7. Intracellular Accumulations
1/48
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
49 Terms
What can cause injured cells to accumulate endogenous by products or exogenous substances?
metabolic abnormalities
genetic mutations
exposure to indigestible exogenous material
T/F: mutations can be harmless or promote cell degeneration and death
true
what are the types of accumulations?
lipids
glycogen
proteins
inclusions
storage disorders
lipidosis
accumulation of lipids within parenchyma cells
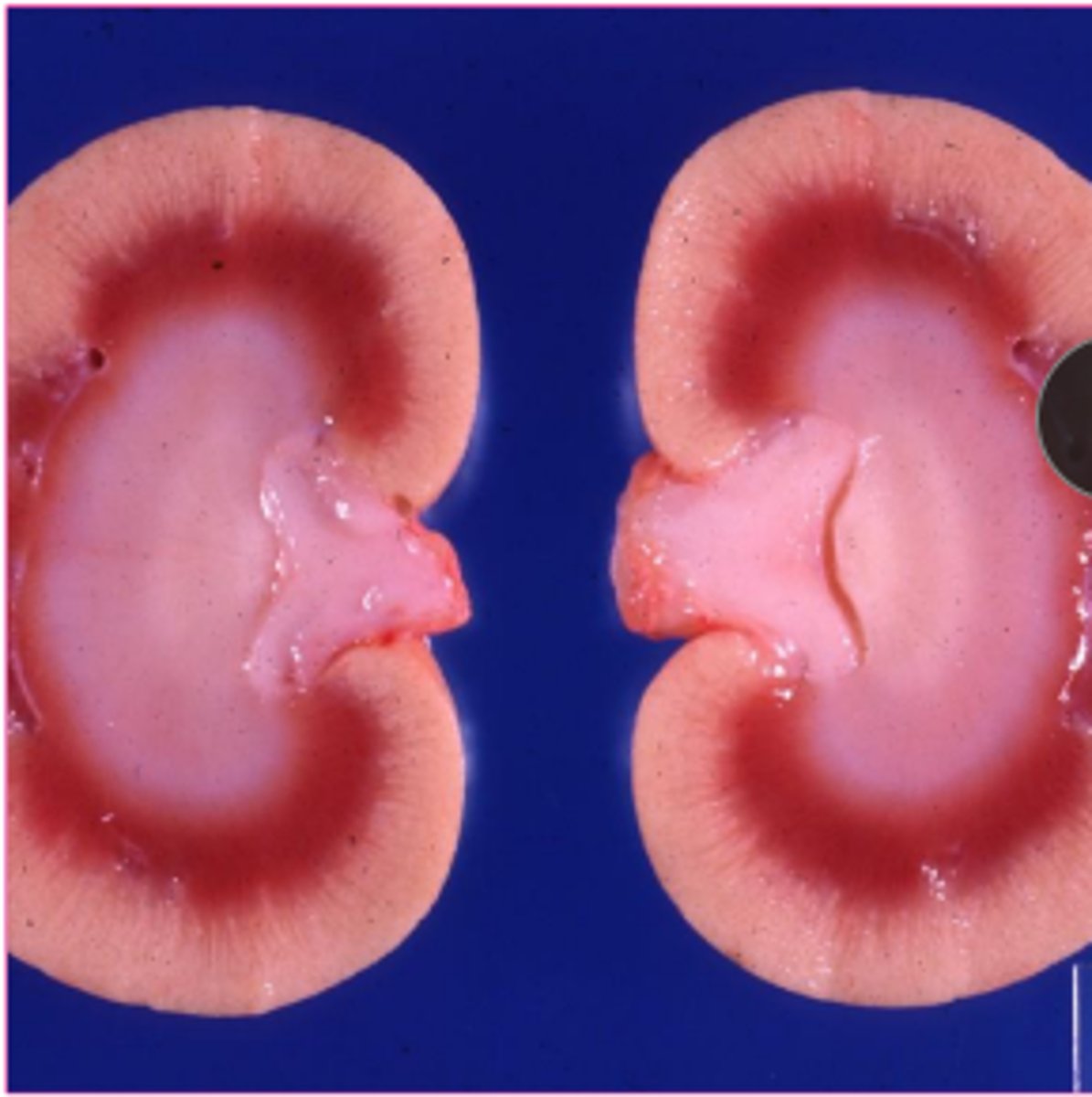
Although lipidosis can occur in many organs and tissues, what are the classic organs?
liver and kidney
_____ plays a major role in lipid metabolism
liver
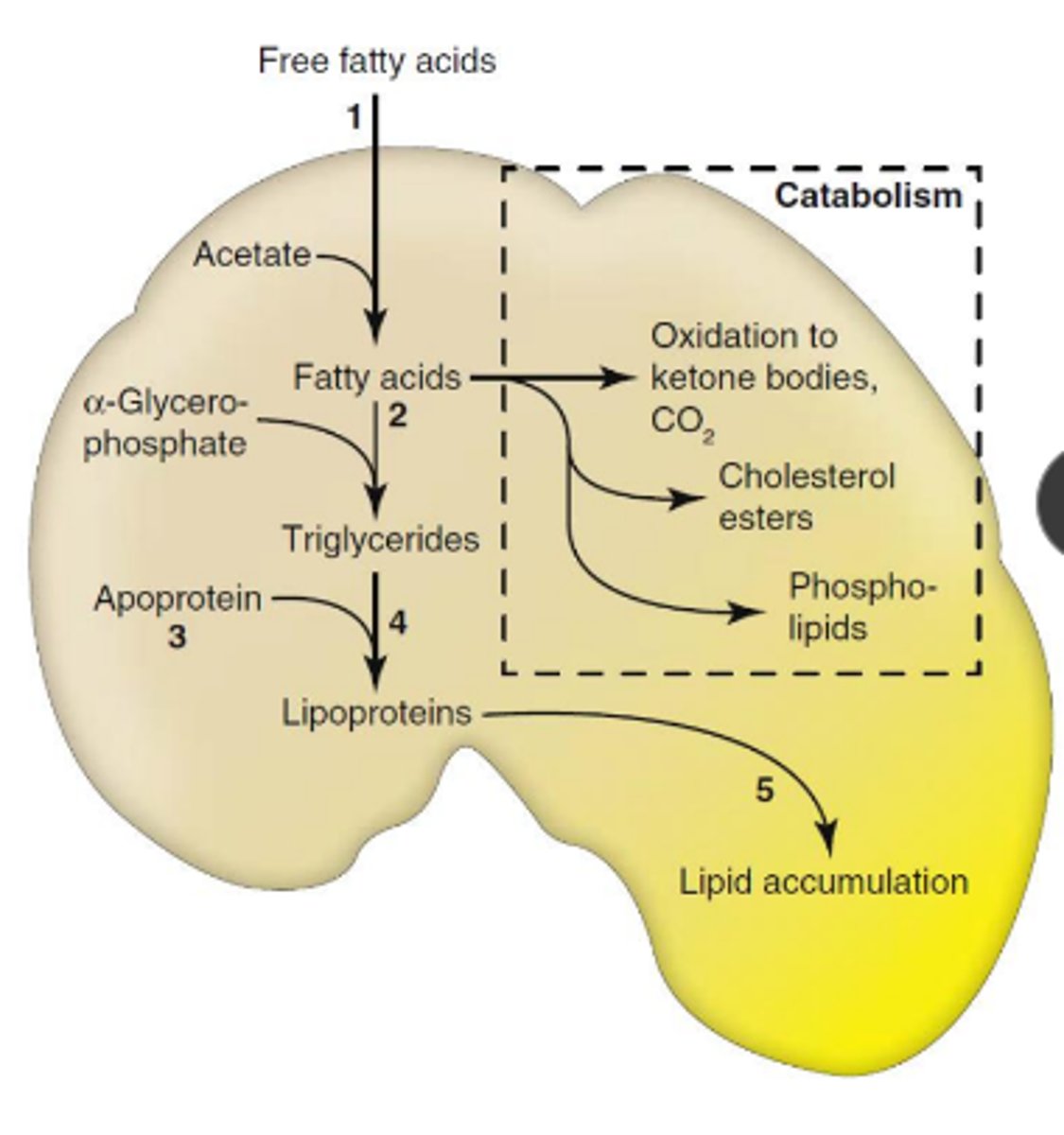
briefly explain lipid metabolsim
lipids from adipose tissue/ GI tract -> liver -> esterified to triglycerides or converted to cholesterol, phospholipids, or ketone bodies
triglycerides can be comeplexed as energy source for tissues
what are some causes of lipidosis?
increased mobilization of free FA
abnormal hepatocellular metabolism
impaired release of lipoproteins
what could increase the mobilization of free fatty acids?
high dietary fat
starvation
diabetes mellitus
lactation
what could cause abnormal hepatocellular metabolism?
hypoxia or cell injury
what is the mechanism of lipidosis?
excess delivery of free FA -> decreased oxidation/ use of FA -> impaired syn of apoprotein -> impaired combination of protein and triglycerides to form lipoproteins -> impaired release of lipoproteins
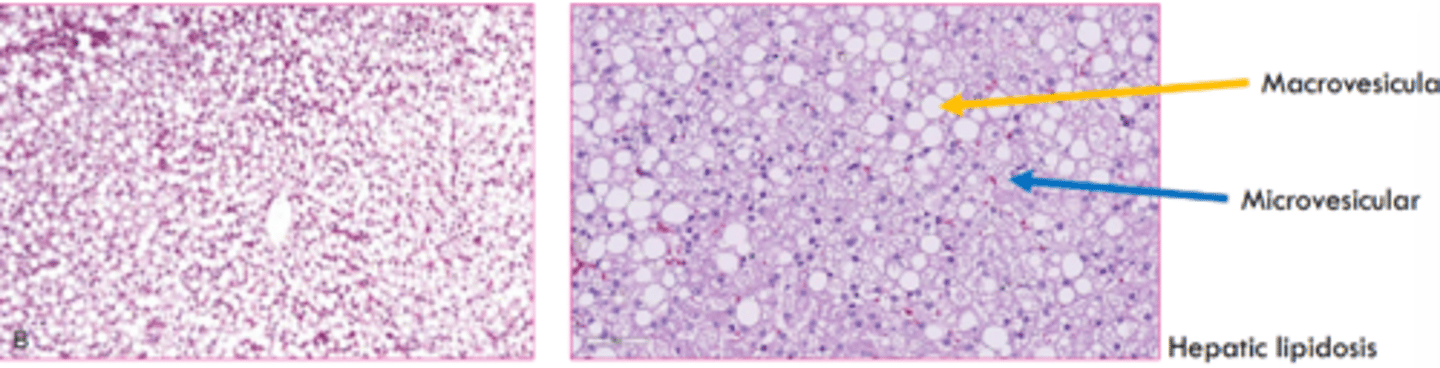
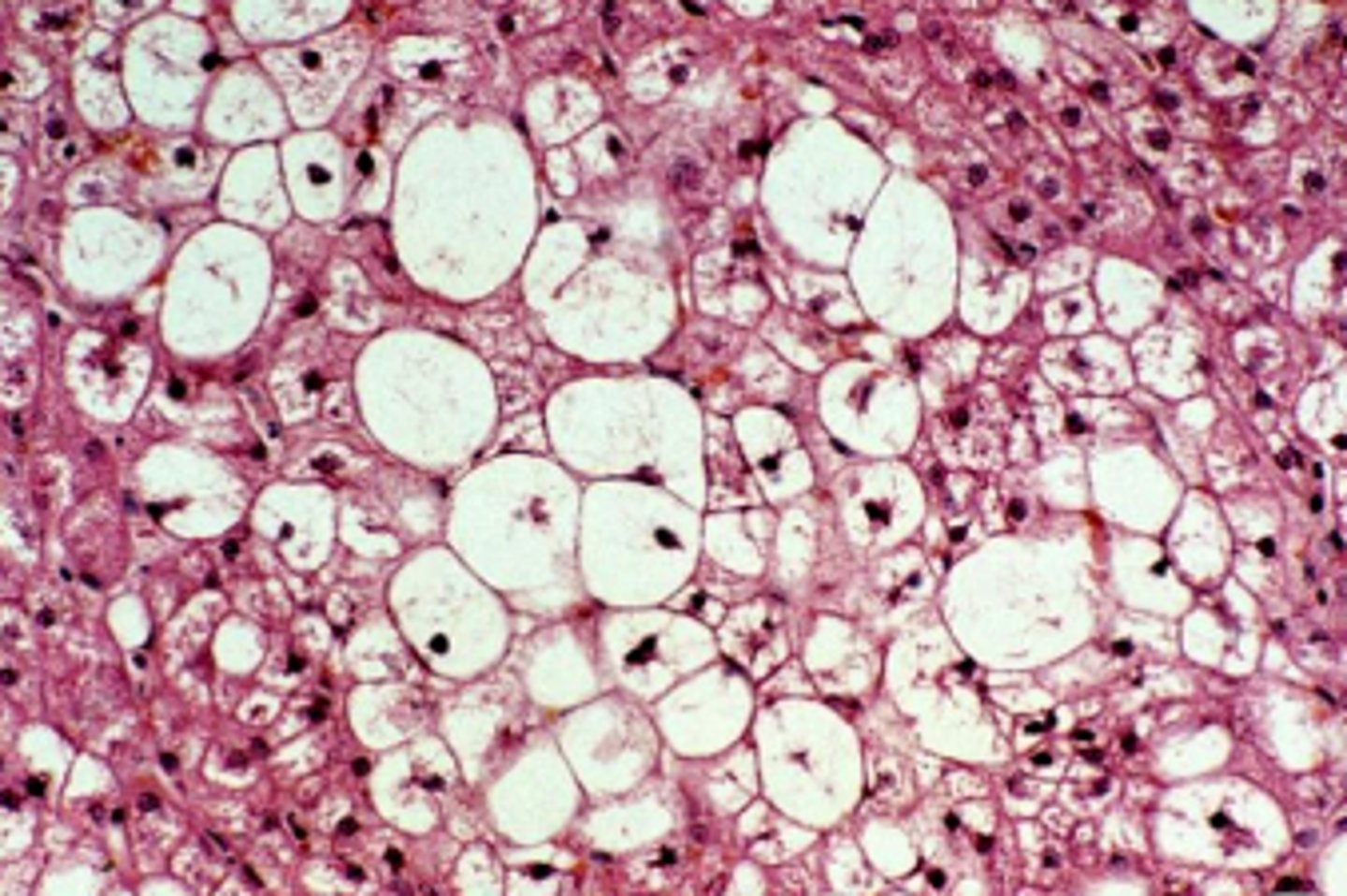
The microscopic appearance of lipolysis can be macrovesicular or microvesicular. Which is most common?
macrovesicular
macrovesicular microscopic changes
large, clear, sharply defined vacuoles that are larger than the nucleus, distend the cytoplasm, and displace the nucleus
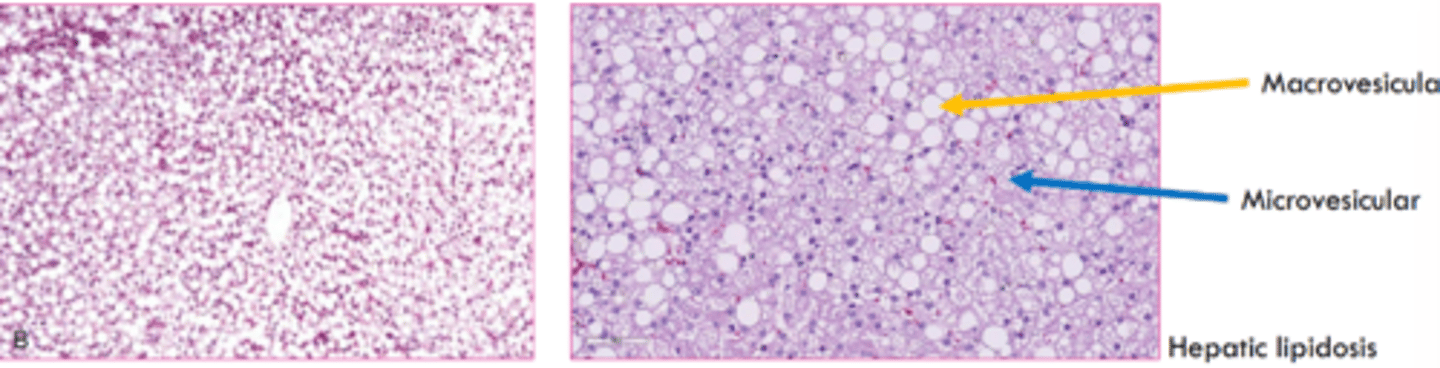
microvesicular changes
multiple small round clear vacuoles that do not displace the nucleus
what stain can we use to confirm lipid? what do they not work on?
Oil red O stain - do not work on paraffin embedding
Sudan Black B
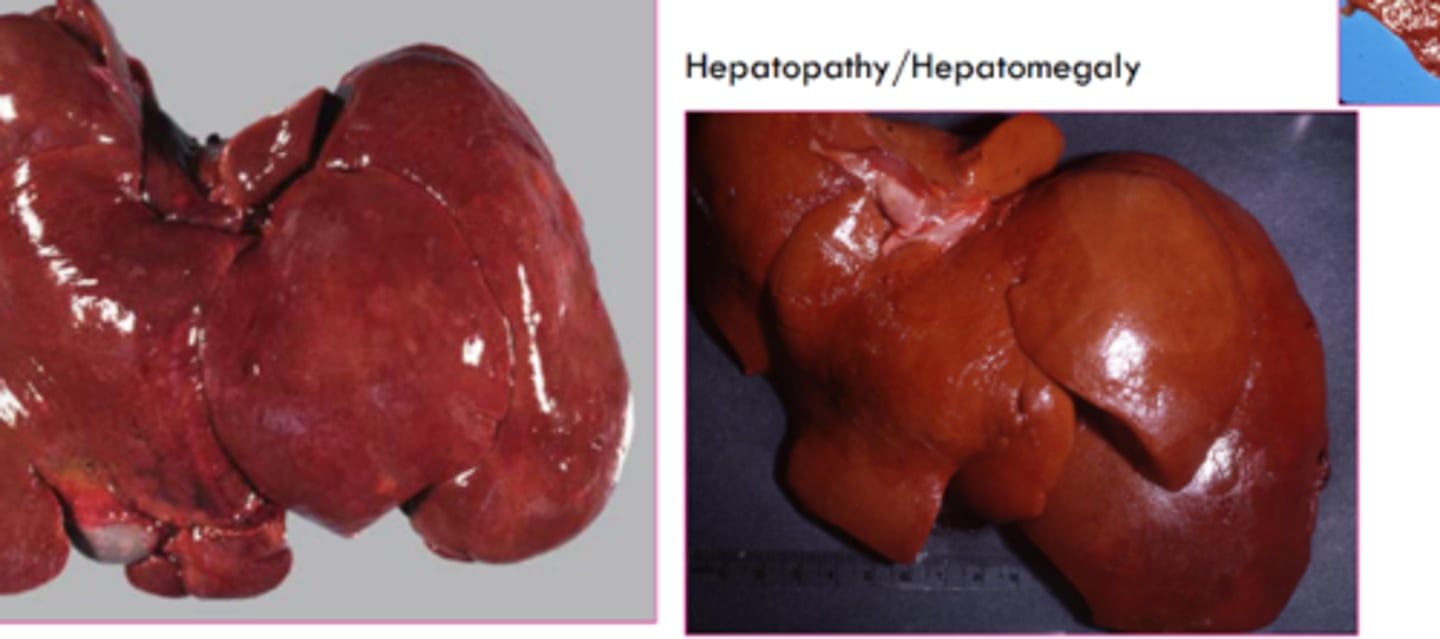
what is the gross appearance of lipidosis?
organ is swollen, yellow, greasy texture, possibly friable, may float
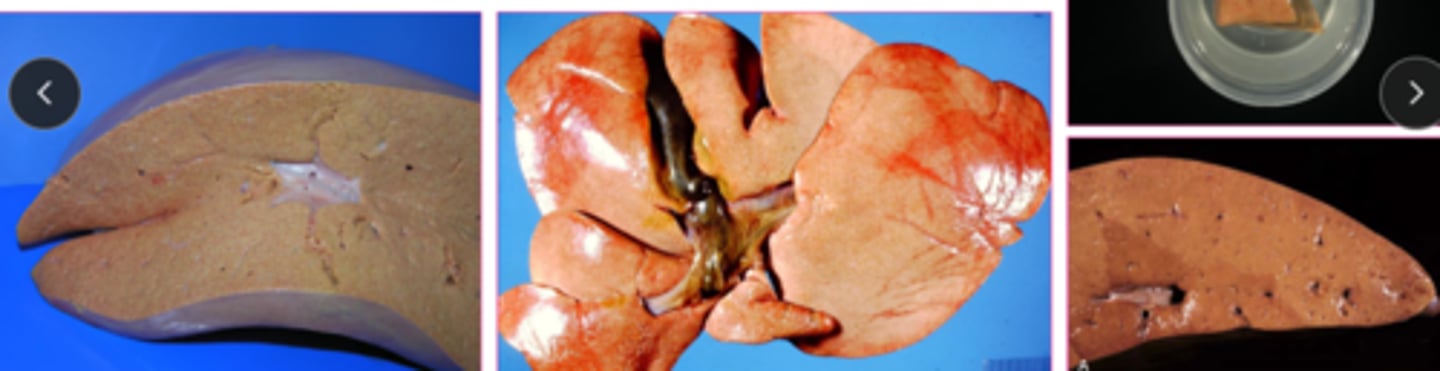
What are some causes of lipidosis in ruminants?
late pregnancy or heavy lactation
physiological- normal
may be due to insufficient dietary energy intake
What are some causes of lipidosis in equines?
equine hyperlipemia
donkeys, mini horses - genetic predisposition to negative energy balance = elevated VLDLs
What are some causes of lipidosis in felines?
feline hepatic lipidosis
obese, nutritionally stressed -> increased mobilization, altered formation/ release of VLDL, alterations in FA oxidation
where is glycogen normally stored?
hepatocytes and skeletal muscle
why would we see glycogen accumulations?
due to depletion in starvation or illness
metabolic abnormalities
storage diseases
endocrine disorder (diabetes mellitus, hyperadrenocorticism)
how does glycogen appear microscopically?
clear granules, vacuoles
less sharply defined than lipid and less likely to displace nucleus
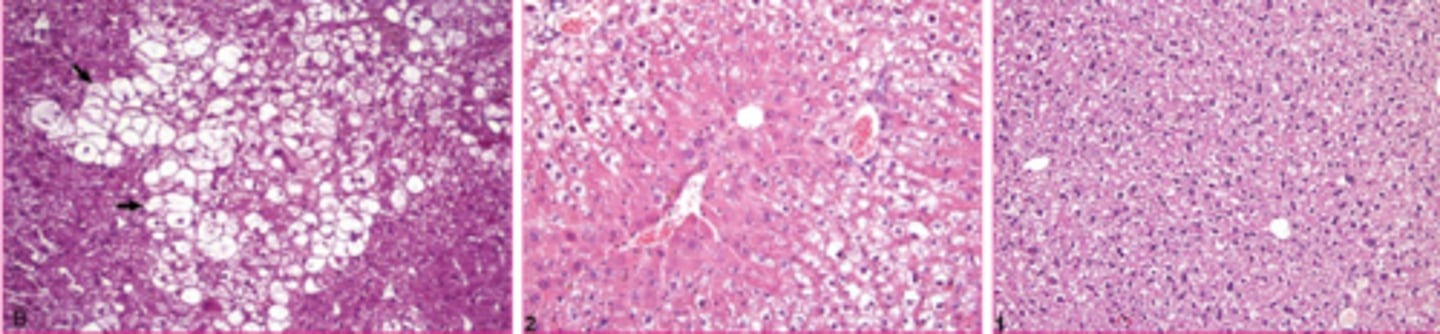
amount of glycogen observed microscopically is dependent on what?
original concentration
delay between death and fixation
type of fixation
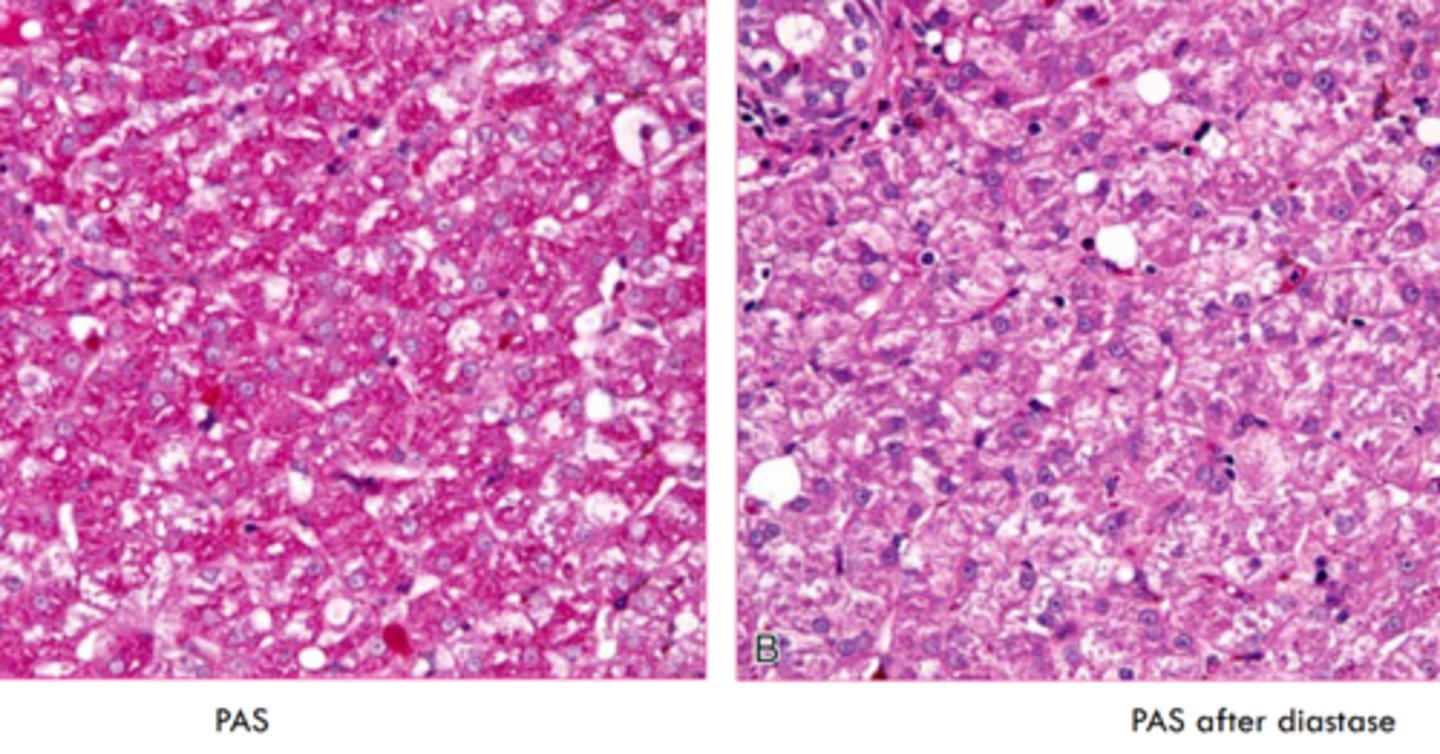
what stain do we use for glycogen?
periodic acid - schiff stain
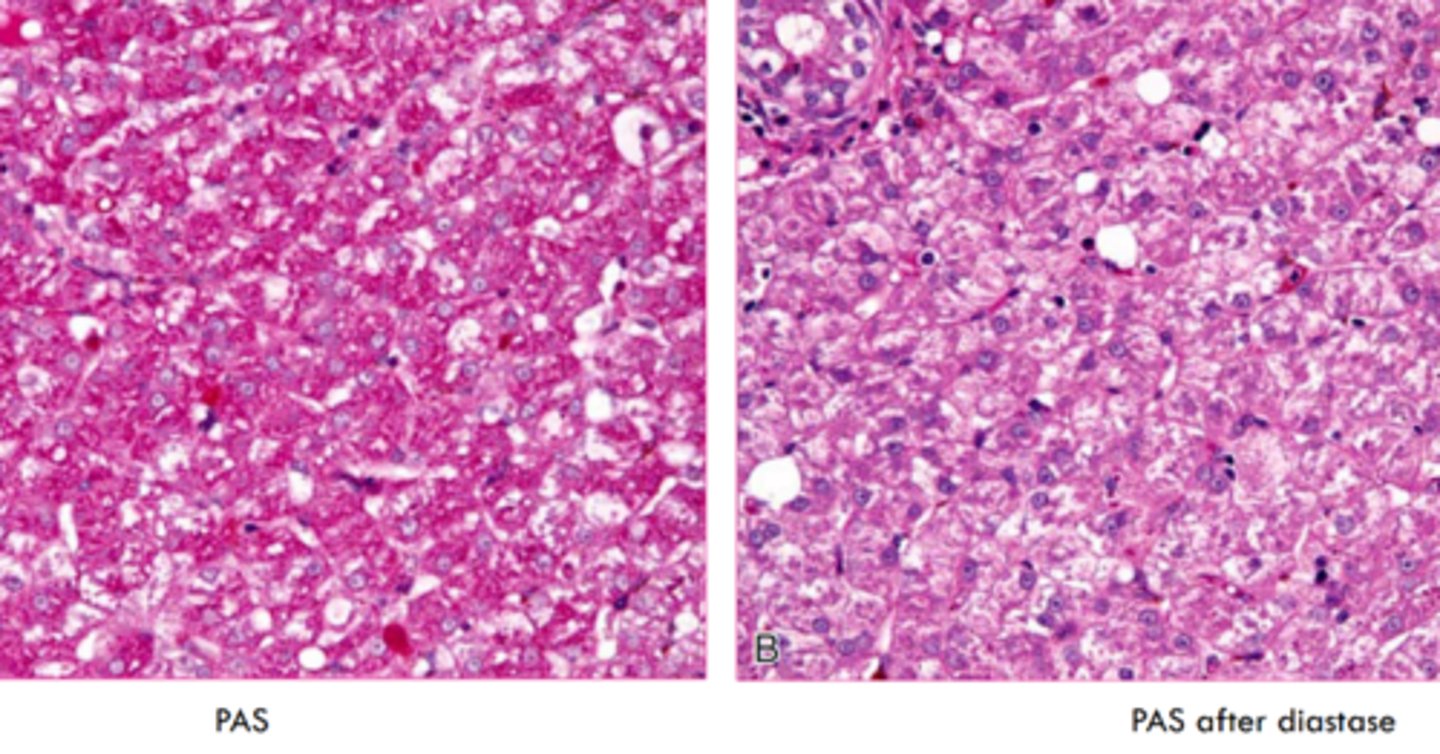
why would we use PAS in conjunction with diastase?
diastase digests glycogen- prove glycogen storage
gross appearance of glycogen accumulation
swollen, pale brown, mottled
glycogen or lipid?
glycogen
spiderwork webbing of cytoplas, and central nucleus
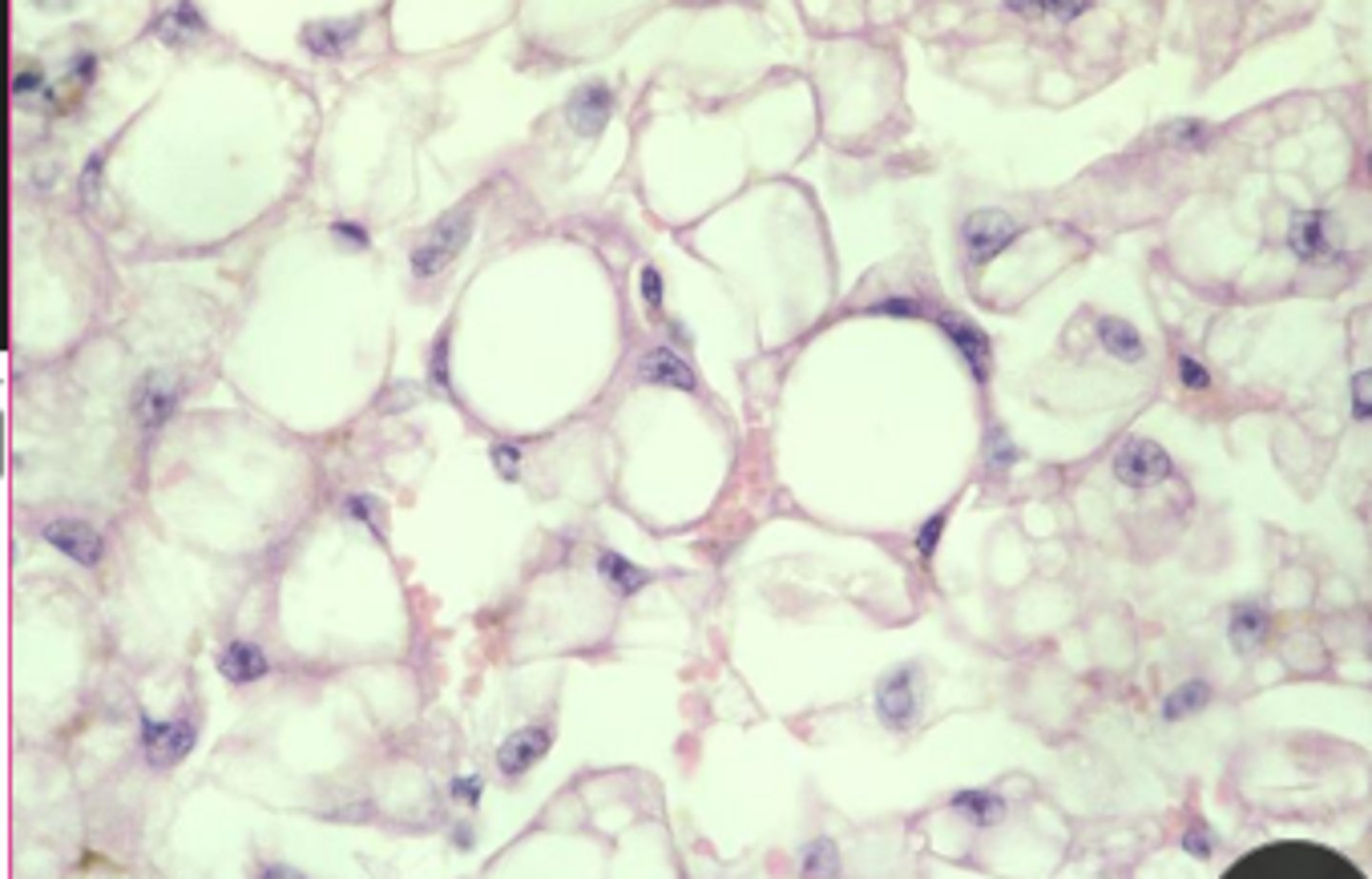
glycogen or lipid?
lipid
displaced nuclei,
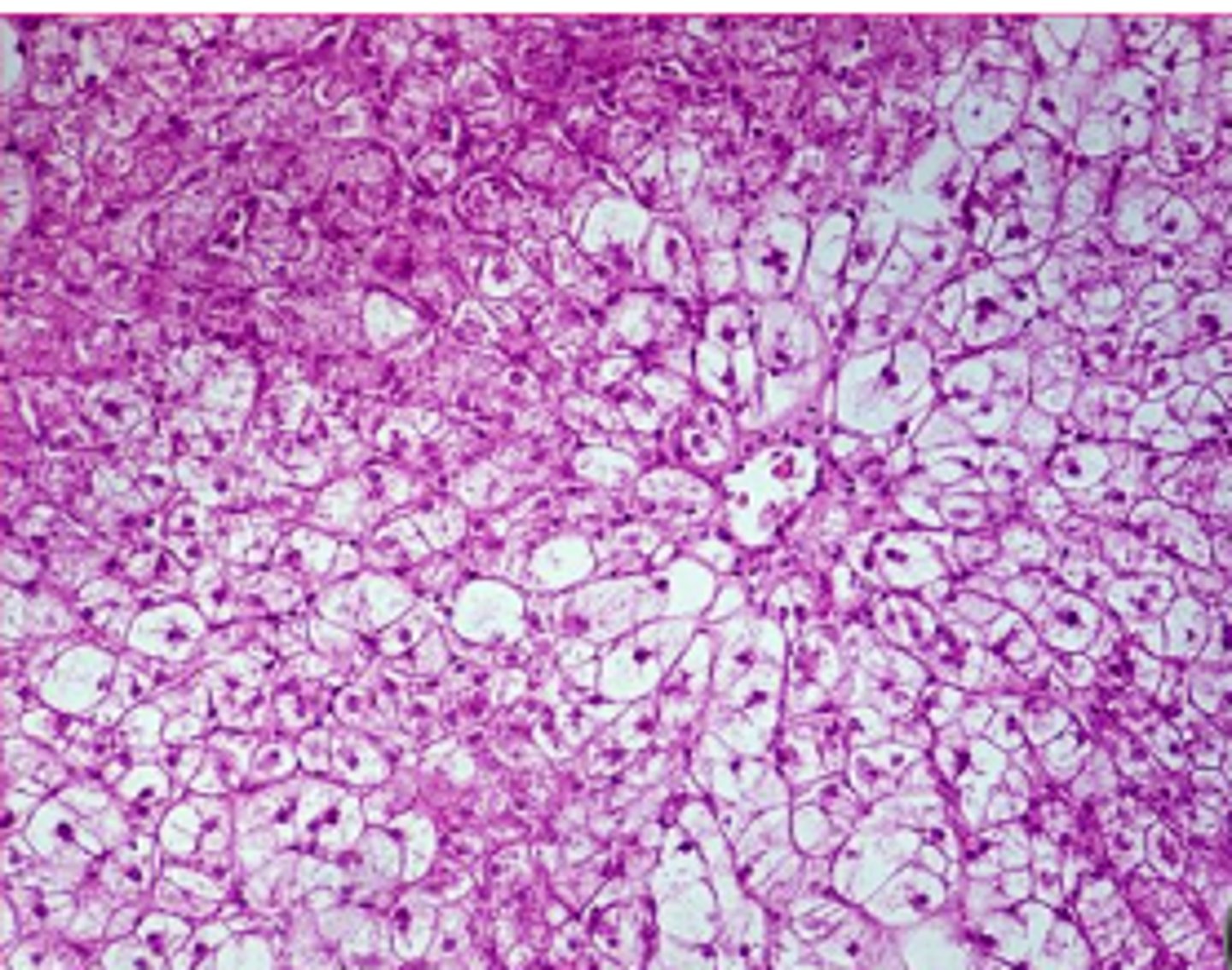
glycogen or lipid?
glycogen
central nuclei, some webbing
are proteins eosinophilic or basophilic?
proteins
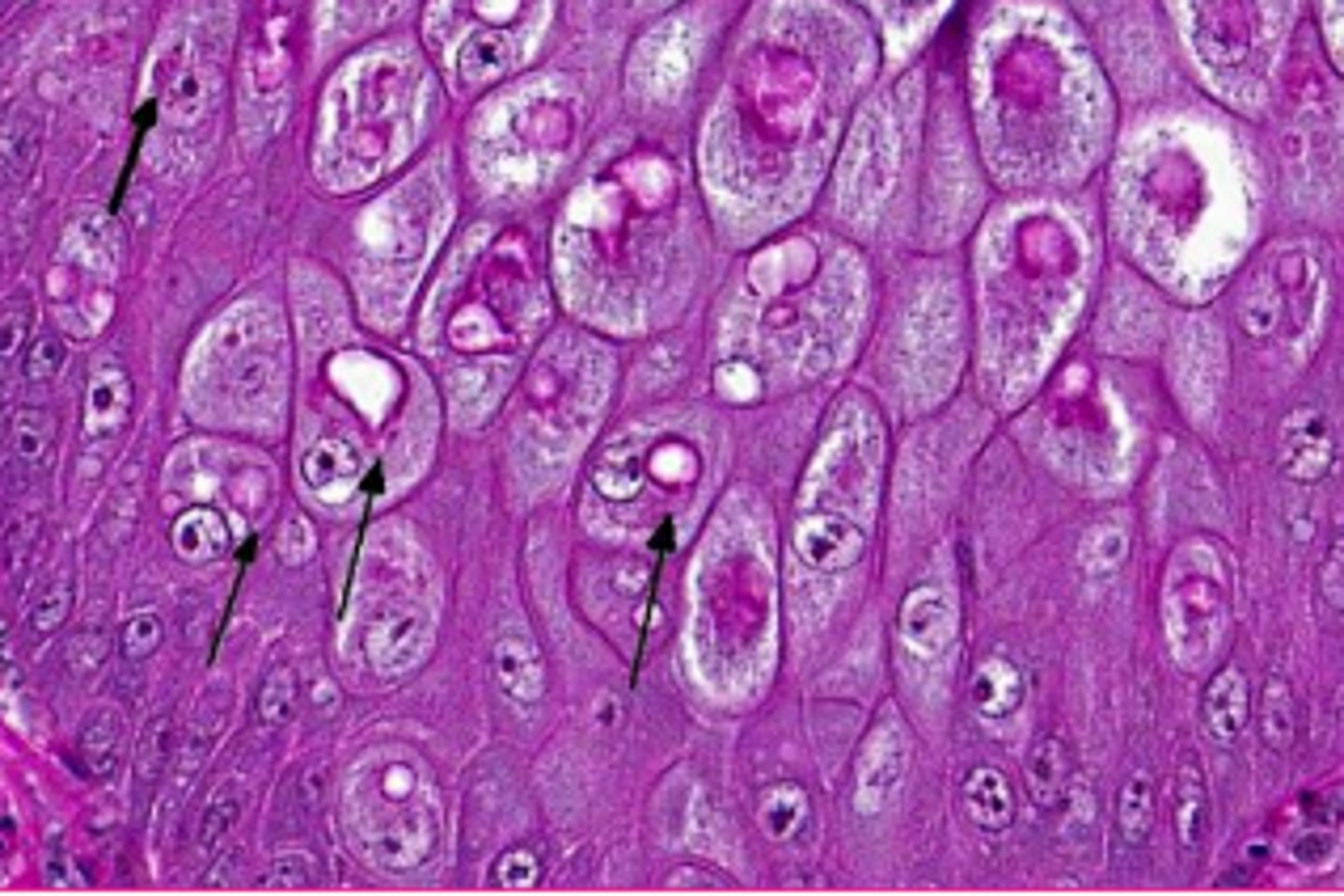
If we say a substance looks hyaline, how does it appear?
homogenous, eosinophilic, and translucent
can be intracellular or extracellular
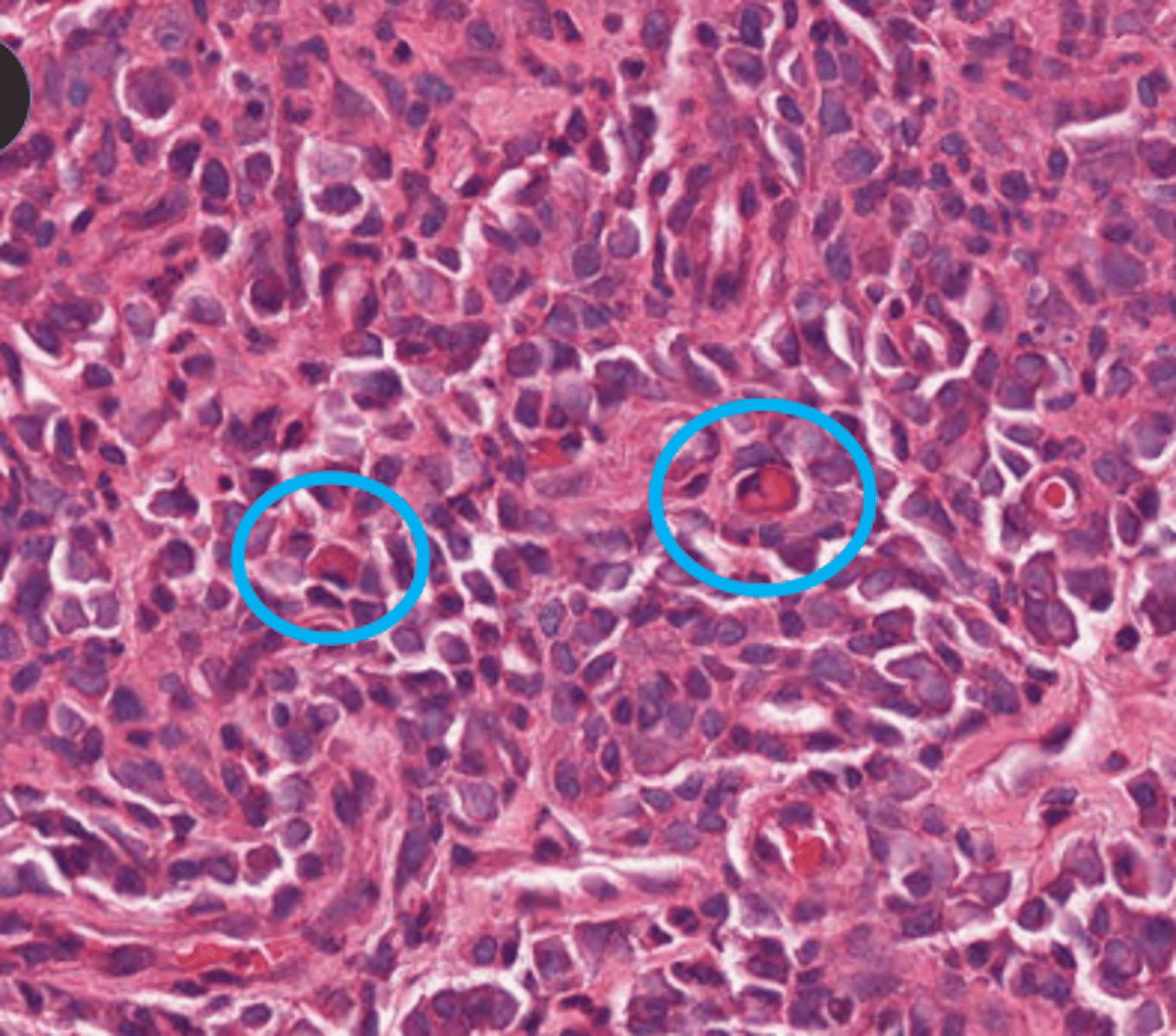
T/F: protein accumulation can be normal in some cells
true, russell bodies in plasma cells
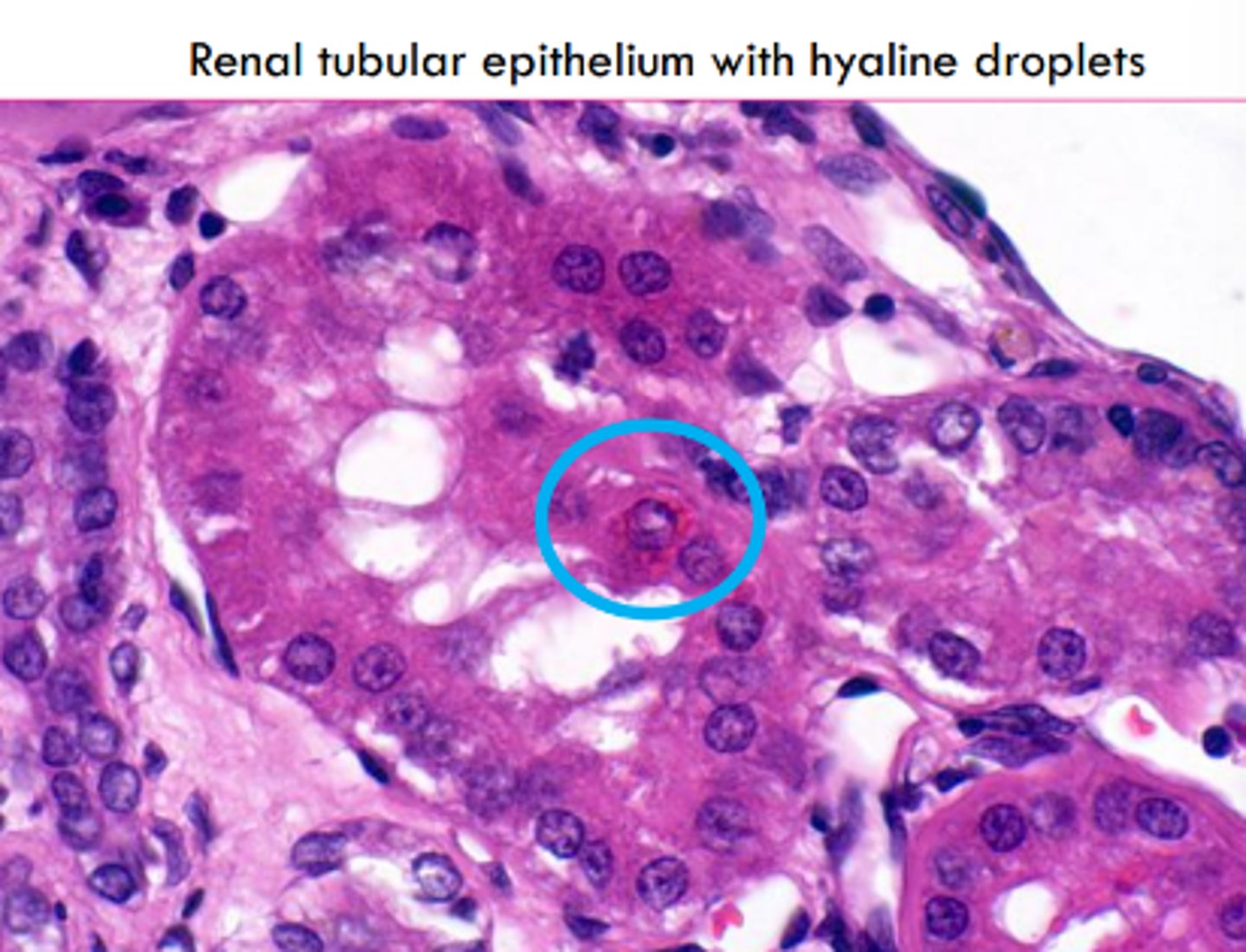
Abnormal protein accumulation can occur in various diseases. Where in the kidney do we see protein resorption vesicles?
cytoplasm of proximal renal tubular epithelial cells
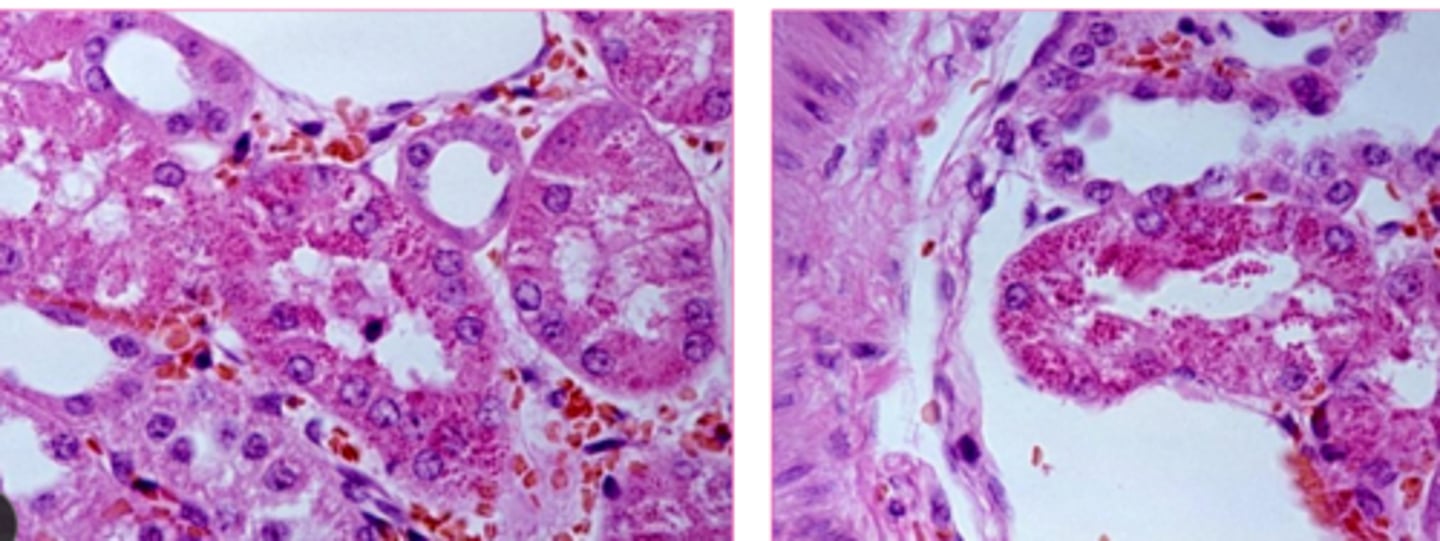
autophagic vacuoles are ___________ _______________ inclusions that may be extruded from a cell or remain as lipofuscin pigment
eosinophilic cytoplasmic
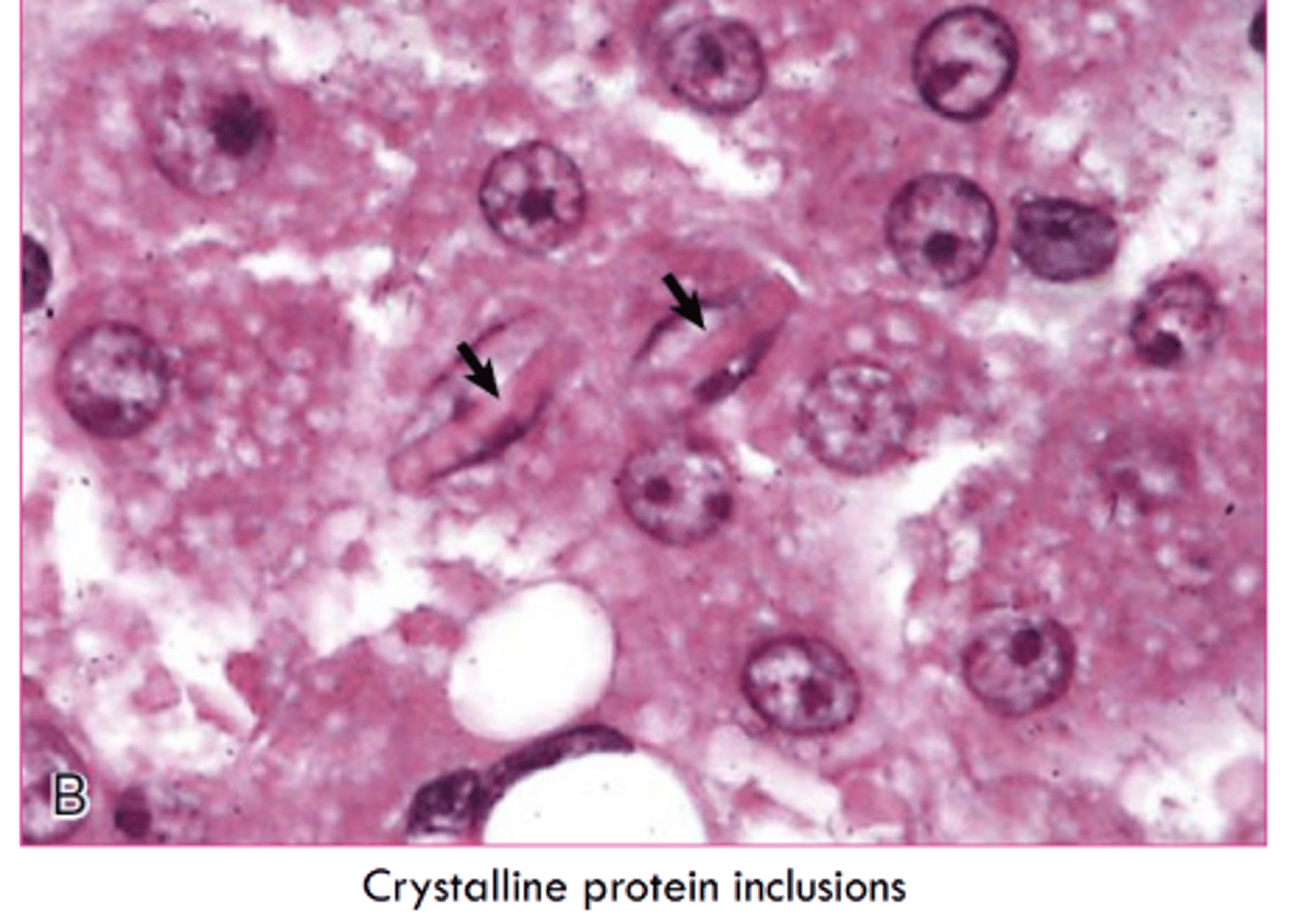
Crystalline protein inclusions have an unknown significance. They increase with ________ and are common where?
age
hepatocytes and rental tubular epithelial cells
Lead inclusions are _____________ inclusions in _______________________________.
intranuclear, renal tubular epithelial cells
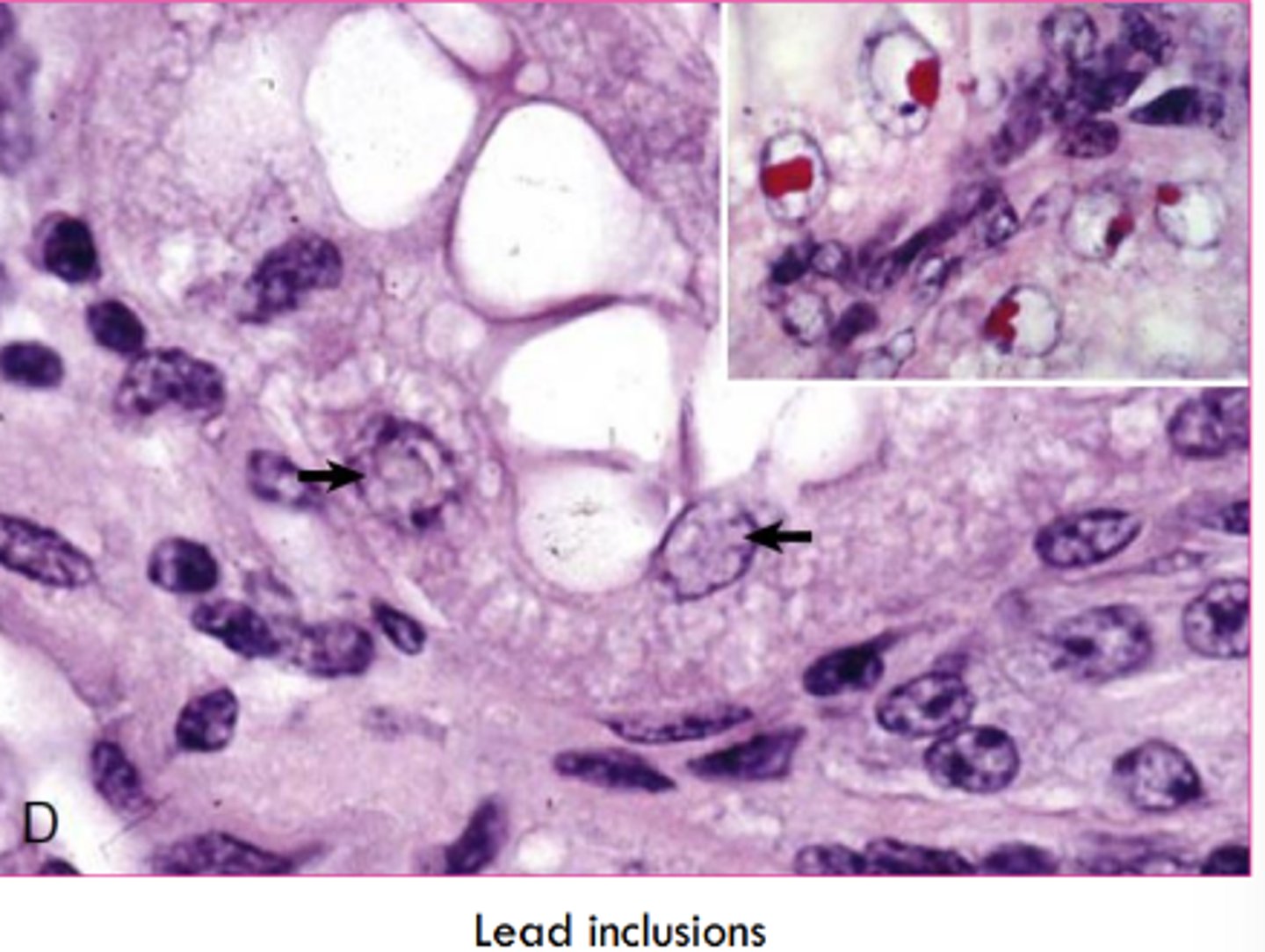
Since lead inclusions are a mix of lead and protein they are best seen with what type of stain?
acid fast
T/F: viral inclusion bodies are only intranuclear
false, they can be intracytoplasmic or intranuclear
what are storage diseases characterized by?
by mutations that result in accumulation of complex substrates or blockage of metabolic pathway
what are some general causes of storage diseases?
defect processing of metabolic substrate -> accumulation
inborn errors of metabolism (lysosomal or glycogen disease)
inhibition of enzymes
what characterizes a storage disease as lysosomal?
deficiency of lysosomal acid hydrolases
what could cause lysosomal storage diseases?
incomplete breakdown of substrates
accumulation of partially degraded, insoluble metabolite within lysosomes
sphingolipidoses
enzymes associated with different products
globoid cell leukodystrophy
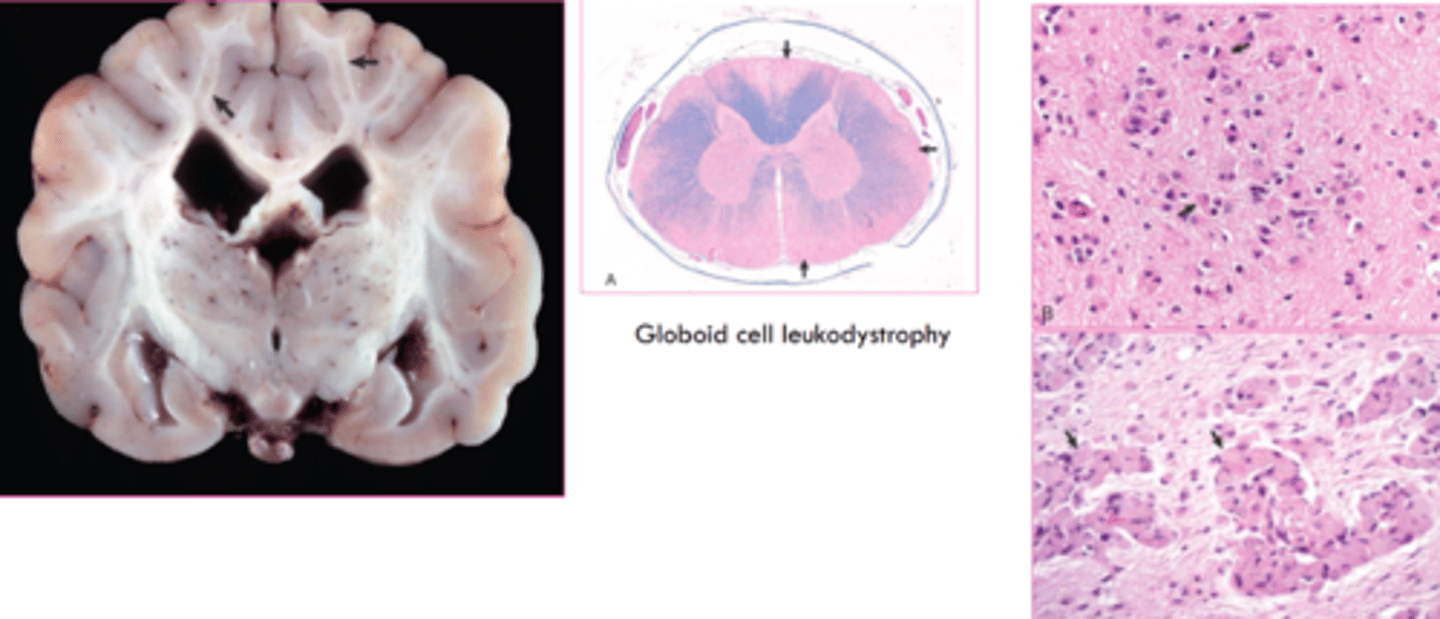
what characterized glycogen storage diseases?
deficiency of an enzyme involved in synthesis or degradation of glycogen
pompe disease
what causes induced storage diseases?
inhibition of enzymes
what is an examples of an induced storage disease?
Locoweed toxicosis which inhibits a lysosomal enzyme
chronic consumption causes proprioceptive defects and abnormal behvaior
what is this?
viral inclusions