,molecular forensic science
1/100
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
101 Terms
Which one of the following statements about balanced equations is false? In a balanced reaction
molecules must be balanced on both sides of the reaction arrow.
When 50.0 mL of a 0.30 M AgNO3 solution is added to 50.0 mL of a solution of MgCl2, an AgCl precipitate forms immediately. The precipitate is then filtered from the solution, dried, and weighed. If the recovered AgCl is found to have a mass of 1.1235 g, what as the concentration of magnesium ions in the original MgCl2 solution? Round your answer to four decimal places as .***
0.0784
A 30.00 mL sample of an oxalate solution (C2O42–) is found to react completely with 29.98 mL of a 0.1383 M solution of MnO4–. What is the oxalate ion concentration in the sample? Round your answer to four decimal places as .***
2MnO4– + 5C2O42– + 16H+ → 2Mn2+ + 8H2O + 10CO2
0.3455
The oxidation number of S in K2SO4 is
6
The oxidation number of Mn in KMnO4 is
7
The oxidation number of Cr in Cr2O72– is
6
The oxidation number of N in NaNO3 is
5
When solid iron(II) hydroxide is added to water, the resulting solution contains 1.4×10–3g of dissolved iron(II) hydroxide per liter of solution. What is the hydroxide ion concentration in this solution?
3.1×10–5 M
One method of determining the concentration of hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) in a solution is through titration with the iodide ion. The net ionic equation for this reaction is
H2O2 + 2I– +2H+ ® I2 + 2H2O
A 50.00 mL sample of a hydrogen peroxide solution is found to react completely with 37.12 mL of a 0.1500 M KI solution. What is the concentration of hydrogen peroxide in the sample?
5.568 × 10–2 M
The concentration of oxalate ion (C2O42–) in a sample can be determined by titration with a solution of permanganate ion (MnO4–) of known concentration. The net ionic equation for this reaction is
2MnO4– + 5C2O42– + 16H+ ® 2Mn2+ + 8H2O + 10CO2
A 30.00 mL sample of an oxalate solution is found to react completely with 21.93 mL of a 0.1725 M solution of MnO4–. What is the oxalate ion concentration in the sample?
0.3152 M
What volume (mL) of a 0.2450 M KOH(aq) solution is required to completely neutralize 55.25 mL of a 0.5440 M H3PO4(aq) solution?
368.0 mL
What volume (mL) of a 0.3428 M HCl(aq) solution is required to completely neutralize 23.55 mL of a 0.2350 M Ba(OH)2(aq) solution?
32.29 mL
34.62 mL of 0.1510 M NaOH was needed to neutralize 50.0 mL of an H2SO4 solution. What is the concentration of the original sulfuric acid solution?
0.0523 M
When 20.0 mL of a 0.250 M (NH4)2S solution is added to 150.0 mL of a solution of Cu(NO3)2, a CuS precipitate forms. The precipitate is then filtered from the solution, dried, and weighed. If the recovered CuS is found to have a mass of 0.3491 g, what was the concentration of copper ions in the original Cu(NO3)2 solution?
2.43 × 10–2 M
When 50.0 mL of a 0.3000 M AgNO3 solution is added to 50.0 mL of a solution of MgCl2, an AgCl precipitate forms immediately. The precipitate is then filtered from the solution, dried, and weighed. If the recovered AgCl is found to have a mass of 0.1183 g, what as the concentration of magnesium ions in the original MgCl2 solution?
8.25 × 10–3 M
When 38.0 mL of 0.1250 M H2SO4 is added to 100. mL of a solution of PbI2, a precipitate of PbSO4 forms. The PbSO4 is then filtered from the solution, dried, and weighed. If the recovered PbSO4 is found to have a mass of 0.0471 g, what was the concentration of iodide ions in the original solution?
3.11 × 10–3 M
A 4.691 g sample of MgCl2 is dissolved in enough water to give 750. mL of solution. What is the concentration of this solution?
6.57 × 10–2 M
A 3.682 g sample of KClO3 is dissolved in enough water to give 375. mL of solution. What is the chlorate ion concentration in this solution?
8.01 × 10–2 M
A 20.00 mL sample of 0.1015 M nitric acid is introduced into a flask, and water is added until the volume of the solution reaches 250. mL. What is the concentration of nitric acid in the final solution?
8.12 × 10–3 M
A 50.0 mL sample of 0.436 M NH4NO3 is diluted with water to a total volume of 250.0 mL. What is the ammonium nitrate concentration in the resulting solution?
8.72 × 10–2 M
What mass of K2CO3 is needed to prepare 200 mL of a solution having a potassium ion concentration of 0.150 M?
2.07 g
What is the concentration of Na+ in a 0.5 M Na3PO4 solution?
1.5 M
What mass of C6H12O6 (glucose) is needed to prepare 450 mL of a 0.650 M solution of glucose in water?
52.7 g
1.00 mole of O2 contains the same number of oxygen atoms as
all of the above
How many oxygen atoms are in 3.00 g of sodium dichromate, Na2Cr2O7?
4.83 × 1022 oxygen atoms
What is the mass of 8.50 × 1022 molecules of NH3?
2.40 g
How many iron(II) ions, Fe2+ are there in 5.00 g of FeSO4?
1.98 × 1022 iron (II) ions
How many moles are in 1.50 g of ethanol, CH3CH2OH?
0.0326 mol
Balance the chemical equation given below, and determine the number of grams of MgO needed to produce 15.0 g of Fe2O3.
___ MgO(s) + ___ Fe(s) → ___ Fe2O3(s) + ___ Mg(s)
11.4 g
How many grams of calcium chloride are needed to produce 10.0 g of potassium chloride?
CaCl2(aq) + K2CO3(aq) → 2 KCl(aq) + CaCO3(aq)
7.44 g
Balance the chemical equation given below, and determine the number of moles of iodine that reacts with 10.0 g of aluminum.
___ Al(s) + ___ I2(s) → ___ Al2I6(s)
0.556 mol
How many moles of BCl3 are needed to produce 25.0 g of HCl(aq) in the following reaction?
BCl3(g) + 3 H2O(l) → 3 HCl(aq) + B(OH)3(aq)
0.229 mol
How many moles of CuO can be produced from 0.450 mol of Cu2O in the following reaction?
2 Cu2O(s) + O2(g) → 4 CuO(s)
0.900 mol
When iron(III) oxide reacts with hydrochloric acid, iron(III) chloride and water are formed. How many grams of iron(III) chloride are formed from 10.0 g of iron(III) oxide and 10.0 g of hydrochloric acid?
14.8 g
When silver nitrate reacts with barium chloride, silver chloride and barium nitrate are formed. How many grams of silver chloride are formed when 10.0 g of silver nitrate reacts with 15.0 g of barium chloride?
8.44 g
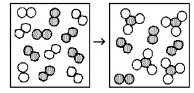
The following diagrams represent the reaction of A2 (shaded spheres) with B2 (unshaded spheres). How many moles of product can be made from 1.0 mol of A2 and 1.0 mol of B2?
0.67 mol product
Predict the products of a reaction between Ba(NO3)2(aq) and K2SO4(aq).
BaSO4(s) and KNO3(aq)
Which substance is the limiting reactant when 2.0 g of sulfur reacts with 3.0 g of oxygen and 4.0 g of sodium hydroxide according to the following chemical equation:
2 S(s) + 3 O2(g) + 4 NaOH(aq) → 2 Na2SO4(aq) + 2 H2O(l)
NaOH (aq)
The reaction HNO3(aq) + KOH(aq) → KNO3(aq) + H2O(l) is best classified as a(n)
acid-base neutralization reaction
5.0 g of iron is reacted with 5.0 g of water according to the chemical equation shown below. Which one of the following statements is false?
3 Fe(s) + 4 H2O(l) → Fe3O4(s) + 4 H2(g)
Water is the limiting reactant
How many grams of the excess reagent are left over when 6.00 g of CS2 gas react with 10.0 g of Cl2 gas in the following reaction:
CS2(g) + 3 Cl2(g) → CCl4(l) + S2Cl2(l)
2.42 g
The density of ethanol, C2H5OH, is 0.789 g/mL. How many milliliters of ethanol are needed to produce 10.0 g of CO2 according to the following chemical equation?
C2H5OH(l) + 3 O2(g) → 2 CO2(g) + 3 H2O(l)
6.63 mL
Which of the following has the smallest mass?
0.050 kg of Br2
What mass of sulfur hexafluoride, SF6, has the same number of fluorine atoms as 25.0 g of oxygen difluoride, OF2?
22.5 g
What is the identity of substance X if 0.380 mol of X weighs 17.5 g?
NO2
What is the mass of 0.500 mol of dichlorodifluoromethane, CF2Cl2?
60.5 g
1.00 mole of O2 contains the same number of molecules as
1.00 mole of CH3CO2H
What is the molar mass of aspartic acid, C4O4H7N
133 g/mol
What is the sum of the coefficients when the following equation is balanced using the lowest, whole numbered coefficients?
___ B2O3(s) + ___ HF(l) → ___ BF3(g) + ___ H2O(l)
none of these
What is the sum of the coefficients when the following equation is balanced using the lowest, whole numbered coefficients? ___ PH3(g) + ___ O2(g) → ___ P4O10(s) + ___ H2O(g)
19
What is the stoichiometric coefficient for oxygen when the following equation is balanced using the lowest, whole-number coefficients ___ C3H8O(l) + ___ O2(g) → ___ CO2(g) + ___ H2O(l)
9
Which one of the following statements about balanced equations is true? A reaction is balanced by
multiplying by suitable coefficients.
Given the chemical equation: N2 + 3 H2 → 2 NH3. On a macroscopic level, what do the coefficients mean?
1 mole of nitrogen reacts with 3 moles of hydrogen to give 2 moles of ammonia.
Given the chemical equation: N2 + 3 H2 → 2 NH3. On a microscopic level, what do the coefficients mean?
1 molecule of nitrogen reacts with 3 molecules of hydrogen to give 2 molecules of ammonia.
Which one of the following statements about balanced equations is true? A reaction is balanced by
multiplying by suitable coefficients
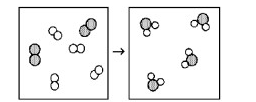
What is the balanced chemical equation for the reaction of element A (unshaded spheres) with element B (shaded spheres) as represented below?
2A2 + B2 → 2A2B
Which one of the following compounds is insoluble in water?
PbSO4
The mixing of which pair of reactants will result in a precipitation reaction?
K2SO4(aq) + Ba(NO3)2(aq)
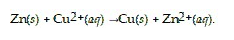
Which species functions as the oxidizing agent in the following reduction-oxidation reaction:
Cu2+(aq)
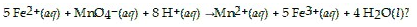
Which species functions as the oxidizing agent in the following reduction-oxidation reaction
MnO4-(aq)
Which species functions as the reducing agent in the following reduction-oxidation reaction:
2 P(s) + 3 Br2(l) → 2 PBr3(l)?
P(s)
Which species functions as the reducing agent in the following reduction-oxidation reaction: ZnO(s) + C(s) → Zn(s) + CO(g)?
C(s)
The mixing of which pair of reactants will result in a precipitation reaction?
Cu(NO3)2(aq) + Na2CO3(aq)
What reagent could be used to separate Br- from NO3- when added to an aqueous solution containing both?
AgNO3(aq)
What reagent could not be used to separate Cl- from OH- when added to an aqueous solution containing both?
AgNO3(aq)
Which pair of reactants will produce a precipitate when mixed together?
HCl(aq) and Pb(NO3)2(aq)
When K2SO4(aq) and Pb(NO3)2(aq) are mixed, a white colored precipitate forms which is
PbSO4
When Na2CrO4(aq) and AgNO3(aq) are mixed, a red colored precipitate forms which is
Ag2CrO4
What reagent would distinguish between Ba2+ and Pb2+?
NaCl
What reagent would distinguish between Ag+ and Fe3+?
NaI
Which of the following compounds is not an Arrhenius acid?
CH3NH2
What ion is provided when Arrhenius bases dissolve in water?
OH-
When dissolved in water, LiOH behaves as
a base that forms Li+ and OH- ions.
Which of the following compounds is an Arrhenius base in water?
NH3
Which of the following compounds is an Arrhenius base?
KOH
Which one of the following compounds behaves as an acid when dissolved in water?
HBr
Which pair of compounds is insoluble in water?
PbSO4 and Pb3(PO4)2
Which one of the following compounds is soluble in water?
Pb(NO3)2
Which pair of compounds is soluble in water?
KI and Ba(NO3)2
The reaction 2 HNO3(aq) + Ba(OH)2(aq) → Ba(NO3)2(aq) + 2 H2O(l) is best classified as a(n)
acid-base neutralization reaction
The reaction Pb(NO3)2(aq) + K2SO4(aq) → PbSO4(s) + 2 KNO3(aq) is best classified as a(n)
precipitation reaction
The reaction Na3PO4(aq) + 3 AgNO3(aq) → Ag3PO4(s) + 3 NaNO3(aq) is best classified as a(n)
precipitation reaction
The reaction Cu(s) + 2 AgNO3(aq) → Cu(NO3)2(aq) + 2 Ag(s) is best classified as a(n)
oxidation-reduction reaction
The reaction C6H12O6(s) + 6 O2(g) → 6 CO2(g) + 6 H2O(l) is best classified as a(n)
oxidation-reduction reaction
The combustion reaction CH4(g) + 2 O2(g) → CO2(g) + 2 H2O(l) can be classified as a(n)
oxidation-reduction reaction.
HBr, HCl, HClO4, KBr, and NaCl are all classified as
strong electrolytes.
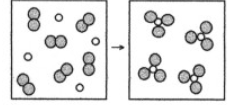
What is the balanced chemical equation for the reaction of element A (unshaded spheres) with element B (shaded spheres) as represented below?
2A + 3B2 → 2AB3
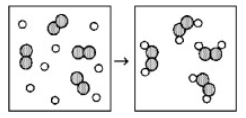
Reaction of A (unshaded spheres) with B2 (shaded spheres) is shown schematically in the following diagram. Which equation best describes the stoichiometry of the reaction?
2 A + B2 → A2B2
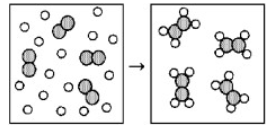
Reaction of A (unshaded spheres) with B2 (shaded spheres) is shown schematically in the following diagram. Which equation best describes the stoichiometry of the reaction?
4 A + B2 → A4B2
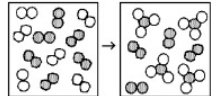
The following diagrams represent the reaction of A2 (shaded spheres) with B2 (unshaded spheres). Identify the limiting reactant and a balanced equation for the reaction.
B2 is the limiting reactant; A2 + 3 B2 → 2 AB3.
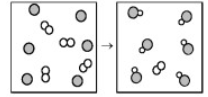
The following diagram represents the reaction of A2 (unshaded spheres) with B (shaded spheres). How many moles of product can be produced from the reaction of 1.0 mol of A2 and 1.0 mol of B?
1.0 mol of product
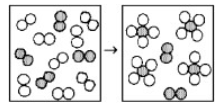
The following diagram represents the reaction of A2 (unshaded spheres) with B2 (shaded spheres). How many moles of product can be produced from the reaction of 1.0 mol of A2 and 1.0 mol of B2?
0.5 mol of product
What volume (mL) of a 0.3584 M HCl(aq) solution is required to completely neutralize 22.19 mL of a 0.2796 M Ba(OH)2(aq) solution? Round your answer to two decimal places as .
34.62
What is the molarity of nitrate ion in 0.10 M Mg(NO3)2 ?
0.20
A 13.51 mL of 4.8918 M nitric acid is diluted with water to a total volume of 120 mL. What is the nitric acid concentration in the resulting solution? Round your answer to four decimal places as .***
0.5508
How many milliliters of a 1.65 M KBr solution contains 90 g KBr? Round your answer to whole number.
458
How many grams of C6H12O6 (glucose) are needed to prepare 220 mL of a 0.60 M solution of glucose in water? Round your answer to one decimal place as **.*
23.8
In the following chemical reaction the oxidizing agent is
5S + 6KNO3 + 2CaCO3 —→ 3K2SO4 + 2CaSO4 + CO2 + 3N2
KNO3
How many total electrons are transferred in the following reaction?
4 P(s) + 5O2(g) ® 2P2O5(s)
20