applied anatomy all
1/487
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
488 Terms
Pelvic girdle
bony ring formed by the sacrum and hip bones which are connected anteriorly at pubic symphysis
Movements of pelvic girdle
lateral/anterior/posterior pelvic rotation/tilt
Functions pelvic girdle
weight bearing, weight transference and protection
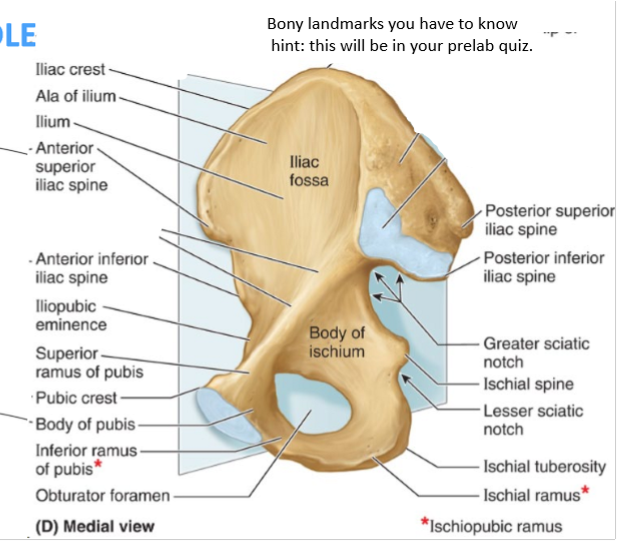
Pelvic bone landmarks
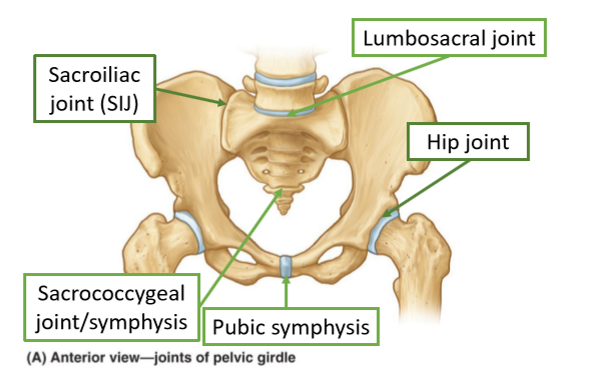
Pelvis Joints
hip joint-femoral acetabular joint, symphysis is not a joint and is stiff
Pelvic Ligaments
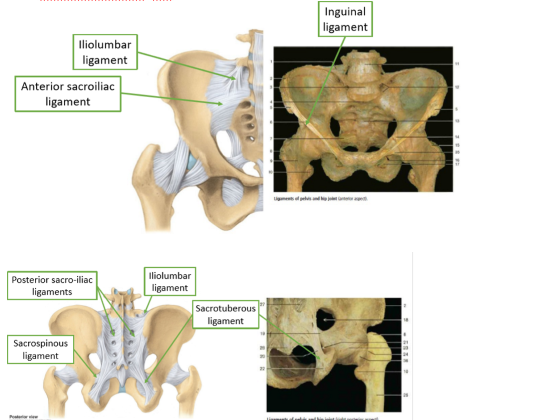
Sacrotuberous ligament
sacrum to ischial tuberosity
Sacrospinous ligament
sacrum to ischial spine
Iliolumbar ligament
L4 & 5 to iliac crest
Ingunial ligament
ASIS to pubic tubericle
posterior sacro iliac ligaments
from PSIS and iliac crest, to sacrum
Anterior sacro iliac ligament
lateral crest of sacrum to PSIS and posterior iliac crest
Pelvis protections
reproductive organs/ viscera, ateries and nerves, urinary system, excretory system
Perineal membrane/body
holds in place and prevents downward drift/prolapse
Pelvic fascia
supported by endopelvic fascia
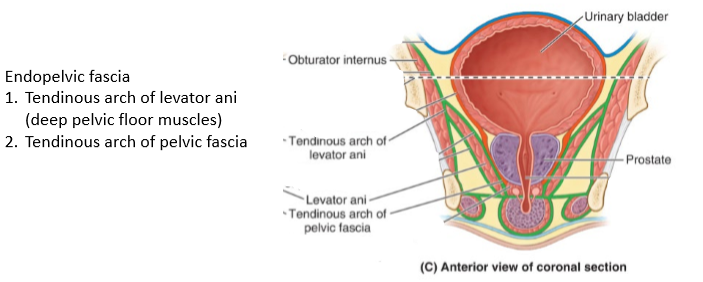
Endopelvic fascia
supports and anchors pelvic floor muscles and pelvic viscera. Contains fatty tissue to protect organs. Attaches to pelvic wall via arcus tendinous laterally. Tearing and stretching of it can result in loss of organ support and prolapse causing incontinence
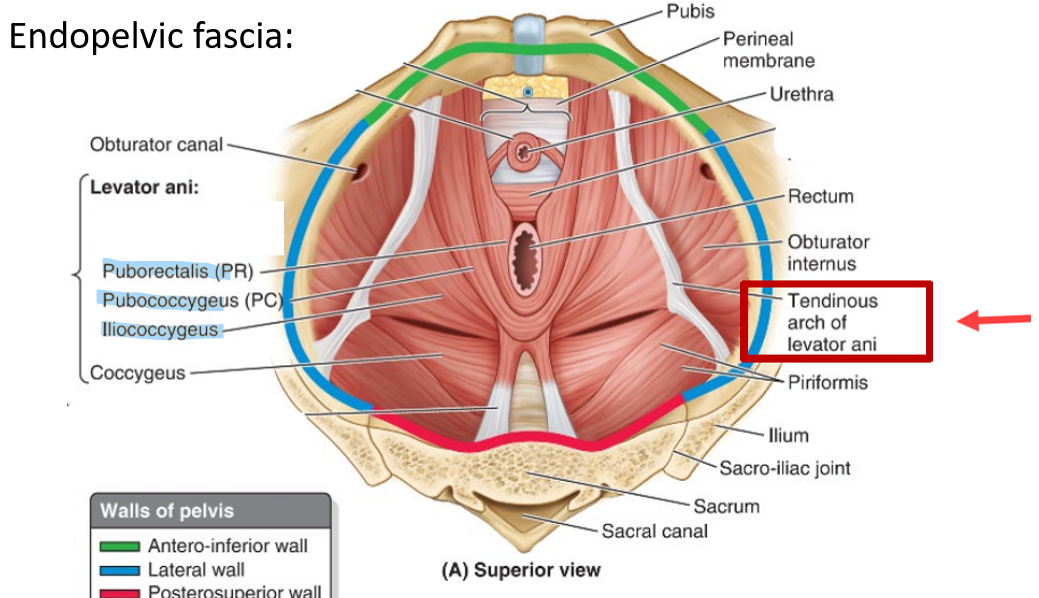
muscles of endopelvic fascia
Perineal body
connective tissue between vagina and testicles and the anus. Lies deep to skin important anchor point. Acts as point attachment for muscle fibres from pelvic floor and perineum
Incontinence
ability to control excretion
Pelvic diaphragm
levator ani and coccygeus
Levator ani
puborectalis, pubococcygeus, illiococcygeus. First line of defence against prolapse. Acts as a sling to increase the angle of anal canal
Coccygeus
coccyx to ishium. Acts to draw coccyx anteriorly following defaecation and parturition
Levator ani
sling lifting anteriorly and superiorly.
Puborectalis
most medial part of levator ani. Thick narrow. Draws distal rectum anteriorly and superiorly. Related to anal sphincter complex
Pubococcygeus
intermediate part of levator ani. Wide but thin. Elevates and laterally compresses closing the urogenital hiatus bringing the vagina urethra and rectum toward the pubic bone and elevates pelvic organs. Serves important role in competence of urethral and rectal sphincators doing increased abdominal pressure
Illliococcygeus
posterolateral part of levator ani, it resists depression of pelvic floor
Pelvic floor muscle functions
support abdominal structures, assist with sexual function, assist with continence and work in conjunction with abdominal muscles
Pudendal nerve
from posterior to sacrospinous ligament, enters lesser sciatic foraman, medial to sichial ramus and pubic ramus. Motor supply- superficial pelvic floor muscles. Sensory supply- skin external genitalia
Iliac region
muscles converge
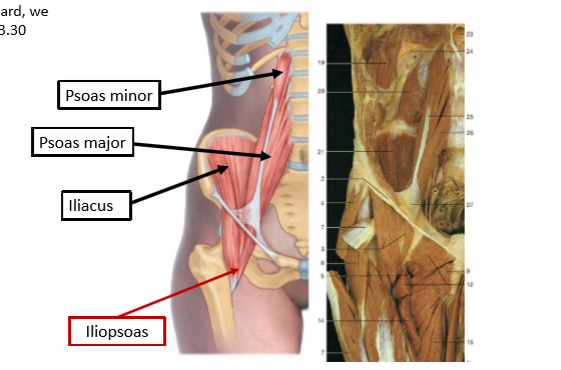
Psoas minor
T12 L1 to iliopubic eminence
Psoas major
proximal- transverse process of lumbar vetrebrae sides of bodies of vetrebrae t12-l5 and IV discs. Distal- lesser trochanter of femur
Psoas major action and NS
hip/trunk flexion.
Iliacus attachments
proximal superior 2/3 of illiac fossa, ala of sacrum and sacroiliac ligaments. Distal- lesser trochanter of femur
Illiacus action and NS
hip flexion and stabilise hip. Femoral nerve
Femoral nerve formed
within psoas major, emerging low on its lateral border and passes between psoas major and iliacus in gutter. Underneath inguinal ligament with the femoral artery and vein to enter the femoral triangle in anterior thigh
Pectineus
adducts and flex hip. Femoral nerve (and obturator) supply
Sartorius
proximal- ASIS. Distal- anterior aspect of medial condyle of tibia. Synergist for hip flexion abduction lateral rotation and knee flexion. Supplied by femoral nerve
Quadriceps
vastus lateralis, rectus femoris, vastus medialis, vastus intermedius. Knee extensors supplied by femoral nerve
Rectus femoris
proximal- Asis, distal- quadriceps tendon, patella, patellar tendon, tibial tuberosity. Hip flexion and knee extension.
Vastus medialis
proximal- intertrochanteric line and medial lip of linea aspera of femur. Distal- quad tendon, patella, patellar tendon, tibial tuberosity
Vastus lateralis
proximal
Vastus intermedius.
Proximal- anterior and lateral surfaces of shaft of femur. Distal- quad tendon, patella, patellar tendon, tibial tuberosity
Femoral navel
nerve, artery, vein, empty space, lymphatic vessels
Muscular branches supplied by femoral nerve
iliacus, pectineus, satorius, rectus femoris, vastus lateralis/medialis/intermedius, articularis genu
Sensory femoral nerve branches
anterior femoral cutaneous and saphenous nerve. Also supplies hip and knee joint
Saphenous nerve
no motor function, sensory. Travels behind satorius in adductor canal, crosses to medial side of knee deep to satorius, becomes superficial between sartorius and gracilis and supplies skin medial side of leg below the knee
Ilioposas muscle group
psoas minor, major and iliacus. Proximal- sides of lumbar vertebrae and superior iliac fossa. Distal- lesser trochanter and pectineal arch
Obturator innervates
adductor longus/brevis/magnus, gracilis and obturator externus
Heart made up of
right atrium right ventricle. Left atrium left ventricle. Valve between. Arteries move away, veins move in.
Order of tubes
large lumen arteries, smaller arteries, arterioles, capillaries venules, veins
Right side of heart
recieves poorly oxygenated blood and pumps into lumps. From superior and inferior vena cava
Left side of heart
recieves well oxygenated blood and pumps into aorta to be distributed. More muscle
Blood supply pathway
aorta, common iliac artery, external iliac artery (under inguinal ligament), becomes femoral artery (inferiorly to femur, medially and eventually posteriorly), passes through adductor magnus hiatus, becomes popliteal artery, then becomes anterior tibial artery and posterior tibial artery at soleal line
Anterior tibial artery
passes through hole in interosseus membrane, becomes dorsal pedis artery between extensor hallucis longus and extensor digitorum longus
Posterior tibial artery
palpate behind medial malleolus. Between flexor digitorum longus and flexor hallucis longus
Deoxygenated blood route
lateral and medial plantar veins, dorsal venous arch, anterior and posterior tibial veins, popliteal vein, femoral vein, external iliac vein, common iliac vein, inferior vena cava
Deep vein thrombosis
blood clot. Common in lower calf. High cholestrol, prolongued sitting, high BP, pregnancy are risks. Clot could move to heart and lungs or brain
Agonist
has the best capacity to work around the axis. Largest bulk/ best mechanical advantage due to attachments in relation to joint axis/ leverage
Synergist
assist by adding force or reducing uneccessary movement
Stabilisers
stabilises another part of the body while the other move
Widespread exercise induced pain
Exercise induced vague pain could mean that not enough oxygen and blood is reaching the muscles. As the patient indicates very clearly that going up stairs is much worse than down stairs, this is a clear indication that the oxygen demand of climbing stairs is not being met by the blood supply. And the poor blood supply is not systemic - as they dont get dizzy - it only seems to affect that left leg. Therefore, narrowing of an artery
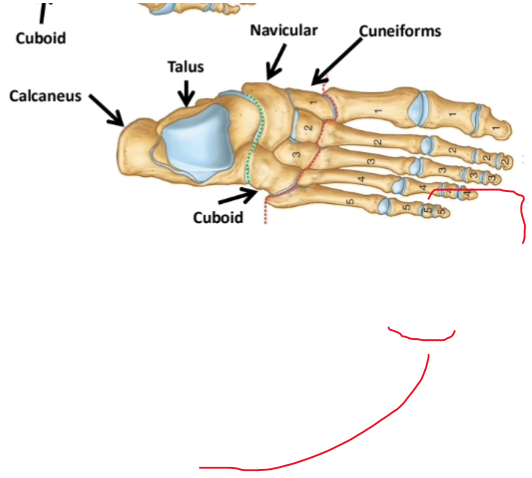
Hindfoot
talus and calcaneus
Midfoot
navicular cuboid and cuneiforms
Forefoot
metatarsals and phalanges
Transverse tarsal joint
calcaneocubiod joint and talonavicular joint. Inversion and eversion of distal parts of foot
Bifurcate ligament
calcaneus to cuboid and navicular. Resists inversion
Lisfranc/tarsometatarsal joints
between tarsals and metatarsals. Accessory movement, glides and slides. Eversion inversion. Sagittal plane axis
Proximal interphalangeal joint
joints between phalanges (none on hallux.) flex extend. Coronal axis through head of proximal phalanx
Metatarsophalangeal joint
between metatarsals and proximal phalanx. Flex and extend. Coronal axis through head of metatarsal
Movements of toes
flex extend, abduct adduct
Plantar ligament functions
maintain longitudinal arches of foot. Absorb load
Plantar fascia/aponeurosis
comes from calcaneus, five different bands to forefoot, attaching to base of proximal phalanges
Intrinsic foot muscles- dorsal
extensor digitorum brevis (doesn’t go to fifth) and extensor hallucis brevis. Supplied by deep fib nerve. Arrise for calcaneus and run into extensor expansion (fibrous extension over prox phalanges. Extend and stabilise)
Intrinsic foot muscles- plantar
layer one- abductor hallucis (medial plantar nerve), flexor digitorum brevis (m), abductor digiti minimi (lat plantar nerve). Layer two- quadratus plantae (L), lumbricals 1-4 (M1, L3). Layer 3- flexor hallucis brevis (M), adductor hallucis (L), flexor digiti minimi (L). Layer four- dorsal interossei and plantar interossei (L)
Abductor digiti minimi
abduct fifth digit
Flexor digitorum brevis
only goes to the middle phalange. Splits for FDl at distal attachment.
Quadratus plantae
from calcaneous to digitorum longus tendon. Orientates line of pull in flexion
Lumbricals
to extensor expansion. Flex metatarsalphalangeal joints by extending interphalangeal joints
Plantar interossei
adduct and help flex MTPJ and extend IPJ. 3
Dorsal interossei
abduct and help flex MTPJ and extend IPJ. 4\
Claw toe
intrinsic muscle malfunction
Medial Longitudinal arch
calcaneum talus navicular, 3 cuneiforms and medial metatarsals
Lateral longitudinal arch
calcaneum, cuboid, lat 2 metatarsals
Arches purpose
distribute weight, shock absorb, springs for walk and jump
Superficial fibular nerve
L4 to S2. supplies lat compartments of leg (fib long and fib brev). Cutaneous dorsal supply
Late
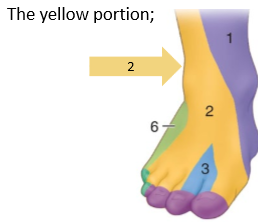
Deep fibular nerve
supplies muscles- tib ant, extensor digitorum longus, extensor hallucis longus, fib tertius, extensor digitorum brev and extensor hallucis brev. Cutaneous branch at 3- dorsal branch at webbing
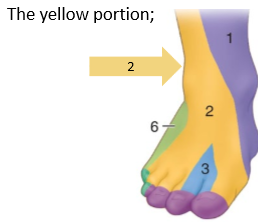
Medial and lateral plantar nerve
from tibial nerve deep to flexor retinaculum. L4-L5. cutaneous distribution
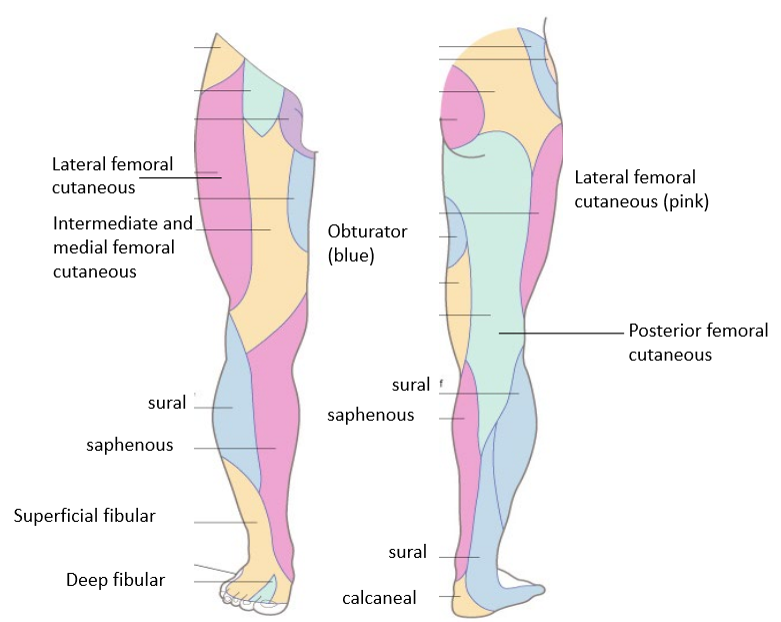
Complete cutaneous nerves
Foot sensory role
many sense receptors as its responsible for balance weight distribution, uneven ground, surface texture, temperature
Foot adaptive role
accessory movements in tarsals and metatarsals mould to uneven ground and toes use lumbrical action.
Tibiofibular joints
proximal tibiofibular joint (synovial), distal/inferior tibiofibular joint (syndesmosis, fibrous)
Tibiofibular ligaments
anterior and posterior, interosseous membrane
Foot bones