Core Concepts- L13-MHC and HLA genes(MHC genetics)
1/10
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
11 Terms
discuss the MHC I structure vs MHC II
alpha chain- alpha1/2/3 domains
beta 2 microglibulin- non covalently associated
peptide binding groove formed by alpha 1/ 2 and sits on beta sheet floor and flanked by alpha helices
a3 domain interacts with CD8
1 alpha chain alpha 1 and alpha 2
1 beta chain beta 1 and beta 2
discuss MHC- what it stands for, what gene is it on etc
region of genome encoding MHC proteins and other AP machinery
major histocompatibility complex
200 genes for humans- on chromosome 6
chromosome 17 on mice
includes genes for MHC I/II, TAP, tapasin
why are mice not great to study for MHC studies- advantages vs disadvantages
as scientific mice are inbred- not genetically diverse and so have genetically identical clonsed
advantages- easy to study effects of knockouts or knocking of genes
disadvantages- lack of diversity, poor model for human diversity.
types of HLA genes- discuss how many etc
class I- HLA A/B/C- present endogenous peptides from proteins to CD8- make 2 of each(6)
class II- HLA DR, DQ, DP-present to CD4
Class III- genes for complement proteins, TNF, stress antigens like MICA
2 copies of each gene one from each parent
talk about the class II HLA genes
HLA DR, DQ, DP
presents exogenous peptides to CD4
DP- 1 alpha and 1 beta gene- combine to make heterodimer
DQ- 1 alpha and 1 beta gene- heterodimer
DR- 1 alpha and 1 beta gene normally but has extra beta gene- alpha can bind to either beta chain- 2 different DR can be made per chromosome and more diversity
everyone makes 6-8 class II chains at cell surface based on DP, DQ, DR. 6-8 class II and 6 class I- make 12-14 MHC molecules per cell
discuss conserved vs polymorphic genes in relation to HLA/MHC
1 conserved- little variation and encode critical proteins where a mutation would be harmful. ie genes for DNA replication
polymorphic genes- eye colour, HLA etc- very polymorphic and have many alleles at each locus like HLA-A/B/C. makes diverse peptide binding capabilities so better immune defense
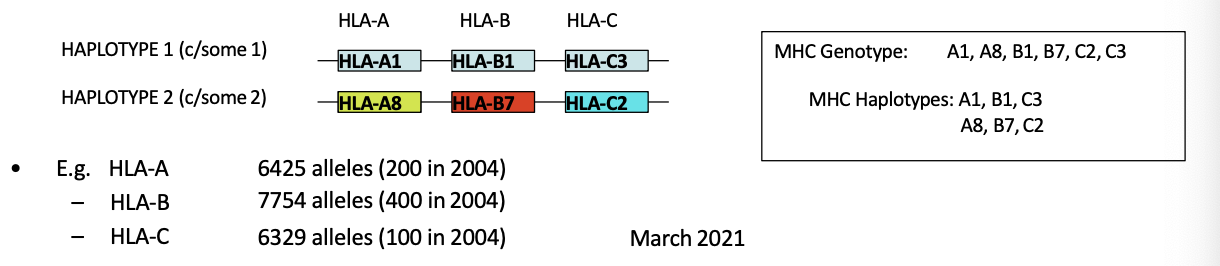
describe difference between haplotype vs genotype
genotype- full set of alleles an individual carries at a locus from both parents ie HLA A, alpha and beta.
haploytpe- set of alleles on a single chromosome that are inherited together as a unit. ie a gene A8-B7-C2- you inherit these as a UNIT
how can MHC cause graft rejection?
as MHC molecules are polymorphic, each person expresses different combinations. this is why even related donors cant donate as they don’t match perfectly
parents segratete chromosome 6 randomly- high variability so host T cell may recognise donor MHC as foreign
where does MHC diversity come from? why are they polymorphic
point mutations- single nucleotide change in the MHC gene and change one amino acid- can alter peptide binding specificity
gene conervsion- misalignment of chromosomes during meiosis. piece of DNA from one gene is copies into another gene and the original gene stays the same mostly but other one gets new DNA. new combo of DNA makes different MHC
recombination
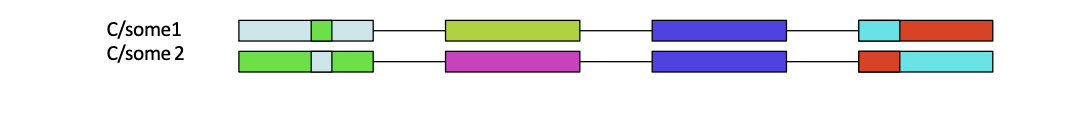
discuss class I HLA gene organisation and HLA II
HLA A/B/C - polymorphic- have 2 alleles of each- 6 proteins
HLA DP: 1 alpha, 1 beta
HLA DQ: 1 alpha 1 beta
HLA DR: 1 alpha 2 beta- alpha binds to either- make 6-8 proteins
all together- 12-14 MHC molecules
how do MHC alleles influence disease susceptibility or advantages?
if you have a mutation that’s advantegeous- will increase- ie gene that helps fight malaria. in west Africa HLA B-B53 allele
negative- autoimmune disease- triggered by antigens- HLA association as it presents this. HLA DR4 in rheumatoid arthritis