Pulmonary exam
1/30
Earn XP
Description and Tags
FF Week 3
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
Tidal volume (TV)
Air inspired (and therefore expired after) during normal, relaxed breathing
Reserve volumes
Reserve volumes are additionals/extras
Inspiratory reserve volume (IRV)
Additional air that can be forcibly inhaled after the inspiration of a normal tidal volume
Extra coming in
5-6x more than tidal volume
Expiratory reserve volume (ERV)
Additional air that can be forcibly exhaled after the expiration of a normal tidal volume
Extra going out
2-2.5x more than tidal volume
Residual volume (RV)
Volume of air remaining in the lungs after the expiratory reserve volume is exhaled
Always present in the lungs
Capacities
Capacities are totals
Total lung capacity (TLC)
Maximum amount of air that can fill the lungs
TLC = TV + IRV + ERV + RV
Inspiratory capacity (IC)
Maximum amount of air that can be inspired
IC = TV + IRV
Vital capacity (VC)
Total amount of air that can be expired after fully inhaling
VC = TV + IRV + ERV
~80% of TLC
Functional residual capacity (FRC)
Amount of air remaining in the lungs after a normal expiration
FRC = RV + ERV
Forced expiratory volume in 1 second (FEV1)
Volume of air exhaled in the first second under force after a maximal inhalation
Forced vital capacity (FVC)
Total volume of air that can be exhaled during a maximal forced expiration effort
What three values are all increased in patients with COPD?
Functional residual capacity, residual volume, & total lung capacity
FaRT
Obstructive lung conditions
Problem with airflow out of the lungs (comes in fine)
CBABE:
Cystic fibrosis
Bronchitis (chronic)
Asthma
Bronchiectasis
Emphysema
& COPD
All values except for FaRT (functional residual capacity, residual volume, and total lung capacity) decrease with obstructive conditions
Restrictive lung conditions
Problem with lung expansion/air volume in, but also coming out too
Sarcoidosis
Lung fibrosis
Ankylosing spondylitis
Obesity
Burns
Pneumonia
Pneumothorax
Hemothorax
Pulmonary effusion
All values decrease with restrictive conditions
GOLD Classification for COPD
30 is your gold #
Mild COPD
FEV1/FVC: < 70%
FEV1: ≥ 80%
Sx: dyspnea due to exercise
Moderate COPD
FEV1/FVC: < 70%
FEV1: 50% ≤ FEV1 < 80%
Sx: dyspnea with long walks
Severe COPD
FEV1/FVC: < 70%
FEV1: 30% ≤ FEV1 < 50%
Sx: dyspnea with ambulation
Very severe COPD
FEV1/FVC: < 70%
FEV1: < 30%
Sx: dyspnea at rest
COPD increases FaRT: functional residual capacity (FRC), residual volume (RV), and total lung capacity (TLC)
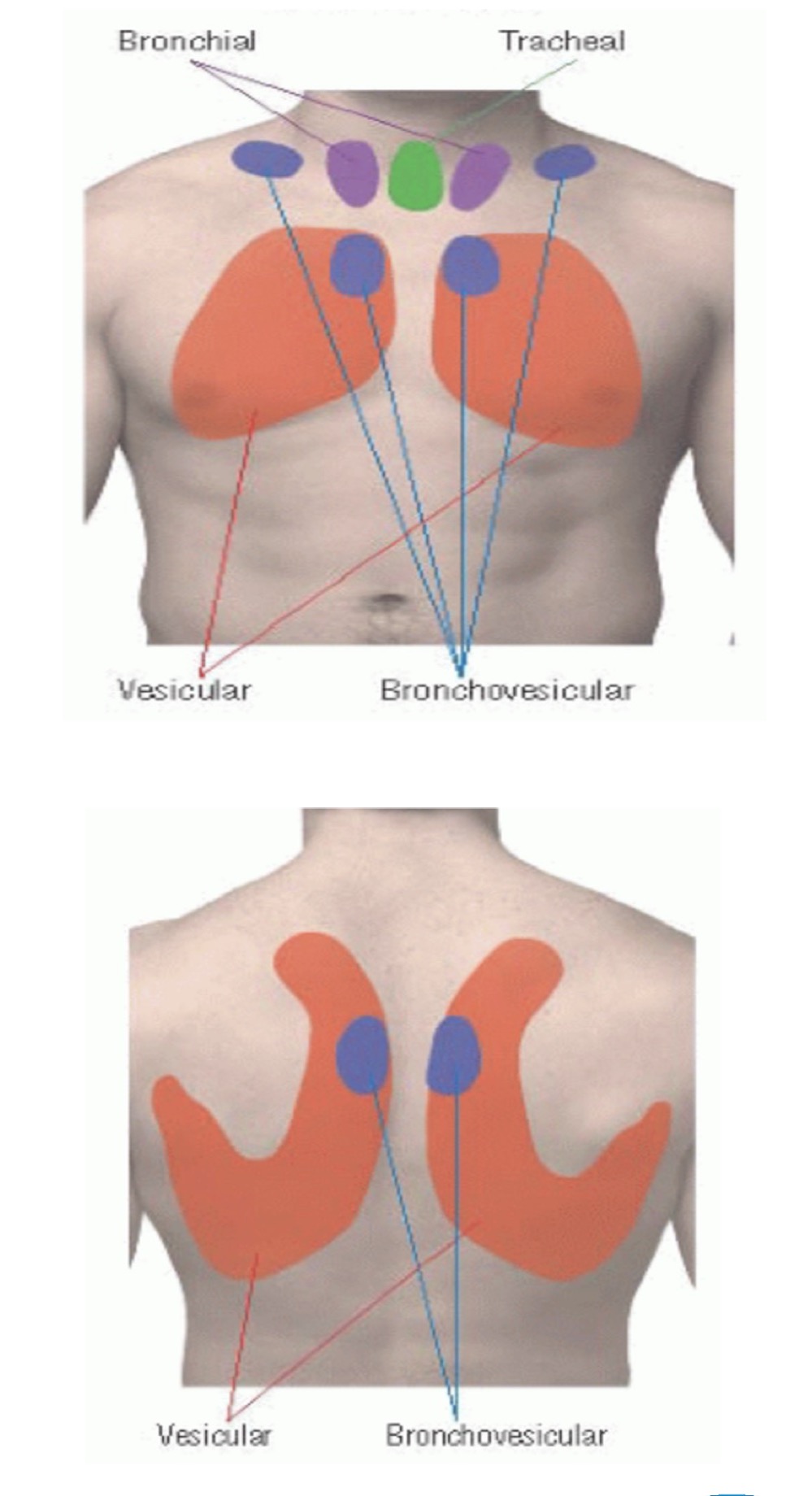
Vesicular breath sounds (normal sound)
Duration: inspiratory are longer
Intensity: soft
Pitch of expiratory: low
Location: over most of lungs
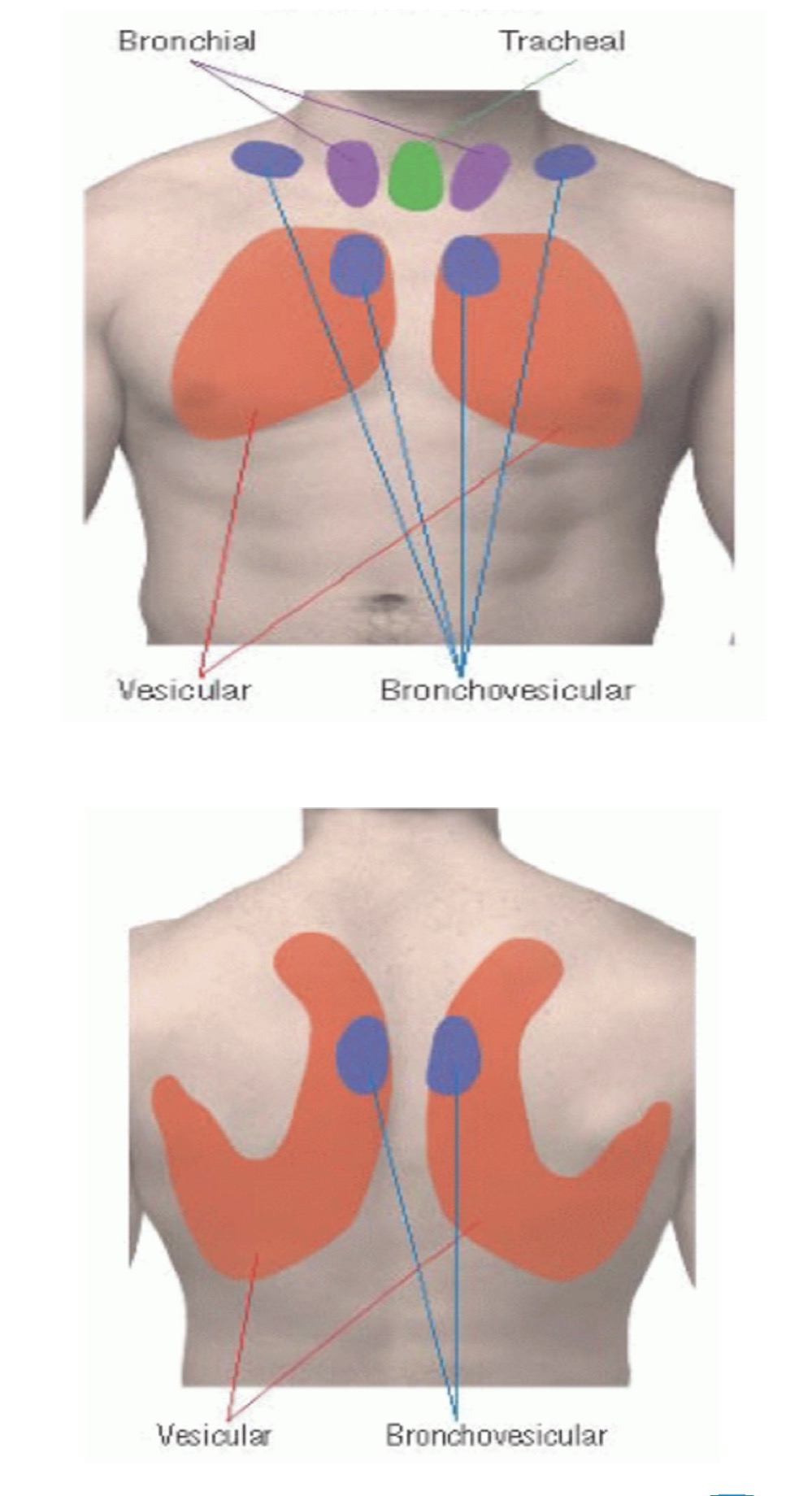
Broncho-vesicular breath sounds (normal sound)
Duration: equal inspiratory/expiratory
Intensity: intermediate
Pitch of expiratory: intermediate
Location: between 1st and 2nd IC space anteriorly and between the scapulae posteriorly
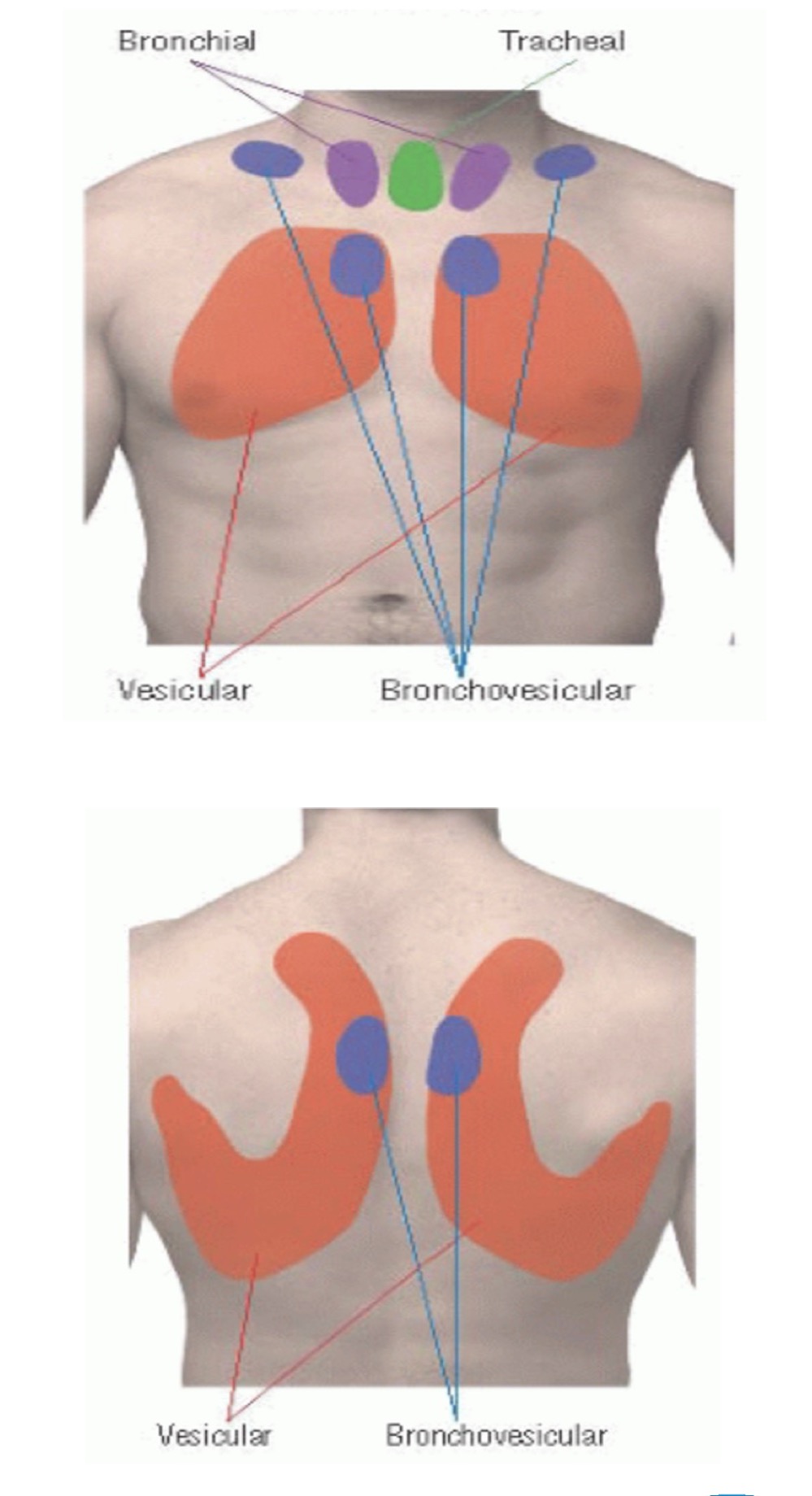
Bronchial breath sounds (normal sound)
Duration: expiratory are longer
Intensity: loud
Pitch of expiratory: high
Location: either side of manubrium
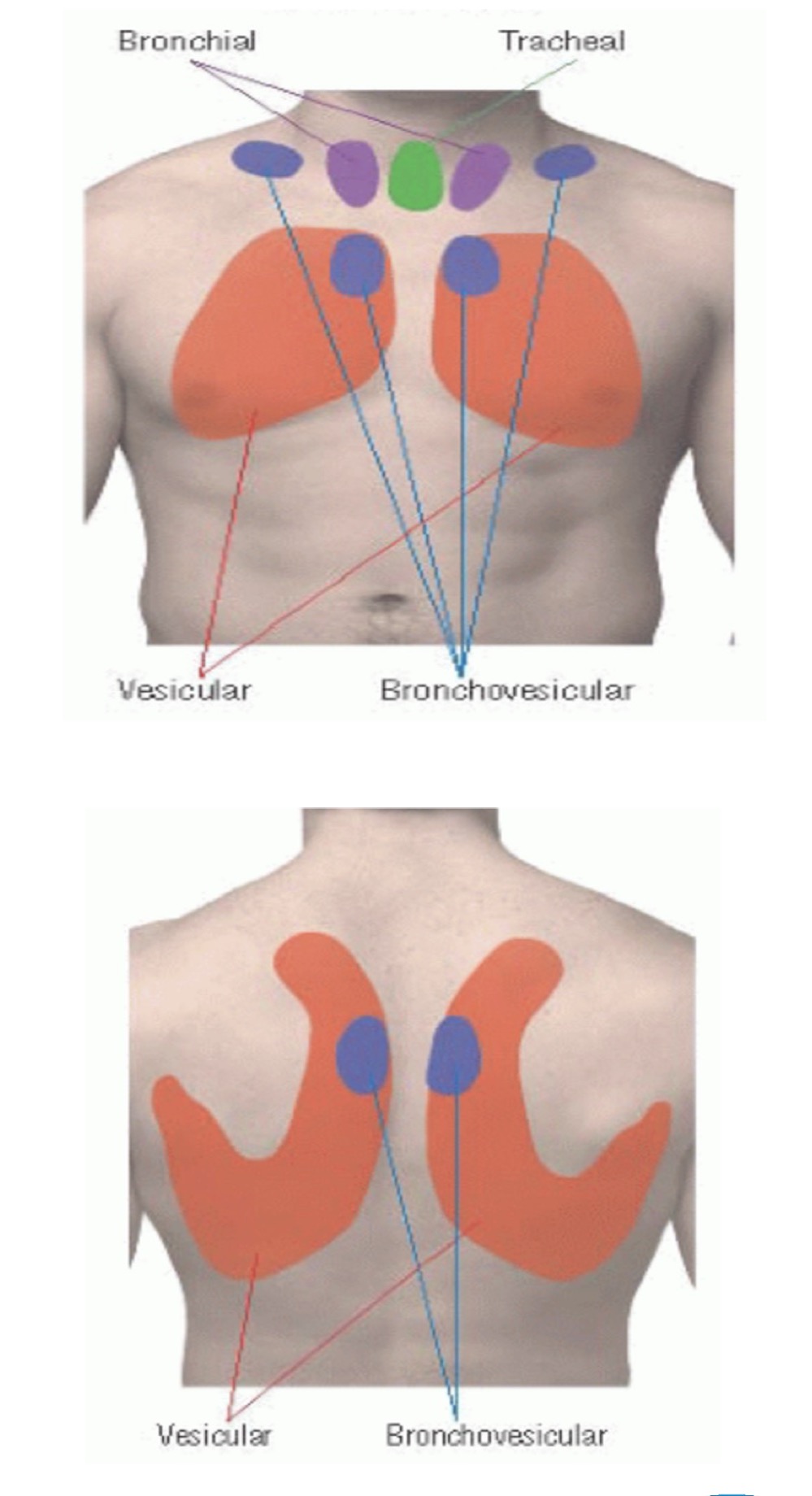
Tracheal breath sounds (normal sound)
Duration: equal inspiratory/expiratory
Intensity: very loud
Pitch of expiratory: relatively high
Location: over trachea in the neck
Rhonchi (abnormal sound)
Continuous, low-pitched, rattling, resembles snoring; heard when inhaling and exhaling
Causes: COPD, bronchiectasis, pneumonia, chronic bronchitis, or cystic fibrosis
Wheeze/whistling (abnormal sound)
High-pitched whistling heard in expiration; can be heard in inspiration as well in cases of severe constriction
Causes: airway obstruction, asthma, COPD, aspiration of foreign body, bronchial spasms
Crackles (abnormal sound)
Brief, discontinuous, popping, high-pitched sounds heard in both phases of respiration
Associated with congestive heart failure (pulmonary edema)
Pleural rub (abnormal sound)
Auscultation in the lower lateral chest areas, occurring with each inspiration and expiration
Can be indicative of pleural inflammation
Bronchophony (abnormal sound)
Increased vocal resonance with greater clarity and loudness of spoken words
“99”
Egophony (abnormal sound)
A form of bronchophony in which the spoken long “E” sounds change to a long, nasal sounding “A”
Whispered pectoriloquy (abnormal sound)
An increased loudness of whispering; recognition of whispered words “1, 2, 3”
What causes louder sounds?
Secretions, also called consolidations
Arterial blood gas norms
pH: 7.35 - 7.45
PaCO2: 35 - 45 mm Hg
HCO3: 22 - 26 mEq/L
CO2 causes respiratory issues
HCO3 causes metabolic issues
Respiratory vs Metabolic & Acidosis vs Alkalosis
CO2 changes = respiratory
HCO3 changes = metabolic
pH increased = alkalosis
pH decreased = acidosis
ROME: respiratory is opposite; metabolic is equal
Respiratory: pH and PaCO2 move in opposite directions
Metabolic: pH and HCO3 move in equal (same) directions
Respiratory Acidosis
pH: decreased
PaCO2: increased
HCO3: normal
Respiratory Alkalosis
pH: increased
PaCO2: decreased
HCO3: normal
Metabolic Acidosis
pH: decreased
PaCO2: normal
HCO3: decreased
Metabolic Alkalosis
pH: increased
PaCO2: normal
HCO3: increased
Compensated = pH is normal
Uncompensated = pH is outside of normal range
Partially compensated = all three (pH, PaCO2, & HCO3) are outside of normal range
Partial pressures of carbon dioxide (PaCO2) and oxygen (PaO2) have an inverse relationship