Salivary gland neoplasms
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
36 Terms
List 5 Benign Salivary Gland Tumours (Most Common
Pleomorphic Adenoma → important one to remember
Warthin Tumour
Cystadenoma
Basal Cell Adenoma
Canalicular Adenoma
List 5 Malignant Salivary Gland Tumours (Most Common to Least)
1) Mucoepidermoid Carcinoma → one to remember
2) Acinic Cell Carcinoma
3) Polymorphous Adenocarcinoma → to remember
4) Adenoid Cystic Carcinoma → to remember
5) Carcinoma Ex-Pleomorphic Adenoma
What are the different types of salivary gland tumours?
Epithelial and Non-epithelial
What is the term given to Epithelial Salivary Gland Benign and malignant Tumours?
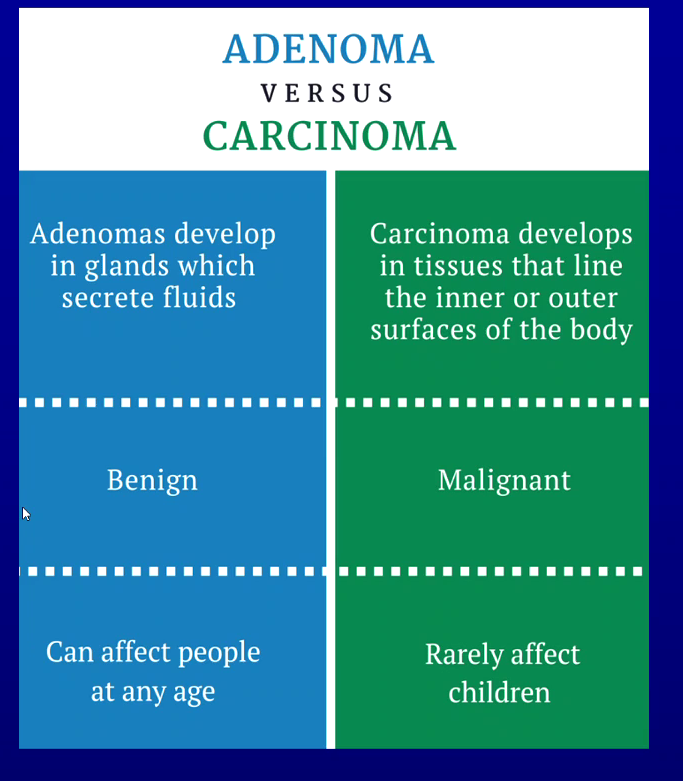
Benign epithelial - adenoma - develop in glands which secrete fluids
Malignant epithelial - carcinoma - develop in tissues that line inner or outer surfaces of body
Which 5 Salivary Gland Tumours are Non-Epithelial in Origin?
1) Soft Tissue Tumours
2) Malignant Lymphomas
3) Secondary Tumours - tumours that have metastasised to salivary glands
4) Unclassified Tumours
5) Tumour-Like Lesions
What is the most common age groups to get Salivary Gland Tumours?
Between ages 40 to 80
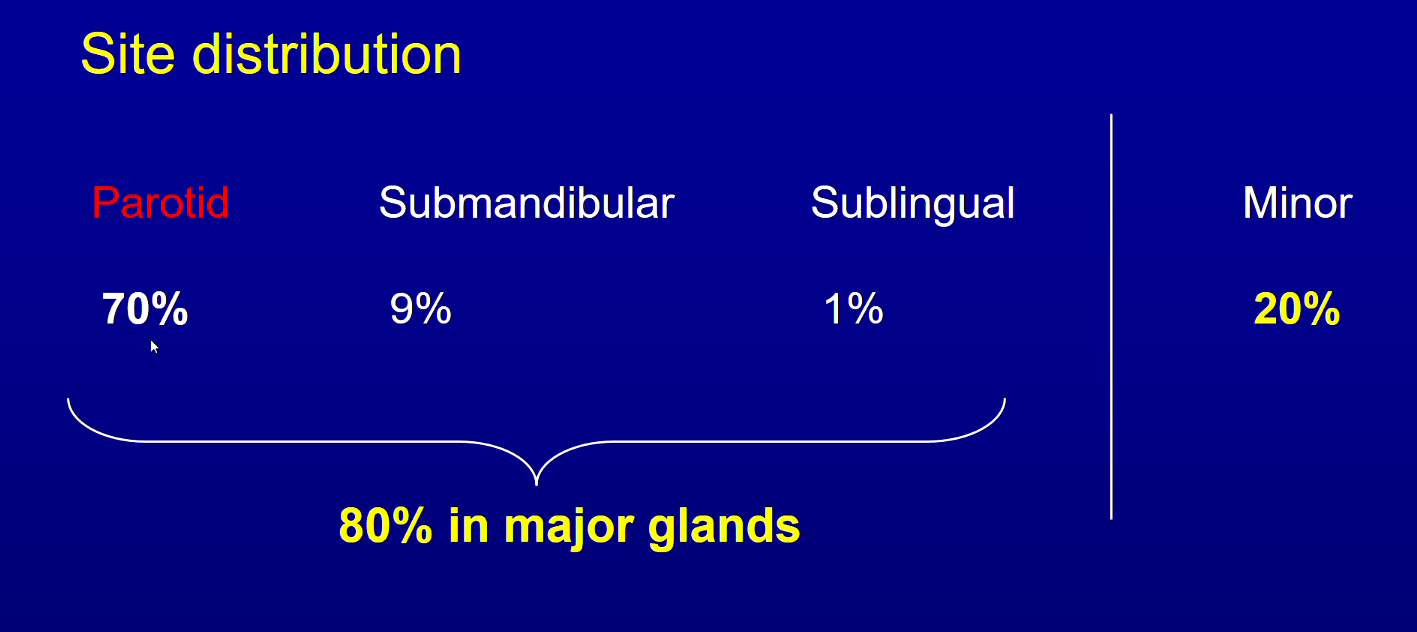
Whats most common site for salivary gland tumours?
parotid - 70% ish
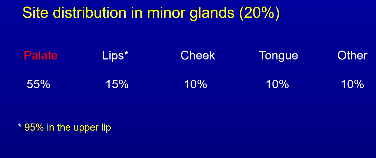
Whats most common site for minor salivary gland tumours
palate 55%
50% of tumours in minor glands are malignant
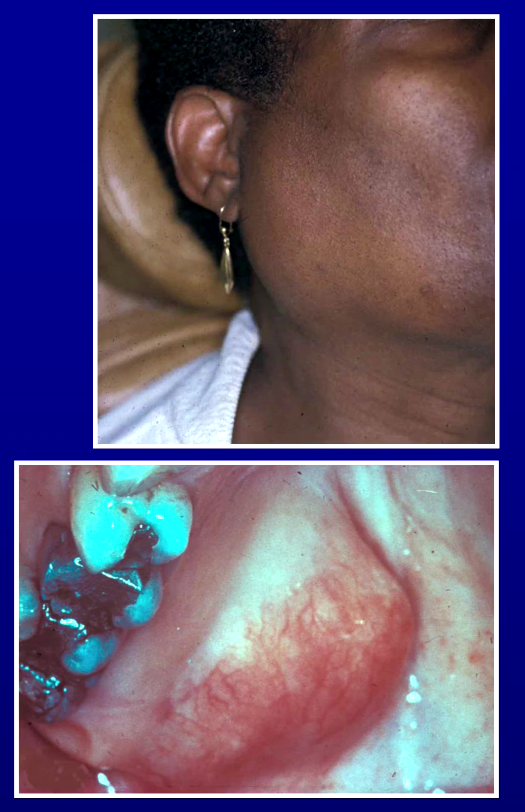
What is pleomorphic adenoma, where are the most common sites and who does it usually affect?
Benign tumour of salivary gland, may recur
Parotid most common followed by palate
M=F, 30-60
What is the Histopathology of Pleomorphic Adenoma?
Mixed Pleomorphic Pattern with Islands and Strands of Epithelial Cells
Ductal Structures are common
Tumour tends to be multi-lobular but encapsulated
Stroma can be Myxoid, Mucoid or Chondroid
Occasionally the tumours are solid
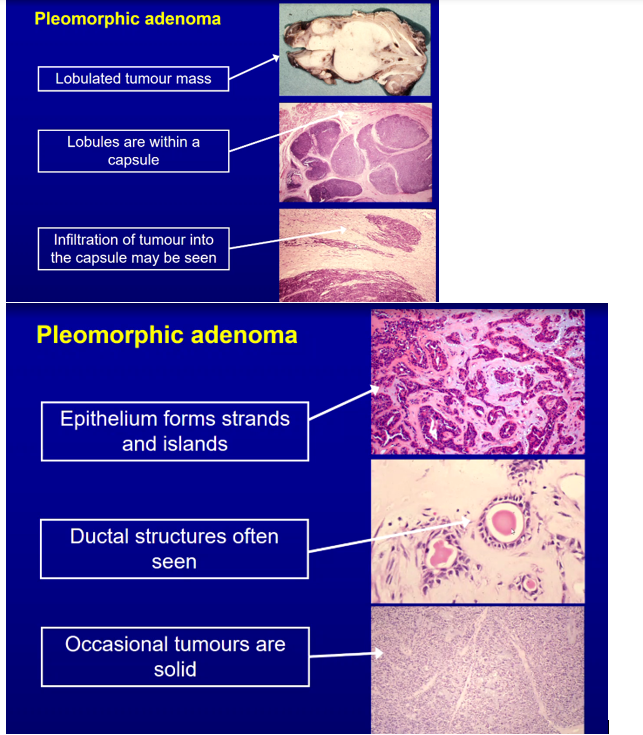
What does mucoid/myxoid and chrondroid stroma look like in pleomorphic adenoma?
Mucoid/myxoid → few cells, more blueish, more loose
Chondroid → more cartilage cells
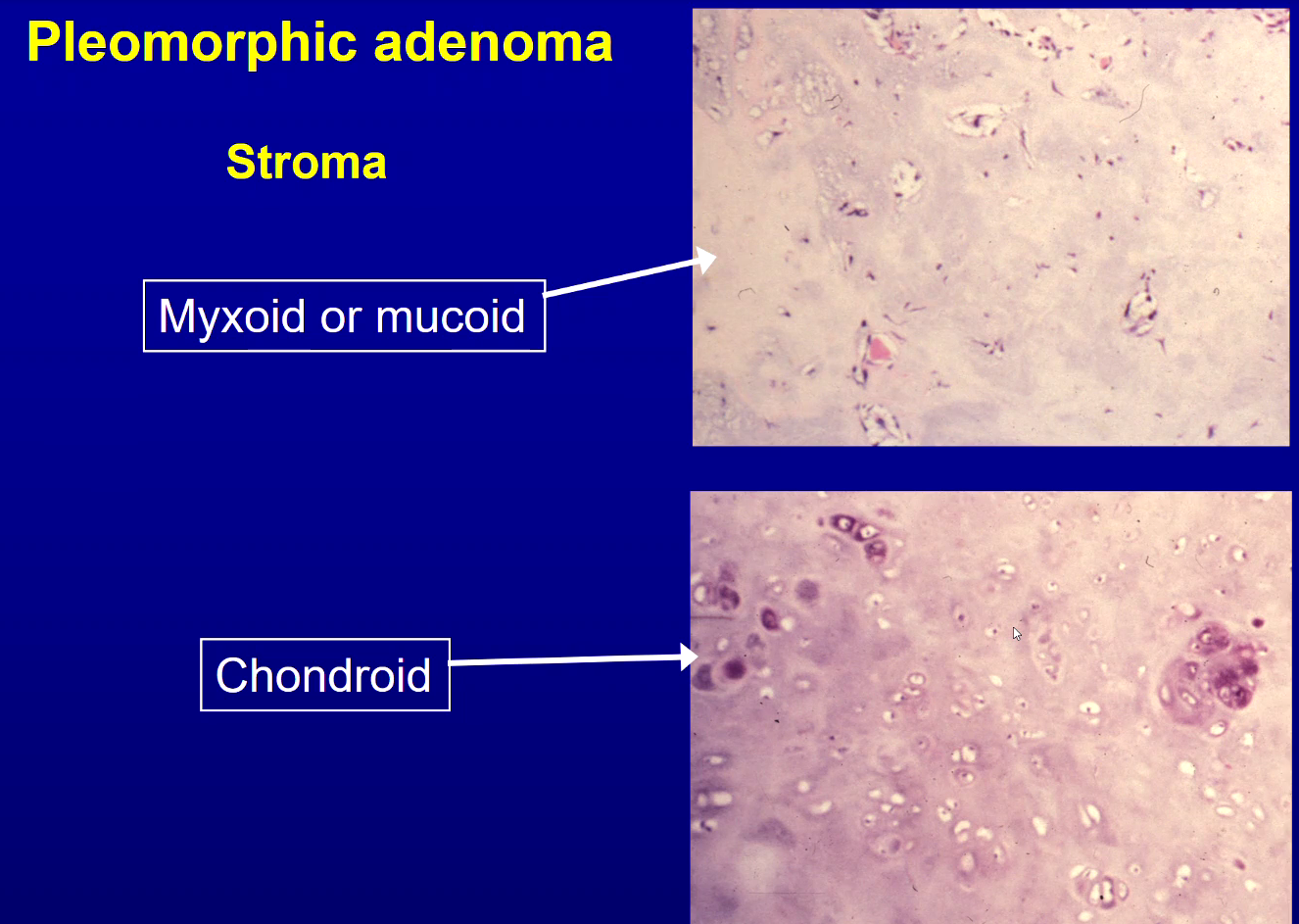
What is Warthin tumour, where is it commonly located and who does it affect?
Benign salivary gland tumour
Always in parotid gland => sometimes bilateral or multifocal (multiple sites but single origin)
M>F
What is the histology of a Warthin tumour?
stroma has dark blue dots - lymphocytes
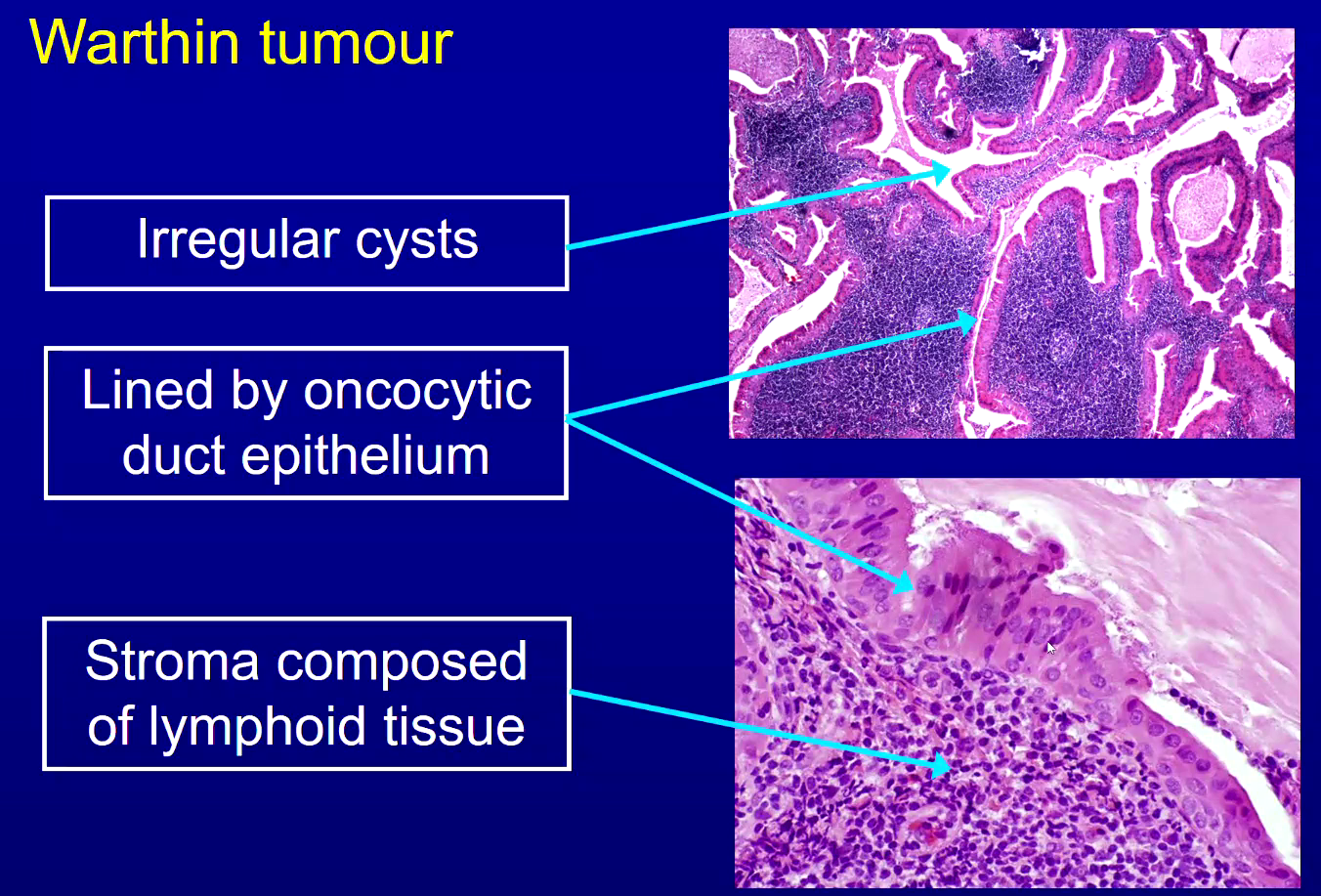
Other salivary adenomas histology
What is mucoepidermoid carcinoma, most common site and who does it affect?
Most common malignant salivary gland tumour → 10-15% metastasise
Parotid most common - also palate, cheek. retromolar
Occ seen in kids - most common malignancy in child in oral cavity
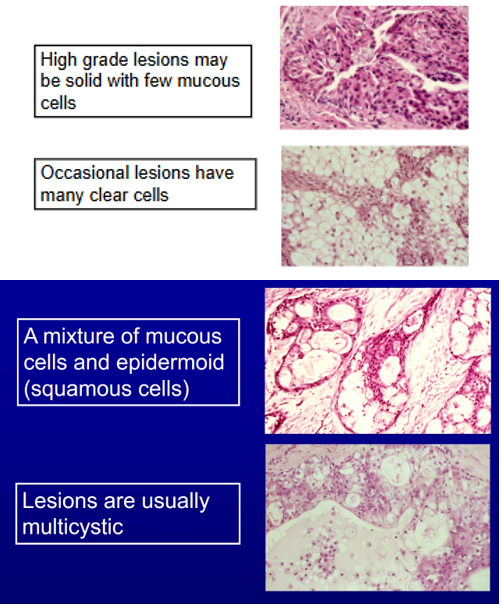
What is the histological appearance of Mucoepidermoid Carcinoma?
A mixture of Mucous Cells and Epidermoid Cells (in the name)
- Lesions are usually multicystic
High Grade Lesions may be solid with few mucous cells
Occasional Lesions have many clear cells
What is Adenoid Cystic Carcinoma, where is it most common ?
malignant tumour of the salivary gland
Parotid most common, also palate, cheek and sinuses
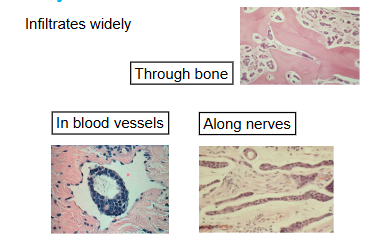
How does adenoid cystic carcinoma metastasise?
Via blood stream and nerve invasion
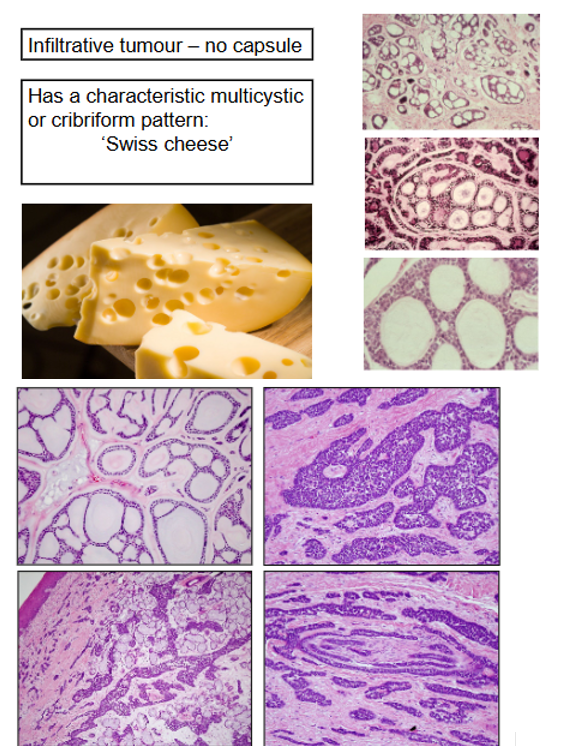
What is the Histological Pattern of Adenoid Cystic Carcinoma?
Infiltrative Tumour with No Capsule
Characteristic Multicystic Cribriform Pattern (swiss cheese)
A common feature of ACC is Perineural Invasion - shown on bottom right quadrant of bottom image
Not just cheese like structure but also other presentations shown on bottom image
What is Polymorphous Adenocarcinoma and where does it commonly affect?
Malignant Salivary Gland Neoplasm
Palate most common then lips and cheek → only seen intraorally
Seen in >50s
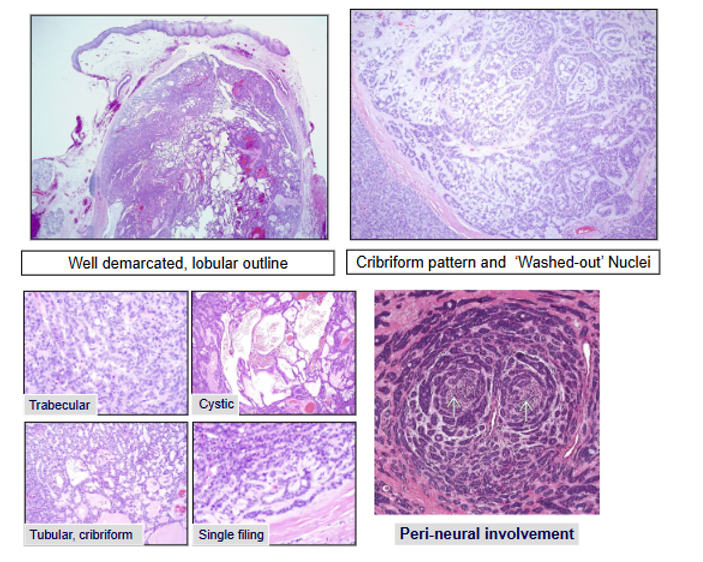
What is the Histological Pattern of Polymorphous Adenocarcinoma?
Lobules
Ductal Structures
Cribriform Areas
Papillary Cystic Pattern
Single Cell Filling
Often see perineural invasion
Polymorphous Adenocarcinoma has a Infiltrative Growth. How does it Metastasize?
Perineural Infiltration Typically
Which 2 salivary gland tumours where you often see perineural invasion?
Adenoidcystic carcinoma
Polymorphous adenocarcinoma
What is Polymorphous Adenocarcinoma commonly misdiagnosed as on incisional biopsies?
1) Pleomorphic Adenoma (Benign)
2) Adenoid Cystic Carcinoma (Malignant)
What is acinic cell carcinoma and where is it most commonly found?
malignant salivary gland tumour
mainly in parotid but also minor glands
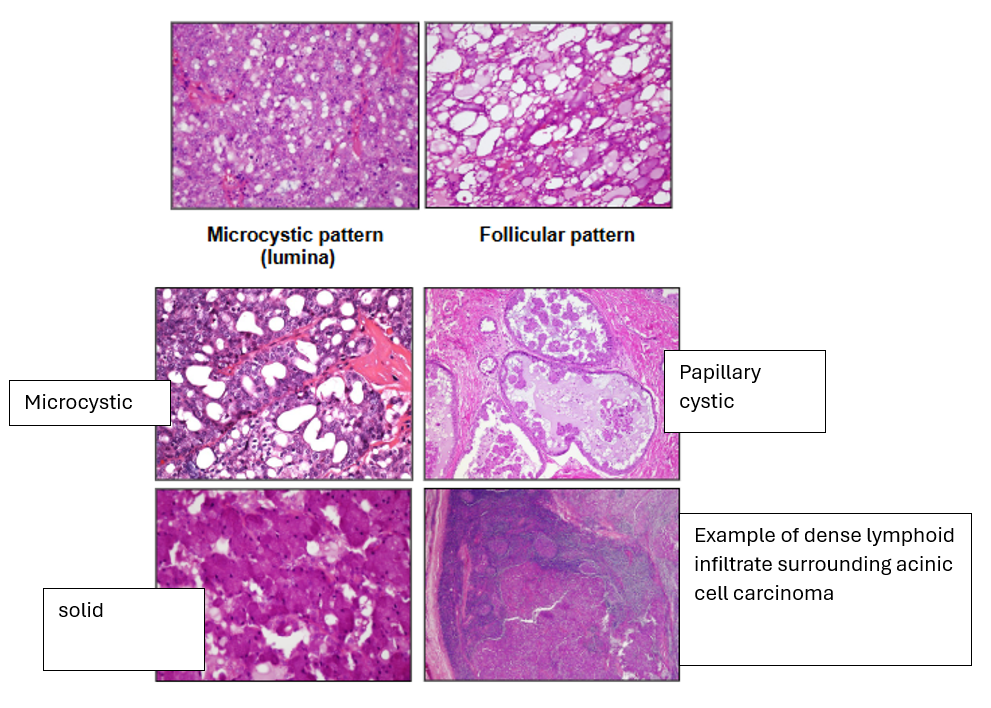
What is the Histological Appearance of Acinic Cell Carcinoma?
1) Solid
2) Microcystic
3) Papillary Cystic
4) Follicular - larger cystic areas than microcystic
You can get lymphoid tissue surrounding it
What is Carcinoma Ex Pleomorphic Adenoma, who does it commonly affect?
When a pleomorphic adenoma turns malignant (in 10% of cases)
60+
Usually longstanding or recurrent lesions
History of a long term slow growing lesion with recent
increase in size
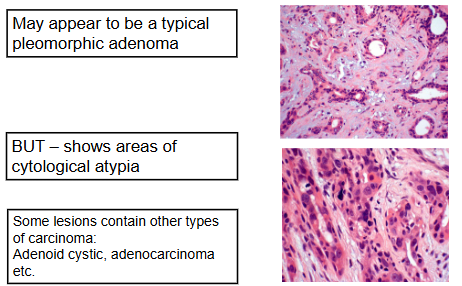
What is the Histological Appearance of Carcinoma Ex Pleomorphic Adenoma?
hyperchromatic cells
dark staining
mitoses
What are the tumour like salivary gland lesions?
Oncocytosis
Necrotising Sialometaplasia
Salivary Gland Cysts
Chronic Sialoadenitis of Submandibular Gland
Lymphoepithelial lesions
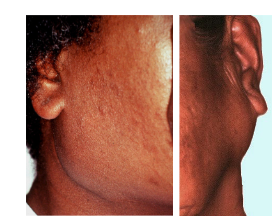
What are Lymphoepithelial lesions?
Tumour Like Lesions of the Parotid Salivary Gland
Diffuse Swelling around the angle of the mandible but linked with Sjogren's Syndrome
What is Sjogren’s syndrome?
Autoimmune disorder → lymphocyte mediated destruction of exocrine glands → dry eyes and mouth
What is primary and secondary Sjogren’s?
Primary - dry eyes and mouth
Secondary - dry eyes and/or dry mouth + associated connective tissue disease (rheumatoid arthritis or Systemic Lupus Erthymatosus)
What are the symptoms of sjogrens?
Oral symptoms - dry mouth (lobulated tongue), infections (candidosis) and caries
Dry eyes
Parotid swelling in 20%
Lymphocytic Infiltrate in Salivary Glands can cause Sjogren's Syndrome. What is the effect of this in Minor and Major Salivary Glands?
Minor Glands
- Focal Sialoadenitis
Major Glands
- Lymphoepithelial Lesions
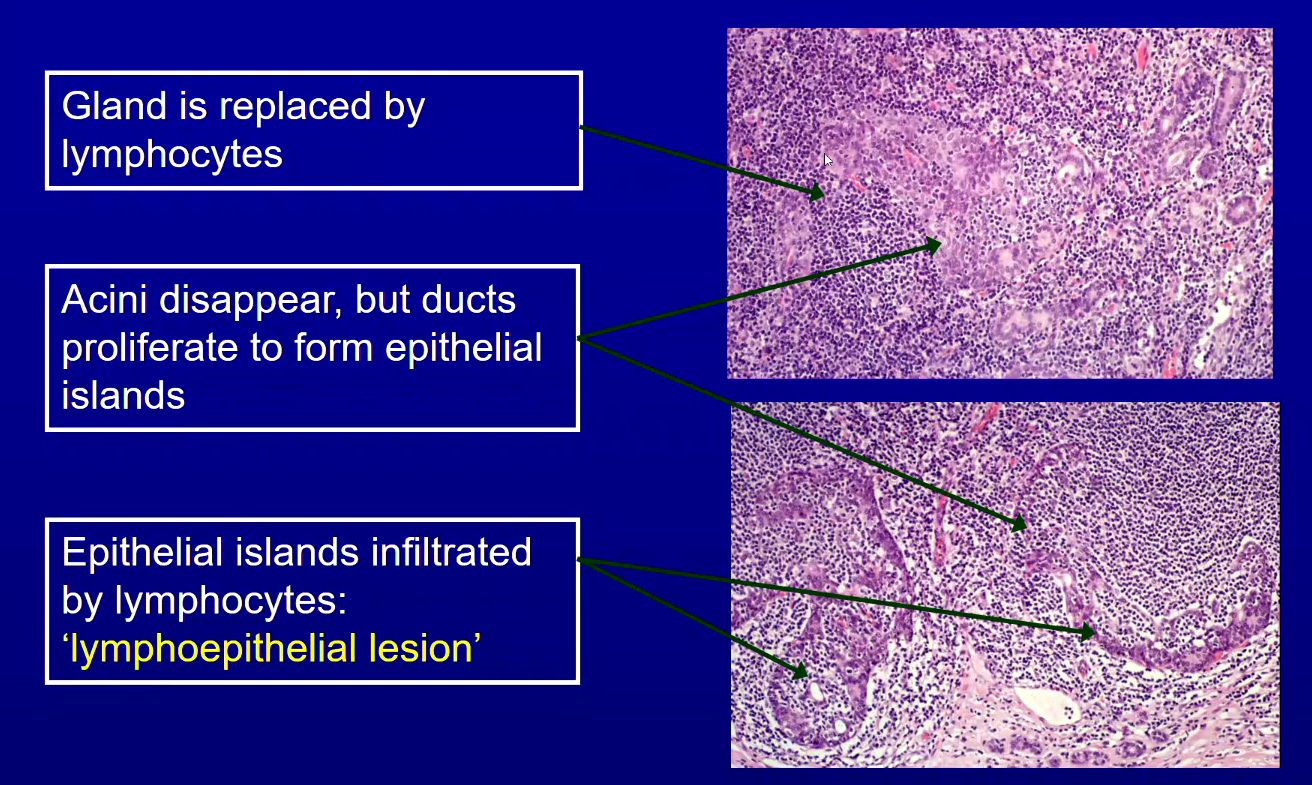
What is the Histological Appearance of Lymphoepithelial Lesions?
Gland is replaced by Lymphocytes
Acini Disappear but Ducts proliferate to form Epithelial Islands forming Lympho-epithelial lesions
What can lymphoepithelial lesion progress into?
3-5% can progress into lymphoma
due to chronic overactivity of lymphocytes