2.3.1 Plant tissues
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
15 Terms
List all the plant tissues
epidermal tissues, palisade mesophyll, spongy mesophyll, xylem and phloem and meristem tissue
Where is meristem tissue found?
Found at the growing tips of shoots and roots
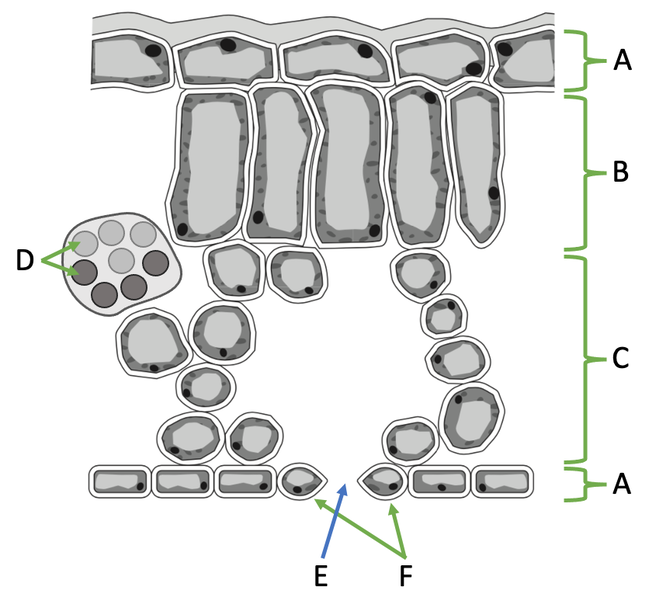
Label these parts of the leaf
A) epidermal tissue
B) palisade mesophyll tissue
C) spongey mesophyll tissue
D) xylem and phloem
E) stomata/ stoma
F) guard cells
What is the structure and function of epidermal tissue in plants?
Thin, transparent outer layer of cells - allows light to pass into leaf.
Covers plant surfaces, protecting against water loss & pathogens.
May secrete waxy cuticle - reduces water evaporation.
What does the palisade mesophyll tissue contain and what can it do?
Contains many chloroplasts, and can photosynthesise
Describe the structure of spongy mesophyll
has some chloroplasts, many air spaces between the cells and a large surface area for diffusion of gases
How is the palisade mesophyll adapted for photosynthesis?
Packed with chloroplasts - maximum light absorption.
Regularly shaped, tightly packed cells - efficient light capture.
Found near upper surface of leaf where light intensity is highest.
What is the structure and role of the spongy mesophyll?
Loosely packed cells with air spaces - allow gas exchange (CO₂ in, O₂ out).
Fewer chloroplasts than palisade cells - some photosynthesis.
Close to stomata - aids diffusion of gases.
What can the meristem tissue do?
It id made of undifferentiated (stem) cells, so it can divide & specialise.
What is the meristem tissue responsible for?
Responsible for plant growth, formation of new leaves, flowers, or roots.
Why are spongy mesophyll cells surrounded by air pockets?
To aid the diffusion of gases
In which plant cells would you expect to find the highest concentration of chloroplasts?
Palisade mesophyll
Which of the following is a function of the upper epidermal tissue in plants?
To reduce water loss
Translocation is the movement of:
Dissolved sugars around the plant through the phloem tissue
What does xylem transport around the plant?
Water and minerals