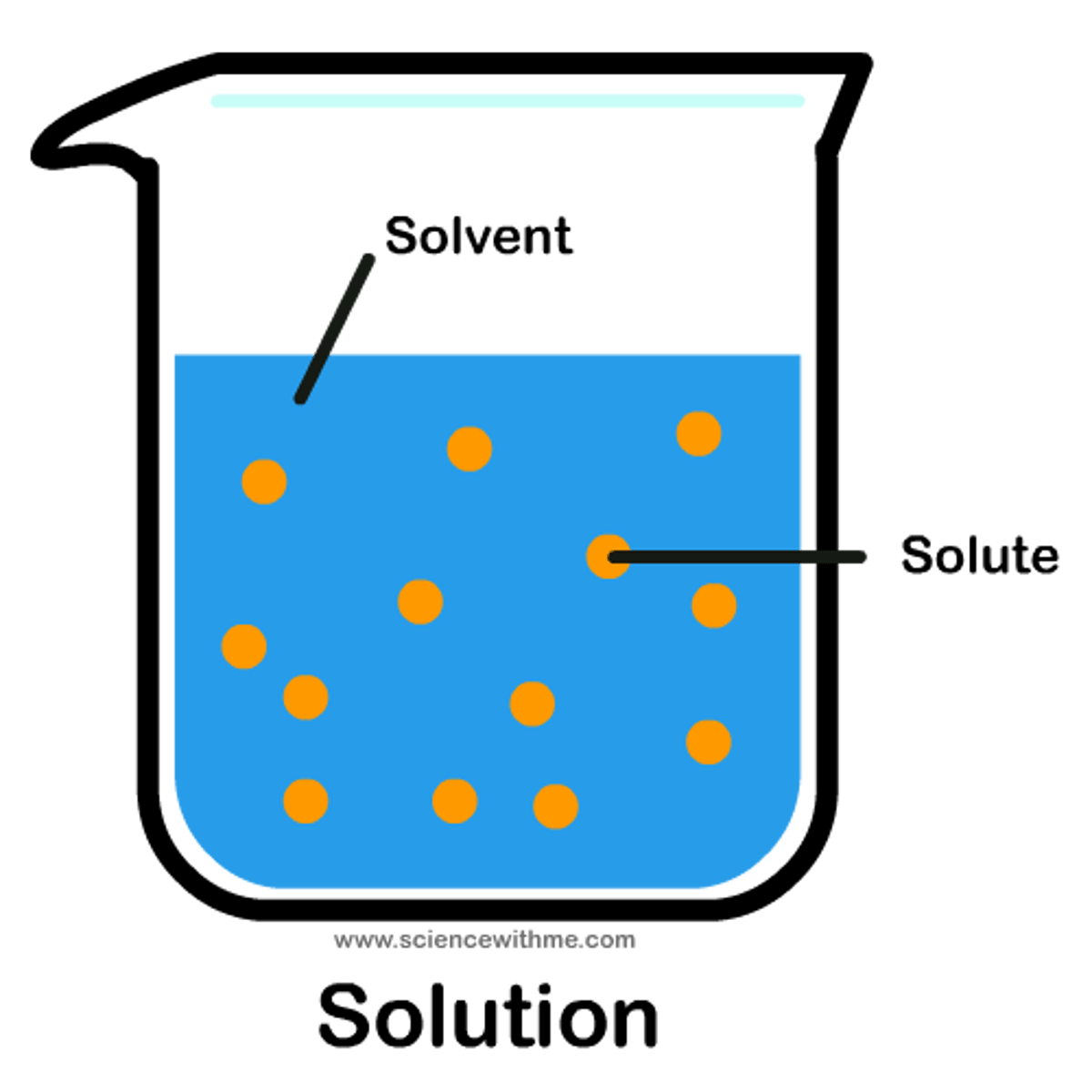
Solvent
A substance is used to dissolve another substance. Water is commonly used for this.
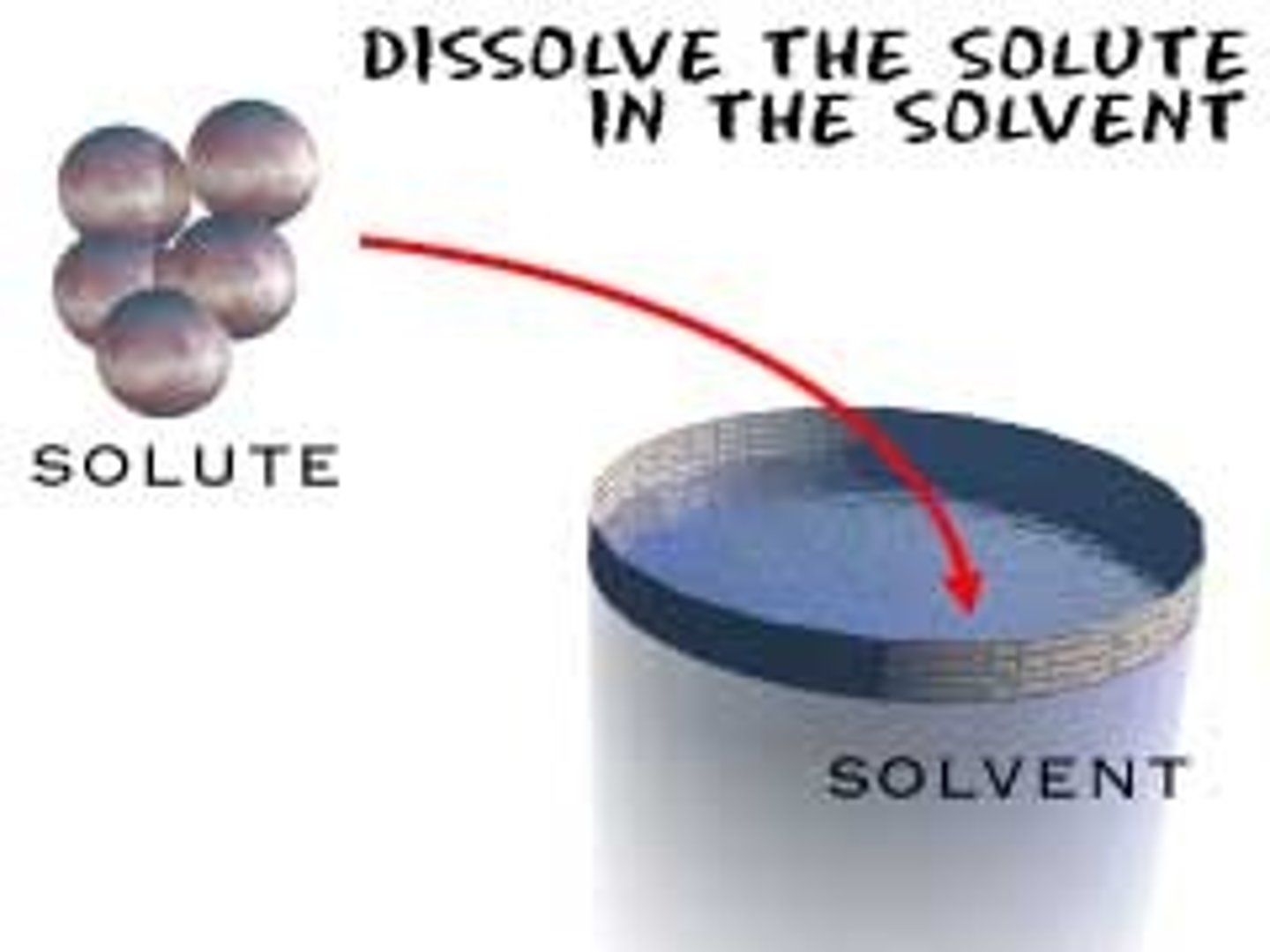
Solute
A substance that becomes dissolved in another substance.

Colloid
A homogeneous mixture that contains large particles, but the contents will not settle. A good example of this is Milk.

Suspensions
A heterogenous mixture of particles that will be stay mixed for a while but will eventually settle. Good examples of these are muddy water and fog.
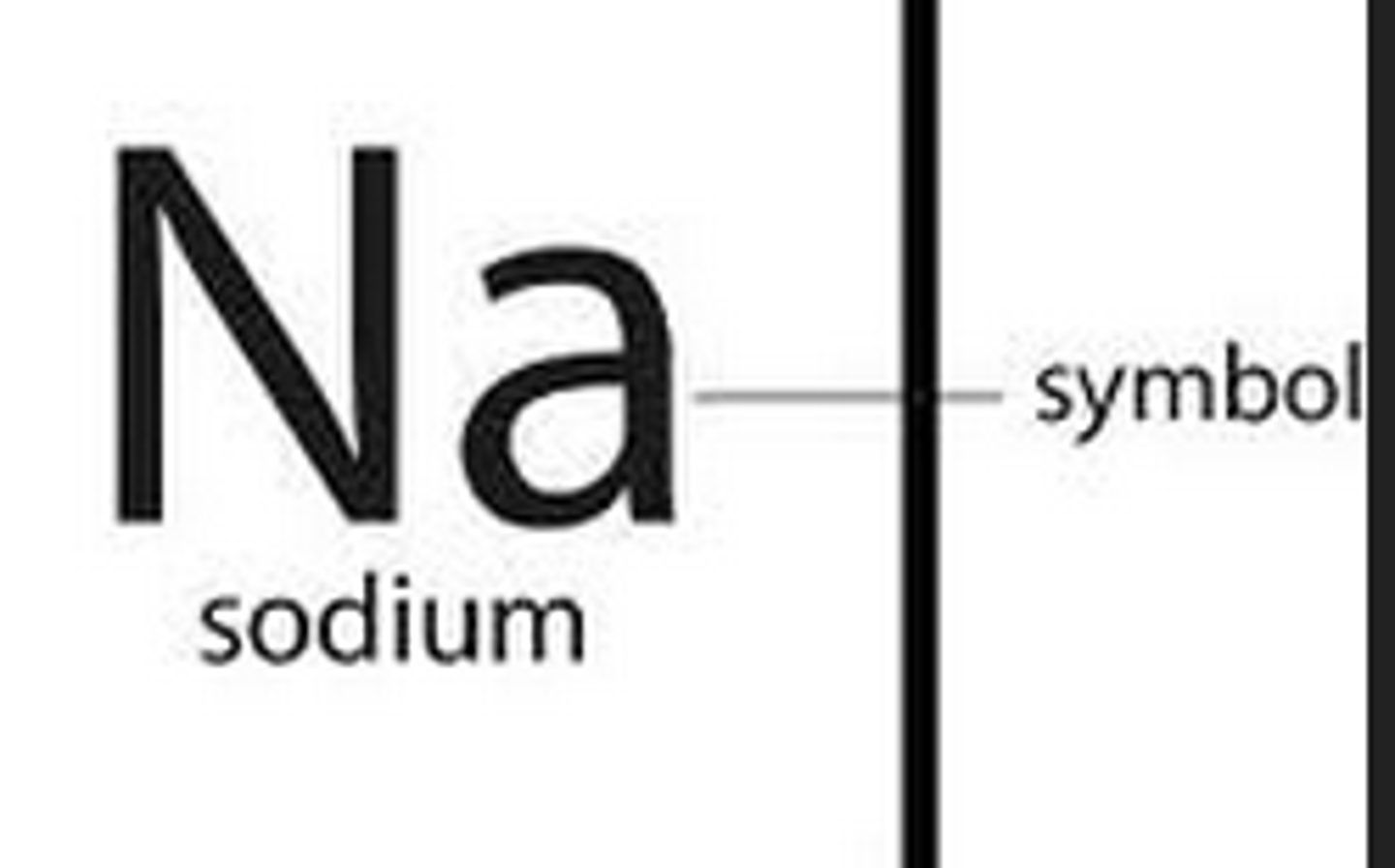
Symbol
This abbreviation is used to represent elements on the periodic table. For example, Na represents Sodium.
Chemical Formula
This abbreviation is used to represent compounds containing multiple elements. For example, NaCl represents Sodium Chloride or table salt.
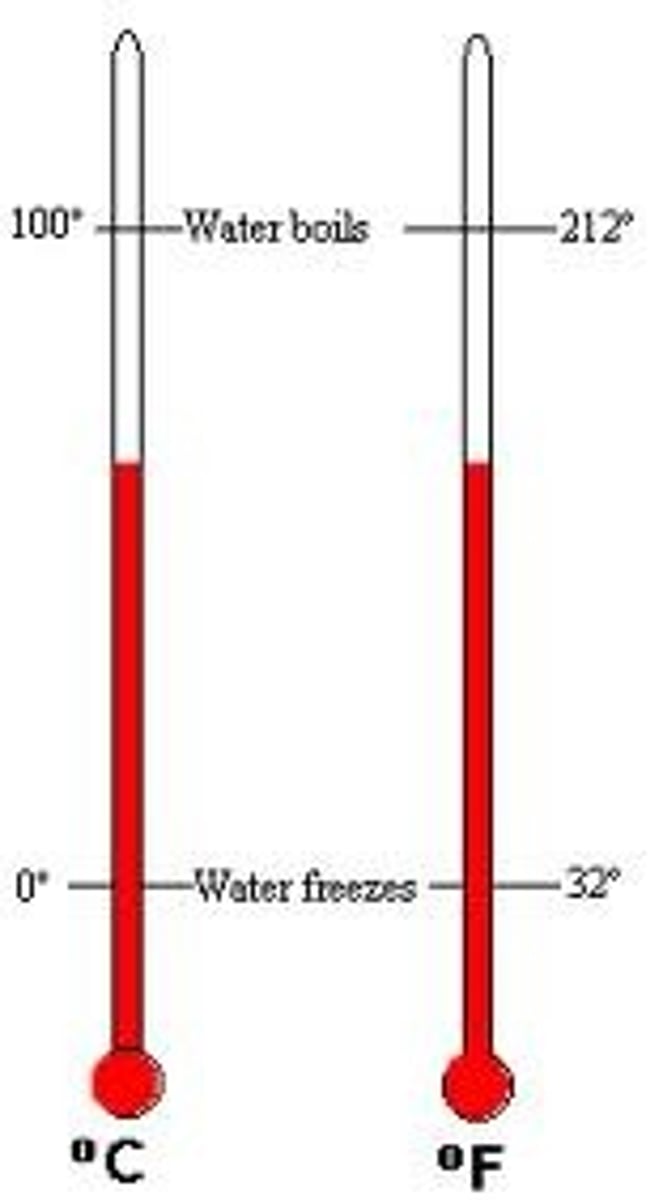
Temperature
A measure of the average kinetic energy of a substances particles.
Kinetic energy
This energy changes when the SPEED of the particles change. Changes when temperature changes.
Potential Energy
This changes when the DISTANCE between particles changes. Changes during a phase change.
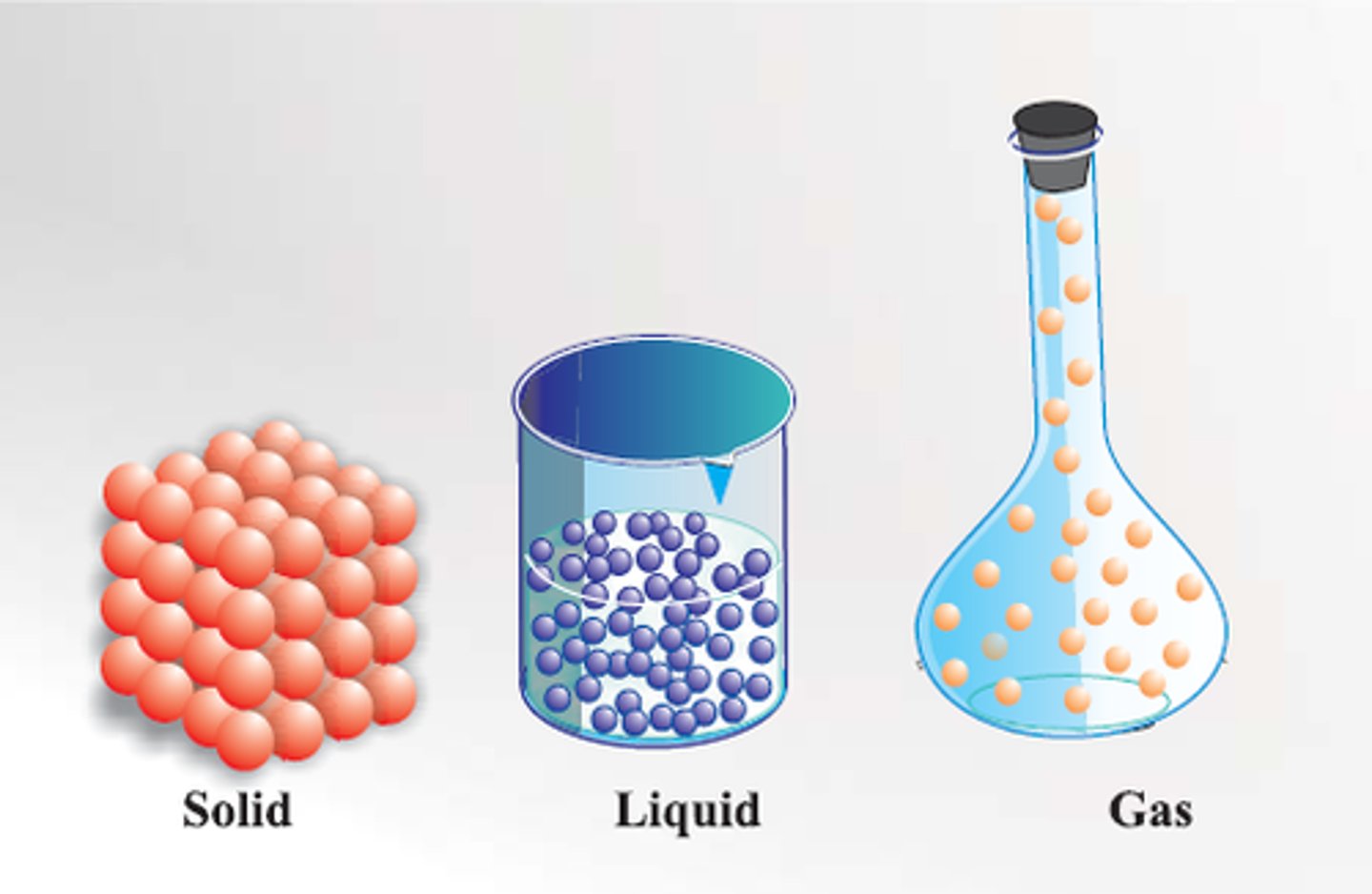
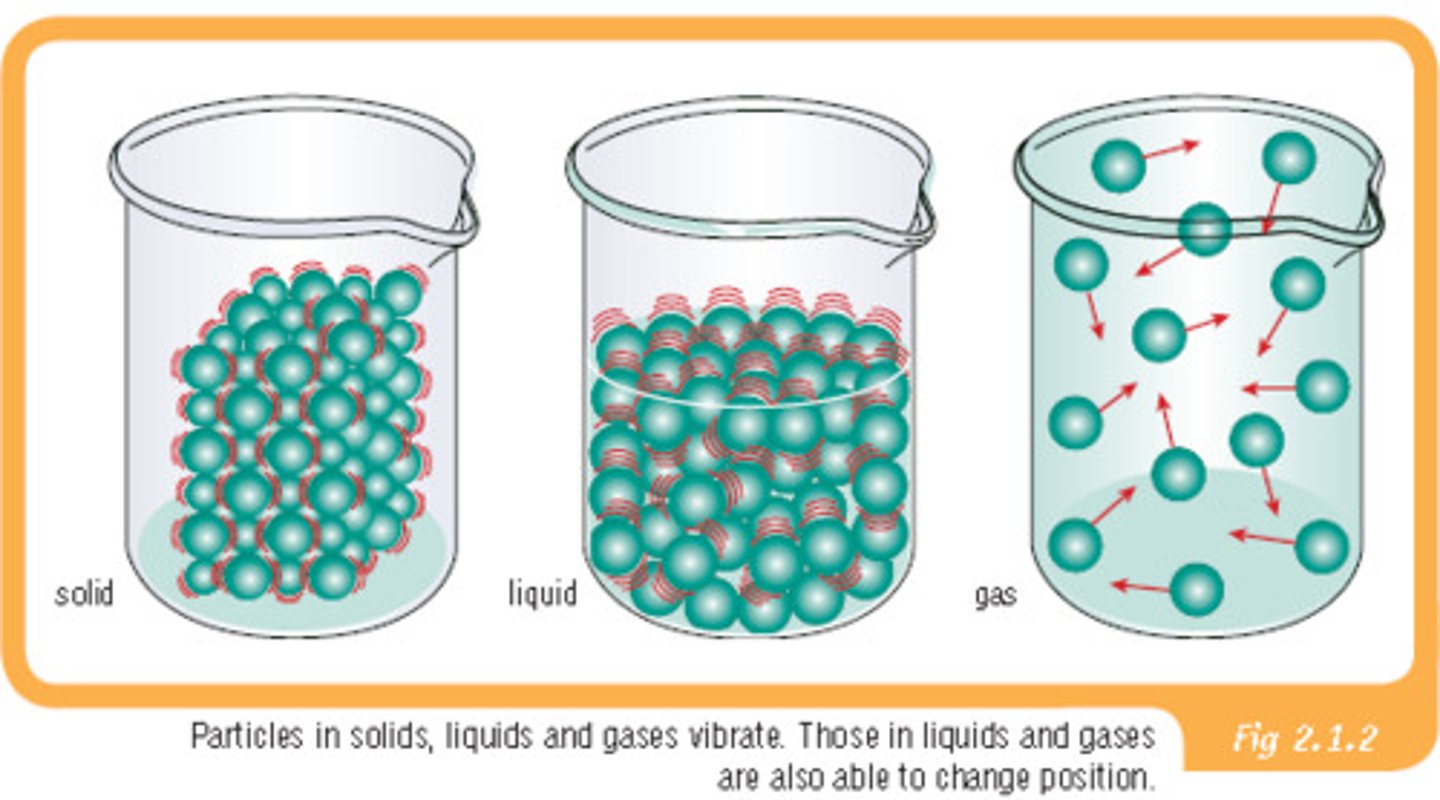
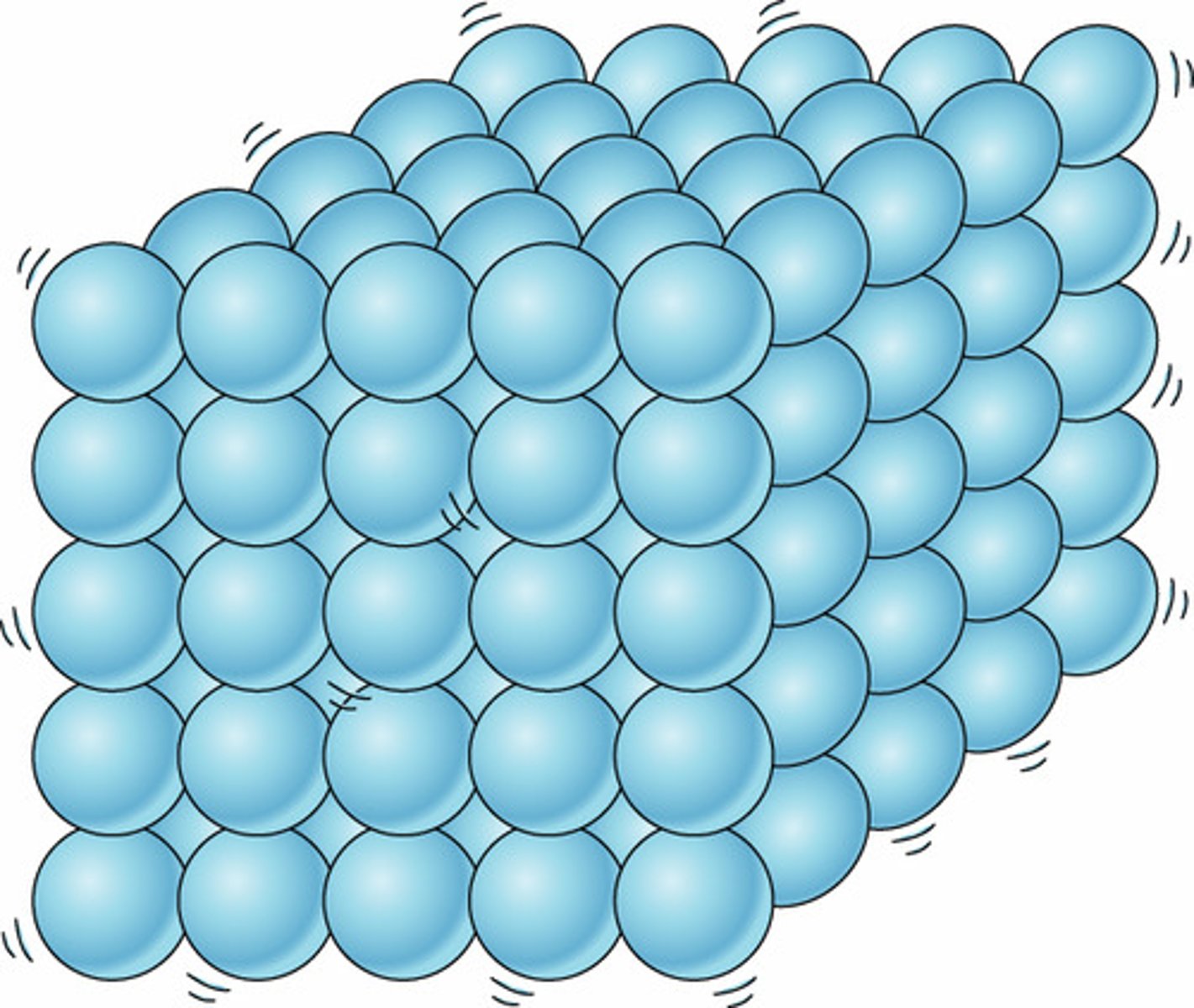
Solid
Particles are packed closely together and are vibrating in place. Because the attraction is strong, this state has a fixed volume and shape.
Liquid
Particles can slide past each other, allowing it to easily flow and take the shape of its container. As a result, substances in this state have a fixed volume but not a fixed shape.
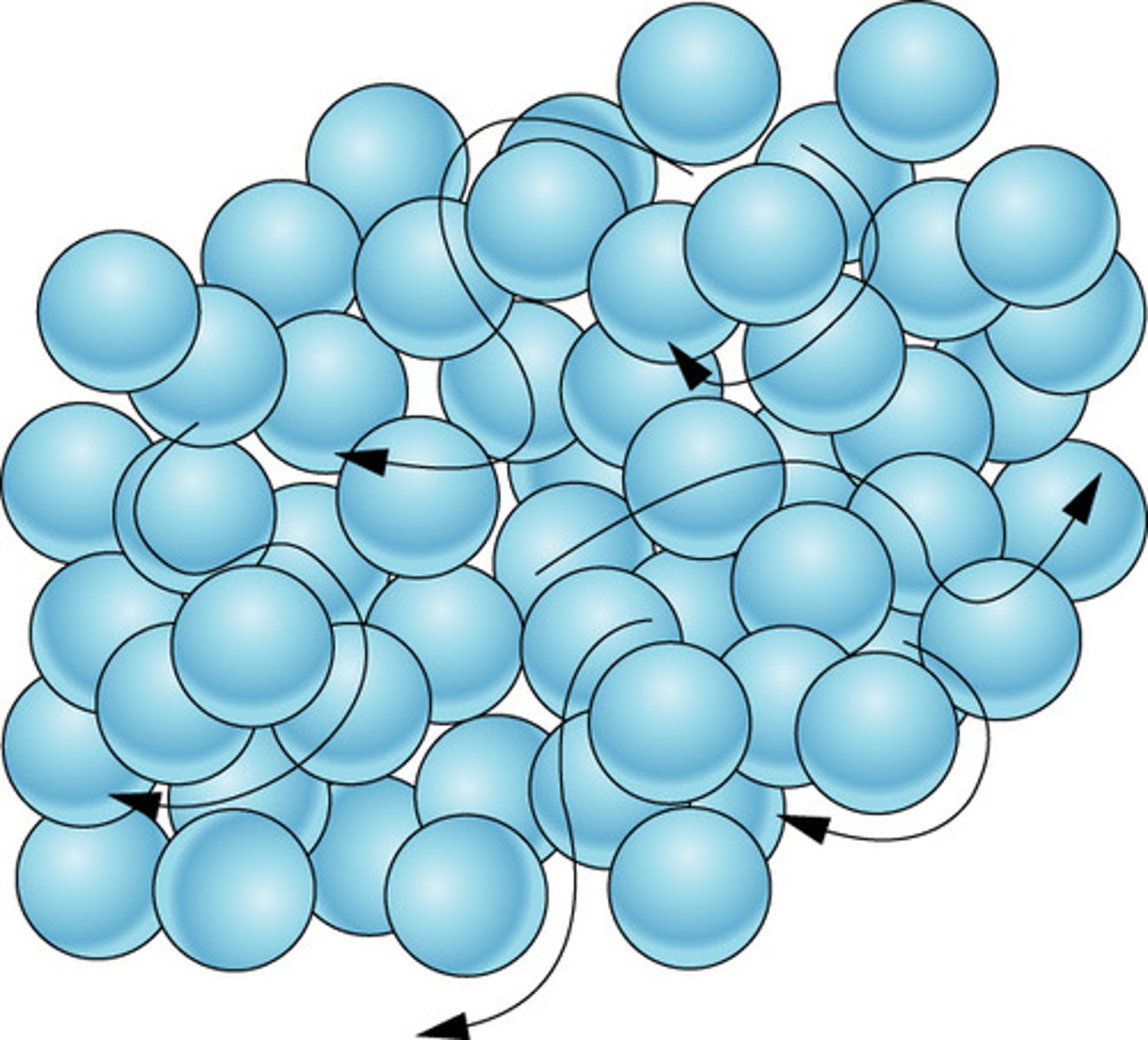
Gas
Particles are much farther apart and attraction forces are weak so particles no longer cling together. Substances in this state do not have a fixed volume or shape.
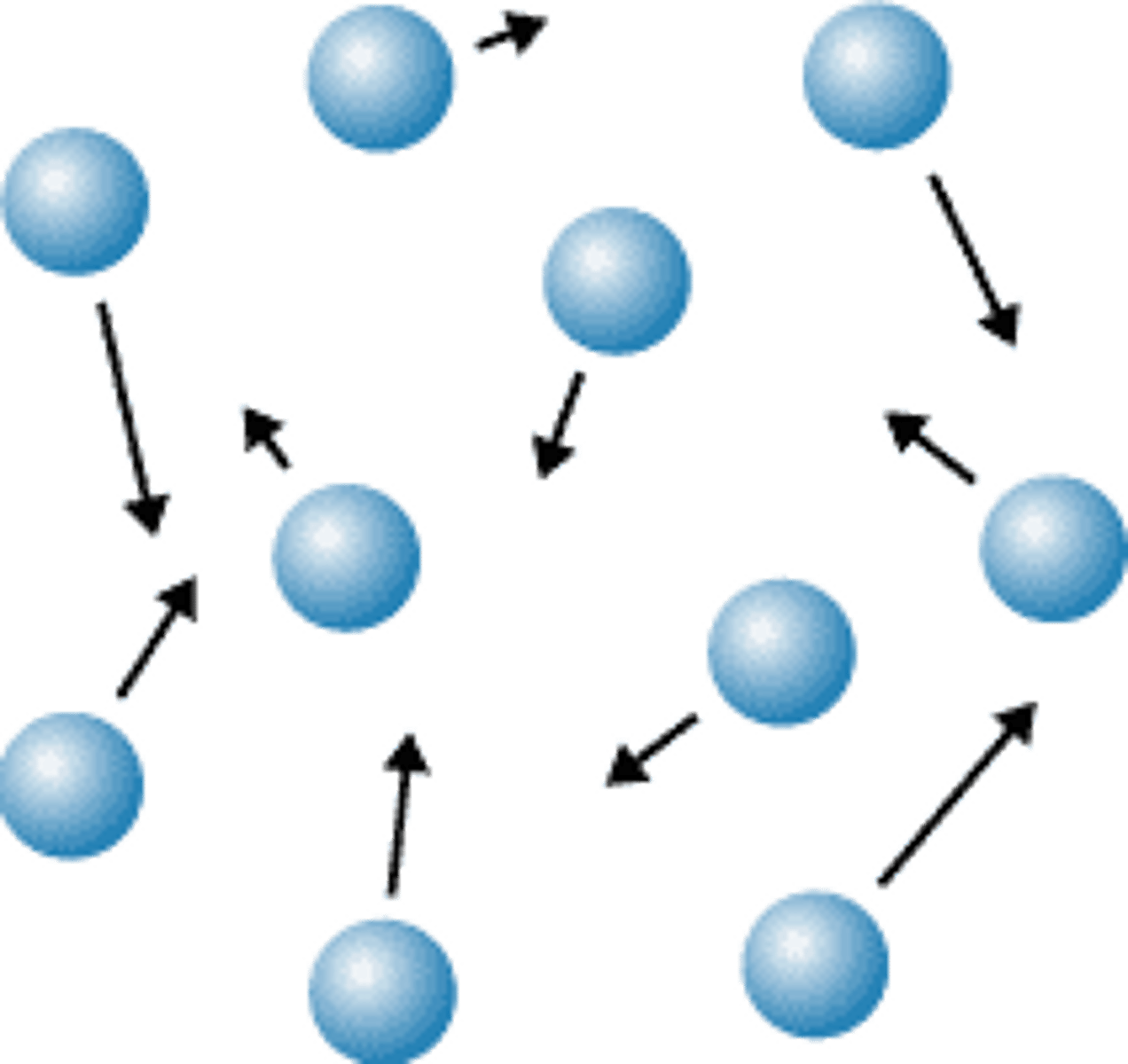
Melting
A change from solid to liquid state
Freezing
A change from liquid to solid state.
Vaporization
A change from liquid to gas state
Condensation
A change from gas to liquid state
Sublimation
A change from solid to gas state
Deposition
A change from gas to solid state
Absolute Zero
The temperature at which all particle movement and vibration stops.
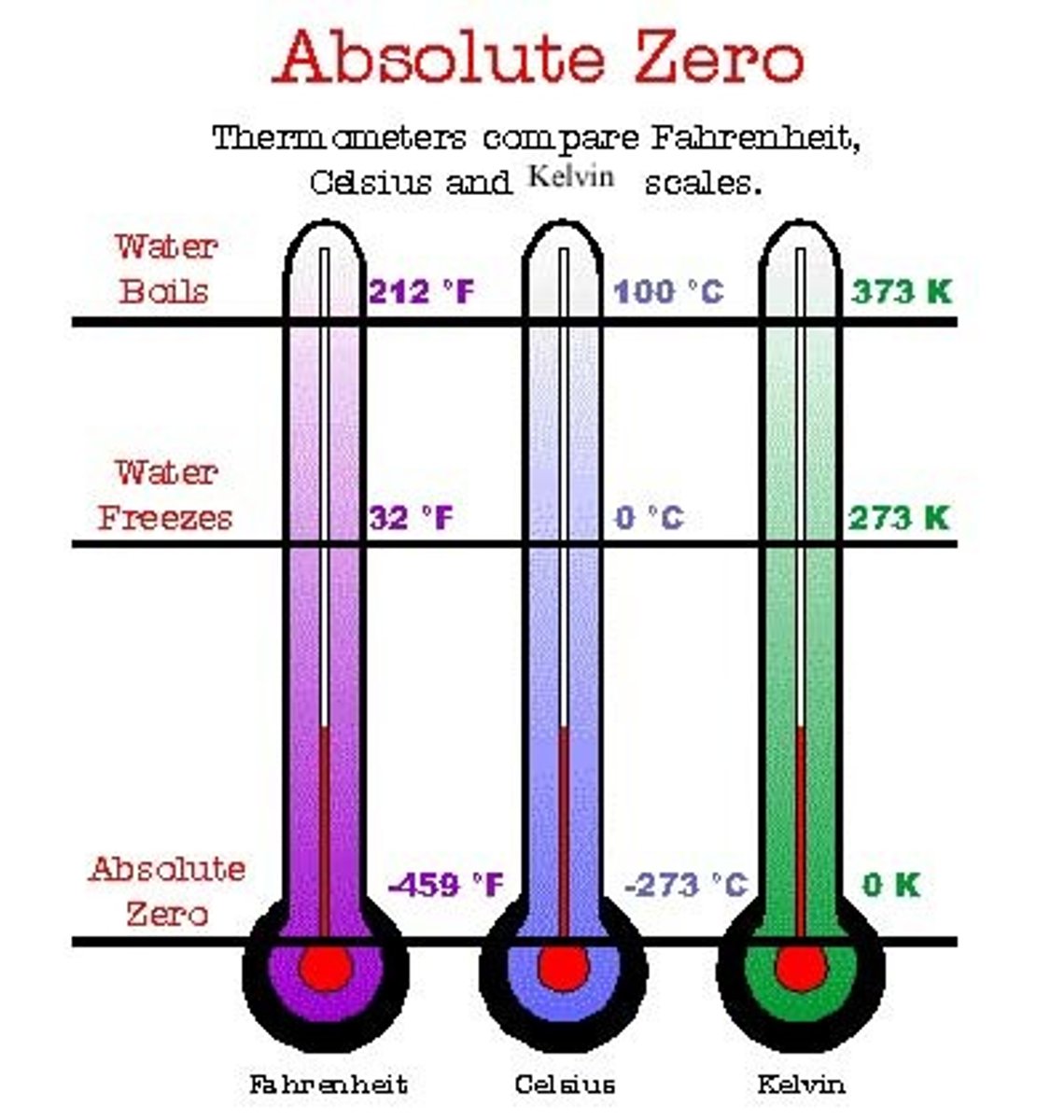
0 deg Celsius
The freezing/melting point of water
100 deg Celsius
The boiling point/condensing point of water
Density
the amount of matter packed in a given space
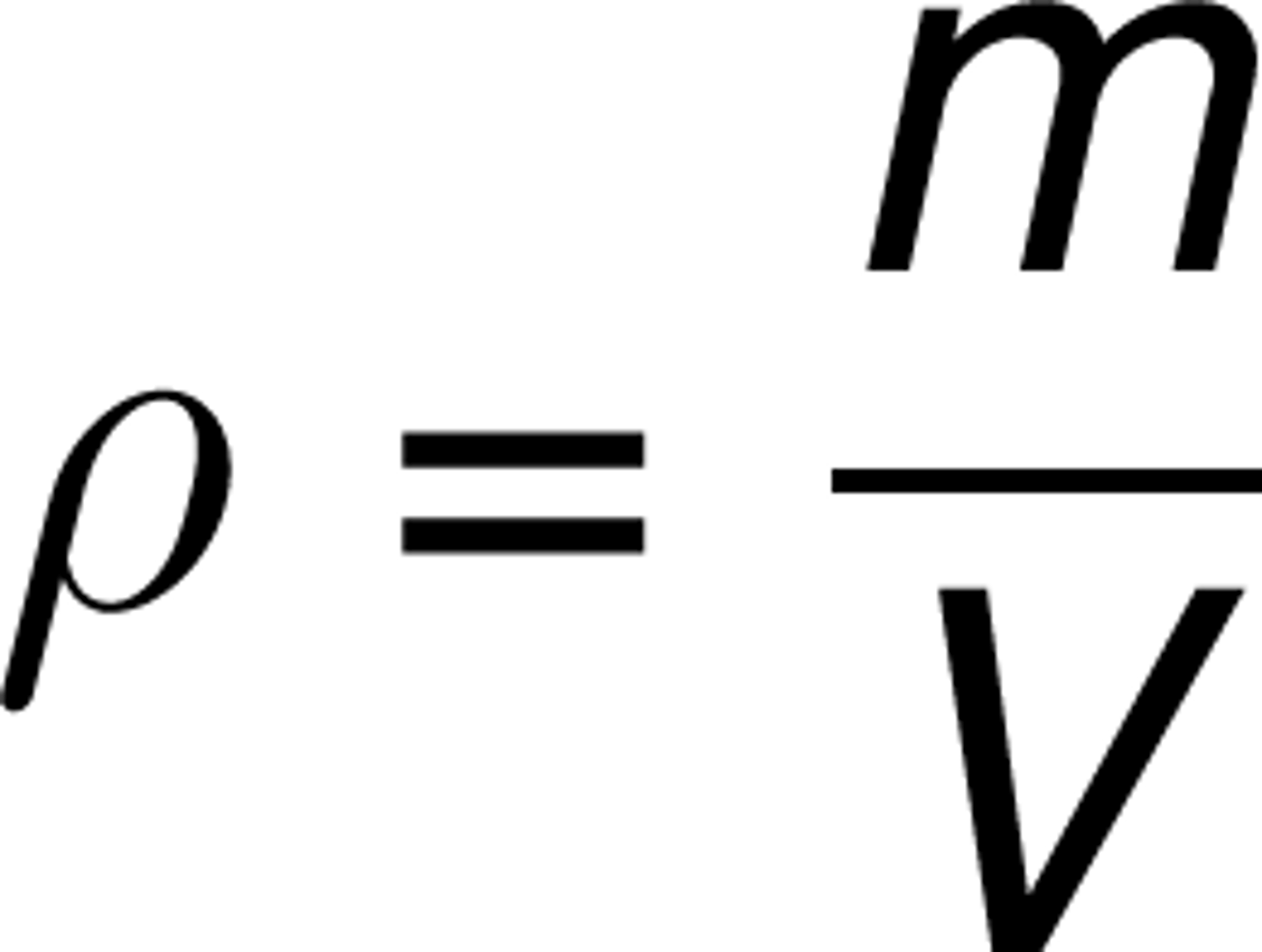
Volume
The amount of space an object takes up
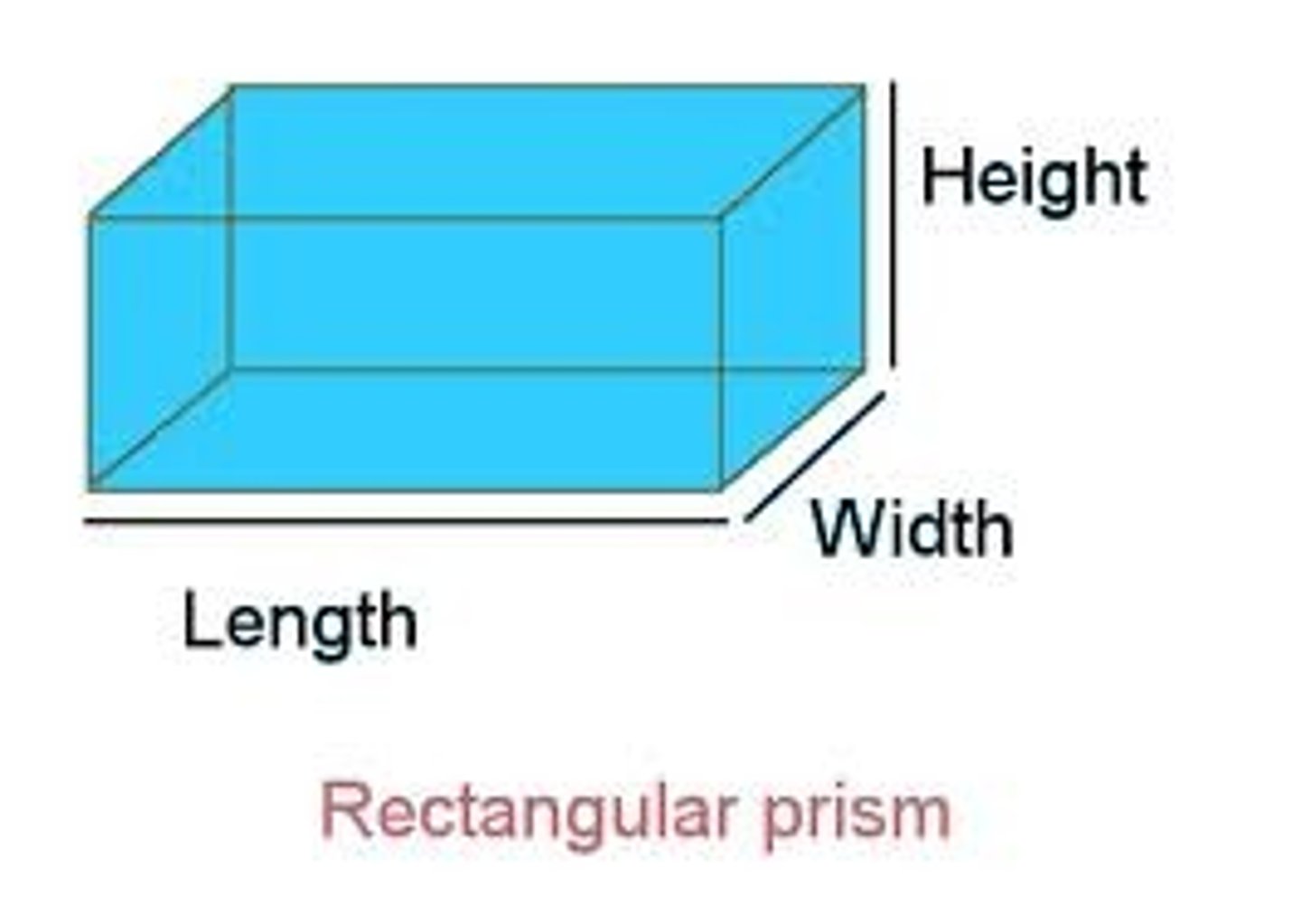
Milliliter (mL)
Common unit to measure volume

Gram or kilograms
Common unit to measure mass

g/mL or g/cm3
Common units to measure density
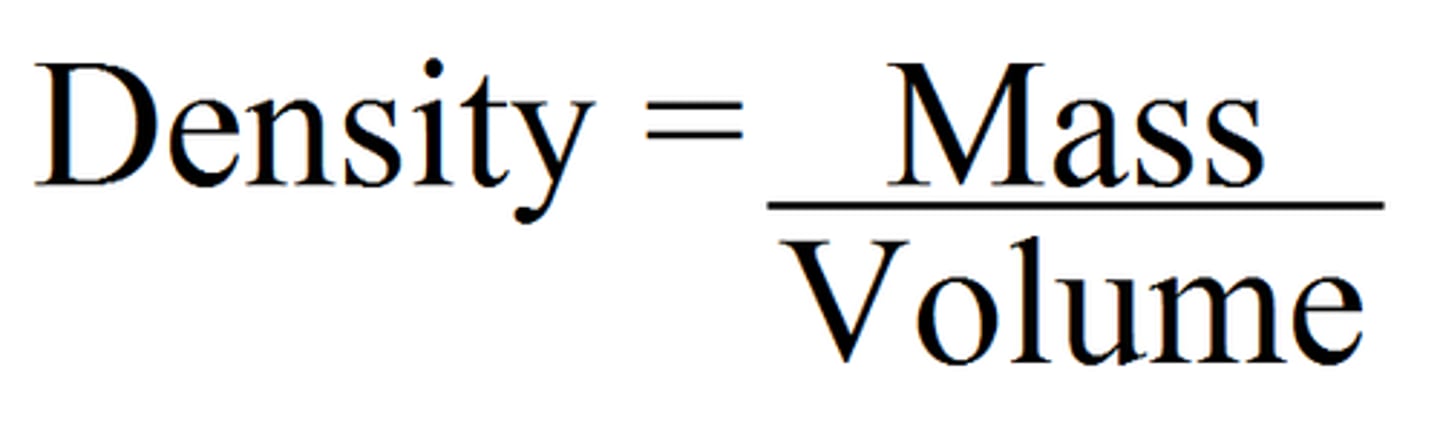
Phase change
Temperature stays the same when this occurs. Energy is going into changing the distance between particles, not the speed.