Freshwater Terms
1/55
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
56 Terms
Abrasion
Is the wearing away of bed and bank by the load carried by the river
Aquifer
Rocks that can hold water
Attrition
Is the wearing away of the load carried by a river. It creates smaller round particles.
Confluence
Where two rivers meet.
Discharge
the volume of water passing a given point over a set time.
Discharge = Area x Velocity
discharge formula
Drainage divide or watershed
the line defining the boundary of a river or stream drainage basin separating it from adjacent basins
Efficiency
Is measured by a rivers hydraulic radius (Cross-section)
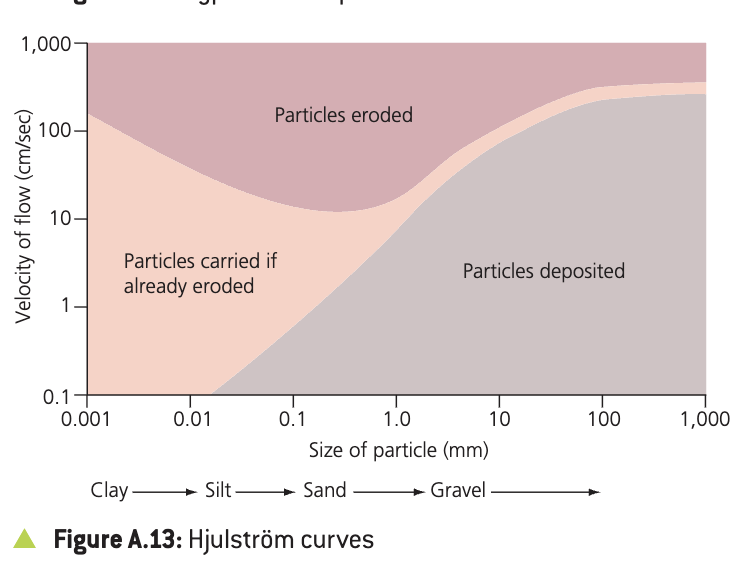
Hjulstrom Curve
A graph that shows the relationship between river velocity and particle size when looking at a rivers' ability to erode. transport and deposit.
Hydraulic Action
Is the force of air and water on the sides of the rivers and in cracks.
Hydrological Cycle
Closed System
Load
Material transported by a river e.g. stones, sand, boulders.
Maximum sustainable yields
the maximum level of extraction of water that can be maintained indefinitely for a region.
Meander
A bend in the river
Mouth
The end of a river. A river may end in a lake, but more normally in the sea
Potential evapotranspiration
the rate of water loss from an area if there were no shortages of water
Runoff
precipitation that does not soak into the ground but flows over it into surface waters.
Saltation
Heavier particles are bounced or bumped along the bed of the river.
Soil moisture excess
when soil moisture and groundwater is replenished. The excess may lead to saturation and increased surface run
Solution
Is the removal of chemical ions, especially calcium, which causes rocks to dissolve.
Source
The beginning of a river. A river may have multiple sources. The source of a river is normally found in upland mountainous areas.
Suspension
Small particles are held up by turbulent flow in the river.
Tributary
A small river that flows into a larger river.
Velocity
This is the speed that the water in a river is travelling at. The unit of measurement is normally meters a second (m/s). River velocity can be measured using a flowmeter
Water balance
the relationship between the inputs and outputs of a drainage basin
Water Balance Equation
P = Q+ E + delta S
P=precipitation
Q=Runoff
E=Evaporization
S=Change in storage (in soil or bedrock)
Wetted Perimeter
The total length of the bed and the banks in contact with the river.
What are the factors affecting erosion?
Load, Velocity and Discharge, Gradient, Geology, pH, Human Impact
Endorheic/ closed basin
a drainage basin that does not flow out to sea but feeds into an inland body of water or groundwater source, e.g. aral sea tributaries
drainage basins are open systems
major input: precipitation
major outputs: evapotranspiration, runoff, leakage
Evapotranspiration
the combined effects of evaporation and transpiration
account for ~100% of precipitation loss in arid areas and ~75% in humid areas
Potential evapotranspiration :)
water loss that would occur if there was an unlimited supply of water in the soil for use by the vegetation
moisture availability: the amount of actual water in soil
infiltration capacity
the maximum rate at which rain can be absorbed by a soil in a given condition
Overland flow
occurs mainly when:
precipitation exceeds infiltration rate
the soil is saturated
throughflow
water flowing through the soil in natural pipes
percolines
lines of concentrated water flow between soil horizons
base flow
the part of a river’s discharge that is provided by
groundwater seeping into the bed of a river
relatively constant flow although it increases slightly following a wet period
Interception
water that is retained by plant surfaces and which is later evaporated away or absorbed by the plant
throughfall: water that either falls through gaps in the vegetation or which drops from leaves, twigs or stems
stemflow: water that trickles along twigs and branches and finally down the main trunk.
Field capacity
amount of water held in the soil after excess water drains away, that is, saturation or near saturation
Wilting point
the range of moisture content in which permanent wilting of plants occurs
Water table
top layer of phreatic zone
varies seasonally
phreatic zone
permanently saturated zone within solid rocks and sediments
Recharge
the refilling of water in pores (of rock) where the water has dried up or been extracted by human activity
cryosphere
the snow and ice environment
Up to 66 per cent of the world’s freshwater is in the form of snow and ice
capacity of a stream
the largest amount of debris that a stream can carry
critical erosion velocity
the lowest velocity at which grains of a given size can be moved
Hjulström curve
shows relationship between velocity of flow and the size of the particle able to be carried, indicates when particle are eroded, carried if already eroded or deposited
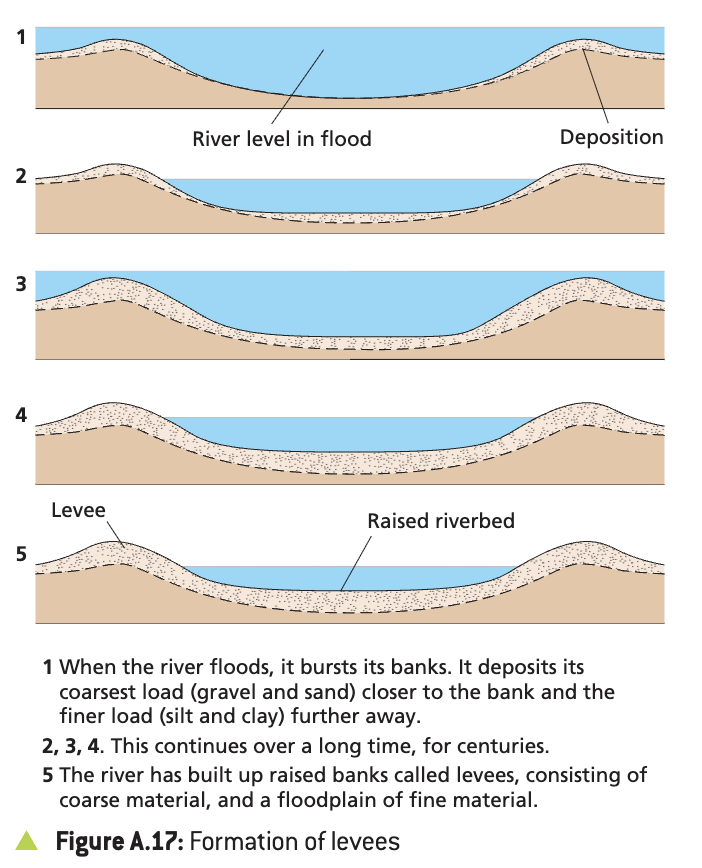
Levees
formed by the deposition of coarse material near the channel, while the finer deposits are carried out into the flood plain
flocculation
salt particles group together and become heavier, so they are deposited
causes formation of river deltas
bioconstruction
vegetation increases the rate of deposition by slowing down the water
Physical water scarcity
where water consumption exceeds 60 per cent of the useable supply
Economic water scarcity
where a country physically has sufficient water to meet its needs, but requires additional storage and transport facilities
water stress
When an area’s per capita water supply is less than 1,700 cubic metres per year
anoxia
oxygen starvation in the water
eutrophication
algal blooms in bodies of freshwater due to runoff from nitrogen-fertilised agricultural land
salinisation
Capillary forces bring water to the surface where it may be evaporated, leaving behind any soluble salts that it is carrying.